The Early Jurassic subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic slab: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic compositions of Sumdo high-Mg diorite
-
摘要:
冈底斯岩浆岩带中东部松多地区新发现的高镁闪长岩对于探讨青藏高原新特提斯俯冲演化历史具有重要意义。通过松多高镁闪长岩的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、锆石Hf同位素和全岩地球化学组成的研究,表明松多闪长岩的锆石U-Pb年龄加权平均值为186.8±1.3Ma。该类岩石具有高硅、高镁的特点,SiO2含量为54.17%~58.81%,MgO含量较高,介于6.26%~7.29%之间,Mg#值介于64~67之间,Cr和Ni含量高。该岩石富集轻稀土元素,具有平滑右倾的稀土元素配分曲线及弱负Eu异常。富集Rb、Ba、Pb、K等大离子亲石元素,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素。锆石负εHf(t)值(-5~-14.3)及远大于其侵入年龄的古老Hf模式年龄(1543~2129Ma),揭示松多早侏罗世闪长岩经历了古老地壳物质的部分熔融。Sr/Y-Y和(La/Yb)N-YbN判别图解显示,其形成可能与赞岐岩的岩浆作用过程相似,形成于消减带之上的地幔楔环境。综合研究表明,松多地区在早侏罗世处于雅鲁藏布新特提斯洋板片向欧亚大陆俯冲的活动陆缘构造背景。
-
关键词:
- 冈底斯 /
- 松多地区 /
- 早侏罗世 /
- LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年 /
- Hf同位素
Abstract:The high-Mg diorite newly discovered in Sumdo area in the eastern part of the Gangdise magmatic belt is of importance for investigating the evolution history of the subduction of Neo-Tethyan oceanic slab of Tibet. This paper reports LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages, zircon Hf isotopic and whole-rock major and trace element compositions of the high-Mg diorite. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic dating indicates that the diorite was emplaced at 186.8±1.3Ma. It is characterized by high content of SiO2 (54.17%~58.81%), MgO (6.26%~7.29%), Mg# (64~67), Cr (294×10-6~373×10-6) and Ni (42×10-6~50×10-6). It is also characterized by smooth gently right-inclined REE patterns with slight enrichment of LREE and a little negative Eu anomaly. The large ion lithophile elements (LILEs) such as Rb, Ba, Pb, K are enriched, and the high field strength elements (HFSEs) such as Nb, Ta, Ti are depleted. LuHf isotopic study demonstrates that its εHf(t) values vary between -5 and -14.3, and the ancient zircon Hf crustal modal ages vary greatly from 1543Ma to 2129Ma, which indicates that the formation of Sumdo diorites resulted from partial melting of ancient crustal rocks. The discrimination diagrams of Sr/Y-Y and (La/Yb)N-YbN show that the high-Mg diorites were likely formed in a mantle wedge setting similar to the magmatic process of sanukitie. The comprehensive studies show that the Sumdo area was located in an active continental margin setting and affected by the subduction of the Yarlung Zangbo Neo-Tethyan oceanic slab towards Eurasia plate before Early Jurassic.
-
Key words:
- Tibetan Plateau /
- Sumdo /
- Early Jurassic /
- LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating /
- Hf isotope
-
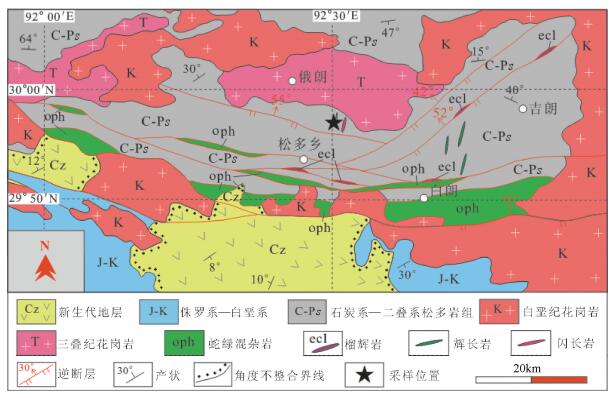
冈底斯构造-岩浆岩带作为青藏高原的重要组成部分,近东西向夹持于印度河-雅鲁藏布江结合带和班公湖-怒江结合带之间,记录了新特提斯洋俯冲消减、印度板块与欧亚板块碰撞、青藏高原隆升等一系列极其复杂的地质过程[1-2]。该区域以发育巨型的构造-岩浆活动为特色,也被称之为冈底斯岩浆岩带。以狮泉河-申扎-嘉黎缝合带和沙莫勒-米拉山断裂带为界进一步将冈底斯划分为北冈底斯(北部拉萨)、中冈底斯(中部拉萨)和南冈底斯(南部拉萨)[3-4]。纪伟强等[5-6]将冈底斯发育的岩浆作用划分为4个阶段:205~152Ma、109~80Ma、65~41Ma、33~ 13Ma,其中205~152Ma的岩浆作用与新特提斯洋的开启、俯冲消减和最终闭合密切相关,具有重要的科学意义[2-3, 7-15],但研究程度较低。冈底斯上早侏罗世的岩浆活动集中分布于东段,前人重点围绕冈底斯南部的早侏罗世叶巴组和桑日群火山岩开展了较深入的研究,认为其是雅鲁藏布江新特提斯洋早期俯冲的岩浆产物,并可能分别代表新特提斯洋俯冲过程中形成的陆缘弧和洋内弧[14]。刘琦胜等[16]根据冈底斯中部宁中早侏罗世白云母二长花岗岩的研究认为,其属于S型花岗岩,是冈底斯印支造山旋回晚期碰撞阶段的产物;有学者认为,侏罗纪岩浆作用可能是班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲消减的结果[17];更多的学者倾向于冈底斯南缘在早侏罗世应处于新特提斯洋板片俯冲的构造背景[2, 13]。目前对早侏罗世侵入岩体的研究仍较少(图 1-b),上述研究结果也并不一致,制约了对新特提斯洋俯冲演化历史的深入认识。
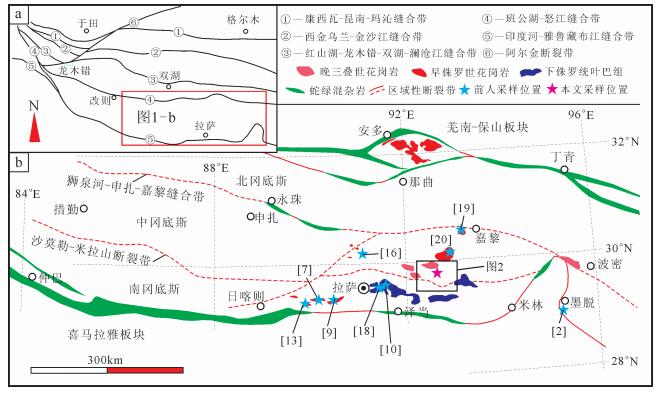 图 1. 冈底斯东段构造简图及其早侏罗世岩浆岩分布[3]Figure 1. Sketch map of eastern Gangdise belt, showing the distribution of Early Jurassic magmatic rocks
图 1. 冈底斯东段构造简图及其早侏罗世岩浆岩分布[3]Figure 1. Sketch map of eastern Gangdise belt, showing the distribution of Early Jurassic magmatic rocks本文以中冈底斯东部松多地区新发现的早侏罗世闪长岩为例,通过详细的岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb定年及锆石Hf同位素研究,探讨其形成时代和岩石成因,为新特提斯洋的俯冲消减演化提供来自岩浆岩方面的约束。
1. 地质概况及样品特征
松多地区处于冈底斯中东部,沙莫勒-米拉山断裂带东段(图 1、图 2),位于南冈底斯地块与中冈底斯地块的交界。自松多榴辉岩报道以来,研究区迅速引起了国内外学者的广泛关注[21]。松多地区出露的地质单元主要包括石炭系—二叠系松多岩组、侏罗系—白垩系火山-沉积地层、晚古生代蛇绿混杂岩(前奥陶系岔萨岗岩组绿片岩)、松多榴辉岩及大面积分布的中—新生代岩浆岩。其中,石炭系—二叠系松多岩组主体为一套小有序而大无序的构造地层,以陆源碎屑岩为主,夹少量碳酸盐岩的沉积岩系,主要岩性为变质石英砂岩、白云母石英片岩、绢云石英片岩、二云(长石)石英片岩及少量黑云石英片岩。晚古生代蛇绿混杂岩是近期的重要发现,岩石端元齐全,主要为变质橄榄岩、堆晶辉长岩、辉长岩、玄武岩、斜长花岗岩等[22]。杨经绥等[21]报道了松多乡以南的松多榴辉岩,呈近东西向展布,以包体形式产于岔萨岗岩组中,主要岩性为金红石榴辉岩、石英榴辉岩、角闪榴辉岩、多硅白云母榴辉岩等。现有研究表明,松多榴辉岩原岩为MORB(大洋中脊玄武岩)型岩石[23],原岩可能形成于石炭纪—二叠纪[24],变质年龄可能为晚二叠世[25-26]。区内断裂构造十分发育,构造形迹以近东西向为主,具有多期次、脆性逆冲断裂构造发育的特点。
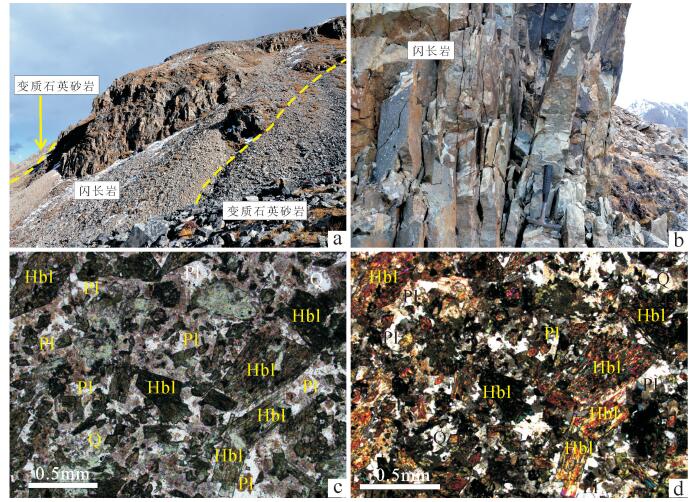
本文研究的闪长岩样品采自松多乡以北,野外露头新鲜,受后期片理化改造较强,与石炭系—二叠系松多岩组变质石英砂岩呈侵入接触关系(图 3-a),具有中粗粒半自形粒状结构,块状构造(图 3-b)。主要由角闪石(35%~40%)、斜长石(55%~60%)、石英(< 5%)及副矿物榍石、磁铁矿等组成。角闪石呈柱状,具有绿色-黄绿色多色性,2组斜交完全解理(图 3-c),二级蓝干涉色(图 3-d),斜消光Ng∧C= 25°;斜长石呈半自形板状,粒度在0.3~0.6mm之间,一级灰白干涉色,聚片双晶可见,有较强的绢云母化;石英呈粒状,粒度在0.2~0.4mm之间,部分呈浑圆状,无色,正低突起,无解理,一级灰白干涉色,分布不太均匀。
2. 样品分析方法
锆石分选在河北廊坊市(宇能)宇恒矿岩技术服务有限公司完成。采用常规的重液和磁选方法进行分选,在双目显微镜下挑纯。锆石的阴极发光(CL)图像分析在中国地质科学院电镜室的阴极荧光分析系统上完成(图 4)。在中国地质大学(北京)地学实验中心进行了透射光、反射光显微照相及锆石LA-ICP-MS微区原位U-Pb同位素分析。测定部位的选取依据显微图像的特点,即根据可见光图像尽量选择无或少包裹体、无裂纹的部位;再根据阴极发光图像,尽量避免测定位置跨越不同世代的晶体区域。这些照片为数据解释提供了依据。使用的ICP-MS为美国Agilent科技有限公司的7500A ICP-MS,激光剥蚀系统为美国New Wave贸易有限公司的UP193SS型:深紫外(DUV)193nm、ArF准分子激光剥蚀系统。激光束斑直径为36μm,剥蚀采样时间为45s。实验中采用的剥蚀物质载气为高纯度氦,流速为0.7L/min,用标准锆石91500为外标进行同位素比值校正,用标准锆石TEM(417Ma)做监控盲样,元素含量以NIST612为外标进行标定,29Si为内标,NIST612和NIST614做监控盲样。采用澳大利亚Glitter 4.4软件对同位素比值及元素含量计算进行处理(ver4.0,Macquarie Univer⁃ sity),采用Isoplot 3.0软件绘制U-Pb谐和图和计算年龄加权平均值[27]。
锆石Hf同位素分析在北京科萃测试技术有限公司实验室利用激光剥蚀多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪完成。激光进样系统为NWR213nm固体激光器,分析系统为多接收等离子体质谱仪(NEPTUNE plus)。检测环境温度为18~22℃,相对湿度小于65%。仪器运行条件及分析方法详见参考文献[28]。利用NWR213nm固体激光器对锆石进行剥蚀,激光剥蚀的斑束直径为40μm,能量密度为10~11J/cm2,频率为10Hz,激光剥蚀物质以高纯氦为载气送入Neptune Plus(MC-ICPMS),接收器配置与溶液进样方式相同。分析数据处理(包括对样品和空白信号的选择、同位素质量分馏校正)采用软件ICP MSD ata Cal[29]完成。
全岩地球化学样品的主量、微量元素分析在中国地质大学(北京)地学实验中心完成。在超净实验室使用电子天平称取50mg样品,采用两酸(HNO3+HF)高压反应釜(Bomb)溶样方法进行样品的化学预处理,分析仪器为美国安捷伦公司生产的Agilent7500a型等离子质谱仪,分析过程中使用美国地质调查局的标样AGV2、W2、BHOV和中国地质测试中心的岩石标样R1、R3进行分析质量检查和监控。
3. 分析结果
3.1 锆石U-Pb定年
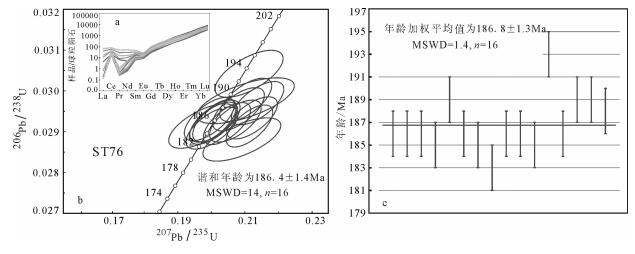
闪长岩(ST76)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年结果见表 1,对应的锆石测点稀土元素分析结果见表 2。样品的锆石阴极发光图像显示(图 4),锆石呈自形-半自形短柱状,个别为长柱状,颗粒长径集中在100~200μm,所有锆石都具有明显的韵律环带结构。锆石测点的Th和U含量变化范围较大,Th和U含量分别为192×10-6~619×10-6和303×10-6~930×10-6,相应的Th/U值为0.36~0.77,平均值为0.51。锆石的稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分模式以重稀土元素相对富集和具有明显的正Ce异常、负Eu异常为主要特征(图 5-a),表明它们均属于岩浆锆石[30]。LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年的16个测点数据在谐和曲线上集中分布,计算的谐和年龄与206Pb/238U年龄加权平均值的定年结果在误差范围内一致(图 5-b、c),206Pb/238U年龄给出的年龄加权平均值为186.8±1.3Ma(图 5-c),代表闪长岩的岩浆结晶年龄。
表 1. 松多闪长岩(ST76)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果Table 1. LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb analyses of zircons from the diorite (ST76) in Sumdo area点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 1 206 580 0.36 0.0498 0.0012 0.2006 0.0048 0.0292 0.0003 186 34 186 4 186 2 2 349 930 0.38 0.0498 0.0011 0.2010 0.0043 0.0293 0.0003 185 29 186 4 186 2 3 238 650 0.37 0.0498 0.0012 0.2011 0.0049 0.0293 0.0003 187 36 186 4 186 2 4 193 303 0.64 0.0491 0.0017 0.1974 0.0067 0.0291 0.0004 154 56 183 6 185 2 5 220 495 0.44 0.0522 0.0013 0.2138 0.0051 0.0297 0.0004 294 34 197 4 189 2 6 303 776 0.39 0.0508 0.0012 0.2047 0.0046 0.0292 0.0003 233 31 189 4 186 2 7 216 580 0.37 0.0499 0.0013 0.2002 0.0051 0.0291 0.0003 191 38 185 4 185 2 8 320 657 0.49 0.0526 0.0020 0.2091 0.0077 0.0288 0.0004 313 90 193 6 183 2 9 218 547 0.40 0.0493 0.0012 0.1994 0.0049 0.0293 0.0004 163 35 185 4 186 2 10 352 700 0.50 0.0524 0.0012 0.2121 0.0050 0.0293 0.0003 304 33 195 4 186 2 11 619 916 0.68 0.0526 0.0011 0.2114 0.0046 0.0291 0.0003 312 28 195 4 185 2 12 192 339 0.57 0.0504 0.0016 0.2112 0.0067 0.0304 0.0004 212 50 195 6 193 2 13 285 659 0.43 0.0514 0.0013 0.2072 0.0051 0.0293 0.0003 257 35 191 4 186 2 14 558 722 0.77 0.0512 0.0024 0.2102 0.0096 0.0298 0.0004 251 111 194 8 189 2 15 542 777 0.70 0.0512 0.0013 0.2102 0.0051 0.0298 0.0004 249 34 194 4 189 2 16 498 830 0.60 0.0511 0.0013 0.2081 0.0051 0.0296 0.0004 244 35 192 4 188 2 表 2. 松多闪长岩(ST76)锆石LA-ICP-MS原位稀土元素分析结果Table 2. The trace element compositions of the zircons in the diorite (ST76) in Sumdo area by LA-ICP-MS10-6 点号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ∑REE 01 1.06 13.52 0.65 2.43 2.93 0.82 14.58 5.99 84.12 35.28 176.75 50.02 653.12 173.49 1215 02 0.04 19.89 0.03 0.69 2.60 1.12 16.78 7.60 106.02 46.08 228.32 63.78 826.25 216.30 1215 03 0.03 15.42 0.03 0.49 1.58 0.86 10.71 4.76 68.08 31.25 162.83 47.74 640.72 181.13 1169 04 0.03 11.07 0.03 0.67 1.36 0.68 7.30 2.67 35.69 14.80 73.49 21.68 299.68 86.18 559 05 0.03 12.04 0.02 0.29 0.98 0.51 6.28 2.42 34.33 15.12 77.90 23.49 325.66 93.27 597 06 9.93 37.44 2.87 14.47 5.09 1.32 17.55 7.02 95.91 40.46 202.72 56.38 731.30 195.07 1424 07 0.05 13.19 0.03 0.39 1.45 0.71 8.26 3.58 50.99 22.82 121.19 36.10 502.57 145.96 914 08 0.04 19.79 0.05 0.69 2.05 1.10 12.39 5.08 71.78 31.91 167.15 50.52 675.85 188.40 1235 09 0.04 15.96 0.03 0.54 1.42 0.79 9.14 3.76 54.75 24.74 130.63 38.96 543.96 162.47 996 10 0.05 18.40 0.04 1.41 3.51 1.23 19.64 7.75 104.23 42.02 203.29 55.23 692.35 178.56 1338 11 2.73 25.86 0.81 4.94 3.28 1.19 14.93 5.51 73.71 29.84 146.62 40.51 524.2 140.75 1026 12 0.16 9.13 0.08 1.81 4.33 1.22 20.39 7.44 91.56 34.18 156.2 40.25 478.05 120.97 978 13 16.65 50.20 4.87 25.11 7.22 1.59 16.45 5.73 75.11 30.49 150.33 42.01 550.88 145.16 1135 14 0.20 21.11 0.12 2.40 4.81 1.57 22.51 8.24 104.69 41.36 196.11 52.39 661.73 163.38 1295 15 0.03 14.71 0.04 0.73 2.18 0.89 12.93 4.98 66.21 26.29 122.53 32.55 413.27 106.38 819 16 4.21 27.21 1.47 7.51 3.62 1.03 10.93 3.97 50.45 21.12 108.11 30.39 402.18 115.79 804 3.2 锆石Hf同位素
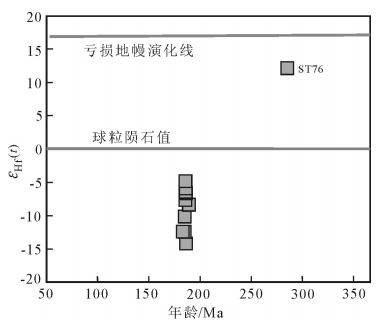
样品锆石Hf同位素分析点位置和锆石U-Pb测点对应,分析结果见表 3。锆石176Lu/177Hf值介于0.0007~0.0026之间,说明这些锆石在形成之后,没有明显的放射性成因Hf的积累,所以本文测定的176Lu/177Hf值应代表锆石形成时体系Hf同位素的组成[31]。每个测点的εHf(t)值和模式年龄根据U-Pb年龄计算。εHf(t)值为-5~-14.3,二阶段模式年龄均远大于花岗岩的结晶时代:单阶段模式年龄TDM1为1032~1402Ma,二阶段模式年龄TDM2为1543~ 2129Ma,揭示岩浆来自地壳岩石的部分熔融。样品的fLu/Hf为-0.92~-0.98,明显小于镁铁质(下地壳)及硅铝质地壳(上地壳)的fLu/Hf值(分别为-0.34和-0.72),所以其二阶段模式年龄更能反映源区物质从亏损地幔被抽取的时间或源区物质在地壳的平均存留年龄[32]。
表 3. 松多闪长岩(ST76)LA-ICP-MS锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成Table 3. The Lu-Hf isotope compositions of the zircons in the diorite (ST76) in Sumdo area as measured by LA-ICP-MS点号 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM1 TDM2 fLu/Hf 01 186 0.034757 0.000514 0.001385 0.000030 0.282468 0.000028 -10.8 -6.9 1121 1662 -0.96 02 186 0.020124 0.000198 0.000731 0.000008 0.282470 0.000018 -10.7 -6.7 1099 1652 -0.98 03 186 0.069570 0.000895 0.002615 0.000053 0.282446 0.000026 -11.5 -7.8 1191 1719 -0.92 04 185 0.039694 0.000791 0.001311 0.000024 0.282307 0.000021 -16.5 -12.6 1347 2021 -0.96 05 189 0.040310 0.000422 0.001442 0.000009 0.282420 0.000021 -12.5 -8.5 1191 1768 -0.96 06 186 0.021209 0.000292 0.000783 0.000011 0.282519 0.000018 -9.0 -5.0 1032 1543 -0.98 07 185 0.042573 0.001080 0.001651 0.000054 0.282373 0.000023 -14.1 -10.3 1265 1877 -0.95 08 183 0.026939 0.000259 0.000966 0.000007 0.282308 0.000018 -16.4 -12.5 1333 2018 -0.97 09 186 0.025039 0.000459 0.000925 0.000016 0.282489 0.000020 -10.0 -6.1 1078 1611 -0.97 10 186 0.026789 0.000106 0.000917 0.000007 0.282257 0.000019 -18.2 -14.3 1402 2129 -0.97 3.3 全岩地球化学
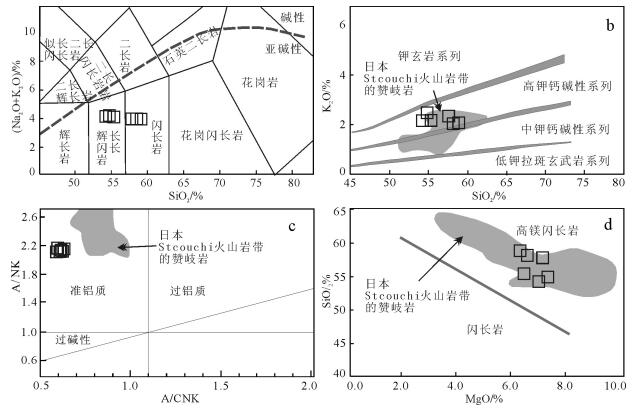
闪长岩样品的主量和微量元素分析结果见表 4。闪长岩样品具有较均一的硅、碱含量,变化范围较小(SiO2=54.17% ~58.81%,K2O + Na2O=3.89% ~4.20%),在TAS图解上,样品点均落在亚碱性系列范围(图 6-a),K2O/Na2O值为1.11~1.45,在SiO2-K2O关系图上落在高钾钙碱性系列区(图 6-b)。Al2O3含量为11.05%~12.09%,CaO含量较高(CaO= 6.93%~8.04%),相对贫TiO2(0.62%~0.71%)和P2O5(0.11% ~0.13%),铝饱和指数A/CNK值(Al2O3/CaO+K2O+Na2O)介于0.59~0.63之间,属于准铝质系列(图 6-c)。MgO含量较高,为6.26%~7.29%,Mg#值为64~67,在SiO2-MgO关系图上落在高镁闪长岩区(图 6-d)。由此可知,该样品属于高钾钙碱性、准铝质高镁闪长岩。
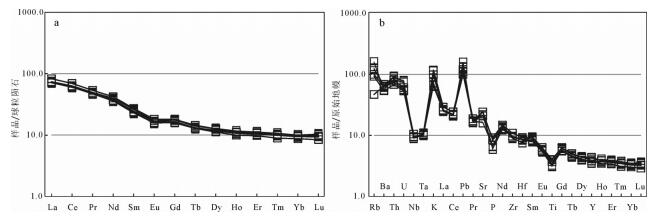
表 4. 松多闪长岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素测定结果Table 4. Major, trace element and REE compositions of the diorite in Sumdo area样号 ST76-1 ST76-2 ST76-3 ST76-4 ST76-5 ST76-6 样号 ST76-1 ST76-2 ST76-3 ST76-4 ST76-5 ST76-6 SiO2 58.81 58.10 57.71 54.85 54.17 55.32 Li 87.20 72.26 60.30 31.12 31.46 24.72 TiO2 0.62 0.65 0.69 0.71 0.67 0.65 P 870.4 794.6 799.4 626.55 565.80 635.40 Al2O3 11.20 11.05 11.26 11.90 12.09 11.72 K 29360 24620 28740 16187 15728 17942 TFe2O3 7.48 7.82 8.18 8.70 8.58 8.41 Sc 51.98 47.56 51.84 36.98 37.56 39.84 MnO 0.12 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.14 0.13 Ti 5220 4766 5140 4038 4090 4286 MgO 6.26 6.54 7.10 7.29 6.97 6.41 V 275.8 249.2 272.6 238.7 244.1 254.0 CaO 6.98 7.36 6.93 7.45 8.04 7.43 Cr 326.8 294.2 339.8 318.8 329.0 373.4 Na2O 1.84 1.84 1.62 1.71 1.97 1.91 Mn 1060.8 981.4 1036.8 1157.4 1185.0 1214.0 K2O 2.06 2.05 2.34 2.49 2.18 2.19 Co 37.80 36.44 39.76 37.60 38.66 42.26 P2O5 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.12 0.11 0.12 Ni 43.78 42.66 45.82 42.74 43.60 51.32 烧失量 4.07 3.91 3.48 4.02 4.46 5.10 Cu 62.48 46.38 34.44 56.76 45.56 34.78 总量 99.57 99.58 99.57 99.38 99.38 99.39 Zn 57.86 59.12 54.62 66.37 70.42 61.22 Na2O+K2 3.90 3.89 3.96 4.20 4.14 4.10 Ga 17.38 15.47 15.53 14.07 14.00 13.83 A/CNK 0.62 0.59 0.63 0.63 0.60 0.62 Rb 29.74 63.58 59.12 76.92 74.72 97.10 A/NK 2.13 2.11 2.16 2.16 2.16 2.13 Sr 441.6 510.0 510.8 440.0 440.0 338.4 La 19.91 17.09 17.85 17.47 16.92 16.85 Y 19.86 17.26 19.53 16.20 15.96 17.54 Ce 43.14 37.72 39.32 37.78 36.74 36.96 Zr 121.46 108.64 107.82 103.66 103.88 99.44 Pr 5.17 4.52 4.77 4.62 4.47 4.62 Nb 7.49 6.73 6.82 6.47 6.39 6.33 Nd 19.94 17.40 18.88 17.28 16.71 17.64 Cs 2.94 2.41 3.29 2.52 2.33 3.06 Sm 4.20 3.67 4.05 3.62 3.49 3.76 Ba 448.0 435.8 374.6 425.2 454.8 383.4 Eu 1.06 0.93 0.99 0.92 0.90 0.95 Hf 2.86 2.61 2.64 2.62 2.60 2.34 Gd 3.73 3.28 3.64 3.40 3.33 3.63 Ta 0.45 0.41 0.42 0.43 0.42 0.41 Tb 0.54 0.48 0.54 0.49 0.48 0.52 Pb 7.79 8.56 7.12 9.07 10.71 8.80 Dy 3.24 2.86 3.21 3.01 2.96 3.22 Th 6.85 6.32 5.79 7.41 7.56 6.80 Ho 0.63 0.57 0.63 0.62 0.61 0.65 U 1.27 1.17 1.12 1.58 1.59 1.50 Er 1.83 1.63 1.83 1.73 1.70 1.84 Ta/Yb 0.27 0.28 0.26 0.27 0.27 0.24 Tm 0.26 0.23 0.25 0.26 0.25 0.27 Th/Yb 4.07 4.24 3.57 4.59 4.74 4.02 Yb 1.68 1.49 1.62 1.62 1.60 1.69 Nb+Y 27.35 23.99 26.35 22.66 22.35 23.87 Lu 0.24 0.21 0.24 0.25 0.25 0.26 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 岩石的稀土元素总量(∑REE)较高,介于90×10-6~106×10-6之间,明显富集轻稀土元素(LREE/HREE=6.68~7.68),相对亏损重稀土元素。在稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图上,样品表现为右倾的平滑曲线(图 7-a),具弱的负Eu异常(δEu=0.79~0.82);轻、重稀土元素分馏较显著(LaN/YbN=7.89~8.49),且主要是轻稀土元素的分馏(LaN/SmN=2.84~3.06),重稀土元素分馏较弱或基本无分馏(GdN/YbN=1.73~1.86)。在微量元素方面,相对富集Rb、Ba、Pb、K等大离子亲石元素,相容元素Cr(294×10-6~373×10-6)和Ni(42×10-6~51×10-6)含量较高,在微量元素原始地幔标准化蛛网图(图 7-b)上,亏损Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素,具有明显的Nb-Ta槽特征。
4. 讨论
4.1 岩石成因
与汇聚板块边缘高镁安山岩的研究相比,具有相似成分的高镁闪长岩的研究较少。由于高镁闪长岩是深成岩,因而常是由非高镁安山质岩浆形成的镁铁质堆晶岩,而不是由高镁安山质岩浆固结而成的[38]。因此,在讨论高镁闪长岩成因时,首先要综合运用矿物(如单斜辉石存在与否)和全岩地球化学成分[39]或Hf同位素判断其由何种岩浆形成。松多高镁闪长岩中不存在单斜辉石,岩石也不具有堆晶结构,显然不是镁铁质堆晶岩。样品相同时代的锆石却具有明显不均一的Hf同位素组成(图 8)和相对“古老”的锆石Hf同位素特征(εHf(t)=-5~-14.3;TDM2=1543~2129Ma),进一步表明有古老地壳物质的卷入,反映高镁闪长岩的源区存在壳幔混合作用。笔者认为,这可能是源于幔源的高镁闪长岩岩浆上升与古老地壳物质同化混染所致。因此,本区的高镁闪长岩应为高镁安山质岩浆固结而成,可以利用全岩地球化学成分对其成因进行探讨。
松多闪长岩的主量元素表明其属于准铝质、中钾钙碱性岩石系列,显示出壳源成因花岗质岩石的特征。岩石具有高的MgO和Mg#值,在微量元素蛛网图中,以富集大离子亲石元素、亏损高场强元素为主要特征,具有明显且较深的Nb-Ta槽,显示典型俯冲带岩浆岩的地球化学特征[40],表明其形成与板块俯冲作用密切相关。与典型的岛弧环境下钙碱性闪长岩相比,松多闪长岩具有更高的MgO、Mg#值和Cr、Ni含量,显示出地幔源区特征,与日本Setouchi火山岩带中赞岐岩类相似[41-42]。在微量元素所确定的高镁安山岩分类图中,样品点均落在赞岐岩区(图 9),表明该高镁闪长岩的形成可能与赞岐岩有相似的岩浆作用过程。
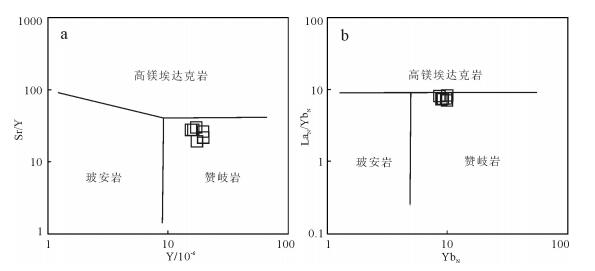 图 9. 松多闪长岩高镁安山岩分类图解[39]Figure 9. The discrimination diagrams for HMA of Sumdo diorite
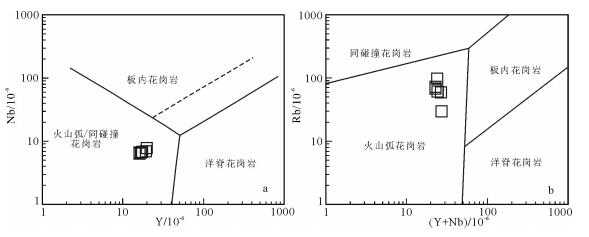
图 9. 松多闪长岩高镁安山岩分类图解[39]Figure 9. The discrimination diagrams for HMA of Sumdo diorite松多高镁闪长岩在Y-Nb图解(图 10-a)上显示火山弧/同碰撞的岩浆特征,而在(Y+Nb)-Rb图解(图 10-b)上均落在火山弧范围,在冈底斯南部出现零散分布的早侏罗世花岗岩及火山岩,均显示火山弧型的微量元素特征[14]。
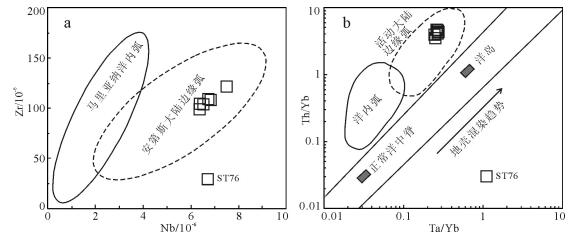
大洋与大陆演化过程常伴随元素的迁移和富集趋势,利用这些元素的活动性可以有效区分大陆边缘弧和洋内弧,在Nb-Zr图解(图 11-a)上,松多闪长岩显示出类似安第斯型大陆边缘弧的特征。利用Th/Yb-Ta/Yb图解(图 11-b)进一步判别,本文样品呈现出活动大陆边缘弧的特征,表明其岩浆源区出现大量陆缘物质混染,暗示其源自大陆边缘。
综合上述分析,松多高镁闪长岩应形成于活动陆缘弧背景。
4.2 对新特提斯洋俯冲的指示
除本文报道的早侏罗世高镁闪长岩外,在中冈底斯东部已经识别出多处早侏罗世的岩浆作用(图 1),揭示出与俯冲相关的弧岩浆作用的特点,但是对于这些岩浆作用究竟归属于“哪个洋”的弧一直争论不休,是北部的班公湖-怒江洋?还是南部的雅鲁藏布新特提斯洋?亦或是中部的松多古特提斯洋?存在较大争议。近期的研究表明,松多地区区域构造变形与糜棱质绿片岩和白云母石英片岩的白云母40Ar/39Ar同位素年龄揭示,松多古特提斯洋在230Ma左右已经关闭,拉萨地体与喜马拉雅板块碰撞[43-44],在陆陆碰撞之后10~15Ma俯冲消减到大陆之下的残余洋壳发生板片断离而逐渐下沉[45],所以冈底斯中部早侏罗世的岩浆作用可能与松多古特提斯洋的俯冲难以建立构造-岩浆演化联系。有学者推测,叶巴组火山岩可能形成于班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲消减[17, 46];班公湖-怒江大洋板片俯冲到南冈底斯以下,在板片回转作用下形成弧后拉张,从而使地幔和下地壳部分熔融,导致叶巴组及相关早侏罗世岩浆作用的出现[10]。如果冈底斯南缘的侏罗系桑日群和叶巴组形成于班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲而导致的弧后盆地环境,那么冈底斯南缘应该存在一些古老地壳,但是最近的研究表明,冈底斯南缘是以新生地壳为主[47];叶巴组分布范围现今距离班公湖-怒江缝合带至少300km以上,而且在早白垩世冈底斯南部曾出现大规模的地壳缩短[48-49],所以在早侏罗世叶巴组产出的位置距离班公湖-怒江洋的位置更远,受到班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲的影响更不太可能[14]。熊秋伟等[50]针对松多地区叶巴组的研究也认为,叶巴组火山岩可能并非是班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲的产物,而应是新特提斯洋壳北向俯冲的产物。
新特提斯洋在早三叠世之前已经打开[9, 51],冈底斯中南部的岩浆作用可能是新特提斯洋北向俯冲的产物。董彦辉等[18]认为,具有岛弧火山岩特点的叶巴组火山岩可能是新特提斯洋北向俯冲的产物,并提出新特提斯洋开始俯冲的时代应在早中侏罗世或更早。在叶巴组火山岩南部还发育大规模的早侏罗世桑日群火山岩,最新研究表明,叶巴组火山岩表现为典型的大陆边缘弧特征,而桑日群为洋内弧火山岩,可能分别代表了新特提斯洋北向俯冲形成的陆缘弧和洋内环境[14]。冈底斯中东部早侏罗世存在较大规模的岩浆侵入作用和连续的火山作用,是冈底斯陆缘岩浆弧形成的重要时期。在冈底斯南部尼木县城以南的尼木河大桥附近获得变形的早侏罗世花岗岩,具有岛弧型花岗岩的地球化学属性,认为其与新特提斯洋向欧亚板块南缘的俯冲消减作用存在密切联系[9]。邱先生等[13]以日喀则东嘎岩体为例,认为侏罗纪冈底斯南缘处于新特提斯洋板片俯冲的构造背景,且在俯冲过程中,存在多次基性岩浆底侵及其诱发的壳幔岩浆混合作用。董汉文等[2]根据产于东喜马拉雅构造结墨脱地区的早侏罗世辉长岩,认为冈底斯带东段早侏罗世存在地壳增长事件,并提出辉长岩的形成与新特提斯板片的俯冲密切相关。综合上述研究表明(表 5),松多地区新发现的高镁闪长岩是早侏罗世活动大陆边缘弧环境的重要证据,进一步揭示冈底斯中南部在早侏罗世已经处于雅鲁藏布新特提斯洋板片向欧亚大陆俯冲的构造背景。
表 5. 冈底斯南缘早侏罗世岩浆岩年龄信息统计Table 5. Age information of Early Jurassic magmatic rocks in southern margin of Gangdese序号 样品编号 样品岩性 测试方法 年龄结果 采样位置 数据来源 1 S16T76 闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 186.4±1.3Ma 松多乡北 本文 2 X-20 辉长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 185.9±0.3Ma 墨脱南背崩 [2] 3 TB-1-6 英云闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 179.7±1.7Ma 东嘎乡 [13] 4 TB-1-4 闪长岩(包体) LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 177.4±1.7Ma 东嘎乡 [13] 5 13GB-10 安山岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 188.8±1.8Ma 得明顶 [50] 6 X03 流纹岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 174.4±1.7Ma 甲马沟叶巴组 [18] 7 Dy1425-2 黑云二长花岗岩 锆石U-Pb 187±10Ma 嘉黎县布久岩体 [19] 8 B553-1 花岗闪长岩 40Ar/30Ar 198.2±0.3Ma 金达地区 [20] 9 DZ05-1 英安岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 174.2±3.6Ma 达孜 [10] 10 T384 变形花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 178±1Ma 尼木大桥 [9] 11 b9041 白云母二长花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 190±8Ma 宁中 [16] 12 b7 白云母二长花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 193±7Ma 宁中 [16] 13 b50-2 白云母二长花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 191±10Ma 宁中 [16] 14 ST134A 花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 188.1±1.4Ma 南木林东 [7] 15 DZ-7 英安岩 锆石U-Pb 181±5Ma 达孜 [46] 5. 结论
(1)冈底斯中部发现的松多高镁闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年研究表明,松多闪长岩的形成年龄为186.4±1.3Ma,形成时代为早侏罗世。
(2)松多高镁闪长岩具高MgO和Mg#值,以及高Cr、Ni含量,以富集大离子亲石元素、亏损高场强元素为主要特征,具有明显的Nb-Ta槽,显示出典型俯冲带之上火山弧的地球化学特征,可能是早侏罗世新特提斯洋北向俯冲早期,存在于冈底斯南缘大陆边缘弧的岩浆记录。
致谢
锆石LA-ICP-MS原位微区U-Pb同位素测定得到中国地质大学(北京)苏犁教授的帮助,在此致以诚挚谢意。
-
图 1 冈底斯东段构造简图及其早侏罗世岩浆岩分布[3]
Figure 1.
图 9 松多闪长岩高镁安山岩分类图解[39]
Figure 9.
表 1 松多闪长岩(ST76)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Th-Pb分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS U-Th-Pb analyses of zircons from the diorite (ST76) in Sumdo area
点号 含量/10-6 Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U Th U 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 年龄/Ma 1σ 1 206 580 0.36 0.0498 0.0012 0.2006 0.0048 0.0292 0.0003 186 34 186 4 186 2 2 349 930 0.38 0.0498 0.0011 0.2010 0.0043 0.0293 0.0003 185 29 186 4 186 2 3 238 650 0.37 0.0498 0.0012 0.2011 0.0049 0.0293 0.0003 187 36 186 4 186 2 4 193 303 0.64 0.0491 0.0017 0.1974 0.0067 0.0291 0.0004 154 56 183 6 185 2 5 220 495 0.44 0.0522 0.0013 0.2138 0.0051 0.0297 0.0004 294 34 197 4 189 2 6 303 776 0.39 0.0508 0.0012 0.2047 0.0046 0.0292 0.0003 233 31 189 4 186 2 7 216 580 0.37 0.0499 0.0013 0.2002 0.0051 0.0291 0.0003 191 38 185 4 185 2 8 320 657 0.49 0.0526 0.0020 0.2091 0.0077 0.0288 0.0004 313 90 193 6 183 2 9 218 547 0.40 0.0493 0.0012 0.1994 0.0049 0.0293 0.0004 163 35 185 4 186 2 10 352 700 0.50 0.0524 0.0012 0.2121 0.0050 0.0293 0.0003 304 33 195 4 186 2 11 619 916 0.68 0.0526 0.0011 0.2114 0.0046 0.0291 0.0003 312 28 195 4 185 2 12 192 339 0.57 0.0504 0.0016 0.2112 0.0067 0.0304 0.0004 212 50 195 6 193 2 13 285 659 0.43 0.0514 0.0013 0.2072 0.0051 0.0293 0.0003 257 35 191 4 186 2 14 558 722 0.77 0.0512 0.0024 0.2102 0.0096 0.0298 0.0004 251 111 194 8 189 2 15 542 777 0.70 0.0512 0.0013 0.2102 0.0051 0.0298 0.0004 249 34 194 4 189 2 16 498 830 0.60 0.0511 0.0013 0.2081 0.0051 0.0296 0.0004 244 35 192 4 188 2 表 2 松多闪长岩(ST76)锆石LA-ICP-MS原位稀土元素分析结果
Table 2. The trace element compositions of the zircons in the diorite (ST76) in Sumdo area by LA-ICP-MS
10-6 点号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ∑REE 01 1.06 13.52 0.65 2.43 2.93 0.82 14.58 5.99 84.12 35.28 176.75 50.02 653.12 173.49 1215 02 0.04 19.89 0.03 0.69 2.60 1.12 16.78 7.60 106.02 46.08 228.32 63.78 826.25 216.30 1215 03 0.03 15.42 0.03 0.49 1.58 0.86 10.71 4.76 68.08 31.25 162.83 47.74 640.72 181.13 1169 04 0.03 11.07 0.03 0.67 1.36 0.68 7.30 2.67 35.69 14.80 73.49 21.68 299.68 86.18 559 05 0.03 12.04 0.02 0.29 0.98 0.51 6.28 2.42 34.33 15.12 77.90 23.49 325.66 93.27 597 06 9.93 37.44 2.87 14.47 5.09 1.32 17.55 7.02 95.91 40.46 202.72 56.38 731.30 195.07 1424 07 0.05 13.19 0.03 0.39 1.45 0.71 8.26 3.58 50.99 22.82 121.19 36.10 502.57 145.96 914 08 0.04 19.79 0.05 0.69 2.05 1.10 12.39 5.08 71.78 31.91 167.15 50.52 675.85 188.40 1235 09 0.04 15.96 0.03 0.54 1.42 0.79 9.14 3.76 54.75 24.74 130.63 38.96 543.96 162.47 996 10 0.05 18.40 0.04 1.41 3.51 1.23 19.64 7.75 104.23 42.02 203.29 55.23 692.35 178.56 1338 11 2.73 25.86 0.81 4.94 3.28 1.19 14.93 5.51 73.71 29.84 146.62 40.51 524.2 140.75 1026 12 0.16 9.13 0.08 1.81 4.33 1.22 20.39 7.44 91.56 34.18 156.2 40.25 478.05 120.97 978 13 16.65 50.20 4.87 25.11 7.22 1.59 16.45 5.73 75.11 30.49 150.33 42.01 550.88 145.16 1135 14 0.20 21.11 0.12 2.40 4.81 1.57 22.51 8.24 104.69 41.36 196.11 52.39 661.73 163.38 1295 15 0.03 14.71 0.04 0.73 2.18 0.89 12.93 4.98 66.21 26.29 122.53 32.55 413.27 106.38 819 16 4.21 27.21 1.47 7.51 3.62 1.03 10.93 3.97 50.45 21.12 108.11 30.39 402.18 115.79 804 表 3 松多闪长岩(ST76)LA-ICP-MS锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成
Table 3. The Lu-Hf isotope compositions of the zircons in the diorite (ST76) in Sumdo area as measured by LA-ICP-MS
点号 年龄/Ma 176Yb/177Hf 2σ 176Lu/177Hf 2σ 176Hf/177Hf 2σ εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM1 TDM2 fLu/Hf 01 186 0.034757 0.000514 0.001385 0.000030 0.282468 0.000028 -10.8 -6.9 1121 1662 -0.96 02 186 0.020124 0.000198 0.000731 0.000008 0.282470 0.000018 -10.7 -6.7 1099 1652 -0.98 03 186 0.069570 0.000895 0.002615 0.000053 0.282446 0.000026 -11.5 -7.8 1191 1719 -0.92 04 185 0.039694 0.000791 0.001311 0.000024 0.282307 0.000021 -16.5 -12.6 1347 2021 -0.96 05 189 0.040310 0.000422 0.001442 0.000009 0.282420 0.000021 -12.5 -8.5 1191 1768 -0.96 06 186 0.021209 0.000292 0.000783 0.000011 0.282519 0.000018 -9.0 -5.0 1032 1543 -0.98 07 185 0.042573 0.001080 0.001651 0.000054 0.282373 0.000023 -14.1 -10.3 1265 1877 -0.95 08 183 0.026939 0.000259 0.000966 0.000007 0.282308 0.000018 -16.4 -12.5 1333 2018 -0.97 09 186 0.025039 0.000459 0.000925 0.000016 0.282489 0.000020 -10.0 -6.1 1078 1611 -0.97 10 186 0.026789 0.000106 0.000917 0.000007 0.282257 0.000019 -18.2 -14.3 1402 2129 -0.97 表 4 松多闪长岩全岩主量、微量和稀土元素测定结果
Table 4. Major, trace element and REE compositions of the diorite in Sumdo area
样号 ST76-1 ST76-2 ST76-3 ST76-4 ST76-5 ST76-6 样号 ST76-1 ST76-2 ST76-3 ST76-4 ST76-5 ST76-6 SiO2 58.81 58.10 57.71 54.85 54.17 55.32 Li 87.20 72.26 60.30 31.12 31.46 24.72 TiO2 0.62 0.65 0.69 0.71 0.67 0.65 P 870.4 794.6 799.4 626.55 565.80 635.40 Al2O3 11.20 11.05 11.26 11.90 12.09 11.72 K 29360 24620 28740 16187 15728 17942 TFe2O3 7.48 7.82 8.18 8.70 8.58 8.41 Sc 51.98 47.56 51.84 36.98 37.56 39.84 MnO 0.12 0.13 0.13 0.14 0.14 0.13 Ti 5220 4766 5140 4038 4090 4286 MgO 6.26 6.54 7.10 7.29 6.97 6.41 V 275.8 249.2 272.6 238.7 244.1 254.0 CaO 6.98 7.36 6.93 7.45 8.04 7.43 Cr 326.8 294.2 339.8 318.8 329.0 373.4 Na2O 1.84 1.84 1.62 1.71 1.97 1.91 Mn 1060.8 981.4 1036.8 1157.4 1185.0 1214.0 K2O 2.06 2.05 2.34 2.49 2.18 2.19 Co 37.80 36.44 39.76 37.60 38.66 42.26 P2O5 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.12 0.11 0.12 Ni 43.78 42.66 45.82 42.74 43.60 51.32 烧失量 4.07 3.91 3.48 4.02 4.46 5.10 Cu 62.48 46.38 34.44 56.76 45.56 34.78 总量 99.57 99.58 99.57 99.38 99.38 99.39 Zn 57.86 59.12 54.62 66.37 70.42 61.22 Na2O+K2 3.90 3.89 3.96 4.20 4.14 4.10 Ga 17.38 15.47 15.53 14.07 14.00 13.83 A/CNK 0.62 0.59 0.63 0.63 0.60 0.62 Rb 29.74 63.58 59.12 76.92 74.72 97.10 A/NK 2.13 2.11 2.16 2.16 2.16 2.13 Sr 441.6 510.0 510.8 440.0 440.0 338.4 La 19.91 17.09 17.85 17.47 16.92 16.85 Y 19.86 17.26 19.53 16.20 15.96 17.54 Ce 43.14 37.72 39.32 37.78 36.74 36.96 Zr 121.46 108.64 107.82 103.66 103.88 99.44 Pr 5.17 4.52 4.77 4.62 4.47 4.62 Nb 7.49 6.73 6.82 6.47 6.39 6.33 Nd 19.94 17.40 18.88 17.28 16.71 17.64 Cs 2.94 2.41 3.29 2.52 2.33 3.06 Sm 4.20 3.67 4.05 3.62 3.49 3.76 Ba 448.0 435.8 374.6 425.2 454.8 383.4 Eu 1.06 0.93 0.99 0.92 0.90 0.95 Hf 2.86 2.61 2.64 2.62 2.60 2.34 Gd 3.73 3.28 3.64 3.40 3.33 3.63 Ta 0.45 0.41 0.42 0.43 0.42 0.41 Tb 0.54 0.48 0.54 0.49 0.48 0.52 Pb 7.79 8.56 7.12 9.07 10.71 8.80 Dy 3.24 2.86 3.21 3.01 2.96 3.22 Th 6.85 6.32 5.79 7.41 7.56 6.80 Ho 0.63 0.57 0.63 0.62 0.61 0.65 U 1.27 1.17 1.12 1.58 1.59 1.50 Er 1.83 1.63 1.83 1.73 1.70 1.84 Ta/Yb 0.27 0.28 0.26 0.27 0.27 0.24 Tm 0.26 0.23 0.25 0.26 0.25 0.27 Th/Yb 4.07 4.24 3.57 4.59 4.74 4.02 Yb 1.68 1.49 1.62 1.62 1.60 1.69 Nb+Y 27.35 23.99 26.35 22.66 22.35 23.87 Lu 0.24 0.21 0.24 0.25 0.25 0.26 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素为10-6 表 5 冈底斯南缘早侏罗世岩浆岩年龄信息统计
Table 5. Age information of Early Jurassic magmatic rocks in southern margin of Gangdese
序号 样品编号 样品岩性 测试方法 年龄结果 采样位置 数据来源 1 S16T76 闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 186.4±1.3Ma 松多乡北 本文 2 X-20 辉长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 185.9±0.3Ma 墨脱南背崩 [2] 3 TB-1-6 英云闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 179.7±1.7Ma 东嘎乡 [13] 4 TB-1-4 闪长岩(包体) LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 177.4±1.7Ma 东嘎乡 [13] 5 13GB-10 安山岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 188.8±1.8Ma 得明顶 [50] 6 X03 流纹岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 174.4±1.7Ma 甲马沟叶巴组 [18] 7 Dy1425-2 黑云二长花岗岩 锆石U-Pb 187±10Ma 嘉黎县布久岩体 [19] 8 B553-1 花岗闪长岩 40Ar/30Ar 198.2±0.3Ma 金达地区 [20] 9 DZ05-1 英安岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 174.2±3.6Ma 达孜 [10] 10 T384 变形花岗岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 178±1Ma 尼木大桥 [9] 11 b9041 白云母二长花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 190±8Ma 宁中 [16] 12 b7 白云母二长花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 193±7Ma 宁中 [16] 13 b50-2 白云母二长花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 191±10Ma 宁中 [16] 14 ST134A 花岗岩 SHRIMP锆石U-Pb 188.1±1.4Ma 南木林东 [7] 15 DZ-7 英安岩 锆石U-Pb 181±5Ma 达孜 [46] -
[1] 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等.冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):521-533. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603001
[2] 董汉文, 许志琴, 李源, 等.冈底斯东段墨脱地区早侏罗世辉长岩的成因及其构造意义[J].岩石学报, 2016, 33(12):3624-3634. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QKC20162017042100246217
[3] 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.西藏冈底斯侏罗纪岩浆作用的时空分布及构造环境[J].地质通报, 2008, 27(4):458-468. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.04.003 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20080403&flag=1
[4] 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 牛耀龄, 等.拉萨地体的起源和古生代构造演化[J].高校地质学报, 2012, 18(1):1-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.001
[5] 纪伟强, 吴福元, 锺孙霖, 等.西藏南部冈底斯岩基花岗岩时代与岩石成因[J].中国科学(D辑), 2009, 39(7):849-871. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200907002.htm
[6] Ji W Q, Wu F Y, Chung S L, et al.Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of the Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet[J].Chemical Geology, 2009, 262(3/4):229-245. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.chemgeo.2009.01.020/
[7] Chu M F, Chung S L, Song B, et al.Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on the Mesozoic tectonics and crustal evolution of southern Tibet[J].Geology, 2006, 34(9):745-748. doi: 10.1130/G22725.1
[8] 和钟铧, 杨德明, 郑常青, 等.冈底斯带门巴花岗岩同位素测年及其对新特提斯洋俯冲时代的约束[J].地质论评, 2006, 52(1):100-106. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2006.01.013
[9] 张宏飞, 徐旺春, 郭建秋, 等.冈底斯南缘变形花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成:新特提斯洋早侏罗世俯冲作用的证据[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(6):1347-1353. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.011
[10] Zhu D C, Pan G T, Chung S L, et al.SHRIMP Zircon Age and Geochemical Constraints on the Origin of Lower Jurassic Volcanic Rocks from the Yeba Formation, Southern Gangdese, South Tibet[J]. International Geology Review, 2008, 50(5):442-471. doi: 10.2747/0020-6814.50.5.442
[11] Guo L S, Liu Y L, Liu S W, et al.Petrogenesis of Early to Middle Jurassic granitoid rocks from the Gangdese belt, southern Tibet:Implications for early history of the Neo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2013, 179:320-333. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.06.011
[12] Kang Z Q, Xu J F, Wilde S A, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Sangri Group volcanic rocks, southern Lhasa terrane:Implications for the early subduction history of the Neo-Tethys and Gangdese magmatic arc[J].Lithos, 2014, 200/201:157-168. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.04.019
[13] 邱检生, 王睿强, 赵姣龙, 等.冈底斯中段早侏罗世辉长岩-花岗岩杂岩体成因及其对新特提斯构造演化的启示:以日喀则东嘎岩体为例[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(12):3569-3580. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201512005
[14] 黄丰, 许继峰, 陈建林, 等.早侏罗世叶巴组与桑日群火山岩:特提斯洋俯冲过程中的陆缘弧与洋内弧[J].岩石学报, 2015, 31(7):2089-2100. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201507022
[15] Dong H W, Xu Z Q, Li Y, et al.The Mesozoic metamorphicmagmatic events in the Medog area, the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis:Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology, trace elements and Hf isotope compositions in granitoids[J].International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2015, 104(1):61-74. doi: 10.1007/s00531-014-1057-y
[16] 刘琦胜, 江万, 简平, 等.宁中白云母二长花岗岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及岩石地球化学特征[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):643-652. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603013
[17] Geng Q R, Pan G T, Zheng L L, et al. The eastern Himalayan syntaxis:Major tectonic domains, ophiolitic mélanges and geologic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 27(3):265-285. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.03.009
[18] 董彦辉, 许继峰, 曾庆高, 等.存在比桑日群弧火山岩更早的新特提斯洋俯冲记录么?[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(3):661-668. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603015
[19] 向树元, 泽仁扎西, 田立富, 等.中华人民共和国1:25万区域地质调查报告嘉黎县幅[M].北京:地质出版社, 2010.
[20] 杨德明, 和钟铧, 王天武, 等.中华人民共和国1:25万区域地质调查报告门巴区幅[M].北京:地质出版社, 2005.
[21] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 耿全如, 等.中国境内可能存在一条新的高压/超高压(?)变质带-青藏高原拉萨地体中发现榴辉岩带[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(12):1787-1792. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.12.001
[22] 王斌, 解超明, 李才, 等.青藏高原松多地区温木朗蛇绿岩的发现及其地质意义[J].地质通报, 2017, 36(11):2076-2081. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.017 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20171117&flag=1
[23] 陈松永, 杨经绥, 罗立强, 等.西藏拉萨地块MORB型榴辉岩的岩石地球化学特征[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(10):1327-1339. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.10.011 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2007010213&flag=1
[24] 徐向珍, 杨经绥, 李天福, 等.青藏高原拉萨地块松多榴辉岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及锆石中的包裹体[J].地质通报, 2007, 26(10):1340-1355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2007.10.012 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2007010214&flag=1
[25] Cheng H, Zhang C, Jeffrey D, et al. Zircon U-Pb and garnet Lu-Hf geochronology of eclogites from the Lhasa Block, Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2012, 155:341-359. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.09.011
[26] Cheng H, Liu Y M, Jeffrey D, et al.Combined U-Pb, Lu-Hf, Sm-Nd and Ar-Ar multichronometric dating on the Bailang eclogite constrains the closure timing of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Lhasa terrane, Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28:1482-1499. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.017
[27] Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al.Accurate U-Pb age and trace elment deteminations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry[J].Geostandards and Geoanlytical Research, 2004, 11:357-370. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=4a8e7a7fca3d10ce694c49bdb9efd4b5&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[28] Hu Z C, Liu Y S, Gao S, et al.Improved in situ Hf isotope ratio analysis of zircon using newly designed X skimmer cone and Jet sample cone in combination with the addition of nitrogen by laser ablation multiple collector ICP-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 2012, 27:1391-1399. doi: 10.1039/c2ja30078h
[29] Liu Y S, Gao S, Hu Z C, et al.Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons of mantle xenoliths[J].Journal of Petrology, 2010, 51:537-571. doi: 10.1093/petrology/egp082
[30] Hoskin P W O, Black L P.Metamorphic zircon formation by solid-state recrystallization of protolith igneous zircon[J].Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 2000, 18:423-439. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=JJ026563309
[31] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等.Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J].岩石学报, 2007, 23(2):185-220. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702001
[32] Amelin Y, Lee D C, Halliday A N, et al. Nature of the Earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons[J].Nature, 1999, 399:252-255. doi: 10.1038/20426
[33] Rickwood P C.Boundary lines within petrologic diagrams which use oxides of major and elements[J].Lithos, 1989, 22:247-263. doi: 10.1016/0024-4937(89)90028-5
[34] Middlemost E A K.Iron oxidation ratios, norms and the classification of volcanic rocks[J].Chemical Geology, 1989, 77:19-26. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(89)90011-9
[35] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M.Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[36] Boynton W V.Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements:Meteorites studies[J].Development in Geochemistry, 1984:63-114. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=a86bc72c95d06bcdf62c0e1eb55bf851&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[37] Sun S S, McDonough W F.Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt:implications for mantle composition and processes[J].Geological Society, London, Specical Publications, 1989, 42:313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[38] 付长亮, 孙德有, 张兴洲, 等.吉林珲春三叠纪高镁闪长岩的发现及地质意义[J].岩石学报, 2010, 26(4):1089-1102. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201004007
[39] Kamei A, Owada M, Nagao T, et al. High-Mg diorites derived from sanukitic HMA magmas, Kyushu Island, southwest Japan arc:Evidence from clinopyroxene and whole rock compositions[J]. Lithos, 2004, 75:359-371. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.03.006
[40] Kelemen P B, Hanghoj K, Greene A R, et al. One View of the Geochemistry of Subduction-Related Magmatic Arcs, with an Emphasis on Primitive Andesite and Lower Crust[J].Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 3:593-659. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234393905_One_View_of_the_Geochemistry_of_Subduction-Related_Magmatic_Arcs_with_an_Emphasis_on_Primitive_Andesite_and_Lower_Crust
[41] 张旗, 王焰, 钱青, 等.晚太古代Sanukite (赞岐岩)与地球早期演化[J].岩石学报, 2004, 20(6):1355-1362. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200406005
[42] 张旗, 钱青, 翟明国, 等.Sanukite(赞岐岩)的地球化学特征、成因及其地球动力学意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 2005, 24(2):117-125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2005.02.005
[43] 李化启, 蔡智慧, 陈松永, 等.拉萨地体中的印支期造山事件及年代学证据[J].岩石学报, 2008, 24(7):1595-1604. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200807015
[44] 李化启, 许志琴, 杨经绥, 等.拉萨地体内松多榴辉岩的同碰撞折返:来自构造变形和40Ar/39Ar年代学的证据[J].地学前缘, 2011, 18(3):66-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201103008
[45] Zedde D, Wortel M. Shallow slab detachment as a transient source of heat at midlithospheric depths[J]. Tectonics, 2001, 20(6):868-882. doi: 10.1029/2001TC900018
[46] 更全如, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 等.西藏冈底斯带叶巴组火山岩同位素地质年代[J].沉积与特提斯地质, 2006, 26(1):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2006.01.001
[47] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al.The Lhasa Terrane:Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2011, 301(1/2):241-255. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-j.epsl.2010.11.005/
[48] England P, Houseman G. Finite strain calculations of continental deformation 2. Comparison with the India-Asia collision zone[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1986, 91(3):3664-3676. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1029-JB091iB03p03664/
[49] Murphy M A, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Tibetan Plateau?[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):719-722. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0719:DTIACA>2.3.CO;2
[50] 熊秋伟, 陈建林, 许继峰, 等.拉萨地块南部得明顶地区叶巴组火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其成因[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(9):1645-1655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.09.006 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150906&flag=1
[51] 王玉净, 松冈笃.藏南泽当雅鲁藏布缝合带中的三叠纪放射虫[J].微体古生物学报, 2002, 19(3):215-227. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0674.2002.03.001
-





 下载:
下载: