The ancient landslides development characteristics and stability evaluation along the Luding Section, Dadu River, western Sichuan Province
-
摘要:
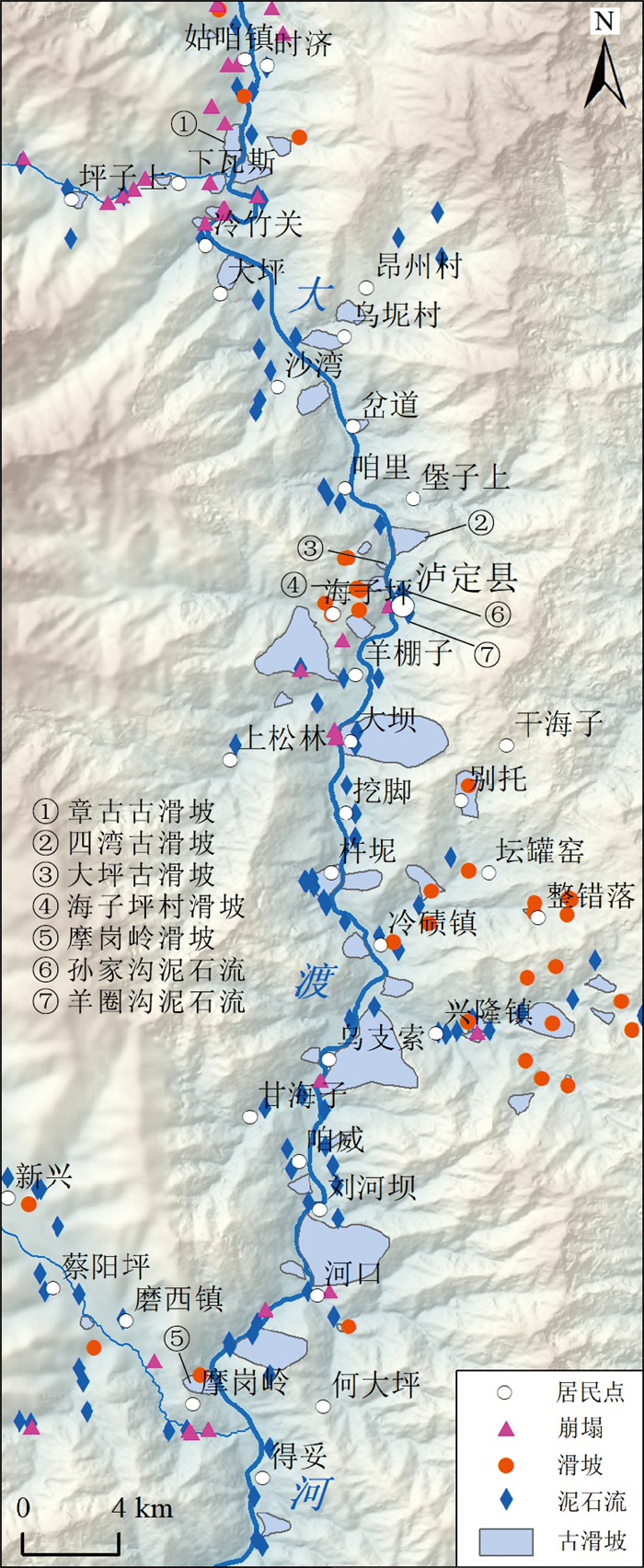
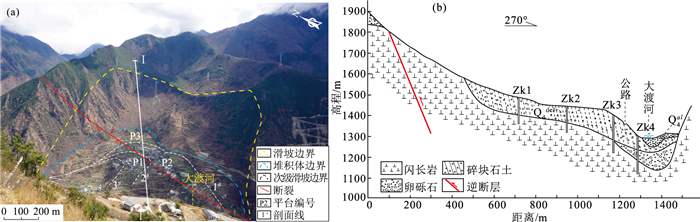
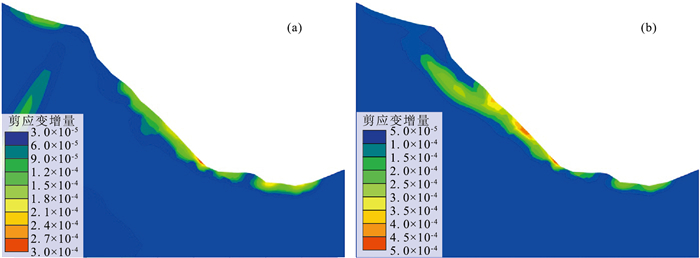
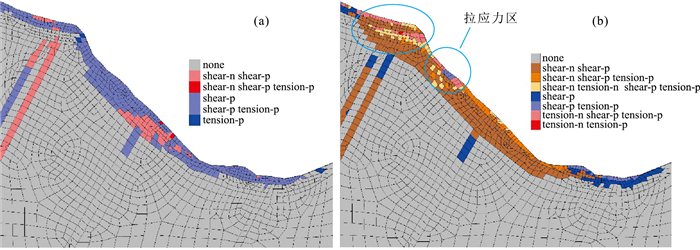
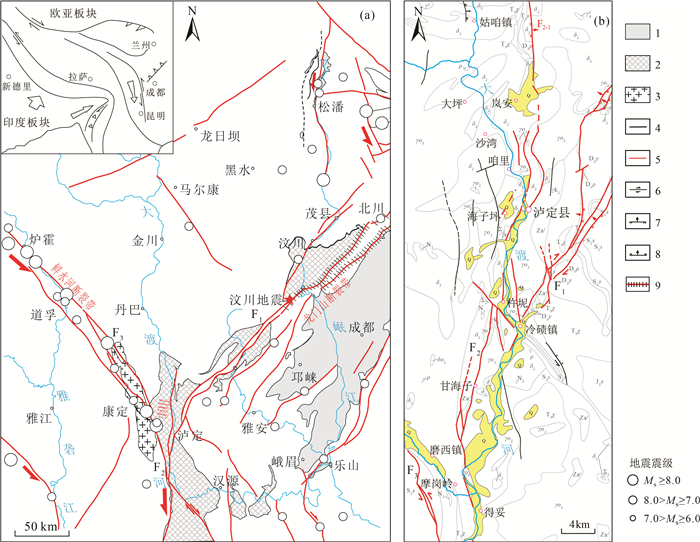
川西大渡河泸定段地形地貌和地质构造复杂,地质灾害特别是古滑坡极发育。通过遥感解译、InSAR形变分析、野外调查等手段,在泸定县城上游约25 km(至姑咱镇)到下游约43 km(至得妥镇)段发现229处崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害,古滑坡规模大、部分具有复活迹象。地质时代测年数据表明,该区古滑坡主要发育于120 ka左右、25~10 ka和全新世3个周期段,与大渡河断裂带活动性密切相关。以泸定县大坪上古滑坡为例,通过ANSYS软件,开展天然状态(自重)和暴雨状态下滑坡的稳定性分析。结果表明,该滑坡在天然状态(自重)和暴雨状态下稳定系数分别为1.2和1.15,暴雨情况下的稳定系数比自重情况下低,并且在暴雨作用下滑坡中下部变形趋势明显加大,有沿边坡临空面滑移的趋势,滑面主要位于陡坡中等风化层中,而天然状态下仅在坡体中部松散堆积层及中等风化层上部形成潜在滑动面。古滑坡的发育特征与稳定性严重影响铁路、公路、水电站等重大工程规划建设,应加强古滑坡的识别、成因机理分析与稳定性评价。
Abstract:The topography and geological structure are very complex along the Luding section of Dadu River, western Sichuan Province. The geological hazards, especially ancient landslides are extremely developed in this area. By means of remote sensing interpretation, InSAR deformation analysis and field investigation, 229 collapses, landslides and mudslides were discovered in the section from about 25 km upstream(to Guzan Town) to about 43 km downstream(to Detuo Town) of the Luding County. In addition, the ancient landslides in this area are large in scale, and some of them have signs of revival. The geological dating data show that the ancient landslides in this area were mainly developed in three periods around 120 ka, 25~10 ka and Holocene, and closely related to the activity of the Dadu River fault. The Dapingshang ancient landslide in Luding County was taken as a study case to analyze the stability of the landslide in natural state (self weight) and heavy rainfall state through ANSYS software. The results show that the stability coefficient of the landslide in natural state (self weight) and heavy rainfall state is 1.2 and 1.15 respectively. The stability coefficient under heavy rainfall conditions is lower than that under self-weight conditions; the deformation of the middle and lower part of the landslide tends to increase obviously under the action of heavy rainfall, and there is a tendency to slip along the empty surface of the slope. The slip surface is mainly developed in the medium weathered layer of the steep slope, but in the natural state, the potential slip surface is only formed in the loose accumulation layer in the middle of the slope and the upper part of the medium weathered layer. The developmental characteristics and stability of ancient landslides seriously affect the planning and construction of railway, highway, and hydroelectric power station projects. Therefore, it should be suggested to strengthen the identification, mechanism analysis and stability evaluation of ancient landslides.
-
Key words:
- western Sichuan /
- Dadu River /
- ancient landslide /
- stability /
- numerical simulation
-

-
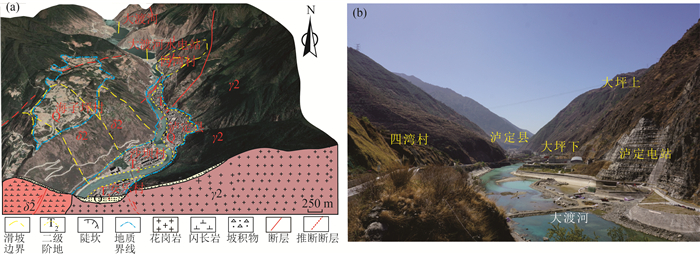
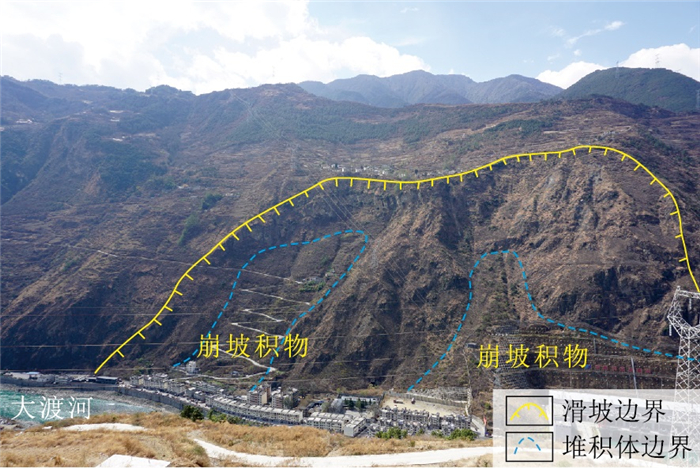
图 5 四湾古滑坡发育特征(据参考文献[16]修改)
Figure 5.
表 1 大渡河流域典型古滑坡形成时间与大渡河断裂分布关系
Table 1. Relationship between the formation time of typical landslides and the Dadu River faults in the Dadu River basin
表 2 数值模拟主要岩土体力学参数
Table 2. Modeled mechanical parameters of rocks and soil
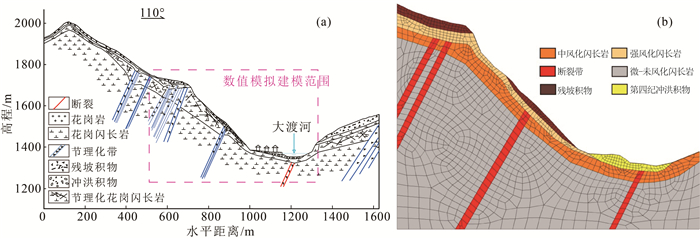
岩组编号 岩性 容重/(kN·m-3) 体积模量K/MPa 剪切模量G/MPa 粘聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/° 泊松比μ 1 残坡积物 2100 800 1450 48 36 0.35 2 强风化闪长岩 1870 1100 650 50 40 0.3 3 断裂带 2100 1500 950 100 45 0.32 7 中风化闪长岩 2600 4100 2100 350 45 0.20 8 微-未风化闪长岩 2750 5000 2600 500 45 0.18 -
[1] 丁俊, 鄢毅, 岳昌桐, 等. 四川省大渡河流域地质灾害分布及其发展趋势浅析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2007, 18(S): 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH2007S1005.htm
[2] 张景华, 张建龙. 遥感技术在泸定县地质灾害调查中的应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2009, 20(2): 100-105. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2009.02.021
[3] 李宗亮, 巴仁基, 倪化勇, 等. 四川泸定地区岩土体类型与地质灾害[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2010, 30(1): 103-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2010.01.018
[4] 巴仁基, 王丽, 郑万模, 等. 大渡河流域地质灾害特征与分布规律[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 38(5): 529-537. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2011.05.009
[5] 陈文军, 谢立香, 张玲珑, 等. 泸(定)石(棉)高速公路沿线地质灾害类型及成因[J]. 四川地质学报, 2014, 34(S2): 162-166. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB2014S2048.htm
[6] 邓茜. 大渡河得妥-加郡河段地质灾害危险性评价研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2011: 12-48.
[7] 吴俊峰. 大渡河流域重大地震滑坡发育特征与成因机理研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2013: 63-68.
[8] 夏银珍. 大渡河流域古滑坡堰塞湖光释光测年研究[D]. 青海师范大学硕士学位论文, 2017: 25-28.
[9] 张永双, 刘筱怡, 吴瑞安, 等. 青藏高原东缘深切河谷区古滑坡: 判识、特征、时代与演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(2): 94-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202102009.htm
[10] 张永双, 吴瑞安, 郭长宝, 等. 古滑坡复活问题研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 2018, 33(7): 728-740. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201807006.htm
[11] 刘筱怡. 基于多元遥感技术的古滑坡识别与危险性评价研究[D]. 中国地质科学院博士学位论文, 2020: 52-58.
[12] 李鸿巍. 大渡河断裂带的分段及活动性研究[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 46-54.
[13] 周荣军, 雷建成, 黎小刚, 等. 晚第四纪以来大渡河断裂活动性的地质地貌判据[C]//中国地震学会第八次学术大会论文摘要集, 2000.
[14] 张永双, 郭长宝, 姚鑫, 等. 青藏高原东缘活动断裂地质灾害效应研究[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(3): 277-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201603004.htm
[15] 任雪梅, 高孟潭, 杨勇, 等. 大渡河流域地震活动特征[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2008, 3(2): 182-188. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2008.02.009
[16] 邓建辉, 陈菲, 尹虎, 等. 泸定县四湾村滑坡的地质成因与稳定评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(10): 1945-1950. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.10.001
[17] 蒋发森. 大渡河章古滑坡演化机制分析及稳定性评价[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2013, 11(3): 138-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201303035.htm
[18] 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 张永双, 等. 川西鲜水河断裂带地质灾害发育特征与典型滑坡形成机理[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(1): 121-134. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.01.010 http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150109&flag=1
[19] Zhang Y S, Yao X, Yu K, et al. Late-Quaternary Slip Rate and Seismic Activity of the Xianshuihe Fault Zone in Southwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica(English edition), 2016, 90(2): 525-536. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12688
[20] 李鸿巍, 吴德超. 大渡河断裂带主要构造特征及活动性分析[J]. 长江大学学报(自科版), 2014, 11(4): 61-63. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJDL201410018.htm
[21] Dai F C, Lee C F. Deng J H, et al. The 1786 earthquake-triggered landslide dam and subsequent dam-break flood on the Dadu River, southwestern China[J]. Geomorphology, 2004, 65(3): 205-221. http://espace.library.uq.edu.au/view/UQ:8988/DIS_DAI1.pdf
[22] 吴俊峰, 王运生, 张桥, 等. 大渡河加郡-得妥河段大型滑坡地质灾害遥感调查[J]. 水土保持通报, 2011, 31(3): 113-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201103026.htm
[23] Wu L Z, Deng H, Huang R Q, et al. Evolution of lakes created by landslide dams and the role of dam erosion: A case study of the Jiajun landslide on the Dadu River, China[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 503(A): 41-50. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040431673610_87d4.html
[24] Deng H, Wu L Z, Huang R Q, et al. Formation of the Siwanli ancient landslide in the Dadu River, China[M]. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2017, 14(1): 385-394.
[25] Wang Y S, Wu L Z, Gu J. Process analysis of the Moxi earthquake-induced Lantianwan landslide in the Dadu River, China[M]. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, 2019, 78(7): 4731-4742.
[26] 许强, 陈伟, 金辉, 等. 大渡河流域河谷深厚覆盖层特征与发育分布规律研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(1): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201001002.htm
[27] 李海龙, 张岳桥, 乔彦松, 等. 青藏高原东缘大渡河中游深切河谷沉积物及其地震地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(1): 104-112. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20150107&flag=1
[28] 刘宇杰, 李宗亮, 宋志, 等. 泸定县孙家沟泥石流成因及防治对策探讨[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2008, 19(3): 15-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZHB200803003.htm
[29] 巴仁基, 王丽, 宋志, 等. 泸定县牧场沟泥石流动力特性预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2008, 224(6): 75-79, 84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200806021.htm
[30] 倪化勇. 四川泸定县城后山泥石流灾害及其风险防御[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1): 229-237. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200901024.htm
[31] 郭晓光. 大渡河流域石棉-泸定段大型古滑坡与河谷侵蚀的孕生关系[D]. 成都理工大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 35-50.
-



 下载:
下载: