High pressure metamorphic belt in central Qiangtang, Tibetan Plateau: Progress and unsolved problems
-
摘要:
羌塘中部高压变质带是目前青藏高原内部延伸规模最大的高压变质带,是理解特提斯演化的关键地质记录。高压变质带主要沿龙木措-双湖-澜沧江缝合带一线出露,主要由榴辉岩、蓝片岩、石榴子石多硅白云母片岩及少量高压麻粒岩组成。其中,榴辉岩主要出露于戈木、果干加年山、冈玛错、巴青及滇西的勐库地区,主要呈透镜状产于石榴子石多硅白云母片岩中。除巴青地区的榴辉岩外,其余地区榴辉岩的峰期变质温度较低且含有硬柱石及其假象,峰期变质条件位于硬柱石榴辉岩相稳定区域,是洋壳冷俯冲的产物。虽然对于戈木地区榴辉岩锆石成因仍有争议,但已有资料显示,羌塘中部高压变质带主体变质时代集中在晚三叠世,其相关高压变质岩石的折返可能与洋盆的闭合及随后的陆-陆碰撞相关。近期研究表明,羌塘中部可能存在二叠纪低温高压变质岩,折返于大洋俯冲阶段,可能与洋岛或海山的俯冲及引发的俯冲侵蚀作用相关。此外,羌塘香桃湖地区出露早古生代的基性高压麻粒岩,是冈瓦纳大陆北缘陆块拼贴的记录。因此,对羌塘中部高压变质带进行进一步系统的研究工作,对于深入理解冈瓦纳北缘构造演化及古特提斯的俯冲与闭合过程具有重要的意义。
Abstract:A 500km-long high-pressure metamorphic belt has been documented in the central Qiangtang Block of northern Tibet, which is thought to have constituted the crucial geological archives of subduction and exhumation of Paleo-Tethys oceanic lithosphere. The high-pressure metamorphic rocks are mostly exposed along the Longmu Co-Shuanghu suture zone, and are composed of eclogites, blueschists, garnet-phengite-schists (Grt-Phn schists), and minor high-pressure mafic granulites. The eclogites in central Qiangtang are reported from Gemu, Guoganjianian Mt., Gangma Co, Baqing, and Mengku area, and occur mainly as blocks or small lenses in Grt-Phn schists. Apart from newly discovered Baqing eclogites, most eclogites from central Qiangtang Block are characterized by low peak temperatures and presence of lawsonite or pseudomorphs of epidote + paragonite, and their peak P-T results lie mainly in the lawsonite-eclogite field. The ages of most eclogites and blueschists from central Qiangtang block have been constrained as Late Triassic which are regarded as the results of closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean and following continental collision. Furthermore, the Permian high-pressure metamorphic rocks were also identified and their P-T-t paths revealed a complete evolutional history for the subduction erosion in response to the subduction of seamounts (or oceanic islands). Moreover, the discovery of Silurian high-pressure granulites in the central Qiangtang block indicates the existence of a previous collisional event on the northern margin of the Indo-Australian Gondwana. Hence, further comprehensive studies of the high-pressure metamorphic belt in central Qiangtang will provide valuable insights into the tectonic evolution of the north margin of Gondwana during the early Paleozoic and the opening and closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean.
-
Key words:
- Tibetan Platean /
- Qiangtang block /
- eclogite /
- blueschist /
- Paleo-Tethys Ocean
-

-
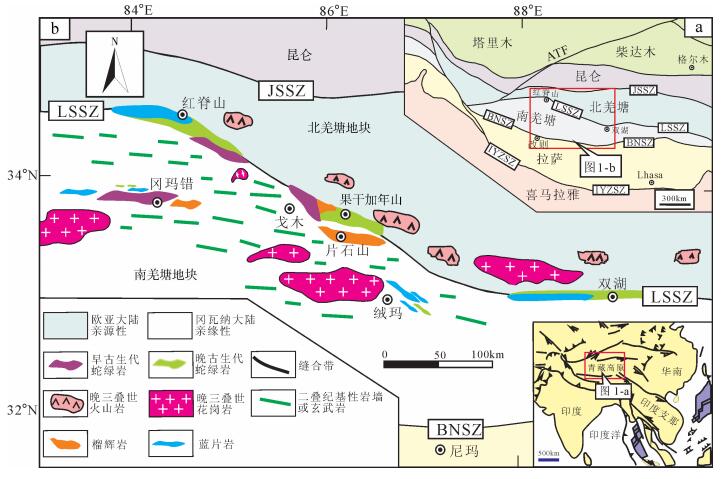
图 1 羌塘地区地质简图(据参考文献[6]修改)
Figure 1.
表 1 羌塘中部榴辉岩中金红石微量元素含量及金红石锆温度计计算结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS analyses of trace elements in rutile grains and peak temperature estimated by zircon-in-rutile thermometer of eclogites from central Qiangtang
元素 GZ85-1 GZ85-14 CM14073-1 CM1407-2 CM1407-3 CM1407-4 CM1407-5 片石山 片石山 果干加年山 果干加年山 果干加年山 果干加年山 果干加年山 Sc 1.63 0.80 1.78 1.15 0.98 1.09 1.24 V 1478 1594 914 893 906 933 908 Cr 40.8 30.6 282 817 464 340 383 Ni 0.00 0.34 0.06 0.34 0.60 0.09 0.36 Y 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.03 0.04 Zr 58.4 39.7 41.0 45.8 37.1 37.1 41.5 Nb 421 468 116 189 106 121 127 Hf 2.41 1.72 2.36 3.04 2.32 2.24 2.29 Ta 23.0 29.4 10.3 20.6 8.11 9.17 10.2 Pb 0.05 0.00 0.10 0.06 0.05 0.05 0.08 T[70] 523 471 475 490 462 462 477 T[71] 526 503 505 511 499 499 506 T[72] 581 557 550 565 553 553 559 -
[1] Carswell D A. Eclogite Facies Rocks[M]. New York:Blackie, 1990.
[2] Carswell D A, O'brien P J. Thermobarometry and geotectonic significance of high-pressure granulites:examples from the Moldanubian Zone of the Bohemian Massif in Lower Austria[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1993, 34(3):427-459. doi: 10.1093/petrology/34.3.427
[3] Ernst W G, Liou J G. Contrasting plate-tectonic styles of the Qinling-Dabie-Sulu and Franciscan metamorphic belts[J]. Geology, 1995, 23:353-356. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0353:CPTSOT>2.3.CO;2
[4] Zhao G C, Cawood P A, Wilde S A, et al. High-pressure granulites (retrograded eclogites) from the Hengshan Complex, North China Craton:petrology and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(6):1141-1170. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.6.1141
[5] Zhao G C, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136:177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
[6] Zhai Q G, Zhang R Y, Jahn B M, et al. Triassic eclogites from central Qiangtang, northern Tibet, China:petrology, geochronology and metamorphic P-T path[J]. Lithos, 2011, 125:173-189. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.02.004
[7] 陆济璞, 张能, 黄位鸿, 等.藏北羌塘中北部红脊山地区蓝闪石+硬柱石变质矿物组合的特征及其意义[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(1):70-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.01.012 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060112&flag=1
[8] 邓希光, 丁林, 刘小汉, 等.藏北羌塘中部冈玛日-桃形错蓝片岩的发现[J].地质科学, 2000, 35(2):227-232. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.02.012
[9] 邓希光, 丁林, 刘小汉, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部蓝片岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2002, 18(4):517-525. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200204010
[10] 翟庆国, 王军, 王永.西藏改则县冈玛错地区发现榴辉岩[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(12):1720-1724. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.12.005 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20091204&flag=1
[11] 翟庆国, 李才, 董永胜, 等.西藏羌塘中部荣玛地区蓝片岩岩石学、矿物学和Ar-Ar年代学[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(9):2281-2288.
[12] 董永胜, 李才.藏北羌塘中部果干加年山地区发现榴辉岩[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1197-1200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.09.006 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090906&flag=1
[13] 李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部发现榴辉岩及其意义[J].科学通报, 2006, 25(1/2):70-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200601014
[14] Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, Zhang R Y, et al. Triassic subduction of thePaleo-Tethys in northern Tibet, China:evidence from the geochemical and isotopic characteristics of eclogites and blueschists of the Qiangtang Block[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 42:1356-1370. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.07.023
[15] 张修政, 董永胜, 施建荣, 等.羌塘中部龙木错-双湖缝合带中硬玉石榴石二云母片岩的成因及意义[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(1):93-103. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201001008
[16] Kapp P, An Y, Manning C E, et al. Tectonic evolution of the early Mesozoic blueschist-bearing Qiangtang metermorphic belt, central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22(4). DOI:10.1029/2001TC001332.
[17] 鲍佩声, 肖序常, 王军, 等.西藏中北部双湖地区蓝片岩带及其构造涵义[J].地质学报, 1999, 73(4):302-314. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199900084713
[18] Zhang Y X, Jin X, Zhang K J, et al. Newly discovered late triassic baqing eclogite in central tibet indicates an anticlockwise west-east qiangtang collision[J]. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1). DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-19342-w.
[19] 徐桂香, 曾文涛, 孙载波, 等.滇西双江县勐库地区(退变)榴辉岩的岩石学、矿物学特征[J].地质通报, 2016, 35(7):1035-1045. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.07.001 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20160701&flag=1
[20] 陈光艳, 徐桂香, 孙载波, 等.滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩中闪石类矿物的成因研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(1):36-47. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.01.003
[21] 孙载波, 李静, 周坤, 等.滇西双江县勐库地区退变质榴辉岩的岩石地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].现代地质, 2017, 31(4):746-756. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2017.04.009
[22] 李静, 孙载波, 黄亮, 等.滇西勐库退变质榴辉岩的P-T-t轨迹及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2017, 33(7):2285-2301. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201707022
[23] 张修政, 董永胜, 李才, 等.从洋壳俯冲到陆壳俯冲和碰撞:来自羌塘中西部地区榴辉岩和蓝片岩地球化学的证据[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(10):2821-2834. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201410003
[24] 李才.龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带与石炭二叠纪冈瓦纳北界[J].长春地质学院学报, 1987, 17(2):155-166. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001164867
[25] 李才.青藏高原龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(1):104-119. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp200801012
[26] Metcalfe I. Origin and assembly of Southeast Asian continental terranes[C]//Audley-Charles M G, Hallam A. Gondwana and Tethys. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 1988, 37: 101-118.
http: //adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1988GSLSP..37..101M [27] Metcalfe I. Gondwanaland origin, dispersion, and accretion of East and Southeast Asian continental terranes[J]. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 1994, 7:333-347. doi: 10.1016/0895-9811(94)90019-1
[28] Metcalfe I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66:1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
[29] Zhang X Z, Dong Y S, Wang Q, et al. Carboniferous and Permian evolutionary records for the Paleo-Tethys Ocean constrained by newly discovered Xiangtaohu ophiolites from central Qiangtang, central Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2016, 35:1670-1686. doi: 10.1002/tect.v35.7
[30] Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, Wang J, et al. The Carboniferous ophiolite in the middle of the Qiangtang terrane, Northern Tibet:SHRIMP U-Pb dating, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168/169:186-199. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.02.005
[31] 李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 等.冈瓦纳大陆北缘早期洋壳信息——来自青藏高原羌塘中部早古生代蛇绿岩依据[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(10):1602-1612. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20081003&flag=1
[32] Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, Wang J, et al. Oldest paleo-tethyan ophiolitic mélange in the Tibetan plateau[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2016, 128(3/4):355-373. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20162017030900015934
[33] Hu P Y, Li C, Wu Y W, et al. Opening of the Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Lancangjiang ocean:constraints from plagiogranites[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2014, 59(25):3188-3199. doi: 10.1007/s11434-014-0434-z
[34] Zhang X Z, Dong Y S, Li C, et al. Silurian high-pressure granulites from Central Qiangtang, Tibet:Constraints on early Paleozoic collision along the northeastern margin of Gondwana[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 405:39-51. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.08.013
[35] Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, Su L, et al. Triassic arc magmatism in the qiangtang area, northern tibet:zircon u-pb ages, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 63:162-178. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.025
[36] Jiang Q Y, Li C, Su L, et al. Carboniferous arc magmatism in the Qiangtang area, Northern Tibet:Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemical and Lu-Hf isotopic characteristics, and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 100:132-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.012
[37] Dan W, Wang Q, Zhang X Z, et al. Magmatic record of late devonian arc-continent collision in the northern qiangtang, Tibet:implications for the early evolution of east paleo-tethys ocean[J]. Lithos, 2018, 308/309:104-117. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2018.03.002
[38] Liu J H, Xie C M, Li C, et al. Early Carboniferous adakite-like and Ⅰ-type granites in central Qiangtang, northern Tibet:Implications for intra-oceanic subduction and back-arc basin formation within the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Lithos, 2018, 296/299:265-280. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.11.005
[39] 董永胜, 李才, 施建荣, 等.羌塘中部高压变质带的退变质作用及其构造侵位[J].岩石学报, 2009, 25(9), 2303-2309. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200909022
[40] 张修政, 董永胜, 李才, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部不同时代榴辉岩的识别及其意义——来自榴辉岩及其围岩40Ar-39Ar年代学的证据[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(12):1815-1824. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.12.009 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20101209&flag=1
[41] 张修政, 董永胜, 李才, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部榴辉岩地球化学特征及其大地构造意义[J].地质通报, 2010, 29(12):1804-1814. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.12.008 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20101208&flag=1
[42] 翟庆国, 李才, 黄小鹏.西藏羌塘中部角木日地区二叠纪玄武岩的地球化学特征及其构造意义[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(12):1419-1427. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.010 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2006012264&flag=1
[43] Fan J J, Li C, Xie C. et al. Remnants of Late Permian-Middle Triassic ocean islands in northern Tibet:implications for the late-stage evolution of the Paleo-Tethys ocean[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 44:7-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.10.020
[44] 朱同兴, 张启跃, 董瀚, 等.藏北双湖才多茶卡一带构造混杂岩中新发现晚泥盆世和晚二叠世放射虫硅质岩[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(12):1413-1418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.12.009 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2006012263&flag=1
[45] 张修政, 董永胜, 李才, 等.羌塘中部晚三叠世岩浆活动的构造背景及成因机制——以红脊山地区香桃湖花岗岩为例[J].岩石学报, 2014, 30(2):547-564. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8248049
[46] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y, et al. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23(4):1429-1454. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002
[47] 李才, 黄小鹏, 翟庆国, 等.龙木错-双湖-吉塘板块缝合带与青藏高原冈瓦纳北界[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(4):136-147. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.04.011
[48] Li C, Zheng A. Paleozoic stratigraphy in the Qiangtang region of Tibet:relations of the Gondwana and Yangtze continents and ocean closure near the end of the Carboniferous[J]. International Geology Review, 1993, 35(9):797-804. doi: 10.1080/00206819309465558
[49] 李才, 翟刚毅, 王立全, 等.认识青藏高原的重要窗口——羌塘地区近年来研究进展评述(代序)[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1169-1177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.09.001 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090901&flag=1
[50] 彭虎, 李才, 解超明, 等.藏北羌塘中部日湾茶卡组物源——LAICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄及稀土元素特征[J].地质通报, 2014, 23(11):1715-1727. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.11.008 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20141108&flag=1
[51] Zhang X Z, Dong Y S, Wang Q, et al. Metamorphic records for subduction erosion and subsequent underplating processes revealed by garnet-staurolite-muscovite schists in central qiangtang, Tibet[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2017, 18:266-279. doi: 10.1002/2016GC006576
[52] Cawood P A, Hawkesworth C J, Dhuime B. Detrital zircon record and tectonic setting[J]. Geology, 2012, 40(10):875-878. doi: 10.1130/G32945.1
[53] Xu W, Dong Y, Zhang X, et al. Petrogenesis of high-timafic dykes from southern qiangtang, tibet:implications for a ca. 290Ma large igneous province related to the early permian rifting of gondwana[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 36:410-422. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.07.016
[54] Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, Su L, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic compositions of a mafic dyke swarm in the Qiangtang terrane, northern Tibet and geodynamic implications[J]. Lithos, 2013, 174:28-43. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.018
[55] Hening A. Eur Petrographic and Geologie Von Sudwest Tibet[C]//Hedin S. Southern Tibet. Stockholm: Noratet, 1915, 5: 220.
http: //www.mendeley.com/research/zur-petrographie-und-geologie-von-sudwest-tibet/ [56] 李才.西藏羌塘中部蓝片岩青铝闪石40Ar/39Ar定年及其地质意义[J].科学通报, 1997, 42:448. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199700343420
[57] Tang X C, Zhang K J. Lawsonite-and glaucophane-bearing blueschists from NW Qiangtang, northern Tibet, China:mineralogy, geochemistry, geochronology, and tectonic implications[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56(2):150-166. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.820866
[58] Zhai Q G, Jahn B M, Li X H, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating of eclogite from the Qiangtang terrane, north-central Tibet:a case of metamorphic zircon with magmatic geochemical features[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2016, 106:1-17. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=e93d47cc9a2e69380780ef55bbd60bb7&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[59] Pullen A, Kapp P, Cehrels G E, et al. Triassic continental subduction in central Tibet and Mediterranean-style closure of the PaleoTethys Ocean[J]. Geology, 2008, 36:351-354. doi: 10.1130/G24435A.1
[60] Hermann J, Rubatto D, Korsakov A, et al. Multiple zircon growth during fast exhumation of diamondiferous, deeply subducted continental crust (Kokchetav massif, Kazakhstan)[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy & Petrology, 2001, 141(1):66-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ023549516
[61] Liu F L, Xu Z Q, Xue H M. Tracing the protolith, UHP metamorphism, and exhumation ages of orthogneiss from the SW Sulu terrane (eastern China):SHRIMP U-Pb dating of mineral inclusionbearing zircons[J]. Lithos, 2004, 78(4):411-429. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.08.001
[62] Dan W, Wang Q, White W M, et al. Rapid formation of eclogites during a nearly closed ocean:revisiting the Pianshishan eclogite in Qiangtang, central Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 477:112-122. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.12.012
[63] Valley J W, Kinny P D, Schulze D J, et al. Zircon megacrysts from kimberlite:oxygen isotope variability among mantle melts[J]. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1998, 133:1-11. doi: 10.1007/s004100050432
[64] Schmidt M W, Poli S. Devolatilization during subduction[C]//Treatise on geochemistry (Second Edition), 2013: 669-701.
[65] 苑婷媛, 赵中宝, 曾庆高, 等.藏西北戈木日榴辉岩岩石学特征及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(12):3729-3742. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20162017042100243938
[66] Cherniak D J. Pb diffusion in rutile[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2000, 139:198-207. doi: 10.1007/PL00007671
[67] Kooijman E, Mezger K, Berndt J. Constraints on the U-Pb systematics of metamorphic rutile from in situ LA-ICPMS analysis[J]. Earth and Planet Science Letters, 2010, 293:321-330. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2010.02.047
[68] 程昊, 曹达迪.石榴石Lu-Hf年代学及其在大别造山带研究中的进展[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(23):2271-2278. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB201323006.htm
[69] 翟庆国.藏北羌塘中部榴辉岩岩石学、地球化学特征及构造演化过程[D].中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2018.
http: //cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-2008177391.htm [70] Zack T, Moraes R, Kronz A. Temperature dependence of Zr in rutile:empirical calibration of a rutile thermometer[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2004, 148:471-488. doi: 10.1007/s00410-004-0617-8
[71] Watson E B, Wark D A, Thomas J B. Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 151:413-433. doi: 10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5
[72] Tomkins H S, Powell R, Ellis D J. The pressure dependence of the zirconium-in-rutile thermometer[J]. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2007, 25:703-713. doi: 10.1111/jmg.2007.25.issue-6
[73] Fialin M, Remy H, Richard C, et al. Trace element analysis with the electron microprobe:new data and perspectives[J]. American Mineralogist, 1999, 84:70-77. doi: 10.2138/am-1999-1-207
[74] 王汝成, 王硕, 邱检生, 等. CCSD主孔揭示的东海超高压榴辉岩中的金红石:微量元素地球化学及其成矿意义[J].岩石学报, 2005, 21(2):465-474. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200502020
[75] Gao X Y, Zheng Y F, Xia X P, et al. U-Pb ages and trace elements of metamorphic rutile from ultrahigh-pressure quartzite in the Sulu orogeny[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 143:87-114. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.04.032
[76] Zheng Y F, Gao X Y, Chen R X, et al. Zr-in-rutile thermometry of eclogite in the Dabie orogen:Constraints on rutile growth during continental subduction-zone metamorphism[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40:427-451. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.09.008
[77] Cawood P A, Buchan C. Linking accretionary orogenesis with supercontinent assembly[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2007, 82:217-256. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2007.03.003
[78] Cawood P A, Johnson M R W, Nemchin A A. Early Palaeozoic orogenesis along the Indian margin of Gondwana:tectonic response to Gondwana assembly[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 255:70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.006
[79] Herwartz D, Nagel T J, Münker C, et al. Tracing two orogenic cycles in one eclogite sample by Lu-Hf garnet chronometry[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2011, 4:178-183. doi: 10.1038/ngeo1060
[80] Root D, Corfu F. U-Pb geochronology of two discrete Ordovician high-pressure metamorphic events in the Seve Nappe Complex, Scandinavian Caledonides[J]. Contrib. Mineral Petrol., 2012, 163:769-788. doi: 10.1007/s00410-011-0698-0
[81] Kirchenbaur M, Pleuger J, Jahn-Awe S, et al. Timing of highpressure metamorphic events in the Bulgarian Rhodopes from LuHf garnet geochronology[J]. Contrib. Mineral Petrol., 2012, 163:897-921. doi: 10.1007/s00410-011-0705-5
[82] Agard P, Yamato P, Jolivet L, et al. Exhumation of oceanic blueschists and eclogites in subduction zones:timing and mechanisms[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2009, 92(1):53-79. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=33d0061b4ba5d96c69153786f7014be9&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[83] Kapp P, Murphy M A, Yin A, et al. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Shiquanhe area of western Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 2003, 22:3-23. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-2001TC001332/
[84] Fan J J, Li C, Xie C M, et al. Petrology and U-Pb zircon geochronology of bimodal volcanic rocks from the Maierze Group, northern Tibet:Constraints on the timing of closure of the BanggongNujiang Ocean[J]. Lithos, 2015, 227:148-160. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.021
[85] Zhang X Z, Wang Q, Dong Y S, et al. High-pressure granulite facies overprinting during the exhumation of eclogites in the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone, central Tibet:Link to flat-slab subduction[J]. Tectonics, 2017, 36:2918-2935. doi: 10.1002/2017TC004774
[86] 赵靖, 钟大赉, 王毅.滇西澜沧变质带的变质作用和变形的关系[J].岩石学报, 1994, 10(1):27-40. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1994.01.003
-



 下载:
下载: