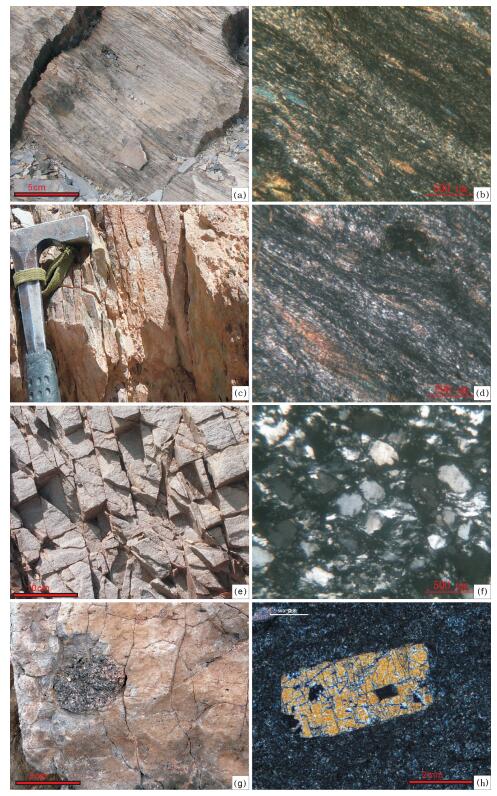
The establishment of Ediacaran Dabure Formation in southern Qiangtang of northern Tibet and its significance
-
摘要:
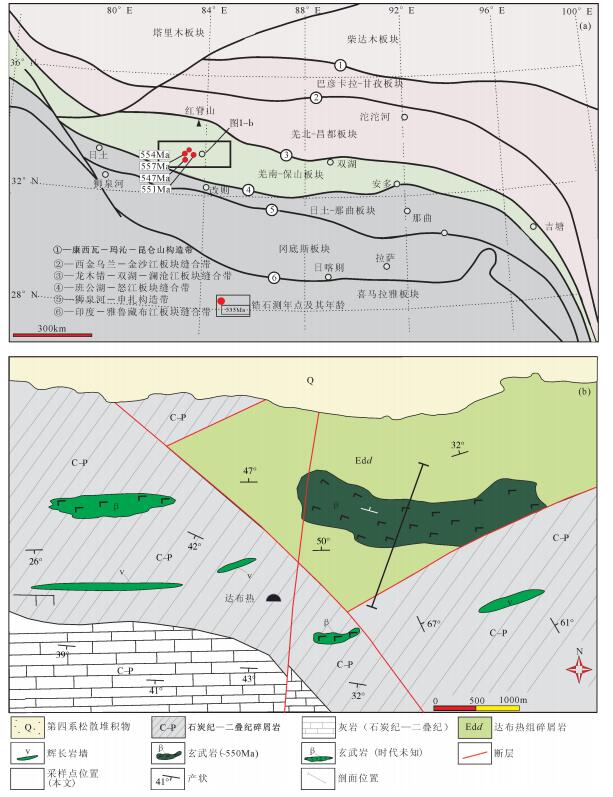
羌塘位于青藏高原腹地,构造上处于冈瓦纳大陆北缘。因其特殊的构造位置,羌塘地体的起源及构造演化对于探讨青藏高原的早期形成演化、冈瓦纳大陆裂解,以及特提斯洋演化等关键科学问题至关重要。最近,在羌塘南部达布热地区发现一套碎屑岩夹玄武岩的岩石组合,碎屑岩具有低成分成熟度的特点,虽然岩石发生了低绿片岩相变质,但仍然保留了原岩类复理石沉积的特点。根据碎屑锆石定年结果,该套地层中碎屑锆石的最年轻年龄为550Ma左右。此外,该套地层中玄武岩夹层的测年结果表明,该套地层形成于埃迪卡拉纪(约550Ma)。结合地层剖面及区域地层对比,建立了埃迪卡拉纪达布热组。达布热组是羌塘地区首次发现的埃迪卡拉纪地层,该组地层的建立为探讨冈瓦纳大陆北缘构造演化提供了重要线索。
Abstract:The Qiangtang terrane is situated in the hinterland of the Tibetan Plateau on the northern margin of Gondwana. Because of its particular tectonic location, the understanding of the origin and tectonic evolution of the Qiangtang terrane is important in examining the formation and evolution of the Tibetan Plateau, the breakup of the Gondwana supercontinent, and the evolution of the Tethys Ocean. The Dabure clastic rocks discovered recently are characterized by low compositional and textural maturity, and have been affected by lower greenschist facies metamorphism. The deposits exhibit the typical features of turbidites. Based on detrital zircons U-Pb dating, the authors obtained the most reliable youngest age of detrital zircons from the Dabure clastic rocks, which is ca. 550Ma. Combining the data obtained by the authors with previous work on the basalts in the Dabure area (the Dabure basalts), the authors tentatively suggest that the Dabure clastic rocks represent the late Ediacaran (ca. 550Ma) sedimentary record of the Qiangtang terrane. On the basis of section measurement and regional correlation, the Ediacaran Dabure Formation was established. The establishment of the Dabure Formation not only has important theoretical significance for revealing the evolutionary history of the Qiangtang terrane in late Neoproterozoic but also provides new clues for tectonic evolution of the northeastern margin of Gondwana.
-
Key words:
- Tibetan Plateau /
- southern Qiangtang /
- clastic rocks /
- basalt /
- Ediacaran
-

-
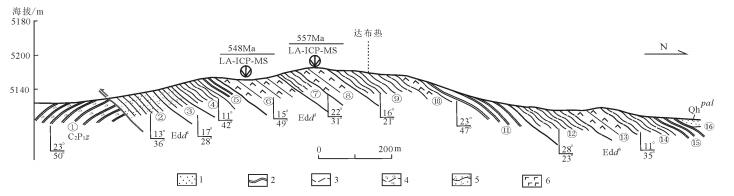
图 2 羌塘南部地区达布热组地层实测剖面图(据参考文献[21]修改)
Figure 2.
-
[1] Allègre C J, Courtillot V, Tapponnier P A, et al. Structure and evolution of the Himalaya-Tibet orogenic belt[J]. Nature, 1984, 307:17-22. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0231908924
[2] Pierce J A, Mei H.Volcanic rocks of the 1985 Tibet Geotra verseLhasa to Golmud[J]. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond., 1988, A327:203-213. http://www.jstor.org/stable/38187
[3] Dewey J F, Shackelton R M, Chang C, et al.The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Phil Trans. R. Soc. Lond., 1988, A327:379-413. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy200906024
[4] Searle M P, Cooper D J W, Rex A J.Collision tectonics of the Ladakh-Znaskar Himalaya[J]. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond., 1991, A326:117-150.
[5] Kapp P, Yin A, Mannin C E, et al. Blueschist-bearing metamorphic core complexes in the Qiangtang block reveal deep crustal structure of northern Tibet[J]. Geology, 2000, 28:19-22. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<19:BMCCIT>2.0.CO;2
[6] 李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部发现榴辉岩及其意义[J].科学通报, 2006, 51:70-74. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.01.014
[7] 李才, 董永胜, 翟庆国, 等.青藏高原羌塘早古生代蛇绿岩——堆晶辉长岩的锆石SHRIMP定年及其意义[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(1):31-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200801002
[8] 王立全, 潘桂棠, 李才, 等.藏北羌塘中部果干加年山早古生代堆晶辉长岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄——兼论原-古特提斯洋的演化[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(12):2045-2056. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.12.010 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20081210&flag=1
[9] Zhai Q G, Li C, Huang X P. The fragment of Paleo-Tethys ophiolite from central Qiangtang, Tibet?-geochemical evidence of metabasites in Guoganjianian[J].Science in China(Series D), 2007, 50(9):1302-1309. doi: 10.1007/s11430-007-0051-7
[10] 胡培远, 李才, 李林庆, 等.藏北羌塘中部早古生代蛇绿岩堆晶岩中斜长花岗岩的地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1297-1308. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.09.019 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090919&flag=1
[11] 吴彦旺, 李才, 董永胜, 等.藏北羌塘中部桃形湖早古生代蛇绿岩的岩石学特征[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1290-1296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.09.018 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090918&flag=1
[12] 董永胜, 张修政, 施建荣, 等.藏北羌塘中部高压变质带中石榴子石白云母片岩的岩石学和变质特征[J].地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1201-1206. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.09.007 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090907&flag=1
[13] 翟庆国, 王军, 李才, 等.青藏高原羌塘中部中奥陶世变质堆晶辉长岩锆石SHRIMP年代学及Hf同位素特征[J].中国科学(D辑), 2010, 40(5):565-573. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=JDXK201005006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[14] 吴彦旺.龙木错-双湖-澜沧江洋历史记录——寒武-二叠纪的蛇绿岩[D].吉林大学博士学位论文, 2013: 1-238.
[15] 李才.龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带与石炭二叠纪冈瓦纳北界[J].长春地质学院学报, 1987, 17(2):155-166. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000001164867
[16] 李才.青藏高原龙木错-双湖-澜沧江板块缝合带研究二十年[J].地质论评, 2008, 54(1):1-15. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2008.01.001
[17] Metcalfe I. Tectonic framework and Phanerozoic evolution of Sundaland[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 19:3-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2010.02.016
[18] Metcalfe I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66:1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
[19] Zhai Q G, Zhang R Y, Jahn B M, et al. Triassic eclogites from central Qiangtang, northern Tibet, China:petrology, geochronology and metamorphic P-T path[J]. Lithos, 2011, 125:173-189. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.02.004
[20] Wang M, Li C, Fan J J. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Dabure basalts, central Qiangtang, Tibet:evidence for~550 Ma rifting of Gondwana[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57:1791-1805. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2015.1024290
[21] Wang M, Li C, Xie C C.Dating of detrital zircons from the Dabure clastic rocks:the discovery of Neoproterozoic strata in central Qiangtang Tibet[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 58:216-227. https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00206814.2015.1065207
[22] 全国地层委员会.中国区域年代地层(地质年代)表说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 2002.
[23] 贵州省地质调查院. 1:25万丁固幅区调报告[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2010.
[24] Li C, Zheng A.Paleozoic stratigraphy in the Qiangtang region of Tibet:relations of the Gondwana and Yangtze continents and ocean closure near the end of the Carboniferous[J]. International Geology Review, 1993, 35:797-804. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=1e7bfac21a0ae6b9571885b085824bd3&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[25] Jin X C. Permo-Carboniferous sequences of Gondwana affinity in southwest China and their paleogeographic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 20:633-646. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=dda55bbdf12edff3e285a41fddfbb693&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[26] 李才, 程立人, 胡克, 等.西藏羌塘南部地区的冰海杂砾岩及其成因[J].长春地质学院学报, 1995, 25(4):368-374. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199500183653
[27] Fan J J, Li C, Wang M, et al.Features, provenance, and tectonic significance of Carboniferous-Permian glacial marine diamictites in the Southern Qiangtang-Baoshan block, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28(4):1530-1542. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ0235568060
[28] Dong C Y, Li C, Wan Y S, et al. Detrital zircon age model of Ordovician Wenquan quartzite south of Lungmuco-Shuanghu Suture in the Qiangtang area, Tibet:Constraint on tectonic affinity and source regions[J]. Sci. China:Earth Sci., 2011, 41:299-308. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=5d0f524a0e43d8facb45e1a798273a8a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[29] 王国芝, 王成善.西藏羌塘基底变质岩系的解体和时代厘定[J].中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(增刊):77-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK200101277821
[30] 黄继钧.藏北羌塘盆地构造特征及演化[J].中国区域地质, 2001, 20:178-186. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2001.02.011
[31] 黄继钧.羌塘盆地基底构造特征[J].地质学报, 2001, 75:333-337. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2001.03.006
[32] 李永铁, 罗建宁, 卢辉楠.青藏高原地层[M].北京:科学出版社, 2001:10-30.
[33] 李才.羌塘基底质疑[J].地质论评, 2003, 49(1):5-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp200301002
[34] 李才, 程立人, 张以春.西藏羌塘南部发现奥陶纪-泥盆纪地层[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(5/6):602-604. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200405107&flag=1
[35] 吉林大学地质调查院. 1:25万玛依岗日幅区域地质调查报告[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 2010.
[36] 杨耀, 赵中宝, 苑婷媛, 等.藏北羌塘奥陶纪平行不整合面的厘定及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2014, 8:2381-2392. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8281608
[37] 姚宗富.青海玉树长青可地区元古界地层特征[J].西藏地质, 1992, 1:1-6. http://qikan.cqvip.com/article/detail.aspx?id=904767
[38] 刘世坤.藏东金沙江一带元古界的大地构造意义[J].西藏地质, 1992, 1:16-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000005846050
[39] Harris N B W, Xu R H, Lewis C L, et al. Isotope geochemistry of the 1985 Tibet Geotraverse, Lhasa to Golmud[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Socicty of London, 1988, A327:263-85. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=17d090aeec3b7cf26b02d6b4838a41b6&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[40] Dewey J F, Cande F S, Pitman W C, et al. Tectonic evolution of the India/Eurasia collision zone[J]. Eclogae Geologicae Helvetiae, 1989, 82:717-734. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3eba5a3d3abab924af5f94b9a2f67cd0&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[41] Hu D G, Wu Z H, Jiang W, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age and Nd isotopic study on the Nyainqentanglha Group in Tibet[J]. Science in China(Series D), 2005, 48:1377-1386. doi: 10.1360/04yd0183
[42] Zhang Z M, Dong X, Geng G S, et al. Precambrian Metamorphism of the Northern Lhasa Terrane, South Tibet and Its Tectonic Implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84:440-456. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201004001
[43] Dong X, Zhang Z M, Liu F, et al. Genesis of the metamorphic rock from southeastern Lhasa terrane and the Mesozoic-Cenozoic orogenesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28:1765-1784. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201206006
[44] 解超明, 李才, 苏黎, 等.藏北安多地区花岗片麻岩锆石LAICP-MS U-Pb定年[J].地质通报, 2010, 29:1737-1744. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2010.12.002 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20101202&flag=1
[45] Gehrels G, Kapp P, DeCelles P, et al.Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan-Himalayan orogeny[J]. Tectonics, 2011, 30(5016):1-27. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0016&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F00206814.2017.1367967&key=10.1029%2F2011TC002868
[46] Guynn J H, Kapp P, Gehrels G, et al. U-Pb geochronology of basement rocks in central Tibet and paleogeographic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 43:23-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.09.003
[47] 王立全, 潘桂棠, 丁俊, 等.青藏高原及邻区地质图及说明书[M].北京:地质出版社, 2013.
[48] Stampfli G M, Borel G D. A plate tectonic model for the Paleozoic and Mesozoic constrained by dynamic plate boundaries and restored synthetic oceanic isochrones[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2002, 196:17-33. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00588-X
[49] Zhang X Z, Dong Y S, Li C, et al. Silurian high-pressure granulites from Central Qiangtang, Tibet:Constraints on early Paleozoic collision along the northeastern margin of Gondwana[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 405:39-51. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=436b8470973775d723919709231fa7bf&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
-



 下载:
下载: