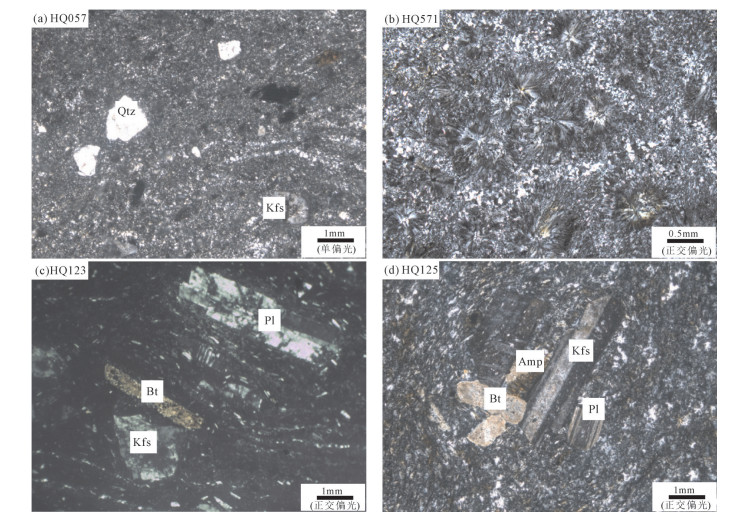
Chronology, geochemical characteristics and its geological significance of Mesozoic volcanic rocks in Ganzhuyinaobao area, Abag Banner, Inner Mongolia
-
摘要:
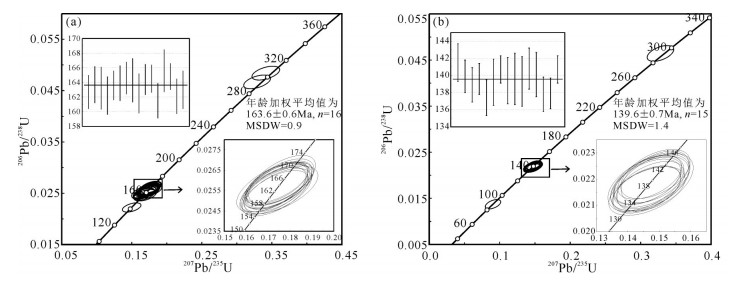
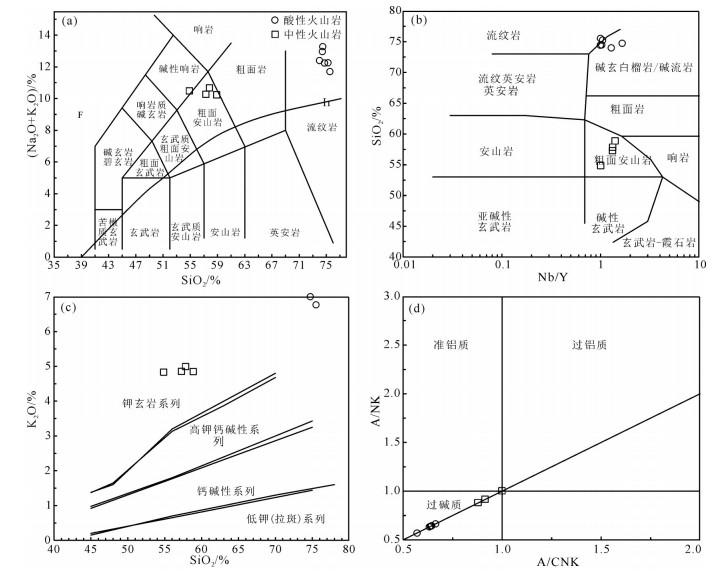
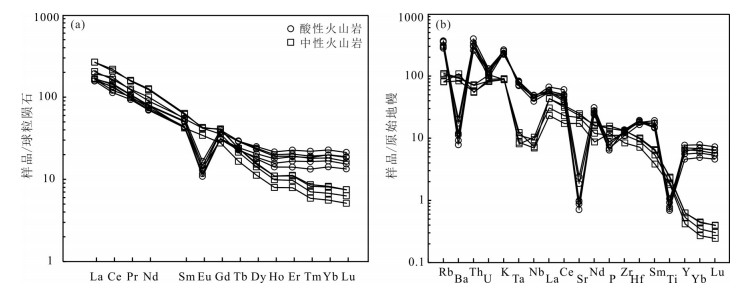
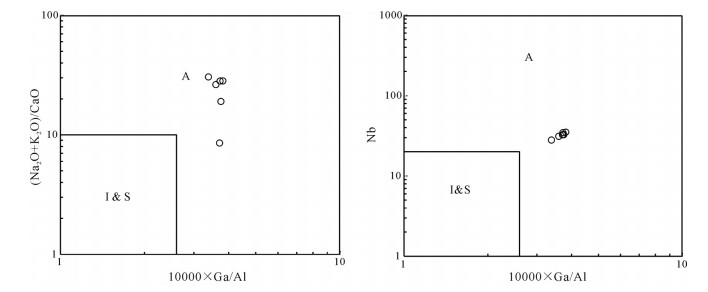
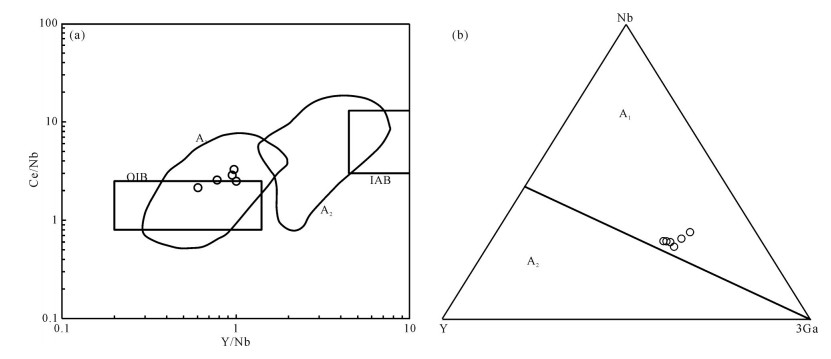
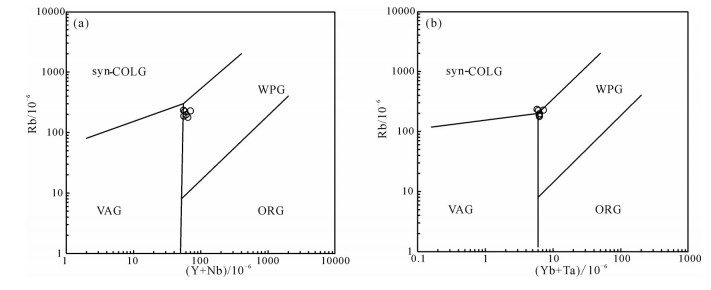
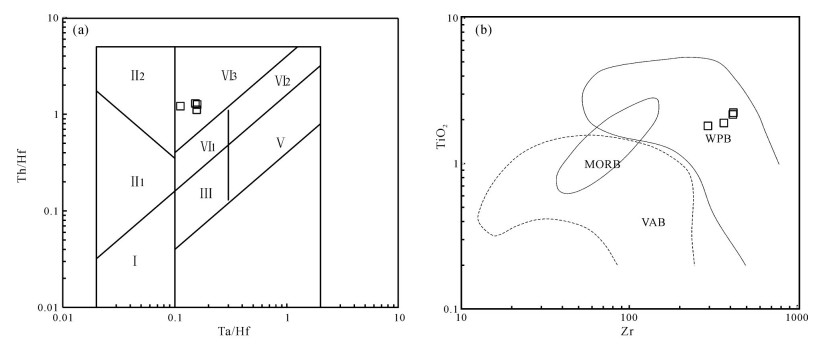
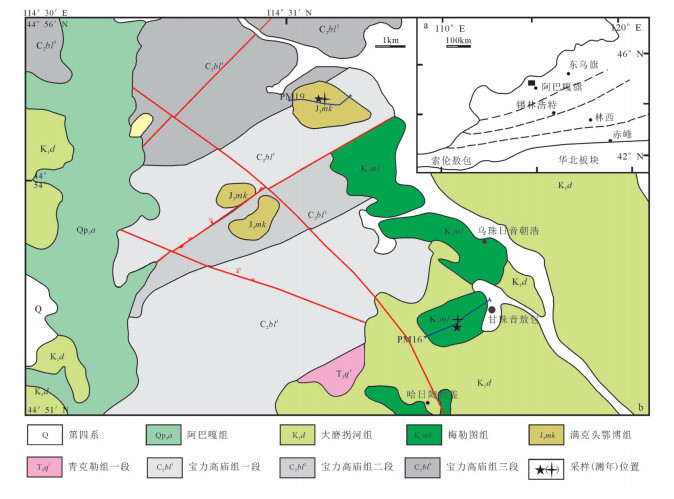
对内蒙古阿巴嘎旗甘珠音敖包地区中生代火山岩进行了锆石U-Pb测年和岩石地球化学研究,对其形成时代、岩石成因及构造背景给予制约。研究区主要发育中生代满克头鄂博组酸性火山岩和梅勒图组中性火山岩。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素定年结果显示,2组火山岩形成年龄分别为163.6±0.6Ma和139.6Ma±0.7Ma。岩石地球化学研究表明,满克头鄂博组酸性火山岩为碱性系列,具有高硅、富碱、低TFeO、Al2O3、TiO2、MgO、CaO和Na2O的特征,轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损、轻重稀土元素分馏明显,Eu强烈亏损,大离子亲石元素Rb、Th、K明显富集,Ba、Sr明显亏损,高场强元素Nb、Ta、P、Ti强烈亏损,具有A型花岗岩特点,形成于陆壳岩石的部分熔融。梅勒图组中性火山岩亦为碱性系列岩石,富碱、富钠、贫钾,高Al2O3、TiO2、MgO,贫CaO,LREE富集,HREE亏损,轻重稀土元素分馏明显,具微弱的负Eu异常,富集大离子亲石元素(LILEs)Rb、Ba、Th、U、K等,亏损高场强元素Nb、Ta、Ti、Y、Yb、Lu等,来源于下地壳镁铁质岩石部分熔融。结合岩石学及该地区构造背景特征,认为满克头鄂博组和梅勒图组火山岩可能形成于蒙古-鄂霍茨克的俯冲作用导致的大兴安岭西坡—冀北—辽西地区加厚陆壳坍塌或拆沉作用的伸展环境。
-
关键词:
- 中生代火山岩 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年 /
- 地球化学 /
- 伸展构造环境 /
- 甘珠音敖包地区
Abstract:LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results and geochemical data for the Mesozoic volcanic rocks from the Ganzhuyinaobao area of Inner Mongolia were presented in order to constrain their chronology, petrogenesis and the regional tectonic evolution. Manketouebo Formation persilicic volcanic rocks and Meiletu Formation intermediate volcanic rocks are extensively distributed in the study area. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating results show that rocks of the two formations were formed at 163.6±0.6Ma and 139.6±0.7Ma, respectively. Geochemical researches indicate that the volcanic rocks in Manketouebo Formation are characterized by rich silica and alkali but poor TFeO, Al2O3, TiO2, MgO, CaO and Na2O, belonging to the alkaline series. The rocks with characteristics of A-type granite are enriched in LREE and LILE (Rb, Ba, Th, U and K) and depleted in HREE, some(Ba, Sr) and HFSE, especially Nb, Ta, P and Ti, with highly negative Eu anomalies, suggesting that they originated from the melting of the crust rocks. The Meiletu Formation intermediate rocks belong to the alkaline series, with enrichment of alkali, K, Al2O3, TiO2, MgO and (LILEs) Rb, Ba, Th, U, K and depletion of HREE as well as Nb, Ta, Ti, Y, Yb and Lu and weak negative Eu anomalies. They were derived from the melting of mafic iron in the lower crust. Combined with characteristics of petrology and tectonic setting of the area, it is held that Manketouebo Formation persilicic volcanic rocks and Meiletu Formation intermediate volcanic rocks occurred in an intense lithopheric extension tectonic setting that was caused by the collapse or delamination of thickening crust resulting from the subduction of Mongolo-Okhotsk heading to the west slope of Da Hinggan Mountains-northern Hebei-western Liaoning region.
-

-
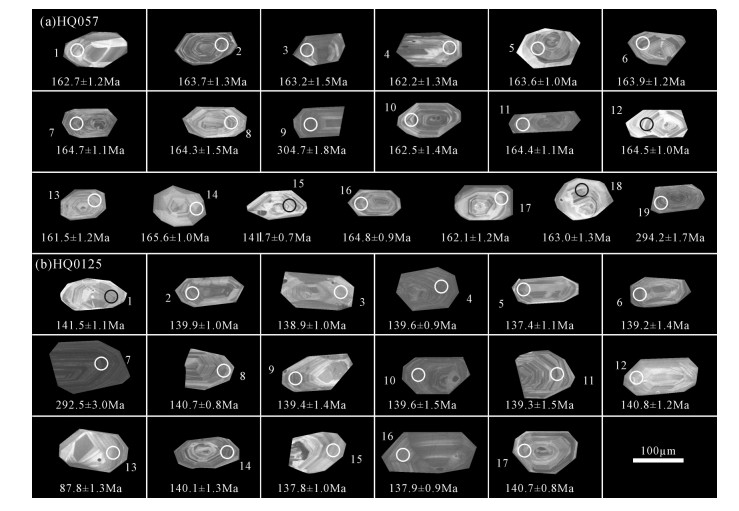
表 1 满克头鄂博组火山岩样品(HQ057)和梅勒图组样品(HQ125)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Th-Pb analytical data of the sample of Manketouebo Formation volcanic rocks (HQ057) and Meiletu Formation (HQ125)
样品编号 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Pb U Th 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 满克头鄂博组 HQ057-1 28 275 97 0.35 0.0256 0.0004 0.1723 0.0061 0.0492 0.0002 161.3 1.5 162.7 1.2 157.9 1.9 HQ057-2 37 226 136 0.60 0.0257 0.0005 0.1741 0.0061 0.0493 0.0002 162.9 1.4 163.7 1.3 161.9 1.4 HQ057-3 22 237 114 0.48 0.0256 0.0005 0.1719 0.0066 0.0492 0.0002 160.9 1.9 163.2 1.5 158.2 2.2 HQ057-4 48 435 197 0.45 0.0255 0.0005 0.1726 0.0063 0.0490 0.0003 161.6 1.6 162.2 1.3 147.0 5.0 HQ057-5 39 433 156 0.36 0.0257 0.0004 0.1751 0.0061 0.0493 0.0002 164.2 1.3 163.6 1.0 160.1 1.4 HQ057-6 21 227 80 0.35 0.0258 0.0005 0.1746 0.0066 0.0492 0.0002 163.2 1.8 163.9 1.2 159.4 1.7 HQ057-7 51 476 188 0.39 0.0259 0.0004 0.1750 0.0062 0.0492 0.0002 163.6 1.5 164.6 1.1 154.8 2.8 HQ057-8 17 154 68 0.44 0.0258 0.0005 0.1753 0.0064 0.0493 0.0002 163.9 1.7 164.3 1.5 163.5 1.5 HQ057-9 60 353 156 0.44 0.0484 0.0005 0.3414 0.0081 0.0509 0.0003 297.8 2.7 304.7 1.8 236.0 8.0 HQ057-10 77 191 308 1.62 0.0255 0.0005 0.1753 0.0071 0.0489 0.0002 164.5 2.5 162.5 1.4 144.0 4.7 HQ057-11 40 369 158 0.43 0.0258 0.0004 0.1752 0.0061 0.0492 0.0002 163.9 1.4 164.4 1.1 157.6 2.6 HQ057-12 41 306 157 0.51 0.0258 0.0004 0.1738 0.0059 0.0492 0.0002 162.7 1.2 164.5 1.0 154.9 2.9 HQ057-13 41 266 187 0.70 0.0254 0.0005 0.1733 0.0062 0.0490 0.0002 162.2 1.5 161.5 1.2 149.4 3.6 HQ057-14 54 167 232 1.39 0.0260 0.0005 0.1764 0.0062 0.0494 0.0002 164.9 1.5 165.6 1.5 165.1 1.9 HQ057-15 77 606 336 0.55 0.0222 0.0004 0.1499 0.0054 0.0485 0.0002 141.8 0.9 141.7 0.7 126.3 3.2 HQ057-16 43 418 182 0.43 0.0259 0.0004 0.1741 0.0058 0.0489 0.0002 162.9 1.2 164.8 0.9 145.0 4.1 HQ057-17 21 219 81 0.37 0.0255 0.0005 0.1746 0.0062 0.0492 0.0002 163.3 1.5 162.1 1.2 156.0 2.5 HQ057-18 16 157 64 0.40 0.0256 0.0005 0.1744 0.0064 0.0492 0.0002 163.7 1.8 163.0 1.3 157.8 2.3 HQ057-19 128 311 287 0.92 0.0467 0.0005 0.3290 0.0078 0.0515 0.0003 288.5 2.6 294.2 1.7 262.0 6.0 梅勒图组 HQ125-1 23 391 150 0.38 0.0222 0.0004 0.1488 0.0045 0.0488 0.0002 141.2 1.4 141.5 1.1 137.2 1.8 HQ125-2 48 683 362 0.53 0.0219 0.0004 0.1465 0.0044 0.0484 0.0002 138.8 1.2 139.9 1.0 120.2 4.4 HQ125-3 24 339 173 0.51 0.0218 0.0004 0.1472 0.0044 0.0487 0.0002 139.4 1.2 138.9 1.0 131.0 2.5 HQ125-4 65 1044 438 0.42 0.0219 0.0004 0.1462 0.0044 0.0484 0.0002 138.5 1.1 139.6 0.9 116.9 4.5 HQ125-5 14 150 102 0.68 0.0216 0.0004 0.1461 0.0050 0.0487 0.0002 138.3 1.6 137.4 1.1 132.7 1.8 HQ125-6 10 157 74 0.47 0.0218 0.0004 0.1470 0.0051 0.0487 0.0002 139.1 1.7 139.2 1.4 136.4 1.5 HQ125-7 18 150 61 0.41 0.0464 0.0007 0.3281 0.0077 0.0515 0.0003 287.6 3.6 292.5 3.0 264.0 7.0 HQ125-8 45 597 334 0.56 0.0221 0.0003 0.1470 0.0042 0.0484 0.0002 139.2 1.0 140.7 0.8 118.8 4.2 HQ125-9 15 142 128 0.90 0.0219 0.0004 0.1462 0.0048 0.0488 0.0001 138.5 1.5 139.4 1.4 137.0 1.4 HQ125-10 10 128 77 0.60 0.0219 0.0004 0.1487 0.0050 0.0488 0.0002 140.7 1.6 139.6 1.5 138.9 1.5 HQ125-11 13 105 90 0.85 0.0219 0.0004 0.1467 0.0053 0.0488 0.0002 138.8 2.0 139.3 1.5 138.2 1.6 HQ125-12 18 230 122 0.53 0.0221 0.0004 0.1487 0.0044 0.0488 0.0001 140.7 1.2 140.8 1.2 138.3 1.4 HQ125-13 39 1257 480 0.38 0.0137 0.0004 0.0905 0.0045 0.0478 0.0001 87.9 1.3 87.8 1.3 88.7 1.3 HQ125-14 20 176 154 0.87 0.0220 0.0004 0.1476 0.0050 0.0488 0.0001 139.7 1.7 140.1 1.3 140.1 1.3 HQ125-15 27 502 194 0.39 0.0216 0.0004 0.1460 0.0045 0.0485 0.0002 138.3 1.2 137.8 1.0 125.6 3.2 HQ125-16 32 612 232 0.38 0.0216 0.0004 0.1461 0.0044 0.0487 0.0002 138.4 1.2 137.9 0.9 131.5 2.4 HQ125-17 45 597 334 0.56 0.0221 0.0003 0.1470 0.0042 0.0484 0.0002 139.2 1.0 140.7 0.8 118.8 4.2 表 2 阿巴嘎旗甘珠音敖包地区晚石炭世花岗岩主量、微量和稀土元素组成
Table 2. Major trace elements and REE chemical compositions of Carboniferous granite
样品号 HQ057 HQ058 HQ059 HQ069 HQ070 HQ071 HQ123 HQ124 HQ125 HQ126 岩性 流纹质凝灰岩 球泡流纹岩 粗安岩 安山质凝灰岩 SiO2 73.59 73.99 74.35 74.76 73.55 72.91 53.48 55.85 57.43 56.17 TiO2 0.15 0.16 0.17 0.15 0.2 0.23 2.18 2.12 1.85 1.76 Al2O3 10.64 10.33 10.09 10.14 9.75 10.22 12.46 12.11 13.73 13.08 Fe2O3T 0.91 1.61 1.25 1.56 0.99 0.94 9.9 9.81 7.47 8.7 MnO 0.03 0.06 0.03 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.08 0.08 0.06 0.06 MgO 0.18 0.16 0.19 0.16 0.27 0.38 2.37 1.5 1.34 1.09 CaO 0.42 0.43 0.46 0.41 0.69 1.43 5.86 5.16 4.96 5.14 Na2O 4.94 5.19 4.59 4.88 5.19 5.22 5.51 5.28 5.25 5.52 K2O 7.88 6.93 7.52 6.7 7.92 7.0 4.71 4.73 4.73 4.85 P2O5 0.14 0.14 0.15 0.19 0.17 0.19 0.92 0.86 0.71 0.75 烧失量 1.10 0.92 1.16 0.98 1.18 1.38 2.45 2.31 2.40 2.75 总计 99.98 99.92 99.96 99.98 99.94 99.93 99.92 99.81 99.93 99.87 Mg# 32.17 23.25 26.22 19.88 28.15 16.45 23.14 16.89 35.08 44.47 Na2O+K2O 12.82 12.12 12.11 11.58 13.11 12.22 10.22 10.01 9.98 10.37 K2O/Na2O 1.6 1.34 1.64 1.37 1.53 1.34 0.85 0.9 0.9 0.88 AR 17.75 55.63 14.4 25.71 347 18.26 3.52 3.76 3.29 3.64 A/NK 0.88 0.88 1.00 0.91 0.64 0.64 0.64 0.66 0.57 0.63 A/CNK 0.50 0.52 0.60 0.55 0.61 0.61 0.61 0.63 0.53 0.54 σ 5.37 4.74 4.68 4.22 5.63 4.99 9.97 7.8 6.9 8.17 SI 1.29 1.15 1.4 1.2 1.88 2.81 10.54 7.04 7.13 5.41 DI 89.54 88.52 89.26 89.4 86.94 86.91 63.13 67.05 76.89 71.16 R1 1294 1436 1548 1655 1190 1357 208 454 639 398 R2 266 259 260 253 282 378 1018 889 891 889 A/MF 6.58 4.2 4.86 4.23 5.01 4.73 0.67 0.74 1.06 0.94 C/MF 0.47 0.32 0.4 0.31 0.64 1.2 0.57 0.57 0.7 0.67 Li 21.60 42.62 22.32 29.84 27.64 34.28 29.56 16.77 21.24 31.22 Sc 1.54 1.62 2.45 1.88 2.13 1.31 9.87 7.69 8.87 7.70 V 10.12 13.45 11.28 14.84 13.45 9.02 129.42 100.26 135.28 104.92 Cr 6.14 7.22 11.08 5.17 17.18 11.12 22.70 22.30 27.60 20.42 Co 0.97 0.75 0.93 0.75 1.06 1.03 12.44 13.16 14.15 10.91 Ni 2.65 1.73 2.35 2.30 3.32 2.50 18.38 18.36 23.62 16.93 Cu 2.35 2.63 3.00 2.90 4.38 3.06 30.28 21.82 33.68 28.16 Zn 26.22 30.62 29.32 32.54 21.18 12.65 125.42 95.16 123.26 92.56 Ga 19.28 20.56 19.446 20.66 19.594 20.36 26.76 25.24 27.68 25.16 Rb 186.48 233.2 197.22 226.8 177.84 223.4 118.48 113.5 93.4 93.8 Ba 78.46 83.68 64.16 54.74 142.14 122.08 1161.6 1136.6 1056 1290.2 Th 21.84 25.32 33.62 25.98 29.08 26.1 11.502 11.314 9.442 9.288 U 2.168 2.35 2.754 2.74 2.454 1.972 3.784 3.182 3.11 3.316 Ta 2.858 3.41 3.234 3.324 2.94 3.21 1.446 1.05 1.336 1.1 Nb 28 34.6 31.14 35.04 32.6 32.46 16.792 22.08 20.6 16.236 Sr 20.66 18.478 20.36 14.948 50.66 39.24 1264 1196.8 1135 963 Nd 32.44 34.5 37.44 36.82 41.98 33.04 57.5 59 46.8 36.64 Zr 150.24 152.72 122.32 141.96 143.8 138.42 416.8 414 366.2 294.2 Hf 5.632 5.968 5.102 5.632 5.524 5.736 9.118 9.338 8.504 7.194 Lu 0.478 0.34 0.422 0.538 0.472 0.392 0.192 0.19 0.156 0.132 Rb/Sr 9.03 12.62 9.69 15.17 3.51 5.69 0.09 0.09 0.08 0.1 Rb/Ba 2.38 2.79 3.07 4.14 1.25 1.83 0.1 0.1 0.09 0.07 Sr/Ba 0.26 0.22 0.32 0.27 0.36 0.32 1.09 1.05 1.07 0.75 Zr/Hf 26.68 25.59 23.97 25.21 26.03 24.13 45.71 44.33 43.06 40.9 Zr/Th 6.88 6.03 3.64 5.46 4.94 5.3 36.24 36.59 38.78 31.68 Nb/Y 1.00 1.66 1.05 1.00 1.03 1.28 1.01 1.32 1.40 1.33 La 37.38 39.12 39.3 39.96 45.7 37.18 63.04 63.08 48.46 39.18 Ce 69.58 73.96 89.4 86.82 106.92 83.14 133.46 127.38 100.54 80.72 Pr 8.87 9.66 10.21 10.05 11.62 9.26 14.86 15.19 11.87 9.33 Nd 32.44 34.5 37.44 36.82 41.98 33.04 57.5 59 46.8 36.64 Sm 6.51 6.71 7.84 7.67 8.5 6.65 9.43 9.71 8.32 6.44 Eu 0.68 0.63 0.85 0.75 0.96 0.78 2.48 2.42 2.43 1.99 Gd 6.45 6.45 7.77 7.65 8.18 6.29 8.28 8.44 7.3 5.69 Tb 0.91 0.87 1.08 1.09 1.1 0.85 0.89 0.89 0.8 0.62 Dy 5.22 4.51 5.93 6.35 6.09 4.72 3.88 4 3.6 2.85 Ho 1.01 0.8 1.08 1.22 1.13 0.89 0.62 0.62 0.56 0.45 Er 3.12 2.33 3.18 3.75 3.36 2.76 1.82 1.85 1.61 1.31 Tm 0.47 0.34 0.46 0.56 0.49 0.42 0.21 0.22 0.18 0.15 Yb 3.38 2.41 3.09 3.87 3.36 2.85 1.37 1.4 1.15 0.95 Lu 0.48 0.34 0.42 0.54 0.47 0.39 0.19 0.19 0.16 0.13 Y 28.1 20.9 29.62 35.1 31.74 25.28 16.7 16.68 14.69 12.22 ΣREE 176.52 182.63 208.04 207.09 239.86 189.22 298.04 294.39 233.78 186.45 LREE 155.46 164.59 185.04 182.07 215.68 170.05 280.77 276.78 218.42 174.3 HREE 21.05 18.05 23 25.02 24.18 19.17 17.27 17.62 15.35 12.15 LREE 7.38 9.12 8.05 7.28 8.92 8.87 16.26 15.71 14.23 14.34 (La/Yb)N 7.92 11.66 9.11 7.41 9.76 9.35 32.96 32.32 30.28 29.52 (La/Sm)N 3.71 3.76 3.23 3.36 3.47 3.61 4.32 4.19 3.76 3.93 (Gd/Yb)N 1.58 2.22 2.08 1.63 2.02 1.82 4.99 4.99 5.26 4.95 δEu 0.32 0.29 0.33 0.3 0.35 0.36 0.84 0.8 0.93 0.98 δCe 0.91 0.91 1.07 1.03 1.11 1.07 1.03 0.98 1 1 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 -
[1] Sengör A M C, Natal' in B A, Burtman V S. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Paleozoic crustal growth in Eurasia[J]. Nature, 1993, 364:299-307. doi: 10.1038/364299a0
[2] Windley B F, Alexeiev D, Xiao W J, et al. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2007, 164(1):31-47. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492006-022
[3] Xu B, Charvet J, Chen Y, et al. Middle Paleozoic convergent orogenic belts in western Inner Mongolia (China):Framework, kinematics, geochronology and implications for tectonic evolution of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23:1342-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.05.015
[4] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Hao J, et al. Accretion Leading to Collision and the Permian Solonker Suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Oragenic Belt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(6):1-8. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4f70f4625c75e2c67f49e664df0bc8b5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[5] Li J Y. Permian geodynamic setting of Northeast China and adjacent regions:closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 26:207-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.001
[6] 邵济安, 唐克东.中国东北地体与东北亚大陆边缘演化[M].北京:地震出版社, 1995.
[7] 许文良, 王枫, 裴福萍, 等.中国东北中生代构造体制与区域成矿背景:来自中生代火山岩组合时空变化的制约[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(2):339-353. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201302001
[8] Wu F Y, Sun D Y, Ge W C, et al. Geochronology of the Phanerozoic granitoids in northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 41(1):1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.11.014
[9] 林强, 葛文春, 孙德有, 等.中国东北地区中生代火山岩的大地构造意义[J].地质科学, 1998, 33(2):129-139. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199800069875
[10] 林强.东北亚中生代火山岩研究若干问题的思考[J].世界地质, 1999, 18(2):14-22. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SJDZ902.002.htm
[11] 邵济安, 张履桥, 牟保磊.大兴安岭中生代伸展造山过程中的岩浆作用[J].地学前缘, 1999, 6(4):339-346. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.04.017
[12] 陈志广, 张连昌, 万博.内蒙古满洲里晚侏罗世火山岩年代学和地球化学特征[C]//2006年全国岩石学与地球动力学研讨会, 2006: 77-79.
http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ200611002039.htm [13] Wu F Y, Lin J, Wilde S A, et al. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233:103-119. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.019
[14] 董树文, 张岳桥, 龙长兴, 等.中国侏罗纪构造变革与燕山运动新诠释[J].地质学报, 2007, 81(11):1449-1457. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.11.001
[15] Wu F Y, Jahn B M, Wilde S, et al. Phanerozoic crustal growth:UPb and Sr-Nd isotopic evidence from the granites in northeastern China[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 328:89-113. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00179-7
[16] Jahn B M, Windley B, Natal' in B, et al. Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23:599-603. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00124-X
[17] Guo F, Fan W M, Gao X F, et al. Sr-Nd-Pb isotope mapping of Mesozoic igneous rocks in NE China:Constraints on tectonic framework and Phanerozoic crustal growth[J]. Lithos, 2010, 120:563-578. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.020
[18] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-inducedmelt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North Chinaorogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements inzircons from Mantle Xenoliths[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51:537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
[19] Ludwig K R. ISOPLOT 3.00:A Geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel[J]. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, 2003:1-70. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.immuni.2011.10.010/
[20] Hanchar J M, Miller C F. Zircon zonation patterns as revealed by cathodoluminescene and backscattered electron images:Implications for interpretation of complex crustal histories[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 110(1):1-13. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8d64888cd884895b52e32a8336ce8325&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[21] Claesson V S, Vetrin T, Bayanova H D. U-Pb zircon ages from a Devonian carbonatite dyke, Kola peninsula, Russia:A record of geological evolution from the Archean to the Palaeozoic[J]. Lithos, 2000, 51(1):95-108. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0ddb8ff4ca8501464c175db302632ae6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[22] Belousova E A, Griffin W L, O'Reilly S Y, et al. Igneous zircon:Trace element composition as an indicator of source rock type[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2002, 143(5):602-622. doi: 10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7
[23] Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20:325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
[24] Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to Southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2):189-200. doi: 10.1007/BF00374895
[25] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic Discrimination of Granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643 doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[26] Boynton W V. Cosmochemistry of the earth elements: Meteorite studies[C]//Henderson R. Rare Earth Element Geochemistry: Developments in Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 89-92.
[27] Sun S S, Mcdonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[28] 彭振安, 李红红, 张诗启, 等.内蒙古北山地区小狐狸山钼矿成矿岩体地球化学特征研究[J].地质与勘探, 2010, 46(2):291-298. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201002015
[29] 杨启军, 徐义刚, 黄小龙, 等.高黎贡构造带花岗岩的年代学和地球化学及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(4):817-834. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200604006
[30] 贺淑赛, 李秋根, 王宗起, 等.内蒙古中部宝力高庙组长英质火山岩U-Pb-Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, (1):50-64. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/bjdxxb201501007
[31] 陈英富, 王根厚, 段炳鑫.内蒙古东乌珠穆沁旗辉音敖包一带晚侏罗世火山岩特征及时代[J].中国地质, 2012, 39(6):1690-1699. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.06.017
[32] 程银行, 滕学建, 李艳锋, 等.内蒙古海莫赛格酸性火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2014, 33(2):211-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2014.02.001
[33] 李鹏川, 李世超, 刘正宏, 等.内蒙古林西地区满克头鄂博组火山岩形成时代及构造环境[J].世界地质, 2016, 35(1):77-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5589.2016.01.008
[34] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A-type granites:geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95:407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
[35] Rollinson H R. Using Geochemical Data:Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation[M]. London:Pearson Education Limited, 1993:1-278.
[36] Patino Douce A E. Generation of metaluminous A-type granites by low-pressure melting of calc-alkaline granitoids[J]. Geology, 1997, 25:743-746. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0743:GOMATG>2.3.CO;2
[37] King P L, Chappell B W, Allen C M, et al. Are A-type granites the high-temperature felsic granites Evidence from fractionated granites of the Wangrah Suite[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2001, 48(4):501-514. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-0952.2001.00881.x
[38] Harris N B W, Tindle A G, Tindle A G. Geochemical characteristics of collision-zone magmatism[J]. Spec. Publ. Geol. Soc. Lond., 1986, 19:67-81. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1986.019.01.04
[39] Pearce J A. Trole of sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at destructive plate margins[C]//Hawkesworth C J, Norry M J. Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths. Nantwich Shiva: Academic Press, 1983: 230-249.
[40] Tischendorf G, Paelchen W. Zur Klassifikation von Granitoiden/Classification of granitoids[J]. Zeitschrift fuer Geologische Wissenschaften, 1985, 13(5):615-627.
[41] McCarron J J, Smellie J L. Tectonic Implications of Fore-Arc Magmatism and Generation of High-Magnesian Andesites:Alexander Island[J]. Antarctica. Journal of the Geological Society, 1998, 155(2):269-280. doi: 10.1144/gsjgs.155.2.0269
[42] Atherton M P, Petford N., Generation of Sodium-Rich Magmas from Newly Underplated Basaltic Crust[J]. Nature, 1993, 362(6416):144-146. doi: 10.1038/362144a0
[43] Rapp P P, Shimizu N, Norman M D, et al. Reaction between slabderived melts and peridotite in the mantle wedge:Experimental constraints at 3.8GPa[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(4):335-356. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00106-0
[44] Dungan M A, Lindstrom M M, McMillan N J, et al. Open system magmatic evolution of the Taos Plateau volcanic field, northern New Mexico:1. The petrology and geochemistry of the Servilleta Basalt[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth (1978-2012), 1986, 91(B6):5999-6028. doi: 10.1029/JB091iB06p05999
[45] 郭锋, 范蔚茗, 王岳军, 等.大兴安岭南段晚中生代双峰式火山作用[J].岩石学报, 2001, 17(1):161-168. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200101017
[46] Taylor S R, McLennan S M. The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution[M]. Oxford:Blackwell, 1985:1-312.
[47] 王焰, 钱青, 刘良, 等.不同构造环境中双峰式火山岩的主要特征[J].岩石学报, 2000, 16(2):169-173. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200002004
[48] Chen B, Jahn B M. Geochemical and isotopic studies of the sedimentary and granitic rocks of the Altai orogen of northwest China and their tectonic implications[J]. Geological Magazine, 2002, 139(1):1-13. doi: 10.1017/S0016756801006100
[49] Hong D W, Zhang J S, Wang T, et al. Continental crustal growth and the supercontinental cycle:evidence from the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2004, 23(5):799-813. doi: 10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00134-2
[50] Zhang X H, Wilde S A, Zhang H F, et al. Early Permian high-K calcalkaline volcanic rocks from NW Inner Mongolia, North China:geochemistry, origin and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2011, 168(2):525-543. doi: 10.1144/0016-76492010-094
[51] Northrup C J, Royden L H, Burchfiel B C. Motion of the Pacific plate relative to Euroasia and its potential relation to Cenozoic extrusion along the eastern margin of Eurasia[J]. Geology, 1995, 23:719-722. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0719:MOTPPR>2.3.CO;2
[52] Kravchinsky V A, Cogné J P, Harbert W P, et al. Evolution of the Mongol-Okhotsk Ocean as constrained by new palaeomagnetic data from the Mongol-Okhotsk suture zone, Siberia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2002, 148(1):34-57. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-246x.2002.01557.x
[53] Sorokin A A, Kotov A B, Sal'nikova E B, et al. Granitoids of the Tyrma-Bureya complex in the northern Bureya-Jiamusi superterrane of the Central Asian fold belt:Age and geodynamic setting[J]. Russian Geology and Geophysics, 2010, 51(5):563-571. doi: 10.1016/j.rgg.2010.04.011
[54] 孟恩, 许文良, 杨德彬, 等.满洲里地区灵泉盆地中生代的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2011, 27(4):1209-1226. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201104029.htm
[55] 徐美君, 许文良, 孟恩, 等.内蒙古东北部额尔古纳地区上护林-向阳盆地中生代火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(9):1321-1338. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.09.001 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20110901&flag=1
[56] Zhang J H, Ge W C, Wu F Y, et al. Large-scale Early Cretaceous volcanic events in the northern Great Xing'an Range, northeastern China[J]. Lithos, 2008, 102(1/2):138-157. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d14ba8be8a38a9512101ffec46cee93d
[57] 王建国, 和钟铧, 许文良.大兴安岭南部钠闪石流纹岩的岩石成因:年代学和地球化学证据[J].岩石学报, 2013, 29(3):853-863. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201303009
[58] Xu M J, Xu W L, Wang F, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Early Jurassic granitoids in the northwestern Lesser Xing'an Range, NE China and its tectonic implications[J]. Acta Petrologina Sinica, 2013, 29(2):354-368.
[59] Loiselle M C, Wones D R. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 1979, 11(7):468. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9108a701005035f04fb9accc13dc243b
[60] Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-typegranitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 5(3):113-124. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=07dacaa13e4b34a1c6df1f2c82941737&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[61] 许保良, 阎国翰, 张臣. A型花岗岩的岩石1学亚类及其物质来源[J].地学前缘, 1998, 5(3):113-124. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1998.03.011
-



 下载:
下载: