Spatial distribution pattern and driving mechanism of heavy metal elements in soils of middle−alpine hilly region, Yunnan Province
-
摘要:
研究目的 查清滇中中高山丘陵区土壤重金属地球化学特征及驱动机制,服务于高原特色农业发展和乡村振兴战略的实施。
研究方法 以滇中大姚县、姚安县和南华县为研究区,依据1∶25万土地质量地球化学调查数据,采用地统计学分析土壤重金属来源、空间分布格局及驱动机制,建立滇中中高山丘陵区土壤重金属表生地球化学过程驱动模式。
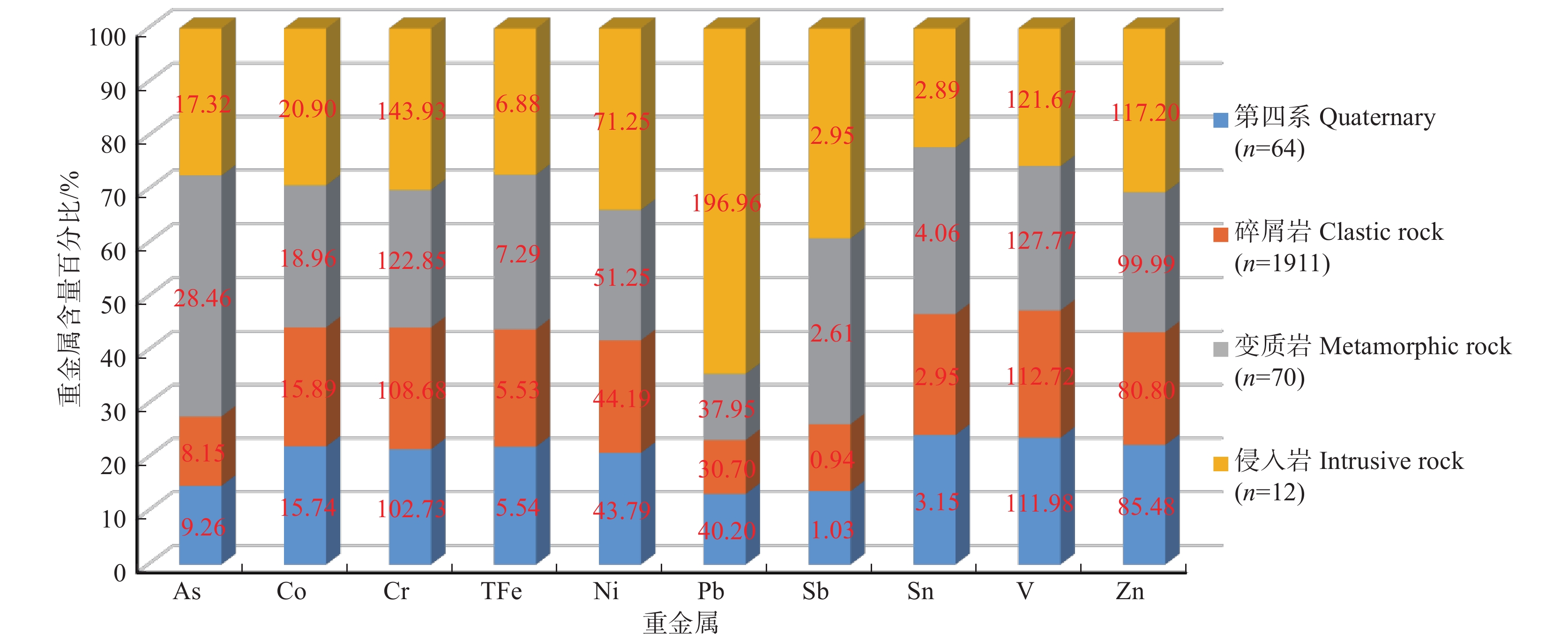
研究结果 研究区表层土壤中Cd、Hg含量均值高于深层土壤背景值,Cr、Ni高于云南省土壤背景值,除As、Hg、Sb外的其他重金属显著高于全国土壤背景值,局部地区土壤可能存在As、Cd、Pb生态风险。构建的最小数据集的元素为As、Co、Cr、TFe、Ni、Pb、Sb、Sn、V、Zn,莫兰指数显示均具有显著的正空间自相关性。空间分布特征呈现变质岩和侵入岩重金属含量高、碎屑岩和第四系冲积物含量低的特点。多元统计分析与重金属空间分布特征表明Co、Cr、TFe、Mn、Ni、V主要来源于成土母质,As、Sb、Sn受原生地层与成矿地质背景影响较大,Cd、Pb、Zn主要受工矿活动等人类活动影响。
结论 重金属元素的分布与地层分布高度耦合,地质背景控制了表层土壤重金属的空间分布格局,不同土壤类型和土地利用类型土壤重金属含量显著差异。岩石风化作用驱动了重金属的垂向迁移和富集,重金属含量与高程呈显著的多项式线性拟合趋势,有机质和pH是不同高程区间控制重金属行为的主控因素。研究区强烈的表生地球化学作用重塑了重金属的宏观分布,受自身化学性质的制约以及环境条件(坡度、pH、有机质等)的影响在土壤中发生分配、迁移、富集,人类活动影响了局部重金属的分布格局。
Abstract:This paper is the result of environmental geological survey engineering.
Objective The investigation of the geochemical behavior of heavy metals in the surface geochemical process has important guiding significance for the construction of life community of mountains, rivers, forests, fields, lakes and grasses. The purpose of this study is to investigate the geochemical behavior and driving mechanism of soil heavy metals in the middle-alpine hilly region of southwest China. It will serve the implementation of the strategy of plateau characteristic agricultural development and rural revitalization.
Methods Based on 1∶250000 land quality geochemical survey data in Dayao County, Yao'an County and Nanhua County in central Yunnan Province, the source, spatial distribution pattern and driving mechanism of soil heavy metals were analyzed by geostatistics, and the driving model of soil epigenetic geochemical process of heavy metals was established in the middle-alpine hilly region of southwest China.
Results The results showed that the average content of Cd and Hg in the surface soil in the study area was higher than the background value of the deep soil, Cr and Ni were higher than the background value of the soil in Yunnan province, and other heavy metals except As, Hg and Sb were significantly higher than the national background value of the soil, and local soil may have ecological risks of As, Cd and Pb. The elements of the constructed minimum dataset are As, Co, Cr, TFe, Ni, Pb, Sb, Sn, V and Zn, and the Moran index shows significant positive spatial autocorrelation. The spatial distribution features high content of heavy metals in metamorphic rocks and intrusive rocks, low content of clastic rocks and quaternary alluvium. Multivariate statistical analysis and spatial distribution characteristics of heavy metals show that Co, Cr, TFe, Mn, Ni and V mainly come from the parent material, As, Sb and Sn are greatly affected by the primary strata and metallogenic geological background, Cd, Pb and Zn are mainly affected by human activities such as industrial and mining activities.
Conclusions The distribution of heavy metals is highly coupled with the ground distribution. The spatial distribution pattern of heavy metals in surface soil is controlled by geological background, and the content of heavy metals in soil varies significantly among different soil types and land use types. The vertical migration and enrichment of heavy metals are driven by rock weathering, and the heavy metal content and elevation show a significant polynomial linear fitting trend. Organic matter and pH are the main factors controlling the heavy metal behavior at different elevation intervals. Strong epigenetic geochemistry in the study area reshaped the macroscopic distribution of heavy metals. Restricted by their own chemical properties and influenced by environmental conditions (slope, pH, organic matter, etc.), distribution, migration and enrichment of heavy metals occurred in the soil. Human activities affected the distribution pattern of local heavy metals.
-

-
图 1 研究区地理位置及地质背景图
1 Figure 1.
表 1 元素分析方法及检出限
Table 1. Element analysis methods and detection limits
元素 实验室检出限 规范检出限 分析方法 Cu 0.46 1 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) Co 0.6 1 Cd 0.03 0.03 Pb 1 2 Mn 5 10 电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES) Zn 2 4 V 3 5 Ni 1 2 Cr 4 5 X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) TFe2O3* 0.01 0.05 Sn 0.5 1 发射光谱法(ES) As 0.63 1 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) Sb 0.031 0.05 Hg 0.003 0.005 pH** 0.1 0.1 离子选择电极法(ISE) Corg* 0.04 0.1 容量法(Vap-Vol) 注:*计量单位为%,**为无量纲,其余计量单位为mg/kg。 表 2 表层土壤重金属统计特征(n=2124)
Table 2. Statistical characteristics of heavy metals in surface soil (n=2124)
元素 最小值/
(mg/kg)最大值/
(mg/kg)平均值/
(mg/kg)标准差/
(mg/kg)变异系数 深层土壤均值/
(mg/kg)云南省土壤背景值/
(mg/kg)全国土壤背景值/
(mg/kg)K1 K2 K3 超标率/% As 0.54 316.00 9.09 10.98 1.21 10.10 10.60 11.20 0.90 0.86 0.81 2.68 Cd 0.04 14.20 0.24 0.36 1.51 0.11 0.27 0.10 2.20 0.90 2.49 18.36 Co 2.07 59.30 16.04 4.91 0.31 17.44 16.40 12.70 0.92 0.98 1.26 — Cr 31.20 572.00 109.35 32.25 0.29 113.70 91.00 61.00 0.96 1.20 1.79 4.66 Cu 1.30 1758.00 34.49 40.61 1.18 34.50 40.00 22.60 1.00 0.86 1.53 5.56 TFe2O3 1.14 15.08 5.60 1.21 0.22 6.06 6.76 2.94 0.92 0.83 1.90 — Hg 0.01 0.58 0.05 0.04 0.85 0.04 0.07 0.07 1.25 0.72 0.77 0.09 Mn 72.60 5119.00 661.73 349.56 0.53 672.29 687.00 583.00 0.98 0.96 1.14 — Ni 7.94 328.00 44.68 16.94 0.38 49.13 38.00 26.90 0.91 1.18 1.66 5.74 Pb 8.53 1819.00 32.16 48.15 1.50 31.29 39.00 26.00 1.03 0.82 1.24 2.31 Sb 0.11 14.60 1.01 0.90 0.89 0.97 1.16 1.21 1.05 0.87 0.84 — Sn 1.42 12.70 2.98 0.66 0.22 3.06 4.60 2.60 0.97 0.65 1.15 — V 27.30 276.00 113.17 24.84 0.22 121.09 125.00 82.40 0.93 0.91 1.37 — Zn 13.40 2403.00 81.85 58.63 0.72 81.35 96.00 74.20 1.01 0.85 1.10 0.99 pH 3.91 8.32 5.76 0.91 0.16 6.04 6.14 6.8 0.95 0.94 0.85 — 注:云南、全国土壤背景值来自文献(侯青叶等,2020);K1、K2、K3分别表示土壤重金属元素平均含量与深层、云南省、全国土壤背景值的比值;“—”表示无相应风险筛选值来计算超标率。 表 3 表层土壤重金属主成分分析及特征值
Table 3. Principal component analysis and characteristic values of heavy metals in surface soil
项目 成分 分组 Norm值 1 2 3 As −0.001 0.749 0.040 2 0.998 Cd 0.066 −0.132 0.665 3 0.731 Co 0.881 0.169 0.159 1 1.994 Cr 0.815 −0.057 −0.034 1 1.830 Cu 0.210 0.071 0.185 0.517 TFe2O3 0.814 0.406 0.081 1 1.905 Hg 0.130 0.496 0.072 0.725 Mn 0.553 0.409 0.198 1 1.370 Ni 0.901 0.054 0.083 1 2.024 Pb −0.132 0.389 0.580 3 0.849 Sb 0.211 0.685 0.228 2 1.054 Sn 0.231 0.641 −0.063 2 1.000 V 0.859 0.286 0.076 1 1.964 Zn 0.203 0.147 0.645 3 0.836 特征值 5.028 1.769 1.090 方差百分比/% 35.91 12.64 7.78 累计贡献率/% 35.91 48.55 56.33 表 4 表层土壤重金属空间自相关分析
Table 4. Spatial autocorrelation analysis of heavy metals in surface soil
项目 As Co Cr TFe Ni Pb Sb Sn V Zn 方差 0.0002 0.0003 0.0003 0.0003 0.0002 0.0001 0.0002 0.0002 0.0003 0.0001 Z 25.39 32.13 30.85 35.6 29.72 24.89 30.61 27.91 35.75 14.95 P 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 指数 0.37 0.51 0.48 0.56 0.46 0.3 0.48 0.44 0.56 0.16 -
[1] Chadwick O A, Brimhall G H, Hendricks D M. 1990. From a black to a gray box— A mass balance interpretation of pedogenesisi[J]. Geomorphology, 3(3/4): 369−390. doi: 10.1016/0169-555X(90)90012-F
[2] Chen Meng, Pan Yongxing, Huang Yixiang, Wang Xiaotong, Zhang Ruidong. 2022. Spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in soil of a typical lead−zinc mining area, Yangshuo[J]. Environmental Science, 43(10): 4545−4555 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen Z Y, Zhao Y Y, Chen D L, Huang H T, Zhao Y, Wu Y J. 2023. Ecological risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal cumulation in the soils near the Luanchuan molybdenum polymetallic mine concentration area, Henan Province, central China[J]. China Geology, 6: 15−26.
[4] Cheng Hangxin, Peng Min, Zhao Chuandong, Han Wei, Wang Huiyan, Wang Qiaolin, Yang Fan, Zhang Fugui, Wang Chengwen, Liu Fei, Zhou Yalong, Tang Shiqi, Li Kuo, Yang Ke, Yang Zheng, Cheng Xiaomeng, Chen Ziwan, Zhang Hua, Mo Chunhu. 2019. Epigenetic geochemical dynamics and driving mechanisms of distribution patterns of chemical elements in soil, Southwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(6): 159−191 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Feng Qianwei, Wang Bing, Ma Xianjie, Jiang Zonghong, Chen Miao. 2020. Characteristics and sources of heavy metal pollution in soils of typical lead-zinc mining areas in northwest Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Peteology and Geochemistry, 39(4): 863−870(in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Guo W J, Zhang Z Y, Wang H, Qin H J, Fu Z Y. 2021. Exposure characteristics of antimony and coexisting arsenic from multi−path exposure in typical antimony mine area[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 289: 112493. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112493
[7] Gong Cang, Wang Liang, Wang Shunxiang, Zhang Zhixiang, Dong Hang, Liu Jiufen, Wang Dewei, Yan Buqing, Chen Ying. 2022. Spatial differentiation and influencing factor analysis of soil heavy metal content at Town level based on geographical detector[J]. Environmental Science, 43(10): 4566−4577 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[8] Gong Wei, Jiang Xiaodian. 2017. Thermal evolution history and its genesis of the Ailoa Shan−Red River fault zone in the Ailoa Shan and Day Nui Con Voi Massif during Oligocene−Early Miocene[J]. Earth Science, 42(2): 223−239 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Guo Zhijuan, Zhou Yalong, Yang Zheng, Zhao Chuandong, Cheng Hangxin, Kong Mu, Peng Min. 2020. Discussion on key issues of geochemical monitoring of soil heavy metal in Xiong'an New District[J]. Environmental Science, 41(9): 4169−4179 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] Hou Lianggang, Yuan Ling, Li Xujin. 2020. The feature and REE prospecting potentialty of Laojiezi alkaline complex body in Yaoan, Yunnan[J]. Yunnan Geology, 39(1): 20−25 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Hou Qingye, Yang Zhongfang, Yu Tao, Cheng Hangxin, Zhou Guohua. 2020. Soil Geochemical Parameters in China [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 16-2573(in Chinese).
[12] Hu Guipeng, Wei Gangjian, Ma Jinlong, Zeng Ti, Liu Zhifeng. 2017. Mobilization and redistribution of major and trace elements during the process of moderate weathering of carbonates in northern Guangdong, South China[J]. Geochemica, 46(1): 33−45 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Hu Yunzhong, Tang Shanghechun, Wang Haiping, Yang Yueqing, Deng Jian. 1995. Geology of Ailaoshan Gold Mine[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1−278(in Chinese).
[14] Ji Z H, Long Z W, Zhang Y, Wang Y K, Pei Y S. 2021. Enrichment differences and source apportionment of nutrients, stable isotopes, and trace mental elements in sediments of complex and fragmented wetland systems[J]. Environmental Pollution, 289: 1−12.
[15] Lai Shuya, Dong Qiuyao, Song Chao, Yang Zhenjing. 2021. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in the Eastern mountainous area of Nanyang Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 42(11): 5500−5509 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Li Desheng, Yang Zhongfang, Jin Zhibin. 2004. Geochemical characters of trace elements of soil from the Taiyuan basin[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 40(3): 86−89 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Li Kuo, Peng Min, Zhao Chuandong, Yang Ke, Zhou Yalong, Liu Fei, Tang Shiqi, Yang Fan, Han Wei, Yang Zheng, Cheng Xiaomeng, Xia Xueqi, Guan Tao, Luo Jianlan, Cheng Hangxin. 2019. Vicennial implementation of geochemical survey of land quality in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(6): 128−158 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Li Minglong. 2021. Geochemical Characteristics and Ecological Effects of Se and Heavy Metals in Supergene Environmental Media: A Case Study of Enshi City, Hubei Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 1−142(in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Ling Yun, Liu Hanyi, Zhang Xiaoting, Wei Shiqiang. 2023. Characteristics of typical soil acidification and effects of heavy metals speciation and availability in Southwest China[J]. Environmental Science, 44(1): 376−386 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Liu Qing, Xia Jiangbao, Xie Wenjun. 2011. Application of semi-variogram and Moran's I to spatial distribution of trace elements in soil: A case study in Shouguang County[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 36(9): 1129−1133 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Liu Shuling, Wu Mei, Liu Zhiyuan, Liu Shuangyan, Liu Yonglin, Zhao Jiayu, Liu Yi. 2023. Soil heavy metal Content, pollution and influencing factors in typical farming areas of Sichuan basin[J]. Environmental Science, 44(1): 347−355 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Liu Yuanyuan, Ma Tengfei, Chen Yang, Yang Xiaofan, Liu Chongxuan. 2021. Scaling behavior of surficial geochemical reactions[J]. Bulletin of Minerallogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 40(5): 1107−1120(in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Nesbitt H W. 1979. Mobility and fractionation of rare earth elements during weathering of a granodiorite[J]. Nature, 279(5710): 206−210. doi: 10.1038/279206a0
[24] Qin Yuanli, Zhang Fugui, Peng Min, Zhang Shunyao, Ma Honghong, Tang Ruiling, Zhao Zhihui, Cheng Hangxin. 2020. Geochemical distribution characteristics and sources of heavy metals in soils of Wuding County, Yunnan Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 56(3): 540−550 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Qiu Zhiteng, Ma Wanzhu, Zhang Mingkui. 2020. Formation characteristics of soils developed from metamorphic rocks in the hilly and mountain areas of Southwest Zhejiang Province[J]. Chingese Journal of Soil Science, 51(5): 1009−1015.
[26] Ruxton B P. 1968. Measures of the degree of chemical weathering of rocks[J]. The Journal of Geology, 76(5): 518−527. doi: 10.1086/627357
[27] Sun Hui, Bi Rutian, Guo Ying, Yuan Yuzhi, Chai Min, Guo Zhixing. 2018. Source apportionment analysis of trace metal contamination in soils of Guangdong Province, China[J]. Acta Science Circumstantiae, 38(2): 704−714 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Wang Jianfei. 2016. Lithology-fault ore-controlling characteristics and deep prospecting prediction of 2108 m and 2073 m middle section of Yao'an lead deposit[J]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 1−75(in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Wang Min, Dong Jiaqi, Bai Longlong, Zhang Yong, Jiang Zhonglong, Jiang Niwen, Wu Jiasen, Zhang Luyao, Fang Jia, Fu Weijun. 2021. Spatial variation and risk assessment of heavy metals in soils of main torreya grandis plantation region in Zhejiang Province[J]. Environmental Science, 42(12): 5949−-5957 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Wang Qiaolin, Song Yuntao, Wang Chengwen, Xu Renting, Peng Min, Zhou Yalong, Han Wei. 2021. Source identification and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in Western Yunnan[J]. China Environmental Science, 41(8): 3693−3703 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Wang Ruiting, Ouyang Jianping. 2002. The situation and progress of supergenic geochemistry mineral[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 16(1): 61−64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Wu Peng, Yang Hang, Han Runsheng, Jiang Longyan, Jiang Xiaojun, Wang Die, Guan Shenjin. 2019. Signature and geological significance of the specularite from the Laojiezi Pb−Ag deposit in the Chuxiong basin, central Yunnan, SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(5): 1489−1502 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.05.11
[33] Wu Xiyong, Luo Jian, Wei Youyi. 2004. Research of rocks weathering and chemical composition of rock[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 40(4): 85−88 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Wu Yongfeng, Liu Congqiang, Tu Chenglong. 2008. Speciation of heavy metals in urban soil of Guiyang[J]. Acta Mineralogical Sinica, 28(2): 177−180 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Xia Zenglu. 1994. Factors affecting regional differentiation of critical levels and environmental capacities of some heavy metals in main soil types of China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 31(2): 161−169 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Xu Jianming. 2019. Soil Science (Fourth Edition) [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 50−80(in Chinese).
[37] Xu Lei, Huang Jiazhong, Zhang Ya, Xiang Jingwei, Ye Lei, Yang Minglong, Duan Xingwu, Guan Jiyun. 2022. Sources and influencing factors of soil heavy metals in the high mountain and hilly area of central Yunnan: Taking Wuding County as an example[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 38(1): 82−92 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yang Jianzhou, Gong Jingjing, Wang Zhenliang, Gao Jianweng, Yang Jiankun, Hu Shuqi, Tang Shixin. 2022. Enrichment factors, health risks and source identification of heavy metals in agricultural soils in semi−arid region of Hainan Island[J]. Environmental Science, 43(10): 4590−4600 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Yang Ling, Tian Lei, Bai Guangyu, Pei Shengliang, Zhang Deqiang. 2022. Ecological risk assessments and source analysis of heavy metals in the soil of Xin Barag Youqi, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology in China, 49(6): 1970−1983 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Yuan G L, Sun T H, Han P, Li J, Lang X X. 2014. Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy melals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: Typical urban renewal arca in Beijing, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 136: 40−47. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.10.002
[41] Zhang C S, Luo L, Xu W L, Valerie L. 2008. Use of local Moran's I and GIS to identify pollution hotspots of Pb in urban soils of Galway, Ireland[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 398(1/3): 212−221. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.03.011
[42] Zhang Pengyan, Qin Mingzhou, Chen Long, Hu Changhui, Zhao Yaping, Dong Wenjun. 2013. Study on distribution characteristics and potential ecological risk of soil heavy metals in the Yellow river beach region in Kaifeng City[J]. Environmental Science, 34(9): 3654−3662 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhang Xiangnian, Xin Cunlin, Li Chunliang. 2010. Geochemical characteristics of heavy metal’s contamination and it’s surface geochemical mechanism in Baiyin City, Gansu Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 29(4): 124−131 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Zhao Kai. 2014. Geochemistry of Ore-forming Processes in the Ailaoshan Orogenic Gold Belt, West Yunnan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1−164(in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhao L, Xu Y F, Hou H, Shangguan Y X, Li F S. 2014. Source identification and health risk assessment of metals in urban soils around the Tanggu chemical industrial district, Tianjin, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 468/469: 654−662.
[46] Zhao Xinna, Yang Zhongfang, Yu Tao. 2023. Review on heavy metal pollution and remediation technology in the soil of mining areas[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 84−101 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] Zhao Yulong, Sun Zhongyuan, Li Pengxiao. 2021. Geochemical characteristics of soil and prospecting prediction of Niutougou gold deposit in western Henan[J]. Western Resources, 63(5): 180−183 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[48] Zheng Fei, Guo Xin, Tang Mingyang, Zhu Dong, Dong Sijun, Kangle, Chen Bing. 2022. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Baiyangdian Lake[J]. Environmental Science, 43(10): 4556−4565 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[49] Zhu Y M, Yang J G, Wang L Z, Lin Z T, Dai J X, Wang R J, Yu Y S, Liu H, Christopher R, Feng R W. 2020. Factors influencing the uptake and speciation transformation of antimony in the soil−plant system, and the redistribution and toxicity of antimony in plants[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 738: 140232. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140232
[50] 陈盟, 潘泳兴, 黄奕翔, 王櫹橦, 张睿东. 2022. 阳朔典型铅锌矿区流域土壤重金属空间分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 43(10): 4545−4555.
[51] 成杭新, 彭敏, 赵传冬, 韩伟, 王惠艳, 王乔林, 杨帆, 张富贵, 王成文, 刘飞, 周亚龙, 唐世琪, 李括, 杨柯, 杨峥, 成晓梦, 陈子万, 张华, 莫春虎. 2019. 表生地球化学动力学与中国西南土壤中化学元素分布模式的驱动机制[J]. 地学前缘, 26(6): 159−191.
[52] 冯乾伟, 王兵, 马先杰, 蒋宗宏, 陈淼. 2020. 黔西北典型铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征及其来源分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 39(4): 863−870.
[53] 龚仓, 王亮, 王顺祥, 张志翔, 董航, 刘玖芬, 王德伟, 严步青, 陈映. 2022. 基于地理探测器的镇域尺度土壤重金属含量空间分异及其影响因素分析[J]. 环境科学, 43(10): 4566−4577.
[54] 宫伟, 姜效典. 2017. 哀牢山—红河断裂带哀牢山—大象山段渐新世—早中新世热史演化及成因[J]. 地球科学, 42(2): 223−239.
[55] 郭志娟, 周亚龙, 杨峥, 赵传冬, 成杭新, 孔牧, 彭敏. 2020. 雄安新区土壤重金属地球化学监测关键问题探讨[J]. 环境科学, 41(9): 4169−4179.
[56] 侯良刚, 袁玲, 李徐瑾. 2020. 云南姚安县老街子碱性杂岩体特征及稀土找矿前景[J]. 云南地质, 39(1): 20−25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2020.01.005
[57] 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 夏学齐, 成杭新, 周国华. 2020. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 16−2573.
[58] 虎贵朋, 韦刚健, 马金龙, 曾提, 刘志锋. 2017. 粤北碳酸盐岩化学风化过程中的元素地球化学行为[J]. 地球化学, 46(1): 33−45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.004
[59] 胡云中, 唐尚鹑, 王海平, 杨岳清, 邓坚. 1995. 哀牢山金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1−278.
[60] 赖书雅, 董秋瑶, 宋超, 杨振京. 2021. 南阳盆地东部山区土壤重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 42(11): 5500−5509.
[61] 李德胜, 杨忠芳, 靳职斌. 2004. 太原盆地土壤微量元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 40(3): 86−89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2004.03.019
[62] 李括, 彭敏, 赵传冬, 杨柯, 周亚龙, 刘飞, 唐世琪, 杨帆, 韩伟, 杨峥, 成晓梦, 夏学齐, 关涛, 骆检兰, 成杭新. 2019. 全国土地质量地球化学调查二十年[J]. 地学前缘, 26(6): 128−158.
[63] 李明龙. 2021. 表生环境介质中硒与重金属的地球化学特征及生态效应研究—以湖北省恩施市为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 1−142.
[64] 凌云, 刘汉燚, 张小婷, 魏世强. 2023. 西南地区典型土壤酸化特征及其与重金属形态活性的耦合关系[J]. 环境科学, 44(1): 376−386.
[65] 刘庆, 夏江宝, 谢文军. 2011. 半方差函数与Moran’s I在土壤微量元素空间分布研究中的应用—以寿光市为例[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 36(9): 1129−1133.
[66] 刘属灵, 吴梅, 刘志远, 刘双燕, 刘永林, 赵家宇, 刘怡. 2023. 四川盆地典型农耕区土壤重金属含量、污染及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 44(1): 347−355.
[67] 刘媛媛, 马腾飞, 陈旸, 杨晓帆, 刘崇炫. 2021. 表生地球化学反应的尺度效应[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 40(5): 1107−1120.
[68] 秦元礼, 张富贵, 彭敏, 张舜尧, 马宏宏, 唐瑞玲, 赵智慧, 成杭新. 2020. 云南省武定县土壤重金属地球化学分布特征及其来源浅析[J]. 地质与勘探, 56(3): 540−550. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2020.03.007
[69] 邱志腾, 麻万诸, 章明奎. 2020. 浙西南丘陵山地变质岩发育土壤的成土特征[J]. 土壤通报, 51(5): 1009−1015.
[70] 孙慧, 毕如田, 郭颖, 袁宇志, 柴敏, 郭治兴. 2018. 广东省土壤重金属溯源及污染源解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 38(2): 704−714.
[71] 王建飞. 2016. 云南姚安铅矿床2108m和2073m中段岩性—断裂控矿特征及深部找矿预测[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 1−75.
[72] 王敏, 董佳琦, 白龙龙, 张勇, 蒋仲龙, 姜霓雯, 吴家森, 张璐瑶, 方嘉, 傅伟军. 2021. 浙江省香榧主产区土壤重金属空间异质性及其生态风险[J]. 环境科学, 42(12): 5949−5957.
[73] 王乔林, 宋云涛, 王成文, 徐仁廷, 彭敏, 周亚龙, 韩伟. 2021. 滇西地区土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 中国环境科学, 41(8): 3693−3703. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2021.08.026
[74] 王瑞廷, 欧阳建平. 2002. 表生地球化学研究现状及进展[J]. 矿产与地质, 16(1): 61−64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2002.01.019
[75] 吴鹏, 杨航, 韩润生, 姜龙燕, 江小均, 王蝶, 管申进. 2019. 滇中楚雄盆地老街子铅−银矿床镜铁矿特征及地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 35(5): 1489−1502.
[76] 巫锡勇, 罗健, 魏有仪. 2004. 岩石风化与岩石化学成分的变化研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 40(4): 85−88.
[77] 武永锋, 刘丛强, 涂成龙. 2008. 贵阳城市土壤重金属元素形态分析[J]. 矿物学报, 28(2): 177−180. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2008.02.010
[78] 夏增禄. 1994. 中国主要类型土壤若干重金属临界含量和环境容量区域分异的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 31(2): 161−169.
[79] 徐建明. 2019. 土壤学(第四版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 50−80.
[80] 徐磊, 黄加忠, 张亚, 向经纬, 叶雷, 杨明龙, 段兴武, 管继云. 2022. 滇中高山丘陵区土壤重金属来源及影响因素—以武定县为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 38(1): 82−92.
[81] 杨剑洲, 龚晶晶, 王振亮, 高健翁, 杨建坤, 胡树起, 唐世新. 2022. 海南岛半干旱区农用地土壤重金属富集因素、健康风险及来源识别[J]. 环境科学, 43(10): 4590−4600.
[82] 杨玲, 田磊, 白光宇, 裴圣良, 张德强. 2022. 内蒙古新巴尔虎右旗土壤重金属生态风险与来源分析[J]. 中国地质, 49(6): 1970−1983.
[83] 张鹏岩, 秦明周, 陈龙, 胡长慧, 赵亚平, 董文君. 2013. 黄河下游滩区开封段土壤重金属分布特征及其潜在风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 34(9): 3654−3662.
[84] 张祥年, 辛存林, 李春亮. 2010. 甘肃省白银市土壤重金属污染地球化学特征及其表生地球化学成因[J]. 地质科技情报, 29(4): 124−131.
[85] 赵凯. 2014. 滇西哀牢山造山带金成矿作用地球化学[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1−164.
[86] 赵鑫娜, 杨忠芳, 余涛. 2023. 矿区土壤重金属污染及修复技术研究进展[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 84−101.
[87] 赵玉龙, 孙中原, 李鹏霄. 2021. 豫西牛头沟金矿土壤地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 西部资源, 63(5): 180−183.
[88] 郑飞, 郭欣, 汤名扬, 朱冬, 董四君, 康乐, 陈兵. 2022. 白洋淀及周边土壤重金属的分布特征及生态风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 43(10): 4556−4565.
-




 下载:
下载: