Zircon fission track(ZFT) age of the Longxianggai pluton in Dachang of Guangxi and its geological significance
-
摘要:
广西大厂多金属矿田是世界级的特大型锡多金属矿床,是中国第二大产锡基地;笼箱盖岩体作为区内规模最大的岩体,与成矿有着密切关系。本文运用锆石裂变径迹测年方法制约多幕岩浆侵入活动时限,探讨其与成矿时空关系。研究表明,笼箱盖岩体的锆石裂变径迹年龄分布在160~70 Ma之间,并可划分为多个年龄组,分别为160~150 Ma、120~100 Ma和90~70 Ma,具有3期明显的次热历史,揭示笼箱盖岩体的形成经历了3期岩浆侵入活动。大厂多金属矿田的成矿与早白垩世(120~100 Ma)环太平洋板块俯冲影响下的岩石圈伸展期的花岗岩侵位事件相关。岩浆侵入活动不仅为成矿提供部分含锡多金属及对活化迁移成矿元素有利的挥发性气体的初始热流体,还为早期矿化的下部地层中成矿物质迁移、富集提供强大的热能和必要的物理化学条件。
Abstract:The Dachang polymetallic orefield in Guangxi is a world-class superlarge tin polymetallic deposit and the second largest tin production base in China.As the largest pluton in this area, Longxianggai pluton is closely related to mineralization.In this paper, zircon fission track dating method was used to restrict the time limit of multi-episode magmatic intrusion activity and explore its temporal and spatial relationship with mineralization.The results show that the zircon fission track ages of the Longxianggai pluton range from 160 Ma to 70 Ma, and can be divided into several age groups, i.e., 160~150 Ma, 120~100 Ma and 90~70 Ma, respectively.It obviously has three stages of thermal history, which reveals that the formation of Longxianggai pluton experienced three stages of magmatic intrusion.The metallogenesis of the Dachang polymetallic orefield was related to the granite emplacement during the lithospheric extension period under the influence of the subduction of the 120~100 Ma circum-Pacific plate in the Early Cretaceous(120~100 Ma).Magmatic intrusion activity not only provided the initial thermal fluid with some tin bearing polymetallic and volatile gases favorable for the activation and migration of ore-forming elements but also provided strong thermal energy and necessary physicochemical conditions for the migration and enrichment of ore-forming materials in the lower strata of early mineralization.
-

-
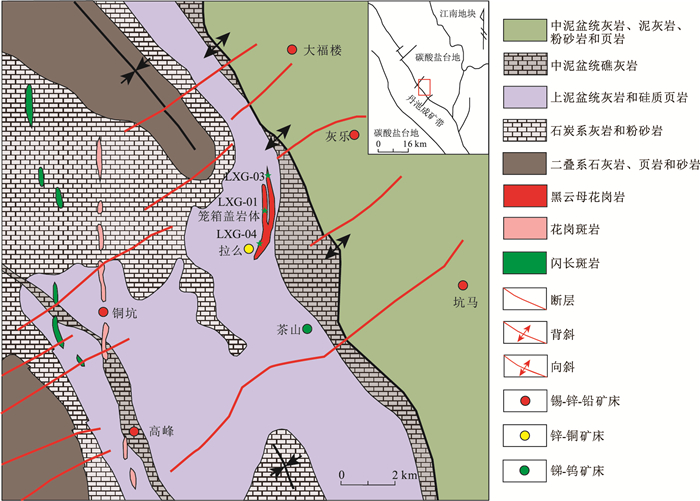
图 1 大厂矿区综合地质图[26]
Figure 1.
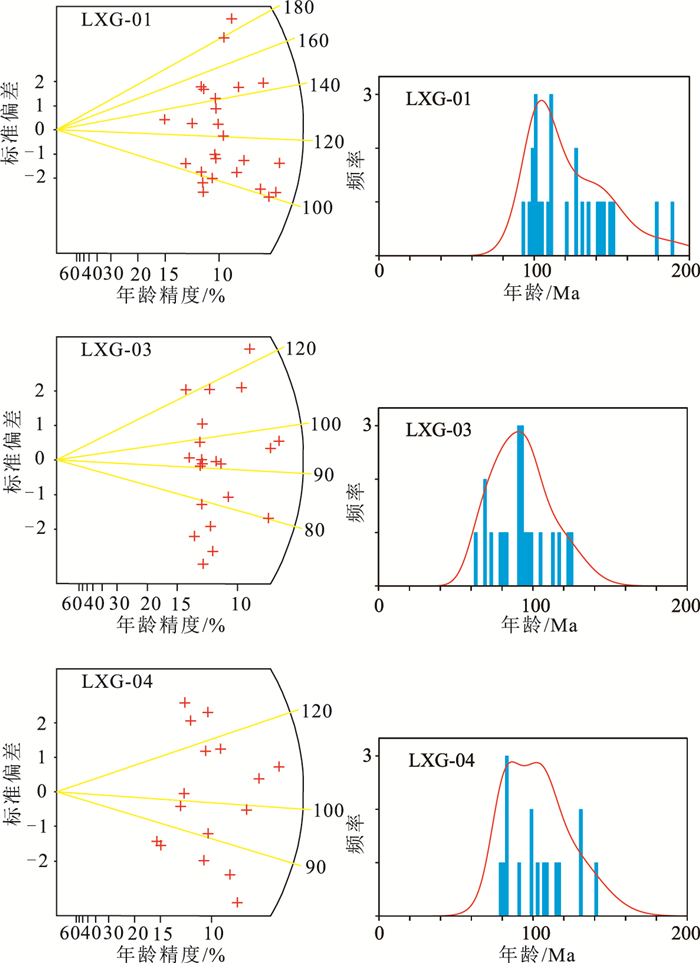
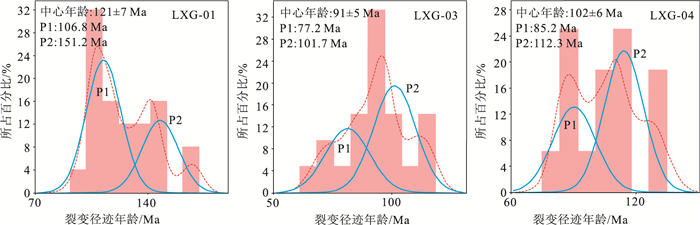
表 1 锆石裂变径迹结果
Table 1. Zircon fission track result
样号 岩性 颗粒数
/nρs/(105·cm-2)
(Ns)ρi/(105·cm-2)
(Ni)ρd /(105·cm-2)
(Nd)P(χ2)
/%中心年龄
/Ma±1σ池年龄
/Ma±1σLXG-01 黑云母花岗岩 25 141.281(6444) 107.013(4881) 18.062(8055) 0 121±7 121±5 LXG-03 黑云母花岗岩 21 99.661(3566) 96.699(3460) 17.604(8055) 0 91±5 92±4 LXG-04 黑云母花岗岩 16 139.83(3615) 120.025(3103) 17.259(8055) 0 102±6 102 ±5 注:Ns为自发径迹数,Ni为诱发径迹数,Nd为标准铀玻璃的外探测器白云母记录的径迹数;ρs、ρi和ρd分别为与Ns、Ni和Nd相对应的径迹密度;n为径迹的条数,P(χ2)为χ2检验几率,锆石年龄运用ζ(Zeta)=90.9 ±2.8(yrcm2/tr)进行计算 -
[1] 陈毓川, 黄民智, 徐珏, 等.大厂锡矿地质[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993.
[2] 蔡明海, 毛景文, 梁婷, 等.广西大厂锡多金属矿床氦-氩同位素特征及其地质意义[J].矿床地质, 2004, 23(2):225-231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.02.011
[3] 秦德先, 洪托, 田毓龙, 等.广西大厂锡矿92号矿体矿床地质与技术经济[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002.
[4] Yan Y F, Liu C M, Qin D X, et al.Geological charac-teristics and metallogenic significance of the Devonian intermediate-basic volcanic rocks in the Dachang deposit, Guangxi Zhuang Autono-mous Region[J].Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 2013, 32(1):110-118. doi: 10.1007/s11631-013-0613-7
[5] 邵主助, 彭振安, 蔡明海, 等.广西大厂锡矿成因研究进展[J].矿产勘查, 2018, 9(6):124-130. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcj201806019
[6] 李华芹, 王登红, 梅玉萍, 等.广西大厂拉么锌铜多金属矿床成岩成矿作用年代学研究[J].地质学报, 2008, 82(7):912-920. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.008
[7] 梁婷, 王登红, 侯可军, 等.广西大厂笼箱盖复式岩体的LA-MC-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(6):1624-1636. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201106005
[8] Hurford A J, Hunziker J C, Stockhert B.Constraints on the late thermotectonic evolution of the Western Alps:Evidence for episodic rapid uplift[J].Tectonics, 1991, 10:758-769. doi: 10.1029/91TC00167
[9] Fitzgerald P G, Sorkhabi R B, Redfield T F, et al.Uplift and denudation of the central Alaska Range:A case study in the use of apatite fission track thermo chronology to determine absolute uplift parameters[J].J.Geophys.Res., 1995, 100:175-191. doi: 10.1029/94JA02135
[10] 郑勇, 余心起, 袁万明, 等.皖南黄山花岗岩体隆升时代的裂变径迹制约[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2011, 41(1):40-51. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201101003
[11] 袁万明.矿床保存变化研究的热年代学技术方法[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(8):2571-2578. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201608023
[12] Feng Y L, Yuan W M, Tian Y T, et al.Preservation and Exhumation History of the Harizha-Halongxiuma Mining Area in the East Kunlun Range, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews 2017, 90:1018-1031. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.029
[13] Piedrahita V A, Bernet M, Chadima M, et al.Detrital zircon fission-track thermochronology and magnetic fabric of the Amagá Formation(Colombia):Intracontinetal deformation and exhumation events in the northwestern Andes[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2017:S0037073817301239. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2017.05.003
[14] 李庶波, 王岳军, 吴世敏.珠江口盆地中-新生代热隆升格局的磷灰石和锆石裂变径迹反演[J].地学前缘, 2018, 25(1):95-107. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.yx.2017-5-20
[15] Donelick R A, O'Sullivan P B, Ketcham R A.Apatite fission track analysis[J].Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2005, 58(1):49-94. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2005.58.3
[16] Leng C B, Cooke D R, Hou Z Q, et al.Quantifying exhumation at the Giant Pulang porphyry Cu-Au deposit using U-Pb-He dating[J].Economic Geology, 2018, 113(5):1077-1092. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.2018.4582
[17] Naeser N D, McCulloh T H.Thermal history of sedimentary basins:Methods and case histories[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1989:1-371.
[18] Wagner G A, Van den Haute P.Fission-track dating[M].Dordrecht:Kulwer Academic Publishers, 1992:1-285
[19] Gallagher K, Brown R, Johnson C.Fission track analysis and its applications to geological problems[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1998, 26:519-572. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.26.1.519
[20] 袁万明, 保增宽, 董金泉, 等.新疆土屋-延东斑岩铜矿区成矿时代与构造活动的裂变径迹分析[J].中国科学(D辑), 2007, (10):1330-1337. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200710005
[21] 陈正乐, 李丽, 刘健, 等.西天山隆升-剥露过程初步研究[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(4):625-636. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200804001
[22] 王立成, 魏玉帅.西藏羌塘盆地白垩纪中期构造事件的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(3):1039-1047. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201303024
[23] Zhao K D, Jiang S Y, Ni P, et al.Sulfur, lead and helium isotopic compositions of sulfide minerals from the Dachang Sn-polymetallic ore district in South China:implication for ore genesis[J].Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 89(3/4):251-273. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=12eb0686501de1e46a30a9eedd2c738f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[24] Chen X C, Hu R Z, Bi X W, et al.Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf-O isotopes, and whole-rock Sr-Nd isotopes of the Bozhushan granite, Yunnan Province, SW China:constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J].J.AsianEarth Sci., 2015, 99:57-71. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=fa389839f473af7b52de4fa5cbf6709f&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] 皮桥辉, 胡瑞忠, 王登红, 等.广西大厂锡多金属矿田西矿带稀散元素铟的富集规律研究——来自矿石组构和闪锌矿地球化学的证据[J].矿床地质, 2015, 34(2):379-396. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201502012
[26] Guo J, Zhang R Q, Sun W, et al.Genesis of tin-dominant polymetallic deposits in the Dachang district, South China:Insights from cassiterite U-Pb ages and trace element compositions[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2018:S016913681730999X. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=127a40facdfb11a99a4263045426d366&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[27] 胡荣国, 赵义来, 蔡永丰, 等.广西大厂花岗斑岩黑云母成分特征及其成岩成矿意义[J].地球科学, 2019:1-29.Doi:10.37991dqkx.2019.130.
[28] 苏晓凯.广西大厂矿田笼箱盖岩体的构造-岩浆演化与找矿方向[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2018.
[29] Galbraith R F, Laslett G M.Statistical models for mixed fission track ages[J].Nucl.Tracks Radiat.Meas., 1993, 21:459-470. doi: 10.1016/1359-0189(93)90185-C
[30] Hurford A J, Green P F.A users' guide to fission track dating calibration[J].Earth Planet.Sci.Lett., 1982, 59:343-354. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90136-4
[31] Green P F.A new look at statistics in fission-track dating[J].Nucl.Tracks.1981, 5:77-86. doi: 10.1016/0191-278X(81)90029-9
[32] Galbraith R F.On statistical models for fission track counts[J].J.Int.Assoc.Math.Geol., 1981, 13:471-478. doi: 10.1007/BF01034498
[33] Brandon M T.Decomposition of fission-track grain-age distributions[J].American Journal of Science, 1992, 292:535-535. doi: 10.2475/ajs.292.8.535
[34] 蔡宏渊, 张国林.广西大厂隐伏花岗岩体发育特征及其含矿性评价[J].矿产地质研究院学报, 1986, (4):1-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KCYD198604000.htm
[35] 尹意求.广西大厂隐伏花岗岩的成因[J].桂林冶金地质学院学报, 1990, 10(4):381-388. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GLGX199004007.htm
[36] Mao J W, Xie G Q, Li X F, et al.Mesozoic large scale mineralization and multiple lithospheric extension in south China[J].Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(1):45-55. http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200401002.htm
[37] 卢友月, 付建明, 程顺波, 等.湘南铜山岭铜多金属矿田成岩成矿作用年代学研究[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2015, 39(6):1061-1071. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201506008
[38] 路远发, 马丽艳, 屈文俊, 等.湖南宝山铜-钼多金属矿床成岩成矿的U-Pb和Re-Os同位素定年研究[J].岩石学报, 2006, (10):2483-2492. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200610009
[39] Peng J T, Zhou M F, Hu R Z, et al.Precise molybdenite Re-Os and mica Ar-Ar dating of the Mesozoic Yaogangxian tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China[J].Miner.Deposita, 2006, 41:661-669. doi: 10.1007/s00126-006-0084-4
[40] Hu, R Z, Wei W F, Bi X W, et al.Molybdenite Re-Os and muscovite 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Xihuashan tungsten deposit, central Nanling district, South China[J].Lithos, 2012, 150:111-118. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.015
[41] Huang X, Lu J.Geological characteristics and Re-Os geochronology of tongshanling polymetallic ore field, South Hunan, China[J].Acta Geol. Sin., 2014, 88:1626-1629. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12385_17
[42] Zhao P, Yuan S, Mao J, et al.Geochronological and petrogeochemical constraints on the skarn deposits in Tongshanling ore district, southern Hunan Province:implications for Jurassic Cu and W metallogenic events in South China[J].Ore Geol.Rev., 2016, 78:120-137. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.03.004
[43] Ling M X, Wang F Y, Ding X, et al.Cretaceous ridge subduction along the lower Yangtze River belt, eastern China[J].Econ.Geol., 2009, 104:303-321. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.303
[44] Li X.Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(3):293-305. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7
[45] Ishihara S, Murakami H, Li X.Indium concentration in zinc ores in plutonic and volcanic environments:Examples at the Dulong and Dachang mines, south China[J].Bulletin Geological Survey of Japan, 2011, 62:259-272. doi: 10.9795/bullgsj.62.259
[46] 徐珏, 杨礼才.广西笼箱盖-拉么地区铜锌多金属矿床的侵入接触构造体系[J].矿床地质, 1988, (1):64-75. https://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_mineral-deposits_thesis/0201254131312.html
[47] 胡瑞忠, 毛景文, 范蔚茗, 等.华南陆块陆内成矿作用的一些科学问题[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(2):13-26. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201002003
[48] 李璞, 戴橦谟, 邱纯一.内蒙和南岭地区某些地区伟晶岩和花岗岩的钾-氩法绝对年龄测定[J].地质科学, 1963, (1):1-9. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX196301000.htm
[49] 徐文忻, 伍勤生.大厂锡多金属矿田同位素地球化学初步研究[J].地质矿产研究院学报, 1987, (2):31-41. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KCYD198602003.htm
[50] 程彦博, 毛景文, 陈小林, 等.滇东南薄竹山花岗岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(4):869-878. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cckjdxxb201004016
[51] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 郭春丽, 等.华南地区中生代主要金属矿床时空分布规律和成矿环境[J].高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4):510-526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.04.005
[52] Gilder S A, Gill J, Coe R S, et al.Isotopic and paleomagnetic constraints on the Mesozoic tectonic evolution of south China[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Solid Earth, 1996, 101(B7):16137-16154. doi: 10.1029/96JB00662
[53] Chung S, Hai C, Jahn B, et al.Major and trace element, and Sr-Nd isotope constraints on the origin of Paleogene volcanism in South China prior to the South China Sea opening[J].Lithos, 1997, 40(2/4):203-220. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=882da55ab56413a8d58a20773e34ac13&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[54] Xu X.Genesis of Young Lithospheric Mantle in Southeastern China:an LAM-ICPMS Trace Element Study[J].Journal of Petrology, 2000, 41(1):111-148. doi: 10.1093/petrology/41.1.111
[55] 邹和平.南海北部陆缘张裂-岩石圈拆沉的地壳响应[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, (1):39-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hydzydsjdz200101007
[56] 孙涛, 周新民.中国东南部晚中生代伸展应力体制的岩石学标志[J].南京大学学报(自然科学版), 2002, (6):737-746. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0469-5097.2002.06.002
[57] 贾大成, 胡瑞忠, 赵军红, 等.湘东北中生代望湘花岗岩体岩石地球化学特征及其构造环境[J].地质学报, 2003, (1):98-103. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.01.011
[58] Li Z X, Li X H.Formation of the 1300 km wide intracontinental orogen and postorogenicmagmatic province in Mesozoic South China:A flat-slab subduction model[J].Geology, 2007, 35(2):179-182. doi: 10.1130/G23193A.1
[59] 周新民, 孙涛, 沈渭洲.华南中生代花岗岩-火山岩时空格局与成因模式[C]//地质与地球化学研究进展.南京: 南京大学出版社, 2006: 25-40.
[60] Li X, Lo C H, Knittel U.Cretaceous magmatism and lithospheric extension in Southeast China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18(3):293-305. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(99)00060-7
[61] Chen J, Jahn B.Crustal evolution of southeastern China:Nd and Sr isotopic evidence[J].Tectonophysics, 1998, 284(1/2):101-133. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0df0cebfc8a7bccfdd1a5807ca83e974&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[62] Hong D, Xie X, Zhang J.Isotope Geochemistry of Granitoids in South China and Their Metallogeny[J].Resource Geology, 2010, 48(4):251-263. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1111-j.1751-3928.1998.tb00022.x/
[63] Hu R Z, Bi X W, Zhou M F, et al.Uranium metallogenesis in South China and its relationship to crustal extension during the Cretaceous to Tertiary[J].Economic Geology, 2008, (103):583-598. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=45a73b3e7f366b58fcb04ed8489cbfb6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[64] Hur Z, Burnard, P G, Bi X W, et al.Mantle-derived gaseous components in ore-forming fluids of the Xiangshan uranium deposit, Jiangxi province, China:Evidence from He, Ar and C isotopes[J].Chemical Geology, 2009, 266(1):86-95. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.chemgeo.2008.07.017/
[65] 李献华, 胡瑞忠, 饶冰.粤北白垩纪基性岩脉的年代学和地球化学[J].地球化学, 1997, (2):19-21+25-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700050343
[66] 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 郭锋, 等.湘赣地区中生代镁铁质岩浆作用与岩石圈伸展[J].地学前缘, 2003, (3):159-169. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.015
[67] 胡瑞忠, 毕献武, 彭建堂, 等.华南地区中生代以来岩石圈伸展及其与铀成矿关系研究的若干问题[J].矿床地质, 2007, (2):139-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.02.001
[68] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 李晓峰, 等.华南地区中生代大规模成矿作用与岩石圈多阶段伸展[J].地学前缘, 2004, 11(1):45-55. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2004.01.003
[69] 陈富文, 李华芹, 梅玉萍.广西龙头山斑岩型金矿成岩成矿锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究[J].地质学报, 2008, (7):921-926. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.07.009
[70] 李文亢.黔西南微细浸染金矿床地质及成矿特征[C]//中国地质科学院沈阳地质矿产研究所文集(13).中国地质学会, 1986: 16.
[71] 成永生.广西大厂矿田岩体地球化学特征及其成矿意义[J].中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 46(2):586-594. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZNGD201502029.htm
[72] 郑浩.广西大厂锡多金属矿田岩浆岩地球化学特征和岩石成因分析[D].广西大学硕士学位论文, 2018.
[73] 赵海, 苏文超, 沈能平, 等.广西大厂矿田高峰锡多金属矿床流体包裹体研究[J].岩石学报, 2018, 34(12):3553-3566. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201812007
[74] 谢鹏, 苏文超, 赵海, 等.广西大厂矿田亢马锡多金属矿床流体包裹体地球化学[J].矿物学报, 2017, 37(6):746-754. doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2017.06.009
[75] 陈懋弘, 毛景文, 吴六灵, 等.滇黔桂矿集区微细浸染型金矿成矿年代学研究[J].桂林工学院学报, 2006, (3):334-340. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2006.03.005
[76] 毛景文, 谢桂青, 李晓峰, 等.大陆动力学演化与成矿研究:历史与现状——兼论华南地区在地质历史演化期间大陆增生与成矿作用[J].矿床地质, 2005, (3):193-205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.03.001
[77] 毛景文, 李晓峰, 李厚民, 等.中国造山带内生金属矿床类型、特点和成矿过程探讨[J].地质学报, 2005, (3):342-372. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.03.008
[78] 李扬.广西南丹县拉么锌铜矿床成因研究[D].中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2017.
-



 下载:
下载: