The effect of iron content on the kinetics of talc dehydration and its geological significance
-
摘要:
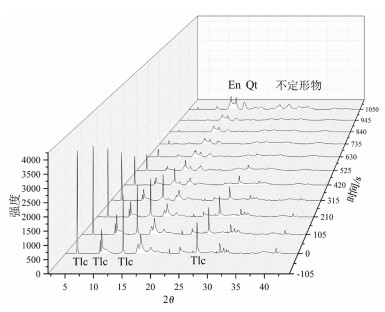
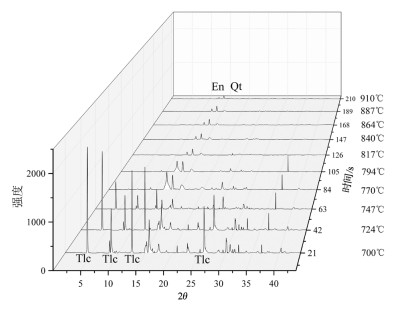
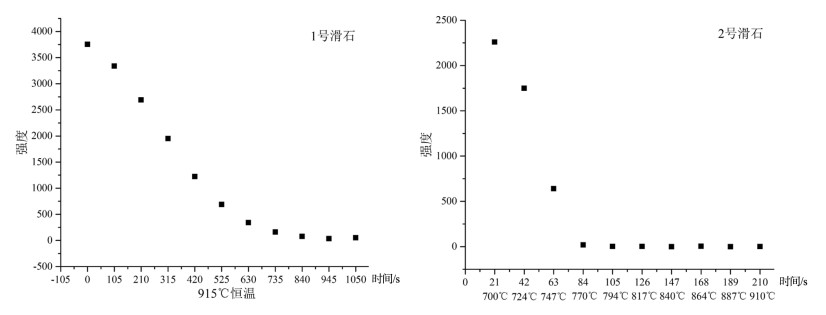
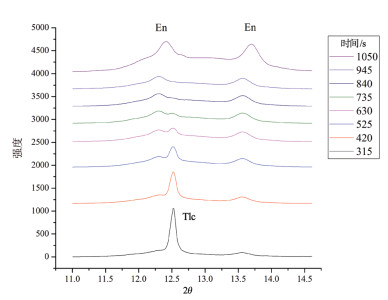
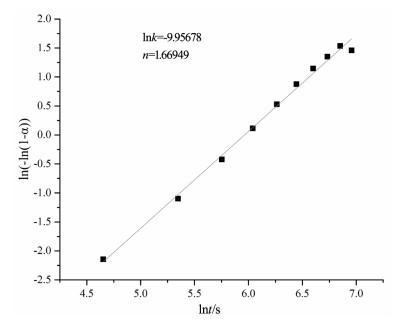
在常压下研究了2种不同铁含量滑石的原位X射线衍射高温脱水反应。选取粒径2~5μm的2种不同铁含量的滑石样品,在常压、空气氛围下进行了同步辐射原位X射线衍射脱水实验。实验结果表明,铁含量高的滑石脱水温度明显偏低,2个滑石样品在常压下发生明显脱水反应的温度相差达127℃以上。滑石在常压下的脱水动力机制为随机成核和生长机制,符合Avrami方程。将实验数据拟合Avrami方程得出:n=1.669。由实验结果可以推测,不同铁含量的滑石脱水深度可能有几十到上百千米的差别,研究铁含量与滑石脱水动力的相关性对于了解俯冲带浅-中源地震的成因机制具有重要意义。
Abstract:The effect of iron content on the kinetics of talc dehydration was studied with talc of different iron values using in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction (XRD).The sample particle size is 2~5μm.The air atmosphere synchrotron radiation in situ XRD de-hydration experiment was carried out under atmospheric pressure.High content of iron obviously resulted in lower dehydration tem-perature.The difference of the dehydration temperature of two samples was above 127℃.The dehydration of talc followed random nucleation and growth mechanism, and fitted Avrami equation, with n being 1.669.The results suggest that the dehydration of differ-ent iron values of talc may occur at the different depths around hundreds of kilometers, so the study was significant to the understand-ing of the genetic mechanism of earthquakes in the subduction zone.
-
Key words:
- talc /
- dehydration /
- iron content /
- in-situ /
- XRD /
- earthquake
-

-
表 1 滑石的组成成分
Table 1. The composition of two kinds of talc
% 编号 SiO2 TiO2 FeO MgO CaO2 K2O Na2O Al2O3 Cr2O3 P2O5 LOI 总计 1 62.35 0.01 0.50 31.31 0.08 0.05 0.01 0.10 0.08 0.04 5.74 100.20 2 63.269 0.012 2.532 29.650 0.023 0.039 0.069 0.055 0.050 95.714 注:1号滑石为X射线荧光分析结果;2号滑石为电子探针分析结果 -
[1] 余日东, 金振民.蛇纹石脱水与大洋俯冲带中源地震(70~300km)的关系[J].地学前缘, 2006, 13(2):191-204. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200602021.htm
[2] Larson K M, Kostoglodov V, Miyazaki S, et al. The 2006 aseismic slow slip event in Guerrero, Mexico:New results from GPS[J]. Geo-physical Research Letters, 2007, 34(13):256-260. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2007GL029912/full
[3] Song T R, Helmberger D V, Brudzinski M R, et al. Subducting slab ultra-slow velocity layer coincident with silent earthquakes in south-ern Mexico[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5926):502-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1167595
[4] Kim Y, Clayton R W, Jackson J M. Geometry and seismic proper-ties of the subducting Cocos plate in central Mexico[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2010, 115(B6):258-273. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2009JB006942/full
[5] Moore D E, Lockner D A. Talc friction in the temperature range 25°-400° C:Relevance for Fault-Zone Weakening[J]. Tectono-physics, 2008, 449(1):120-132. https://pubs.er.usgs.gov/publication/70032195
[6] Mysen B O, Ulmer P, Konzett J, et al. The upper mantle near con-vergent plate boundaries[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy, 1998, 37:97-138. http://rimg.geoscienceworld.org/content/37/1/97
[7] Bose K, Ganguly J. Thermogravimetric study of the dehydration ki-netics of talc[J]. American Mineralogist, 1994, 79(7):692-699. https://arizona.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/thermogravimetric-study-of-the-dehydration-kinetics-of-talc
[8] Chollet M, Daniel I, Koga K T, et al. Dehydration kinetics of talc and 10Å phase:Consequences for subduction zone seismicity[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 2009, 284(1/2):57-64. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X09002271
[9] Wang D, Karato S I. Electrical conductivity of talc aggregates at 0.5GPa:influence of dehydration[J]. Physics & Chemistry of Miner-als, 2012, 40(1):11-17. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00269-012-0541-9
[10] Zhang M, Hui Q, Lou X J, et al. Dehydroxylation, proton migra-tion, and structural changes in heated talc:An infrared spectroscop-ic study[J]. American Mineralogist, 2006, 91(5):816-825.
[11] Taylor H F W, Taylor H F W. Homogeneous and Inhomogeneous Mechanisms in the Dehydroxylation of Minerals[J]. Clay Minerals, 1962, 5(28):45-55. doi: 10.1180/claymin
[12] Molinamontes E, Donadio D, Hernándezlaguna A, et al. Water Re-lease from Pyrophyllite during the Dehydroxylation Process Ex-plored by Quantum Mechanical Simulations[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(15):7526-7532. doi: 10.1021/jp310739y
[13] Wang D, Yi L, Huang B, et al. High-temperature dehydration of talc:a kinetics study using X-ray powder diffraction[J]. Phase Tran-sitions, 2015, 88(6):1-7. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/01411594.2014.1002092?needAccess=true&journalCode=gpht20
[14] 王艳, 王多君, 易丽.空气气氛中滑石的热分解动力学实验研究[J].中国科学院大学学报, 2015, 32(1):70-73. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKYB201501013.htm
[15] Avrami M. Kinetics of Phase Change 2[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1939, 7(12):1103-1112. doi: 10.1063/1.1750380
[16] Avrami M. Kinetics of Phase Change:Ⅱ. Transformation-Time Relation for Random Distribution of Nuclei[J]. Journal of Chemi-cal Physics, 1940, 8(2):212-224. doi: 10.1063/1.1750631
[17] Collettini C, Viti C, Smith S A F, et al. Development of intercon-nected talc networks and weakening of continental low-angle nor-mal faults[J]. Sem. Hop., 2009, 33(6):2102-16. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/240305277_Cation_disordering_in_dolomitetheoretical_and_experimental_approach
[18] Omori S, Komabayashi T, Maruyama S. Dehydration and earth-quakes in the subducting slab:empirical link in intermediate and deep seismic zones[J]. Physics of the Earth &Planetary Interiors, 2004, 146(1/2):297-311. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031920104001293
[19] Syracuse E M, Keken P E V, Abers G A. The global range of sub-duction zone thermal models[J]. Physics of the Earth & Planetary Interiors, 2010, 183(1/2):73-90. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031920110000300
[20] 申婷婷, 张立飞, 陈晶.俯冲带蛇纹岩的变质过程[J].岩石学报, 2016, 32(4):1206-1218. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201604019.htm
[21] Mohsen M D. Dictionary of Gems and Gemology[M]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2009:575.
[22] 赵永红, 施旭, Zimmerman, M, 等.含水对富铁橄榄石流变性的影响[J].岩石学报, 2006, 22(9):2381-2386. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200609013.htm
-



 下载:
下载: