The structural mapping in exposed bedrock areas: methods, practice and exploration
-
摘要:
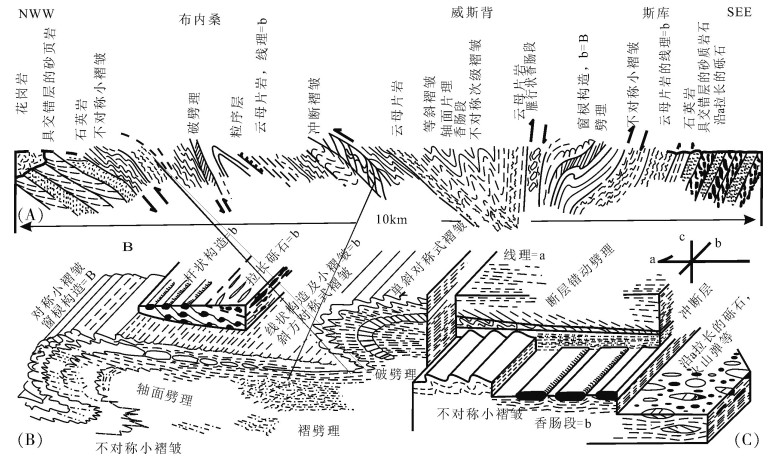
构造地质填图是地质填图的重要内容,也是构造地质研究的基础源泉。填图的主要目标是确定地质体的空间展布规律、变形的几何学和运动学特征,建立填图区构造格架和构造演化序列,探讨构造运动与岩浆活动、变质作用和成矿作用的关系;主要内容是确定填图单元、表示各种(可填的)构造要素。填图的详细程度根据填图的比例尺而定,比例尺越大,可填制和表示的构造要素越多。填图中要重视中小构造要素的观察和描述,构造要素的测量要尽可能多。主要方法包括穿越法、追索法和查证法;比例尺越大,追索法的重要性越大。卫星遥感影像是填图的重要基础,影像的使用贯穿填图的始终。
Abstract:Structural mapping is not only an important part of basic geological mapping but also the source and foundation of structural geology. The major objectives of structural geology mapping lie in finding out the spatial distribution, geometric characteristics and the kinematic properties of the geological units. Furthermore, the structural framework and the evolution can be established in mapping areas so that researchers can have a better understanding of structures'relationships with magma activities, metamorphic events, and mineralization. The primary task of structure field mapping is to define mappable units and measure various structural elements in outcrops. The details of mapping depends on the mapping scale:the larger the scale, the more the mappable structural elements. Attention should be paid to the observation and description of medium-small structures. Mappable elements need to be measured and depicted in detail. There are three methods used in the field mapping, namely crosscutting, tracking and checking. In general, the tracking method plays a more important role as the mapping scale becomes larger. Depending upon the actual conditions, these methods can be flexibly selected or modified. Various kinds of satellite images are useful throughout the field mapping.
-
Key words:
- structural mapping /
- bedrock /
- mapping methods /
- structural elements /
- remote sensing image
-

-
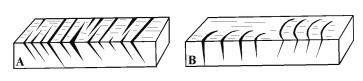
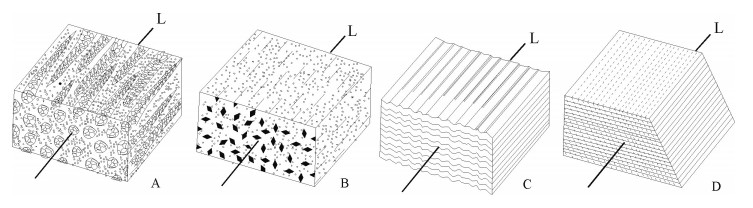
图 1 小型线理主要类型[7]
Figure 1.
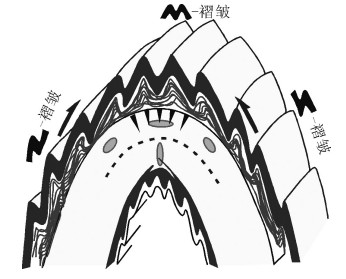
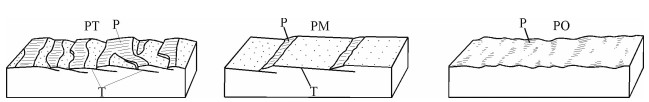
图 2 褶皱不同部位的次级褶皱类型[11]
Figure 2.
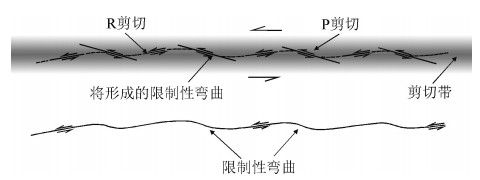
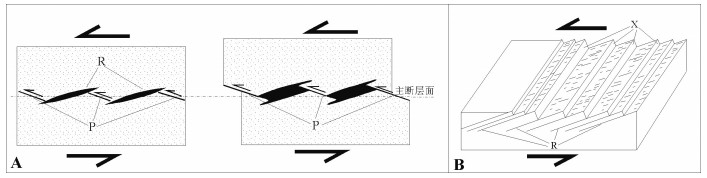
图 3 主断层及其派生次级断层(裂)[18]
Figure 3.
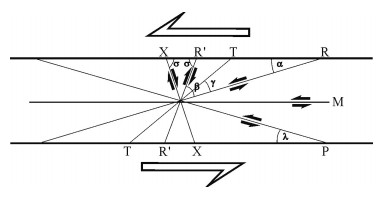
图 4 P、R剪切面组合形成的走滑断层带波状延伸特征[31]
Figure 4.
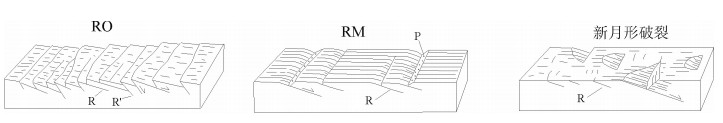
图 5 R剪切断层面表现类型(右行剪切)[12]
Figure 5.
图 6 PR和RX断面类型[30]
Figure 6.
图 8 P剪切断层面表现类型(右行剪切)[12]
Figure 8.
图 9 张性破裂与断层面关系[12]
Figure 9.
图 10 露头尺度构造与区域尺度构造的关系[44]
Figure 10.
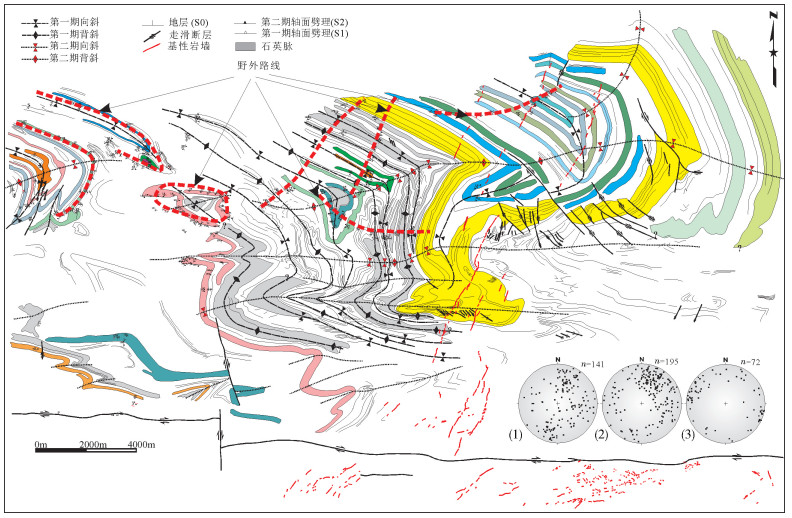
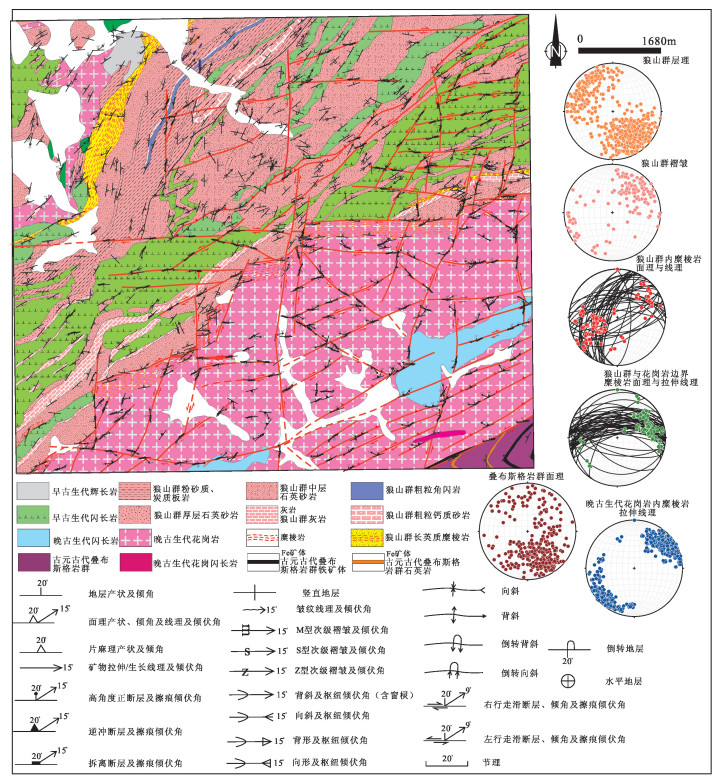
图 11 北山造山带二叠系叠加褶皱地质图[68]
Figure 11.
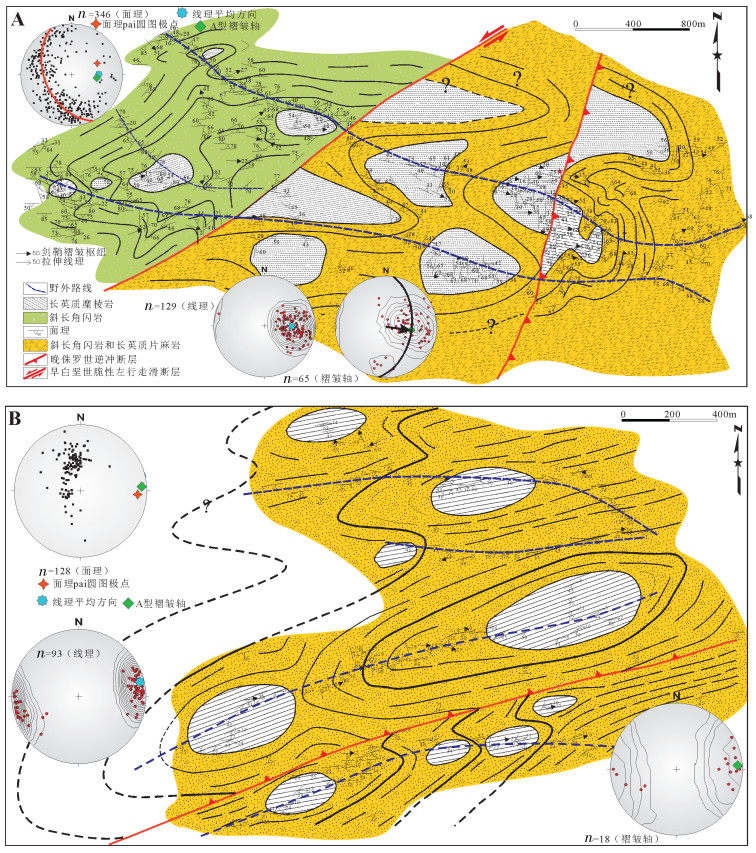
图 12 巴彦乌拉山中段(A)和南段(B)地质图[76]
Figure 12.
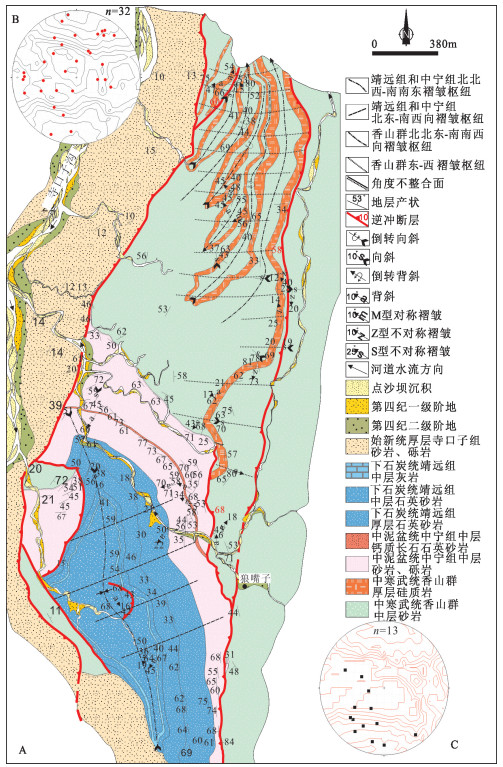
图 14 小峡背斜地质图[82]
Figure 14.
-
[1] 高秉璋, 洪大卫, 郑基俭, 等.花岗岩类区1:5万区域地质填图方法指南[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1991.
[2] 房立民, 杨振升, 李勤, 等.变质岩区1:5万区域地质填图方法指南[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1991.
[3] 熊家镛, 卢重明, 徐怀艾, 等.沉积岩区1:5万区域地质填图方法指南[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1991.
[4] 熊家镛, 张志斌, 蔡麟荪.陆内造山带1:50000区域地质填图方法研究——以哀牢山造山带为例[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1998.
[5] McClay K. The Mapping of Geological Structures[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2nd edition, 2004.
[6] Davis G H, Reynolds S J, Kluth C F. Structural geology of rocks and regions (Third edition)[M]. John Wiley & Sons, 2012.
[7] Turner F J, Weiss L E. Structural analysis of metamorphic tectonites[M]. Me. Graw-Htll Book Comp., 1963.
[8] Sander B. Gefugekunde der Gesteine[M]. Vienna. Julius Springer, 1930.
[9] Backlund H. Petrogenetische Studien an Taimyrgesteinen[J]. GFF, 1918, 40(2):101-203. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/11035891809444435?needAccess=true
[10] Holmes A. The Nomenclature Of Petrology[M]. London, HardPress Publishing, 1928.
[11] Fossen H. Structural Geology. Structural geology[M]. Cambridge University Press, 2010.
[12] Petit J P. Criteria for the sense of movement on fault surfaces in brittle rocks[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1987, 9:597-608. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(87)90145-3
[13] Doblas M. Slickenside kinematic indicators[J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 295:187-197. doi: 10.1016/S0040-1951(98)00120-6
[14] Angelier J. Fault slip analysis and palaeostress reconstruction[C]//Hancock P L. Continental Deformation. London: Pergamon Press, 1994: 53-100.
[15] Tjia H D. Slickensides and fault movements[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1964, 75:683-686. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1964)75[683:SAFM]2.0.CO;2
[16] Riedel W. Zur Mechanik geologischer brucherscheinungen[J]. Zentralblatt fur Mineralogie, Geologie und Palaontologie, 1929, 1929B:354-368. http://www.oalib.com/references/19190949
[17] Groshong R H J. Low-temperature deformation mechanisms and their interpretation[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1988, 100:1329-1360. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1988)100<1329:LTDMAT>2.3.CO;2
[18] Logan J M, Dengo C A, Higgs N G, et al. Fabrics of experimental fault zones: their development and relationship to mechanical behavior[C]//Evans B, Wong T. Fault mechanics and transport properties of rocks. San Diego: Academic Press, 1992: 33-67.
[19] Brosch F J, Kurz W. Fault damage zones dominated by high-angle fractures within layer-parallel brittle shear zones:examples from the eastern Alps[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 2008, 299(1):75-95. doi: 10.1144/SP299.5
[20] Richard P D, Naylor M A, Koopman A. Experimental models of strike-slip tectonics[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 1995, 1:71-80. doi: 10.1144/petgeo.1.1.71
[21] Keller J V A, Hall S H, McClay K R. Shear fracture pattern and microstructural evolution in transpression fault zones from field and laboratory studies[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1997, 19:1173-1187. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(97)00042-4
[22] Tindall S E. Development of oblique-slip basement-cored uplifts: Insights from the Kaibab uplift and from physical models[D]. The University of Arizona: Ph D Thesis, 2000.
[23] Tindall S E, Davis G H. Monocline development by oblique-slip fault-propagation folding:the East Kaibab monocline, Colorado Plateau, Utah[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1999, 21:1303-1320. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(99)00089-9
[24] Naylor M A, Mandl G, Sijpesteijn C H K. Fault geometries in basement-induced wrench faulting under different initial stress states[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1986, 8:737-752. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(86)90022-2
[25] Kim Young-Seog, Peacock D C P, Sanderson D J. Fault damage zones[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2004, 26:503-517. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2003.08.002
[26] Hancock P L, Barka A A. Kinematic indicators on active normal faults in western Turkey[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1987, 9:573-584. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(87)90142-8
[27] Chester F M, Chester J S. Stress and deformation along wavy frictional faults[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2000, 105(B10):23421-23430. doi: 10.1029/2000JB900241
[28] Davis G A, 郑亚东.变质核杂岩的定义、类型及构造背景[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(4):185-192. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20020457&flag=1
[29] Sagy A, Brodsky E E, Axen G J. Evolution of fault-surface roughness with slip[J]. Geology, 2007, 35(3):283-286. doi: 10.1130/G23235A.1
[30] Gamond J F. Displacement features associated with fault zones:a comparison between observed examples and experimental models[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1983, 5:33-45. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(83)90005-6
[31] Cowgill E, Arrowsmith J R, Yin A, et al. The akato tagh bend along the altyn tagh fault, northwest Tibet 2:active deformation and the importance of transpression and strain hardening within the Altyn Tagh system[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2004, 116:1443-1464. doi: 10.1130/B25360.1
[32] Woodcock N H, Schubert C. Continent strike-slip tectonics[C]//Hancock P L. Continental Deformation. London: Pergamon Press, 1994: 251-263.
[33] Hancock P L. Brittle microtectonics:principles and practice[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1985, 7:437-457. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(85)90048-3
[34] Pollard D D, Segall P, Delaney P T. Formation and interpretation of dilatant echelon cracks[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1982, 93(12):1291-1303. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1982)93<1291:FAIODE>2.0.CO;2
[35] Rothery E. En echelon vein array development in extension and shear[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1988, 10(1):63-71. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(88)90128-9
[36] Aydin A, Schultz R A. Effect of mechanical interaction on the development of strike-slip faults with echelon patterns[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1990, 12(1):123-129. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(90)90053-2
[37] Tjia H D. Fault movement, reoriented stress field and subsidiary structures[J]. Pacific Geology, 1971, 5, 49-90. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0031920176900650
[38] Doblas M, Mahecha V, Hoyos M. Slickenside and fault surface kinematic indicators on active normal faults of the Alpine Betic cordilleras, Granada, southern Spain[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1997, 19(2):159-170. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(96)00086-7
[39] Platt J P, Vissers R L M. Extensional structures in anisotropic rocks[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1980, 2:397-410. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(80)90002-4
[40] Hancock P L. The analysis of en-echelon veins[J]. Geological Magzine, 1972, 109:269-276. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800039315
[41] Norris D K, Barron K. Structural analysis of features on natural and artificial faults[C]//Baer A, Norris D K. Research in Tectonics. Geological Survey of Canada Paper, 1969: 68-52, 136-167.
[42] Means W D. A newly recognized type of slickenside striation[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1987, 9:585-590. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(87)90143-X
[43] Engelder J T. Microscopic wear grooves on slickensides:Indicators of paleoseismicity[J]. Journal of geophysical Research, 1974, 79(29):4387-4392. doi: 10.1029/JB079i029p04387
[44] Wilson G. The tectonic significance of small scale structures and their importance to the geologist in the field[M]. Societé Geologique de Belgique, 1961.
[45] Hansen E. Strain Facies[M]. Berlin, New York, Springer-Verlag, 1971.
[46] Julivert M, Marcos A. Superimposed folding under flexural conditions in the Cantabrian Zone (Hercynian Cordillera, northwest Spain)[J]. American Journal of Science, 1973, 273(5):353-375. doi: 10.2475/ajs.273.5.353
[47] Hatcher R D. Macroscopic polyphase folding illustrated by the Toxaway dome, eastern Blue Ridge, South Carolina-North Carolina[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1977, 88(11):1678-1688. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1977)88<1678:MPFIBT>2.0.CO;2
[48] Grujic D, Walter T R, Gärtner H. Shape and structure of analogue models of refolded layers[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2002, 24(8):1313-1326. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8141(01)00134-1
[49] Ramsay J G. Folding and Fracturing of Rocks[J]. New York-London, 1967. http://is.muni.cz/publication/472138
[50] Ramsay J G, Huber I M. The Techniques of modern structural geology. volume 2:folds and fractures[M]. London-San Diego, 1987.
[51] Ramsay J G, Lisle R J. The Techniques of modern structural geology. volume 3:applications of continuum mechanics in structural geology[M]. London-San Diego, 2000.
[52] Thiessen R. Two-dimensional refold interference patterns[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1986, 8(5):563-573. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(86)90005-2
[53] Thiessen R L, Means W D. Classification of fold interference patterns:a reexamination[J]. Journal of structural Geology, 1980, 2(3):311-316. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(80)90019-X
[54] Moore R R, Johnson S E. Three-dimensional reconstruction and modelling of complexly folded surfaces using mathematica[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2001, 27(4):401-418. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300400000790
[55] Grasemann B, Wiesmayr G, Draganits E, et al. Classification of refold structures[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2004, 112(1):119-125. doi: 10.1086/379696
[56] Weiss L E. Geometry of superposed folding[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1959, 70(1):91-106. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1959)70[91:GOSF]2.0.CO;2
[57] Watkinson A J. Patterns of fold interference:influence of early fold shapes[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1981, 3(1):19-23. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(81)90053-5
[58] Johns M K, Mosher S. Physical models of regional fold superposition:the role of competence contrast[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1996, 18(4):475-492. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/019181419500100R
[59] Ghosh S K, Ramberg H. Buckling experiments on intersecting fold patterns[J]. Tectonophysics, 1968, 5(2):89-105. doi: 10.1016/0040-1951(68)90083-8
[60] Ghosh S K, Mandal N, Khan D, et al. Modes of superposed buckling in single layers controlled by initial tightness of early folds[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1992, 14(4):381-394. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(92)90100-B
[61] Ghosh S K, Mandal N, Sengupta S, et al. Superposed buckling in multilayers[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1993, 15(1):95-111. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(93)90081-K
[62] Gruji cD. The influence of initial fold geometry on type 1 and type 2 interference patterns:an experimental approach[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1993, 15(3/5):293-307. http://cat.inist.fr/?aModele=afficheN&cpsidt=4716735
[63] Li J Y. Late Neoproterozoic and paleozoic tectonic framework and evolution of eastern Xinjiang, NW China[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(3):304-322. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1342937X12001852
[64] 左国朝, 刘义科, 刘春燕.甘新蒙北山地区构造格局及演化[J].甘肃地质学报, 2003, 12(1):1-15. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/730ef92187c24028915fc3a3.html
[65] Xiao W J, Zhang L C, Qin K Z, et al. Paleozoic accretionary and collisional tectonics of the Eastern Tianshan (China):implications for the continental growth of central Asia[J]. American Journal of Science, 2004, 304(4):370-395. doi: 10.2475/ajs.304.4.370
[66] Xiao W, Han C, Yuan C, et al. Middle cambrian to permian subduction-related accretionary orogenesis of northern Xinjiang, NW China:implications for the tectonic evolution of central asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2008, 32(2):102-117. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912007001708
[67] 甘肃省地质矿产局.甘肃省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989.
[68] Zhang J, Cunningham D. Kilometer-scale refolded folds caused by strike-slip reversal and intraplate shortening in the Beishan region, China[J]. Tectonics, 2012, 31:1-19. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2011TC003050/full?scrollTo=footer-citing
[69] 沈其韩, 耿元生, 王新社, 等.阿拉善地区前寒武纪斜长角闪岩的岩石学、地球化学、形成环境和年代学[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2005, 24(1):21-31. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_yskwxzz200501003.aspx
[70] 杨振德, 潘行适, 杨易福.阿拉善断块及邻区地质构造特征与矿产[M].北京:科学出版社, 1988.
[71] 内蒙古自治区地质矿产局.内蒙古自治区岩石地层[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1996.
[72] Wu S J, Hu J M, Ren M H, et al. Petrography and zircon U-Pb isotopic study of the bayanwulashan complex:constrains on the paleoproterozoic evolution of the alxa block, westernmost north China craton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 94:226-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.05.011
[73] 李俊建, 沈保丰, 李惠民, 等.内蒙古西部巴彦乌拉山地区花岗闪长岩质片麻岩的单颗粒锆石U-Pb法年龄[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(12):1243-1245. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.12.013 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2004012224&flag=1
[74] 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等.内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质基底阿拉善群的再厘定[J].中国地质, 2006, 33(1):138-145. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200601015
[75] 耿元生, 王新社, 沈其韩, 等.内蒙古阿拉善地区前寒武纪变质岩系形成时代的初步研究[J].中国地质, 2007, 34(2):77-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200702006
[76] Zhang J, Li J Y, Xiao W X, et al. Kinematics and geochronology of multistage ductile deformation along the eastern alxa block, NW China:new constraints on the relationship between the north China plate and the alxa block[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2013, 57:38-57. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2013.10.002
[77] Zhang J, Li J Y, Zhang B H, et al. Timing of amalgamation of the alxa block and the north China block:constraints based on detrital zircon U-Pb ages and sedimentologic and structural evidence[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016:668-669. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195115006642
[78] Zhang J, Zhang Y P, Xiao W X, et al. Linking the alxa terrane to the eastern gondwana during the early paleozoic:Constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb ages and cambrian sedimentary records[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(3):1168-1182. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.012
[79] Liu S. The coupling mechanism of basin and orogen in the western Ordos Basin and adjacent regions of China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 1998, 16(4):369-383. doi: 10.1016/S0743-9547(98)00020-8
[80] 张进, 马宗晋, 任文军.鄂尔多斯西缘逆冲褶皱带构造特征及其南北差异的形成机制[J].地质学报, 2004, 78(5):600-611. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKX201502005.htm
[81] 王进寿, 张开成, 王占昌, 等.西宁盆地深部构造与地震[J].高原地震, 2006, 18(3):16-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gydz200603004
[82] Zhang J, Cunningham D. Polyphase transpressional development of a NNE-striking basement-cored anticline in the Xining basin, northeastern qinghai-tibetan plateau[J]. Geological Magazine, 2013, 150:626-638. doi: 10.1017/S0016756812000866
[83] Darby B J, Ritts B D. Mesozoic contractional deformation in the middle of the asian tectonic collage:the intraplate western ordos fold-thrust belt, China[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 205(1):13-24. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0012821X02010269
[84] Darby B J, Ritts B D. Mesozoic structural architecture of the lang shan, north-central China:intraplate contraction, extension, and synorogenic sedimentation[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 2007, 29(12):2006-2016. doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2007.06.011
[85] Zhang J, Li J Y, Li Y F, et al. Mesozoic-Cenozoic multi-stage intraplate deformation events in the Langshan region and their tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(1):78-102. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2014.88.issue-1
[86] Dan W, Li X H, Wang Q, et al. Phanerozoic amalgamation of the alxa block and north China craton:evidence from paleozoic granitoids, U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf-O isotope geochemistry[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 32:105-121. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.02.011
[87] Zhao G, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136(2):177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
[88] 浙江省地质矿产局.浙江省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1989.
[89] 福建省地质矿产局.福建省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1985.
[90] 广东省地质矿产局.广东省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社, 1988.
[91] 水涛.中国东南大陆基底构造格局[J].中国科学(B辑), 1987(4):78-86. http://engine.scichina.com/publisher/scp/journal/SSPC-B0/17/4/10.1360/zb1987-17-4-414
[92] 水涛, 徐步台, 梁如华, 等.中国浙闽变质基底地质[M].北京:科学出版社, 1988.
[93] 水涛, 徐步台, 梁如华, 等.绍兴-江山古陆对接带[J].科学通报, 1986, 31(6):444-448. http://www.oalib.com/paper/1675500
[94] 孔祥生, 包超民, 顾明光.浙江诸暨地区陈蔡群主要地质特征及其构造演化探讨[J].浙江地质, 1994, (1):15-29. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/83464A/199401/3001299207.html
[95] 孔祥生, 李志飞, 冯长根, 等.浙江陈蔡地区前寒武纪地质(前寒武纪地质第7号)[M].北京:地质出版社, 1995.
[96] 程海.浙西北晚元古代早期碰撞造山带的初步研究[J].地质论评, 1991, 37(3):203-213. http://www.oalib.com/paper/4888365
[97] 程海.浙西北晚元古代岛弧火山岩的地球化学研究[J].地球化学, 1993, (1):18-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX601.005.htm
[98] Li Z X, Li X H, Wartho J A, et al. Magmatic and metamorphic events during the early Paleozoic WuyiYunkai orogeny, southeastern South China:New age constraints and pressure-temperature conditions[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2010, 122(5/6):772-793. http://gsabulletin.gsapubs.org/content/122/5-6/772.abstract
[99] 胡艳华, 顾明光, 徐岩, 等.浙江诸暨地区陈蔡群加里东期变质年龄的确认及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2011, 30(11):1661-1670. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.11.002 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20111102&flag=1
[100] 赵国春, 孙德有, 贺同兴.陈蔡群构造变形特征及变形时代讨论[J].浙江地质, 1994, (1):38-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201111003.htm
[101] 赵国春, 孙德有.浙西南陈蔡群变质阶段划分及变质作用p-TD轨变研究[J].吉林大学学报, 1994, (3):246-253. https://www.wenkuxiazai.com/doc/7bbf447902768e9951e738b9.html
[102] Zhao G, Cawood P A. Tectonothermal evolution of the Mayuan Assemblage in the Cathaysia Block; implications for Neoproterozoic collision-related assembly of the South China Craton[J]. American Journal of Science, 1999, 299(4):309-339. doi: 10.2475/ajs.299.4.309
[103] Zhang J, Li J Y, Xiao W X, et al. Multistage Deformation in the Northeastern Segment of the Jiangshao Fault (Suture) Belt:Constraints for the Relationship between the Yangtze Plate and the Cathaysia Old Land[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(4):948-978. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2013.87.issue-4
[104] 高林志, 丁孝忠, 刘燕学, 等.江山-绍兴断裂带陈蔡岩群片麻岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2014, 33(5):641-648. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20140505&flag=1
[105] Wang D, Zheng J, Ma Q, et al. Early Paleozoic crustal anatexis in the intraplate Wuyi-Yunkai orogen, South China[J]. Lithos, 2013, 175:124-145. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024493713001412
[106] Xiao W, He H. Early Mesozoic thrust tectonics of the northwest Zhejiang region (Southeast China)[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2005, 117(7/8):945-961. http://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/117/7-8/945
[107] Zhou X, Zhu Y. Late Proterozoic colisional orogen and geosuture in Southeastern China:Petrological evidence[J]. Acta Geochimica, 1993, 12(3):239-251. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02843363
[108] Zhang J, Qu J F, Zhao H, et al. Paleozoic to Mesozoic deformation of eastern Cathaysia, a case study of Chencai Complex, Zhejiang Province, eastern China and its tectonic implications[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2018(accepted). https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article-abstract/130/1-2/114/353730/paleozoic-to-mesozoic-deformation-of-eastern
-



 下载:
下载: