Main ore deposit types and resource potential analysis of gold copper tin iron deposits in Bolivia
-
摘要:
玻利维亚的铜矿规模以中小型为主,主要成矿类型为红层型(砂岩层)、沉积相关脉状型、VMS型和IOCG型等。金矿规模以中小型为主,主要成矿类型有火山成因浅成热液型、与深成岩相关的脉状矿床、造山型矿床和砂金矿。锡矿发育众多大型、超大型矿床,成矿类型以玻利维亚型多金属脉状矿床和与长英质深成岩相关的脉状矿床为主,少量砂锡矿。铁矿以ElMutún超大型BIF型铁锰矿著称。西科迪勒拉和玻利维亚高原有重要的浅成低温热液贵金属资源潜力;东科迪勒拉北部主要为钨、锡、金、锑资源,中部为锡、银、金、锑资源,南部有金、锑、银、铅、锌潜力;次安第斯带南部有银-锌资源潜力;查科-贝尼平原带有广泛的砂金矿资源;前寒武纪克拉通内金、铂、镍、钽、铜和铁锰资源潜力丰富。
Abstract:This paper systematically summarizes the characteristics of mineralization types and resource potential of gold, copper, tin and iron deposits. The copper deposits are from small to medium in size in Bolivia, and the main mineralization types are red-bed copper, sediment-associated vein-type deposits, VMS, IOCG and some other types. The gold deposits are from small to medium in size, and the main deposit types are the volcanogenic epithermal deposits (vein-type or porphyry), vein-type deposits associated with felsic plutons, orogenic gold (±antimony) deposits and placer gold deposits. Bolivia has many large and superlarge tin deposits, and the typical mineralization types are "Bolivia-type" polymetallic veins and pluton-associated polymetallic vein deposits, with minor placer tin deposits. The superlarge Mutún iron-manganese deposit is hosted in Banded Iron Formation (BIF). Western Cordillera and Altiplano have important potentiality for discovering epithermal precious metal resources. North Eastern Cordillera mainly contains potential of tungsten, tin, gold, antimony resources, and central Eastern Cordillera has potential of tin, silver and gold, antimony resources, with gold, antimony, silver, lead and zinc in the south segment. Important silver-zinc resources occur in south Subandean. Chaco-Beni plain has extensive placer gold resources. Precambrian craton contains potential of gold, platinum, nickel, tantalum, copper, iron and manganese resources.
-

-
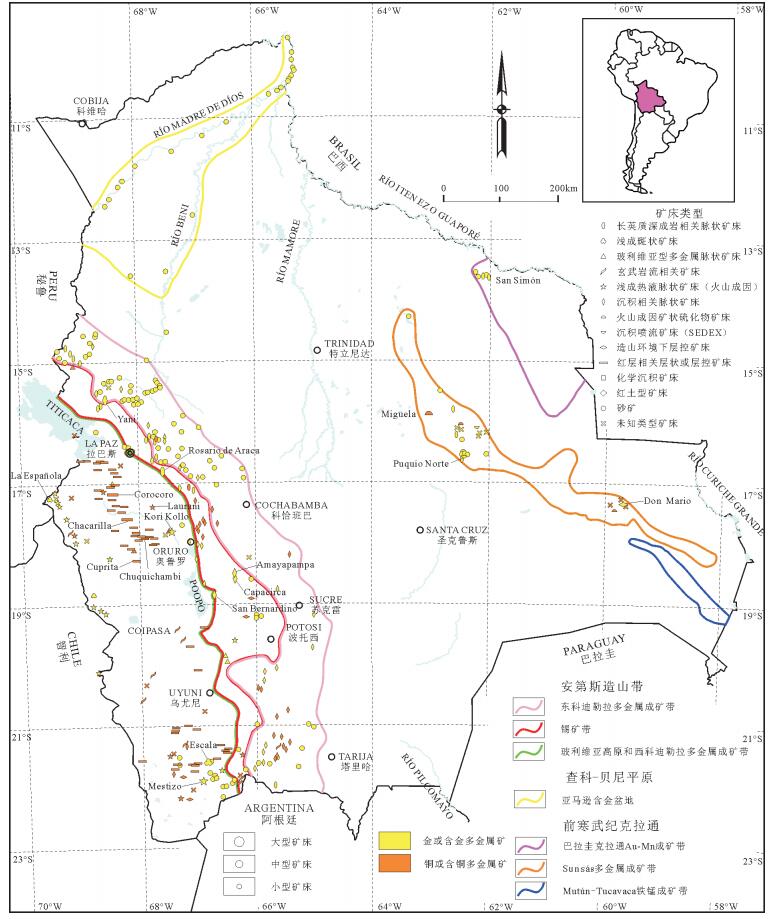
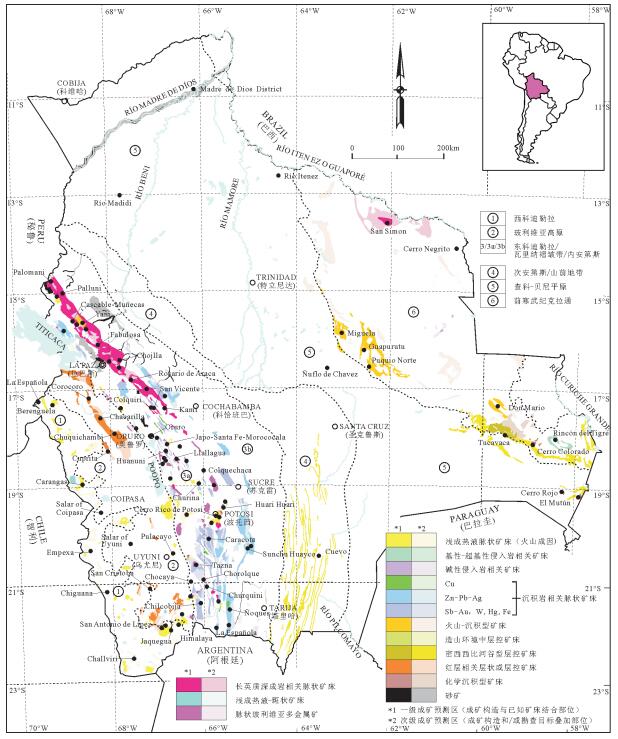
图 2 玻利维亚主要铜、金矿床类型与分布(据参考文献[1]修改)
Figure 2.
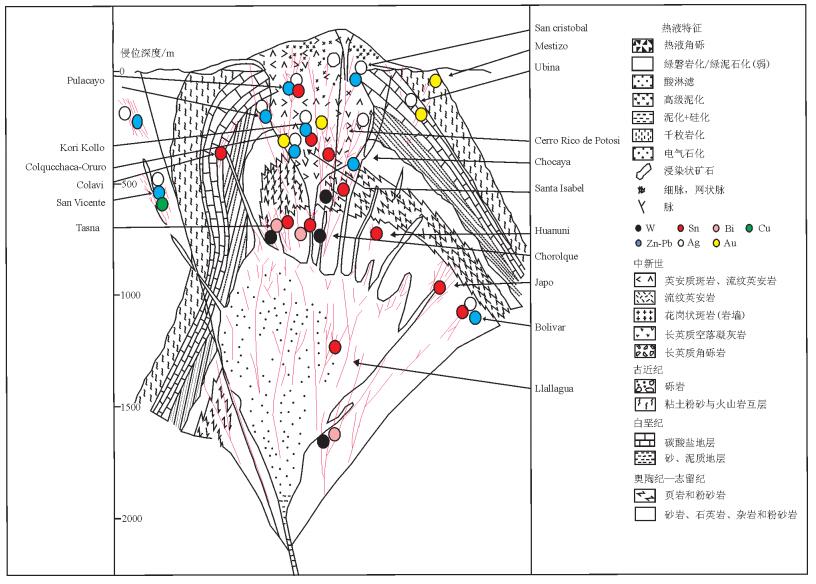
图 3 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床概念模型(据参考文献[1]修改)
Figure 3.
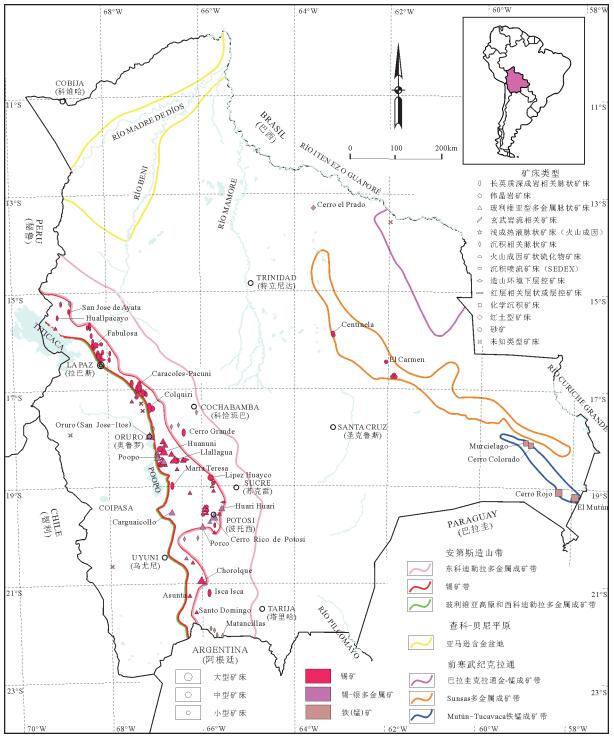
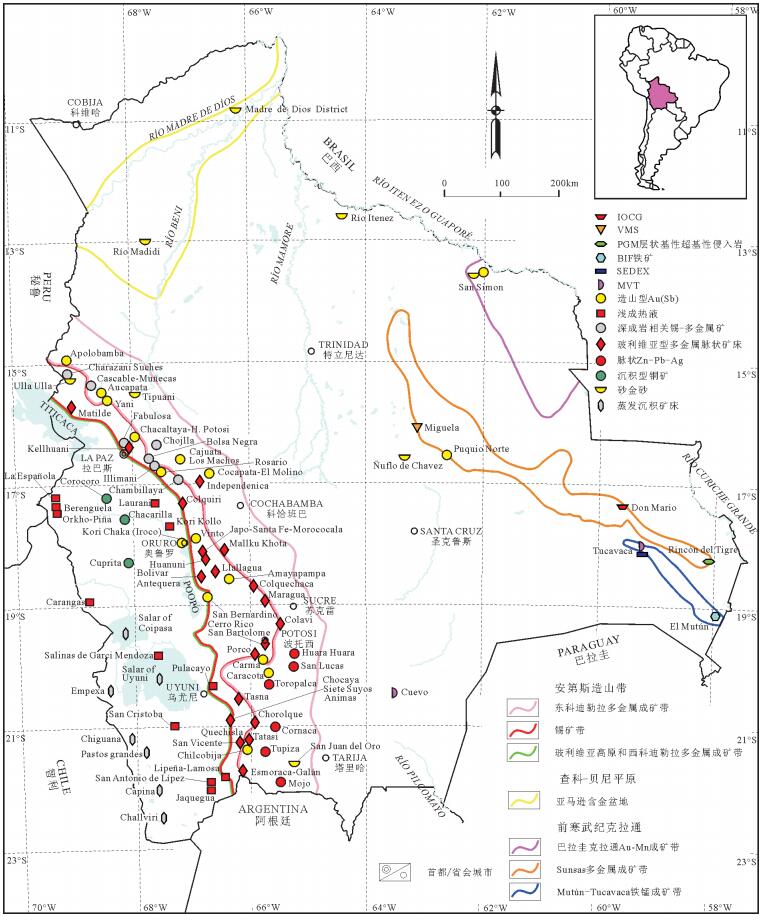
图 4 玻利维亚主要成矿带划分及锡、铁矿床类型与分布(据参考文献[1]修改)
Figure 4.
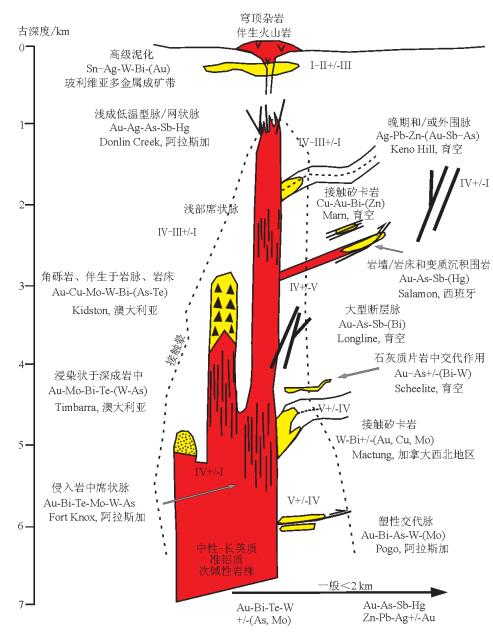
图 5 深成岩相关脉状多金属矿床模式(据参考文献[14]修改)
Figure 5.
图 6 玻利维亚前寒武纪克拉通地质简图(据参考文献[20]修改)
Figure 6.
表 1 玻利维亚主要金(银、铜、锑、铋)矿床(据参考文献[2]修改)
Table 1. Major gold (silver, copper, antimony, bismuth) deposits in Bolivia
矿床名称 构造带 矿床类型 当前状态 估计历史产量 估计历史产量 当前资源量 品位 Yani-Aucapata Gold district 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 地下开采 5t Au 5t Au 15t Au 3.8g/t Au Liphlchi 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 未开采 2t Au 2t Au 9.5t Au 3.8g/t Au Apolobamba Gold district 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 地下开采 10t Au 10t Au 84t Au 7g/t Au Rosario de Araca 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 历史地下开采 5t Au 5t Au 34t Au 1.3~2.5g/t Au Kori Kollo 玻利维亚高原 Transitional 历史露天开采 167t Au, 907t Ag 167t Au, 907t Ag 8t Au, 40t Ag 2 g/t Au, 11g/t Ag San Bernardino 玻利维亚高原 造山型金(锑) 未开采 1t Au 1t Au 72t Au 1.4g/t Au Laurani 玻利维亚高原 浅成低温热液 历史地下开采 0.5t Au, 0.3Mt Cu, 40t Ag 0.5t Au, 0.3Mt Cu, 40t Ag 20t Au, 1Mt Cu, 1500t Ag 1g/t Au 8% Cu, 40g/t Ag Iroco (Kori Chaka) 玻利维亚高原 造山型金(锑) 露天开采 30t Au 30t Au 5t Au 0.7g/t Au Vinto 玻利维亚高原 造山型金(锑) 未开采 0.3t Au 0.3t Au 9t Au 1.1g/t Au Amayapampa district 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 未开采 2t Au 2t Au 17t Au 1.68g/t Au Mallku Khota 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 未开采 未知 未知 1700t Ag, 14t Au 50g/t Ag, 0.4g/t Au Cajuata district 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 地下开采 7t Au, 0.01Mt Sb 7t Au, 0.01Mt Sb 50t Au, 0.06Mt Sb 5g/t Au, 2% Sb Cocapata Gold district 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 历史地下开采 2t Au, 0.05Mt Sb 2t Au, 0.05Mt Sb 20t Au, 0.4Mt Sb 1g/t Au, 2% Sb Carma 东科迪勒拉 造山型金(锑) 历史地下开采 0.2t Au 0.2t Au 23.5t Au 1.5g/t Au Pulacayo 玻利维亚高原 浅成低温热液 勘探 1t Au, 5000t Ag 1t Au, 5000t Ag 77t Au, 7153t Ag 65g/t Ag, 0.7g/t Au Tasna 东科迪勒拉 Transitional 地下开采 0.5t Au, 0.05Mt Bi 0.5t Au, 0.05Mt Bi 48t Au, 0.5Mt Bi 1.2g/t Au, 1.3% Bi Lipeña-Lamosa 西科迪勒拉(Lípez) Transitional 未开采 0.05t Au, 10000t Cu. 0.3Mt Ag 0.05t Au, 10000t Cu. 0.3Mt Ag 15t Au, 0.14Mt Cu, 8Mt Ag 1.5~1.8g/t Au, 1.5%~2% Cu, 30g/t Ag Don Mario 前寒武纪克拉通 IOCG 地下及露天开采 10t Au, 100t Ag, 40000t Cu 10t Au, 100t Ag, 40000t Cu 21t Au, 254t Ag, 82000t Cu 1.4g/t Au, 47g/t Ag, 1.5% Cu San Simón 前寒武纪克拉通 造山型金 历史地下开采 2t Au 2t Au 20t Au 5g/t Au Miguela 前寒武纪克拉通 VMS 未开采 --- --- 5.3t Au, 56.5t Ag 1.26g/t Au, 11.3g/t Ag Puquio Norte 前寒武纪克拉通 造山型金 历史露天开采 28t Au 28t Au --- 2.8g/t Au 表 2 玻利维亚主要锡(银)及贱金属矿床(据参考文献[2]修改)
Table 2. Major tin (silver) and base metal deposits in Bolivia
矿床名称 构造带 矿床类型 当前状态 估计历史产量 当前资源量 品位 Cerro Rico Potosí 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 60000t Ag, 0.2Mt Sn 55182t Ag, 0.8Mt Sn 102g/t Ag, 0.15% Sn San Bartolome 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地表开采 --- 35Mt Ag 108g/t Ag Llallagua 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 历史地下开采 1Mt Sn --- 5% Sn Huanuni 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 0.1Mt Sn 0.2Mt Sn 3% Sn Colquiri 东科迪勒拉 深成岩相关多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 0.05Mt Sn, 0.3Mt Zn 0.1Mt Sn, 0.8Mt Zn 1% Sn, 8% Zn Japo, Sta Fe, oroco-cala 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 0.05Mt Sn 0.07Mt Sn 0.4% Sn Bolivar 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 0.1Mt Sn, 0.2Mt Zn, 0.15Mt Pb 0.15Mt Sn, 0.5Mt Zn, 0.4Mt Pb 3% Sn, 10% Zn, 8% Pb Oruro district 玻利维亚高原 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 0.1Mt Sn, 10000t Ag, 0.1Mt Pb 0.5Mt Sn, 9200t Ag, 3.2Mt Pb 200g/t Ag, 1% Sn, 7% Pb Colquechaca 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 5000t Ag, 0.4Mt Zn, 0.05Mt Sn 6, 749t Ag, 1.85Mt Zn, 0.37 Mt Sn 55g/t Ag, 1.5% Zn, 0.3% Sn Chorolque Group 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 0.2Mt Sn, 3000t Ag 2.4Mt Sn, 9600t Ag 2% Sn, 80g/t Ag Colavi 东科迪勒拉 玻利维亚多金属脉状矿床 地下开采 1000t Ag, 0.05Mt Sn, 0.05Mt Pb, 0.1Mt Zn 6400t Ag, 0.4Mt Sn, 0.4Mt Pb, 0.64Mt Zn 80g/t Ag, 0.5% Sn, 0.5% Pb, 0.8% Zn -
[1] Bertrand H, Jorge B L T, Vitaliano M A, et al.Las Areas Prospectivas de Bolivia Para Yacimientos Metaliferos[M].La Paz:Servicio Nacional de Geologia y Mineria, 2002:1-152.
[2] Arce Burgoa O R.Metalliferous ore deposits of Bolivia, Second Edition[M].La Paz:SPC Impresores S.A.2009:1-233 and three Appendices.
[3] Ramiro S S.Compendio de Geologia de Bolivia[C]//La Paz:Servicio Nacional de Geologia Y Mineria, Yacimientos Petroliferos Fiscales Bolivianos, 2000:1-216.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312465982_Compendio_de_geologia_de_Bolivia [4] 裴荣富, 梅燕雄, 瞿泓滢, 等.大型-超大型矿床找矿新认知[J].矿床地质, 2013, 32(4):661-664. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=kcdz201304004&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[5] Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al.Orogenic gold deposits:A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13(1/5):7-27. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136897000127
[6] Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Robert F, et al.Gold deposits in metamorphic belts:Overview of current understanding, outstanding problems, future research, and exploration significance[J].Economic Geology, 2003, 98:1-29. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80015919027
[7] Arce Burgoa O R, Goldfarb R J.Metallogeny of Bolivia[J].SEG Newsletter, 2009, 79(1):8-15.
[8] Redwood S D.The Metallogeny of the Bolivian Andes[M].Vancouver:University of British Columbia, 1993:1-125.
[9] Ludington S, McKee E, Shew N.K-Ar ages of Bolivian Tertiary polymetallic vein deposits[C]//Richard W S.Advances related to U.S.and international mineral resources:Developing frameworks and exploration technologies, 1992:87-93.
https://eurekamag.com/research/019/261/019261238.php [10] Sugaki A, Kitakaze A.Tin-bearing minerals from Bolivian polymetallic deposits and their mineralization stages[J].Mining Geology, 1988, 38(5):419-435. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/40001206533
[11] Sugaki A, Shimada N, Ueno H, et al.K-Ar ages of tin-polymetallic mineralization in the Oruro mining district, Central Bolivian tin belt[J].Resource Geology, 2003, 53(53):273-282. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1751-3928.2003.tb00176.x/full
[12] Cunningham C G, Mcnamee J, Vasquez J P, et al.A model of volcanic dome-hosted precious metal deposits in Bolivia[J].Economic Geology, 1991, 86(2):415-421. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.86.2.415
[13] Zartman R E, Cunningham C G.U-Th-Pb zircon dating of the 13.8-Ma dacite volcanic dome at Cerro Rico de Potosí, Bolivia[J].Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1995, 133(3/4):227-237. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X9500093R
[14] Lang J R, Baker T.Intrusion-related gold systems:the present level of understanding[J].Mineralium Deposita, 2001, 36(6):477-489. doi: 10.1007/s001260100184
[15] Pinto Vásquez J.Volcanic dome-associated precious and base metal epithermal mineralization at Pulacayo, Bolivia[J].Economic Geology, 1993, 88(3):697-700. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.88.3.697
[16] Phillipson S E, Romberger S B.Volcanic stratigraphy, structural controls, and mineralization in the san cristobal Ag-Zn-Pb deposit, southern bolivia[J].Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2004, 16(8):667-683. doi: 10.1016/j.jsames.2003.11.002
[17] Thompson J F H, Sillitoe R H, Baker T, et al.Intrusion-related gold deposits associated with tungsten-tin provinces[J].Mineralium Deposita, 1999, 34(4):323-334. doi: 10.1007/s001260050207
[18] Entwistle L P, Gouin L O.The chalcocite-ore deposits at Corocoro, Bolivia[J].Economic Geology, 1955, 50(6):555-570. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.50.6.555
[19] Ljunggren P, Meyer H C.The copper mineralization in the Corocoro Basin, Bolivia[J].Economic Geology, 1964, 59(1):110-125. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.59.1.110
[20] Litherland M, Annellls R N, Appleton J D, et al.The geology and mineral resources of the Bolivian Precambrain Shield[M].British Geological Survey, Overseas Memoir, 1986, 9:1-153.
[21] Walde D H G, Hagemann S G.The Neoproterozoic Urucum/Mutún Fe and Mn deposits in W-Brazil/SE-Bolivia:assessment of ore deposit models[Die neoproterozoischen Fe-und Mn-Lagerstätten Urucum/Mutún in W-Brasilien/SE-Bolivien:Bewertung der Modelle zur Lagerstättenbildung] [J].Zeitschrift Der Deutschen Gesellschaft Für Geowissenschaften, 2006, 158(1):45-55.
[22] 李丽文, 温彬, 黄明生.玻利维亚阿力安萨铜矿床地质特征与成因分析[J].甘肃冶金, 2015, 37(3):98-101. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=gsye201503031&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[23] Hyrsl J, Petrov A.Famous mineral localities:Llallagua, Bolivia[J].Mineralogical Record, 2006, 37(2):117-162. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285702442_Famous_mineral_localities_Llallagua_Bolivia
[24] Wilson W E, Petrov A.Famous mineral localities:Cerro Rico de Potosi Bolivia[J].Mineralogical Record, 1999, 30(1):9-36. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289133466_Famous_mineral_localities_Cerro_Rico_de_Potosi_Bolivia
[25] Arqués L, Cacho A, Artiaga D, et al.The Huanuni Sn-W-PbZn-Ag vein deposits, Bolivia:Structure and mineralogy[C]//Mineral Deposit Research for a High-Tech World.Uppsala:12th SGA Biennial Meeting, 2013:1236-1238.
http://www.researchgate.net/publication/271270041_The_Huanuni_Sn-W-Pb-Zn-Ag_vein_deposits_Bolivia_Structure_and_mineralogy [26] Bertrand H, Vitaliano M A, Jorge B T, et al.Sinopsis de La Metalogenia en Bolivia[M].La Paz:Servicio Nacional de Geologia Y Mineria, 2000:1-56.
[27] Kesler S E, Gruber P W, Medina P A, et al.Global lithium resources:Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48(5):55-69. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136812001539
[28] Redwood S D.The Metallogeny of the Eastern Cordillera of the Bolivian Andes[C]//Colegio De Geologos De Bolivia Bodas De Oro Seminario Tecnico-Cientifico.Bolivianan San Pablo:Colegio de geologos de Bolivia, 2011:81-86.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/294893796_The_Metallogeny_of_the_Eastern_Cordillera_of_the_Bolivian_Andes -



 下载:
下载: