Evolution Characteristics and Change Mechanism of Arsenic and Fluorine in Shallow Groundwater from a Typical Irrigation Area in the Lower Reaches of the Yellow River (Henan) in 2010—2020
-
摘要:
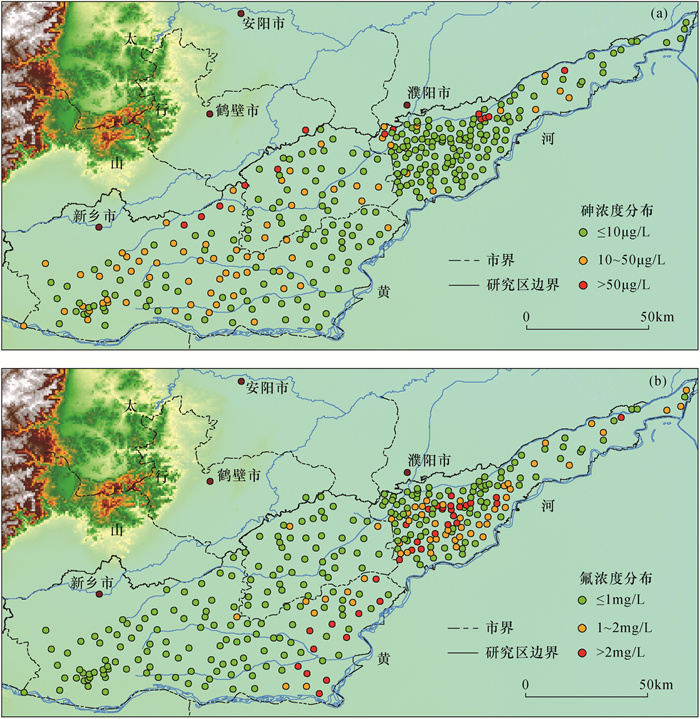
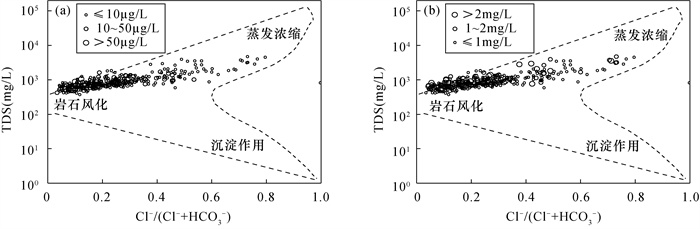
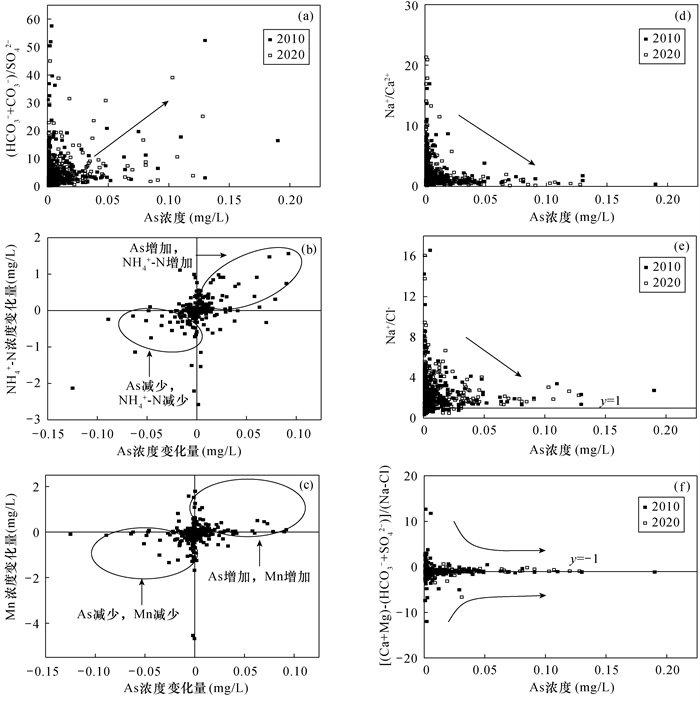
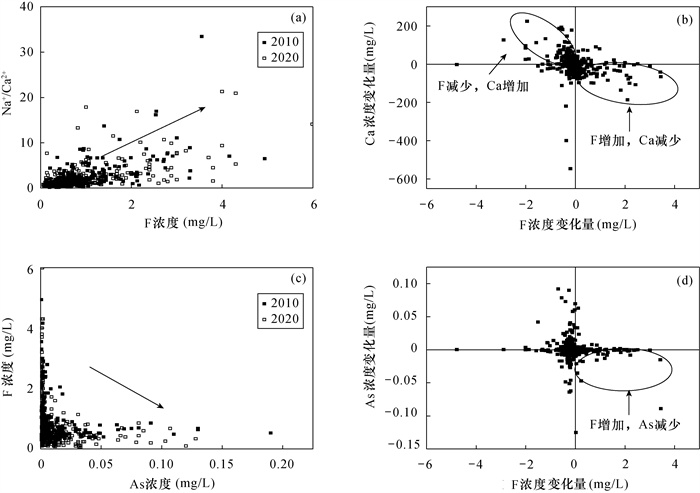
黄河下游典型灌区河南段是豫北平原重要的农业种植区。该地区浅层水质整体较差,因常用于作物灌溉或家畜饮用,会对人体健康产生风险,因此对该地区地下水中砷与氟浓度变化特征和机制的研究将有助于提高对该地区地下水污染的认识水平。本文基于2010年和2020年在灌区范围内采集的327组浅层地下水样品,研究区内地下水砷和氟分布情况,并在此基础上对比研究十年间灌区浅层地下水中砷、氟的演化特征,探索分析砷与氟浓度及空间变化机制。研究结果表明:该地区浅层地下水中存在砷与氟超标问题,2020年浅层地下水中高砷(砷浓度大于10μg/L)和高氟(氟浓度大于1mg/L)的样品数量分别占总数的26.1%和26.06%。高砷水分布在太行山前洼地与黄河冲积平原等泥沙互层结构的沉积环境中,还原性较强,同时地下水径流不畅,较强的阳离子交换作用使得其所处环境中Ca2+浓度较高。近十年间砷浓度增加的水样占总数31.8%,砷浓度减少的水样占36.7%。砷浓度的增长(减少)是地下水还原性增强(减弱)使得锰氧化物溶解释放(吸附)导致。近十年间不同地区农业灌溉和水源置换等用水方式导致水位变化是引起砷浓度变化的潜在因素。高氟水主要分布在河南新乡与濮阳的黄河沿线,氟离子浓度受到沉积物中萤石等钙质矿物溶解影响,使得高氟地下水出现在低钙环境中。近十年间研究区中氟离子浓度减少的占总数60.2%,氟离子浓度增加的占32.1%,整体变化趋势向好,但是高氟区中氟离子浓度继续增加。氟浓度的变化同样受到Ca2+变化影响,在Ca2+浓度降低(升高)时氟浓度进一步升高(降低)。地下水中氟升高地区分布在黄河沿线,因此受到黄河水补给影响较大,地下水径流条件较好,阳离子交换作用减弱,使得Ca2+浓度降低,此时地下水中砷浓度受到环境影响而降低,因此研究区氟增加地区中砷与氟的分布和演化呈现反向关系。
Abstract:BACKGROUND A typical irrigation area of the downstream Yellow River (Henan) is an important agricultural planting area in the northern Henan Plain. The shallow water quality in this area is generally poor, which is often used for crop irrigation or livestock drinking, posing a risk to human health. Therefore, the study on the variation characteristics and mechanism of arsenic and fluorine content in groundwater in this area will help to improve the level of understanding of pollution in this area.
OBJECTIVES To investigate the spatial variation characteristics and mechanism of arsenic and fluorine concentration.
METHODS Based on 327 groups of shallow groundwater samples collected in 2010 and 2020 in the irrigated area, the distribution of arsenic and fluorine in the groundwater of the irrigated area was analyzed, and compared to the evolution characteristics of arsenic and fluorine in the shallow groundwater of the irrigated area in the last ten years.
RESULTS In 2020, the number of samples with high arsenic concentration (>10μg/L) and high fluorine concentration (>1mg/L) in shallow groundwater accounted for 26.1% and 26.06%, respectively. The high-arsenic groundwater was distributed in the sedimentary environments with interbedding structure of sediment, such as the Taihang Mountain depression and the Yellow River alluvial plain, with strong reducibility, poor groundwater runoff and strong cation exchange, resulting in high concentration of Ca2+ in the environment. Arsenic concentration increased in 31.8% of water samples and decreased in 36.7% of water samples in the last ten years. The increase of arsenic content was caused by the dissolution and release of manganese oxide due to the enhanced reducibility of groundwater. The variation of water level caused by agricultural irrigation and water replacement in different areas during the last ten years was a potential factor of arsenic concentration change. The high-fluorine groundwater was mainly distributed along the Yellow River in Xinxiang and Puyang, Henan Province. The concentration of fluorine ion was affected by the dissolution of calcareous minerals such as fluorite in the sediments, which made the high-fluorine groundwater appear in the low-calcium environment. In the last ten years, the study area with decreased fluorine ion concentration accounted for 60.2%, whereas areas with increased fluorine ion concentration accounted for 32.1%. The overall change trend was good, but the fluorine ion concentration in the high fluorine area continued to increase. Changes in fluorine concentration were also affected by changes in Ca2+, with further increases (decreases) as Ca2+ concentration decreased (increased). Elevated fluorine in groundwater was distributed along the Yellow River, affected greatly by the Yellow River water supply. So, the groundwater flow condition was good and the cation exchange was weakened, reducing the Ca2+ content. At this time, the arsenic content in the groundwater was less affected by the environment, so the study area with fluorine increase showed an inverse relationship between arsenic and fluorine in terms of regional distribution and evolution.
CONCLUSIONS This study will provide support for rational utilization of groundwater in the study area.
-

-
表 1 2010年和2020年研究区主要离子浓度分布
Table 1. Main ions concentration distribution of the study area in 2010 and 2020
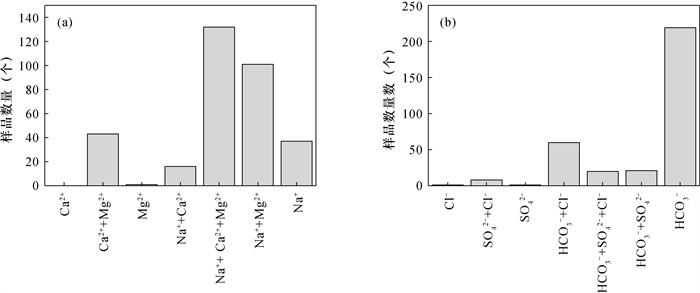
离子类型 2010年测试值 2020年测试值 最大值(mg/L) 最小值(mg/L) 平均值(mg/L) 最大值(mg/L) 最小值(mg/L) 平均值(mg/L) K+ 225 0.02 4.11 226 0.380 5.89 Ca2+ 680 15.1 95.7 470 2.40 95.1 Na+ 1.97×103 16.8 203 894 17.6 188 Mg2+ 834 15.9 76.7 417 5.95 72.6 HCO3- 1.48×103 209 626 1.21×103 252 617 Cl- 2.49×103 10.1 195 1.38×103 8.51 165 SO42- 4.43×103 5.82 200 1.58×103 5.76 182 TDS 9.37×103 326 1.10×103 4.73×103 374 1.04×103 -
[1] 沈照理, 郭华明, 徐刚, 等. 地下水化学异常与地方病[J]. 自然杂志, 2010, 32(2): 83-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2010.02.006
Shen Z L, Guo H Y, Xu G, et al. Abnormal groundwater chemistry and endemic disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Nature, 2010, 32(2): 83-89. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-9608.2010.02.006
[2] 邓安琪, 董兆敏, 高群, 等. 中国地下水砷健康风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017(9): 3556-3565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.09.044
Deng A Q, Dong Z M, Gao Q, et al. Health risk assessment of arsenic in groundwater across China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017(9): 3556-3565. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.09.044
[3] Senthil R B, Senthil K P. A review on sources, identification and treatment strategies for the removal of toxic arsenic from water system[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 418: 126299. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126299
[4] 吴功建, 李家熙, 黄怀曾, 等. 硒氟的地球化学特征与人体健康[J]. 岩矿测试, 1996, 15(4): 241-250. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19960481
Wu G J, Li J X, Huang H Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium and fluorine and human health[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 1996, 15(4): 241-250. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_19960481
[5] Manish K, Ritusmita G, Arbind K P, et al. Scenario, perspectives and mechanism of arsenic and fluoride Co-occurrence in the groundwater: A review[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 249: 126126. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126126
[6] Kumar Y M, Saidulu B D, Kumar G A, et al. Status and management of arsenic pollution in groundwater: A comprehensive appraisal of recent global scenario, human health impacts, sustainable field-scale treatment technologies[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2021, 9: 105203. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105203
[7] 何锦, 张福存, 韩双宝, 等. 中国北方高氟地下水分布特征和成因分析[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3): 621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.012
He J, Zhang F C, Han S B, et al. The distribution and genetic types of high-fluoride groundwater in northern China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3): 621-626. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.012
[8] 郭华明, 杨素珍, 沈照理. 富砷地下水研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2007.22(11): 1109-1117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.11.002
Guo H M, Yang S Z, Shen Z L. High arsenic groundwater in the world: Overview and research perspectives[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(11): 1109-1117. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.11.002
[9] Ruohan W, Podgorski J, Berg M, et al. Geostatistical model of the spatial distribution of arsenic in groundwaters in Gujarat State, India[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2021, 43(7): 2649-2664. doi: 10.1007/s10653-020-00655-7
[10] Janardhana R N. Arsenic in the geo-environment: A review of sources, geochemical processes, toxicity and removal technologies[J]. Environmental Research, 2022, 203: 111782. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111782
[11] Shakir A, Sachin T, Aditya S, et al. Worldwide contamination of water by fluoride[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2016, 14(3): 291-315. doi: 10.1007/s10311-016-0563-5
[12] 王焰新, 苏春利, 谢先军, 等. 大同盆地地下水砷异常及其成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(3): 771-780. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.033
Wang Y X, Su C L, Xie X J, et al. The genesis of high arsenic groundwater: A case study in Datong Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(3): 771-780. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.03.033
[13] 高存荣. 河套平原地下水砷污染机理的探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 1999, 10(2): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH902.003.htm
Gao C R. Research on the mechanism of arsenic pollution in groundwater in the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1999, 10(2): 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH902.003.htm
[14] 汤洁, 卞建民, 李昭阳, 等. 吉林省饮水型砷中毒区地下水砷的分布规律与成因研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2014, 21(4): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404004.htm
Tang J, Bian J M, Li Z Y, et al. A study of the distribution and causes of groundwater arsenic in the arsenism area of drinking water type in Jilin Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(4): 30-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201404004.htm
[15] Guo H M, Wen D G, Liu Z Y. A review of high arsenic groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: Distribution, characteristics and geochemical processes[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 41: 196-217. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.12.016
[16] 毛若愚, 郭华明, 贾永锋, 等. 内蒙古河套盆地含氟地下水分布特点及成因[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 260-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602029.htm
Mao R Y, Guo H M, Jia Y F, et al. Distribution characteristics and genesis of fluoride groundwater in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science Frontier, 2016, 23(2): 260-268. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602029.htm
[17] 郭华明, 郭琦, 贾永锋, 等. 中国不同区域高砷地下水化学特征及形成过程[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2013, 35(3): 83-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.008
Guo H M, Guo Q, Jia Y F, et al. Chemical characteristics and geochemical processes of high arsenic groundwater in different regions of China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2013, 35(3): 83-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2013.03.008
[18] 张怀胜, 蔡五田, 边超, 等. 衡水市桃城区浅层高氟地下水水化学特征与成因分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(24): 10191-10198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.24.013
Zhang H S, Cai W T, Bian C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of shallow high-fluorine groundwater in Taocheng District, Hengshui City[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(24): 10191-10198. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.24.013
[19] 申月芳, 马晗宇, 杨耀栋, 等. 武清凹陷浅层含氟地下水演化特点及成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(2): 528-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202102031.htm
Shen Y F, Ma H Y, Yang Y D, et al. Evolution characteristics and genesis of shallow fluorine-bearing groundwater in Wuqing Sag[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 528-535. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH202102031.htm
[20] 黄冠星, 孙继朝, 荆继红, 等. 珠江三角洲典型区水土中砷的分布[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 49(1): 131-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ201001030.htm
Huang G X, Sun J C, Jing J H, et al. Distribution of arsenic in water and soil in the representative area of the Pearl River Delta[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2010, 49(1): 131-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSDZ201001030.htm
[21] 朱其顺, 许光泉. 中国地下水氟污染的现状及研究进展[J]. 环境科学与管理, 2009(1): 42-44, 51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.01.012
Zhu Q X, Xu G Q. The current situation and research progress of ground water fluorine pollution, in China[J]. Environmental Science and Management, 2009(1): 42-44, 51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1212.2009.01.012
[22] Guo H M, Yang S Z, Tang X H, et al. Groundwater geochemistry and its implications for arsenic mobilization in shallow aquifers of the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2008, 393(1): 131-144. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.12.025
[23] 曹文庚, 董秋瑶, 谭俊, 等. 河套盆地晚更新世以来黄河改道对高砷地下水分布的控制机制[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2021, 19(1): 140-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202101014.htm
Cao W G, Dong Q Y, Tan J, et al. Mechanism of Yellow River diversion in controlling high arsenic groundwater distribution since Late Pleistocene[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2021, 19(1): 140-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD202101014.htm
[24] 王喜宽, 黄增芳, 赵锁志, 等. 河套地区盐碱化和砷氟中毒问题探讨[J]. 岩矿测试, 2007, 26(4): 328-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.04.017 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_200704105
Wang X K, Huang Z F, Zhao S Z, et al. A preliminary study on soil salification and arseniasis-fluorosis in Hetao area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(4): 328-330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.04.017 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_200704105
[25] 赵锁志, 王喜宽, 黄增芳, 等. 内蒙古河套地区高氟水成因分析[J]. 岩矿测试, 2007, 26(4): 320-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.04.015 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_200704103
Zhao S Z, Wang X K, Huang Z F, et al. Study on formation causes of high fluorine groundwater in Hetao area of Inner Mongolia[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2007, 26(4): 320-324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2007.04.015 http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/id/ykcs_200704103
[26] 韩双宝, 李甫成, 王赛, 等. 黄河流域地下水资源状况及其生态环境问题[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(4): 1001-1019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104004.htm
Han S B, Li F C, Wang S, et al. Groundwater resource and eco-environmental problem of the Yellow River Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(4): 1001-1019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202104004.htm
[27] Banning A. Geogenic arsenic and uranium in Germany: Large-scale distribution control in sediments and groundwater[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 405: 124186. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124186
[28] 杨文蕾, 沈亚婷. 水稻对砷吸收的机理及控制砷吸收的农艺途径研究进展[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(4): 475-492. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202004160052
Yang W L, Shen Y T. A review of research progress on the absorption mechanism of arsenic and agronomic pathways to control arsenic absorption[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(4): 475-492. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.202004160052
[29] 吴昆明, 郭华明, 魏朝俊. 天然磁铁矿化学改性及其在水体除砷中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2017, 36(1): 32-39. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.005
Wu K M, Guo H M, Wei C J. Chemical modification of natural magnetite and its application in arsenic removal from a water environment[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2017, 36(1): 32-39. http://www.ykcs.ac.cn/article/doi/10.15898/j.cnki.11-2131/td.2017.01.005
[30] 王继华, 朱洪生, 潘登. 豫北平原地下水水化学和水质分布特征[J]. 水电能源科学, 2020, 38(12): 49-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY202012012.htm
Wang J H, Zhu H S, Pan D. Hydrochemistry character-istics and water quality distribution of groundwater in North Henan Plain[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2020, 38(12): 49-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY202012012.htm
[31] 仝长水, 吴继臣, 苗晋祥, 等. 豫北平原地下水开发利用与水质演化规律[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2005(5): 13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.05.004
Tong C S, Wu J C, Miao J X, et al. A study of the development and water quality evolution of groundwater in the Northern Henan Plain[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2005(5): 13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2005.05.004
[32] 左奎孟. 延津县氟(苦)水区状况及治理[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2007, 26(4): 164-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS2007S1075.htm
Zuo K M. Status and management of fluoride (bitter) water area in Yanjin County[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2007, 26(4): 164-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GGPS2007S1075.htm
[33] 芦天成, 何光星, 张明俊. 新乡市地方性砷中毒流行病学调查[J]. 河南预防医学杂志, 2010, 25(5): 290-291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF201004023.htm
Lu T C, He G X, Zhang M J. Epidemiological survey of endemic arsenism in Xinxiang City[J]. Henan Journal of Preventive Medicine, 2010, 25(5): 290-291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYF201004023.htm
[34] 胡冰殊, 柳西亚, 王宁, 等. 河南省东部平原浅层地下水水质特征分析[J]. 地下水, 2021, 43(2): 33-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU202102010.htm
Hu B S, Liu X Y, Wang N, et al. Analysis of groundwater quality in the shallow aquifers of the east plain in Henan[J]. Ground Water, 2021, 43(2): 33-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU202102010.htm
[35] Cao W G, Guo H M, Zhang Y L, et al. Controls of paleo-channels on groundwater arsenic distribution in shallow aquifers of alluvial plain in the Hetao Basin, China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2017, 613-614(1): 958-968. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0048969717325330
[36] Gibbs R J. Mechanisms of controlling world water chemistry[J]. Science, 1970, 170: 1088-1090. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1088
[37] 柳凤霞, 史紫薇, 钱会, 等. 银川地区地下水水化学特征演化规律及水质评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(9): 2055-2066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201909013.htm
Liu F X, Shi Z W, Qian H, et al. Evolution of groundwater hydrochemical characteristics and water quality evaluation in Yinchuan area[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(9): 2055-2066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201909013.htm
[38] 吴丁丁, 姚震, 贾凤超, 等. 新疆哈密盆地地下水水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020.34(7): 133-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202007019.htm
Wu D D, Yao Z, Jia F C, et al. Hydro-geochemical characteristics and genetic analysis of groundwater in Hami Basin, Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(7): 133-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202007019.htm
[39] Huq M E, Su C L, Fahad S, et al. Distribution and hydrogeochemical behavior of arsenic enriched groundwater in the sedimentary aquifer comparison between Datong Basin (China) and Kushtia District (Bangladesh)[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2018, 25(16): 15830-15843. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29582329
[40] 李巧, 周金龙, 曾妍妍. 奎屯河及玛纳斯河流域平原区地下水中氮素对砷迁移富集的影响[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(10): 2227-2234. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017021307
Li Q, Zhou J L, Zeng Y Y. Effects of nitrogens on the migration and enrichment of arsenic in the groundwater in the plain area of Kuitun River and Manas River Basin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(10): 2227-2234. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2017021307
[41] Omolola A A, Reda M A, Jeffrey S H, et al. Pleistocene sands of the Mississippi River Alluvial Aquifer produce the highest groundwater arsenic concentrations in southern Louisiana, USA[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2021, 595: 125995. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.125995
[42] Haugen E A, Jurgens B C, Arroyo-Lopez J A, et al. Groundwater development leads to decreasing arsenic concentrations in the San Joaquin Valley, California[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2021, 771: 145223. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145223
[43] 张景涛, 史浙明, 王广才, 等. 柴达木盆地大柴旦地区地下水水化学特征及演化规律[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4): 194-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202104026.htm
Zhang J T, Shi Z M, Wang G C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Dachaidan area, Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(4): 194-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202104026.htm
[44] 宋晨, 马斌, 梁杏, 等. 玛纳斯河流域山前平原地下水水化学特征与补给来源[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(1): 160-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202101024.htm
Song C, Ma B, Liang X, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and recharge of groundwater in piedmont plain in the Manas River Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(1): 160-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202101024.htm
[45] Wang Y X, Li J X, Ma T, et al. Genesis of geogenic contaminated groundwater: As, F and I[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2020. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1807452.
[46] 刘圣锋, 高柏, 张海阳, 等. 海拉尔盆地地下水氟的分布特征及富集机理[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(10): 169-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202110024.htm
Liu S F, Gao B, Zhang H Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and enrichment mechanism of groundwater fluorine in Hailaer Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(10): 169-177. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202110024.htm
[47] 吕晓立, 刘景涛, 朱亮, 等. 甘肃省秦王川盆地地下水氟富集特征及影响因素[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2020, 34(3): 188-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202003027.htm
Lv X L, Liu J T, Zhu L, et al. Evolution feature and gensis of fluoride groundwater in shallow aquifer from Qin Wangchuan Basin[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2020, 34(3): 188-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHZH202003027.htm
[48] 张茂增. 黄土的活性氟与黄土中地下水含氟量[J]. 第四纪研究, 1986(1): 28-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ198601005.htm
Zhang M Z. Active fluorine in loess and fluoride content in groundwater of loess[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 1986(1): 28-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ198601005.htm
[49] Li J X, Wang Y X, Xie X J, et al. Hierarchical cluster analysis of arsenic and fluoride enrichments in groundwater from the Datong Basin, Northern China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 118: 77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.05.002
[50] 刘文波. 河套平原地下水化学特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
Liu W B. Groundwater hydro-chemical characteristic study in Hetao Plain[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
-



 下载:
下载: