Geology and mineralization of the Candelaria-Punta del Cobre Fe oxide Cu-Au deposits, Chile
-
摘要:
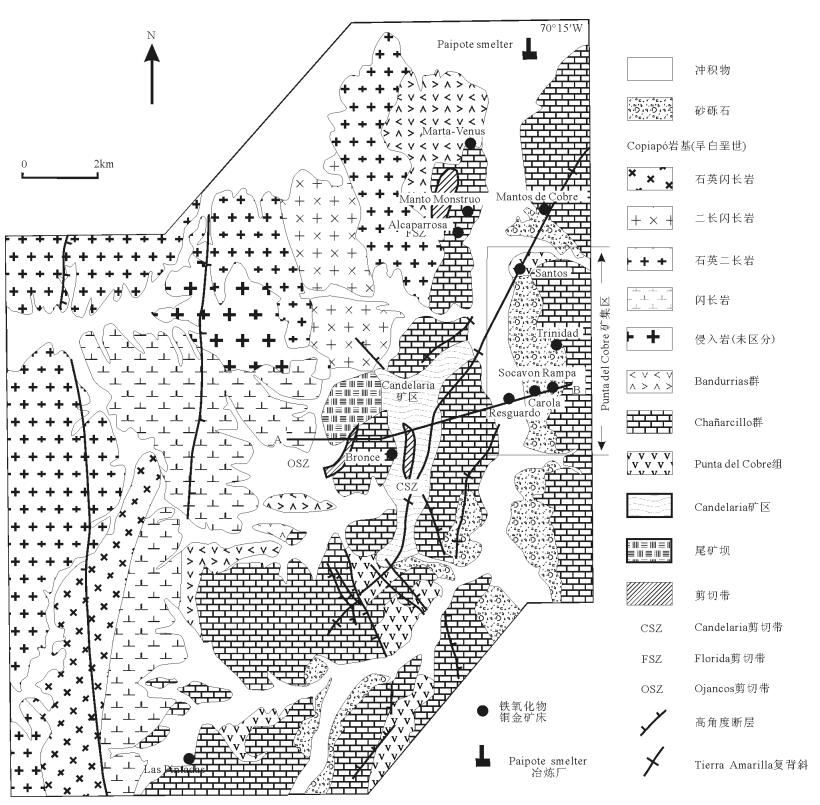
智利Copiapó附近海岸东部边缘有一宽5km、长20km的铁氧化物铜金矿床带,包括Candelaria矿床和位于其北东方向3km处的Punta del Cobre矿集区的中小型矿床。初步估计,该成矿带的铜矿石资源量可达7×108~8×108t(含铜量1%)。矿石矿物主要为黄铜矿、黄铁矿、磁铁矿、赤铁矿。矿石产状为脉状、角砾状、细脉状等。含矿围岩主要为Punta del Cobre组的火山岩及火山碎屑岩。该矿带中大部分大型矿脉位于北西-北北西向高角度脆性断层与块状火山岩和火山碎屑岩接触带交汇处。Candelairia矿区主要发育黑云母-钾长石±钙角闪石±绿帘石蚀变矿物组合。在Punta del Cobr矿集区,矿床深部的矿石围岩蚀变情况与Candelairia地区一致,但是浅部的矿石赋存于黑云母-钾长石或钠长石-绿泥石±方解石蚀变带中。
-
关键词:
- 地质 /
- 成矿作用 /
- Candelaria矿床 /
- Punta del Cobre矿集区 /
- 铁氧化物铜金矿床 /
- 智利
Abstract:There is a 5km wide and 20km long belt of Fe oxide Cu-Au deposits along the eastern margin of the coastal batholith near Copiapó, Chile. It includes the Candelaria deposit and a group of middle and small sized deposits in the Punta del Cobre district, which is located about 3km northeast of the Candelaria mine. It is estimated that the amount of copper ore resources in the belt is 700-800 million tons at 1.0 percent Cu. The ore minerals are mainly chalcopyrite, pyrite, magnetite, hematite. The ores occur in veins, breccia and stringer bodies. The orebodies are hosted mainly by volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks of the Punta del Cobre Formation. Most of the larger orebodies in the belt are situated along NW to NNW trending high-angle brittle faults which intersect the contact between massive volcanic and volcaniclastic rocks. The ores occur mainly in zones with biotite-K feldspar±calcic amphibole±epidote alteration at Candelaria. In the Punta del Cobre district, alteration associated with ores in the deeper parts of the deposits is similar to that at Candelaria, whereas at their shallow levels ores occur in biotite-K-feldspar or albite-chlorite±calcite alteration zones.
-
Key words:
- geology /
- mineralization /
- Candelaria deposit /
- Punta del Cobre district /
- Fe oxide Cu-Au deposit /
- Chile
-

-
表 1 Candelaria -Punta del Cobre成矿带中矿床简介
Table 1. The description of mineral deposits along the Candelaria-Punta del Cobre belt
矿床名称 矿石矿物组合 蚀变矿物 矿石储量和品位 Alcaparrosa mt, cpy, py kspar, bio, act, qtz 10Mt 1.4% Cu Bronce mt, cpy, py scap, gt Candelaria mt, cpy, py bio, kspar, act, qtz 470Mt 0.95% Cu, 0.22g/t Au, 3.1g/t Ag Carola mt, hm, cpy, py kspar, bio, chl, cte 20Mt 1.4% Cu Las Pintadas mt, cpy, py gt, act, kspar 4.0Mt 1.0%~1.5% Cu Manto Monstruo mt, cpy, py calc-silicate Mantos de Cobre mt, cpy, py kspar/ab-chl 1.5Mt 1.45% Cu Resguardo cpy, py, hm, mt ab, chl, cte 6Mt 1.8%~2.0% Cu, 0.4~0.5g/t Au, 7.0g/t Ag Santos mt, cpy, py, hm kspar, bio, chl 20Mt 1.5% Cu, 0.4~0.5g/t Au, 7.0g/t Ag Socavon Rampa cpy, hm, py ab, chl, cte 25Mt 1.2%~2% Cu, 0.2~0.3g/t Au, 7.0g/t Ag Trinidad mt, hm, cpy, py kspar, bio, chl 15Mt 1.5% Cu, 0.2~0.3g/t Au, 7.0g/t Ag Marta -Venus mt, cpy, py, hm gt, act 注:ab—钠长石;act—阳起石;bio—黑云母;chl—绿泥石;cpy—黄铜矿;cte—方解石;gt—石榴石;hm—赤铁矿;kspar—钾长石;mt—磁铁矿;po—磁黄铁矿;py—黄铁矿;qtz—石英;scap—方柱石;sl—闪锌矿;calc-silicate—钙硅酸盐 -
[1] Marschik R, Leveille R A, Martin W.La Candelaria and the Punta del Cobre district, Chile:Early Cretaceous iron oxide cu-au (-ZnAg) mineralization[J].Hydrothermal iron oxide copper-gold and related deposits, 2000, 1:163-175. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/312470464_La_Candelaria_and_the_Punta_del_Cobre_district_Chile_early_Cretaceous_iron-oxide_Cu-_Au-Zn-Ag_mineralization?ev=auth_pub
[2] Segerstrom K, Ruiz C.Geología del Cuadrángulo Copiapó, Provincia de Atacama[J].Carta Geológica de Chile, 1962, 3(1):115
[3] Hitzman M W, Oreskes N, Einaudi M T.Geological characteristics and tectonic setting of proterozoic iron oxide (Cu-U-Au-REE) deposits[J].Precambrian Research, 1992, 58(1/4):241-287. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0301926892901214
[4] Gow P A, Wall V J, Oliver N H S, et al.Proterozoic iron oxide (Cu-U-Au-REE) deposits:Further evidence of hydrothermal origins[J].Geology, 1994, 22(7):633-636. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0633:PIOCUA>2.3.CO;2
[5] Rotherham J F, Blake K L, Cartwright I, et al.Stable isotope evidence for the origin of the Mesoproterozoic Starra Au-Cu deposit, Cloncurry district, northwest Queensland[J].Economic Geology, 1998, 93(8):1435-1449. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.93.8.1435
[6] Williams P J.Metalliferous economic geology of the Mt Isa eastern succession, Queensland[J].Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1998, 45(3):329-341. doi: 10.1080/08120099808728395
[7] Williams P J, Dong G, Pollard P J, et al.Fluid inclusion geochemistry of Cloncurry (Fe)-Cu-Au deposits[J].Mineral deposits:Processes to processing:Rotterdam, Balkema, 1999, 1:111-114. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262151869_Fluid_inclusion_geochemistry_of_Cloncurry_Fe-Cu-Au_deposits
[8] Battles D A, Barton M D.Arc-related sodic hydrothermal alteration in the western United States[J].Geology, 1995, 23(10):913-916. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0913:ARSHAI>2.3.CO;2
[9] Haynes D W, Cross K C, Bills R T, et al.Olympic Dam ore genesis:a fluid-mixing model[J].Economic Geology, 1995, 90(2):281-307. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.2.281
[10] Barton M D, Johnson D A.Evaporitic-source model for igneousrelated Fe oxide-(REE-Cu-Au-U) mineralization[J].Geology, 1996, 24(3):259-262. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1996)024<0259:ESMFIR>2.3.CO;2
[11] Hopf S.The Agustina mine, a volcanic-hosted copper deposit in northern Chile[C]//Stratabound Ore Deposits in the Andes.Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1990:421-434.
http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-642-88282-1_32 [12] Marschik R, Fontboté L.Copper (-iron) mineralization and superposition of alteration events at the Punta del Cobre belt, northern Chile[J].Special Publication of the Society of Economic Geologists, 1996, 5:171-189. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284698183_Copper-iron_mineralization_and_superposition_of_alteration_events_in_the_Punta_del_Cobre_belt_northern_Chile?ev=auth_pub
[13] Ullrich T D, Clark A H.The Candelaria copper-gold deposit, Region Ⅲ, Chile:Paragenesis, geochronology and fluid composition[C]//Mineral deposits:Processes to processing:Rotterdam, Balkema, 1999:201-204.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309456889_The_Candelaria_copper-gold_deposit_Region_III_Chile_Paragenesis_geochronology_and_fluid_composition [14] Mathur R, Marschik R, Ruiz J, et al.Age of mineralization of the Candelaria Fe oxide Cu-Au deposit and the origin of the Chilean iron belt, based on Re-Os isotopes[J].Economic Geology, 2002, 97(1):59-71. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.97.1.59
[15] Scheuber E, Hammerschmidt K, Friedrichsen H.40 Ar/39 Ar and Rb-Sr analyses from ductile shear zones from the Atacama Fault Zone, northern Chile:the age of deformation[J].Tectonophysics, 1995, 250(1):61-87. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0040195195000448
[16] Dallmeyer R D, Brown M, Grocott J, et al.Mesozoic Magmatic and Tectonic Events within the Andean Plate Boundary Zone, 26°-27°30'S, North Chile:Constraints from Mineral Ages[J].The Journal of Geology, 1996, 104(1):19-40. doi: 10.1086/629799
[17] Menard J J.Relationship between altered pyroxene diorite and the magnetite mineralization in the Chilean Iron Belt, with emphasis on the El Algarrobo iron deposits (Atacama region, Chile)[J].Mineralium Deposita, 1995, 30(3):268-274. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF00196362
[18] Tilling R.El Batolito Andino cerca de Copiapó, Provincía de Atacama.Geologíay Petrología[J].Revista Geológica de Chile, 1976, 3:1-24. http://bosques.ciren.cl/handle/123456789/23791
[19] Marschik R, Fontboté L.The Punta del Cobre Formation, Punta del Cobre-Candelaria area, northern Chile[J].Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 2001, 14(4):401-433. doi: 10.1016/S0895-9811(01)00036-0
[20] Arévalo C, Grocott J, Martin W, et al.Structural Setting of the Candelaria Fe Oxide Cu-Au Deposit, Chilean Andes (27°30'S)[J].Economic Geology, 2006, 101(4):819-841. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.101.4.819
[21] Arévalo C, Grocott J.The tectonic setting of the Chañarcillo Group and the Bandurrias Formation:An Early-Late Cretaceous sinistral transpressive belt between the Coastal Cordillera and the Precordillera, Atacama region, Chile[J]:Congreso Geológico Chileno, 8th, Antofagasta, 1997, 3:1604-1607.
[22] 方维萱, 李建旭.智利铁氧化物铜金型矿床成矿规律、控制因素与成矿演化[J].地球科学进展, 2014, 29(9):1011-1024. doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2014.09.1011
[23] 李建旭, 方维萱, 刘家军.智利铁氧化物-铜-金矿床区域定位构造-矿田构造类型与特征[J].地质与勘探, 2011, 47(2):323-332. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzykt201102025
[24] Ryan P J, Lawrence A L, Jenkins R A, et al.The Candelaria copper-gold deposit, Chile[J].Arizona Geological Society Digest, 1995, 20:625-645. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284671519_The_Candelaria_copper-gold_deposit_Chile
[25] Sillitoe R H, Clark A H.Copper and copper iron sulphides as the initial products of supergene oxidation, Copiapó mining district, northern Chile[J].American Mineralogist, 1969, 54(11-1):1684-1710. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285630985_Copper_and_copper-iron_sulfides_as_the_initial_products_of_supergene_oxidation_Copiao_Mining_district_Northern_Chile
[26] Marschik R, Fontboté L.The Candelaria-Punta del Cobre iron oxide Cu-Au(-Zn-Ag) deposits, Chile[J].Economic Geology, 2001, 96(8):1799-1826. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/247864095_The_Candelaria-Punta_del_Cobre_Iron_Oxide_Cu-Au(-Zn-Ag)_Deposits_Chile
[27] Marschik R, Singer B S, Munizaga F, et al.Age of Cu (-Fe)-Au mineralization and thermal evolution of the Punta del Cobre district, Chile[J].Mineralium Deposita, 1997, 32(6):531-546. doi: 10.1007/s001260050120
[28] Taylor G K, Grocott J, Pope A, et al.Mesozoic fault systems, deformation and fault block rotation in the Andean forearc:a crustal scale strike-slip duplex in the Coastal Cordillera of northern Chile[J].Tectonophysics, 1998, 299(1):93-109. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195198002005
[29] Mpodozis C, Allmendinger R W.Extensional tectonics, Cretaceous Andes, northern Chile (27°S)[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1993, 105(11):1462-1477. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1993)105<1462:ETCANC>2.3.CO;2
[30] Perez E, Cooper M R, Covacevich V.Aptian ammonite-based age for the Pabellón Formation, Atacama Region, northern Chile[J].Andean Geology, 1990, 17(2):181-185. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/284565651_Aptian_ammonite-based_age_for_the_Pabellon_Formation_Atacama_Region_northern_Chile
[31] Vila T.Geology of the Manto Verde copper deposit, northern Chile:a speculariterich, hydrothermal-tectonic breccia related to the Atacama fault zone[C]//Andean Copper Deposits:New Discoveries, Mineralization Styles and Metallogeny.Soc.Econ.Geol.Spec.Publ.1996, 5:157-169.
[32] Orrego M, Zamora R.Manto Ruso:Un yacimiento de cobre ligado a la Falla de Atacama, Norte de Chile[J].Actas 6th Congr.Geol.Chileno.1991, 1:174-178.
[33] Hopper D, Correa A.The Panulcillo and Teresa de Colmo copper deposits:Two contrasting examples of Fe-ox Cu-Au mineralization from the coastal Cordillera of Chile[C]//Porter T M.Hydrothermal iron oxide copper-gold and related deposits:A global perspective.Australian Mineral Foundation, Adelaide, 2000:177-189.
[34] Cesar E, Vidal C, Injoque-Espinoza J, et al.Amphibolitic Cu-Fe skarn deposits in the central coast of Peru[J].Economic Geology, 1990, 85(7):1447-1461. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.85.7.1447
[35] Vivallo W, Espinoza S, Henriquez F.Metasomatismo y alteración hidrotermal en el distrito ferrífero Cerro Negro Norte, Copiapó, Chile[J].Andean Geology, 1995, 22(1):75-88. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/273139884_Metasomatismo_y_alteracion_hidrotermal_en_el_Distrito_Ferrifero_Cerro_Negro_Norte_Copiapo_Chile
① Arévalo C. The Coastal Cordillera-Precordillera boundary in the Copiapó area, northern Chile and the structural setting of the Candelaria Cu-Au ore deposit. Kingston University, 1999.
② Arévalo C. Mapa Geológico de la Hoja Copiapó, Región de Atacama: Santiago,Chile, SERNAGEOMIN, Documentos de Trabajo 8, scale 1∶ 100000, 1995.
③ Rotherham J F. Origin and Fluid Chemistry of the Starra Ironstones and High Grade Au- cu Mineralisation, Cloncurry District, Mount Isa Inlier, Australia. James Cook University of North Queensland, 1997.
④ Haller A. The Raul-Condestable iron oxides-Cu-Au deposit, Lima department, Peru: preliminary results. Abstract volume & Field trip guidebook, 2000.
-




 下载:
下载: