Experimental study on porosity and permeability and stress sensitivity of shale under pressurization
-
摘要:
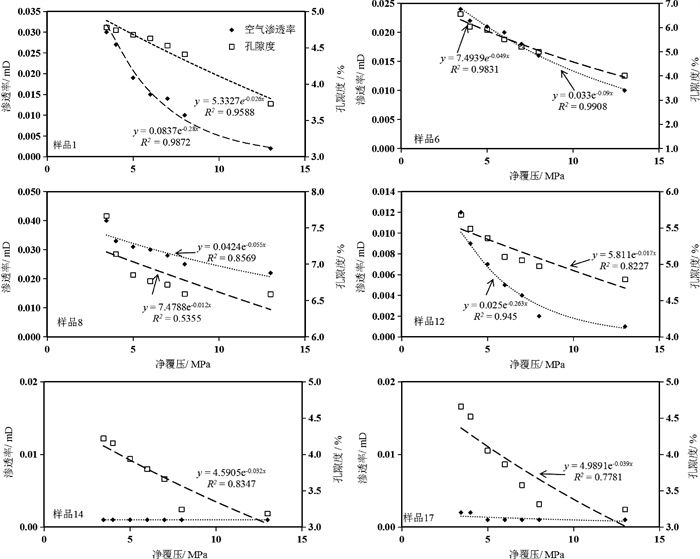
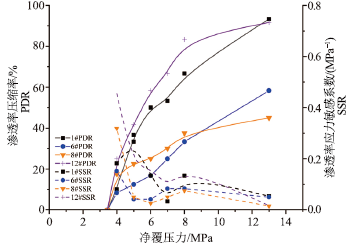
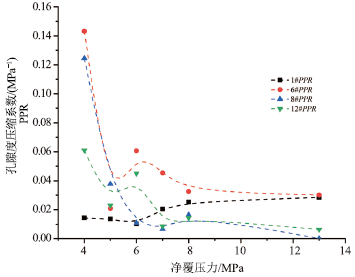
为了研究页岩在应力作用下的孔渗变化及孔隙结构特征,采用四川盆地昭通区块页岩样,不同压力条件下对页岩的孔隙度和渗透率进行实验分析,建立了页岩样孔隙度、渗透性与净覆压之间的相关关系和模型;采用渗透率损害率和应力敏感系数分析了页岩储层的应力敏感性。研究结果表明,页岩基质孔隙度和渗透率随有效应力的增加呈负指数函数规律降低,渗透率与孔隙结构有关,页岩地层中包括基质孔隙和裂隙共同发育的双重介质体系。当净覆压小于5 MPa时,页岩储层应力敏感系数变化较大,应力敏感性强;当净覆压大于5 MPa时,页岩储层应力敏感系数随有效应力的增加下降速度整体减缓,且存在波动变化,应力敏感性减弱,渗透率损害率随有效应力的增大而缓慢增加。研究发现,不同孔径的孔隙度随应力的增大而减小,反映了页岩中不同孔径对孔隙度的协同效应,对揭示页岩储层的孔径变化,指导深部页岩储层的物性特征具有一定的实际意义。
Abstract:In order to study the pore and permeability changes and pore structure characteristics of shale under stress, the porosity and permeability of shale in net confining stress were analyzed through experiment using the shale samples in Zhaotong area, Sichuan Basin.The stress sensitivity of shale reservoir was analyzed by permeability damage rate and stress sensitivity coefficient.The results indicate that the porosity and permeability of shale matrix decrease by a negative exponential function with the increasing effective stress, and permeability is related to pore structure.Shale formation consists of a dual media system including matrix pores and fractures.If the net confing stress is less than 5 MPa, the stress sensitivity coefficient of shale reservoir varies significantly and the shale reservoir is highly sensitive to stress.If the net confing stress is greater than 5 MPa, the stress sensitivity coefficient of the shale reservoir decreases as the effective stress increases slowly, and there is a fluctuation.Stress sensitivity weakens and permeability damage rate increases slowly with the increase of effective stress.It is found that the porosity of different pore sizes decreases with the increase of stress, which reflects the synergistic effect of different pore sizes on porosity in shale, and has certain practical significance to reveal the pore size change of shale reservoir and guide the physical properties of deep shale reservoir.
-
Key words:
- pressurization /
- shale /
- porosity /
- permeability /
- stress sensitivity
-

-
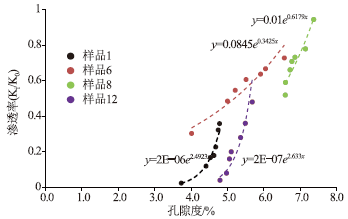
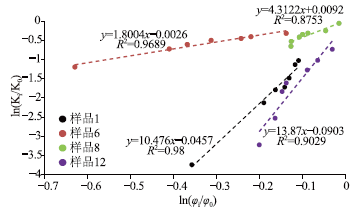
图 7 由孔渗幂指数判断孔隙结构图(据参考文献[5]修改)
Figure 7.
表 1 实验样品基础数据
Table 1. Basic data of the shale samples
样品编号 直径/cm 长度/cm 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3μm2 密度/(g·cm-3) 样品描述 1 2.457 6.452 5.33 0.08371 2.58 平行层理 6 2.462 4.597 7.49 0.0333 2.56 平行层理 8 2.472 4.966 7.47 0.04242 2.53 平行层理 12 2.477 3.813 5.85 0.025 2.58 垂直层理 14 2.474 5.210 4.59 0.00016 2.58 垂直层理 17 2.474 5.242 4.99 0.00061 2.59 垂直层理 表 2 页岩样品孔隙度、渗透率和净覆压力之间的统计分析结果
Table 2. Statistic analysis results of relationship between porosity and permeability of shale and the effective confining pressure
样品编号 压缩系数(Cp)/(MPa-1) 孔隙度(φ0)/% 相关系数(R12) 渗透率应力敏感系数(a)/(MPa-1) 渗透率(K0)/mD 相关系数(R22) 1 0.026 5.333 0.959 0.280 0.0837 0.987 6 0.049 7.494 0.983 0.090 0.033 0.991 8 0.012 7.479 0.536 0.012 0.042 0.857 12 0.017 5.811 0.823 0.263 0.025 0.945 14 0.032 4.591 0.835 — 0.00016 — 17 0.039 4.989 0.778 — 0.00061 — -
[1] Cai J, Yu B, Zou M, et al. Fractal characterization of spontaneous co-current imbibition in porous media[J]. Energy Fuel., 2010, 24: 1860-1867. doi: 10.1021/ef901413p
[2] Dutta R, Lee C, Odumabo S, et al. Experimental investigation of fracturing-fluid migration caused by spontaneous imbibition in fractured low-permeability sands[J]. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering, 2014, 7(1): 74-81. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000037967035110_160f.html
[3] 李继山. 表面活性剂体系对渗吸过程的影响[D]. 河北: 中国科学院研究生院(渗流流体力学研究所)博学位论文, 2006.
[4] King G E. Thirty Years of Gas Shale Fracturing: What Have We Learned?[C]//Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2010, 62(11): 88-90.
[5] Zhang R, Ning Z F, Yang F, et al. A laboratory study of the porosity-permeability relationships of shaleand sandstone under effective stress[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2016, (81): 19-27. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Rui_Zhang139/publication/284232801_A_laboratory_study_of_the_porosity-permeability_relationships_of_shale_and_sandstone_under_effective_stress/links/571e2e5e08aead26e71a82e0.pdf
[6] Arthur J D, Bohm B, Coughlin B J, et al. Hydraulic fracturing considerations for natural gas wells of the Fayetteville Shale[M]. All Consulting, 2008.
[7] 张金川, 徐波, 聂海宽, 等. 中国页岩气资源勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(6): 136-140. doi: 10.3787/j.issn.1000-0976.2008.06.040
[8] 秦积舜, 李爱芬. 油层物理学[M]. 东营: 石油大学出版社, 2001: 178-182.
[9] Biot M A. Theory of deformation of a porous viscoelastic anisotropic solid[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1956, (27): 457-467. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035968482110_5b1c.html
[10] Lubinski A. Theory of elasticity for porous bodies displaying a strongpore structure[C]//Proc. 2nd U.S. National Congress of Applied Mechanics, 1954: 247-256.
[11] 贾文瑞, 李福恺, 肖敬修. 低渗透油田开发部署中几个问题的研究[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 1995, 22(4): 47-51. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.1995.04.017
[12] Reyes L, Osisanya S O. Empirical correlation of effective stress dependent shalerock properties[J]. J. Can. Pet. Tech., 2002, (27): 47-53. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039246541510_435b.html
[13] 伍向阳, 陈祖安, 孙德明, 等. 静水压力下砂岩孔隙度变化实验研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 1995, 38(S1): 275-280. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX5S1.027.htm
[14] Cho Y, Ozkan E, Apaydin O G. Pressure-dependent natural-fracture permeabilityin shale and its effect on shale-gas well production[M]. Paper SPE, 2013: 159801.
[15] Chalmers G, Ross D, Bustin R. Geological controls on matrix permeability ofDevonian gas shales in the Horn River and Liard basins, northeastern British Columbia, Canada[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2012, (103): 120-131. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-S0166516212001401&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1471375787&md5=a8ab08c04009e9b0e1ec570bd2b075ce
[16] Petunin V V, Yin X, Tutuncu A N. Porosity and permeability changes in sandstones and carbonates under stress and their correlation to rock texture[M]. Paper SPE, 2011: 147401.
[17] Meng Z P, Li G Q. Experimental research on the permeability of high-rank coal under varying stress and its influencing factors[J]. Engineering Geology, 2013, (162): 108-117. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/jccs/jccs/2012/00000037/00000003/art00012
[18] Abass H H, Ortiz I, Khan M R., et al. Understanding stress dependant permeability of matrix, natural fractures, and hydraulic fractures in carbonate formations[M]. Paper SPE, 2007: 110973.
[19] Julia F W, Robert M Reed, Jon Holder. Natural fractures in the Barnett Shale and their importance for hydraulic fracture treatments[J]. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 2007, 91(4), 603-622. doi: 10.1306/11010606061
[20] David C, Wong T, Zhu W, et al. Laboratory measurement of compaction-induced permeability change in porous rocks: implications for the generation and maintenance of pore pressure excess in the crust[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 1994, (143): 425-456. doi: 10.1007/BF00874337
[21] Dehghanpour H, Zubair H A, Chhabra A, et al. Liquid intake of organic shales[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2012, 26(9): 5750-5758. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ef3009794
[22] Dehghanpour H, Lan Q, Saeed Y, et al. Spontaneous Imbibition of Brine and Oil in Gas Shales: Effect of Water Adsorption and Resulting Microfractures[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2013, 27(6): 3039-3049. http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ef4002814
[23] Xu M, Dehghanpour H. Advances in Understanding wettability of gas shales[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2014: 4362-4375. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036675409510_3029.html
[24] Hu Y, Devegowda D, Striolo A, et al. Microscopic dynamics of water and hydrocarbon in shale-kerogen pores of potentially mixed-wettability[C]//SPE unconventional resources conference, Society of Petroleum Engineers Alberta, Canada, 2014.
[25] Zhu W, Montesi L, Wong T. Characterizing the permeability-porosity relationship during compactive cataclastic flow[M]. Paper ARMA, 2008.
[26] Kwon O. Permeability of Wilcox shale and its effective pressure law[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2001, (106): 19339-19353.
[27] Meng Y, Li Z P, Lai F P, et al. Characteristics of black shale in the Upper Ordovician Wufeng and lower Silurian Longmaxi formations in the Sichuan Basin and its periphery, China[J]. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 2017, (5): 667-687. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/08120099.2017.1321581
[28] 腾格尔, 卢龙飞, 俞凌杰, 等. 页岩有机质孔隙形成、保持及其连通性的控制作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2021, 48(4): 687-699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202104003.htm
[29] 周彤, 王海波, 李凤霞, 等. 层理发育的页岩气储集层压裂缝扩展模拟[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(5): 1039-1051. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202005021.htm
-



 下载:
下载: