Analysis on geological characteristics and prospecting potential of the Central African Cu-Co metallogenic belt
-
摘要:
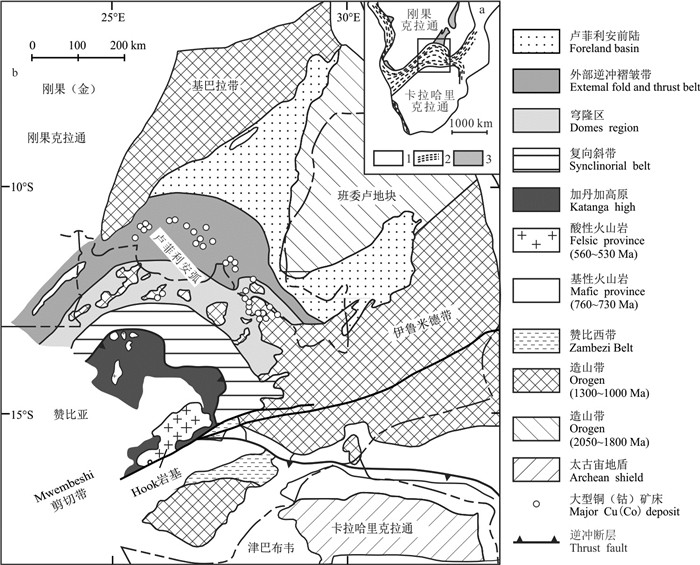
研究目的 横跨刚果(金)和赞比亚边境地区的中非铜钴成矿带是世界上著名的沉积岩层控型铜钴成矿带,是全球第三大铜产地和第一大钴产地,然而其成矿规律和成矿潜力仍不明朗。
研究方法 本文通过对中非铜钴成矿带地质背景、构造演化与成矿、矿床时空分布规律、矿床模型等方面的研究,选择地层、构造、地球化学、遥感蚀变等与成矿密切相关的地质要素图层,采用模糊证据权法圈出32个铜(钴)远景区。依据成矿后验概率计算了在不同概率下每个远景区未发现矿床数量。
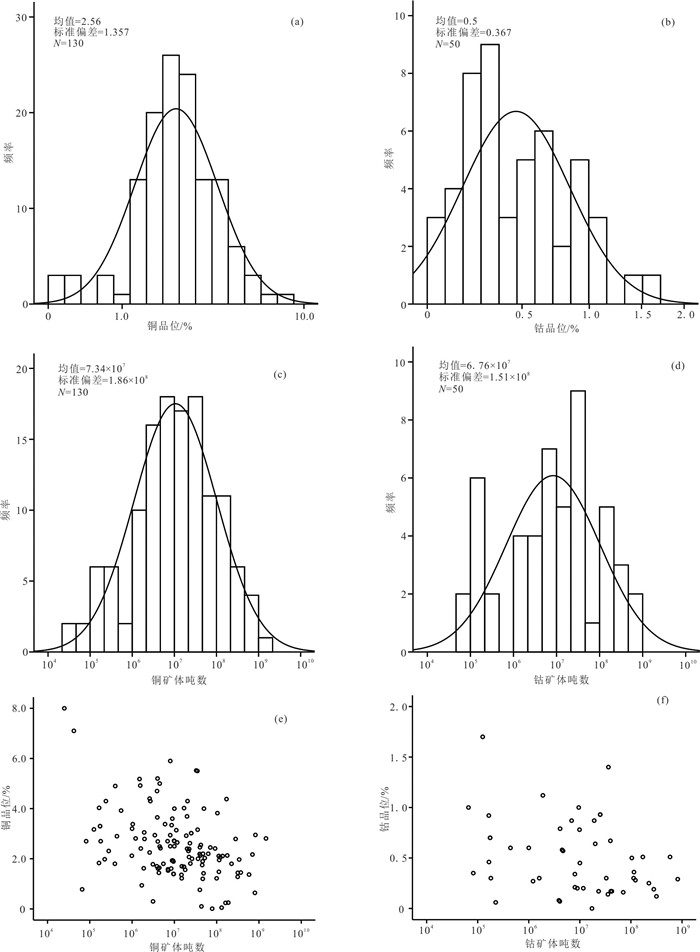
研究结果 结合吨位-品位模型所开展的蒙特卡洛模拟表明,该地区未发现的铜资源量平均估计为2.88亿t,钴资源量平均估计为1992万t。
结论 中非铜钴成矿带复杂的演化历史形成了该地区沉积成矿、热液成矿、表生富集等多种成矿作用的叠加,铜(钴)成矿作用贯穿成矿带演化过程,成矿作用与地层和构造密切相关。其中,刚果(金)利卡西-科卢韦齐地区可能存在很好的找矿前景。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
Objective The Central African copper-cobalt metallogenic belt which straddles the border area between the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and Zambia, is the world's most famous sediment-hosted stratabound copper-cobalt metallogenic belt. It is the world's third-largest copper and first-largest cobalt producer, but its mineralization pattern and potential are still unclear.
Methods In this paper, the geological setting, tectonic evolution and mineralization, temporal-spatial distribution rules of deposits, deposit models of the Central African copper-cobalt metallogenic belt were studied. 32 copper (cobalt) prospective areas were delineated by applying the fuzzy weight of evidence method with stratigraphic, tectonic, geochemical, remote sensing alteration and other geological elements that are closely related to mineralization. The number of undiscovered deposits in each prospective area was calculated based on the posterior probability of mineralization at different probabilities.
Results Monte Carlo simulation combined with the tonnage-grade model indicate that the average undiscovered copper resource in this area is estimated to be 288 million tons and the average cobalt resource is estimated to be 19.92 million tons, respectively.
Conclusions The complex evolutionary history of the Central African copper and cobalt metallogenic belt has resulted in the superposition of multiple metallogenic interactions such as sedimentary mineralization, hydrothermal mineralization and epigenetic enrichment in this region, with copper (cobalt) mineralization running through the evolution of the belt and mineralization closely related to stratigraphy and tectonics. In particular, the Likasi-Kolwezi area of the Democratic Republic of the Congo may have good prospects for mineralization.
-

-
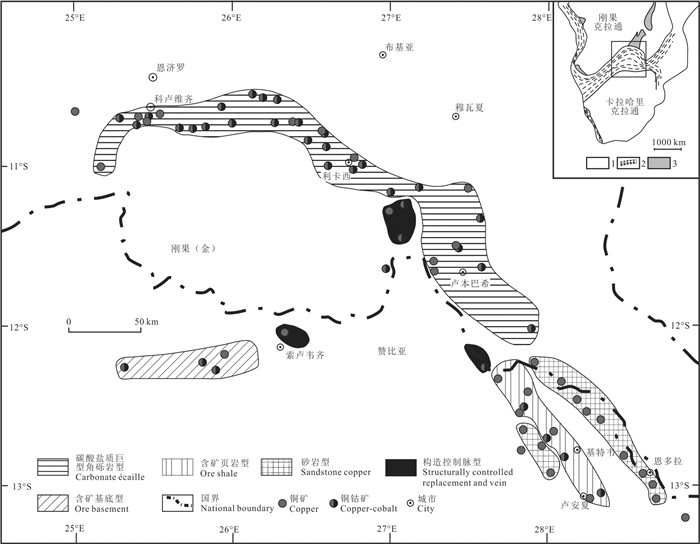
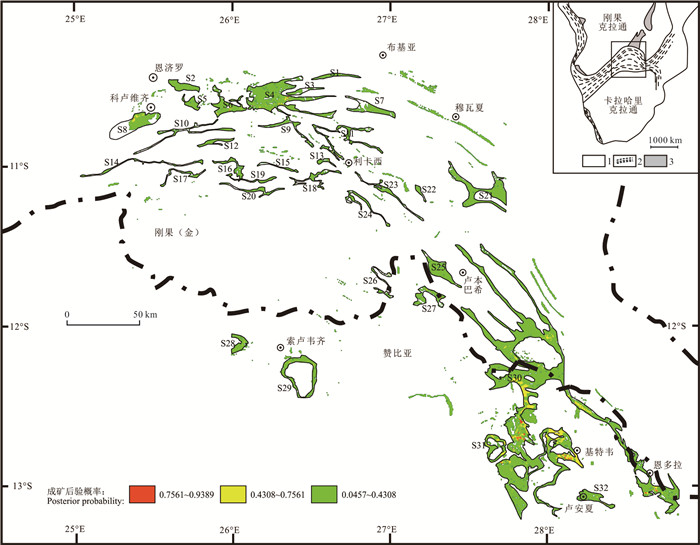
图 1 中非铜钴成矿带地质简图(据Selley et al., 2005; Kampunzu et al., 2009修改)
Figure 1.
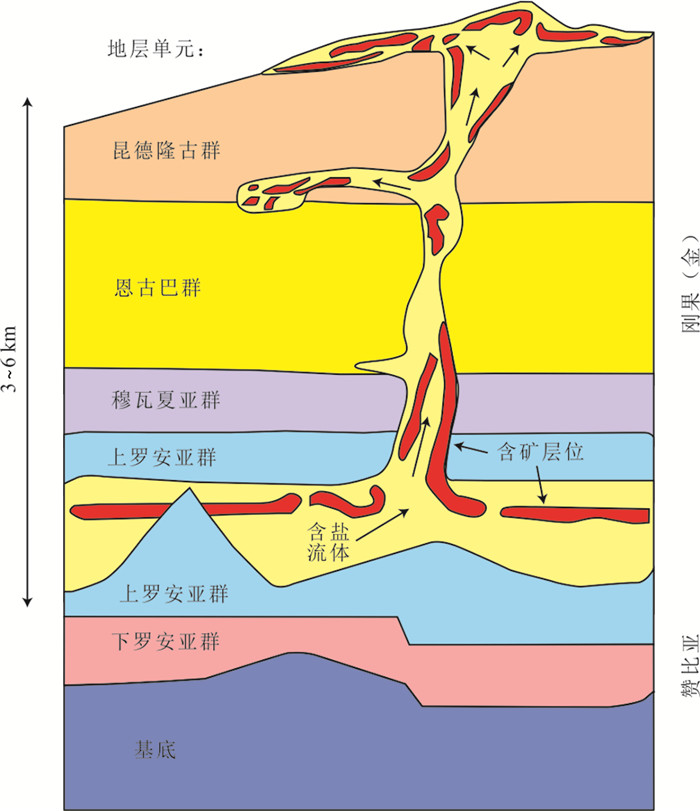
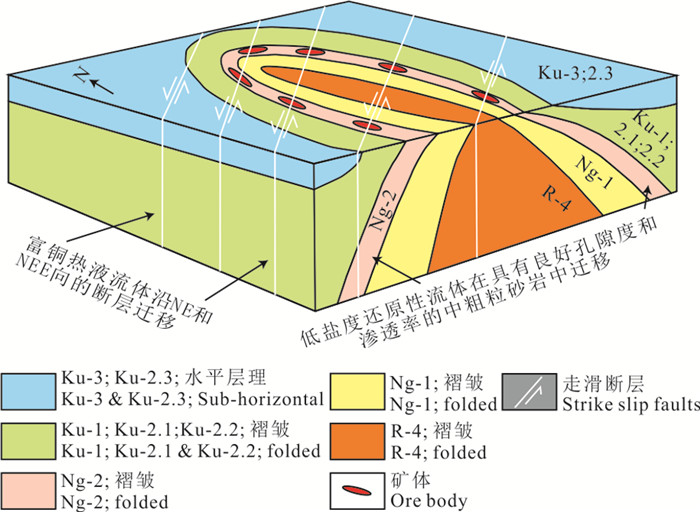
图 3 含矿页岩型铜(钴)矿床成矿模式示意图(据Large et al., 2017)
Figure 3.
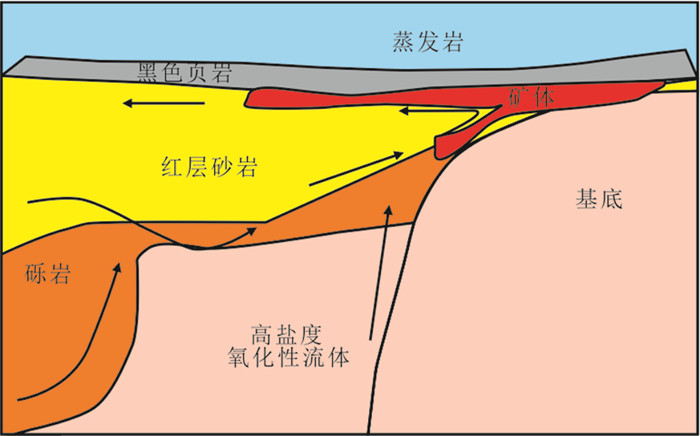
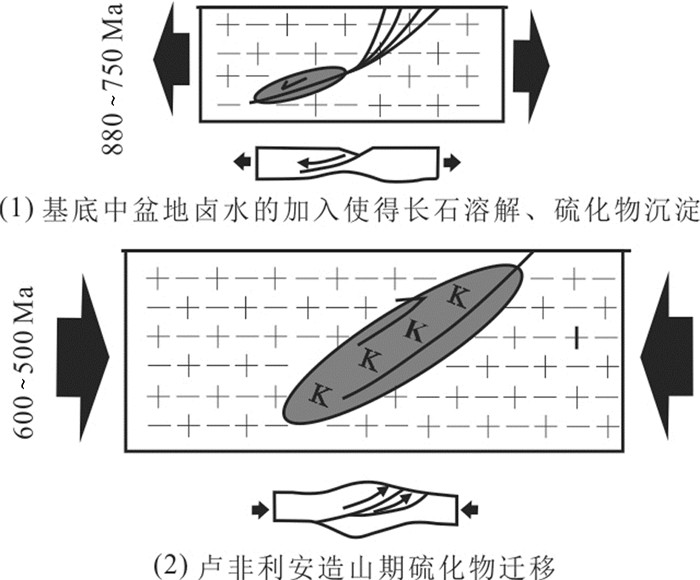
图 4 碳酸盐岩质巨型角砾岩型铜(钴)矿床成矿模式示意图(据Hitzman et al., 2012)
Figure 4.
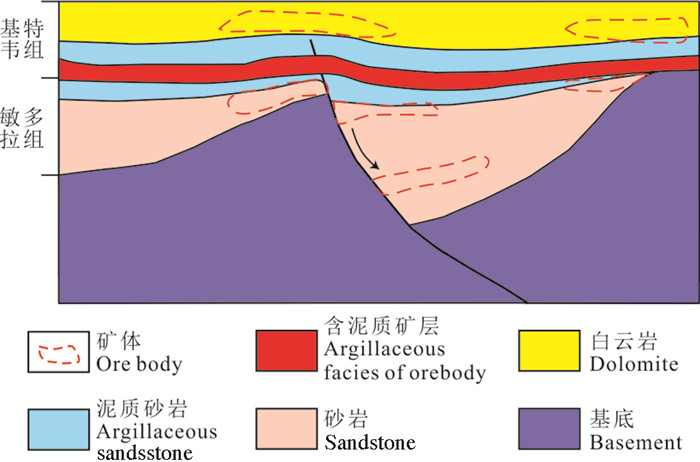
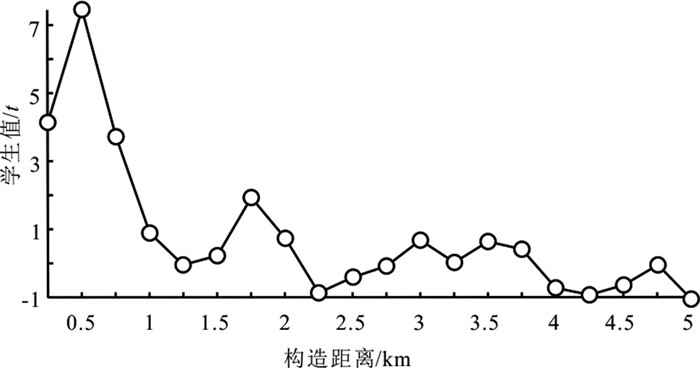
图 5 砂岩型铜(钴)矿床成矿模式示意图(据Selley et al., 2005)
Figure 5.
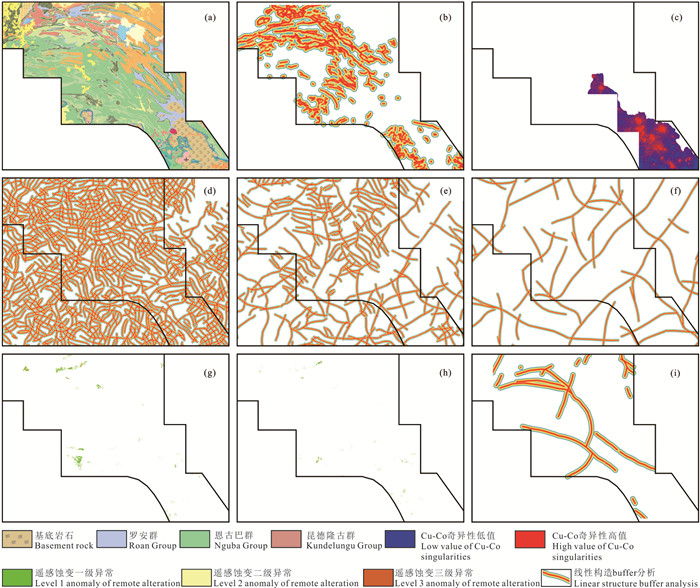
图 6 构造控制脉型铜(钴)矿床成矿模式示意图(据El Desouky et al., 2008)
Figure 6.
图 7 含矿基底型铜矿成矿模式示意图(据Bernau, 2007)
Figure 7.
表 1 加丹加超群地层层序(据Cailteux et al., 1995; Bull et al., 2011; Cailteux and De Putter, 2019修改)
Table 1. Lithostratigraphic units of the Katanga Supergroup (modified from Cailteux et al., 1995; Bull et al., 2011; Cailteux and De Putter, 2019)
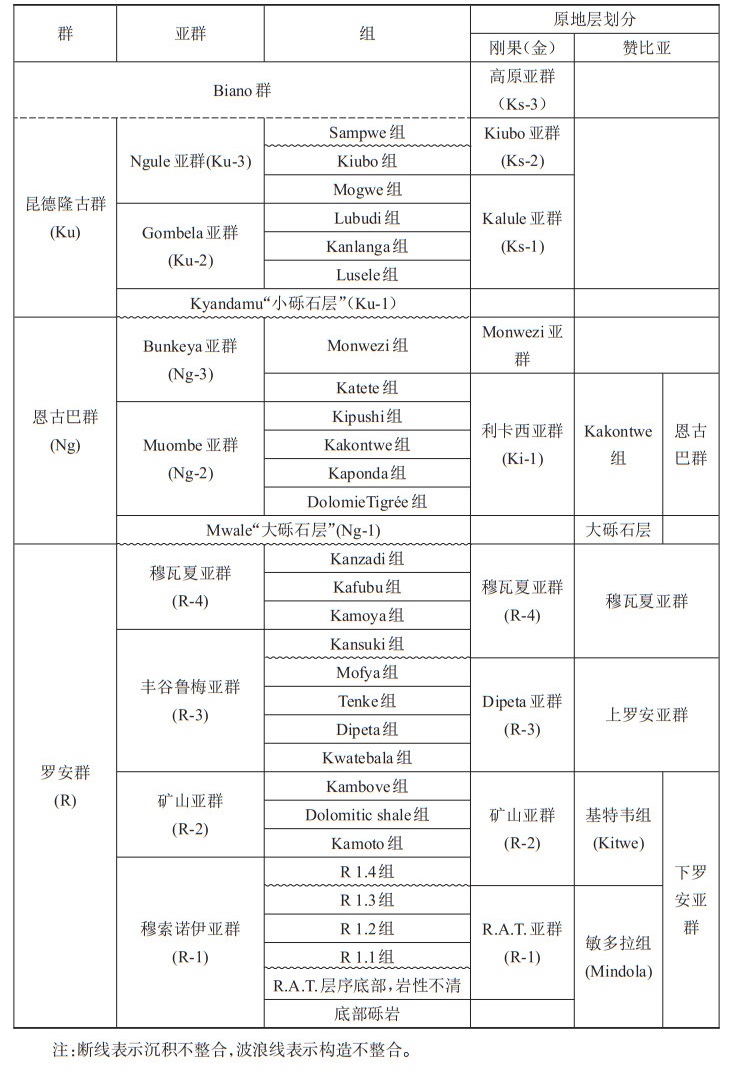
表 2 中非铜钴成矿带成矿可行性地段未发现矿床数的估计
Table 2. Estimation of the number of undiscovered deposits in each tract of Central African Copper belt

表 3 中非铜钴成矿带每个成矿可行性地段评价结果
Table 3. Quantitative assessment result for each tract of Cu (Co) deposit in Central African Copper belt

-
Batumike M J, Cailteux J L H, Kampunzu A B. 2007. Lithostratigraphy, basin development, base metal deposits, and regional correlations of the Neoproterozoic Nguba and Kundelungu rock successions, central African Copper belt[J]. Gondwana Research, 11(3): 432-447. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2006.04.012
Batumike M J, Kampunzu A B, Cailteux J H. 2006. Petrology and geochemistry of the Neoproterozoic Nguba and Kundelungu Groups, Katangan Supergroup, southeast Congo: Implications for provenance, paleoweathering and geotectonic setting[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 44: 97-115. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.11.007
Bernau R. 2007. The Geology and Geochemistry of the Lumwana Basement Hosted Copper-Cobalt (Uranium) Deposits, NW Zambia[D]. University of Southampton: 1-187.
Bull S, Selley D, Broughton D, Hitzman M, Cailteux J, Large R, McGoldrick P. 2011. Sequence and carbon isotopic stratigraphy of the Neoproterozoic Roan Group strata of the Zambian copperbelt[J]. Precambrian Research, 190(1): 70-89. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301926811001598
Cailteux J. 1994. Lithostratigraphy of the Neoproterozoic Shaba-type (Zaire) Roan Supergroup and metallogenesis of associated stratiform mineralization[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 19(4): 279-301. doi: 10.1016/0899-5362(94)90015-9
Cailteux J, Binda P L, Kampunzu A B, Katekesha W M, Kaunda C, Wendorff M. 1995. Results of lithostratigraphic correlation of the Late Proterozoic Roan Supergroup between Zambia and Zaire, Central African Copperbelt[J]. Royal Museum of Central Africa (Belgium), Annales des Sciences Géologiques, 101: 21-27. https://www.academia.edu/5994061/Results_of_lithostratigraphic_correlation_of_the_late_Proterozoic_Roan_Supergroup_between_Zambia_and_Zaire_Central_African_Copperbelt
Cailteux J L H, De Putter T. 2019. The Neoproterozoic Katanga Supergroup (D. R. Congo): State-of-the-art and revisions of the lithostratigraphy, sedimentary basin and geodynamic evolution[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 150: 522-531. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.07.020
Cailteux J L H, Kampunzu A B H, Batumike M J. 2005b. Lithostratigraphic position and petrographic characteristics of R.A.T. ("Roches Argilo-Talqueuses") Subgroup, Neoproterozoic Katangan Belt (Congo)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 42(1): 82-94. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005JAfES..42...82C/abstract
Cailteux J L H, Kampunzu A B, Lerouge C. 2007. The Neoproterozoic Mwashya-Kansuki sedimentary rock succession in the central African Copperbelt, its Cu-Co mineralisation, and regional correlations[J]. Gondwana Research, 11(3): 414-431. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2006.04.016
Cailteux J, Kampunzu A B, Lerouge C, Kaputo A K, Milesi J P. 2005a. Genesis of sediment-hosted stratiform copper-cobalt deposits, central African Copperbelt[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 42(1): 134-158. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1464343X05000920
Cheng Q. 2008. Non-linear theory and power-law models for information integration and mineral resources quantitative assessments[J]. Mathematical Geosciences, 40(5): 503-532. doi: 10.1007/s11004-008-9172-6
Cheng Qiuming, Chen Zhijun, Ali Khaled. 2007. Application of fuzzy weights of evidence method in mineral resource assessment for gold in Zhenyuan district, Yunnan province, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 32(2): 175-184 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Cheng Qiuming, Zhao Pengda, Zhang Shengyuan, Xia Qinglin, Chen Zhijun, Chen Jianguo, Xu Deyi, Wang Wenlei. 2009. Application of singularity theory in prediction of tin and copper mineral deposits in Gejiu district, Yunnan, China: Information integration and delineation of mineral exploration targets[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 34(2): 243-252 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2009.022
Corner B. 2000. Crustal framework of Namibia derived from magnetic and gravity data[J]. Communications of the Geological Survey of Namibia, 12: 15-22. http://www.mme.gov.na/files/publications/f42_Corner_crustal%20framework_plus%20maps.pdf
Cosi M, De Bonis A, Gosso G, Hunziker J, Martinotti G, Moratto S, Robert J P, Ruhlman F. 1992. Late Proterozoic thrust tectonics, high-pressure metamorphism and uranium mineralization in the Domes Area, Lufilian Arc, Northwestern Zambia[J]. Precambrian Research, 58(1): 215-240. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000036171362910_e276.html
Decrée S, Deloule é, De Putter T, Dewaele S, Mees F, Yans J, Marignac C. 2011. SIMS U-Pb dating of uranium mineralization in the Katanga Copperbelt: Constraints for the geodynamic context[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 40(1): 81-89. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.05.003
Delpomdor F, Callec Y, Bailly L, Mashigiro E H, Ilunga S, Sebagenzi S, Mupande J F, Kampata D, Cailteux J. 2020. Sedimentary evolution and chemostratigraphy of the post-Sturtian cap carbonate-like DolomieTigrée Formation (Katanga Supergroup) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 162: 103727. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2019.103727
Dewaele S, Muchez P, Vets J, Fernandez-Alonzo M, Tack L. 2006. Multiphase origin of the Cu Co ore deposits in the western part of the Lufilian fold-and-thrust belt, Katanga (Democratic Republic of Congo)[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 46: 455-469. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2006.08.002
Duval J S. 2000. A Microsoft Windows version of the MARK3 Monte Carlo mineral resource simulator[CP/OL]. http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/2000/of00-415/.
Eberle D, Hutchins D, Rebbeck R J, Somerton I. 1996. Compilation of the Namibian airborne magnetic surveys: Procedures, problems and results[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 22(2): 191-205. doi: 10.1016/0899-5362(96)00117-0
Eglinger A, André-Mayer A, Vanderhaeghe O, Mercadier J, Cuney M, Decrée S, Feybesse J, Milesi J. 2013. Geochemical signatures of uranium oxides in the Lufilian belt: From unconformity-related to syn-metamorphic uranium deposits during the Pan-African orogenic cycle[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 54: 197-213. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.04.003
El Desouky H A, Muchez P, Tyler R. 2008. The sandstone-hosted stratiform copper mineralization at Mwitapile and its relation to the mineralization at Lufukwe, Lufilian foreland, Democratic Republic of Congo[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 34(4): 561-579. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.09.004
François A. 1973. L'extremité occidentale de l'arc cuprifére shabien. étude géologique. Département Géologiques Gécamines, Likasi, Shaba, Zaire.
François A. 1987. Synthèse géologique sur l'arc cuprifère du Shaba (Rép. du Zaïre)[J]. Centenaire de la Société Belge de Géologie: 15-65.
Garlick W G, Fleisher V D. 1972. Sedimentary environment of Zambian copper deposition[J]. Geologieen Mijnbouw, 51(3): 277-298.
Hanson R E, Wardlaw M S, Wilson T J, Mwale G. 1993. U-Pb zircon ages from the Hook granite massif and Mwembeshi dislocation: constraints on Pan-African deformation, plutonism, and transcurrent shearing in Central Zambia[J]. Precambrian Research, 63(3): 189-209. http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/el/03019268/1993/00000063/00000003/art00002
Hayes T S, Landis G P, Whelan J F, Rye R O, Moscati R J. 2012. The spar lake strata-bound Cu-Ag deposit formed across a mixing zone between trapped natural gas and metals-bearing brine[J]. Economic Geology, 107(6): 1223-1249. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.107.6.1223
Hitzman M W, Selley D, Bull S. 2010. Formation of sedimentary rock-hosted stratiform copper deposits through Earth History[J]. Economic Geology, 105(3): 627-639. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.3.627
Hitzman M W, Broughton D, Selley D, Woodhead J, Wood D, Bull S. 2012. The Central African copper belt: Diverse stratigraphic, structural, and temporal settings in the world's largest sedimentary copper district[J]. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publication, 16: 487-514. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/segweb/books/book/1385/chapter/107056968/The-Central-African-CopperbeltDiverse
Jackson M P A, Warin O N, Woad G M, Hudec M R. 2003. Neoproterozoic allochthonous salt tectonics during the Lufilian orogeny in the Katangan Copperbelt, central Africa[J]. GSA Bulletin, 115(3): 314-330. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/gsabulletin/article-abstract/115/3/314/183967/Neoproterozoic-allochthonous-salt-tectonics-during
John T, Schenk V, Haase K, Scherer E, Tembo F. 2003. Evidence for a Neoproterozoic ocean in south-central Africa from mid-oceanic-ridge-type geochemical signatures and pressure-temperature estimates of Zambian eclogites[J]. Geology, 31(3): 243-246. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0243:EFANOI>2.0.CO;2
John T, Schenk V, Mezger K, Tembo F. 2004. Timing and PT evolution of Whiteschist metamorphism in the Lufilian Arc-Zambezi Belt Orogen (Zambia): Implications for the assembly of Gondwana[J]. The Journal of Geology, 112(1): 71-90. doi: 10.1086/379693
Kampunzu A B, Cailteux J. 1999. Tectonic evolution of the Lufilian Arc (Central Africa Copper Belt) during Neoproterozoic Pan African orogenesis[J]. Gondwana Research, 2(3): 401-421. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70279-3
Kampunzu A B, Cailteux J L H, Kamona A F, Intiomale M M, Melcher F. 2009. Sediment-hosted Zn-Pb-Cu deposits in the Central African copper belt[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 35(3-4): 263-297. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.02.003
Key R M, Liyungu A K, Njamu F M, Somwe V, Banda J, Mosley P N, Armstrong R A. 2001. The western arm of the Lufilian Arc in NW Zambia and its potential for copper mineralization[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 33(3): 503-528. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0899536201000987
Large R R, Mukherjee I, Gregory D D, Steadman J A, Maslennikov V V, Meffre S. 2017. Ocean and atmosphere geochemical proxies derived from trace elements in marine pyrite: Implications for ore genesis in sedimentary basins[J]. Economic Geology and the Bulletin of the Society of Economic Geologists, 112(2): 423-450. doi: 10.2113/econgeo.112.2.423
Lefebvre J J. 1975. Les roches ignées dans le Katangien du Shaba (Zaïre), le district du cuivre[J]. Annales de la Société géologique de Belgique, 98: 47-73.
Lefebvre J J. 1979. Le Groupe de Mwashya, mégacyclothème terminal du Roan (Shaba, Zaïre Sud-Oriental); I approche lithostratigraphique et étude de l'environnement sédimentaire[J]. Annales de la Societe Geologique de Belgique, 101(1978): 209-225. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283737220_Le_Groupe_de_Mwashya_megacycloteme_terminal_du_Roan_Shaba_Zaire_Sud-Oriental_L'approche_stratigraphique_et_etude_de_l'environnement_sedimentaire
Lerouge C, Cocherie A, Cailteux J, Kampunzu A B, Breton J, Gilles C, Milesi J P. 2004. Preliminary U-Th-Pb electron microprobe dating of monazite: Chronological constraints on the genesis of the Luisweshi Cu-Co-U ore deposit, D.R. Congo[C]//Geoscience Africa 2004, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa, 382-383.
Li Xiangqian, Mao Jingwen, Yan yanling, Gao Hongshan, Li Mengwen, Xu Xianli. 2009. Regional geology and characteristics of ore deposits in Katangan copper-cobalt belt within Congo (Kinshasa), Central Africa[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(3): 366-380 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=KCDZ200903013&dbcode=CJFD&year=2009&dflag=pdfdown
Li Xiangqian. 2011. Metallogenic Series and Metallogeny in Congo (Kinshasa) Part of Central African Copperbelt[D]. China University of Geosciences (Beijing): 1-117 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Loris N B T, Charlet J M, Pechman E, Clare C, Chabu M, Quinif Y. 1997. Caractéristiques minéralogiques, cristallographiques, physico-chimiques et ages des minéralisations uranifères de Luiswishi (Shaba, Zaïre)[J]. Actes du Colloque International Cornet: 285-306.
Lu Yiguan, Hao Bo, Sun Kai, He Shengfei, Xu Kangkang, Gong Penghui, Zhang Hang. 2020. General situation of cobalt resource and its utilization analysis[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 43(1): 72-80 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304386X1931076X
MacGabhann B A. 2005. Age constraints on Precambrian glaciations and the subdivision of Neoproterozoic time[C]. IUGS Ediacaran Subcommission Circluar: 1-13.
McGowan R R, Roberts S, Foster R P, Boyce A J, Coller D. 2003. Origin of the copper-cobalt deposits of the Zambian Copper belt: An epigenetic view from Nchanga[J]. Geology, 31(6): 497-500. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0497:OOTCDO>2.0.CO;2
Muchez P, André-Mayer A, El Desouky H A, Reisberg L. 2015. Diagenetic origin of the stratiform Cu-Co deposit at Kamoto in the Central African Copperbelt[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 50(4): 437-447. doi: 10.1007/s00126-015-0582-3
Porada H. 1989. Pan-African rifting and orogenesis in southern to equatorial Africa and eastern Brazil[J]. Precambrian Research, 44(2): 103-136. doi: 10.1016/0301-9268(89)90078-8
Qiu Ruizhao, Li Tingdong, Xiao Qinghui, Sun Kai, Liu Yong, Qiu Lei, Chen Xiufa, Zhao Hongjun, Wang Liangliang, Zhu Quanlong, Ren Xiaodong, Zhao Like. 2021. A new pattern of the tectonic units in Africa continent in terms of lithosphere[J]. China Geology. doi:10.31035/cg2021073.
Rainaud C, Master S, Armstrong R A, Phillips D, Robb L J. 2005. Monazite U-Pb dating and 40Ar-39Ar thermochronology of metamorphic events in the Central African Copperbelt during the Pan-African Lufilian Orogeny[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 42(1): 183-199. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1464343X05000981
Richards J, Cumming G, Krstic D, Wagner P, Spooner E. 1988. Pb isotope constraints on the age of sulfide ore deposition and U-Pb age of late uraninite veining at the Musoshi stratiform copper deposit, Central Africa copper belt, Zaire[J]. Economic Geology, 83: 724-741. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.4.724
Schulz K J, DeYoung J H, Seal R R, Bradley D C, Abdelsalam M G. 2017. Critical mineral resources of the United States-Economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply: Professional Paper[Z]. Reston, VA: 2017862.
Selley D, Broughton D, Scott R, Hitzman M, Bull S, Large R, McGoldrick P, Croaker M, Pollington N, Barra F. 2005. A new look at the geology of the Zambian copper belt[J]. Economic Geology, One Hundredth Anniversary Volume: 965-1000. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Robert_Scott9/publication/284791953_A_new_look_at_the_geology_of_the_Zambian_Copperbelt/links/567e3ebe08ae19758387c518.pdf
Sillitoe R H, Perelló J, Creaser R A, Wilton J, Wilson A J, Dawborn T. 2017. Age of the Zambian Copperbelt[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 52(8): 1245-1268. doi: 10.1007/s00126-017-0726-8
Singer D A. 1995. World class base and precious metal deposits; a quantitative analysis[J]. Economic Geology, 90(1): 88-104. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.90.1.88
Taylor C D, Causey J D, Denning P D, Hammarstrom J M, Hayes T S, Horton J D, Kirschbaum M J, Parks H L, Wilson A B, Wintzer N E, Zientek M L. 2013. Descriptive Models, Grade-tonnage Relations, and Databases for the Assessment of Sediment-hosted Copper Deposits-With Emphasis on Deposits in the Central African Copperbelt, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia[R]. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5090-J: 1-154.
Teng Fei, Peng Lina, Meng Qinglong, Xing Yi. 2021. Applying weight of evidence to predict Ag-Pb-Zn potentiality in Fengning region, Hebei[J]. North China Geology, 44(1): 21-26(in Chinese with English abstract).
Twite F, Broughton D, Nex P, Kinnaird J, Gilchrist G, Edwards D. 2019. Lithostratigraphic and structural controls on sulphide mineralisation at the Kamoa copper deposit, Democratic Republic of Congo[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 151: 212-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2018.12.016
Twite F, Nex P, Kinnaird J. 2020. Strain fringes and strain shadows at Kamoa (DRC), implications for copper mineralisation[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 122: 103536. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103536
Unrug R. 1988. Mineralization controls and source of metals in the Lufilian fold belt, Shaba (Zaire), Zambia, and Angola[J]. Economic Geology, 83(6): 1247-1258. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.6.1247
Vrána S, Prasad R, Fediuková E. 1975. Metamorphic kyanite eclogites in the lufilian arc of Zambia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 51(2): 139-160. doi: 10.1007/BF00403755
Wang Denghong. 2019. Study on critical mineral resources: significance of research, determination of types, attributes of resources, progress of prospecting, problems of utilization, and direction of exploitation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(6): 1189-1209 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jiaying, Liu Xing, Xue Shengsheng, Zhang Xiaojun, Zhang Qi, Li Guangyao, Xie Yu. 2021. Application of singularity theory in weak information extraction for ore prospecting in the Dalaimiao Grassland-covered Area[J]. North China Geology, 44(2): 14-24(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Jiaying, Zhang Xiaojun, Yao Chunliang, Zhang Qi, Xie Yu, Li Guangyao, Ding Ning. 2019. Application of nonlinear theory and fuzzy weights of evidence method in metallogenic prediction for Mo Polymetalic deposits in the Dalaimiao grassland-covered area, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 42(3): 174-184 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Yan Guangsheng, Qiu Ruizhao, Lian Changyun, Li Jinyi, Xiao Keyan, Mao Jingwen. 2010. Quantitative Assessment of the Resource Potential of Porphyry Copper and Sandstone Copper Systems in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House: 1-218 (in Chinese).
Yan Guangsheng, Qiu Ruizhao, Lian Changyun, Warren J. Nokleberg, Cao Li, Chen Xiufa, Mao Jingwen, Xiao Keyan, Li Jinyi, Xiao Qinghui, Zhou Su, Wang Mingyan, Liu Dawen, Yuan Chunhua, Han Jiuxi, Wang Liangliang, Chen Zheng, Chen Yuming, Xie Guiqing, Ding Jianhua. 2007. Quantitative assessment of the resource potential of porphyry copper systems in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(5): 27-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60034-7
Yu Jinjie, Liu Xiaoyang, Wang Jie, Wang Tiezhu, Lu Bangcheng, Liu Shuaijie. 2015. Geological setting and ore-controlling factors of the central African Cu-Co metallogenic belt[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 30(S1): 119-128 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhai Mingguo, Wu Fuyuan, Hu Ruizhong, Jiang Shaoyong, Li Wenchang, Wang Rucheng, Wang Denghong, Qi Tao, Qin Kezhang, Wen Hanjie. 2019. Critical metal mineral resources: Current research status and scientific issues[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 33(2): 106-111 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yin, Hu Dengpan, Yu Can, Cui Jianjun. 2021. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential of Kanunka copper-cobalt deposit in Lualaba, Democratic Republic of Congo[J]. Geology and Resources, 30(4): 450-455 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zientek M L, Bliss J D, Broughton D, Christie M, Denning P D, Hayes T S, Hitzman M W, Horton J D, Frostkillian S, Jack D J. 2014. Sediment-hosted stratabound copper assessment of the Neoproterozoic Roan Group, central African copperbelt, Katanga Basin, Democratic Republic of the Congo and Zambia[R]. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2010-5090-7: 1-162.
成秋明, 陈志军, Ali Khaled. 2007. 模糊证据权方法在镇沅(老王寨)地区金矿资源评价中的应用[J]. 地球科学, 32 (2): 175-184. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2007.02.004
成秋明, 赵鹏大, 张生元, 夏庆霖, 陈志军, 陈建国, 徐德义, 王文磊. 2009. 奇异性理论在个旧锡铜矿产资源预测中的应用: 综合信息集成与靶区圈定[J]. 地球科学, 34(2): 243-252. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2009.02.003
李向前, 毛景文, 闫艳玲, 高洪山, 李蒙文, 徐宪立. 2009. 中非刚果(金)加丹加铜钴矿带主要矿化类型及特征[J]. 矿床地质, 28(3): 366-380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.03.012
李向前. 2011. 中非铜带刚果(金)段成矿系列和成矿规律[D]. 中国地质大学(北京): 1-117.
卢宜冠, 郝波, 孙凯, 何胜飞, 许康康, 龚鹏辉, 张航. 2020. 钴金属资源概况与资源利用情况分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 43(1): 72-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2020.01.008
滕菲, 彭丽娜, 孟庆龙, 邢怡. 2021. 证据权法在河北丰宁地区银铅锌多金属矿成矿预测中的应用[J]. 华北地质, 44(1): 21-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202101004.htm
王登红. 2019. 关键矿产的研究意义、矿种厘定、资源属性、找矿进展、存在问题及主攻方向[J]. 地质学报, 93(6): 1189-1209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.003
王佳营, 刘行, 薛生升, 张晓军, 张琪, 李光耀, 谢瑜. 2021. 奇异性理论在达来庙草原覆盖区找矿弱信息提取中的应用[J]. 华北地质, 44(2): 14-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHWJ202102003.htm
王佳营, 张晓军, 姚春亮, 张祺, 谢瑜, 李光耀, 丁宁. 2019. 非线性理论和模糊证据权方法在内蒙古达来庙草原覆盖区钼多金属矿产预测中的应用[J]. 地质调查与研究, 42(3): 174-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2019.03.003
严光生, 邱瑞照, 连长云, Warren J. Nokleberg, 曹黎, 陈秀法, 毛景文, 肖克炎, 李锦轶, 肖庆辉, 周肃, 王明燕, 刘大文, 元春华, 韩九曦, 王靓靓, 陈正, 陈玉明, 谢桂青, 丁建华. 2007. 中国大陆斑岩铜矿资源潜力定量评价[J]. 地学前缘, 14(5): 27-41. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.05.004
严光生, 邱瑞照, 连长云, 李锦轶, 肖克炎, 毛景文. 2010. 中国斑岩铜矿砂岩铜矿资源潜力定量评价[M]. 地质出版社: 1-218.
余金杰, 刘晓阳, 王杰, 王铁柱, 陆邦成, 刘帅杰. 2015. 中非新元古代铜钴成矿带的地质背景和控矿因素[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 30(S1): 119-128. doi: 10.6053/j.issn.1001-1412.2015.S1.015
翟明国, 吴福元, 胡瑞忠, 蒋少涌, 李文昌, 王汝成, 王登红, 齐涛, 秦克章, 温汉捷. 2019. 战略性关键金属矿产资源: 现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 33(2): 106-111.
张银, 胡登攀, 余璨, 翟建军. 2021. 刚果(金)卢阿拉巴省康隆卡铜钴矿床地质特征及找矿前景[J]. 地质与资源, 30(4): 450-455.
-



 下载:
下载: