Dataset of Field Testing of the Groundwater in the Fangchenggang Area of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region
-
摘要:
广西防城港是我国华南沿海酸性地下水发育的典型地区,2013—2015年在该地区开展了地下水调查,获取了一批地下水现场测试数据。广西防城港地下水现场测试数据集包含丰水期和枯水期现场测试数据2个Excel数据表格。每个Excel数据表格包含调查点位置、地下水埋深、地下水类型、地下水物理和化学特征等地下水现场测试数据。本数据集共采集水点323组,分析结果表明防城港地区地下水以pH为5.50~6.50的偏酸性地下水为主,此结果不仅能为防城港地下水资源评价和开发提供资料支撑, 还可为华南沿海酸性地下水的研究提供典型范例。
Abstract:The Fangchenggang area of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region is a typical coastal area in South China where acidic groundwater is well developed. A groundwater survey was carried out in this area during 2013—2015. As a result, a batch of field-testing data of the groundwater was obtained and a dataset was developed (also referred to as the Dataset). The Dataset consists of 2 Excel data tables that respectively contain the field-testing data of the groundwater during the wet and dry seasons. Each of the data tables is comprised of data items such as survey point locations, burial depth of groundwater, groundwater type and the physical and chemical characteristics of the groundwater. It can be shown from the Dataset that the groundwater in Fangchenggang is weakly acidic with a pH value ranging from 5.50–6.50. The Dataset will provide data for the assessment and development of groundwater resources in the Fangchenggang area and also offer a typical demonstration for research on acidic groundwater in the coastal areas of South China.
-
Key words:
- groundwater hydrochemical analysis /
- pH value /
- field testing /
- dataset /
- hydrogeological survey engineering /
- Fangchenggang /
- Guangxi
-

-
表 1 数据库(集)元数据简表
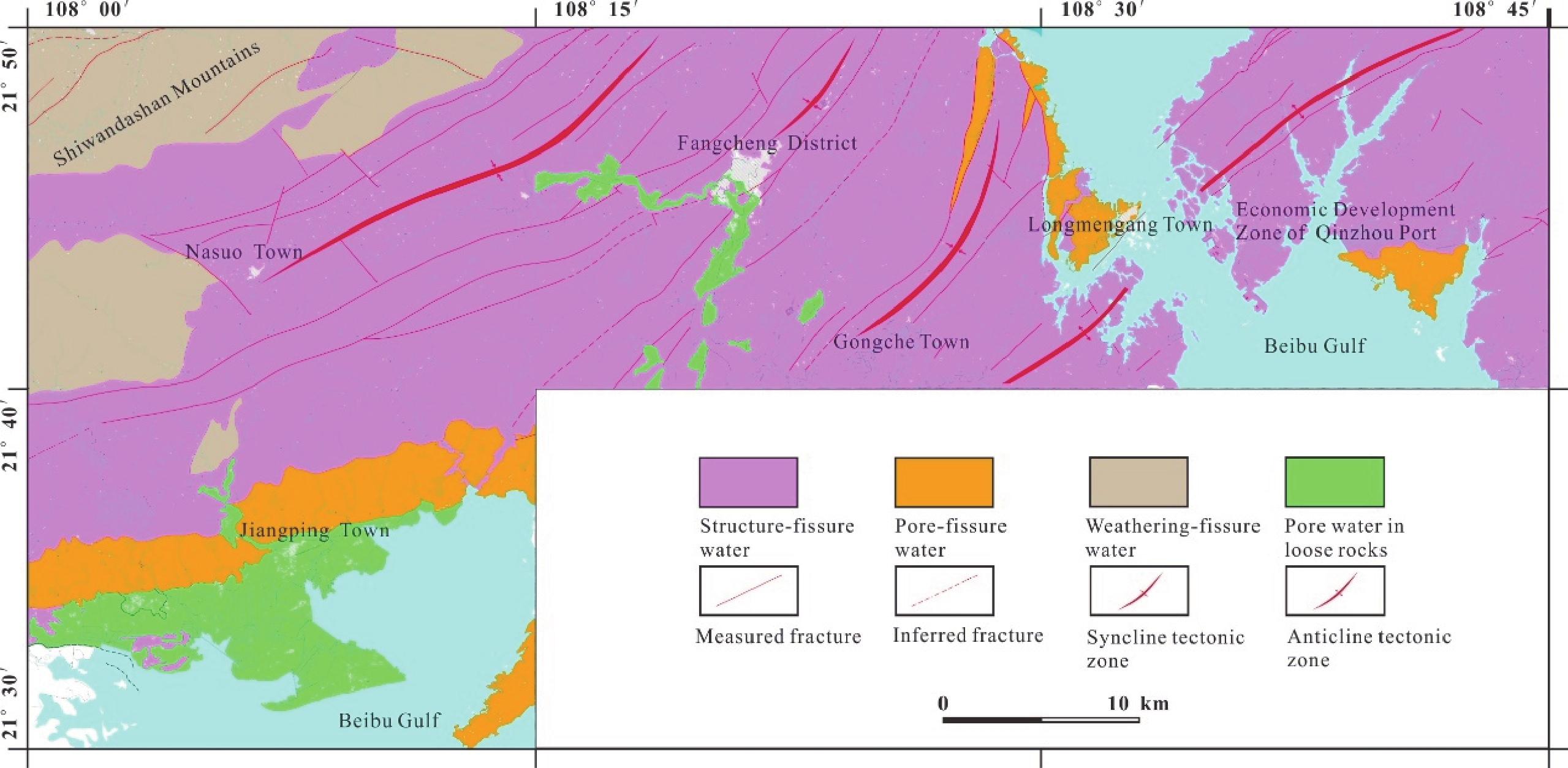
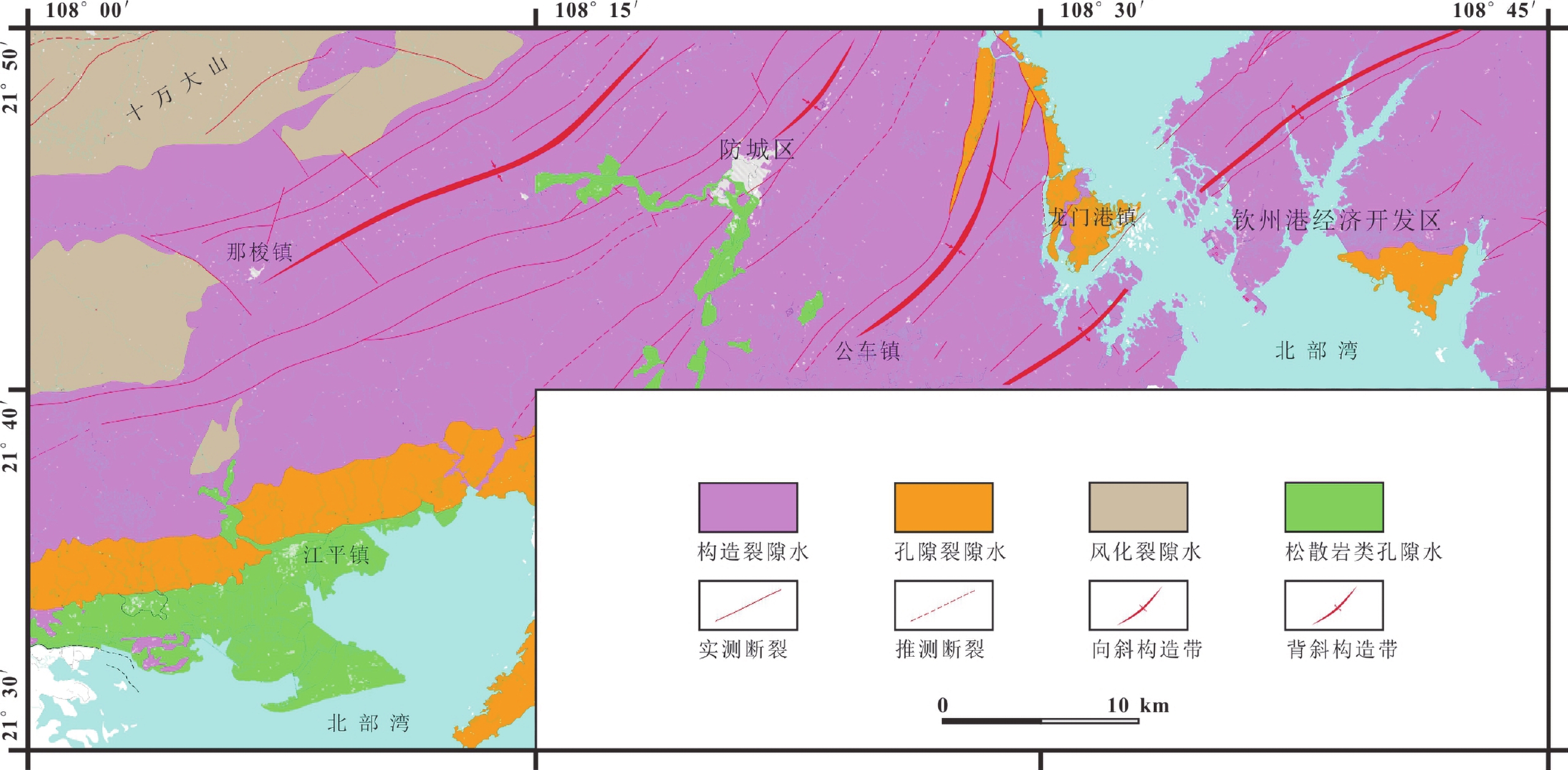
条目 描述 数据库(集)名称 广西防城港地区地下水现场测试数据集 数据库(集)作者 陈 雯,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
刘怀庆,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
黎清华,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
余绍文,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
陈双喜,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
王 清,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心
张宏鑫,中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心数据时间范围 2013—2015年 地理区域 广西壮族自治区南部,包括防城港市辖区的港口区、防城区、东兴市和钦州市辖区的钦州港区,地理坐标为东经108°00′~108°45′,北纬21°30′~21°50′ 数据格式 *.xls 数据量 48 KB 数据服务系统网址 http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn 基金项目 中国地质调查局地质调查项目“海口江东新区综合地质调查”(DD20190304)、“北海海岸带陆海统筹综合地质调查”(DD20189502)、“防城港地区水文地质工程地质调查评价”(12120113004100)项目资助 语种 中文 数据库(集)组成 数据集为Excel表格形式数据,包含丰水期现场测试数据和枯水期现场测试数据两个Excel工作表。每个Excel数据表格中包含野外编号、坐标、井口高程、水位埋深、井深、地下水类型、取水层位、水温、味、色度、气味、透明度、pH、溶解氧、电导率、氧化还原电位等17项信息 表 2 防城港地区现场测试数据表
序号 数据项名称 数据类型 单位 实例 1 野外编号 字符型 − NS2-176 2 X坐标 字符型 − 2416182 3 Y坐标 字符型 − 19203890 4 水位埋深 浮点型 m 0.20 5 井口高程 浮点型 m 9.00 6 井深 浮点型 m 1.00 7 地下水类型 字符型 − 风化裂隙水 8 取水层位 字符型 − 潜水 9 水温 浮点型 ℃ 25.0 10 味 字符型 − 无味 11 色度 字符型 − 无色 12 气味 字符型 − 无 13 透明度 字符型 − 透明 14 pH 浮点型 − 5.12 15 DO 浮点型 mg/L 7.76 16 EC 浮点型 μs/cm 31.0 17 Eh 浮点型 mV 194.2 表 3 防城港地区地下水样pH分布情况表
pH <5.50 5.50~6.50 >6.50 丰水期样品数 33 89 71 枯水期样品数 40 73 17 Table 1. Metadata Table of Database (Dataset)
Items Description Database (dataset) name Dataset of Field Testing of the Groundwater in the Fangchenggang Area of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Database (dataset) authors Chen Wen, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Liu Huaiqing, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Li Qinghua, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Yu Shaowen, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Chen Shuangxi, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Wang Qing, Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey
Zhang Hongxin, Wuhan Center, China Geological SurveyData acquisition time 2013—2015 Geographical area Lies in the southern part of the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, consisting of the areas governed by Fangchenggang City; including Gangkou District, Fangcheng District, Dongxing City and also Qinzhou Port; which is governed by Qinzhou City. The geological coordinates are E 108°00′–108°45′ and N 21°30′–21°50′ Data format *.xls Data size 48 KB Data service system URL http://dcc.cgs.gov.cn Fund project China Geological Survey projects titled “Comprehensive Geological Survey in the Jiangdong New District, Haikou City” (DD20190304), “Overall Comprehensive Geological Survey in Marine Areas and Land Along the Coastal Zone of Beihai City as a Whole” (DD20189502), and “Hydrogeological and Engineering Geological Survey and Assessment in the Fangchenggang Area” (12120113004100) Language Chinese Database (dataset) composition The Dataset consists of two Excel data tables that respectively contain the field-testing data of the groundwater in the wet and dry seasons. Each of the data tables includes 17 data items, which are: field No., coordinates, wellhead elevation, burial depth of water level, well depth, groundwater type, water intaking horizon and the temperature, taste, chroma, odor, transparency, pH value, DO, EC and Eh of water Table 2. Field Testing Data of Groundwater in the Fangchenggang Area, Guangxi
No. Name of data item Data type Unit Example 1 Field No. char − NS2-176 2 X coordinate char − 2416182 3 Y Coordinate char − 19203890 4 Burial depth of groundwater level float m 0.20 5 Wellhead elevation float m 9.00 6 Well depth float m 1.00 7 Groundwater type char − Weathering-fissure water 8 Water intaking horizon char − Phreatic water 9 Water temperature float ℃ 25.0 10 Taste char − Tasteless 11 Chroma char − Colorless 12 Odor char − Odorless 13 Transparency char − Transparent 14 pH value float − 5.12 15 DO float mg/L 7.76 16 EC float μs/cm 31.0 17 Eh float mV 194.2 Table 3. The pH Distribution of the Groundwater Samples in the Fangchenggang Area
pH value <5.50 5.50–6.50 >6.50 Number of samples from the wet season(s) 33 89 71 Number of samples from the dry season(s) 40 73 17 -
[1] Egbueri JC. 2020. Groundwater quality assessment using pollution index of groundwater (PIG), ecological risk index (ERI) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA): A case study[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10, 100292.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100292.
[2] Kurosawa K, Egashira K, Tani M. 2013. Relationship of arsenic concentration with ammonium-nitrogen concentration, oxidation reduction potential and pH of groundwater in arsenic-contaminated areas in Asia[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 58-60: 85−88. doi: 10.1016/j.pce.2013.04.016
[3] Lee J, Kim G. 2015. Dependence of coastal water pH increases on submarine groundwater discharge off a volcanic island[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 163(part B): 15−21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=13edd5f8e5b56b3b7d5bac9f0d38197c
[4] Leyden E, Cook F, Hamilton B, Zammit B, Barnett L, Lush AM, Stone D, Mosley L. 2016. Near shore groundwater acidification during and after a hydrological drought in the Lower Lakes, South Australia[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 189: 44−57. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2016.03.008
[5] Loh YSA, Akurugu BA, Manu E, Abdul-Samed A. 2019. Assessment of groundwater quality and the main controls on its hydrochemistry in some Voltaian and basement aquifers, northern Ghana[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 100296, in press, available online.
[6] Owamah HI. 2020. A comprehensive assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose in a Nigerian rural Niger delta community[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10, 100286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100286.
[7] Thockchom L, Kshetrimayum KS. 2019. Assessment of quality contributing parameters using hydrochemistry and hydrogeology for irrigation in intermontane Manipur valley in northeast India[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 8: 667−679. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2018.08.003
[8] 程新伟, 孙继朝. 2017. 珠江三角洲地区酸性地下水分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 地下水, 39(5): 25−27, 87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1184.2017.05.008
[9] 李锐, 周训, 张理, 欧业成, 黄喜新. 2006. 北海市偏酸性地下水pH值的特点及其影响因素简析[J]. 勘察科学技术, (5): 46−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3946.2006.06.012
[10] 张玉玺, 孙继朝, 陈玺, 黄冠星, 荆继红, 刘景涛, 向小平, 王金翠, 支兵发. 2011. 珠江三角洲浅层地下水pH值的分布及成因浅析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 38(1): 16−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2011.01.004
[11] 自然资源部中国地质调查局. 2019. 水文地质调查技术要求(1∶50 000)[S]. 1−32.
[1] China Geological Survey, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2019. Technical requirement for hydrogeological survey (1: 50 000)[S]. 1–32 (in Chinese).
[2] Cheng Xinwei, Sun Jichao. 2017. Study on distribution characteristics of acid groundwater and its influencing factors in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Ground water, 39(5): 25−27,87 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dixs201705008
[3] Egbueri JC. 2020. Groundwater quality assessment using pollution index of groundwater (PIG), ecological risk index (ERI) and hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA): A case study[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10: 100292. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100292
[4] Kurosawa K, Egashira K, Tani M. 2013. Relationship of arsenic concentration with ammonium–nitrogen concentration, oxidation reduction potential and pH of groundwater in arsenic-contaminated areas in Asia[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C, 58–60: 85−88. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=2b78ebdcfa5d115ace7cbcc033668e03
[5] Lee J, Kim G. 2015. Dependence of coastal water pH increases on submarine groundwater discharge off a volcanic island[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 163(part B): 15−21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=13edd5f8e5b56b3b7d5bac9f0d38197c
[6] Leyden E, Cook F, Hamilton B, Zammit B, Barnett L, Lush AM, Stone D, Mosley L. 2016. Near shore groundwater acidification during and after a hydrological drought in the Lower Lakes, South Australia[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 189: 44−57. doi: 10.1016/j.jconhyd.2016.03.008
[7] Li Rui, Zhou Xun, Zhang Li, Ou Yecheng, Huang Xixin. 2006. Characteristics of the pH in weak acidic groundwater near Beihai and preliminary analyses of its affecting factors[J]. Site Investigation Science and Technology, (5): 46−50 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kckxjs200605013
[8] Loh YSA, Akurugu BA, Manu E, Abdul-Samed A. 2019. Assessment of groundwater quality and the main controls on its hydrochemistry in some Voltaian and basement aquifers, northern Ghana[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 100296, in press, available online.
[9] Owamah HI. 2020. A comprehensive assessment of groundwater quality for drinking purpose in a Nigerian rural Niger delta community[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 10: 100286. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100286
[10] Thockchom L, Kshetrimayum KS. 2019. Assessment of quality contributing parameters using hydrochemistry and hydrogeology for irrigation in intermontane Manipur valley in northeast India[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, (8): 667−679. doi: 10.1016/j.gsd.2018.08.003
[11] Zhang Yuxi, Sun Jichao, Chen Xi, Huang Guanxing, Jing Jihong, Liu Jingtao, Xiang Xiaoping, Wang Jincui, Zhi Bingfa. 2011. Characteristics and preliminary analyses of the formation of pH in shallow groundwater in the Pearl River delta[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 38(1): 16−21 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz201101004
-



 下载:
下载: