The 1.5 Ga metamorphic gabbro at the Lixi area, S: chuan Province in the western margin of the Yangtze Block: Implications for the breakup of the Columbia supercontinent
-
摘要:
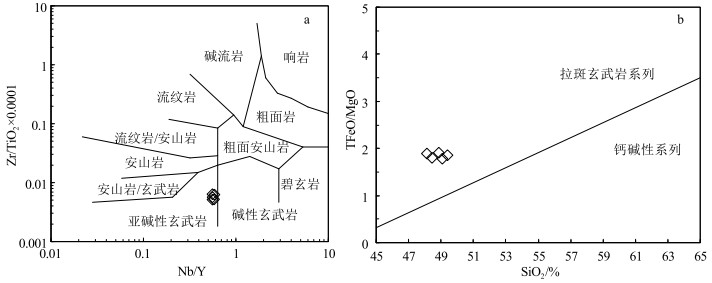
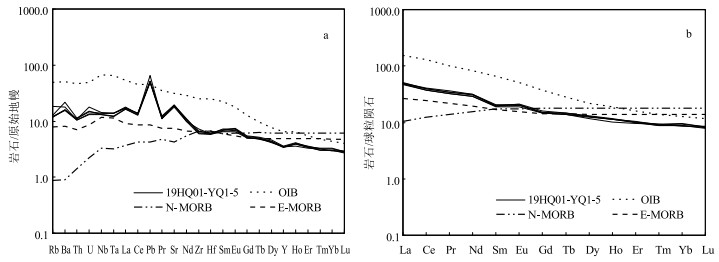
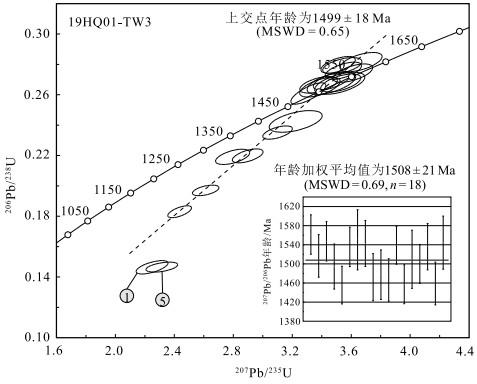
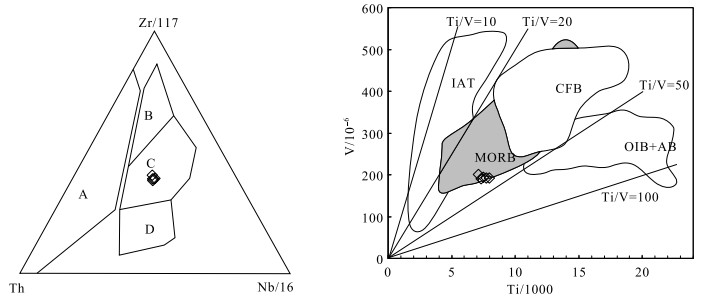
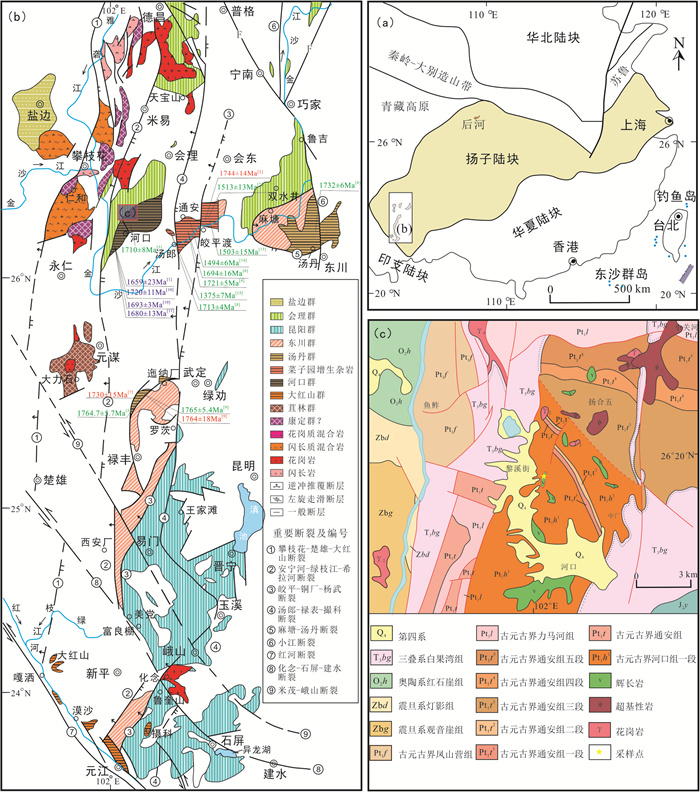
扬子陆块西缘黎溪—菜子园—通安地区前寒武纪地质体分布广泛,是探讨扬子陆块前寒武纪地质演化的重要载体。对会理黎溪地区变辉长岩开展岩石学、全岩地球化学及锆石U-Pb定年研究。结果显示,黎溪变辉长岩形成于1508±21 Ma;在岩石地球化学组成上,它们属于亚碱性拉斑岩石系列,总体上略微富集轻稀土元素,高场强元素Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf等无明显亏损,大离子亲石元素Ba、Sr等不同程度富集。通过岩石成因分析认为,岩浆在上升过程中经历了一定程度的分离结晶作用,但并未受到明显的地壳混染,母岩浆可能来自软流圈地幔。地球化学和区域地质特征综合分析表明,黎溪变辉长岩与富集洋中脊型玄武岩的地球化学特征相似,可能形成于洋中脊及附近的海山环境,是Columbia超大陆裂解在扬子陆块的响应。
Abstract:Precambrian strata are widely distributed in the Lixi-Caiziyuan-Tong'an area, which is an important window to study Precambrian geological evolution of the western margin of the Yangtze Block.Petrology, whole-rock geochemistry and zircon U-Pb chronology of metamorphic gabbro in the Lixi area of Huili were studied.The results show that Lixi metamorphic gabbro was formed at 1508±21 Ma.In terms of petrogeochemical composition, it belongs to the subalkaline tholeiitic series, and is slightly enriched in light rare earth elements (LREE) on the whole, with no obvious depletion of high field strength elements such as Nb, Ta, Zr and Hf.Under the influence of later weathering, large ionic lithophile elements such as Ba, Sr incompatible elements are enriched in varying degrees.According to the petrogenesis analysis, the magma experienced a certain degree of separation and crystallization during the ascent, but was not obviously contaminated by the crust, and the mother magma might have come from the depleted asthenosphere mantle.The comprehensive analysis of geochemical and regional geological characteristics shows that the geochemical characteristics of Lixi metamorphic gabbro are similar to the E-MORB basalt, which might be formed in mid-ocean ridges or nearby seamount environment as a response to the breakup of Columbia supercontinent in the Yangtze Block.
-
Key words:
- Yangtze Block /
- gabbro /
- Mesoproterozoic /
- geochemistry /
-
/ - Columbia supercontinent
-

-
表 1 黎溪变辉长岩主量、微量和稀土元素分析结果
Table 1. Analytical results of the major, trace and rare earth elements of the Lixi metamorphic gabbro
元素 19HQ01- YQ1 19HQ01- YQ2 19HQ01- YQ3 19HQ01- YQ4 19HQ01- YQ5 元素 19HQ01- YQ1 19HQ01- YQ2 19HQ01- YQ3 19HQ01- YQ4 19HQ01- YQ5 SiO2 46.01 46.79 46.93 47.48 46.37 Zr 81.0 65.9 69.2 71.8 74.0 TiO2 1.24 1.26 1.28 1.31 1.35 Nb 9.30 9.22 9.58 9.82 10.0 Al2O3 16.75 16.89 16.85 16.82 16.77 Sn 0.63 0.74 0.75 0.72 0.73 TFeO 17.64 16.67 17.09 16.53 17.23 Cs 0.55 0.65 0.45 0.47 0.51 MnO 0.20 0.18 0.18 0.18 0.18 Ba 153 125 107 111 111 MgO 6.72 6.27 6.53 6.29 6.65 La 11.4 11.1 11.5 11.9 12.1 CaO 7.85 8.11 8.46 8.33 8.30 Ce 23.1 22.9 24.2 24.5 24.1 Na2O 2.38 2.72 2.72 2.85 2.54 Pr 3.09 3.08 3.23 3.40 3.25 K2O 0.33 0.35 0.32 0.29 0.31 Nd 13.3 13.5 14.6 14.9 14.2 P2O5 0.15 0.14 0.15 0.16 0.16 Sm 2.88 2.94 3.19 3.02 3.09 烧失量 4.42 3.97 3.85 3.63 4.11 Eu 1.09 1.16 1.20 1.25 1.20 总计 100.21 99.85 100.43 100.15 100.24 Gd 3.01 3.11 2.99 3.27 3.14 FeO 4.90 4.80 5.25 5.00 5.08 Tb 0.52 0.51 0.52 0.55 0.55 Li 23.1 18.8 16.6 17.5 18.7 Dy 3.00 3.15 3.25 3.35 3.26 Be 0.58 0.58 0.47 0.52 0.52 Ho 0.58 0.64 0.64 0.67 0.65 Sc 27.9 28.0 27.4 26.2 26.8 Er 1.59 1.64 1.68 1.67 1.71 V 190 182 186 184 184 Tm 0.24 0.22 0.22 0.24 0.23 Cr 108 97.6 93.0 91.1 94.0 Yb 1.47 1.49 1.50 1.61 1.57 Co 63.6 48.2 48.1 48.2 50.5 Lu 0.22 0.21 0.20 0.21 0.21 Ni 122 97.5 99.0 95.4 106 Hf 1.82 1.80 1.83 1.90 1.89 Cu 22.5 15.8 16.3 14.5 18.9 Ta 0.51 0.49 0.57 0.57 0.57 Zn 242 203 200 196 210 Tl 0.082 0.091 0.054 0.064 0.077 Ga 18.3 17.8 17.6 17.5 18.2 Pb 4.56 3.46 3.53 3.60 3.74 Rb 8.12 11.6 7.69 7.32 7.68 Th 0.96 0.89 0.90 0.94 0.91 Sr 374 407 394 405 399 U 0.32 0.27 0.28 0.31 0.38 Y 15.6 15.4 15.8 16.1 16.0 注:主量元素含量单位为%,微量和稀土元素含量单位为10-6 表 2 黎溪变辉长岩(19HQ01-TW3)锆石U-Th-Pb同位素分析结果
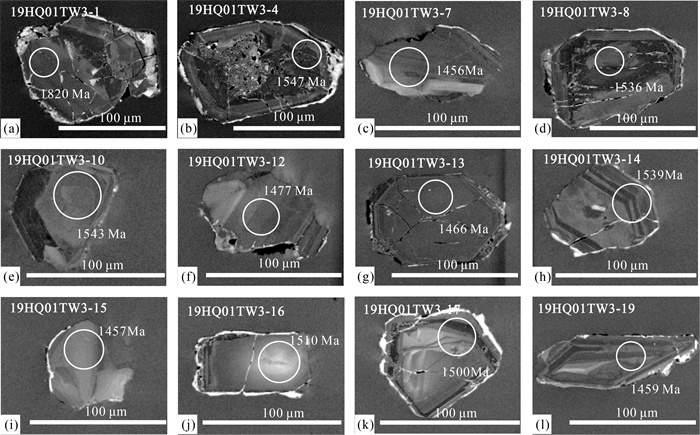
Table 2. Results of zircon U-Th-Pb dating of the metamorphic gabbro in the Lixi area
测点 含量/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值1σ 同位素年龄/Ma 谐和度 Pb 232Th 238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 19HQ01-TW3-1 836 1730.48 446.07 3.88 0.1112 0.0033 2.2491 0.0716 0.1464 0.0029 1820 54 1196 22.4 881 16.4 69% 19HQ01-TW3-2 1657 2761.53 564.59 4.89 0.0967 0.0021 2.4359 0.0534 0.1830 0.0026 1561 41.2 1253 15.8 1083 14.1 85% 19HQ01-TW3-3 322 310.82 182.17 1.71 0.0944 0.0023 3.6668 0.0947 0.2815 0.0042 1517 44.6 1564 20.6 1599 21.0 97% 19HQ01-TW3-4 798 1144.22 629.85 1.82 0.0960 0.0021 2.6126 0.0596 0.1970 0.0023 1547 41.2 1304 16.8 1159 12.4 88% 19HQ01-TW3-5 1448 3054.24 788.11 3.88 0.1137 0.0028 2.3153 0.0710 0.1465 0.0022 1859 44.4 1217 21.8 881 12.3 68% 19HQ01-TW3-6 479 421.88 335.51 1.26 0.0933 0.0021 3.5466 0.0817 0.2758 0.0037 1494 47.2 1538 18.3 1570 18.9 97% 19HQ01-TW3-7 1259 1308.32 557.37 2.35 0.0909 0.0019 3.5114 0.0772 0.2797 0.0036 1456 39.4 1530 17.4 1590 18.3 96% 19HQ01-TW3-8 1312 1903.14 878.39 2.17 0.0954 0.0021 2.8980 0.0689 0.2197 0.0030 1536 41.2 1381 18.0 1281 16.0 92% 19HQ01-TW3-9 804 949.23 285.53 3.32 0.0961 0.0032 3.2235 0.1188 0.2424 0.0047 1550 63.0 1463 28.6 1399 24.4 95% 19HQ01-TW3-10 1294 1351.32 536.14 2.52 0.0957 0.0024 3.5294 0.0898 0.2678 0.0039 1543 48.1 1534 20.2 1529 19.9 99% 19HQ01-TW3-11 1310 1326.42 556.29 2.38 0.0922 0.0023 3.3088 0.0784 0.2609 0.0046 1472 49.2 1483 18.5 1494 23.7 99% 19HQ01-TW3-12 1521 1673.09 651.29 2.57 0.0925 0.0025 3.3878 0.0908 0.2650 0.0043 1477 51.9 1502 21.0 1515 21.8 99% 19HQ01-TW3-13 687 1031.30 366.32 2.82 0.0920 0.0022 2.7955 0.0766 0.2191 0.0033 1466 44.4 1354 20.5 1277 17.6 94% 19HQ01-TW3-14 1679 2055.85 643.76 3.19 0.0955 0.0020 3.1003 0.0664 0.2351 0.0029 1539 39.7 1433 16.5 1361 15.1 94% 19HQ01-TW3-15 500 470.35 330.54 1.42 0.0914 0.0020 3.5399 0.0879 0.2791 0.0036 1457 40.7 1536 19.7 1587 18.1 96% 19HQ01-TW3-16 515 529.36 255.18 2.07 0.0941 0.0030 3.4657 0.1090 0.2677 0.0049 1510 60.8 1519 24.8 1529 24.9 99% 19HQ01-TW3-17 985 1067.38 540.71 1.97 0.0931 0.0020 3.4677 0.0825 0.2691 0.0039 1500 40.6 1520 18.8 1536 19.7 98% 19HQ01-TW3-18 979 1084.37 330.57 3.28 0.0954 0.0022 3.6112 0.0889 0.2743 0.0040 1536 48.6 1552 19.6 1562 20.2 99% 19HQ01-TW3-19 1065 1141.42 597.66 1.91 0.0916 0.0022 3.3787 0.0844 0.2665 0.0036 1459 44.8 1499 19.6 1523 18.3 98% 19HQ01-TW3-20 190 154.66 217.08 0.71 0.0953 0.0028 3.5223 0.1123 0.2675 0.0048 1544 55.6 1532 25.2 1528 24.4 99% -
[1] 耿元生, 旷红伟, 柳永清, 等. 扬子地块西、北缘中元古代地层的划分与对比[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 91(10): 2151-2174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201710001.htm
[2] 耿元生, 柳永清, 高林志, 等. 扬子克拉通西南缘西南缘中元古代通安组的形成时代——锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(9): 1479-1491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.09.009
[3] 郭阳, 王生伟, 孙晓明, 等. 扬子地台西南缘古元古代末的裂解事件——来自武定地区辉绿岩锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学证据[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(9): 1651-1665. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201409003.htm
[4] 耿元生, 旷红伟, 杜利林, 等. 华北、华南、塔里木三大陆块中-新元古代岩浆岩的特征及其地质对比意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(8): 2276-2312. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202008003.htm
[5] 关俊雷, 郑来林, 刘建辉, 等. 四川省会理县河口地区辉绿岩体的锆石SHRIMPU-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(4): 482-490. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201104005.htm
[6] 王冬兵, 尹福光, 孙志明, 等. 扬子陆块西缘古元古代基性侵入岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(4): 617-630. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2013.04.010 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130410&flag=1
[7] 王子正, 郭阳, 杨斌, 等. 扬子克拉通西缘1.73Ga非造山型花岗斑岩的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 83(7): 931-942. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.07.003
[8] Geng Y S, Du L L, Kuang H W, et al. Ca. 1.7 Ga Magmatism on Southwestern Margin of the Yangtze Block: Response to the Breakup of Columbia[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(6): 2031-2052. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/1755-6724.14614
[9] 杨斌, 王伟清, 董国臣, 等. 扬子地台西南缘康滇断隆带海孜双峰式侵入岩体年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(5): 1361-1373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201505013.htm
[10] 于文佳, 罗照华, 刘永顺, 等. 拉拉铁铜矿床成因: 来自隐爆角砾岩结构定量化和锆石U-Pb年代学的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 31(5): 925-942. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201703019.htm
[11] 周家云, 毛景文, 刘飞燕, 等. 扬子地台西缘河口群钠长岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2011, 31(3): 66-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2011.03.010
[12] 孙志明, 尹福光, 关俊雷, 等. 云南东川地区昆阳群黑山组凝灰岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及其地层学意义[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(7): 876-900. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20090709&flag=1
[13] 庞维华, 任光明, 孙志明, 等. 扬子地块西缘古-中元古代地层划分对比研究: 来自通安组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄的证据[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(4): 921-936. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2015.04.010
[14] Fan H P, Zhu W G, Li Z X, et al. Ca. 1.5 Ga mafic magmatism in South China during the break-up of the supercontinent Nuna/Columbia: The Zhuqing Fe-Ti-V oxide ore-bearing mafic intrusions in western Yangtze Block[J]. Lithos, 2013, 168/169: 85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.02.004
[15] 任光明, 庞维华, 潘桂棠, 等. 扬子陆块西缘中元古代菜子园蛇绿混杂岩的厘定及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2017, 36(11): 2061-2075. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2017.11.016 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20171116&flag=1
[16] 王生伟, 蒋小芳, 杨波, 等. 康滇地区元古宙构造运动Ⅰ: 昆阳陆内裂谷、地幔柱及其成矿作用[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(6): 1353-1377. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201606001.htm
[17] 尹福光, 王冬兵, 孙志明, 等. 哥伦比亚超大陆在扬子陆块西缘的探秘[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(3): 31-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2012.03.003
[18] Liu Y S, Hu Z C, Gao S, et al. In Situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 257(1): 34-43. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035368794210_7e0b.html
[19] Zong K Q, Klemd R, Yuan Y, et al. The As-sembly of Rodinia: the correlation of Early Neoprotero zoic(Ca. 900 Ma) high-grade metamorphism and continental arc formation in the southern Beishan Orogen, Southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt(CAOB)[J]. Precam-brian Research, 2017, 290: 32-48. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.12.010
[20] Winchester J A, Floyd P A. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements[J]. Chemical Geology, 1977, 20: 325-343. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2
[21] Miyashiro A. Volcanic rock series in island arcs and active continental margins[J]. American Journal of Science, 1974, 274: 321-355. doi: 10.2475/ajs.274.4.321
[22] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: Implications for mantle composition and process[C]//Saunders A D, Norry M J. Magmatism in the ocean basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42: 313-345.
[23] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004, 49(16): 1859-1604. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200416001.htm
[24] Condie K C. Incompatible element ratios in oceanic basalts and komatiites: tracking deep mantle sources and continental growth rates with time[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(1): 1-28. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Kent_Condie/publication/222234755_Source_of_Proterozoic_mafic_dyke_swarms_Constraints_from_ThTa_and_LaYb_ratios/links/0912f5000d3e5d5557000000.pdf
[25] Thompson R N, Morrison M A. Asthenospheric and lower-lithospheric mantle contributions to continental extensional magmatism: an example from the British Tertiary Province[J]. Chemical Geology, 1988, 68: 1-15. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(88)90082-4
[26] Frey F, Green D, Roy S, et al. Integrated models of basalt petrogenesis: a study of quartz tholeiites to olivine melilitites from south eastern Australia utilizing geochemical and experimental petrological data[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1978, 19: 463-513. doi: 10.1093/petrology/19.3.463
[27] Fitton J G, James D, Kempton P D, et al. The role of lithospheric mantle in the generation of late Cenozoic basic magmas in the western United States[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1988, 1: 331-349. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/J_Fitton/publication/303855460_The_role_of_lithospheric_mantle_in_the_generation_of_late_Cenozoic_basic_magmas_in_the_western_United_States/links/5798bd8008aeb0ffcd08b5da.pdf
[28] 王伟, 卢桂梅, 黄思访, 等. 扬子陆块古-中元古代地质演化与Columbia超大陆重建[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(1): 30-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201901004.htm
[29] 王生伟, 廖震文, 孙晓明, 等. 云南东川铜矿区古元古代辉绿岩地球化学——Columbia超级大陆裂解在扬子陆块西缘的响应[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(12): 1834-1852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201312007.htm
[30] 王金荣, 张旗, 焦守涛, 等. N-MORB和E-MORB数据挖掘玄武岩判别图及洋中脊源区性质的讨论[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(3): 993-1005. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201703023.htm
[31] Mahoney J J, Sinton J M, Kurz M D, et al. Isotope and trace element characteristics of a super-fast spreading ridge: East Pacific Rise at 13~23°S[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1994, 121(1/2): 173-193. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X94900396
[32] Davis A S, Clague D A, Cousens B L, et al. Geochemical of basalt from theNorth Gorda segment of the Gorda Ridge: Evolution toward uhraslow spreading ridge lavas due to decreasingmagmasupply[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysic, Geosystems, 1977, 9(4): Q04004.
[33] Wood D A, Joron J L, Treuil M, et al. A re-appraisal of the use of trace elements to classify and discriminate between magma series erupted in different tectonic settings[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1979, 45(2): 326-336. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(79)90133-X
[34] Shervais J W. Ti-V plots and the petrogenesis of modern and ophiolitic lavas[J]. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1982, 59: 101-118. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(82)90120-0
[35] Niu Y L, Collerson K D, Batiza R, et al. Origin of enriched-type mid-ocean ridge basalt at ridges far from mantle plumes: The East Pacific Rise at 11° 20' N[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1999, 104(B4): 7067-7087. doi: 10.1029/1998JB900037
[36] Hemond C, Hofmann A W, Vlast L I, et al. Origin of MORB enrichment and relative trace element compatibilities along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between 10° and 24° N[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 2006, 12(7): 1-22. http://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/docs/00/12/89/27/PDF/G3-Hemond-06.pdf
[37] Hawkins J W. Geology of supra-subduction zones: Implications for the origin of ophiolits[C]//Dilek Y, Newcomb S. Ophiolite concept and the evolution of geological thought. Geological Society of America Special Paper, 2003, 373: 227-268.
[38] Cole R B, Nelson S W, Layer P W, et al. Eocene volcanism above a depleted mantle slab window in southern Alaska[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2006, 118(1/2): 140-158. http://sitesmedia.s3.amazonaws.com/geo/files/2012/02/Cole-et-al.-2006-GSABulletin-v118.pdf
[39] 李继亮, 张绍宗. 通安-小关河元古代碰撞缝合线的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质科学, 1987, 1: 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198701007.htm
[40] 李怀坤, 张传林, 姚春彦, 等. 扬子西缘中元古代沉积地层锆石U-Pb年龄及Hf同位素组成[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(8): 1287-1298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201308005.htm
[41] Wang X C, Li X H, Li Z X, et al., Episodic Precambrian crust growth: Evidence from U-Pb ages and Hf-O isotopes of zircon in the Nanhua Basin, central South China[J]. Precambrian Res., 2011, 222/223: 386-403. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Qi-Rui_Zhang/publication/251561584_Episodic_Precambrian_crust_growth_Evidence_from_U-Pb_ages_and_Hf-O_isotopes_of_zircon_in_the_Nanhua_Basin_central_South_China/links/00b4953b105d7d5de5000000.pdf
① 四川省地质局第一区域地质测量队. 1∶20万会理幅区域地质测量报告. 1970.
② 四川省地质局攀西地质大队区调二队. 1∶5万关河幅区域地质测量报告. 1994.
-



 下载:
下载: