The characteristics and formation mechanism of the faults in the southern part of the Zhongsha Bank
-
摘要:
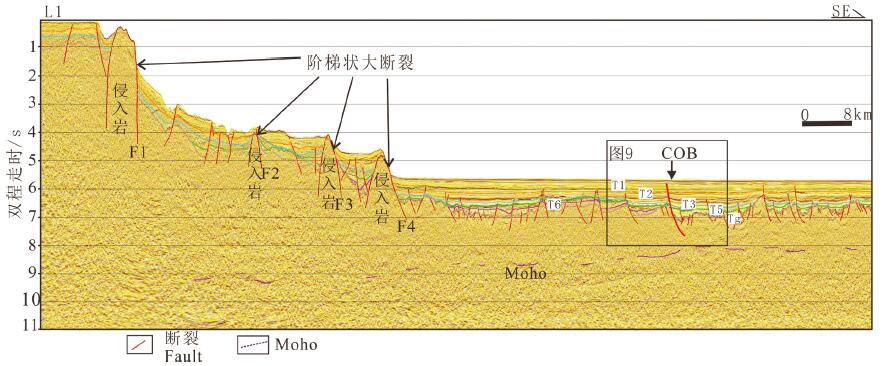
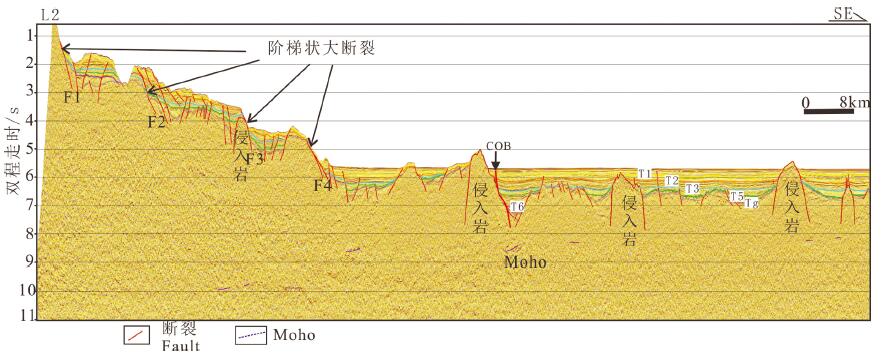
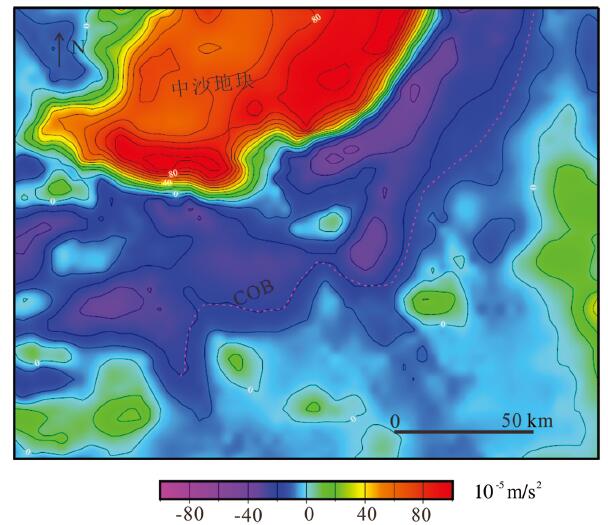
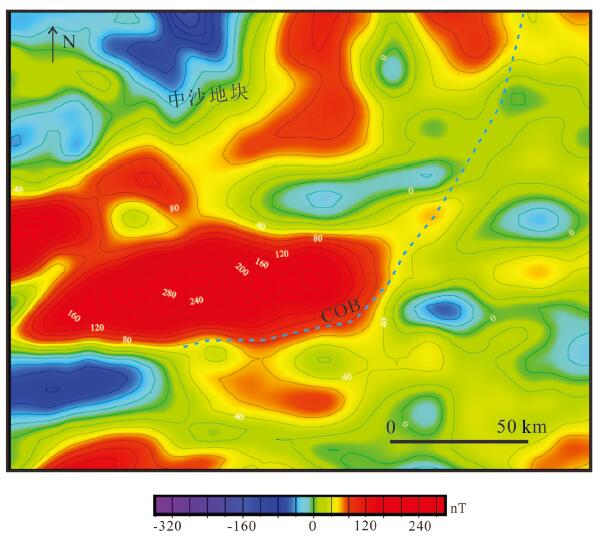
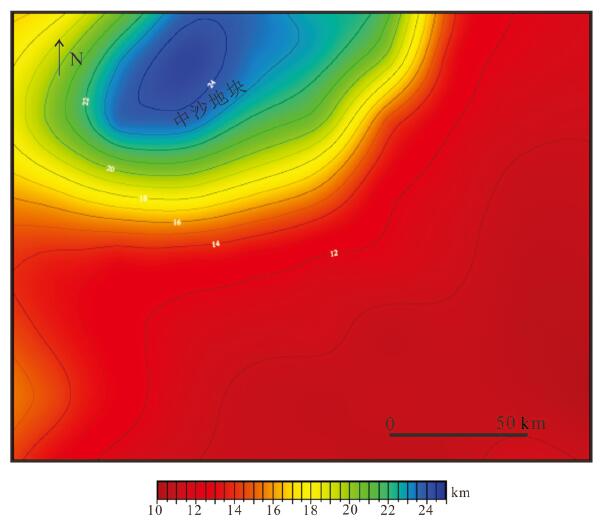
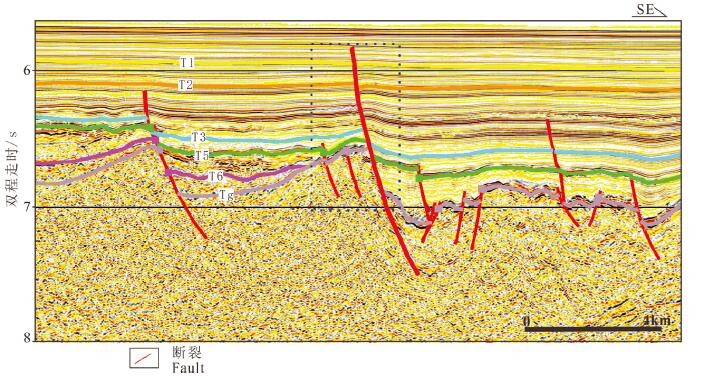
利用最新多道地震剖面资料,结合重力、磁力、地形等地球物理资料,揭示了中沙地块南部断裂空间展布特征、断裂发育时期、断裂内部构造形变特征及深部地壳结构,并基于认识探讨了断裂的发育机制。研究结果认为,中沙地块南部陆缘构造属性为非火山型被动大陆边缘:地壳性质从西北向东南由减薄陆壳向洋陆过渡壳再向正常洋壳发育变化;Moho面埋深从中沙地块下方的26 km快速抬升到海盆的10~12 km;从中沙地块陡坡至其前缘海域的重力异常明显负异常区为洋陆过渡带,在重力由高值负异常上升到海盆的低值正、负异常的边界为洋陆边界。中沙地块南部发育有4组阶梯状向海倾的深大正断裂,主要发育时期为晚渐新世到中中新世。断裂早期发育与南海东部次海盆近NS向扩张有关,后期遭受挤压变形、与菲律宾海板块向南海的NWW向仰冲有关。该研究有助于更好认识南海海盆的扩张历史和南海被动大陆边缘的类型。
Abstract:On the basis of the latest multi-channel seismic profiles and geophysical data such as gravity, magnetism and topography, the spatial distribution characteristics of faults, the development period of faults, the internal structural deformation feature of faults and deep crustal structure in the southern Zhongsha Bank (ZB) were revealed, and the formation mechanism of the faults was also discussed. The results show that the tectonic property of the southern continental margin of ZB is non-volcanic passive continental margin. From northwest to southeast, the crustal properties change from thinned continental crust to oceanic-continental transitional crust and then to normal oceanic crust. The depth of Moho discontinuity rises rapidly from 26 km beneath the ZB to 10-12 km beneath the ocean basin. The obvious negative gravity anomaly area from the steep slope of the ZB to the coast front is the oceaniccontinental transitional zone, and the boundary of gravity anomaly change from high value negative anomaly to low value positive and negative anomaly in the ocean basin is the oceanic-continental boundary. There are four sets of deep and large normal faults with stepped sea-dipping in the southern part of the ZB, which were mainly developed in the Late Oligocene to the Middle Miocene. The early extension of the fault development mechanism was related to the NS-trending extension of the sub-basin in the eastern South China Sea (SCS), and the later compressive stress was related to the NW-trending subduction of the Philippine plate towards the SCS. This study is helpful to the better understanding of the expansion history of the South China Sea basin and the types of passive continental margins in the SCS.
-

-
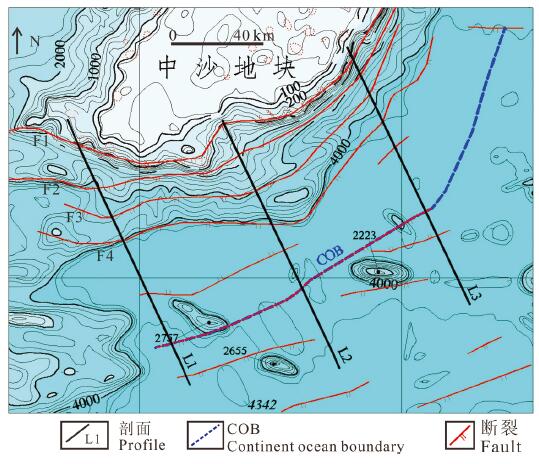
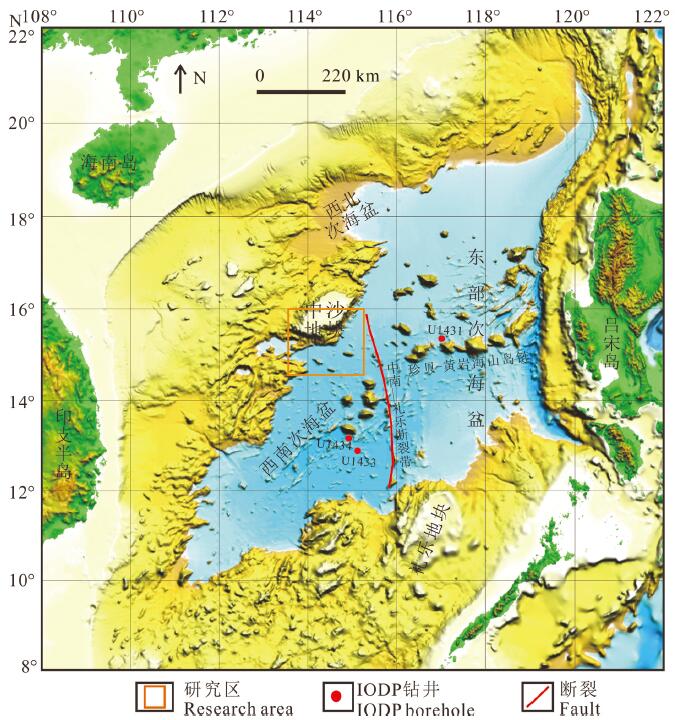
图 1 南海地形图(据杨胜雄等,2015)及研究区位置示意图
Figure 1.
-
Chen Changmin, Shi Hesheng, Xu Shice. 2003. The Conditionof Oil and Gas Reservoir Formation in the East of Zhujiangkou Basin[M]. Beijing:Science Press, 1-30(in Chinese).
Hao Tianyao, Xu Ya, Sun Fuli, You Qingyu, Lü Chuanchuan, Huang Song, Qiu Xuelin, Hu Weijian, Zhao Minghui. 2011. Integrated geophysical research on the tectonic attribute of conjugate continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(12): 3098-3116(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1002/cjg2.1679
Huang Haibo, He Enyuan, Guo Xingwei, Fan Jianke, Zhang Xunhua. 2019. Insights about the structure and development of Zhongsha Bank in the South China Sea from integrated geophysical modelling[J]. International Geology Review, 68(14): 1938-2839. http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/00206814.2019.1653798
Jin Xianglong. 1989. Geosciences research report of South China Sea[J].Donghai Marine Science, 7(4):30- 42 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/
Li Chunfeng, Xu Xing, Lin Jian, Sun Zhen, Zhu Jian, Yao Yongjian, Zhao Xixi, Liu Qingsong. 2014. Ages and magnetic structures of the South China Sea constrained by deep tow magnetic surveys and IODP Expedition 349[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 15(12):4958-4983. doi: 10.1002/2014GC005567
Liu Jianhua, Xu Deqiong. 1986. Thecharaeteristies and origin of the trough south of Zhongsha Islands[J]. Donghai Marine Science, 4 (3): 25-32(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DHHY198603005.htm
Ruan Aiguo, Wei Xiaodong, Niu Xiongwei, Zhang Jie, Dong Chongzhi, Wu Zhenli, Wang Xinyang. 2016. Crustal structure and fracture zone in the Central Basin of the South China Sea from wide angle seismic experiments using OBS[J]. Tectonophysics, 688:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.09.022
Sun Jiashi. 1987. A discussion of the formation ages of the bedrock in the xisha Islands[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 7(4): 5-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11434-006-9107-x
Wan Ling, Yao Bochu, Zeng Weijun, Wu Nengyou, Xia Bin, Zhu Benduo. 2006.Lithospheric structure and petroleum distribution in the South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 33(4):874- 884(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200604017
Xu Ziying, Wang Jun, Gao Hongfang, Sun Meijing. 2014. Fault developmental characteristics and structure style of the southern part of the Zhongsha block[C]//Third Congress Earth System Science, Shanghai (in Chinese).
Xu Ziying, Wang Jun, Gao Hongfang, Sun Guihua, Sun Meijing, Nie Xin, Zhou Rongwei.2019.Research progress on the ZhongnanLiyue Fault Zone in the South China Sea Oceanic Basin[J].Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(2): 86- 94(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-RDHY201902010.htm
Yang Shengxiong, Qiu Yan, Zhu Benduo, Chen Jie, Guan Yongxian, Peng Xuechao, Gao Hongfang, Guo Lihua. 2015. Atlas of Geology and Geophysics of the South China Sea[M].Tianjin: China Navfangigation Publications(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Wei, Liang Jinqiang, Su Pibo, Wei Jiangong, Sha Zhibin, Lin Lin, Liang Jin, Huang Wei. 2018. Migrating pathways of hydrocarbons and their controlling effects associated with high saturation gas hydrate in Shenhu area, northern South China Sea[J].Geology in China, 45(1): 1- 14(inChinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801001
Zhao Bin, Gao Hongfang, Zhang Hen, Li Liqing. 2019. Structure study of the northeastern Zhongsha Trough Basin in the South China Sea based on prestack depth migration seismic imaging[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 38(2): 95- 102(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rdhy201902011
陈长民, 施和生, 许仕策.2003.珠江口盆地(东部)第三系油气藏形成条件[M].北京:科学出版社.
郝天珧, 徐亚, 孙福利, 游庆瑜, 吕川川, 丘学林, 胡卫剑, 赵明辉.2011.南海共轭大陆边缘构造属性的综合地球物理研究[J].地球物理学报, 54(12): 3098-3116. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201112011
金翔龙.1989.南海地球科学研究报告[J].东海海洋, 7(4):30-42. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.1998.04.007
刘建华, 徐德琼.1986.中沙南海槽的特征及其形成[J].东海海洋, 4(3):25-32. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DHHY198603005.htm
孙嘉诗.1987.西沙基底形成时代的商榷[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 7(4):5-6. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-HYDZ198704001.htm
万玲, 姚伯初, 曾维军, 吴能友, 夏斌, 朱本铎. 2006.南海岩石圈结构与油气资源分布[J].中国地质, 33(4):874-884. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200604017
徐子英, 高红芳, 汪俊, 孙美静.2014.中沙海台南部断裂发育特征及其构造样式[C].上海: 第三届地球系统科学大会, 405.
徐子英, 汪俊, 高红芳, 孙桂华, 孙美静, 聂鑫, 朱荣伟.2019.南海海盆中南-礼乐断裂带研究进展[J].热带海洋学报, 38(2): 86-94. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_rdhy201902010.aspx
杨胜雄, 邱燕, 朱本铎, 陈洁, 关永贤, 彭学超, 高红芳, 郭丽华. 2015.南海地质地球物理图系[M].天津:中国航海图书出版社.
张伟, 梁金强, 苏丕波, 尉建功, 沙志彬, 林霖, 梁劲, 黄伟.2018.南海北部陆坡高饱和度天然气水合物气源运聚通道控藏作用[J].中国地质, 45(1): 1-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801001
赵斌, 高红芳, 张衡, 李丽清.2019.基于深度域地震成像的中沙海槽盆地东北部结构构造研究[J].热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(2):95-102. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rdhy201902011
-



 下载:
下载: