Analysis of Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Oil and Gas Geochemical Exploration Samples by Fluorescence Spectrometry
-
摘要: 荧光光谱法避免了色谱法所需的大量分离工作,具有灵敏度高、检测限低、分析速度快等特点,非常适用于油气化探样品分析。本文对常规荧光光谱分析的样品前处理方法和仪器测定参数进行优化,建立了适用于测定油气化探样品中芳烃的荧光光谱分析方法。实验采用农残级正己烷作为溶剂,简化了溶剂提纯操作,采用振荡器间歇振荡方式有效地提高了芳烃的提取效果。在优化的仪器条件下对油气化探样品中的芳烃进行检测,选择萘、菲、 (䓛) 三种标准物质,采用单点外标法对样品激发波长265 nm,发射波长为320 nm、360 nm、405 nm的三个特征光谱峰进行定量分析,测定结果采用量化后的浓度值代替常用的荧光强度值,使不同实验室、不同型号仪器间的荧光指标具有统一的定量标准,提高了数据的可比性。本方法检测限为1.8 ng/g(以萘计算),优于行业标准(SY/T 6009.8—2003)规定的检出限≤2 ng/g要求,方法精密度(RSD,n=12)为4.5%(320 nm)、9.6%(360 nm)、14.7%(405 nm)。通过质量控制与质量管理体系的完善,本方法已经在大庆地区油气化探工作中得到实际应用,荧光指标对样品采样深度确定及异常点发现具有良好的指示作用。Abstract: Fluorescence spectrometry, with the characteristics of high sensitivity, low detection limits and rapid analysis, avoids complex separating work in the chromatography method, and is suitable for oil and gas geochemical exploration samples requiring a large number of assays. In this paper, sample pretreatment methods and analytical conditions that were optimized in order to analyse aromatic hydrocarbons in oil samples by fluorescence spectrometry are reported. Ultra pesticide residue grade n-hexane was selected as the extraction solvent, which simplified the purification operation, and intermittent oscillation was selected to improve the extraction effect of aromatics. Through selecting proper standard materials (naphthalene, phenanthrene and chrysene) and adopting an external standard method, aromatic hydrocarbon in the samples was determined under the optimal analytical conditions. With the excitation wavelength of 265 nm and the emission wavelength of 320 nm, 360 nm and 405 nm, the fluorescent spectra of aromatic hydrocarbon were studied. The relative intensities were converted into the concentration of a certain standard material, which could then be used to compare the fluorescence data between different laboratories and different instruments. The detection limit of the method was 1.8 ng/g (naphthalene), which was lower than the limit of the national industry standard (2.0 ng/g, SY/T 6009.8—2003). The precision results of the method (RSD, n=12) were 4.5% (320 nm), 9.6% (360 nm) and 14.7% (405 nm), respectively. Through improving the quality control and management, the proposed method has been conducted successfully in the Daqin oil field, and it was found that the fluorescent data could effectively indicate sampling depth and anomalies.
-

-
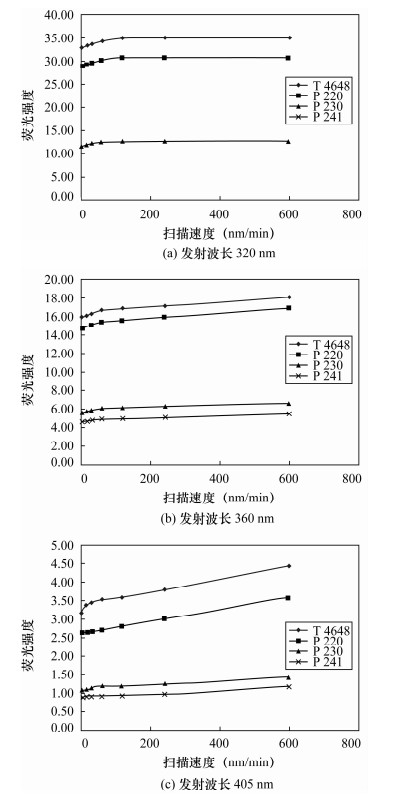
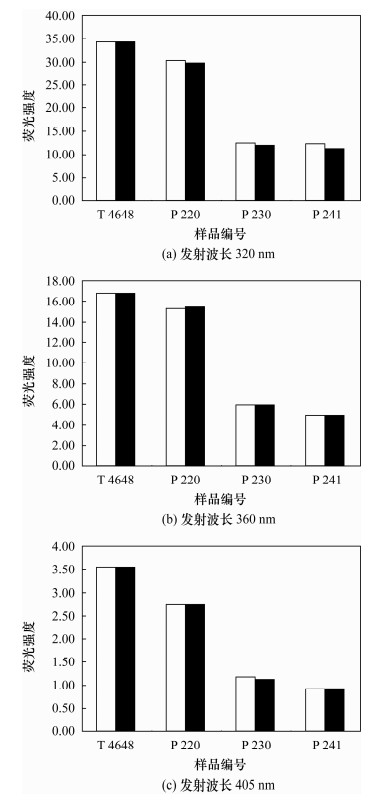
表 1 不同仪器测定相同样品量化测试结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of quantitative results for the same sample determined with different instruments
激发波长为
265 nm时
的发射波长样品
编号参数 T4648 P220 P230 P241 320 nm 1 荧光强度 34.35 30.23 12.63 12.39 芳烃浓度(μg/g) 7.875 6.839 2.735 2.628 2 荧光强度 101.4 87.40 49.70 49.20 芳烃浓度(μg/g) 8.068 7.029 2.93 2.913 360 nm 1 荧光强度 16.70 15.28 5.983 4.953 芳烃浓度(μg/g) 0.123 0.111 0.041 0.033 2 荧光强度 79.60 66.80 40.00 38.80 芳烃浓度(μg/g) 0.142 0.122 0.043 0.035 405 nm 1 荧光强度 3.533 2.753 1.177 0.918 芳烃浓度(μg/g) 0.071 0.054 0.018 0.014 2 荧光强度 16.80 11.70 9.900 6.800 芳烃浓度(μg/g) 0.079 0.060 0.022 0.015 注:1号样品由中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学勘查研究所测定,2号样品由天津医科大学测定。 表 2 荧光光谱法测定2 μg/mL萘、菲、䓛标准品荧光强度的精密度
Table 2. The precision tests of 2 μg/mL naphthalin, phenanthrene, chrysene as standard samples determined by fluorescence spectrometry
测定次数 激发波长为265 nm时各发射波长的荧光强度 发射波长320 nm 发射波长360 nm 发射波长405 nm 1 11.83 353.6 139.9 2 11.78 353.9 140.1 3 11.86 353.6 140.2 4 11.56 350.5 140.1 5 11.68 351.6 140.3 6 11.75 352.3 140.5 7 11.62 350.5 140.0 8 11.26 335.5 138.9 9 11.48 345.1 137.6 10 11.57 354.6 141.7 11 11.68 356.0 141.1 12 11.68 354.1 141.7 RSD(%) 1.4 1.6 0.8 表 3 荧光光谱法测定2 μg/mL萘、菲、䓛标准品荧光强度的长期精密度
Table 3. The long-term precision tests of 2 μg/mL naphthalin, phenanthrene, chrysene as standard samples determined by fluorescence spectrometry
测定次数 激发波长为265 nm时各发射波长的荧光强度 发射波长320 nm 发射波长360 nm 发射波长405 nm 1 13.08 395.1 155.5 2 13.43 403.2 156.5 3 13.15 396.3 154.7 4 12.57 378.5 148.5 5 12.63 379.9 148.1 6 12.06 361.5 139.4 7 10.88 328.4 129.0 8 10.72 324.7 127.9 9 10.60 321.1 126.1 10 11.46 348.3 136.8 11 11.36 347.0 135.4 12 11.58 351.0 138.1 长期RSD(%) 8.3 8.0 7.8 表 4 荧光光谱法测定实际样品(10号样品)中芳烃的精密度
Table 4. The precision tests of aromatic hydrocarbon in actual sample (No.10) determined by fluorescence spectrometry
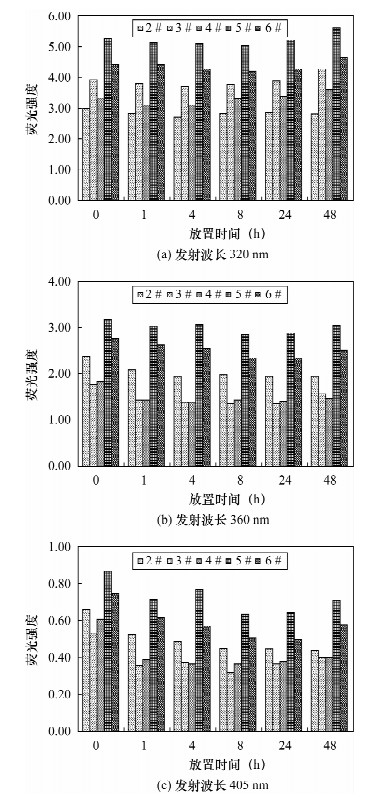
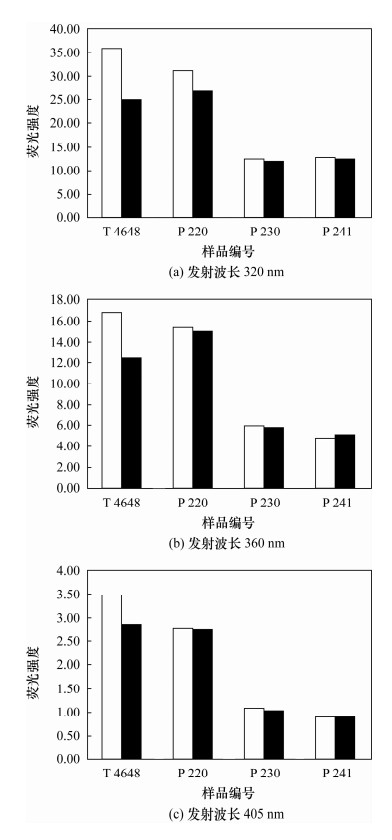
测定次数 激发波长为265 nm时各发射波长的荧光强度 发射波长320 nm 发射波长360 nm 发射波长405 nm 1 9.146 5.410 1.484 2 9.043 4.924 1.212 3 8.329 4.810 1.220 4 8.868 5.291 1.142 5 9.563 4.516 1.469 6 8.794 5.776 1.686 7 9.388 5.871 1.562 标准偏差 0.41 0.50 0.21 平均值 9.02 5.23 1.40 RSD(%) 4.5 9.6 14.7 表 5 实际样品中芳烃重复分析的结果
Table 5. The reduplicate analysis of aromatic hydrocarbon in actual samples
发射波长 样品T4648的荧光强度 样品P220的荧光强度 样品P230的荧光强度 样品P241的荧光强度 第1次 第2次 第1次 第2次 第1次 第2次 第1次 第2次 320 nm 34.10 34.35 29.63 30.23 12.37 12.63 11.98 12.39 360 nm 16.23 16.70 14.93 15.28 5.811 5.983 4.794 4.953 405 nm 3.533 3.588 2.753 2.819 1.177 1.171 0.918 0.935 以320 nm萘计算的相对偏差 0.52% 1.42% 1.47% 0.53% -
[1] 朱扬明.塔里木原油芳烃的地球化学特征[J].地球化学,1996,25(1):10-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201101019.htm
[2] Requejo A G, Sassen R, Mcdonald T, Denoux G, Kennicutt Ⅱ M C, Brooks J M.Polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (PAH) as indicators of the source and maturity of marine crude oils[J].Organic Geochemistry, 1996,25(11):1017-1033.
[3] 刘洛夫,王伟华,徐新德,毛东风.塔里木盆地群5井原油芳烃地球化学研究[J].沉积学报,1996,14(2):49-57. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB602.005.htm
[4] 宋继梅,胡刚.芳烃分析在油气化探中的作用和意义[J].物探与化探,2003,27(2):97-100. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200302004.htm
[5] 宋继海,黄建军.油气化探样品芳烃分析中干扰因素的识别[J].化学通报,2004(9):695-699. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXTB200409014.htm
[6] 蒋涛,汤玉平,李武,张恒启.分析和认识我国油气化探技术[J].物探与化探,2011,35(1):7-11. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201101003.htm
[7] Jonny B, Grete J, Cinta P, Margaret M K, Freek A.Analytical methods for determining metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollutants in fish bile: A review[J].Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2010, 35:224-244.
[8] 李庆霞,刘亚轩,王正武,陈卫明,张勤.微波辅助萃取及其联用技术在有机污染物分析中的应用[J].物探与化探,2010,34(2):134-140. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXTB201002009.htm
[9] 胡斌,李武,程桂.HPLC-DAD-FD联用检测油气化探样品的芳烃[J].物探与化探,2003,27(2):101-103. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200302005.htm
[10] 李武,雍克岚.三维荧光光谱指纹技术应用研究[J].石油勘探与开发,1996,23(4):32-34. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK604.008.htm
[11] 孙忠军.真武油田水中紫外荧光异常与油气关系[J].世界地质,1990(3):94-97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJDZ199003012.htm
[12] 崔树宝.紫外分光光度法测定石油产品中芳烃含量[J].天津化工,2006,20(6):51-52. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TJHG200606020.htm
[13] 宁丽荣,汤玉平,赵克斌,李吉鹏,陈浙春,蒋涛.油气勘探荧光光谱法在土壤与其上方积雪的对比实验[J].物探与化探,2011,35(3):337-339. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201103012.htm
[14] 程军,刘伟,程正发,宋明水,李学田.近地表荧光光谱特征及其与烃源岩关系初探——以合肥盆地为例[J].安徽地质,2004,14(4):277-281. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AHDZ200404012.htm
[15] 程同锦,戴联善.油气化探技术的现状与发展、问题与对策[C]//第四届全国油气化探学术会议论文集.武汉:中国地质大学出版社,1998:7-13.
[16] 陈国珍,黄贤纠,郑朱梓.荧光分析法(第二版)[M].北京:科学出版社,1990:31-57.
[17] Hegazi E, Hamdan A, Mastromarino J.New approach for spectral characterization of crude oil using time-resolved fluorescence spectra[J].Applied Spectroscopy,2001,55(2):202-207. doi: 10.1366/0003702011951515
[18] 宁丽荣,沈洪久,李武,张庆珍,王波舫.影响荧光光谱分析质量的因素[J].物探与化探,2008,32(6):675-677. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200806023.htm
[19] 胡斌,赵淑华,王凌峰,程桂英.油气化探荧光指标量化方法初探[J].物探与化探,2001,25(1):132-134. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200102008.htm
[20] SY/T 6009.8—2003,油气化探试样测定方法;第8部分:稠环芳烃测定;荧光法[S].
-



 下载:
下载: