Establishment and application of evaluation system for development and utilization of selenium−rich land: A case study in Lintong District, Xi'an
-
摘要:
研究目的 人体日常摄入的硒主要通过食物链源于土壤,而中国是富硒土地资源相对匮乏的国家,面对有限且珍贵的富硒土地资源,亟需构建科学合理的富硒土地开发利用评价体系,为特色土地资源的高效开发提供依据。
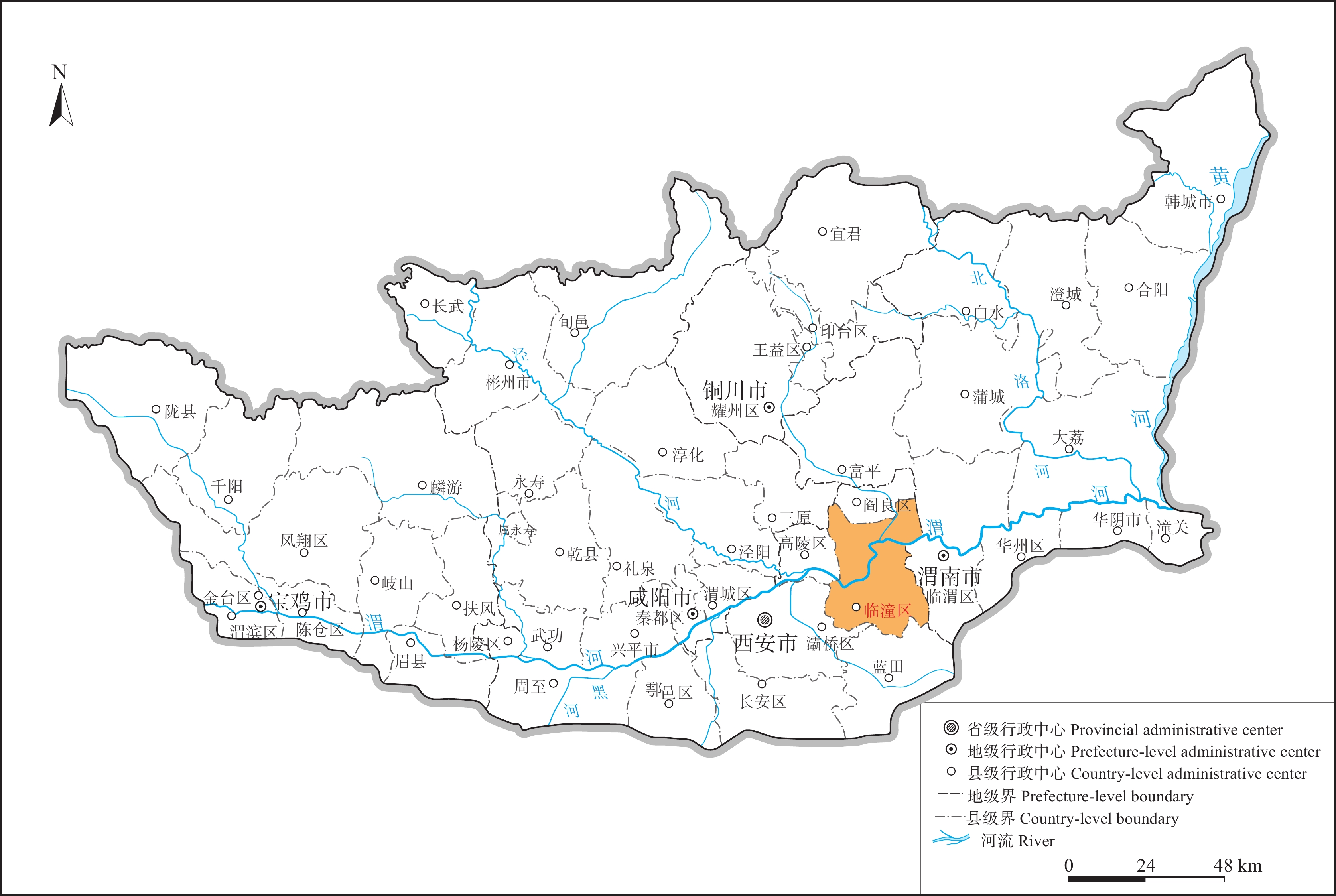
研究方法 本文以陕西关中地区为研究区,在土地质量地球化学调查成果基础上,融合反映农用地自然条件、基础设施水平的评价指标,构建了涵盖立地条件、土壤硒含量、理化性质、土壤质量和土地管理等5大类12项指标的关中地区富硒土地开发利用评价体系。同时以西安市临潼区为例,开展了临潼区富硒土地开发利用适宜性评价。
研究结果 将临潼区土地划分为高度适宜区、适宜区、较不适宜区、不适宜区和极不适宜区共5个等级,其中高度适宜开发区及适宜区开发面积共248.35 km2,主要分布在临潼区北部的新市乡、栎阳镇、徐杨乡、相桥镇及中东部的何寨镇。基于不同适宜评价区内小麦硒含量及富硒比例,发现其富硒土地适宜性与小麦富硒程度高度耦合。
结论 说明构建的富硒土地开发利用评价体系对富硒土地资源的开发利用具有较好的科学指导价值及重要的示范意义。
Abstract:This paper is the result of agricultural geological survey engineering.
Objective Selenium (Se) intake in the human body primarily originates from the food chain, mostly derived from soil. The research aims to establish a scientific and rational evaluation system for the development and utilization of selenium−rich land due to the limited and valuable selenium−enriched soil resources in China.
Methods This study focuses on the Guanzhong region, particularly Lintong District, integrating geophysical survey findings with assessment criteria reflecting agricultural land's natural conditions and infrastructure levels. The developed evaluation system encompasses five major categories and twelve indicators, including site conditions, soil selenium content, physicochemical properties, soil quality, and land management. Moreover, suitability assessment for selenium-rich land development and utilization was conducted in Lintong District as a case study.
Results The land in Lintong District was categorized into five levels: highly suitable, suitable, moderately unsuitable, unsuitable, and highly unsuitable. The highly suitable and suitable development areas covered 248.35 km2, mainly distributed in the northern areas of Lintong District, as Xinshi Town, Liyang Town, Xuyang Town, Xiangqiao Town, and the central-eastern parts of Hezhai Town. Analysis of wheat Se content and Se enrichment ratios within different suitability evaluation zones revealed a strong correlation between the suitability of selenium-rich land and the degree of selenium enrichment in wheat.
Conclusions The developed evaluation system demonstrates significant scientific guidance and exemplary significance for the utilization of selenium−rich land resources. It underscores the need for a systematic approach to efficiently develop and utilize these resources, emphasizing the critical link between soil suitability and the selenium enrichment of agricultural produce.
-

-
表 1 研究区富硒土地开发利用评价层次模型
Table 1. Hierarchical model of evaluating the development and utilization of Selenium−rich land in the study area
目标层(A) 准则层(B) 指标层(C) 关中地区富硒土地
开发利用评价体系立地条件 地块大小 盐渍化程度 土壤类型 地形坡度 土壤硒含量 土壤全硒含量 土壤理化性质 土壤质地 有机质 pH值 土壤质量 土壤养分(氮、磷、钾) 土壤环境(镉、汞、砷、铅、铬、铜、镍、锌) 土地管理 排水条件 灌溉保证率 表 2 准则层对目标层的比较判断矩阵A及权重向量
Table 2. Comparison matrix A and weight vector of the criterion layer to the target layer
A 立地条件 理化性质 土壤质量 土壤硒含量 土地管理 权重向量 立地条件 1 1/5 1/3 1/7 2 0.0586 理化性质 5 1 2 1/3 7 0.2419 土壤质量 3 1/2 1 1/5 5 0.1406 土壤硒含量 7 3 5 1 9 0.5227 土地管理 1/2 1/7 1/5 1/9 1 0.0362 表 3 立地条件指标对准则层的比较判断矩阵B1及权重向量
Table 3. Comparison matrix B1 and weight vector of the site condition index to the criterion layer
B 地块大小 盐渍化程度 土壤类型 地形坡度 权重向量 地块大小 1 3 1/3 5 0.2622 盐渍化程度 1/3 1 1/5 3 0.1175 土壤类型 3 5 1 7 0.5650 地形坡度 1/5 1/3 1/7 1 0.0553 表 4 富硒土地开发利用评价指标权重表
Table 4. Evaluation index weight of Selenium−rich land development and utilization
项目 立地条件 理化性质 土壤质量 土壤硒含量 土地管理 组合权重 0.0585 0.2419 0.1406 0.5227 0.0362 地块大小 0.2622 0.0154 盐渍化程度 0.1175 0.0069 土壤类型 0.5650 0.0331 地形坡度 0.0553 0.0032 土壤质地 0.1047 0.0253 有机质 0.2583 0.0625 pH值 0.6370 0.1541 土壤养分 0.5000 0.0703 土壤环境 0.5000 0.0703 土壤硒含量 1.0000 0.5227 排水条件 0.1667 0.0060 灌溉保证率 0.8333 0.0302 表 5 各评价指标隶属度函数界限值
Table 5. Threshold values of membership functions of all evaluation indexes
指标 函数类型 界限值 指标 函数类型 界限值 地块大小 戒上型 U=12385.6
L=1518.0土壤环境—锌 戒下型 U=79.0
L=66.8土壤硒含量 戒上型 U=0.22
L=0.13土壤环境—铜 戒下型 U=28.95
L=23.94有机质 戒上型 U=1.76
L=1.19土壤环境—镍 戒下型 U=35.60
L=30.12土壤养分—氮 戒上型 U=1024
L=740土壤环境—砷 戒下型 U=14.40
L=12.30土壤养分—磷 戒上型 U=1058
L=733土壤环境—镉 戒下型 U=208
L=160土壤养分—钾 戒上型 U=2.17
L=1.94土壤环境—铬 戒下型 U=77.9
L=70.6pH值 峰值型 L=6.5; O1=7.5
O2=8.5; U=9.0土壤环境—汞 戒下型 U=74.00
L=27.73地形坡度 戒下型 U=25
L=2土壤环境—铅 戒下型 U=27.1
L=22.4注:地块大小单位为m2;有机质、钾单位为%;pH值无量纲;地形坡度单位为°;镉、汞单位为μg/kg;其他指标单位为mg/kg。 表 6 各评价指标分级、得分
Table 6. Grading and score of all evaluation indexes
指标名称 分级标准 等级 得分 盐渍化程度 无盐渍化 1级 1 轻度盐渍化 2级 0.7 中度盐渍化 3级 0.4 重度盐渍化 4级 0.1 表层土壤
质地壤土 1级 1 黏土 2级 0.7 砂土 3级 0.4 砾质土 4级 0.1 排水条件 排水体系健全 1级 1 排水体系基本健全 2级 0.9 排水体系一般 3级 0.7 无排水体系 4级 0.5 灌溉保证率 充分满足 1级 1 基本满足 2级 0.8 一般满足 3级 0.5 无灌溉条件 4级 0.1 土壤类型 褐土 1级 1 新积土、潮土、水稻土 2级 0.7 黄绵土、黑垆土、风沙土、沼泽土、棕壤 3级 0.4 粗骨土、红土、石质土 4级 0.1 表 7 关中地区富硒土地开发利用综合指数等级
Table 7. Comprehensive index grades of Selenium−rich land development and utilization in Guanzhong Region
综合指数 > 0.77 0.68~0.77 0.51~0.68 0.37~0.51 ≤ 0.37 等级 一等 二等 三等 四等 五等 含义 高度适宜 适宜 较不适宜 不适宜 极不适宜 颜色 R∶G∶B 0∶176∶80 146∶208∶80 255∶255∶0 255∶192∶0 255∶0∶0 表 8 临潼区富硒土地开发利用适宜性评价统计
Table 8. Statistics of suitability evaluation of Selenium−rich land development and utilization in Lintong district
等级 开发利用适宜性 综合指数 地块数/个 面积/km2 地块平均
面积/km2土壤硒平均值/
(mg/kg)地形坡度<2°
地块占比/%有灌溉条件
地块占比/%一级 高度适宜 > 0.77 2866 112.08 0.039 0.27 98.26 93.58 二级 适宜 0.68~0.77 4464 136.27 0.031 0.25 94.62 90.59 三级 较不适宜 0.50~0.68 5651 134.71 0.024 0.19 77.10 74.50 四级 不适宜 0.37~0.50 5270 118.79 0.023 0.16 48.99 39.28 五级 极不适宜 ≤ 0.37 3299 63.18 0.019 0.15 25.40 18.70 表 9 临潼区不同适宜性评价区的小麦硒含量特征值及富硒比例统计
Table 9. Statistics of Selenium content eigenvalue and Selenium enrichment ratio of wheat in areas with different suitability evaluations of Lintong district
评价等级 小麦样品数/件 最小值/(mg/kg) 最大值/(mg/kg) 平均值/(mg/kg) 标准差 变异系数 DB 61/T 556–2018 富硒范围/(mg/kg) 富硒比例/% 高度适宜 55 0.031 0.528 0.162 0.110 0.678 ≥ 0.05 94.55 适宜 69 0.034 1.395 0.313 0.313 0.998 85.51 较不适宜 7 0.026 0.265 0.108 0.089 0.831 42.86 不适宜 1 0.028 0.028 0.028 0.000 0.000 0.00 极不适宜 0 - - - - - - -
[1] Broadley M R, White P J, Bryson R J, Meacham M C, Bowen H C, Johnson S E, Hawkesford M J, McGrath S P, Zhao F J, Breward N, Harriman M, Tucker M. 2006. Biofortification of UK food crops with selenium[J]. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 65: 169−181. doi: 10.1079/PNS2006490
[2] Dinh Q T, Cui Z W, Huang J, Tran T A T, Wang D, Yang W X, Zhou F, Wang M K, Yu D S, Liang D L. 2018. Selenium distribution in the chinese environment and its relationship with human health: A review[J]. Environment International, 112: 294−309. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2017.12.035
[3] Dumanski J, Pieri C. 2000. Land quality indicators: Research plan[J]. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 81(2): 93−102.
[4] Eswayah A S, Smith T J, Gardiner P H E. 2016. Microbial transformations of selenium species of relevance to bioremediation[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 82: 4848–4859.
[5] Falco S D, Penov I, Aleksiev A, Van Rensburg T M. 2010. Agrobiodiversity, farm profits and land fragmentation: Evidence from Bulgaria[J]. Land Use Policy, 27(3): 763−771. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2009.10.007
[6] Fan Huimin, Xu Mingxiang, Li Binbin, Zhang Rongrong, Zhang Shengmin, Ma Luyang. 2017. Influence of soil physical properties on salt content in soil profile of farmland in Weibei region[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 31(4): 198−204 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Fan J X, Zeng Y, Sun J X. 2018. The transformation and migration of selenium in soil under different Eh conditions[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 18: 2935–2947.
[8] Gao Bei, Wei Haiyan, Guo Yanlong, Gu Wei. 2015. Potential distribution of Amorphophallus rivieri in the Qinling mountains based on analytic hierarchy process and geographic information system[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 35(21): 7108−7116 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Ge K, Yang G. 1993. The epidemiology of selenium deficiency in the etiological study of endemic diseases in China[J]. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 57(Suppl.): 259−263.
[10] Guo Jinyu, Zhang Zhongbin, Sun Qingyun. 2008. Study and applications of analytic hierarchy process[J]. China Safety Science Joumal, 18(5): 148−153 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] Guo Zhaoyuan, Huang Zili, Fenglixiao. 1992. Soil of Shaanxi Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[12] Han Huijie, Xia Xueqi, Wu Haidong, Tang Ming, Jiang Mingliang. 2019. Evaluation of rice planting suitability using GIS and geochemical land quality data: A case study of Qingyang County, Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco−Agriculture, 27(4): 591−600 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Hou Xianhui, Wang Zhanqi, Yang Jun. 2015. Cultivated land quality evaluation using partition in the Selenium−rich Area of Sanyuan, Fujian Province[J]. Resources Science, 37(7): 1367−1375 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Ji Huawei, Ren Rui, Chen Jiping, Zhang Jijun, Li Aorui, Feng Huawei. 2021. Characteristics of selenium content in different soil types in Guanzhong and its influence on selenium content of corn grain[J]. Northwestern Geology, 54(4): 239−249 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Ju Zilong, Hu Shangjun, Chen Si, Yin Meng, Xia Kun, Wan Xiang. 2022. Research progress and evaluation methods of health geological survey[J]. Resources Environment and Engineering, 36(5): 594−603 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Latruffe L, Piet L. 2014. Does land fragmentation affect farm performance? A case study from Brittany, France[J]. Agricultural Systems, 129: 68−80. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2014.05.005
[17] Li Jiaxi, Huang Huaizeng, Liu Xiaorui. 1999. The application of environmental geochemistry to agriculture and life science[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 19(3): 224−230 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Li Yigeng, Dong Yanxiang, Zheng Jie, Li Yan, Wu Xiaoyong, Zhu Chaohui. 2005. Selenium: Abundant soil survey and assessment in Zhejiang[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 25(3): 323−330 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Li Z, Wu L H, Zhang H, Luo Y M, Christie P. 2015. Effects of soil drying and wetting–drying cycles on the availability of heavy metals and their relationship to dissolved organic matter[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 15: 1510−1519. doi: 10.1007/s11368-015-1090-x
[20] Lintong County Annals Compilation Committee of Shaanxi Province. 1991. Lintong County Annals[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai People's Publishing House (in Chinese).
[21] Liu N N, Wang M, Zhou F, Zhai H, Qi M X, Liu Y, Li Y N, Zhang N C, Ma Y Z, Huang J, Ren R, Liang D L. 2021. Selenium bioavailability in soil–wheat system and its dominant influential factors: A field study in Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 770: 144664. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.144664
[22] Liu Zhaoliang. 2013. Study on application of AHP in agricultural system[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 40(13): 228−232 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Niu Yingchao, Zhou Zhongfa, Wang Li, Dan Yusheng, Feng Qian. 2018. Comprehensive evaluation of soil nutrients in Guizhou agricultural products areas based on the fractal interpolation model[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 37(10): 2207−2218 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Peng Q, Guo L, Ali F, Li J, Qin S Y, Feng P Y, Liang D L. 2016. Influence of Pak choi plant cultivation on Se distribution speciation and bioavailability in soil[J]. Plant Soil, 403: 331−342. doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-2810-8
[25] Peng Q, Wang M K, Cui Z W, Huang J, Chen C, Guo L. 2017. Assessment of bioavailability of selenium in different plant–soil systems by diffusive gradients in thin–films (DGT)[J]. Environmental Pollution, 225: 637−643. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2017.03.036
[26] Qian Fengkui, Wang Qiubin, Li Na. 2015. High−standard prime farmland planning based on evaluation of farmland quality and site conditions[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 31(18): 225−232 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Rayman M P. 2012. Selenium and human health[J]. Lancet, 379: 1256−1268. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61452-9
[28] Ren Rui, Wang Mingxia, Chen Jiping, Chao Xu, Wang Hui, Xie Ying, Meng Qinyu. 2018. Distribution of soil selenium in Guanzhong area and its influencing factors[J]. Mineral Exploration, 9(9): 1827−1833 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Ren Rui, Zhang Zhimin, Wang Hui, Chen Jiping, Qiao Xinxing, Liang Dongli. 2023. Exploring selenium enrichment criteria for soils in the Guanzhong area, Shaanxi Province: A case study of wheat[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 47(5): 1354−1360 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[30] Sklenicka P. 2016. Classification of farmland ownership fragmentation as a cause of land degradation: A review on typology, consequences, and remedies[J]. Land Use Policy, 57: 694−701. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.06.032
[31] Sun Kuangling. 2021. Focus on genetic quality strengthen agricultural brand[J]. Chinese Brands, 3: 83−85,82 (in Chinese).
[32] Wang D, Zhou F, Yang W X, Peng Q, Man N, Liang D L. 2017. Selenate redistribution during aging different Chinese soils and the dominant influential factors[J]. Chemosphere, 182: 284−292. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.05.014
[33] Winkel L H E, Johnson C A, Lenz M, Grundl T, Leupin O X, Amini M, Charlet L. 2012. Environmental selenium research: From microscopic processes to global under–standing[J]. Environmental. Science & Technology, 46: 571–579.
[34] Wu Guanhua. 2019. Evaluation of New Cultivated Land Quality in Land Exploitation at Plot Scale: A Case Study of Fuping County[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1–99 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Wu Kening, Zhao Rui. 2019. Soil texture classification and its application in China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 56(1): 227−240 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Xu Xuesheng, Luo Jianlan, Huang Fengqiu, Wang Huanhuan, Xia Xueqi, Lu Jiang, Zhang Zihu, Zhu Lifen. 2022. Construction of the evaluation system for Se−rich arable land and its application in Xinxu Town, Xintian County, Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(3): 789−801 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Yan Yifan, Liu Jianli, Zhang Jiabao. 2014. Evaluation method and model analysis for productivity of cultivated land[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 30(5): 204−210 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Yu Jinpeng. 2015. The Applied Research of Different Methods in the Natural Productivity Evaluation of Cultivated Land in Jiangxi Province[D]. Jiangxi: Jiangxi Agricultural University, 1–83 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Zhang Jiangzhou, Li Yizan, Li Ying, Zhang Junling, Zhang Fusuo. 2022. Advances in the indicator system and evaluation approaches of soil health[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 59(3): 603−616 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Zhao Huafu, Wu Kening. 2021. Discussion of soil survey, land type, and cultivated land evaluation: Based on academic thoughtofmr Ni Shaoxiang’s land evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning, 42(10): 245−252 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Zhao Qiguo, Yin Xuebin, Sun Min, Liu Yongxian, Hou Feifan, Zhang Ning. 2018. A ten−year overview of functional agriculture from 2008 to 2018[J]. Soils, 50(6): 1061−1071 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Zhao Yeting. 2015. Spatial Characteristics and Changes of Soil Nutrients in Cultivated Land of Guanzhong Region in Shaanxi Province Based on GIS[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture & Forestry University, 1–190 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhu Yongguan, Li Baozhi, Lin Tao. 2021. Fostering healthy soil to push forward rural revitalization[J]. Science and Technology Review, 39(23): 54−58 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] 樊会敏, 许明祥, 李彬彬, 张蓉蓉, 张圣民, 马露洋. 2017. 渭北地区农田土壤物理性质对土壤剖面盐分的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 31(4): 198−204.
[45] 高蓓, 卫海燕, 郭彦龙, 顾蔚. 2015. 基于层次分析法和GIS的秦岭地区魔芋潜在分布研究[J]. 生态学报, 35(21): 7108−7116.
[46] 郭金玉, 张忠彬, 孙庆云. 2008. 层次分析法的研究与应用[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 18(5): 148−153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3033.2008.05.025
[47] 郭兆元, 黄自立, 冯立孝. 1992. 陕西土壤[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[48] 韩慧杰, 夏学齐, 吴海东, 汤明, 姜明亮. 2019. 基于GIS和土地质量地球化学数据的水稻种植适宜性评价—以安徽省青阳县为例[J]. 中国生态农业学报(中英文), 27(4): 591−600.
[49] 侯现慧, 王占岐, 杨俊. 2015. 富硒区耕地质量评价及利用分区研究—以福建省三元区为例[J]. 资源科学, 37(7): 1367−1375.
[50] 姬华伟, 任蕊, 陈继平, 张继军, 李傲瑞, 冯伟华. 2021. 关中不同类型土壤硒含量特征及其对玉米籽粒硒含量的影响[J]. 西北地质, 54(4): 239−249.
[51] 居字龙, 胡尚军, 陈思, 尹猛, 夏坤, 万翔. 2022. 健康地质调查研究进展及其评价方法[J]. 资源环境与工程, 36(5): 594−603.
[52] 李家煕, 黄怀曾, 刘晓瑞. 1999. 环境地球化学在农业和生命科学上的应用研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 19(3): 224−230. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.03.005
[53] 郦逸根, 董岩翔, 郑洁, 李琰, 吴小勇, 朱朝晖. 2005. 浙江富硒土壤资源调查与评价[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(3): 323−330. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2005.03.008
[54] 刘朝亮. 2013. 层次分析法在农业系统中的应用研究[J]. 广东农业科学, 40(13): 228−232. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-874X.2013.13.066
[55] 牛颖超, 周忠发, 王历, 但雨生, 冯倩. 2018. 基于分形插值模型的贵州农产品区土壤养分综合评价研究[J]. 环境化学, 37(10): 2207−2218. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017112805
[56] 钱凤魁, 王秋兵, 李娜. 2015. 基于耕地质量与立地条件综合评价的高标准基本农田划定[J]. 农业工程学报, 31(18): 225−232. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2015.18.031
[57] 任蕊, 王明霞, 陈继平, 晁旭, 王晖, 谢颖, 孟秦宇. 2018. 陕西关中地区土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 矿产勘查, 9(9): 1827−1833. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2018.09.023
[58] 任蕊, 张志敏, 王晖, 陈继平, 乔新星, 梁东丽. 2023. 陕西关中土壤富硒标准研究与探讨—以小麦为例[J]. 物探与化探, 47(5): 1354−1360.
[59] 陕西省临潼县志编纂委员会. 1991. 临潼县志[M]. 上海: 上海人民出版社.
[60] 孙矿玲. 2021. 聚焦品种品质塑强农业品牌[J]. 中国品牌, 3: 83−85, 82.
[61] 吴冠华. 2019. 地块尺度土地开发的新增耕地质量评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1–99.
[62] 吴克宁, 赵瑞. 2019. 土壤质地分类及其在我国应用探讨[J]. 土壤学报, 56(1): 227−240. doi: 10.11766/trxb201803120129
[63] 徐雪生, 骆检兰, 黄逢秋, 王欢欢, 夏学齐, 鲁江, 张子虎, 朱丽芬. 2022. 富硒耕地质量评价体系构建及其在湖南省新田县新圩镇的应用[J]. 中国地质, 49(3): 789−801. doi: 10.12029/gc20220308
[64] 闫一凡, 刘建立, 张佳宝. 2014. 耕地地力评价方法及模型分析[J]. 农业工程学报, 30(5): 204−210. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-6819.2014.05.026
[65] 余锦鹏. 2015. 不同方法在江西省省级耕地地力评价中的应用研究[D]. 江西: 江西农业大学, 1–83.
[66] 张江周, 李奕赞, 李颖, 张俊伶, 张福锁. 2022. 土壤健康指标体系与评价方法研究进展[J]. 土壤学报, 59(3): 603−616.
[67] 赵华甫, 吴克宁. 2021. 试论土壤调查、土地类型与耕地评价—兼论倪绍祥先生的土地评价思想[J]. 中国农业资源与区划, 42(10): 245−252.
[68] 赵其国, 尹雪斌, 孙敏, 刘永贤, 侯非凡, 张宁. 2018. 2008—2018年功能农业的理论发展与实践[J]. 土壤, 50(6): 1061−1071.
[69] 赵业婷. 2015. 基于GIS的陕西省关中地区耕地土壤养分空间特征及其变化研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 1–190.
[70] 朱永官, 李宝值, 吝涛. 2021. 培育健康土壤, 助力乡村振兴[J]. 科技导报, 39(23): 54−58.
-



 下载:
下载:


