The Occurrence Characteristics of Nickel and Molybdenum in Sedimentary Exhalative Polymetallic Deposit
-
摘要: 喷流沉积型矿床是矿床地质学研究的前沿课题,查明矿石中重要组分(镍和钼)的赋存状态是该类矿床地质学研究的重要内容。湘黔地区天鹅山—黄家湾、大坪—大浒镍钼矿带是典型的海底喷流沉积矿床,本文采集该矿区的样品,应用化学和光谱定量分析、偏光显微镜和X射线衍射、扫描电镜、电子探针等大型现代仪器相结合的分析手段,研究了矿石中镍和钼的赋存状态。化学和光谱分析确定矿石中镍含量为3.76%,钼含量为4.99%;偏光显微镜下观察发现金属矿物零星分布,颗粒细小,结晶程度差,光学特征极不明显,晶体形貌特征难以观察,初步推断矿石矿物以胶状形式存在,但在光学显微镜下很难为这些矿物定名和描述;X射线衍射分析验证了偏光显微镜鉴定结果,印证了样品中存在很多非晶质矿物,仅有钨钼钙矿和镍黄铁矿两种矿物含有镍钼,且矿物含量很低(分别为0.4%和0.8%),对比化学分析结果,可推断样品还存在其他富含镍钼元素的矿物。进一步对富集镍钼元素的区域进行电子探针分析,最终确定了镍除了赋存于辉砷镍矿、方硫镍矿中,在胶状黄铁矿和磁黄铁矿边缘呈蠕虫状花边的镍黄铁矿中也有富集;钼主要赋存于碳硫钼矿中。矿石中的镍钼主要赋存于由胶态向结晶态过渡的金属矿物中,研究成果为该类矿床的矿石矿物学研究、选矿、冶炼及矿石综合利用提供重要的信息和依据。
-
关键词:
- 喷流沉积型多金属矿床 /
- 镍钼赋存状态 /
- 电子探针 /
- 线扫描分析 /
- 面扫描分析
Abstract: Exhalative sedimentary polymetallic deposit is an attractive subject in the study of mineral deposit geology. Ascertaining the occurrence state of main ore components (nickel, molybdenum) is the important study focus for this kind of mineral deposit. The Swan Hill-Huangjiawan and Daping-Dahu nickel molybdenum ore belts of Xiang-Qian area are typical submarine exhalative sedimentary deposits. In this article, an account of samples that were collected from the ore district, and analyzed using large modern instruments including those for chemical and spectral analysis, Optical Microscope and X-ray Diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscope and Electron Probe is given, to study the occurrence states of nickel and molybdenum in the ores. The content of nickel was 3.76%, and the content of molybdenum was 4.99% using chemical and spectral analysis. Observations were made of the metal minerals in the polished section, which were distributed sporadically and occurred as fine particles. Since there is weak crystalline degree, low reflectivity and unclear crystal morphology under the polarizing microscope, it was preliminary inferred that the ore mineral existed in colloidal form, but it is difficult to name and describe these ore minerals. The X-ray Diffraction analysis results for the samples supported the observation under the Polarizing Microscope, which confirmed that there were many amorphous minerals hosted in the analyzed samples. The nickel and molybdenum occurred mainly in the tungsten-powellite and pyrrhotite with low contents of 0.4% and 0.8%, respectively. Comparing with the results of chemical analysis, it is hinted that there are other minerals which enrich nickel and molybdenum. Further analysis by electron microprobe in the nickel molybdenum enriched area indicate that nickel not only occurs in gersdorffite and vaesite, but is also concentrated in the edge of colloidal pyrite and pyrrhotite within a worm-like lace. Molybdenum mainly occurred in the carbon sulphur molybdenum ore. The nickel and molybdenum mainly occurred in the transition ore minerals from colloidal to crystalline. The research results provided important information and the basis for the study of ore mineralogy, mineral processing, smelting and comprehensive utilization of the mineral ores for this kind of deposit. -
喷流沉积型矿床是极为重要的矿床类型,产有大型贱金属、有色金属、贵金属及稀有金属矿床[1-4],因此喷流沉积型矿床是矿床地质学研究的前沿课题[5-6],查明矿石中重要组分(钼、镍)的赋存状态是该类矿床地质学研究的重要内容。在我国华南扬子克拉通南缘早寒武世也发育了一系列黑色岩系岩层,这套黑色岩系富集镍、钼,产出一系列镍、钼矿床和矿点,岩系及矿床的形成机制多数观点认为海底喷流说[7-11]。由于这类矿床成矿条件独特,矿石中一些有用组分赋存状态不易准确鉴定,因此关于这套镍、钼富集层的矿物组合和元素赋存状态的研究目前还不是很深入[12]。本文对湘黔地区天鹅山—黄家湾与大坪—大浒的喷流沉积型镍钼矿带矿石,应用化学和光谱定量分析、偏光显微镜和X射线衍射、扫描电镜、电子探针等大型现代仪器相结合的分析手段,研究了矿石中镍、钼的赋存状态,研究成果可为矿山开采、选矿、冶炼及矿石综合利用提供重要的信息和依据。 1. 地质背景
华南扬子克拉通南缘早寒武世发育了一系列黑色岩系岩层,此岩系在湘西主要由黑色页岩、硅质页岩、硅质岩、粉砂岩、磷块岩等组成。黑色岩系的颜色随着碳质、钙质和硅质成分的变化而变化,有黑色、深灰色、浅灰色。主要矿物成分为石英、伊利石和黄铁矿以及有机质,另外还含有极少量重晶石、磷灰石和方解石。根据有机碳含量(Corg)、黏土矿物和石英等主要矿物的含量,将黑色岩系划分为硅质页岩(Corg< 3%,石英含量35%~75%)、硅质岩(石英> 75%)和富碳硅质页岩(Corg为3%~5%,石英含量35%~75%)、石煤(Corg> 5%,石英含量35%~75%)、磷块岩和重晶石岩[13]。 天鹅山—黄家湾、大坪—大浒镍钼矿带就产出自上述黑色岩系,属于典型的海底喷流沉积矿床[14]。镍钼矿体呈层状、似层状及透镜状赋存于下寒武统牛蹄塘组黑色岩系底部。牛蹄塘组黑色岩系不整合于震旦系灯影组白云岩之上,黑色岩系下部为含磷结核硅质岩-镍钼硫化物富集层,其中含磷结核硅质岩厚度一般为0.05~0.5 m,镍钼多金属富集层厚一般为0.05~0.3 m;上部为碳质叶岩-碳质泥岩组合,厚度一般为20~60 m[15]。样品采自以上的矿点中,为含镍钼黑色叶岩。2. 样品分析与结果讨论
样品分析的具体流程为:①粉末样品的化学定量和光谱半定量分析,确定样品中大体元素组成和镍、钼元素的准确含量。②偏光显微镜薄片及光片镜下鉴定,确定矿物组成。③粉末样品的X射线衍射分析结晶矿物成分,验证光片鉴定结果。④对制好的光片样品进行扫描电镜形貌、成分像观察,并进行线扫描和面扫描分析,研究样品中镍、钼元素的赋存特点。⑤对富集镍、钼元素的区域进行电子探针波谱定量分析,结合原子组成,确定富含镍、钼元素矿物的名称及赋存状态。2.1 化学和光谱分析
对加工成粉末的样品进行化学定量和光谱半定量分析,确定样品中大体元素组成和镍、钼元素的准确含量,结果见表 1。按元素含量的高低排序为:硫、全铁(TFe)、二氧化硅、氧化钙、五氧化二磷、钼、镍、氧化镁等,在组成矿物的元素配比中主要以阳离子占位元的元素为镍、钼、铁,主要以阴离子占位元的元素为硫和硅。其中镍含量为3.76%,钼含量为4.99%。表 1. 样品中主次量元素分析Table 1. Analytical results of major and minor elements in samples测试元素 化学定量分析wB/% 测试元素 光谱半定量分析wB/(μg·g-1) S 21.90 As 9706 TFe 19.64 Sr 302 SiO2 15.70 Ba 245 CaO 10.80 V 211 P2O5 5.13 Y 190 Mo 4.99 Cr 164 Ni 3.76 Co 70.5 MgO 3.18 Nb 48.1 Al2O3 2.44 Zr 31.3 2.2 偏光显微镜下光片鉴定
使用Axioskop 40Apol偏光显微镜(德国普瑞赛司公司)进行薄片及光片鉴定,确定矿物组成。在薄片中岩石有碳酸岩化、绿泥石-碳酸岩化、硅化、绿泥石-黄铁矿化、绢云母-石英-黄铁矿化等蚀变;光片鉴定发现金属矿物零星分布,颗粒细小,结晶程度较差,反射率较低,晶体形貌特征难以观察,光学特征极不明显,初步推断矿石矿物以胶状形式存在,但在光学显微镜下很难为这些矿物定名和描述。初步确定可能赋存镍、钼元素的矿物主要有以下几类:①颗粒细小(一般小于5 μm)、呈条带状分布的矿物:含量约为8%;②圆粒状、同心圆状胶状矿物:聚集呈草莓状集合体,粒径0.05~0.1 mm,重结晶后粒径变为0.35~1.25 mm,约占60%;③灰色,非均质矿物:大量存在,不规则粒状,隐晶质集合体,部分矿物表面还零星分布有白色片状结晶矿物;④磁黄铁矿中固熔体分解,乳黄色、亮黄色,羽毛状、星状、丝状,固熔体分离后沿边缘花边状分布的矿物。2.3 X射线衍射分析
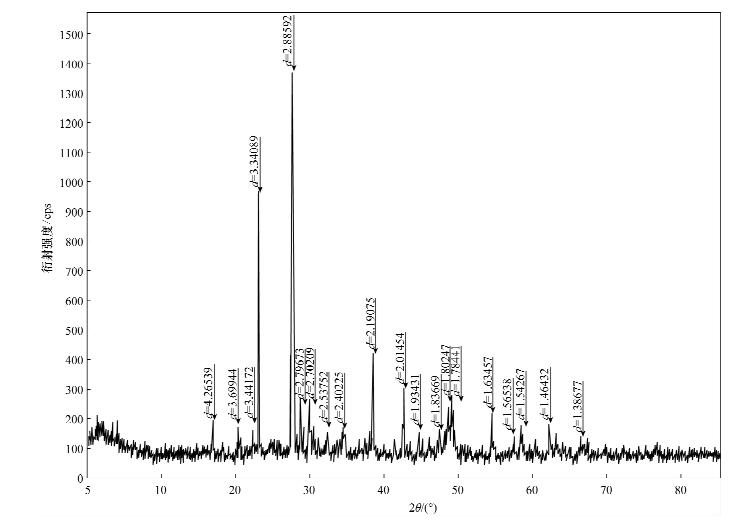
为了进一步验证显微镜光片鉴定描述的现象,使用Bruker-D8型X射线粉晶衍射仪(德国布鲁克公司)对其余粉末样品进行X射线衍射分析,测量条件为:X射线管选用铜靶,管压为40 kV,管流40 mA,扫描范围:2θ角为4°~65°;检测器为固体计数器(XOL-D),DS(发散狭缝)和SS(防散射狭缝)均为2.0 mm,RS(接收狭缝)为0.1 mm,步长为0.03°/步,扫描速度为0.4 s/步。获得的分析谱图见图 1。 由X射线衍射谱图(图 1)可以看出,谱线背景高,出现大量噪音峰,表明被分析样品中存在很多非晶质矿物。进一步对衍射图谱进行解析标定可知,此粉末样品可能包含的矿物成分含量为:黄铁矿约10%,方解石约3.3%,钨钼钙矿约0.4%,磁黄铁矿约4.0%,石英约20.6%,白云石约45.6%,镍黄铁矿约0.8%,磷灰石约13.8%。 X射线衍射分析结果中仅有钨钼钙矿和镍黄铁矿包含镍、钼元素,且这两种矿物含量很低,分别为0.4%和0.8%。根据这一分析结果计算得出镍、钼元素的含量明显低于表 1的化学分析结果(镍含量3.76%,钼含量4.99%),可以说明样品中的钼、镍还以其他赋存方式存在。偏光显微镜及X射线衍射仪由于分析方法本身的限制无法给出鉴定和分析结果,难以定名和描述,只能初步判断矿石为非晶质。2.4 电子探针分析
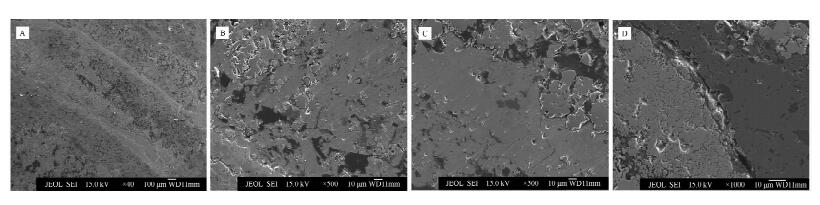
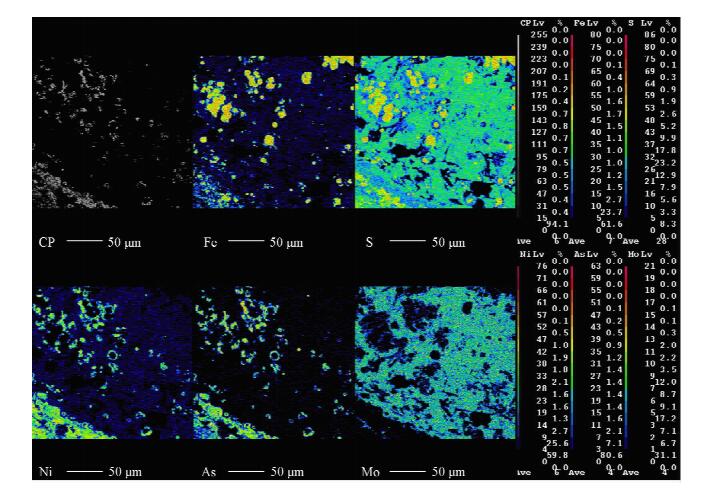
结合偏光显微镜光片鉴定和X射线衍射分析结果,对可能含有镍、钼元素的四类矿物所在区域进行电子探针分析,以最终查明镍、钼元素的赋存状态。使用JXA-8100型电子探针,配备X射线能谱仪(EDS,英国牛津公司),加速电压为15 kV,工作电流为2×10-8 A。首先通过电子探针的扫描电镜功能观察光片,利用二次电子像反映的形貌特征,找到光片中难以定名和描述的矿物所在区域,明确分析范围,即明暗相间的条带状构造区域(图 2A);圆粒状、同心圆状胶状矿物(图 2B);表面零星分布白色片状结晶矿物的隐晶质集合体(图 2C);磁黄铁矿边缘花边状分布的矿物(图 2D)。 利用电子探针配备的X射线能谱仪快速定性分析出待测区的元素组成。在条带状构造区域,除了含有大量铁、硫元素外,还含有砷、镍、钼等元素;圆粒状、同心圆状胶状矿物组成元素主要为铁、镍、砷、硫等;表面分布白色片状结晶体的隐晶质集合体所含的元素主要为钼、钙、硫等;磁黄铁矿边缘花边状分布的矿物主要含有镍、铁、硫等元素。为了进一步确定镍、钼元素的赋存状态,对待测区域使用电子探针进行背散射图像观察及线扫描、面扫描分析。2.4.1 条带状构造区域的电子探针分析
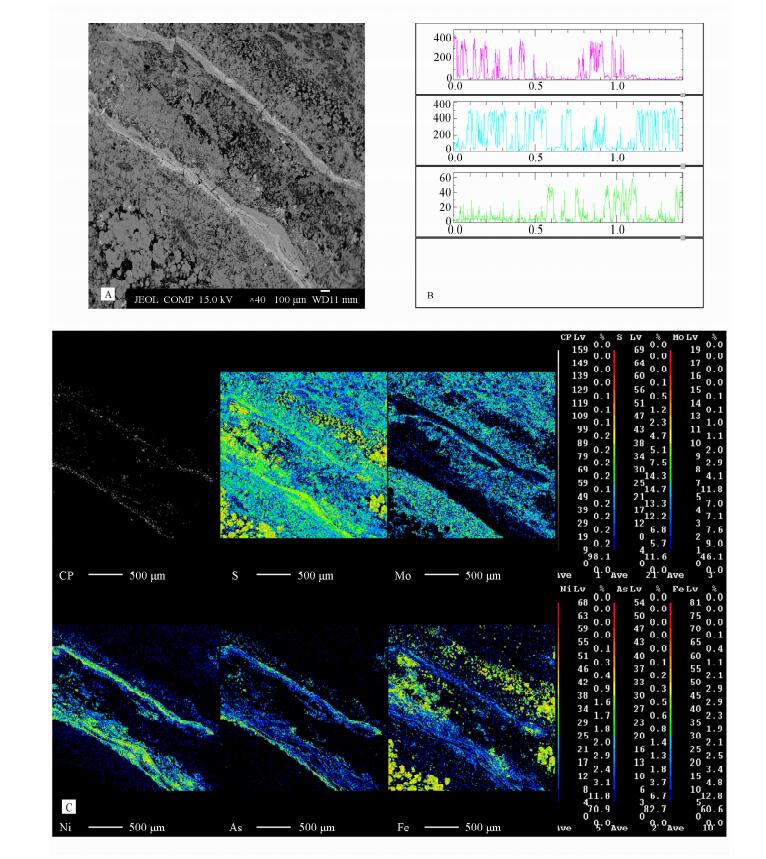
根据X射线能谱仪定性分析结果,对条带状构造区域进行背散射电子图像观察(图 3A)、线扫描分析(图 3B)和面扫描分析(图 3C),以得到该区域内镍、钼、铁、硫、砷等元素的分布情况。由背散射电子图像(图 3A)可以看出,条带状构造区域分别由含有不同元素的几种矿物构成,再结合线扫描分析(图 3B)、面扫描分析(图 3C)及显微镜光片鉴定结果,可以看出几个明显条带区域的元素组成,第一即为光片鉴定中大量的灰色隐晶质矿物条带,较宽,主要富集钼和硫元素;夹杂在钼、硫条带之间的有富集镍、砷和硫元素的条带;富集镍、硫及少量铁元素的条带,还有富集铁及硫元素的条带。2.4.2 圆粒状和同心圆状胶状矿物的电子探针分析
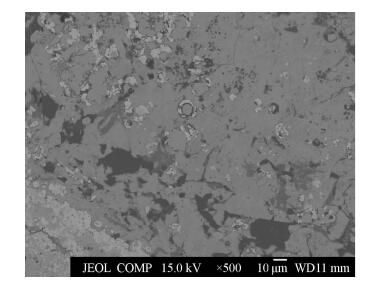
提高扫描电镜观察倍数,研究条带上方圆粒状、同心圆状胶状矿物区域内镍、钼、铁、硫、砷等元素的分布情况(图 4、图 5)。结合显微镜光片鉴定描述,对比研究圆粒状、同心圆状胶状矿物的背散射电子图像(图 4)和面扫描分析结果(图 5),可以看出:圆粒状矿物主要由铁、硫元素组成,有的胶状形态矿物中除了铁、硫元素还含有少量的镍;同心圆内部圆形矿物组成为铁、硫元素,外环矿物主要由镍、砷和硫元素组成,圆粒状矿物中间的裂隙中也穿插有包含镍、砷、硫元素的矿物。磁黄铁矿边缘花边状分布的矿物特征比较明显,故没有进行线扫描和面扫描分析。2.4.3 白色条状、片状结晶矿物电子探针分析
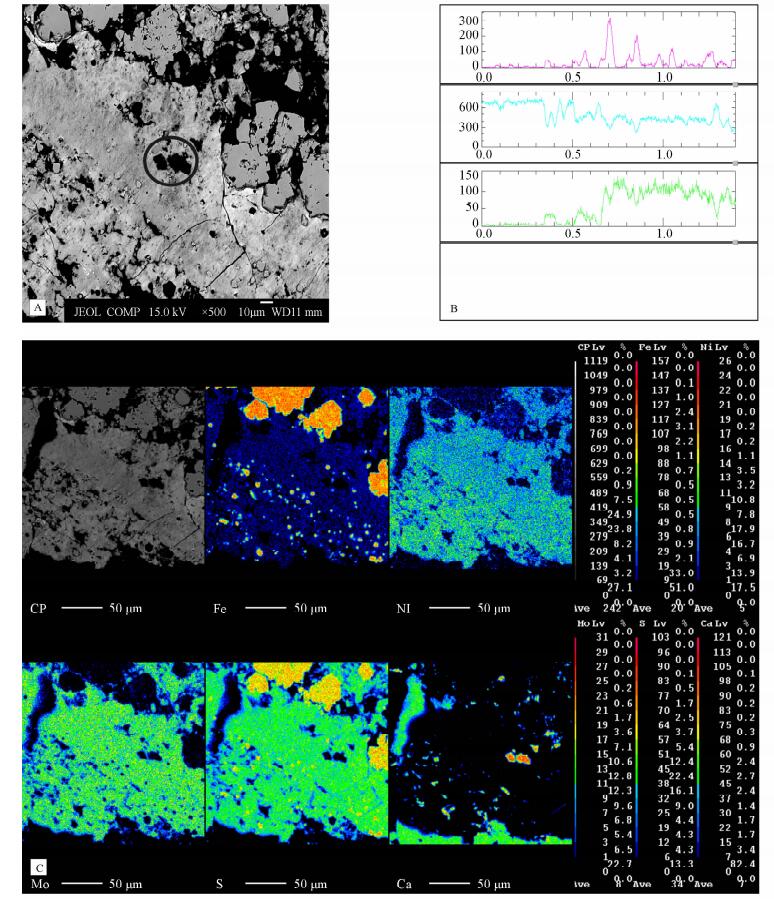
结合X射线能谱仪定性分析结果和X射线衍射分析结果,表面零星分布白色片状结晶矿物的隐晶质集合体可能为钨钼钙矿。使用电子探针分析验证,对所确定的分析区域进行背散射电子图像观察(图 6A)、线扫描分析(图 6B)和面扫描分析(图 6C),得到该区域内钼、钙、硫等元素的分布情况。由背散射电子图像(图 6A)可以看出,偏光显微镜下呈白色的片状结晶矿物(图 6A圆圈内矿物),在背散射电子图像中颜色发暗,由于在背散射电子图像中,颜色越暗的区域所包含元素的原子序数越低,所以证明该片状结晶矿物所包含元素的原子序数较低,再结合线扫描分析(图 6B)和面扫描分析结果,可以发现该片状结晶矿物富含钙元素,并不含有钨、钼、镍等元素,与X射线衍射分析所得出的钨钼钙矿存在很大差异,样品中是否存在钨钼钙矿还需要在电子探针定量分析中进一步验证。2.4.4 电子探针定量分析
综合以上分析结论,根据待测区域中元素的分布规律,确定进行波谱分析(元素定量测试)的靶区,使用波谱定量分析得到分析点所包含元素的准确含量,并计算原子配比,得出矿物名称,见表 2。表 2中电子探针波谱定量分析数据与光片鉴定描述及线扫描、面扫描分析结果吻合,基本可以确定镍元素主要赋存于辉砷镍矿、方硫镍矿中,在胶状黄铁矿和磁黄铁矿边缘呈蠕虫状花边的镍黄铁矿中也有富集;钼主要赋存于碳硫钼矿中。 由于X射线衍射分析结果中存在钨钼钙矿,而电子探针线扫描、面扫描分析中没有出现钨、钼等元素富集,因此,为了进一步查明钨钼钙矿的存在,对该片状结晶矿物进行电子探针波谱定量分析。其定量分析结果显示,该样品中不含钼、钨、镍、硫、砷等元素,主要成分为钙、磷,其中氧化钙的含量为55.361%,五氧化二磷的含量为41.283%,根据原子配比,片状结晶含钙矿物为磷灰石。所以,样品中不含有钨钼钙矿,大量非晶质矿物存在所引起的干扰峰影响了X射线衍射分析的结果。表 2. 电子探针定量分析结果和矿物定名Table 2. EPMA quantitative analysis results and mineral naming样品编号 基本特征 wB/% 矿物名称 Ni Mo Fe S As 1 隐晶质条带上端富含镍砷硫元素的条带 34.833 0.417 1.389 21.436 42.672 辉砷镍矿 2 隐晶质条带下端富含镍砷硫元素的条带 33.439 0.535 1.496 21.484 43.423 辉砷镍矿 3 同心圆状矿物外环 32.674 0.647 1.007 20.773 44.684 辉砷镍矿 4 圆粒状矿物间裂隙 32.354 0.409 1.014 19.624 47.432 辉砷镍矿 5 富含镍、硫和少量铁元素的条带 43.865 1.096 3.601 49.342 0.677 方硫镍矿 6 同心圆状矿物内部圆粒状矿物 0.404 1.008 44.420 51.572 1.798 粒状黄铁矿 7 胶状形态圆粒状矿物 6.507 0.590 26.312 61.815 0.432 胶状黄铁矿 8 富含钼、硫元素的灰色隐晶质条带 2.326 30.625 2.948 24.928 1.400 碳硫钼矿 9 磁黄铁矿边缘花边状矿物 34.646 0.503 32.087 33.294 0.315 镍黄铁矿 3. 喷流沉积型多金属矿床镍钼赋存形态的基本特征
结合以上各种分析手段,可以得出研究的喷流沉积型镍钼赋存形态的特点如下。 (1)含镍主要矿物为辉砷镍矿、方硫镍矿、镍黄铁矿三种。在胶状黄铁矿中也有镍富集,镍以类质同像的形式替代铁。 (2)含钼主要矿物为碳硫钼矿。 (3)研究的矿石中蚀变矿物组合(绿泥石-碳酸岩化、硅化、绿泥石-黄铁矿化、绢云母-石英-黄铁矿化)特征均具有喷流沉积型矿床的特征[16-17]。4. 结语
本文对湘黔地区天鹅山—黄家湾、大坪—大浒镍钼矿带矿石进行研究。化学定量分析结果显示,矿石主要化学成分为硫、铁、二氧化硅、氧化钙、五氧化二磷、钼、镍和氧化镁等。偏光显微镜下薄片鉴定得出矿石中蚀变矿物组合,但由于富含镍、钼元素的矿物大都以胶状形式存在,在光片鉴定时很难为这些矿物定名和描述。进一步使用X射线衍射分析,验证了样品中含有大量的非晶质矿物,图谱解析结果仅发现含镍、钼元素的结晶矿物可能为钨钼钙矿和镍黄铁矿,而且矿物含量很低,矿物中镍、钼元素的含量明显低于化学分析结果,引起原因主要是X射线衍射分析对象为结晶物质,当存在大量非晶质矿物时,X射线衍射分析方法就会有一定的局限性,影响分析结果,所以可以推断还有一些富含镍、钼元素矿物存在。由于电子探针分析技术不受矿物结晶状态的影响,应用电子探针最终查明了湘黔地区喷流沉积型矿床矿石中的镍主要赋存于辉砷镍矿、方硫镍矿、镍黄铁矿中;钼主要赋存于碳硫钼矿中;矿石中的镍、钼主要赋存于由胶态向结晶态过渡的金属矿物中。可见,查明该研究区矿石中重要组分(钼、镍)的赋存状态需要多种分析方法相互结合应用,对测试数据进行综合分析判断。 -
表 1 样品中主次量元素分析
Table 1. Analytical results of major and minor elements in samples
测试元素 化学定量分析wB/% 测试元素 光谱半定量分析wB/(μg·g-1) S 21.90 As 9706 TFe 19.64 Sr 302 SiO2 15.70 Ba 245 CaO 10.80 V 211 P2O5 5.13 Y 190 Mo 4.99 Cr 164 Ni 3.76 Co 70.5 MgO 3.18 Nb 48.1 Al2O3 2.44 Zr 31.3 表 2 电子探针定量分析结果和矿物定名
Table 2. EPMA quantitative analysis results and mineral naming
样品编号 基本特征 wB/% 矿物名称 Ni Mo Fe S As 1 隐晶质条带上端富含镍砷硫元素的条带 34.833 0.417 1.389 21.436 42.672 辉砷镍矿 2 隐晶质条带下端富含镍砷硫元素的条带 33.439 0.535 1.496 21.484 43.423 辉砷镍矿 3 同心圆状矿物外环 32.674 0.647 1.007 20.773 44.684 辉砷镍矿 4 圆粒状矿物间裂隙 32.354 0.409 1.014 19.624 47.432 辉砷镍矿 5 富含镍、硫和少量铁元素的条带 43.865 1.096 3.601 49.342 0.677 方硫镍矿 6 同心圆状矿物内部圆粒状矿物 0.404 1.008 44.420 51.572 1.798 粒状黄铁矿 7 胶状形态圆粒状矿物 6.507 0.590 26.312 61.815 0.432 胶状黄铁矿 8 富含钼、硫元素的灰色隐晶质条带 2.326 30.625 2.948 24.928 1.400 碳硫钼矿 9 磁黄铁矿边缘花边状矿物 34.646 0.503 32.087 33.294 0.315 镍黄铁矿 -
[1] 曾明果.遵义黄家湾镍钼矿地质特征及开发前景[J].贵州地质, 1998, 15(4): 305-310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ199804005.htm
[2] 张爱云,伍大茂,郭丽娜,王云龙.海相黑色页岩建造地球化学与成矿意义[M].北京: 科学出版社, 1987: 25-81.
[3] 范德廉,张焘,叶杰.缺氧环境与超大矿床的形成[J].中国科学: D辑, 1998, 28(Z1): 57-62. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK1998S2008.htm
[4] 蒲心纯.中国南方寒武纪岩相古地理与成矿作用[M].北京:地质出版社, 1994: 46-73.
[5] 吴朝东,储著银.黑色页岩微量元素形态分析及地质意义[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(1): 14-20. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200101004.htm
[6] 叶杰,范德廉.黑色岩系型矿床的形成作用及其在我国的产出特征[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2000, 19 (2): 95-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200002003.htm
[7] Coveney R M, Nansheng C. Ni-Mo-PGE-Au-rich ores in Chinese black shales and speculations on possible analogues in the United States[J].Mineralium Deposita, 1991, 26(2): 83-88.
[8] 李胜荣,高振敏.湘黔寒武系底部黑色岩系贵金属元素来源示踪[J].中国科学: D辑, 2000, 30(2): 169-174. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200002008.htm
[9] Michael S, Wallis E, Redtmann B D. Submarine-hydro-thermal exhalative ore layers in the black shales from South China and associated fossils-insights into a lower Cambrian facies and bio-evolution[J].Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2001,169(2): 165-191.
[10] 温汉捷,裘愉卓,刘世荣.硒在干酪根中的两种不同赋存状态: TEM证据[J]. 地球化学, 2003, 32(1): 21-27. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200301002.htm
[11] Jiang S Y, Chen Y Q, Ling H F.Trace-and rare-earth element geochemistry and Pb-Pb dating of black shales and intercalated Ni-Mo-PGE-Au sulfide ores in Lower strata, Yangtze Platform, South China [J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2006, 41(5): 453-467. doi: 10.1007/s00126-006-0066-6
[12] 畅斌,温汉捷. 贵州遵义黄家湾下寒武统牛蹄塘组镍钼富集层电子探针研究[J].矿物学报,2008,28(1): 439-445. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200804016.htm
[13] 吴朝东,杨承运,陈其英.湘西黑色岩系地球化学特征和成因意义[J].岩石矿物学杂志,1999, 18(2): 26-39. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW901.004.htm
[14] Mao J W, Lehmann B, Du A D. Re-Os dating of polymetallic Ni-Mo-PGE-Au mineralization in lower Cambrian black shales of South China and its geological significance[J].Economic Geology, 2002, 97(1): 1051-1061.
[15] 潘家永,马东生,夏菲.湘西北下寒武统镍-钼多金属富集层镍与钼的赋存状态[J].矿物学报, 2005, 25(3): 283-289. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB200503012.htm
[16] 于炳松,林畅松.塔里木盆地下寒武统底部黑色页岩地球化学及其岩石圈演化意义[J].中国科学: D辑, 2002,32(4): 374-382. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200205003.htm
[17] 曾明果.遵义黄家湾镍钼矿地质特征及开发前景[J].贵州地质,1998,15(4): 305-310. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZDZ199804005.htm
-





 DownLoad:
DownLoad: