Determination of Lead, Cadmium, Copper and Iron Contents in Water by Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes-solid Phase Extraction
-
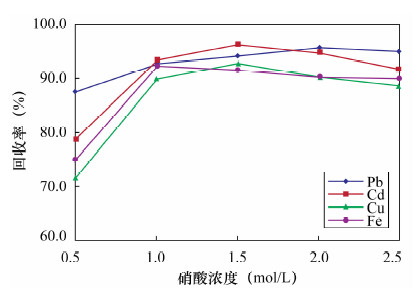
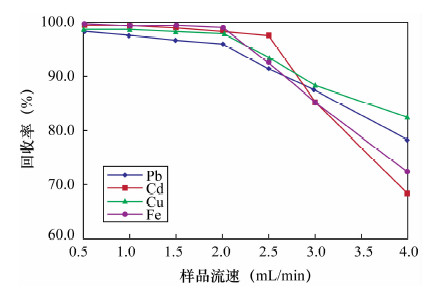
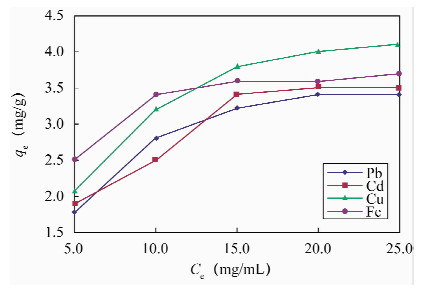
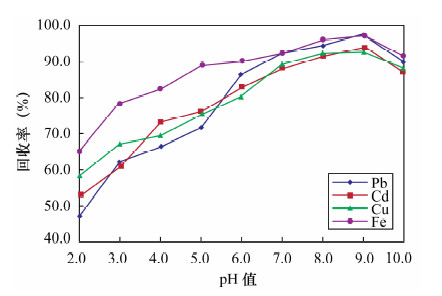
摘要: 传统的固相萃取填料应用于环境样品的重金属处理过程中,存在pH不稳定和不同极性萃取物共同萃取较为困难等方面的不足,因此寻找新型固相萃取填料显得尤为重要。本文采用多壁碳纳米管填充固相萃取柱,萃取水中金属元素铅、镉、铜和铁,采用石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定铅和镉,电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定铜和铁。实验考察了多壁碳纳米管的性质、溶液pH值、洗脱溶液、样品流速以及基体效应对测定结果的影响。结果显示:溶液pH=9,1 mol/L硝酸为洗脱溶液,样品流速为2 mL/min时,外径<8 nm未修饰的多壁碳纳米管有较好的萃取效率,对溶液中铅、镉、铜和铁的最大吸附容量分别为44.91、42.31、54.68和49.07 mg/g,四种元素的吸附容量均衡;钾、钠、钙、镁离子以及苯和甲苯等基质对四种金属元素的萃取影响不大。方法回收率为95.3%~99.5%,精密度(RSD,n=7)为1.2%~3.2%。本方法采用外径<8 nm的多壁碳纳米管固相萃取,与传统萃取方法相比,富集效果好、回收率较高,而且操作简便、准确度高;与前人采用外径20~30 nm的多壁碳纳米管的性能相比,镉和铜的吸附容量更高,还可实现对铁的吸附,且铅、镉、铜和铁四种元素的吸附容量均衡,更适合用于检测水样中的金属元素。Abstract: The traditional solid phase extraction sorbent contains certain deficiencies in the progress of processing heavy metals in environmental samples, such as pH instability and co-extraction difficulty. Therefore, it is particularly important to find more efficient sorbents. A solid-phase extraction method using multi-walled carbon nanotube as absorbent materials for Pb, Cd, Cu and Fe in water has been determined. The effects of solution pH, elution solution, sample volume and matrix effects were investigated. Pb and Cd were determined by Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry; alternatively, Cu and Fe were determined by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry. Experimental results show that the extraction of the metal elements is most efficient when the pH value is 9.0 and flow rate is 2 mL/min with 1 mol/L HNO3 as the elution solution by using the unmodified multi-walled carbon nanotube (outer diameter <8 nm). The maximum adsorption capacities of multi-walled carbon nanotube for Pb, Cd, Cu and Fe are 44.91, 42.31, 54.68 and 49.07 mg/g, respectively. K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, benzene and toluene have little effect on Pb, Cd, Cu and Fe extraction. The recoveries of Pb, Cd, Cu and Fe were 95.3%-99.5%, and RSD values (n=7) were 1.2%-3.2%, respectively. Compared with the traditional extraction method, this new method not only has high recovery and enrichment effect, but also is simple and accurate, which can be used in the detection of Cd, Cu, Fe and Pb in environmental water samples.
-
Key words:
- water samples /
- Pb /
- Cd /
- Cu /
- Fe /
- solid phase extraction /
- multi-walled carbon nanotubes
-

-
表 1 多壁碳纳米管性质对金属离子吸附效率的影响
Table 1. Effect of MWCNTs property on extraction recovery
材料名称 外径(nm) 金属元素回收率(%) Pb Cd Cu Fe 多壁碳纳米管 < 8 94.9 95.3 96.2 97.0 多壁碳纳米管 8~15 91.2 94.2 94.3 95.7 多壁碳纳米管 10~20 90.9 91.1 93.7 94.3 多壁碳纳米管 20~30 88.1 90.3 93.3 94.7 多壁碳纳米管 30~50 87.9 85.3 90.0 91.4 多壁碳纳米管 >50 85.7 83.0 84.7 87.9 羟基化多壁碳纳米管 < 8 87.1 93.7 94.0 97.2 羧基化多壁碳纳米管 < 8 94.6 94.4 93.6 98.0 表 2 基体效应对金属离子萃取的影响
Table 2. Effect of matrix effects on extraction recovery
组分 加入量(mg/L) 回收率(%) Pb Cd Cu Fe K+ 5000 97.1 98.3 95.4 99.2 Na+ 10000 99.5 98.5 97.6 97.4 Ca+ 5000 96.9 98.7 99.1 99.8 Mg+ 2000 97.3 98.5 99.4 99.7 苯 1.0 95.1 96.7 98.9 97.7 甲苯 2.0 96.4 95.9 97.0 96.9 表 3 方法准确度和精密度
Table 3. Precision and recovery tests of the method
元素 m(μg) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 元素 m(μg) 回收率(%) RSD(%) 加入量 测定值 加入量 测定值 Pb 0 <LOD - - Cu 0 <LOD - - 5 4.83 96.6 2.4 5 4.79 95.8 2.1 10 9.71 97.1 1.2 10 9.53 95.3 2.5 20 19.3 96.5 1.4 20 19.21 96.1 2.1 Cd 0 <LOD - - Fe 0 1.20 - 3.2 5 4.91 98.2 2.8 5 6.02 96.4 2.1 10 9.82 98.2 2.3 10 10.95 97.5 2.0 20 19.5 97.5 1.9 20 21.1 99.5 2.3 注:“<LOD”为小于方法检出限,下表同。 表 4 不同吸附剂的吸附容量比较
Table 4. Comparison of adsorption capacity of different adsorption agents
表 5 实际水样分析结果
Table 5. Analytical results of the actual water samples
实际水样 金属元素含量(mg/L) Cd Cu Fe Pb 甘河滩 0.08 3.1 14.3 0.2 湟水河 <LOD 1.2 9.8 <LOD 大通河 <LOD 0.9 10.6 <LOD -
[1] Sprynskyy M, Buszewski B, Terzyk A P. Study of the selection mechanism of heavy metal (Pb2+, Cu2+, Ni2+ and Cd2+) adsorption on clinoptilolite [J].Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2006, 304(1):21-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2006.07.068
[2] Liang P, Sang H B. Determination of trace lead in biological and water samples with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction preconcentration [J].Analytical Bio-chemistry, 2008, 380:21-25.
[3] Naseii M T, Hosseini M R, Assadi Y, Kiani A. Rapid determination of lead in water samples by dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction coupled with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry[J].Talanta,2008,75:56-62. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2007.10.029
[4] Liang P, Zhao E H, Li F. Dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction preconcentration of palladium in water samples and determination by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry[J].Talanta, 2009, 77:1854-1857. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.10.033
[5] 台希, 李海涛, 李德良, 胡秋芬, 杨光宇, 尹家元. 固相萃取富集高效液相色谱法测定环境水样中的重金属元素[J].干旱环境监测, 2004, 32(2):67-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHJC200402001.htm
[6] Wu Y W, Jiang Y Y, Wang F, Han D Y. Extraction of chromium, copper, and cadmium in environmental samples using cross-linked chitosanbound FeC nano-particles as solid-phase extractant and determination by flame atomic absorption spectrometry [J].Atomic Spectroscopy, 2007, 28(5):183-188.
[7] 黄海涛, 李忠, 陈章玉, 王保兴, 施红林, 杨光宇. 固相萃取富集-高效液相色谱法测定烟草和烟草添加剂中的重金属元素[J].理化检验(化学分册),2004,40(5):251-254. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LHJH200405002.htm
[8] 杨亚玲, 杨国荣, 胡秋芬, 杨光宇, 尹家元. 固相萃取富集-高效液相色谱法测定4种中草药中的重金属元素[J].药物分析杂志, 2004, 24(4):441-443. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWFX200404035.htm
[9] 周骁腾, 侯静怡, 卢恒, 刘金欣, 魏英勤, 孟繁蕴. 萃取技术在中药材重金属检测样品前处理中应用[J].中医药导报, 2013, 19(5):5-7. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNZB201305001.htm
[10] Anastassiades M, Lehotay S J, Stajnbaher D, Schenck F J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and "dispersive solid-phase extraction" for the determination of pesticide residues in produce[J].Journal of AOAC International, 2003, 86(2):412-431.
[11] Nigel J K S. Solid-Phase Extraction: Principles, Tech-niques, and Applications [M].New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 2000.
[12] 成会明. 纳米碳管——制备、结构、物性及应用[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2002.
[13] Endo M, Takeuchi K, Kobori K, Katsushi T, Harold W K, Sarkar A. Pyrolytic carbon nanotubes from vapor-grown carbon fibers [J].Carbon, 1995, 33:873-881. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(95)00016-7
[14] 辜萍, 王宇, 李广海. 碳纳米管的力学性能及碳纳米管复合材料研究[J].力学进展, 2002, 32(4):563-568. doi: 10.6052/1000-0992-2002-4-J2001-114
[15] 朱宏伟, 吴德海, 徐才录. 碳纳米管(第一版)[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社, 2003.
[16] Chen W, Duan L, Zhu D. Adsorption of polar and non-polar organic Chemicals to carbon nanotubes[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2007, 41(24):8295-8300.
[17] Yang K, Wang X L, Zhu L Z, Xing B S. Competitive sorption of pyrene, phenanthrene, and naphthalene on multiwalled carbon nanotubes[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(18):5804-5810.
[18] Li Y H, Ding J, Luan Z K, Di Z C, Zhu Y F, Xu C L, Wu D H, Wei B Q. Competitive adsorption of Pb2+, Cu2+and Cd2+ions from aqueous solutions by multiwalled carbon nanotubes[J].Carbon, 2003, 41(14):2787-2792. doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(03)00392-0
[19] Peng X J, Luan Z K, Di Z C, Zhang Z Z, Zhu C L. Carbon nanotubes-iron oxides magnetic composites asadsorbent for removal of Pb(Ⅱ) and Cu(Ⅱ) from water[J].Carbon, 2005, 43(4):880-883. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.11.009
[20] Lu C, Chiu H, Liu C. Removal of zinc(Ⅱ) from aqueous solution by purified carbon nanotubes: Kinetics and equilibrium studies [J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2006, 45(8):2850-2855.
[21] Rao G P, Lu C, Su F. Sorption of divalent metal ions from aqueous solution by carbon nanotubes: A review[J].Separation and Purification Technology, 2007, 58(1):224-231. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2006.12.006
[22] Fu F L, Wang Q. Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewaters: A review[J].Journal of Environmental Management, 2011, 92:407-418.
[23] Maquieira A, Elmahadi H A M, Puchades R. Imm-obilized cyanobacteria for online trace metal enrichment by flow injection atomic absorption spectrometry [J].Analytical Chemistry, 1994, 66(21):3632-3638. doi: 10.1021/ac00093a016
[24] Mohan D, Pittman C U, Bricka M, Smith F, Yancey B, Mohammad J, Steele P H, Alexandre-Franco M F, Gomez-Serrano V, Gong H.Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production[J].Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2007, 310:57-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2007.01.020
[25] Rao M M, Ramana D K, Seshaiah K, Wang M C, Chien S W C. Removal of some metal ions by activated carbon prepared from Phaseolus aureus hulls[J].Journal of Hazard Materials, 2009, 166:1006-1013. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.12.002
[26] Ayala J, Blanco F, Garcia P, Rodriguez P, Sancho J. Asturian fly ash as a heavy metals removal material[J].Fuel, 1998, 77:1147-1154. doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(98)00027-1
[27] Pavasant P, Apiratikul R, Sungkhum V, Suthiparinya-nont P, Wattanachira S, Marhaba T F. Biosorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+ using dried marine green macroalga caulerpa lentillifera[J].Bioresource Technology, 2006, 97:2321-2329. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2005.10.032
-



 下载:
下载: