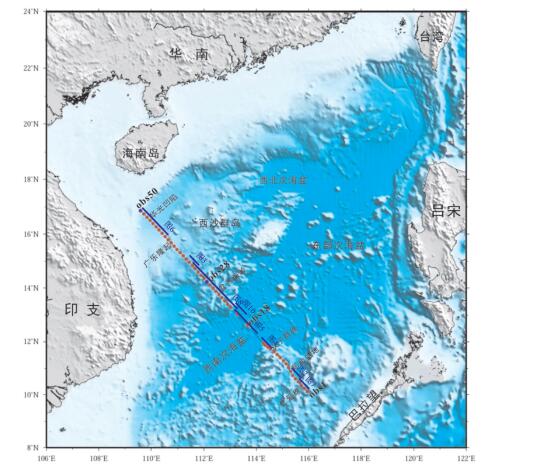
Tectonic characteristics and sedimentary responses of the southwest Subbasin of the South China Sea
-
摘要:
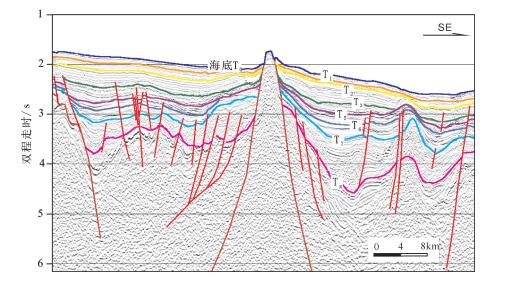
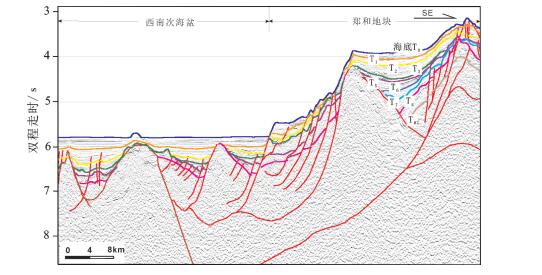
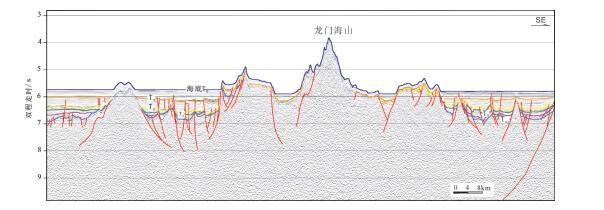
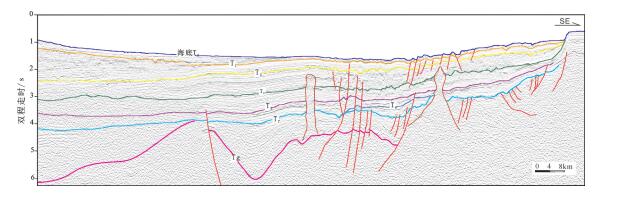
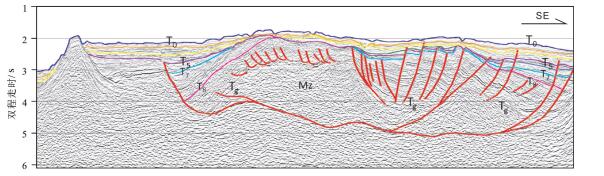
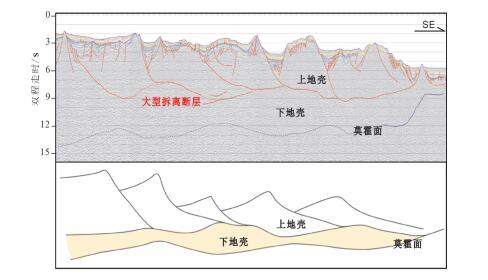
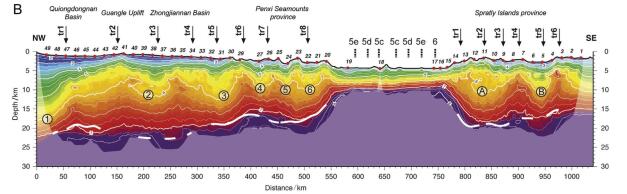
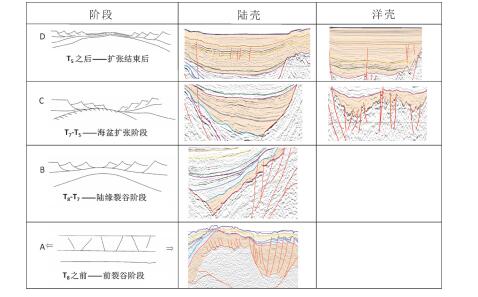
本文对穿过南海西南次海盆的逾1000 km的多道地震测线CFT剖面进行了地震界面特征的识别和地震层序的划分,分段分析了拆离断层对其减薄陆壳的拆离作用。结合前人研究成果,对南海西南次海盆地壳结构特征开展了分析,并总结了其构造特征。西南次海盆在发生陆缘张裂—海盆扩张、洋壳出现—扩张后稳定沉积这一系列过程中,可划分为4个阶段的沉积响应:A阶段(古新世之前)——前裂谷阶段,表现为地壳在拉张应力下产生小的断层;B阶段(始新世—早渐新世)——陆缘的裂谷阶段,地壳在拉张应力下拉张减薄,A阶段产生的断层出现了旋转,出现了大型掀斜的拆离断层,沉积物为同裂谷沉积,该阶段以产生了破裂不整合结束;C阶段(晚渐新世—早中新世)——海盆扩张阶段,海盆开始扩张,张应力从陆缘转移到了洋盆;D阶段(中中新世以来)——海盆扩张结束以后,以一套稳定沉积为特征。
Abstract:In this paper, the authors analyzed over 1000 kilometers'multi- channel seismic line (the CFT profile) across the southwestern subbasin of the South China Sea, with identification of seismic interface characteristics and seismic sequence division, and analyzed the detachment effect of detachment faults on the thinning of continental crust in segments. On the basis of the previous research results, an analysis of the crustal structure characteristics of the South China Sea was carried out, and its structural characteristics were summarized. The southwest sub-basin can be divided into four stages of sedimentary response during the series of continental marginal rifting and sea basin spreading and post-expansion: Stage A was the pre-rift stage, showing that the small faults was generated under tensile stress; Stage B was the rifting stage, when the crust of continental margin was thinning in the tensile stress, the fault generated in Stage A was rotated, and the large tilting detachment fault appeared. The sediments were the synrift deposits, and this stage ended with the breakup unconformity; Stage C was the basin expansion stage, during which the sea basin began to expand and the tensile stress shifted from the continental margin to the ocean basin; Stage D was the post-spreading stage, after ending of the basin expansion, the sediments were a set of stable deposits.
-

-
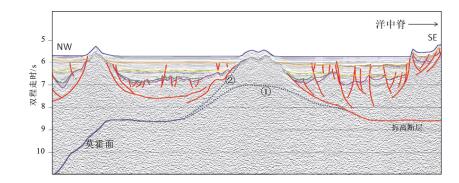
图 9 OBS反演CFT速度剖面(据Pichot, 2014)
Figure 9.
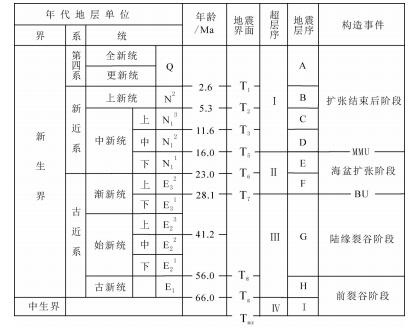
表 1 地震层序划分
Table 1. Seismic sequence division table
-
Braitenberg C, Wienecke S, Wang Y. 2006. Basement structures from satellite-derived gravity field: South China Sea ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111: B05407. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/2005JB003938/pdf
Cannat M, Sauter D, Mendel Ⅴ, Ruellan E, Okino K, Escartin J, Combier Ⅴ, Baala, M. 2006. Modes of seafloor generation at a melt-poor ultraslow-spreading ridge[J]. Geology, 34(7): 605-608. Franke D, Savva D, Pubellier M, Steuer S, Mouly B, Auxietre J L, Meresse F, Chamot- Rooke N. 2014. The final rifting evolution in the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 704-720. doi: 10.1130/G22486.1
Franke D, Savva D, Pubellier M, Steuer S, Mouly B, Auxietre J L,Meresse F, Chamot-Rooke N. 2014. The final rifting evolution in the South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 704-720. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.11.020
Fyhn M B W, Boldreel L O, Nielsen L H, 2009. Geological development of the Central and South Vietnamese margin: Implications for the establishment of the South China Sea, Indochinese escape tectonics and Cenozoic volcanism[J]. Tectonophysics, 478(3): 184-214. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195109004181
Geoffroy L. 2005. Volcanic passive margins[J]. C. R. Geoscience, 337: 1395-1408. doi: 10.1016/j.crte.2005.10.006
Gozzard S, Kusznir N, Franke D, Cullen A, Reemst P, Henstra G. 2018. South China Sea crustal thickness and oceanic lithosphere distribution from satellite gravity inversion[J]. Petroleum Geoscience, 25(1):112-128. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/pg/article/25/1/112/530431/south-china-sea-crustal-thickness-and-oceanic
Hopper J R, Funck T, Tucholke B E, Larsen H C, Holbrook W S, Louden K E, Shillington D, Lau H. 2004. Continental breakup and the onset of ultra- slow seafloor spreading off Flemish Cap on the Newfoundland rifted margin[J].Geology, 32: 93-96. doi: 10.1130/G19694.1
Li Jiabiao, Ding Weiwei, Gao Jinyao, Wu Ziyin, Zhang Jie. 2011. Cenozoic evolution model of the sea- floor spreading in South China sea: new constraints from high resolution geophysical data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(12): 3004- 3015 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/cjg2.1672
Li Jiabiao, Ding Weiwei, Wu Ziyin, Zhang Jie, Dong Congzhi. 2012. The propagation of seafloor spreading in the southwestern subbasin, South China Sea[J].Chinese Science Bulletin, 57 (20): 1896- 1905 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1360/csb2012-57-20-1896
McIntosh K, Lavier L, van Avendonk H, Lester R, Eakin D, Liu C S. 2014. Crustal structure and inferred rifting processes in the northeast South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 612-626. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.03.012
Minshull T A, Muller M R, Robinson C J, White R S, Bickle M J. 1998. Is the oceanic Moho a serpentinization front?. Geological Record. London: Geological Society, London, Special Publications: 71-80. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA40838009?l=ja
Pichot T, Delescluse M, Chamot- Rooke N, Pubellier M, Qiu Y, Meresse F, Sun G, Savva D, Wong K P, Watremez L, Auxietre J-L. 2014. Deep crustal structure of the conjugate margins of the SW South China Sea from wide- angle refraction seismic data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 627-643. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.10.008
Qiu Yan, Zeng Weijun, Li Tanggen. 2005. Fracture Systems and their tectonic significance in the central and southern parts of the South China Sea[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia. 29(2):166- 175(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200502002
Savva D, Meresse F, Pubellier M, Chamot-Rooke N, Lavier L, Wong K P, Franke D, Steuer S, Spain F, Auxietre J L, Lamy G. 2013. Seismic evidence of hyper- stretched crust and mantle exhumation offshore Vietnam[J].Tectonophysics, 608: 72-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.07.010
Song Haibin. 1998. Integrated Geophysical Researches on the Basement Fault System and Rifted Continental Margin ofSouth China Sea[D].Beijing: Institute of Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
Tang Renmin, Zhang Jian. 2006. Gravity gradient inversion of deep structure in the Southwest Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 12(1):49-54(in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200601008
White R S, McKenzie D, O'Nions R K. 1992. Oceanic crustal thickness from seismic measurements and rare earth element inversions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 97(B13): 19683-19715. doi: 10.1029/92JB01749
Yan Wei, Zhang Guangxue, Zhang Li, Xia Bin, Yang Zhen, Lei Zhenyu, Lin Zhen, Qian Xing, Luo Shuaibing. 2018. Focused fluid flow systems and their implications for hydrocarbon accumulations on the southern margin of South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 45(1): 39-47(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801004
Yang Zhen, Zhang Guangxue, Zhang Li, Yan Wei, Lin Zhen, Luo Shuaibin, Qian Xing. 2017. The style and hydrocarbon prospects of reefs in the Beikang Basin, southern South China Sea[J]. Geology in China, 44(3): 428-438(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201703002
Yao Bochu. The sea floor spreading in the SW subbasin of South China Sea and its tectonic significance[M]// Geological research of South China Sea (memoir 9). Wuhan: China University of Geoscience Press, 20-36 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Lei, Zhang Xiaoliang, Bai Ling yan, Cai Xiangmin, Wang Jiming, Yang Tianshui. Quaternary magnetic stratigraphy and its sedimentary response to new tectonic movement in Shahe depression, plain area of Beijing[J]. Geology in China, 2016, (3): 1076-1084(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201603029
Zhao Changyi, Song Haibin, Li Jiabiao, Song Yang, Tian Lihua. 2011. Tectonic and seismic interpretation of line NH973- 1 along southwest sub-basin in South China Sea[J]. Chinese J.Geophys., 54(12):3258-3268 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201112024
李家彪, 丁巍伟, 高金耀, 吴自银, 张洁. 2011.南海新生代扩张的构造演化模式:来自高分辨率地球物理数据的新认识[J].地球物理学报, 54(12): 3004-3015. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQWX201112005.htm
李家彪, 丁巍伟, 吴自银, 张洁, 董崇志. 2012.南海西南海盆的渐进式扩张[J].科学通报. 57 (20):1896-1905. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201220007
邱燕, 曾维军, 李唐根. 2005.南海中、南部断裂体系及其构造意义[J].大地构造与成矿学. 29(2):166-175. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200502002
宋海斌.1998.南海基底构造格架及张裂大陆边缘的综合地球物理研究[D].北京: 中国科学院地球物理研究所.
唐仁敏, 张健.2006.利用重力梯度反演南海西南海盆深部构造[J].地质力学学报.12(1):49-54 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200601008
鄢伟, 张光学, 张莉, 夏斌, 杨振, 雷振宇, 林珍, 钱星, 骆帅兵.2018.南海南部陆缘地质流体类型及其油气成藏意义[J].中国地质, 45 (1): 39-47. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201801004
杨振, 张光学, 张莉, 鄢伟, 林珍, 骆帅兵, 钱星.2017.南海南部北康盆地生物礁的类型及油气勘探前景[J].中国地质, 44(3): 428-438. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201703002
姚伯初.1997.南海西南海盆的扩张及其构造意义[M]//南海地质研究(九).武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 20-36.
张磊, 张晓亮, 白凌燕, 蔡向民, 王继明, 杨天水.2016.北京平原沙河凹陷第四纪磁性地层学研究及其新构造运动的沉积响应[J].中国地质, (3): 1076-1084. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201603029
赵长煜, 宋海斌, 李家彪, 宋洋, 田丽花.2011.南海西南次海盆NH973-1测线地震解释[J].地球物理学报, 54(12):3258-3268. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqwlxb201112024
-



 下载:
下载: