Influence of Geological Environment on Vegetation Coverage in the Eastern Edge of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau: A case study of Mianning
-
摘要:
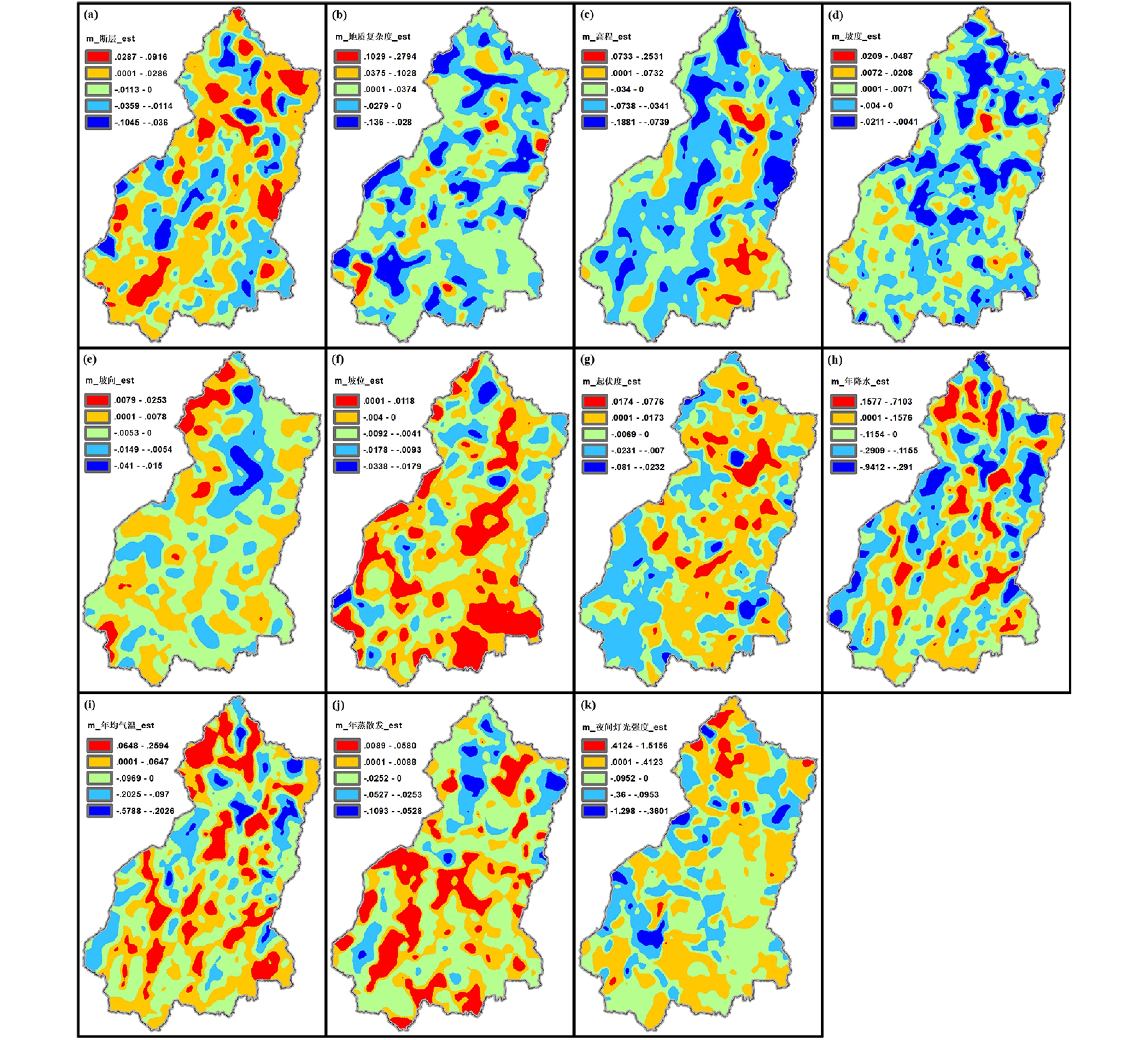
研究地质环境对植被覆盖度的影响,有利于认识地质本底对生态环境的影响,促进生态保护与修复。本文选择2003—2018年的MODIS归一化植被指数(NDVI)与增强型植被指数(EVI)的多年平均值与年际变化率作为植被覆盖度的静态和动态刻画指标,应用Pearson相关性统计揭示地质因素、地形因素、气象因素和人类活动因素对植被指数的静态相关影响,使用地理加权回归模型(GWR)分析影响因子与植被覆盖度在空间尺度的回归关系。研究结果表明:高程、年均气温和年蒸散发在Pearson分析中对NDVI/EVI平均值有较强相关性,而起伏度、年均气温、年蒸散发和地质复杂度等因子对NDVI/EVI年际变化率有较好的解释作用;GWR分析显示,靠近断层的位置有利于植被发育和改善;当地质复杂度处于中等水平时,更易形成中高植被覆盖,同时利于植被覆盖度提高,当地质复杂度过高时植被覆盖度更易出现中低值;海拔较低、地势平坦和阴坡等地形条件利于植被发育和植被覆盖度升高。
Abstract:Studying the influence of the geological environment on vegetation coverage is conducive to understand the effect of geological background on ecological environment and promote ecological protection and restoration. The multi-year mean of MODIS-Normalized Vegetation Index (NDVI) and Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) from 2003 to 2018 was selected as the static indicator of vegetation coverage, while the inter-annual variation rate was used as the dynamic index. Pearson correlation statistics were used to reveal the static correlation effects of geological factors, topographic factors, meteorological factors and human activities on vegetation index, as well as the regression relationship between influencing factors and vegetation coverage in spatial scale were obtained by geographic weighted regression (GWR). The results showed that elevation, annual average temperature and annual evapotranspiration were of great significance to the multi-year mean of NDVI / EVI, and the factors such as relief, annual average temperature, annual evapotranspiration and geological complexity performed quite well in explanation for the inter-annual variation rate of NDVI / EVI in Pearson analysis. GWR analysis indicated that the location closed to the fault is conducive to the development and improvement of vegetation. The geological complexity in the middle level was prone to form medium and high vegetation coverage, at the same time, it was in favor of increasing vegetation coverage. When the geological complexity was high, the vegetation coverage was probable to middle and low value. Low altitude, flat terrain and shady slope were favorable for vegetation development and increasing vegetation coverage.
-

-
表 1 植被指数与影响因子的Pearson相关性统计结果
Table 1. Pearson correlation coefficients of vegetation indexs and impact factors
因子类别 因子名称 NDVI_mean NDVI_slope EVI_mean EVI_slope 地质 断层欧氏距离 - 0.0609 **- 0.1012 **- 0.1603 **- 0.2050 **地质复杂度 0.1703 **0.1651 **0.2813 **0.2326 **高程 - 0.3898 **- 0.2262 **- 0.7001 **- 0.3207 **起伏度 0.1185 **- 0.2215 **- 0.1684 **- 0.2623 **坡度 0.1231 **- 0.1633 **- 0.1169 **- 0.1955 **坡向 0.0418 **- 0.0244 **- 0.0428 **- 0.0150 *坡位 - 0.0972 **0.0383 **0.0690 **0.0761 **气象 年降水 - 0.3021 **0.0191 *- 0.2718 **- 0.0281 **年均气温 0.4089 **0.2470 **0.0505 **0.0187 **年蒸散发 - 0.3524 **- 0.1595 **- 0.5385 **- 0.2412 **人类活动 夜间灯光强度 - 0.0999 **0.1236 **0.0675 **0.0863 **注:*在0.05级别(双尾),**在0.01级别(双尾),相关性显著。 表 2 EVI多年平均值与EVI年际变化率的GWR估计系数均值
Table 2. Estimated coefficients mean of EVI_mean and EVI_slope
因子名称 EVI_mean EVI_slope 因子名称 EVI_mean EVI_slope 断层欧氏距离 0.0017 - 0.00017 起伏度 - 0.0004 - 0.00020 地质复杂度 0.0054 0.00005 年降水 - 0.0497 0.00286 高程 - 0.0295 - 0.00043 年均气温 - 0.0154 0.00123 坡度 0.0009 0.00000 年蒸散发 - 0.0047 - 0.00015 坡向 - 0.0017 - 0.00003 夜间灯光强度 - 0.0037 0.00003 坡位 - 0.0038 - 0.00003 -
[1] Brunsdon C, Fotheringham S, Charlton M, 2002. Geographically Weighted Regression[J]. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, 47(3): 431-443.
[2] 曹建华, 袁道先, 章程, 等, 2004. 受地质条件制约的中国西南岩溶生态系统[J]. 地球与环境, 32(1): 1-8
Cao J H, Yuan D X, ZHANG C, et al. , 2004. Karst ecosystem constrained by geological conditions in Southwest China[J]. Earth and Environment, 32(1): 1-8.
[3] 陈超男, 朱连奇, 田莉, 等, 2019. 秦巴山区植被覆盖变化及气候因子驱动分析[J]. 生态学报, 39(9): 3257-3266
Chen C N, Zhu L Q, Tian L, et al. , 2019. Spatial-temporal changes in vegetation characteristics and climate in the Qinling-Daba Mountains[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(9): 3257-3266.
[4] 崔步礼, 李小雁, 姜广辉, 等, 2011. 基于DEM的山地丘陵区土地利用/覆被研究——以青海湖流域为例[J]. 自然资源学报, 26(5): 871-880
Cui B L, Li X Y, Jiang G H, et al. , 2011. Study on land use/cover in mountain area based on the DEM—taking the Qinghai Lake Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 26(5): 871-880.
[5] Ferguson D K, 2003. Geology and Plant Life: The Effects of Landforms and Rock Types on Plants[J]. 28(4): 808.
[6] 黄建军, 2015. 生态环境与地质构造的耦合关系研究[J]. 地球环境学报, 6(4): 231-237
Huang J J, 2015. Study on the coupling relation between eco-environment and geotectonic[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 6(4): 231-237.
[7] 李贵仁, 曾玉清, 2005. 地质环境与生态环境雏论[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 16(1): 45-48
Li G R, Zeng Y Q, 2005. A discussion on geological environment and ecological environment[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation, 16(1): 45-48.
[8] 李恒凯, 刘小生, 李博, 等, 2014. 红壤区植被覆盖变化及与地貌因子关系——以赣南地区为例[J]. 地理科学, 34(1): 103-109
Li H K, Liu X S, Li B, et al. , 2014. Vegetation coverage variations and correlation with geomorphologic factors in Red Soil Region: a case in South Jiangxi Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 34(1): 103-109.
[9] 李石华, 金宝轩, 周峻松, 等, 2017. 抚仙湖流域植被覆盖度时空分异及其与坡度的关系[J]. 地域研究与开发, 36(3): 165-170
Li S H, Jin B X, Zhou J S, et al. , 2017. Spatio-temporal variations of fractional vegetation cover and correlation with slope in Fuxian Lake Watershed[J]. Areal Research and Development, 36(3): 165-170.
[10] 李学梅, 任志远, 张翀, 2013. 气候因子和人类活动对重庆市植被覆盖变化的影响分析[J]. 地理科学, 33(11): 1390-1394
Li X M, Ren Z Y, Zhang C, 2013. Spatial-temporal variations of vegetation cover in Chongqing City (1999-2010): impacts of climate factors and human activities[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 33(11): 1390-1394.
[11] 李宗省, 何元庆, 辛惠娟, 等, 2010. 我国横断山区1960-2008年气温和降水时空变化特征[J]. 地理学报, 65(5): 563-579
Li Z X, He Y Q, Xin H J, et al. , 2010. Spatio-temporal variations of temperature and precipitation in Mts. Hengduan Region during 1960-2008[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65(5): 563-579.
[12] 刘洪,黄瀚霄,欧阳渊,等,2020.基于地质建造的土壤地质调查及应用前景分析—以大凉山区西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,40(1):91-105.
Liu H,Huang H X,Ouyang Y,et al.,2020.Soil’s geologic investigation in Daliangshan, Xichang, Sichuan[J].Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,40(1):91-105.
[13] Lu B, Brunsdon C, Charlton M, et al. , 2017. Geographically weighted regression with parameter-specific distance metrics[J]. International Journal of Geographical Information Systems, 31(5): 982-998. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2016.1263731
[14] Mao D, Wang Z, Luo L, et al. , 2012. Integrating AVHRR and MODIS data to monitor NDVI changes and their relationships with climatic parameters in Northeast China[J]. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 18: 528-536. doi: 10.1016/j.jag.2011.10.007
[15] Matsushita B, Yang W, Chen J, et al. , 2007. Sensitivity of the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) and Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) to topographic effects: A case study in high-density cypress forest[J]. Sensors, 7(11): 2636-2651. doi: 10.3390/s7112636
[16] 孟丹, 李小娟, 宫辉力, 等, 2015. 京津冀地区NDVI变化及气候因子驱动分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 17(8): 1001-1007
Meng D, Li X J, Gong H L, et al. , 2015. Analysis of spatial-temporal change of NDVI and its climatic driving factors in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Metropolis Circle from 2001 to 2013[J]. Journal of Geo-information Science, 17(8): 1001-1007.
[17] Nemani R R, Keeling C D, Hirofumi H, et al. , 2003. Climate-driven increases in global terrestrial net primary production from 1982 to 1999[J]. Science, 300(5625): 1560-1563. doi: 10.1126/science.1082750
[18] 倪猛, 陈波, 岳建华, 等, 2007. 洛河流域蒸散发遥感反演及其与各参数的相关性分析[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 23(6): 34-37
Ni M, Chen B, Yue J H, et al. , 2007. Estimating evaporation in Luo River Basin using remote sensing and analyzing correlation between evaporation and various parameters[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science, 23(6): 34-37.
[19] 倪向南, 郭伟, 2013.2001-2010年青海湖流域植被覆盖时空变化特征[J]. 地球环境学报, 4(4): 1363-1370
Ni X N, Guo W, 2013. Spatial variations of vegetation change in Qinghai Lake Basin during 2001-2010[J]. Journal of Earth Environment, 4(4): 1363-1370.
[20] Wang Y, Bo Z, Jia L, 2017. Mechanism of the catastrophic June 2017 landslide at Xinmo Village, Songping River, Sichuan Province, China[J]. Landslides, 15(4): 1-13.
[21] 王正兴, 刘闯, 陈文波, 等, 2006. MODIS增强型植被指数EVI与NDVI初步比较[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 31(5): 407-410
Wang Z X, Liu C, Chen W B, et al. , 2006. Mining weights of land evaluation factors based on cloud model and correlation analysis[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 31(5): 407-410.
[22] 位宏, 徐丽萍, 李晓蕾, 等, 2018. 玛纳斯河流域植被覆盖度随地形因子的变化特征[J]. 中国农业气象, 39(12): 814-824
Wei H, Xu L P, Li X L, et al. , 2018. Variation characteristics of vegetation coverage based on terrain factors in the Manas River Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Agrometeorology, 39(12): 814-824.
[23] 温媛媛, 赵军, 王炎强, 等, 2020. 基于MOD16的山西省地表蒸散发时空变化特征分析[J]. 地理科学进展, 39(2): 255-264 doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.007
Wen Y Y, Zhao J, Wang Y Q, et al. , 2020. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics of surface evapotranspiration in Shanxi Province based on MOD16[J]. Progress in Geography, 39(2): 255-264. doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2020.02.007
[24] 吴婧, 梁巧, 童新华, 2020. 地形因素对广西水稻分布和产量的影响研究[J]. 陕西理工大学学报(自然科学版), 36(6): 85-92
Wu J, Liang Q, Tong X H, et al. , 2020. Study on the influence of topographic factors on the distribution and yield of rice in Guangxi[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 36(6): 85-92.
[25] 肖建勇, 王世杰, 白晓永, 等, 2018. 喀斯特关键带植被时空变化及其驱动因素[J]. 生态学报, 38(24): 8799-8812
Xiao J Y, Wang S J, Bai X Y, et al. , 2018. Determinants and spatial-temporal evolution of vegetation coverage in the karst critical zone of South China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 38(24): 8799-8812.
[26] 许向宁, 王文俊, 黄润秋, 2004. 基于GIS的安宁河流域生态环境地质质量评价[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 31(3): 25-30
Xu X N, Wang W J, Huang R Q, 2004. Evaluation of eco-environmental geological quality in Anning River area based on GIS technology[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 31(3): 25-30.
[27] 杨洁, 王朝辉, 2014. 植被覆盖类型在高程上的空间分布特征分析: 江苏省测绘地理信息学会2014年学术年会[C], 中国江苏南京.
Yang J, Wang Z H, 2014. Analysis of spatial distribution characteristics of vegetation cover types on elevation: 2014 Academic Annual Meeting of Jiangsu Society for Geodesy Photogrammetry and Cartography[C], Nanjing, Jiangsu, China.
[28] 杨群兴, 曾土荣, 吴海燕, 2006. 浅析地质因素对生态环境的影响[J]. 广东地质, 19(2): 35-40
Yang Q X, Zeng T R, Wu H Y, 2006. Analysis the impacts of geological factors on the ecological environment[J]. Guangdong Geology, 19(2): 35-40.
[29] 张会平, 杨农, 张岳桥, 等, 2006. 岷江水系流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J]. 第四纪研究, 26(1): 126-135
Zhang H P, Yang N, Zhang Y Q, et al. , 2006. Geomorphology of the Min Jiang drainage system (Sichuan, China) and its structural implications[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 26(1): 126-135.
[30] 张景华, 欧阳渊, 刘洪, 等, 2020. 西昌市生态地质特征与脆弱性评价[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1 − 153.
Zhang J H, Ouyang Y, Liu H, et al., 2020. Ecological geological characteristics and vulnerability assessment of Xichang City[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1 − 153.
[31] 张丽君, 贾跃明, 刘明辉, 1999. 国外环境地质研究和工作的主要态势[J]. 水文地质工程地质, (6): 1-5
Zhang L J, Jia Y M, Liu M H, 1999. Main trends in environmental geology research and work abroad[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, (6): 1-5.
[32] 张腾蛟,刘洪,欧阳渊,等,2020.中高山区土壤成土母质理化特征及主控因素初探——以西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质,40(1):106-114.
Zhang T J,Liu H,Ouyang Y,et al.,2020. A preliminary discussion on the physical and chemical characteristics and main controlling factors of soil and parent material in the middle and high mountain area—Take Xichang as an example[J].Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology,40(1):106-114.
[33] 张岩, 张清春, 刘宝元, 2002. 降水变化对陕北黄土高原植被覆盖度和高度的影响[J]. 地球科学进展, 17(2): 268-272
Zhang Y, Zhang Q C, Liu B Y, 2002. Study on vegetative coverage and height variation in Northern Loess Plateau[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 17(2): 268-272.
[34] 张宇镭, 党琰, 贺平安, 2005. 利用Pearson相关系数定量分析生物亲缘关系[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 41(33): 83-86
Zhang Y L, Dang Y, He P A, 2005. Quantitative analysis of the relationship of biology species using Pearson correlation coefficient[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 41(33): 83-86.
[35] Zhang Y, Gao J, Liu L, et al. , 2013. NDVI-based vegetation changes and their responses to climate change from 1982 to 2011: A case study in the Koshi River Basin in the middle Himalayas[J]. Global & Planetary Change, 108: 139-148.
[36] 张宗祜, 2005. 环境地质与地质灾害[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(1): 1-5
Zhang Z H, 2005. Environmental geology and geological hazard[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 25(1): 1-5.
[37] 赵法锁, 宋飞, 王艳婷, 等, 2006. 基于GIS的略阳县地质环境质量评价[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 28(1): 88-91
Zhao F S, Song F, Wang Y T, et al. , 2006. Geoenvironmental Quality Assessment of Lueyang County based on GIS[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 28(1): 88-91.
[38] 赵鹏大, 王京贵, 饶明辉, 等, 1995. 中国地质异常[J]. 地球科学, 20(2): 117-127
Zhao P D, Wang J G, Rao M H, et al. , 1995. Geologic anomaly of China[J]. Earth Science, 20(2): 117-127.
-




 下载:
下载: