Geochemical characteristics and tectonic setting of Carboniferous sandstone in the eastern part of north Qiangtang depression
-
摘要:
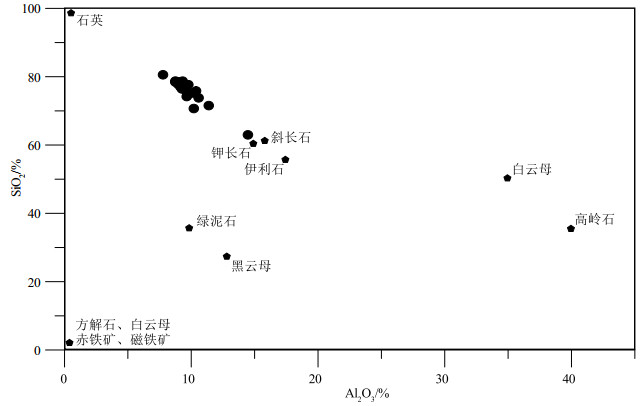
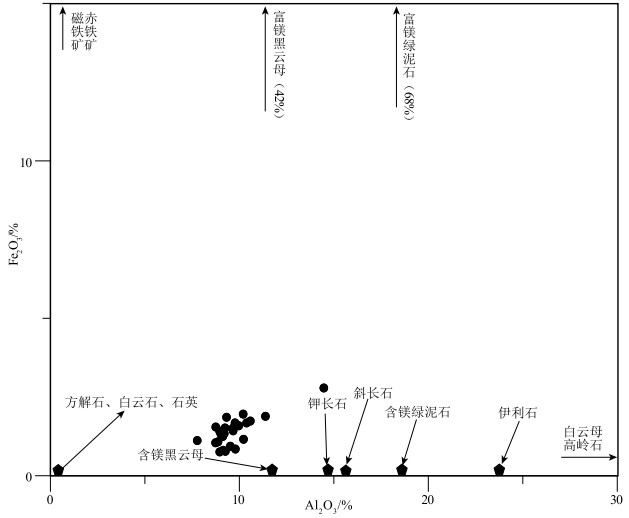
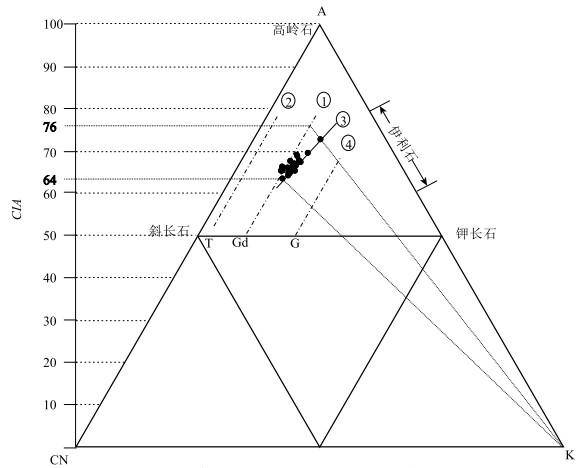
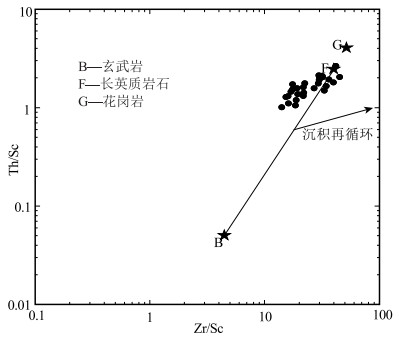
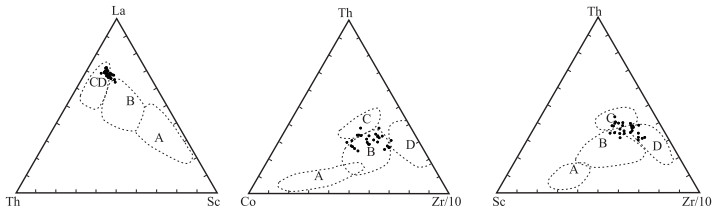
为了探讨羌塘盆地石炭纪的演化特征,于羌塘盆地北坳陷东部刻莫地区采集了一批早石炭世早期杂多群砂岩样品,对其进行了全岩地球化学测试。地球化学研究结果表明,岩石矿物成分主要在方解石-石英到含镁黑云母组分端元之间,部分样品接近钾长石组分端元;化学风化作用指标(CIW)、化学蚀变作用指标(CIA)和A-CN-K图解,反映该组砂岩的碎屑成分受到了中等的风化作用,并在风化过程中发生微弱钾交代,长石发生伊利石化。化学组分指标(ICV)表明岩石碎屑为第一次旋回沉积物,受沉积分选和再循环作用影响不大;A-CN-K图解还反映出砂岩碎屑源岩中斜长石含量高于钾长石含量,主要在花岗岩和花岗闪长岩之间变化。主量、微量和稀土元素特征指示,该组砂岩的沉积构造背景为活动大陆边缘和大陆岛弧的性质,说明在早石炭世早期古特提斯大洋已经开始进入俯冲消亡和萎缩阶段。
Abstract:In order to explore the evolution history of Carboniferous Qiangtang basin, samples were collected from Early Carboniferous Zaduo Group sandstone in the Kemo area, the east of north depression of Qiangtang basin, to carry out the geochemical studies.The results indicate that the sandstones mainly consist of K-feldspar, calcite, magnesium biotitea and quartz etc.The chemical indexes of weathering (CIW), alteration (CIA) parameters and the A-CN-K plot of the sandstone suggest that the clastic constituents were moderately weathered in the area, and the clastic constituents underwent K-metasomatisim and replacement of feldspar by illite during weathering processes.The chemical composition index (ICV) indicates that some clastics represent the first cycle sediment, which is not affected by sedimentation sorting and recycling.The A-CN-K diagram also shows that the content of plagioclase in sandstone source rocks is higher than that of potash feldspar, and the variation is mainly between granite and granodiorite.The characteristics of major, trace and rare earth elements indicate that the sedimentary tectonic background of sandstone represents active continental margin and continental island arc, which suggests that the ancient Tethys Ocean began to enter the stage of subduction extinction and shrinkage in the Early Carboniferous.
-
Key words:
- Carboniferous /
- sandstone /
- element geochemistry /
- tectonic setting /
- eastern Qiangtang depression
-

-
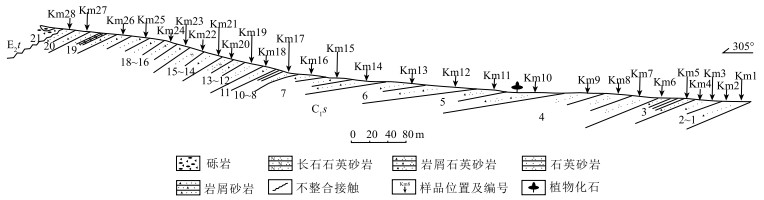
表 1 刻莫地区杂多群砂岩地球化学元素测试结果
Table 1. Geochemical analytical results of the Zaduo Group sandstone in the Kemo area
样品号 SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 FeO CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 Co Sc Zr Th La CIA CIW ICV KM-1 76.46 9.26 0.78 1.94 1.70 1.38 1.38 1.86 0.78 8.44 9.63 350.00 19.40 73.80 65.21 72.23 0.85 KM-2 77.10 9.14 0.81 1.82 1.67 1.28 1.36 1.90 0.69 8.50 6.56 296.00 14.00 51.70 64.96 71.91 0.84 KM-3 74.99 9.79 0.85 1.92 2.18 1.33 1.50 1.88 0.56 8.27 7.33 198.00 12.00 40.70 63.78 70.69 0.85 KM-4 63.01 14.47 2.79 2.57 1.74 2.32 2.81 1.36 0.77 16.70 12.70 179.00 13.30 45.10 71.00 82.36 0.81 KM-5 78.51 8.96 0.76 1.70 1.44 1.11 1.28 1.91 0.60 7.28 6.90 238.00 11.90 43.40 65.93 72.79 0.79 KM-6 75.29 10.22 1.16 1.86 1.50 1.38 1.58 1.89 0.52 8.55 6.95 151.00 9.51 35.30 67.28 75.09 0.79 KM-7 74.56 9.69 1.53 1.57 2.12 1.46 1.47 1.88 0.68 8.32 7.13 284.00 13.40 49.40 63.92 70.78 0.94 KM-8 70.72 10.20 1.96 1.77 3.19 1.64 1.76 1.67 0.55 10.70 7.38 137.00 8.07 28.50 60.64 67.73 1.06 KM-9 73.84 10.58 1.74 1.79 1.58 1.33 2.00 1.63 0.48 11.00 6.85 129.00 8.49 32.00 67.00 76.72 0.83 KM-10 75.28 9.97 1.59 1.75 1.70 1.20 1.73 1.70 0.41 9.34 6.45 104.00 7.40 28.70 66.03 74.57 0.84 KM-11 77.54 9.52 0.94 1.49 1.56 1.02 1.54 1.87 0.47 6.88 5.91 196.00 9.16 32.20 65.70 73.51 0.78 KM-12 77.70 9.77 1.68 1.04 1.01 0.93 1.61 1.89 0.46 8.02 6.10 117.00 10.00 32.90 68.42 77.11 0.78 KM-13 78.74 9.32 1.86 0.80 0.90 0.85 1.50 1.85 0.54 7.90 6.36 189.00 14.10 45.50 68.68 77.22 0.80 KM-14 71.58 11.38 1.89 1.93 1.77 1.60 2.09 1.76 0.53 12.10 7.50 115.00 10.00 33.30 66.94 76.32 0.85 KM-15 78.25 9.12 1.25 1.42 1.35 0.98 1.66 1.77 0.38 7.15 5.75 97.50 8.68 29.50 65.61 74.51 0.81 KM-16 78.30 9.02 1.33 1.19 1.56 0.89 1.60 1.81 0.41 7.67 6.45 113.00 11.60 36.60 64.47 72.80 0.84 KM-17 78.75 8.75 1.55 1.19 1.38 0.88 1.59 1.74 0.48 6.05 5.11 154.00 10.80 36.90 65.01 73.72 0.87 KM-18 78.24 9.20 1.34 1.46 1.08 1.02 1.66 1.71 0.58 6.98 7.02 210.00 14.00 45.60 67.40 76.73 0.80 KM-19 78.05 9.13 1.36 1.42 1.29 0.97 1.67 1.70 0.55 7.11 5.63 179.00 12.30 39.90 66.21 75.33 0.83 KM-20 80.60 7.77 1.12 1.48 1.52 0.70 1.34 1.68 0.42 5.05 6.52 146.00 12.00 40.40 63.12 70.83 0.87 KM-21 75.86 10.38 1.68 1.72 0.98 1.14 1.96 1.69 0.42 9.30 6.38 102.00 8.67 28.60 69.15 79.54 0.76 KM-22 77.45 9.24 1.52 1.31 1.54 0.97 1.69 1.74 0.54 7.19 4.52 189.00 12.50 37.10 65.02 73.80 0.87 KM-23 77.85 8.96 1.41 1.48 1.60 1.02 1.63 1.66 0.41 7.01 5.47 120.00 8.05 29.40 64.69 73.32 0.86 KM-24 75.42 9.67 1.43 1.57 2.10 1.11 1.81 1.69 0.45 8.79 7.72 150.00 11.00 37.00 63.33 71.84 0.89 KM-25 78.04 9.04 1.42 1.50 1.35 1.03 1.64 1.72 0.45 7.25 6.25 136.00 10.50 35.50 65.75 74.65 0.84 KM-26 74.23 9.64 1.49 1.42 2.83 1.15 1.86 1.67 0.38 8.10 6.01 105.00 9.54 30.30 60.25 68.18 0.97 KM-27 78.55 8.87 1.08 1.50 1.56 0.90 1.62 1.74 0.42 7.62 4.70 138.00 8.62 30.20 64.32 72.88 0.83 KM-28 78.48 8.74 1.05 1.50 1.65 0.98 1.60 1.70 0.44 6.90 4.60 147.00 9.77 32.20 63.84 72.29 0.85 平均值 76.19 9.64 1.41 1.58 1.64 1.16 1.68 1.75 0.51 8.36 6.64 166.77 11.03 37.92 65.49 73.91 0.85 CIA(蚀变作用指标)=Al2O3/(Al2 O3+CaO+Na2O+K2O)×100;CIW(化学风化作用指标)= Al2O3/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O)×100;ICV(化学组分指标)=(Fe2O3+K2O+Na2O+CaO+MgO+TiO2)/Al2O3;主量元素含量单位为%,微量元素含量单位为10-6 -
[1] Bhatia M R. Plate tectonics and geochemical composition of sandstones[J]. Journal of Geology, 1983, 91: 611-627. doi: 10.1086/628815
[2] McLennan S M, Taylor S R. Sedimentary rocks and crustal evolution: tectonic setting and secular trends[J]. Journal of Geology, 1991, 8: 1-21. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035569919510_6082.html
[3] 王成善, 伊海生, 李勇, 等. 羌塘盆地地质演化与油气远景评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001: 184-251.
[4] 王剑, 丁俊, 王成善, 等. 青藏高原油气资源战略选区调查与评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2009: 210-214.
[5] 黄继钧. 羌塘盆地性质及构造演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 2000, 6(4): 58-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2000.04.008
[6] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等. 青藏高原大地构造特征与盆地演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 23-25.
[7] 李勇, 李亚林, 段志明, 等. 中华人民共和国区域地质调查报告——温泉兵站幅(I46C003002)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015: 27-31.
[8] Cullers R L. The controls on the major and trace element variation of shale, silt stones, and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age from up lifted continental blocks in Colorado to platform sedimentin Kansas, USA[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochim Acta, 1994, 58: 4955-4972. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90224-0
[9] Pettijohn F J, Potter P E, Siever R. Sand and sandstone[M]. NewYork: Stringer-Verlag, 1972: 1-618.
[10] McLennan S M. Weathering and global denudation[J]. The Journal of Geology, 1993, 101: 295-303. doi: 10.1086/648222
[11] Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for weathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology, 1995, 23: 921-924. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<0921:UTEOPM>2.3.CO;2
[12] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature, 1982, 299: 715-717. doi: 10.1038/299715a0
[13] Cullers R L. The geochemistry of shales, siltstones and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age, Colorado, USA: implications for provenance and metamorphic studies[J]. Lithos, 2000, 51: 181-203. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00063-8
[14] Van de Kamp P C, Leake B E. Petrography and geochemistry of feldspathic and mafic sediments of the northeastern Pacific margin[J]. Trans. R. Soc. Edinburgh Earth Sci., 1985, 76: 411-449. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300010646
[15] Cox R, Low D R, Cullers R L. The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J]. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1995, 59: 2919-2940. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9
[16] Johnsson M J. Tectonic assembly of east central Alaska: Evidence from Cretaceous Tertiary sandstones of the Kandik River terrane[J]. Geol. Soc. Amer. Bull., 2000, 112: 1023-1042. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(2000)112<1023:TAOEAE>2.0.CO;2
[17] McLennan S M. Rare earth elements in sedimentary rocks; influence of provenance and sedimentary processes[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 1989, 21(1): 169-200. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/303145235_Rare_earth_elements_and_sedimentary_rocks_influence_of_provenance_and_sedimentary_processes
[18] McLennan S M. A geochemical approach to sedimentary provenance[C]//GSA. GSA Abstracts with Programs. Boulder: GSA, 1991, 23(5): 108.
[19] Bhatia M R, Crook K A W. Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basin[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1986, 92: 181-193. http://lib.gig.ac.cn/local/ejournal/CMP/CMP1986/CMP-1986-92(2)-181-193.pdf
[20] Roser B, Korsch R. Determination of tectonic setting of sandstone-mudstone suites using content and ratio[J]. Journal of Geology, 1986, 94(5): 635-650. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0068&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F0035919X.2017.1405853&key=10.1086%2F629071
[21] Pan Y S. Geological Evolution of the Karakorum and Kunlun Mountains[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1996: 1-288.
[22] 潘裕生, 方爱民. 中国青藏高原特提斯的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 2010, 45(1): 92-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2010.01.009
① 青海省第二区调队.1∶20万《杂多县幅》区域地质调查报告(地质部分).1982:12-31.
-




 下载:
下载: