Application of in-situ Micro-X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry in the Identification of Lead-Zinc Ore
-
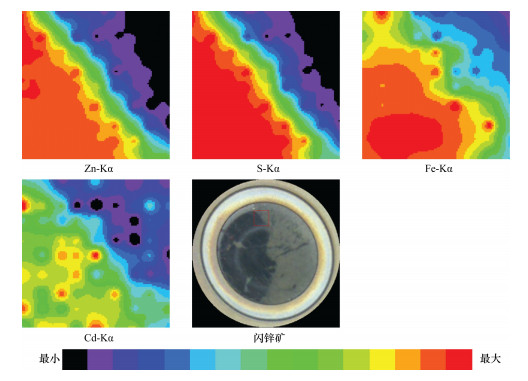
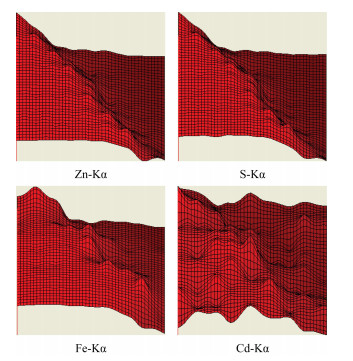
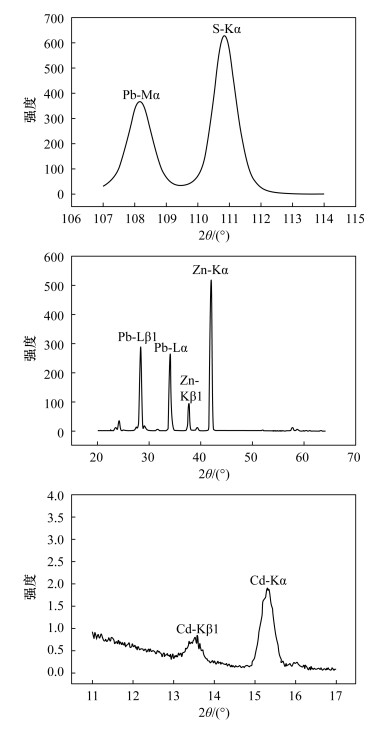
摘要: 自然界很多矿物存在类质同象现象,它们在显微镜下特征相似难以区分,对于这类矿物的鉴定,需要借助X射线衍射分析、电子显微镜、电子探针分析和离子探针分析等手段,获取矿物的化学成分和结构,为矿物鉴别提供有用的信息。本文以铅锌矿石中比较典型且易于收集的方铅矿(Pb 86.60%、S 13.40%)和闪锌矿(Zn 67.10%、S 32.90%)为例,借助偏反光显微镜,初步鉴定矿石的矿物特征;再利用X射线荧光光谱仪微区分析功能,对铅锌矿石标本进行定性和定量鉴定,对矿石所表现的各种特征做矿物学解释。实验结果表明,铅锌矿石标本中存在S、Pb、Zn、Cd等异常元素,并对闪锌矿标本中Zn、S、Fe、Cd等异常元素进行分布分析,绘制组分的二维或三维分布图显示各元素分布的异常区域高度一致;在电荷耦合器的实时监控下,对铅锌矿石标本靶区进行定点定量测定,根据所测组分含量,并结合矿物化学成分理论值定名为方铅矿和闪锌矿。本方法测定闪锌矿标本各组分的相对标准偏差(RSD,n=11)均小于4%,测定结果与电子探针测定结果吻合。本方法只要将矿石制成光片,无需喷碳处理,即可对铅锌矿石中主次量元素进行原位微区定性和定量分析,测定速度快且不破坏矿石标本,解决了类质同象矿物(如方铅矿和硒铅矿、闪锌矿和含铁闪锌矿等)在光学显微镜下鉴定困难的问题,提高了铅锌矿石定名的准确性,为岩矿鉴定工作提供一种新的技术手段。Abstract: Since isomorphous properties are common in many natural minerals, it is difficult to distinguish these minerals due to their similar characteristics under a microscope. The chemical composition and structure of these kinds of minerals can be obtained by using X-ray Diffraction Analysis, Electron Microscope Analysis, Electron Microprobe Analysis and Ion Probe Analysis, which can provide useful information for mineral identification. Galena (Pb 86.60%, S 13.40%) and sphalerite (Zn 67.10%, S 32.90%) contained in lead-zinc ore are more typical and are readily available to use as examples. The characteristic of minerals were determined preliminarily under the optical microscopy, and then the lead-zinc ore were qualitatively determined by using the in-situ micro-analysis function of RIGAKU ZSX Primus X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometer, which was applied to explain various characteristic of minerals. The experimental results show that the anomaly elements (S, Pb, Zn and Cd) were distinguished in some lead-zinc ores. According to the distribution analysis of the anomaly elements (Zn, S, Fe and Cd) in some sphalerite, 2D or 3D distribution images were established and the anomaly areas of elements are highly consistent. Under the real-time monitoring by charge-coupled device, the target area at the ore sample was quantitatively analyzed to identify the ore with its theoretical chemical components. The relative standard deviation (RSD, n=11) of determination of sphalerite sample components was less than 4%, which is comparable to the values obtained by Electron Microprobe. A new in-situ micro-analysis method of determining major and minor elements in lead-zinc ore is presented and is proved to be a fast non-invasive analytical technique. On the basis of the above analysis, a novel reasonable qualitative or quantitative analytical method for the identification of lead-zinc ore has been established, which provides a new method for the identification rock and minerals.
-
Key words:
- lead-zinc ore /
- X-ray Fluorescence Spectrometry /
- Micro-analysis
-

-
表 1 仪器参数
Table 1. Working parameters of the instrument
仪器参数 种类及范围 X射线管 端窗型,Rh靶材,4 kW 工作电压 20~60 kV 工作电流 2~160 mA 铍窗厚度 30 μm 视野光栏 0.5~30 mm 准直器 S2,S4 探测器 PC,SC 探测器窗膜厚度 0.6 μm 滤光片 Zr,Cu,Ti,Al 分光晶体 RX25,Ge,PET,LiF200,LiF220 样品观察装置 电荷耦合器 测试位置指定法 样品台驱动装置 表 2 分析元素测定条件
Table 2. Determination conditions of analyzed elements
元素 分析线 分析晶体 准直器 探测器 电压 电流 2θ/(°) 背景/(°) 脉冲高度分析器(PHA) 滤光片 U/kV i/mA LL UL S Kα Ge S4 PC 55 60 110.81 116.70 130 300 无 Fe Kα LiF200 S4 SC 55 60 57.51 60.30 90 380 无 Zn Kα LiF200 S4 SC 55 60 41.79 42.50 90 340 无 Pb Lβ1 LiF200 S4 SC 55 60 28.24 29.60 90 300 无 Cd Kα LiF200 S4 SC 55 60 15.29 17.50 100 300 Zr 表 3 实验用标准物质
Table 3. Standard reference materials in experiment
分类使用编号 标准物质名称 D14 钨酸锌 J6 铁 J10 锌 J18 铅 J31 镉 J72 硫化锑 J73 碲镉汞 J74 铅锡 K3 歪长石 K4 蔷薇辉石 K7 白铅矿 K18 黄铁矿 K21 橄榄石 K26 磷灰石 K31 钼铅矿 K32 硫砷玻璃 K37 蓝晶石 K51 方铅矿 K52 闪锌矿 K55 辉铋矿 K56 辉钼矿 K58 辰砂 K60 黄铜矿 K64 毒砂 K68 铬铅矿 K69 黑钨矿 K73 硫化镉 K81 硬玉 K82 菱镁矿 K83 氟化铅 表 4 精密度试验
Table 4. Precision tests of the method
组分 测定平均值
w/%RSD/% S 31.88 1.9 Fe 5.78 3.6 Zn 60.70 0.4 表 5 XRF微区分析与电子探针分析结果对照
Table 5. Comparison of analytical results by XRF microanalysis and electron microprobe analysis
元素 方铅矿1 方铅矿2 闪锌矿1 闪锌矿2 XRF
微区
分析电子
探针XRF
微区
分析电子
探针XRF
微区
分析电子
探针XRF
微区
分析电子
探针S 13.37 13.86 13.25 12.97 32.60 32.85 32.32 33.34 Fe - - - - 8.83 8.11 4.96 4.57 Zn - - - - 57.55 57.38 61.46 60.93 Pb 84.51 85.48 85.60 85.67 - - - - 表 6 铅锌矿石定性鉴定条件
Table 6. The conditions for qualitative analysis of lead-zinc ore
2θ/(°) 滤光片 分光晶体 探测器 衰减器 11~17 Zr LiF200 SC 1/1 20~64 无 LiF200 SC 1/10 107~114 无 Ge PC 1/1 -
[1] 潘巨祥,吴应荣,肖延安.北京同步辐射光源的微区X射线荧光分析[J].物理,1995,24(11): 691-693. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLZZ511.011.htm
[2] 闻莺,袁汉章,朱腾,刘亚雯.半导体硅材料中掺杂元素锗的SRXRF微区分析研究[J].分析试验室,1994,13(3): 77-79. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FXSY403.025.htm
[3] 吴强,刘亚雯,魏成连,袁汉章.用XRF微探针研究掺杂元素锗在单晶硅中的分布[J].光谱学与光谱分析,1995,15(2): 99-102. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN502.020.htm
[4] 吴强,刘亚雯,魏成连,袁汉章,朱腾,闻莺.用同步辐射X射线荧光微区分析技术测定单晶硅中的掺杂元素As[J].核技术,1994,17(8): 476-480. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJSU408.004.htm
[5] 刘亚雯,范钦敏,吴应荣,魏成连,肖辉.硅中掺杂元素砷的三维微分析[J].光谱学与光谱分析,1997,17(4): 96-99. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN704.020.htm
[6] 吴应荣,潘巨祥.同步辐射微束X射线荧光分析及其在生物医学中的应用[J].广东微量元素科学, 1998,10(5): 1-5. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWYS199810000.htm
[7] Adams F.Synchrotron radiation micro-X-ray fluorescence analysis: A tool to increase accuracy in microscopic analysis[J]. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B,2003,199: 375-381. doi: 10.1016/S0168-583X(02)01563-X
[8] 吴应荣,巢志瑜,潘巨祥,洪蓉,肖延安,李光诚,黄宇营,赵利敏.同步辐射微束X射线荧光分析实验站[J].高能物理与核物理,1997,21(5): 475-480. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KNWL705.013.htm
[9] 罗立强.2004欧洲X射线光谱分析会议[J].岩矿测试,2004,23(4): 285-286. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS200404010.htm
[10] 初学莲,林晓燕,程琳,潘秋丽,杨君,丁训良.微束X射线荧光分析谱仪及其对松针中元素的分布分析[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2007,43(5): 530-532. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ200705014.htm
[11] Vittiglio G, Janssens K, Vekemans B, Adams F, Oost A.A compact small-beam XRF instrument for in-situ analysis of objects of historical and/or artistic value[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy,1999,54: 1697-1710. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(99)00100-7
[12] Alsecz A. Analytical performance of different X-ray spectroscopic techniques for the environmental monitoring of the recultivated uranium mine site[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy , 2007,62: 769-776. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2007.06.002
[13] 宋卫杰,葛良全,杨健,张帮,殷经鹏.微束微区X荧光探针分析仪在矿石微粒分析中的应用[J].核电子学与探测技术,2009,29(4): 828-831. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HERE200904028.htm
[14] Isaure M P.Localization and chemical forms of cadmium in plant samples by combining analytical electron microscopy and X-ray spectromicroscopy[J]. Spectro-chimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy ,2006,61: 1242-1252. doi: 10.1016/j.sab.2006.10.009
[15] Ramos S S.Study and dating of medieval ceramic tiles by analysis of enamels with atomic absorption spectroscopy, X-ray fluorescence and electron probe microanalysis[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part B: Atomic Spectroscopy ,2002,57: 689-700. doi: 10.1016/S0584-8547(01)00395-0
-



 下载:
下载: