Characteristics and thematic geological mapping of mélanges
-
摘要:
混杂岩是造山带内最常见的地质体和最基本的大地构造相单元,是由多种地质作用共同形成的可作为一定比例尺(1:25000或更大)的地质填图单元,并由块体和基质共同构成的内部无序的岩石混杂体。混杂岩的形成和就位构造环境不一致,并非所有混杂岩都具有古板块构造格局指示意义。蛇绿混杂岩和增生杂岩可作为古洋盆和汇聚板块边界的直接判别标志,其结构、组成与时空配置共同记录了古大洋板块地层系统发展及大陆地壳侧向与垂向增生历史。以大洋板块地层、海山理想层序和蛇绿岩"彭罗斯"层序模型为指导,专题地质填图是揭示造山带蛇绿混杂岩和增生杂岩结构、组成及其时空配置关系与形成机制的有效手段。这可为洋-陆转换研究及提高造山带结构深化认知程度提供直接证据,同时指导混杂岩相关矿床勘探与找矿预测。
Abstract:Mélange is the commonest geological body and the most fundamental tectonic facies of the orogenic belt around the world. It represents a mappable (1:25000 or more) geological unit formed by multiple geological processes and consists of blocks and matrix showing high stratigraphic disruption and a chaotic internal structure. The formation environment of mélanges is unequal to their emplacement environment, and hence not all of the mélanges were formed around the plate boundary reflecting plate tectonics. Ophiolitic mélanges and accretionary complexes can be used as the direct discriminating marks of ancient oceanic basin and convergent plate boundaries, and their texture and composition as well as spatial and temporal relationship have coevally recorded the development of oceanic plate stratigraphy and the lateral and vertical growth of the continental crust. On the basis of an ideal model of oceanic plate stratigraphy (including seamount) and Penronse ophiolite sequence, thematic geological mapping is the most effective way to clarify the texture and composition, spatial and temporal relationship, and formation mechanism of mélanges. The data obtained can provide direct evidence for reconstructing ocean-continental framework and improving our knowledge on the texture of orogenic belts, and can also guide mineral deposit exploration and ore prospecting plan.
-
Key words:
- orogenic belt /
- mélange /
- ophiolitic mélange /
- subductionary complex /
- thematic geological mapping
-

-
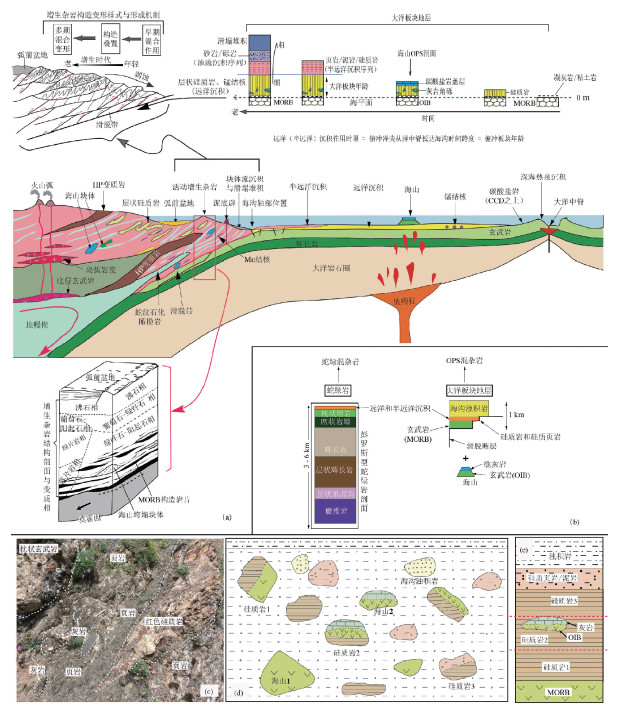
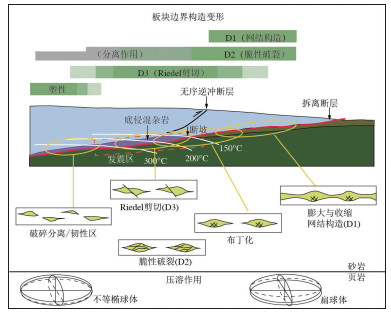
图 1 俯冲带中岩石发生持续构造变形过程[22]
Figure 1.
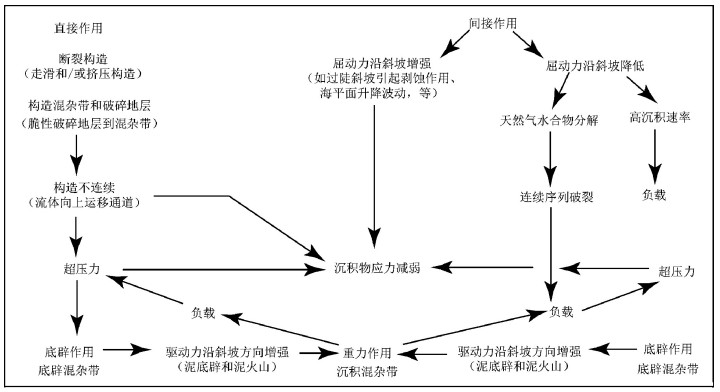
图 3 混杂岩形成过程中构造作用作为主要驱动力的间接和直接作用[9]
Figure 3.
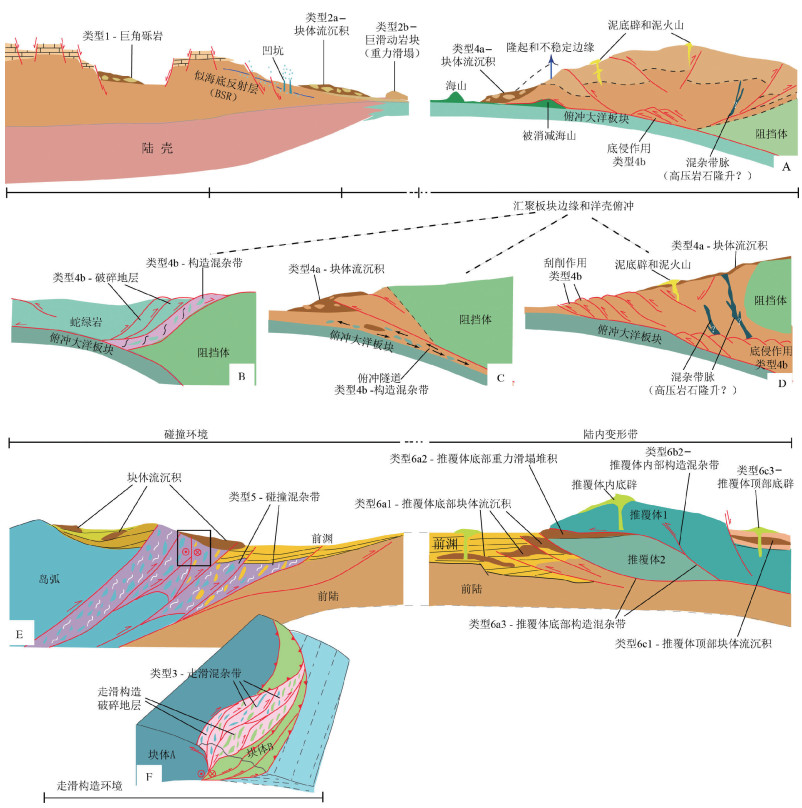
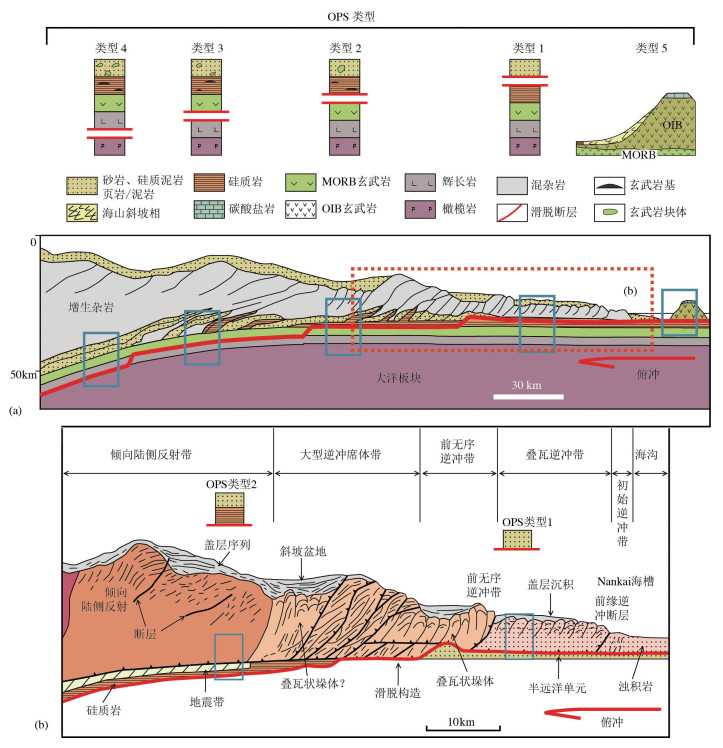
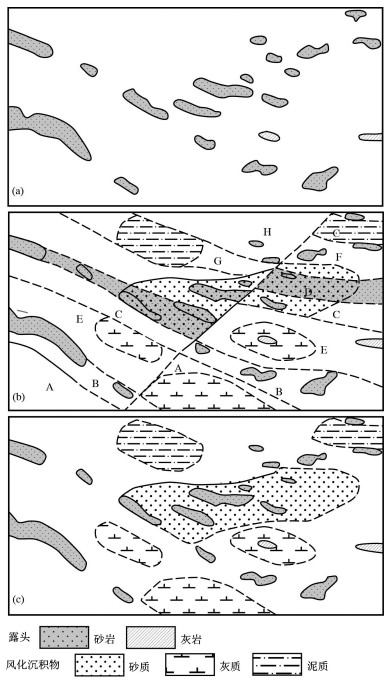
图 7 混杂岩两种不同解释地质图(据参考文献[5]修改)
Figure 7.
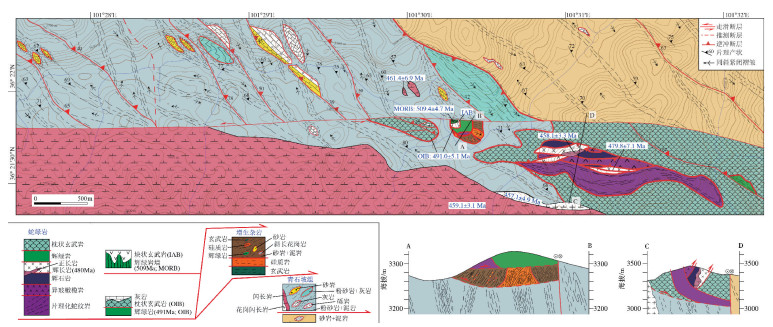
图 8 南祁连拉脊山口混杂岩地质图(剖面AB比例尺夸大;地形资料据参考文献[108])
Figure 8.
表 1 增生杂岩中不同构造背景玄武岩及岛弧玄武岩主要岩石组合、岩石学、地球化学特征
Table 1. Major features of rock assemblage, petrology, and geochemistry of basalts hosted by accretionary complex and island arc
火山系列 增生杂岩岩石组合 岩石学特征 主要矿物 斑晶结晶顺序 地球化学特征 构造背景 碱性 熔岩流和枕状玄武岩、岩席;碳酸盐岩盖层、碳酸盐岩角砾,火山成因碳酸盐岩,表生碎屑、硅质页岩、硅质岩 橄榄石、单斜辉石和斜长石斑晶 Ti-辉石,Ti-角闪石(钛闪石),Ti-黑云母,霓辉石,斜方辉石 橄榄石→单斜辉石(Ti-辉石)→斜长石 高Ti、Nb、P和LREE;Zr/Nb<10;Al2O3/TiO2<8;Nb/Lapm>1 洋岛,海山,洋底高原 拉斑 枕状熔岩和岩墙、岩席;硅质岩及少量硅质页岩 隐晶质,橄榄石和斜长石斑晶 透辉石-普通辉石,易变辉石 橄榄石→斜长石→(单斜辉石) 中Ti和LREE;低Nb;Al2O3/TiO2=8-17;Nb/Lapm≤1 洋中脊,大洋高原,洋内岛弧,弧后盆地 钙碱性 熔岩流和火山碎屑岩;陆棚沉积;陆源碎屑岩,碳酸盐岩 橄榄石, 单斜辉石和斜长石斑晶 低Ti-Al单斜辉石,斜方辉石 橄榄石→单斜辉石→斜长石 TiO2<1(Al2O3/TiO2>17),Th/Nbpm>2;Zr/ Nb>25;Nb/Lapm<0.5 大陆边缘弧;岛弧 -
[1] Şengör A M C. How scientometry is killing science[J]. GSA Today, 2014, 12:44-45.
[2] Wakita K. Mappable features of mélanges derived from ocean plate stratigraphy in the Jurassic accretionary complexes of Mino and Chichibu terranes in southwest Japan[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 568/569:74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.10.019
[3] Şengör A M C. Outcrops, isotopic ages, terranes and the undesirable fate of tectonic interpretations[J]. Geodinamica Acta, 2014, 26:159-174. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/09853111.2013.858953
[4] Safonova I, Maruyama S, Kojima S, et al. Recognizing OIB and MORB in accretionary complexes:a new approach based on ocean plate stratigraphy, petrology and geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 33:92-114. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.013
[5] Hsü K. The principles of mélanges and their bearing on the Franciscan-Knoxville Paradox[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1968, 79:1063-1074. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1968)79[1063:POMATB]2.0.CO;2
[6] Silver E A, Beutner E C. Mélanges[J]. Geology, 1980, 8:32-34. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1980)8<32:M>2.0.CO;2
[7] Raymond L A. Classification of mélanges[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1984, 198:7-20. doi: 10.1130/SPE198
[8] Festa A, Pini G A, Dilek Y, et al. Mélanges and mélange-forming processes:a historical overview and new concepts[J]. International Geology Review, 2010, 52:1040-1105. doi: 10.1080/00206810903557704
[9] Festa A, Dilek Y, Pini G A, et al. Mechanisms and processes of stratal disruption and mixing in the development of mélanges and broken formations:redefining and classifying mélanges[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 568/569:7-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.05.021
[10] 李继亮.碰撞造山带大地构造相.现代地质学论文集(上)[M].南京:南京大学出版社, 1992:9-29. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4885403
[11] 李继亮.全球大地构造相刍议[J].地质通报, 2009, 28:1375-1381. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.10.002 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20091002&flag=1
[12] Robertson A H F. Role of the tectonic facies concept in the orogenic analysis and its application to Tethys in the eastern Mediterranean region[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1994, 37:139-213. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90028-0
[13] 潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等.大地构造相的定义、划分、特征及其鉴别标志[J].地质通报, 2008, 27:1614-1637. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20081004&flag=1
[14] Mitchell A H G. Flysch-ophiolite successions:polarity indicators in arc and collision-type orogens[J]. Nature, 1974, 248:748-749. http://www.nature.com/doifinder/10.1038/248747a0
[15] Maruyama S. Pacific-type orogeny revised:Miyashiro-type orogeny proposed[J]. Island Arc, 1997, 6:91-120. doi: 10.1111/iar.1997.6.issue-1
[16] Xiao W J, Windley B F, Hao J, et al. Accretion leading to collision and Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:termination of the central Asian orogenicbelt[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22:1069, doi:10.1029/2002TC001484.
[17] Kusky T, Windley B, Safonova I, et al. Recognition of ocean plate stratigraphy in accretionary orogens through Earth history:a record of 3.8 billion years of sea floor spreading, subduction, and accretion[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 24:501-547. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.01.004
[18] Şengör A M C. The repeated rediscovery of mélanges and its implication for the possibility and the role of objective evidence in the scientific enterprise[J]. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 2003, 373:385-445.
[19] Cawood P A, Kroner A, Collins W J, et al. Earth accretionary orogens in space and time[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 2009, 318:1-36. doi: 10.1144/SP318.1
[20] Wakabayashi J, Dilek Y. Introduction:Characteristics and tectonic settings of mélanges, and their significance for societal and engineering problems[J]. The Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2011, 480:Ⅴ-Ⅹ.
[21] Dilek Y, Festa F, Ogawa Y, et al. Chaos and geodynamics:mélanges, mélange-forming processes and their significance in the geological record[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 568/569:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.08.002
[22] Kitamura Y, Kimura G. Dynamic role of tectonic mélange during interseismic process of plate boundary mega earthquakes[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 568/569:39-52. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.07.008
[23] Isozaki Y, Maruyama S, Furuoka F. Accreted oceanic materials in Japan[J]. Tectonophysics, 1990, 181:179-205. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(90)90016-2
[24] 王宗起, 闫臻, 王涛, 等.秦岭造山带主要疑难地层时代研究的新进展[J].地球学报, 2009, 30(5):561-570. http://doi.wanfangdata.com.cn/10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2009.05.001
[25] 李荣社, 计文化, 辜平阳, 等.造山带(蛇绿)构造混杂带填图方法[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2016:1-128.
[26] 中国地质调查局.中国地质调查局地质调查专报G1:青藏高原区域地质调查野外工作手册[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2001:1-282.
[27] NACSN (North American Commission on Stratigraphic Nomenclature). Amendments to the American stratigraphic code[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 2005, 89:1459-1464. doi: 10.1306/05230505015
[28] Vannucchi P, Bettelli G. Myths and recent progress regarding the Argille scagliose, northern Apennines, Italy[J]. International Geology Review, 2010, 52:1106-1137. doi: 10.1080/00206810903529620
[29] 全国地层委员会.中国地层指南及中国地层指南说明书(修订版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001:1-59.
[30] Greenly E. The Geology of Anglesey[I]. Great Britain Geological Survey Memoir 1, 1919: 1-980.
[31] Bailey E B, McCallien W J. The Ankara mélange and the Anatolian thrust[J]. Nature, 1950, 166:938-943. doi: 10.1038/166938a0
[32] Bailey E B, McCallien W J. Serpentinite lavas, the Ankara mélange and the Anatolian thrust[J]. Philosophical Transaction of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1953, 62:403-442.
[33] Gansser A. New aspects of the geology in central Iran[C]//Proceedings of the 4th World Petroleum Congress: Rome, Casa Editrice Carlo Colombo, Section 1/A/5, 1955: 279-300.
[34] Studer B. Index der petrographie und stratigraphie der schweiz und ihrer umgebungen[M]. Bern, Verlag Der J Dalp' schen Buch-Und Kunstdhandlung (K. Schmid), 1872:1-272.
[35] Kaufmann F J. Emmen-und schlierengegenden nebst umgebungen bis zur brünigstrasse und linie lungern-grafenort[M]. Beiträge zur Geologische Karte der Schweiz, 1886, 24(1):1-608.
[36] Flores G. Les résultats des études pour les recherches pétroliféres en sicile: discussion[C]//Proceedings of the 4th World Petroleum Congress: Rome, Casa Editrice Carlo Colombo, Section 1/A/2, 1955: 121-122.
[37] Flores G. The results of the studies on petroleum exploration in Sicily: discussion[C]//Bollettino del Servizio Geologico d'Italia, 1956, 78: 46-47.
[38] Flores G. Evidence of slump phenomena (olistostromes) in areas of hydrocarbon exploration in Sicily[C]//Proceedings of the 5th World Petroleum Congress, New York, USA, Section 1, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 1959: 259-275.
[39] Hsü K J. Mélanges and their distinction from olistostromes[C]//Dott R H Jr, Shaver R H. Modern and Ancient Geosynclinal Sedimentation. SEPM Special Publication, 1974, 19: 321-333.
[40] Raymond L A, Terranova T. The mélange problem-a review[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1984, 198:1-5. doi: 10.1130/SPE198
[41] Cowan D S. Structural styles in Mesozoic and Cenozoic mélanges in the western Cordillera of north America[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1985, 96:451-462. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1985)96<451:SSIMAC>2.0.CO;2
[42] Wakita K. Origin of chaotically mixed rocked bodies in the Early Jurassic to Early Cretaceous sedimentationary complex of the Mino terrane, central Japan[J]. Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Japan, 1988, 39:675-757. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BB15538951
[43] Bailey R H, Skehan J W, Dreier R B, et al. Olistostromes of the Avalonian terrane of southeastern New England[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1989, 228:93-112. doi: 10.1130/SPE228
[44] Tull J F, Telle W R. Tectonic setting of olistostromal units and associated rocks in the Talladega slate belt, Alabama Appalachians[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1989, 228:247-269. doi: 10.1130/SPE228
[45] Muller P D, Candela P A, Wylie A G. Liberty complex; polygenetic mélange in the central Maryland Piedmont[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1989, 228:113-134. doi: 10.1130/SPE228
[46] Lacazette A J J, Rast N. Tectonic mélange at Chunky Gal mountain, north Carolina[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1989, 228:217-227. doi: 10.1130/SPE228
[47] Rast N, Horton J W J. Mélanges and olistostromes in the Appalachians of the United States and mainland Canada:an assessment[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1989, 228:1-15. doi: 10.1130/SPE228
[48] Mori R, Ogawa Y, Hirano N, et al. Role of plutonic and metamorphic block exhumation in a forearc ophiolite mélange belt:an example from the Mineoka belt, Japan[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2011, 480:95-116. doi: 10.1130/9780813724805
[49] Osozawa S, Pavlis T, Flowers M F J. Sedimentary block-in-matrix fabric affected by tectonic shear, Miocene Nabae complex, Japan[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2011, 480:189-206. doi: 10.1130/9780813724805
[50] Wakabayashi J. Mélanges of the Franciscan complex, California:diverse structural settings, evidence for sedimentary mixing, and their connection to subduction processes[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2011, 480:117-142. doi: 10.1130/9780813724805
[51] Ernst W G. Franciscan mélanges:coherent blocks in a low-density, ductile matrix[J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 58:626-642. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/00206814.2015.1108879
[52] Malatesta C, Crispini L, Federico L, et al. The exhumation of high pressure ophiolites (Voltri Massif, Western Alps):insights from structural and petrologic data on metagabbro bodies[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 568/569:102-123. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2011.08.024
[53] Byrne T. Early deformation in mélange terranes of the ghost rocks formation, Kodiak Islands, Alaska[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 1984, 198:21-51. doi: 10.1130/SPE198
[54] Cloos M, Shreve R L. subduction-channel model of prism accretion, mélange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins; part Ⅱ, implications and discussion[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1988, 128:501-545. doi: 10.1007/BF00874549
[55] Codegone G, Festa A, Dilek Y. Formation of taconic mélanges and broken formations in the hamburg klippe, central Appalachian orogenic belt, eastern Pennsylvania[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 568/569:215-229. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.03.017
[56] Bailey E H, Irwin W P, Jones D L. Franciscan and related rocks, and their significance in the geology of western California[J]. California Division of Mines and Geology Bulletin, 1964, 83:1-177. http://www.worldcat.org/title/franciscan-and-related-rocks-and-their-significance-in-the-geology-of-western-california/oclc/1666013
[57] Saleeby J B. Kings River ophiolite, southwest Sierra Nevada foothills, California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1978, 89:617-636. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1978)89<617:KROSSN>2.0.CO;2
[58] Saleeby J B. Kaweah serpentinite melange, southwest Sierra Nevada foothills, California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1979, 90:29-46. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1979)90<29:KSMSSN>2.0.CO;2
[59] Wakita K. Geology of the mino district with geological sheet map at 1:50, 000[M]. Geology of Survey Japan, 1995:1-36.
[60] Gansser A. The ophiolitic mélange, a world-wide problem on Tethyan examples[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1974, 67:479-507.
[61] Wakita K. OPS mélange:a new term for mélanges of convergent margins of the word[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57:529-539. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2014.949312
[62] Wakita K, Metcalfe I. Ocean plate stratigraphy in East and Southeast Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2005, 24:670-702. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S136791200400080X
[63] Safonova I Yu, Santosh M. Accretionary complexes in the asia-pacific region:tracing archives of ocean plate stratigraphy and tracking mantle plumes[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25:126-158. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.10.008
[64] Anonymous. Penrose field conference on ophiolites[J]. Geotimes, 1972, 17:24-25. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10030371794
[65] Marsaglia K M. Interarc and backarc basins[C]//Busby C J, Ingersoll RV. Tectonic Sedimentary Basins. Blackwell Science: 1995: 299-330.
[66] Taylor B. Backarc Basins:Tectonics and magmatism[M]. Plenum Press, New York and London, 1995:1-524.
[67] Taylor B, Natland J. Active margins and marginal basins of the western Pacific[M]. Geophysical Monograph Series, 1995, 88:1-417.
[68] Barr S R, Temperley S, Tarney J. Lateral growth of the continental crust through deep level subduction-accretion:a reevaluation of central Greek Rhodope[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:69-94. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00055-3
[69] Sano H, Kojima S. Carboniferous to Jurassic oceanic rocks of Mino-Tamba-Ashio terrane, southwest Japan[J]. Memories of the Geological Society of Japan, 2000, 55:123-144. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10347-004-0002-0
[70] Dilek Y, Furnes H. Ophiolite genesis and global tectonics:geochemical and tectonic fingerprinting of ancient oceanic lithosphere[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011, 123:387-411. doi: 10.1130/B30446.1
[71] Bangs N L B, Gulick S P S, Shipley T H. Seamount subduction erosion in the Nankai trough and its potential impact on the seismogenic zone[J]. Geology, 2006, 34:701-704. doi: 10.1130/G22451.1
[72] Strasser M, Moore G F, Kimura G, et al. Origin and evolution of a splay fault in the Nankai accretionary wedge[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2009, 2:648-652. doi: 10.1038/ngeo609
[73] Karig D E, Sharman G F. Subduction and accretion in trenches[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1975, 86:377-389. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1975)86<377:SAAIT>2.0.CO;2
[74] Taira A, Byrne T, Ashi J. Photographic atlas of an accretionary prism[M]. Springer, Berlin, 1992.
[75] Lallemand S E, Schnurle P, Malavieille J. Coulomb theory applied to accretionary and nonaccretionary wedges-possible causes for tectonic erosion and or frontal accretion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1994, 99:12033-12055. doi: 10.1029/94JB00124
[76] Von Huene R, Scholl D W. Observations at convergent margins concerning sediment subduction, subduction erosion, and the growth of continental crust[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1991, 29:279-316. doi: 10.1029/91RG00969
[77] Dewey J F, Bird J M. The origin and emplacement of the ophiolite suite:Appalachian ophiolites in Newfoundland[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76:3179-3206. doi: 10.1029/JB076i014p03179
[78] Coleman R G. Ophiolites[M]. New York, Springer-Verlag, 1977:1-220.
[79] Nicolas A. Structure of ophiolites and dynamics of oceanic lithosphere[M]. Dordrecht, the Netherlands, Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1989:1-367.
[80] Dilek Y, Flower M F J. Arc-trench roll-back and forearc accretion:2. a model template for ophiolites in Albania, Cyprus, and Oman[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 2003, 218:43-68. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2003.218.01.04
[81] Cloos M. Lithosphere buoyancy and collisional orogenesis:subduction of oceanic plateaus, continental margins, island arcs, spreading ridges, and seamounts[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1993, 105:715-737. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1993)105<0715:LBACOS>2.3.CO;2
[82] Lagabrielle Y, Guivel C, Maury R, et al. Magmatic-tectonic effects of high thermal regime at the site of active ridge subduction:the Chile triple junction model[J]. Tectonophysics, 2000, 326:255-268. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00124-4
[83] Shervais J W. Island arc and ocean crust ophiolites: contrasts in the petrology, geochemistry and tectonic style of ophiolite assemblages in the california coast ranges[C]//Malpas J, Moores E, Panayiotou A, et al. Ophiolites Oceanic Crustal Analogues: Proceedings of the Symposium 'Troodos 1987'. The Geological Survey Department Ministry of Agriculture and Natural Resources, Nicosia, 1990: 507-520.
[84] Wakabayashi J. Anatomy of a subduction complex:architecture of the Franciscan complex, California, at multiple length and time scales[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(8/9):669-746. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00206814.2014.998728
[85] Lister G, Forster M. Tectonic mode switches and the nature of orogenesis[J]. Lithos, 2009, 113:274-291. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2008.10.024
[86] Coleman R G, Irwin W P. Ophiolites and ancient continental margins[M]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1974:921-931.
[87] Shervais J W, Choi S H, Sharp W D, et al. Serpentinite matrix mélange:implications of mixed provenance for mélange formation[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2011, 480:1-30. doi: 10.1130/9780813724805
[88] Gass I G. Is the Troodos massif of cyprus a fragment of mesozoicocean floor[J]. Nature, 1968, 220:39-42. doi: 10.1038/220039a0
[89] Coleman R G. Plate tectonic emplacement of upper mantle peridotites along continental edges[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1971, 76:1212-1222. doi: 10.1029/JB076i005p01212
[90] Moores E M, Vine F J. The Troodos massif, Cyprus, and other ophiolites as oceanic crust:evaluation and implications[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1971, 268A:443-466. http://www.jstor.org/stable/info/73820
[91] Cann J R. The Troodos ophiolite and the upper ocean crust:a reciprocal traffic in scientific concepts[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2003, 373:309-321.
[92] Kerr A C, Pearson D G, Nowell G. M. Magma source evolution beneath the Caribbean oceanic plateau:new insights from elemental and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf isotopic studies of ODP Leg 165 Site 1001 basalts[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 2009, 328:809-827. doi: 10.1144/SP328.31
[93] White R V, Tarney J, Kerr A C, et al. Modification of an oceanic plateau, Aruba, Dutch Daribbean:implications for the generation of continental crust[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46:43-68. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00061-9
[94] Kusky T M, Polat A. Growth of granite-greenstone terrane at convergent margins, and stabilization of Archean cratons[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 305:43-73. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(99)00014-1
[95] Coleman R G. Prospecting for ophiolites along the California continental margin[J]. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2000, 349:351-364.
[96] Choi S H, Shervais J W, Mukasa S B. Supra-subduction and abyssal mantle peridotites of the coast range ophiolite, California[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2008, 156:551-576. doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0300-6
[97] Ernst W G. Mineral chemistry of eclogites and related rocks from the Coltri group, western Liguria, Italy[J]. Tschermaks Mineralogische Und Petrographische Mitteilungen, 1976, 56:293-343. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00371635
[98] Baldwin S L, Harrison T M. The P-T-t history of blocks in serpentinite-matrix mélange, west-central Baja California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1992, 104:18-31. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1992)104<0018:TPTTHO>2.3.CO;2
[99] Tsujimori T, Matsumoto K, Wakabayashi J, et al. Franciscan eclogite revisited:reevaluation of the P-T evolution of tectonic blocks from Tiburon Peninsula, California, U.S.A[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 88:243-267. doi: 10.1007/s00710-006-0157-1
[100] Coleman R G. The diversity of ophiolites[J]. Geologie en Mijnbouw, 1984, 63:141-150.
[101] Wakita K. Geology of the Hachiman district[M]. Quadrangle Series 1:50000 Geological Survey of Japan, 1984:1-89.
[102] 吴浩若, 潘正莆."构造杂岩"及其地质意义——以西准噶尔为例[J].地质科学1991, 1:1-8. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/611ccbc3a8956bec0875e362.html
[103] 张克信, 殷鸿福, 朱云海, 等.造山带混杂岩区地质填图理论、方法与实践:以东昆仑造山带为例[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2001:1-165.
[104] 罗建宁.大陆造山带沉积地质学研究的几个问题[J].地学前缘, 1994, 1:177-183. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98600X/1994Z1/3001295059.html
[105] 陈克强, 汤加富.构造地层单位研究[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996:1-92.
[106] 全国地层委员会.中国地层指南及中国地层指南说明书(修订版)[M].北京:地质出版社, 2001:1-59.
[107] 黎敦朋, 肖爱芳, 张汉军.构造-蛇绿混杂岩工作方法、研究途径及填图单位划分[J].陕西地质, 2001, 19(2):91-97. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_sxdizhi200102013.aspx
[108] Shuttle Radar Topography Mission[EB/OL](2008-11-24)[2017-02-22] http://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/SELECTION/inputCoord.asp.2008.
-



 下载:
下载: