Determination of 1,4-dioxane in Groundwater by Purge and Trap-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry
-
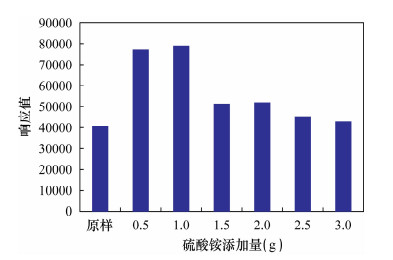
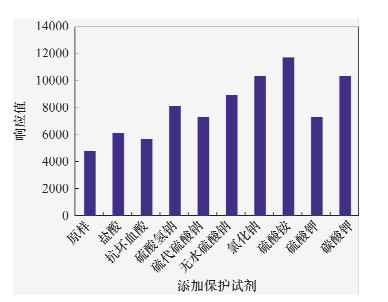
摘要: 1,4-二噁烷有毒,极易进入生态系统对人体及环境造成危害,在自然环境中对水的亲和性较强,且不易为生物所降解,是地下水中一种新型有机污染物,已被世界卫生组织(WHO)定为一种受控物质。但仅有少数国家对地下水中1,4-二噁烷含量作出限量规定,如日本为50 μg/L;我国在此方面尚未作出规定,有关检测方法也未见文献报道。吹扫捕集-气相色谱-质谱法(P&T-GC/MS)具有分析快捷、方法简便、检出限低等优点,近年来被广泛应用于水样分析,本文应用该方法测定地下水中的痕量1,4-二噁烷。通过添加硫酸铵作为样品保护剂,提高了样品的保存时间及防止样品因微生物降解等因素产生变质的问题,同时改善了1,4-二噁烷吹扫脱附效果,仪器响应值提升了1倍。在优化的实验条件下,方法精密度为5.9%~6.6%;检出限为1.02 μg/L,已经达到了WHO饮用水质量标准限量(0.05 mg/L)要求,且低于同位素稀释-GC-MS的检出限(3.2 μg/L)。本方法可以满足地质调查及环境评价的需求。Abstract: 1,4-dioxane is toxic, easily entering the ecological system to cause damage of the environment and people health. It is relatively strong affinity for water, and not easy to be biodegradable in the natural environment. 1,4-dioxane is a new type of organic contaminants in groundwater, has been defined as one of the controlled substances by World Health Organization (WTO). But only few countries defined the limited value of 1,4-dioxane content in groundwater, as Japan is 50 μg/L. In China, this research field is rarely concerned, and there is none report for detection method of 1,4-dioxane in groundwater either. Purge and Trap-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry(P&T-GC/MS) is a fast, simple analytical method with low detection limit, in recent years it has been widely used in water analysis. This paper chooses P&T-GC/MS for the determination of trace 1,4-dioxane in groundwater. In the experiment, ammonium sulfate was added as sample protective agent to increase the sample storage time and prevent the deterioration from microbial degradation and other factors, but also improve the efficiency of the purge desorption for 1,4-dioxane, the instrument response value increased by one times. Under the optimized operating conditions of the instrument, the precision is 5.9%-6.6%; the detection limit is 1.02 μg/L, has been reached WHO standard for drinking water quality limit (0.05 mg/L), and is lower than the isotope dilution-GC-MS detection limit of 3.2 μg/L. This method can meet the demands during geological investigation and environmental assessment.
-
Key words:
- groundwater /
- 1,4-dioxane /
- purge and trap /
- Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
-

-
表 1 水中1,4-二噁烷分析方法精密度及回收率
Table 1. The precision and recovery for 1,4-dioxane analysis in water
技术指标 1,4-二噁烷添加标准 5 μg/L 1,4-二噁烷添加标准 50 μg/L 平均回收率(%) 98.0 104.7 7次平均测定值(μg/L) 4.90 52.3 RSD(%) 6.6 5.9 表 2 实际样品的1,4-二噁烷检测结果
Table 2. Analytical results of 1,4-dioxane in actual samples
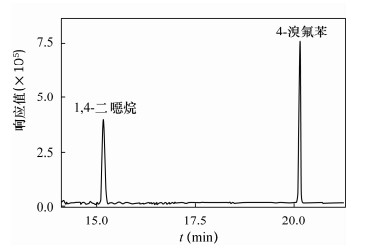
检测项目 测定值(μg/L) 样品1(地下水①) 样品2(地下水②) 样品3(自来水) 样品4(雨水) 样品5(自来水平行样) 1,4-二噁烷 - - - - - 4-溴氟苯(替代物)回收率(%) 102.1 97.8 89.4 107.4 101.6 表 3 样品加标检测结果
Table 3. The spike recovery tests of the method
检测指标 测定值(μg/L) 平均加标回收率(%) 平行样相对偏差(%) 加标量 加标样1 加标样2 1,4-二噁烷 5.00 4.96 5.12 100.8 2.2 1,4-二噁烷 20.0 20.2 19.7 99.8 2.0 4-溴氟苯替代物回收率(%) - 99.4 98.5 - - -
[1] 陈平,李文攀,刘廷良.日本地下水环境质量标准及监测方法[J].中国环境监测,2011,27(6): 59-63. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-IAOB201106017.htm
[2] 国家食品药品监督管理局关于化妆品中二噁烷限量值的公告(第4号). 2012.
[3] Rastogi S C.Headspace analysis of 1,4-dioxane in products containing polyethoxylated surfactants by GC-MS chromatographia[J].Chromatographia,1990,29(5):441-445.
[4] Black R E, Hurley F J, Havery D C.Occurrence of 1,4-dioxane in cosmetic raw materials and finished cosmetic products[J].Journal of AOAC International, 2001, 84(3):666-701.
[5] 张智宏,孙晓娟.烷基醇聚氧乙烯中1,4-二噁烷的测定[J].色谱, 1998, 16(3): 244-246.
[6] Scalia S.Reversed phase high performance liquid chr-omatographic method for the assay of 1,4-dioxane in sulphated polyoxyethylene alcohol surfactants [J].Analysis, 1990, 8:867-870.
[7] 黄业茹,施钧慧,唐莉.固相萃取工业废水中二噁烷的GC/MS分析[J].质谱学报,2000, 22(1):71-24. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPXB200101011.htm
[8] 林晓珊,吴惠勤,黄晓兰,马叶芬,黄芳,朱志鑫,邓欣,罗辉泰.顶空气相色谱-质谱法测定洗浴用品及原材料中1,4-二氧杂环己烷残留量[J].理化检验(化学分册),2010,46(8):938-942. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH201008028.htm
[9] 顶空气质联用法快速检测洗发水中的二噁烷[R]//岛津应用报告.2010.
[10] 常宇文,田野,曹红,周相娟,赵玉琪,李伟,许华,谢精精.1,4-二噁烷含量测定中固相微萃取头的选择研究[J].分析测试学报,2008, 27(11): 130-133. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TEST2008S1051.htm
[11] Kawata K, Ibaraki T, Tanabe A, Yasuhara A. Dis-tribution of 1,4-dioxane and N,N-dimethylformamide in river water from Niigata, Japan [J].Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology,2003(70):876-882.
[12] Fuh C B, Lai M, Tsai H Y, Chang C M. Impurity analysis of 1,4-dioxane in nonionic surfactants and cosmetics using headspace solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography and gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J].Journal of Chromatography A,2005, 1071(1-2): 141-145. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2004.09.012
[13] Florida Department of Environmental Protection Bureau of Laboratories.Analytical Methods and Recommend-ations for the Analysis of 1,4-Dioxane[R]. 2010.
[14] EPA 524.1.Measurement of Purgeable Organic Compo-unds in Water by Packed Column Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry[S].
-



 下载:
下载: