Structural ore−controlling mechanism of the Qingshan lead−zinc deposit in northwestern Guizhou, China and its implications for deep prospecting
-
摘要:
研究目的 青山铅锌矿床地处扬子地块西南缘的黔西北矿集区威宁—水城成矿亚带中段,严格受构造控制,资源潜力巨大。基于前期资料综合分析及野外地质调研,发现矿区构造成生发展过程和构造控矿机理不清、深部找矿勘查方向不明等问题制约了找矿突破。
研究方法 本文应用矿田地质力学理论和方法,通过大比例尺构造剖面精测、不同方向控矿构造力学性质鉴定与不同期次、序次构造筛分,结合区域构造应力场变化特征,揭示了构造控矿机理。
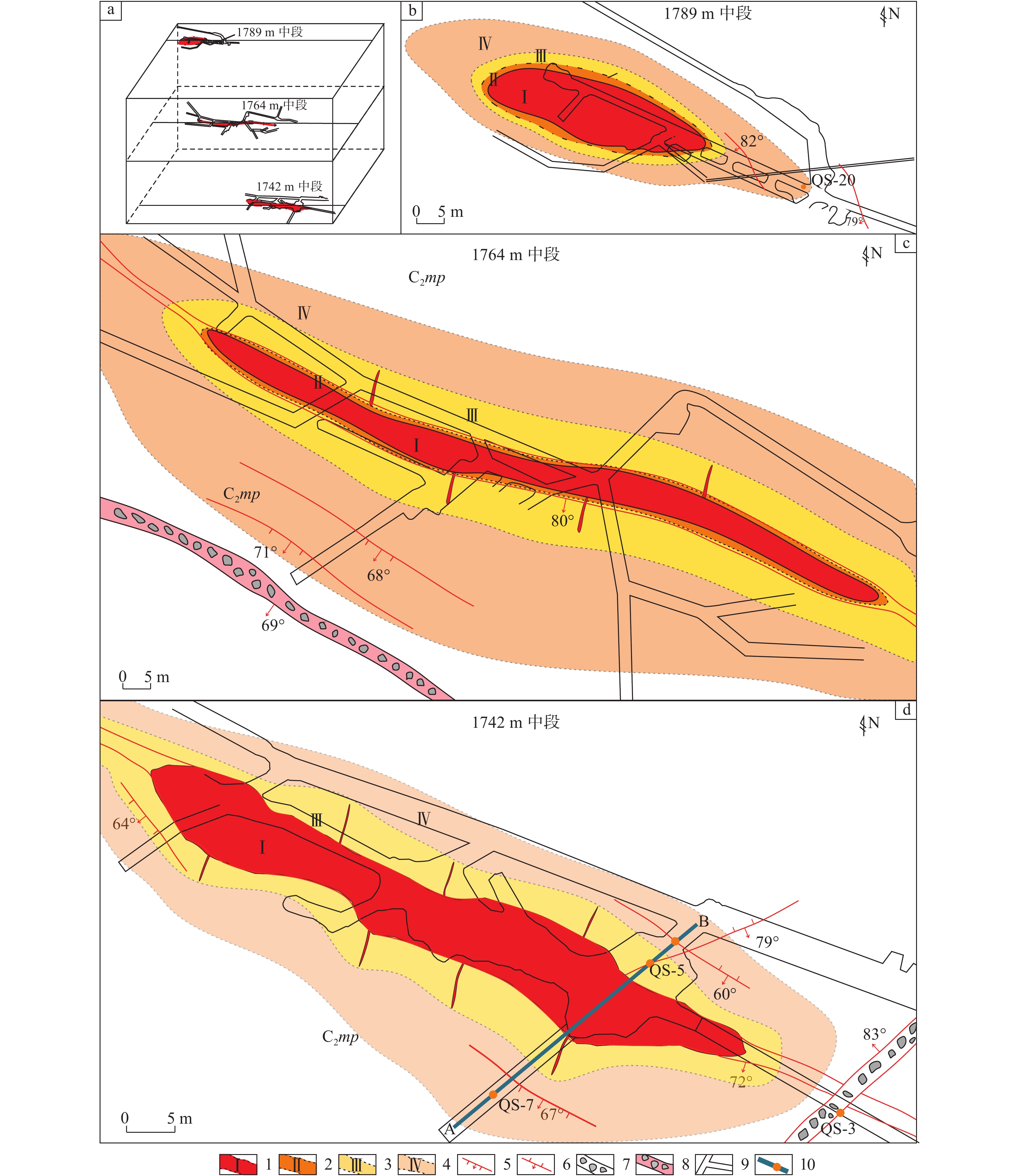
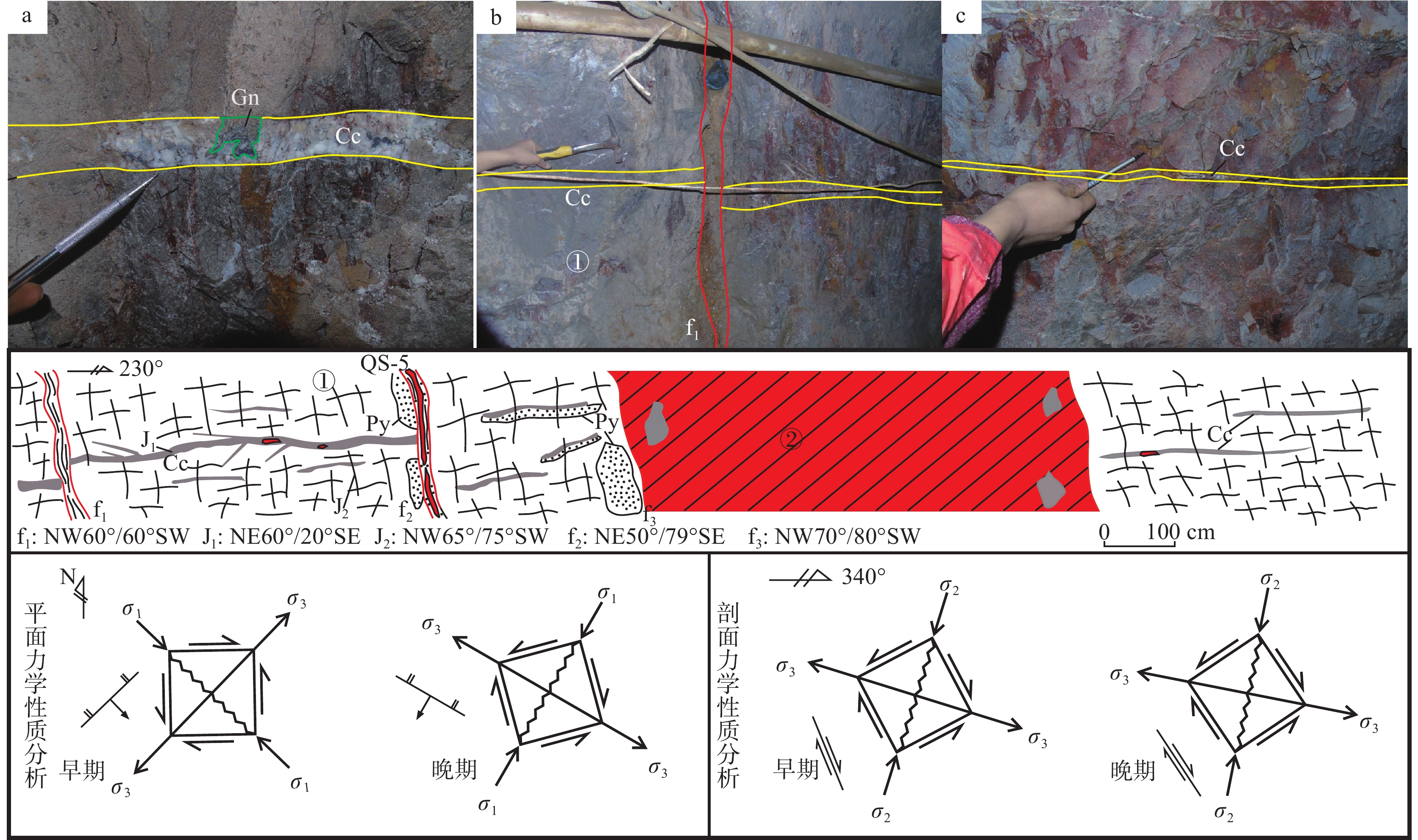
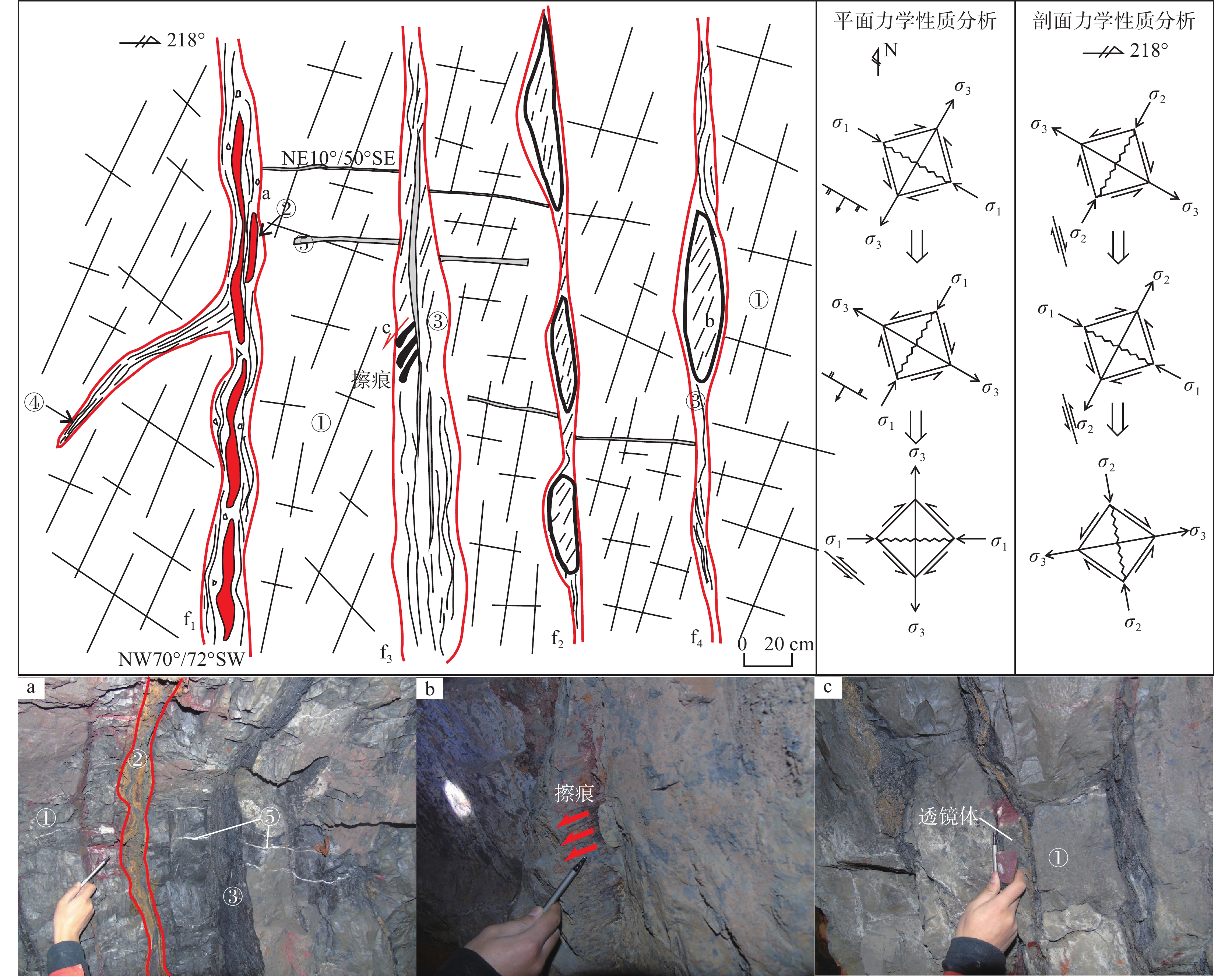
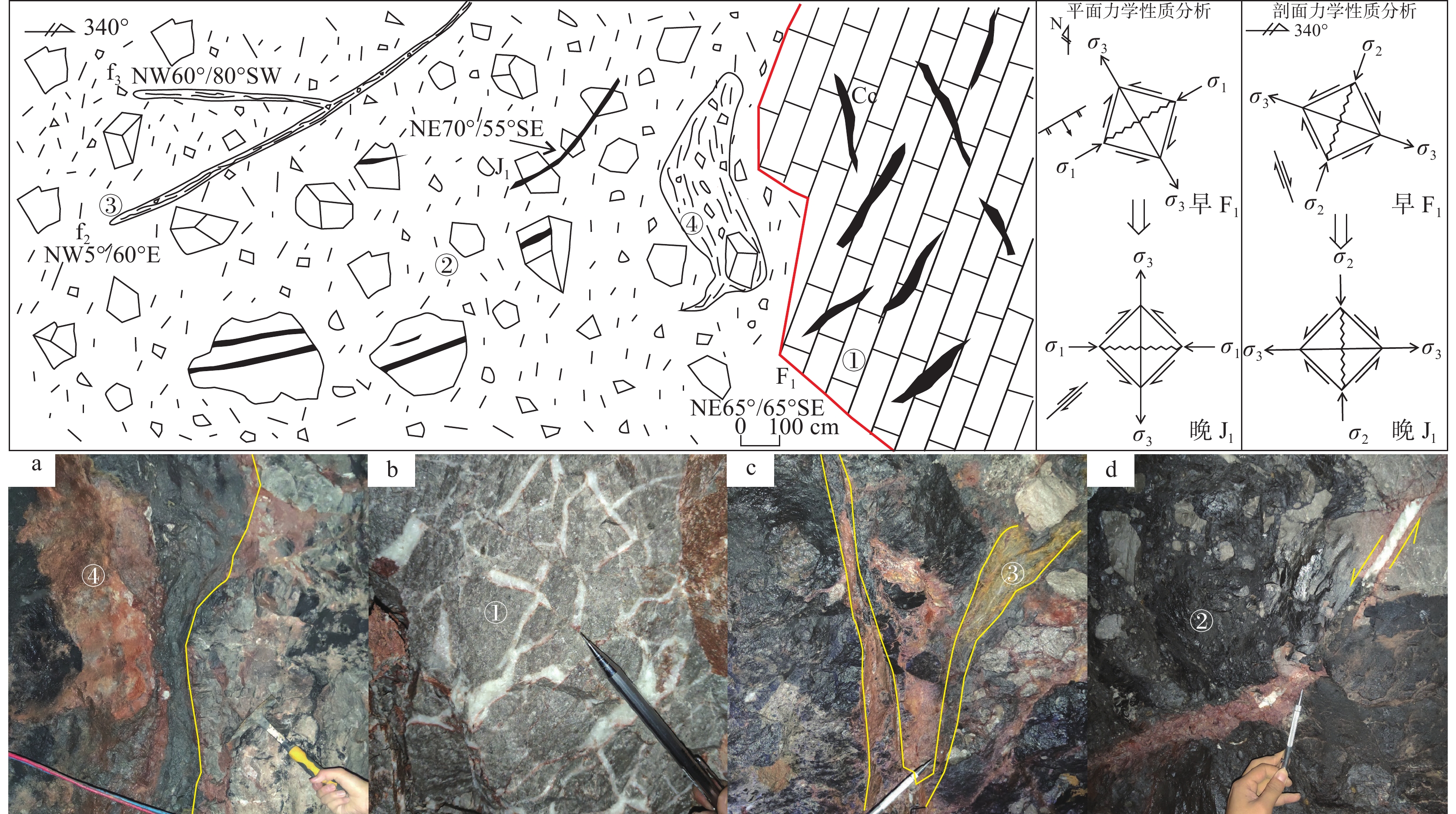
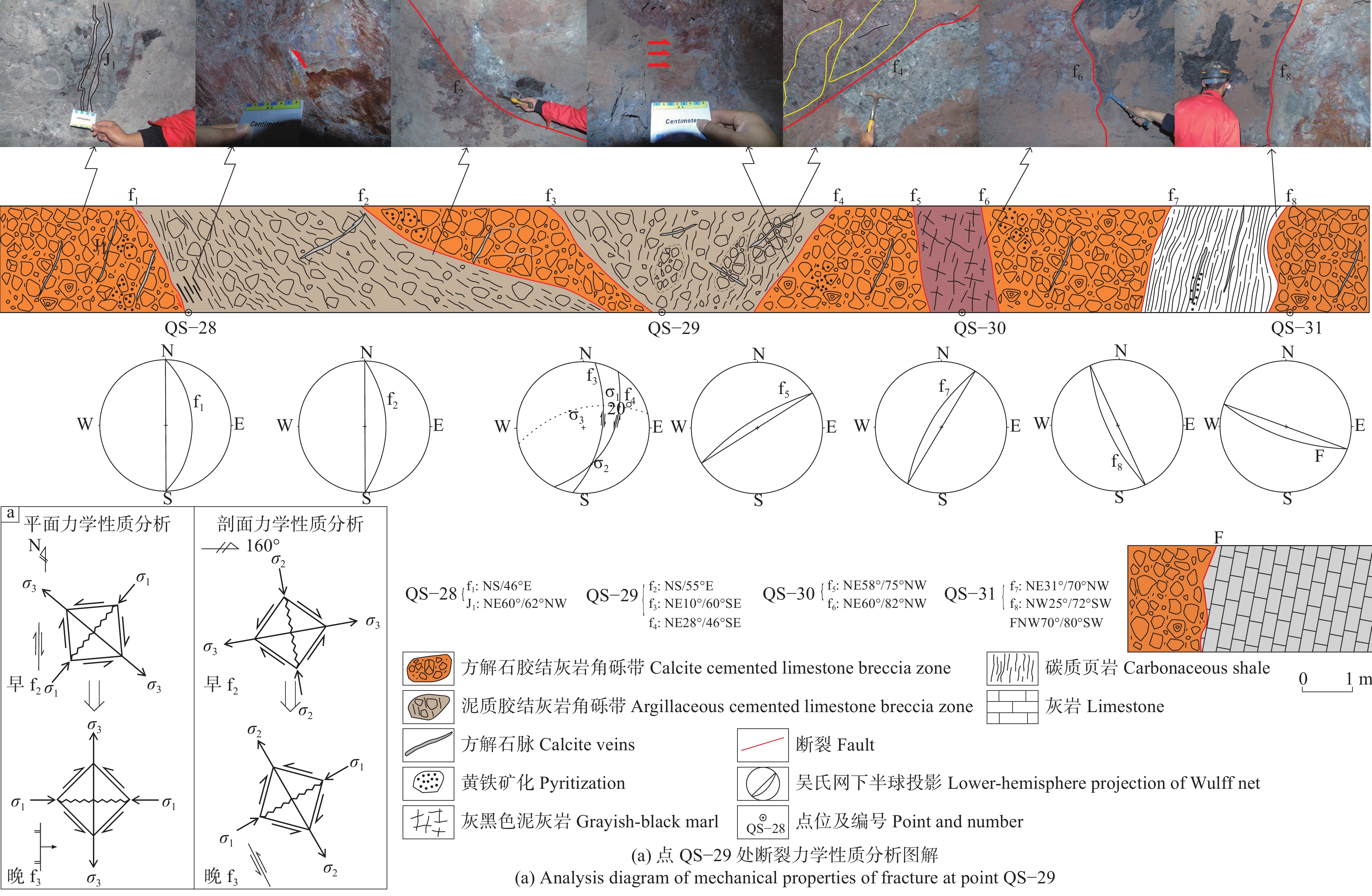
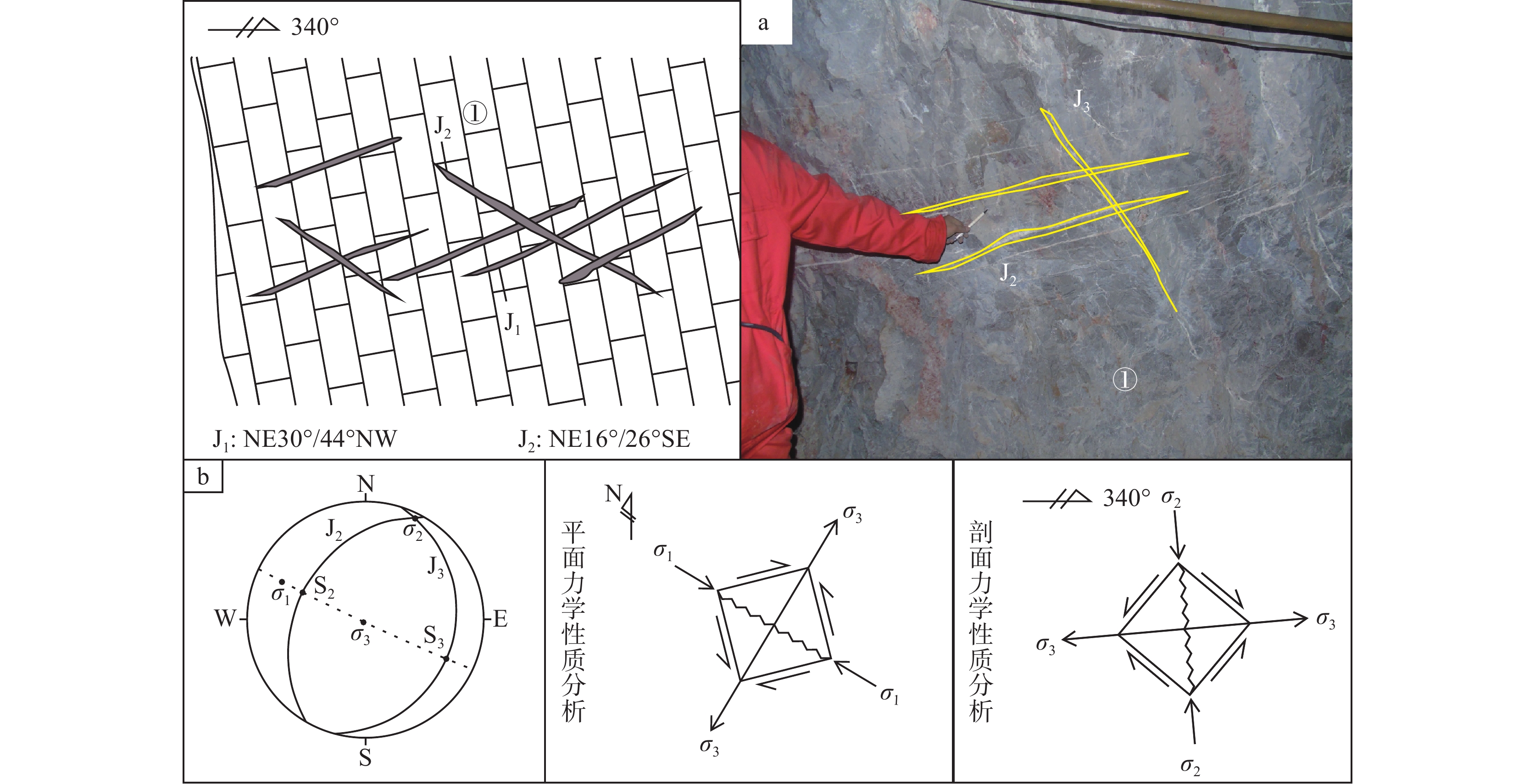
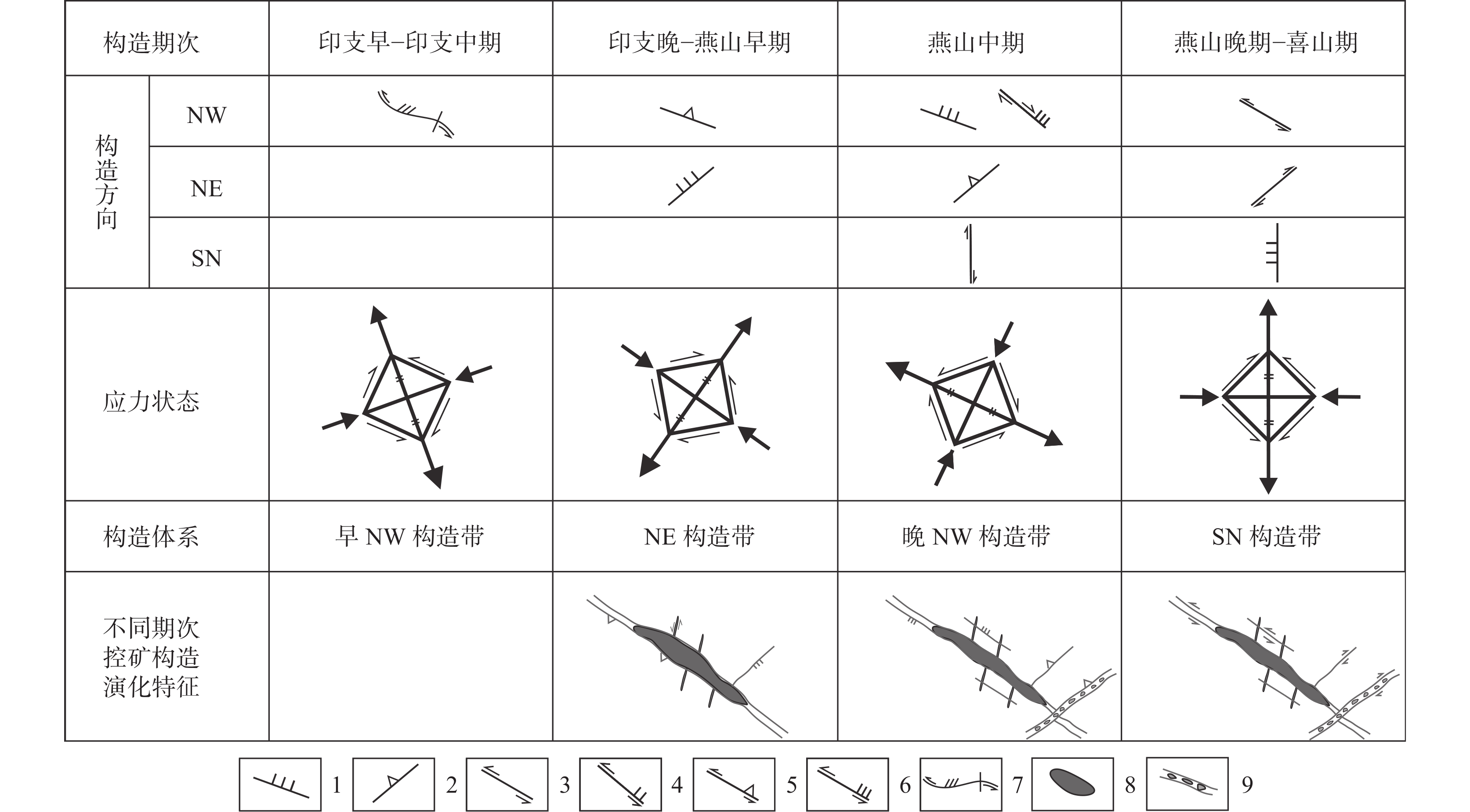
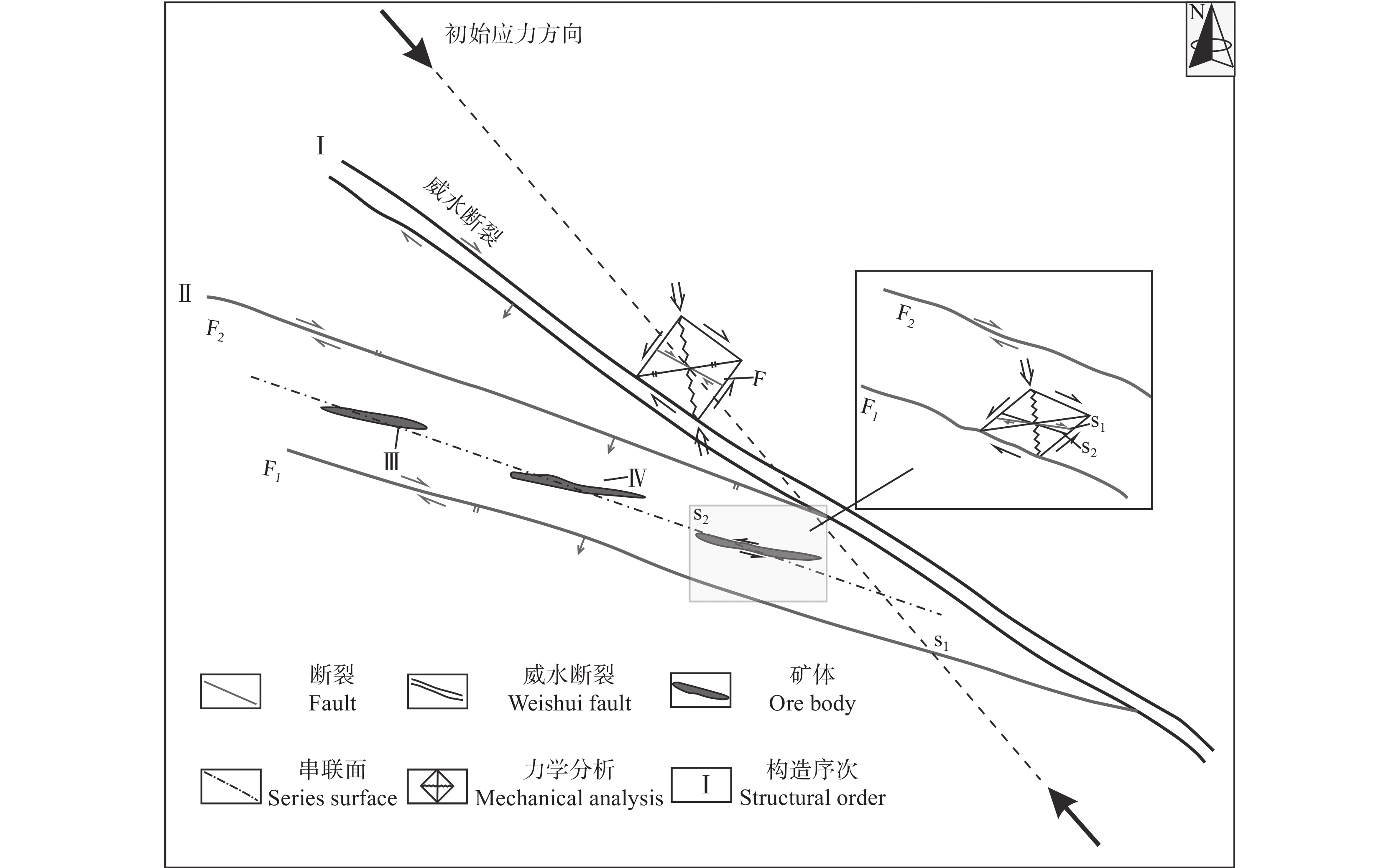
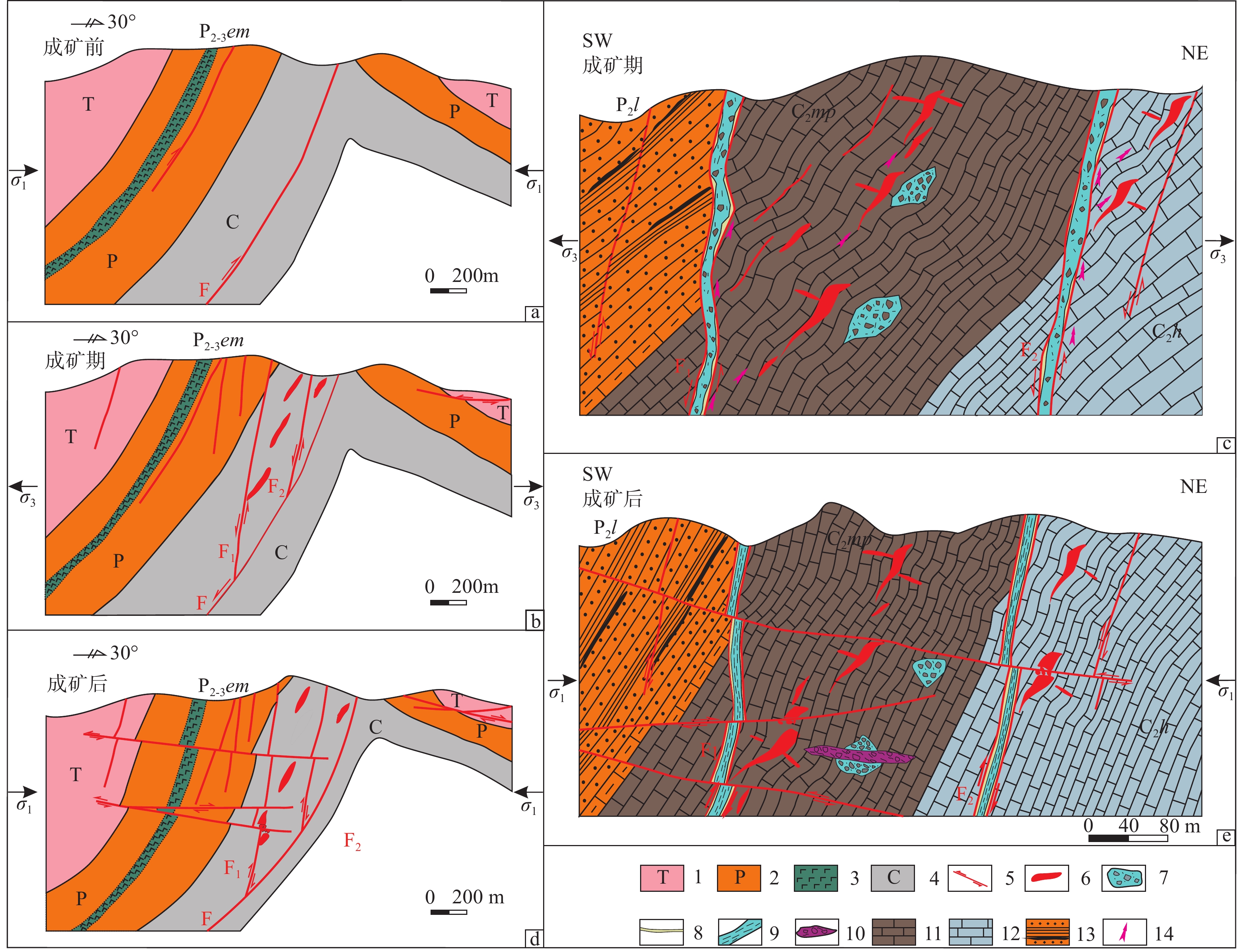
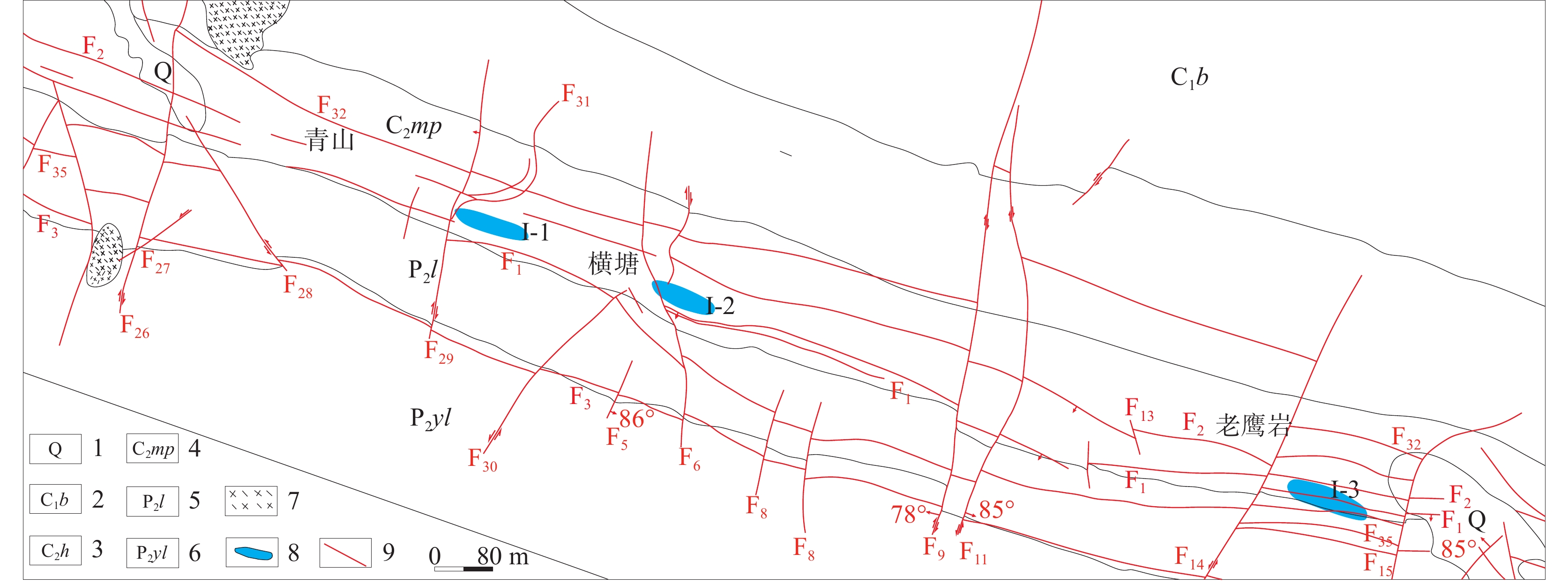
研究结果 自印支期以来,该区的主压应力方向主要历经了北东−南西向→北西−南东向→北东−南西向→近东西向的转变过程,依次形成了早北西构造带、北东构造带、晚北西构造带、南北构造带(构造体系)。通过成矿构造解析及其与成矿关系讨论,厘定了北东构造带为该矿区的成矿构造体系,揭示了构造分级控矿规律:北西向威宁—水城断裂、威水背斜为矿区的一级控矿构造,控制了威宁—水城矿化带或矿田的展布;威宁—水城断裂扭动作用派生的北西向断裂F1、F2,控制了矿床(矿体群)的分布,为矿区的二级控矿构造;F1、F2断裂间的层间断裂破碎带,直接控制了矿体的形态和产状,为三级控矿构造;矿体旁侧的节理裂隙带控制矿脉,为四级控矿构造。
结论 青山铅锌矿床构造分级控矿规律明显,主要受四个等级的控矿构造控制,并形成了与其相对应的4种矿化样式。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
Objective The Qingshan medium−size Pb−Zn deposit is located in the middle of the Weining−Shuicheng metallogenic sub−belt in the southwest margin of the Yangzi Block. The ore−body of the Qingshan deposit is strict controlled by structure and the resource potential is huge.
Methods Based on the theory and method of orefield geomechanics, this research has revealed the mechanism of structural ore control by the fine survey of large−scale structural profile, the identification of mechanical properties of typical ore−controlling structures in different directions and the screening of structures in different periods and orders, combined with the characteristics of regional tectonic stress field.
Results The results show that the principal compressive stress direction of the mining area since the Indosinian had changed from NE−SW−trending to NW−SE−trending to NE−SW−trending to near EW−trending, sequentially forming tectonic systems of the early NW tectonic belt, the NE tectonic belt, the late NW tectonic belt and the SN tectonic belt in turn. By the analysis of ore−controlling structure and the discussion of its relationship with mineralization, the metallogenic structural system of the north−east tectonic belt has been determined, and the hierarchical ore−controlling regularity of structure is revealed, it is, the northwest−trending Weining−Shuicheng fault and Weining−Shuicheng anticline are the first−grade ore−controlling structures, which control the distribution of the Weining−Shuicheng metallogenic sub−belt or orefield; The NW−trending faults (F1 and F2) derived from the Weining−Shuicheng fault, control the distribution of the deposit or orebody group, and are the second−grade ore−controlling structures in the mining area; The interlayer fracture zones between F1 and F2 faults directly control the feature and attitude of orebodies, which is the third−grade ore−controlling structure in the mining area; The joint fissures on the sides of orebodies control the ore−veins, which is the fourth−grade ore−controlling structure.
Conclusions The regularities of structural classification control are obvious for the Qingshan Pb−Zn deposit, which is mainly controlled by the ore−controlling structures of four grades, and has formed the four types of mineralization styles.
-

-
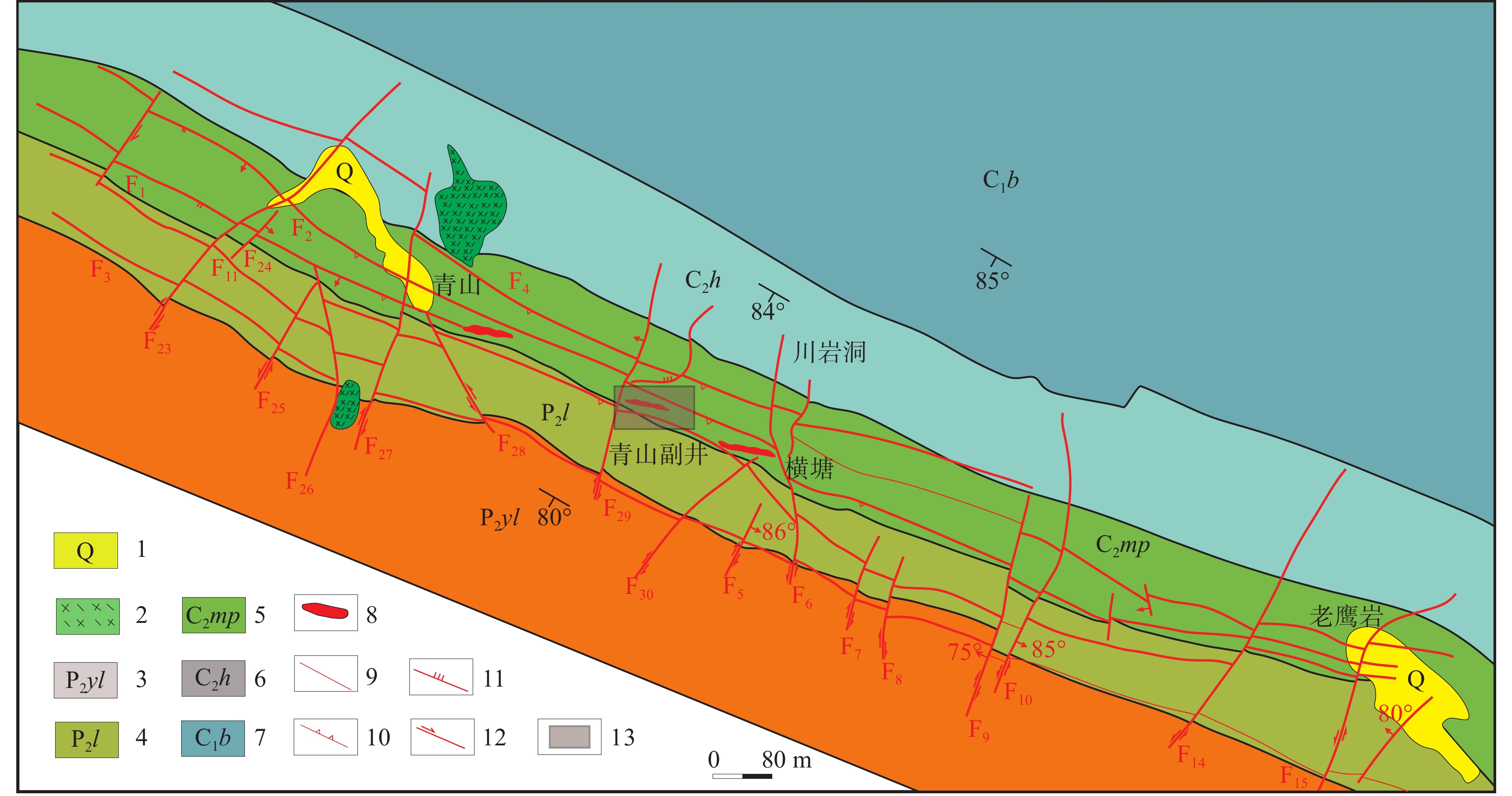
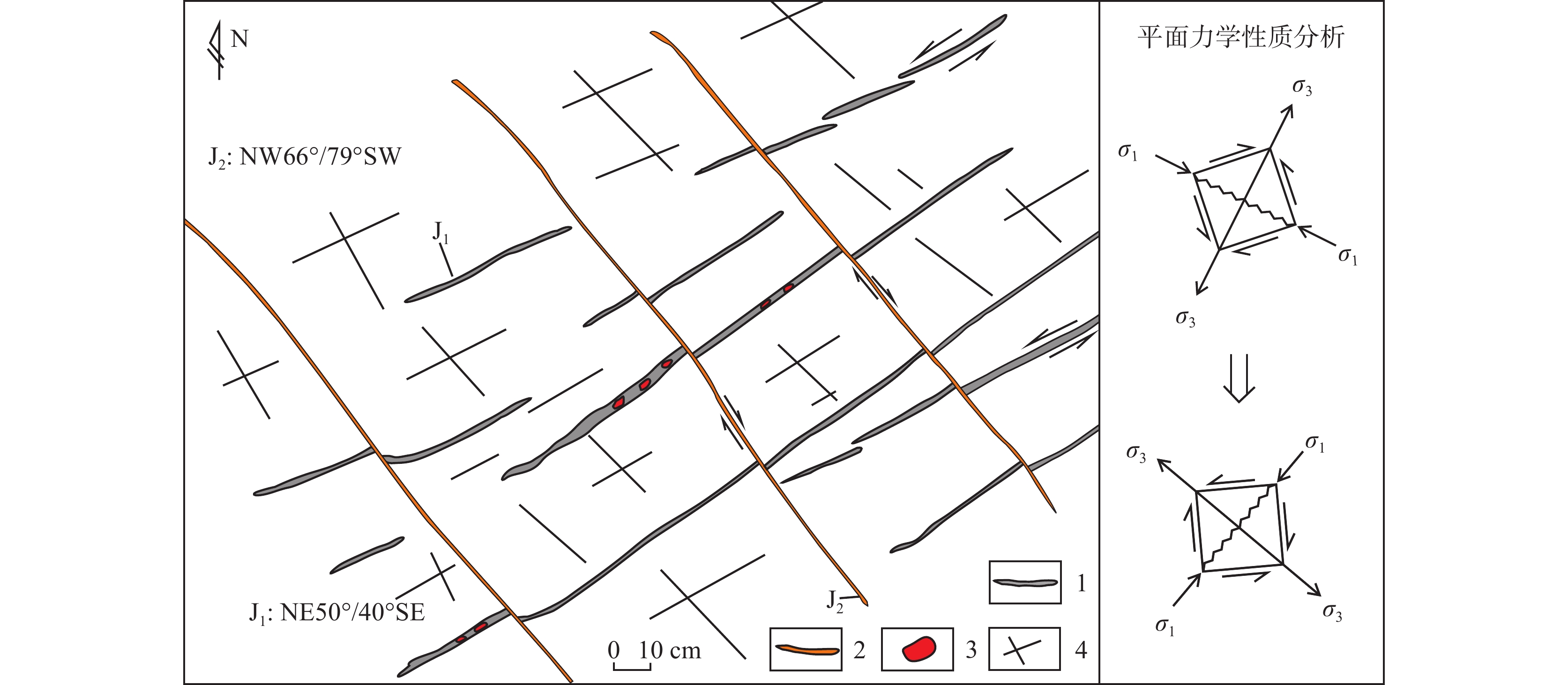
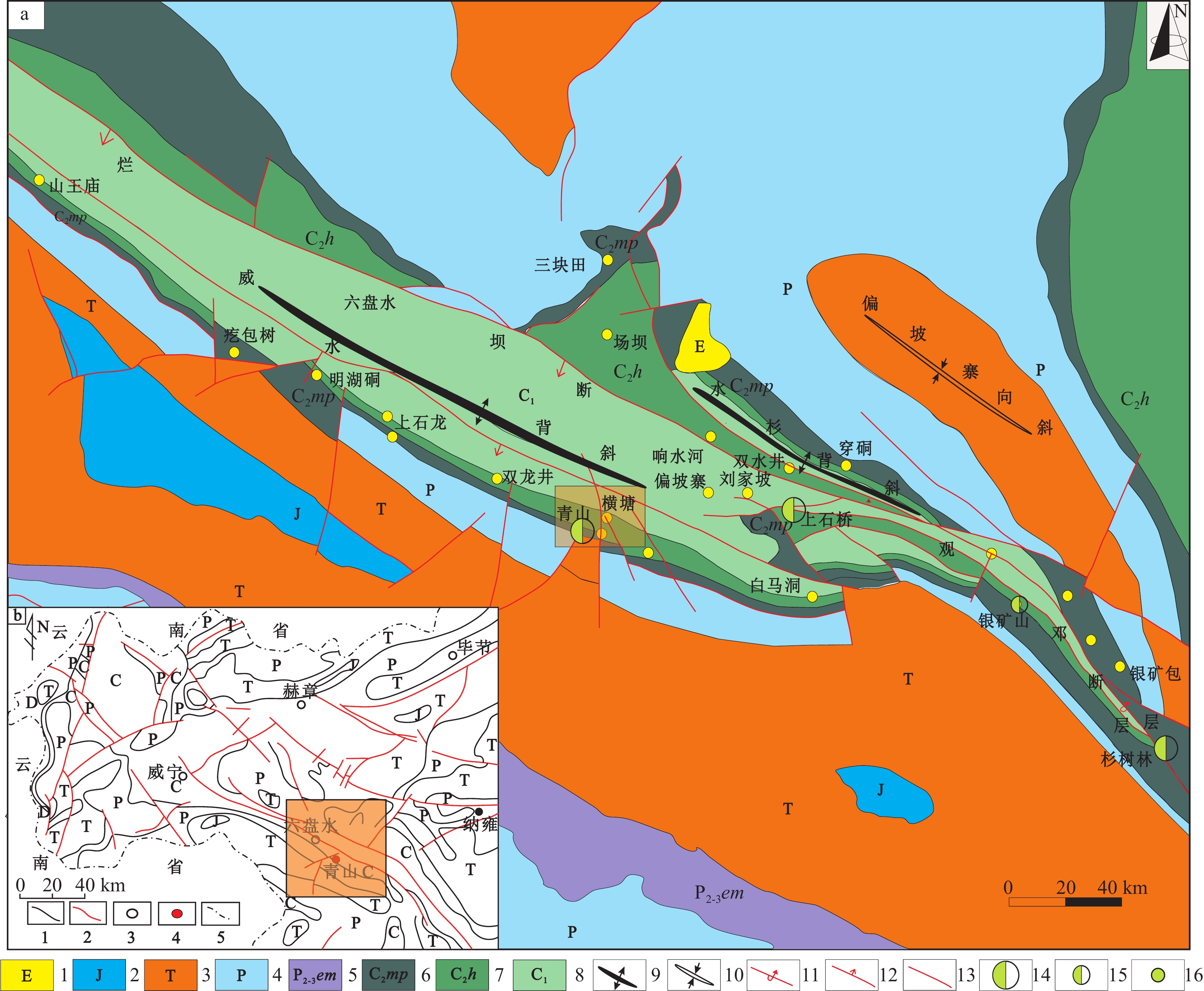
图 1 黔西北地质构造略图(a,据金中国, 2008修改;b,据汪新伟等, 2013修改)
Figure 1.
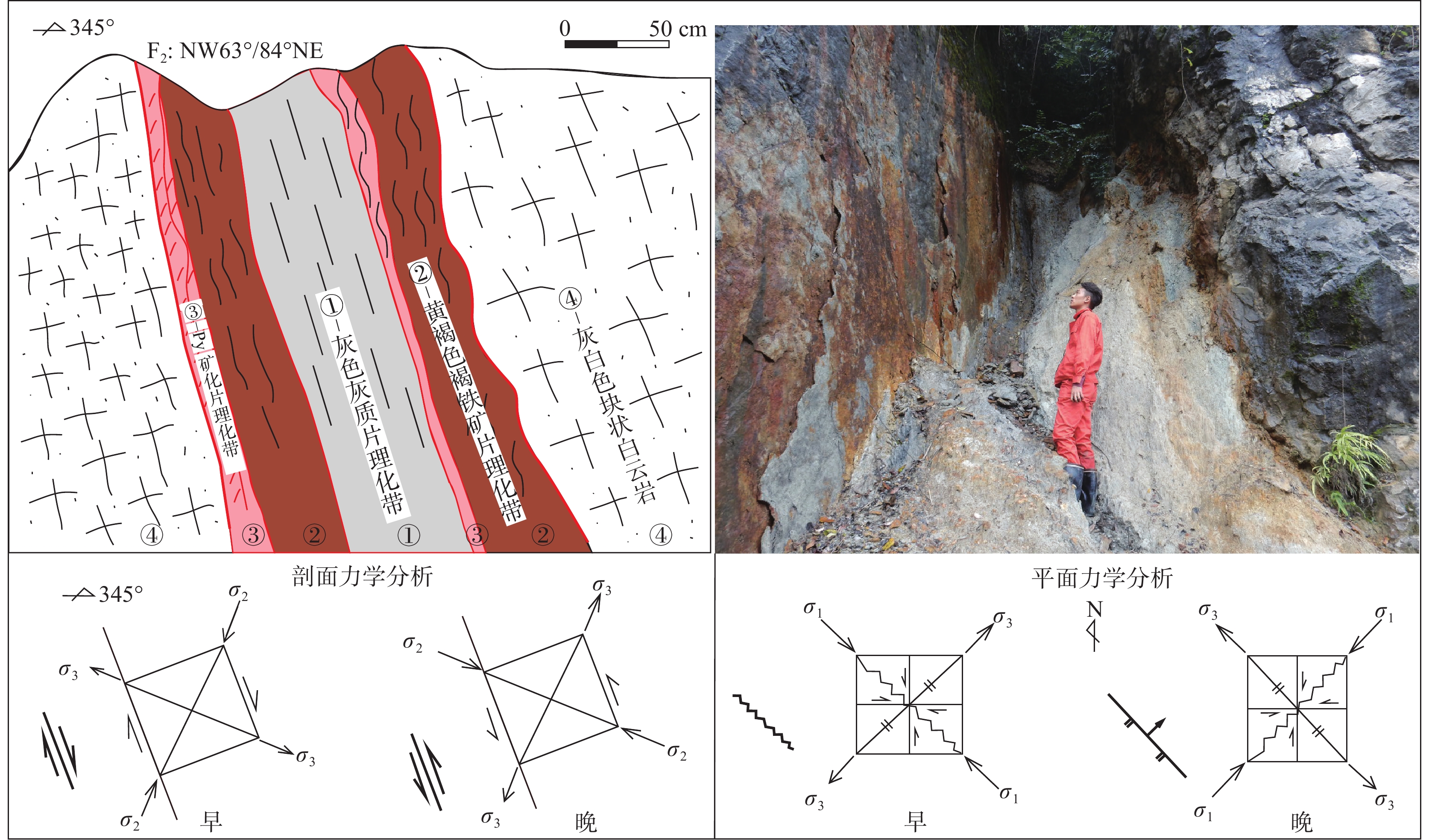
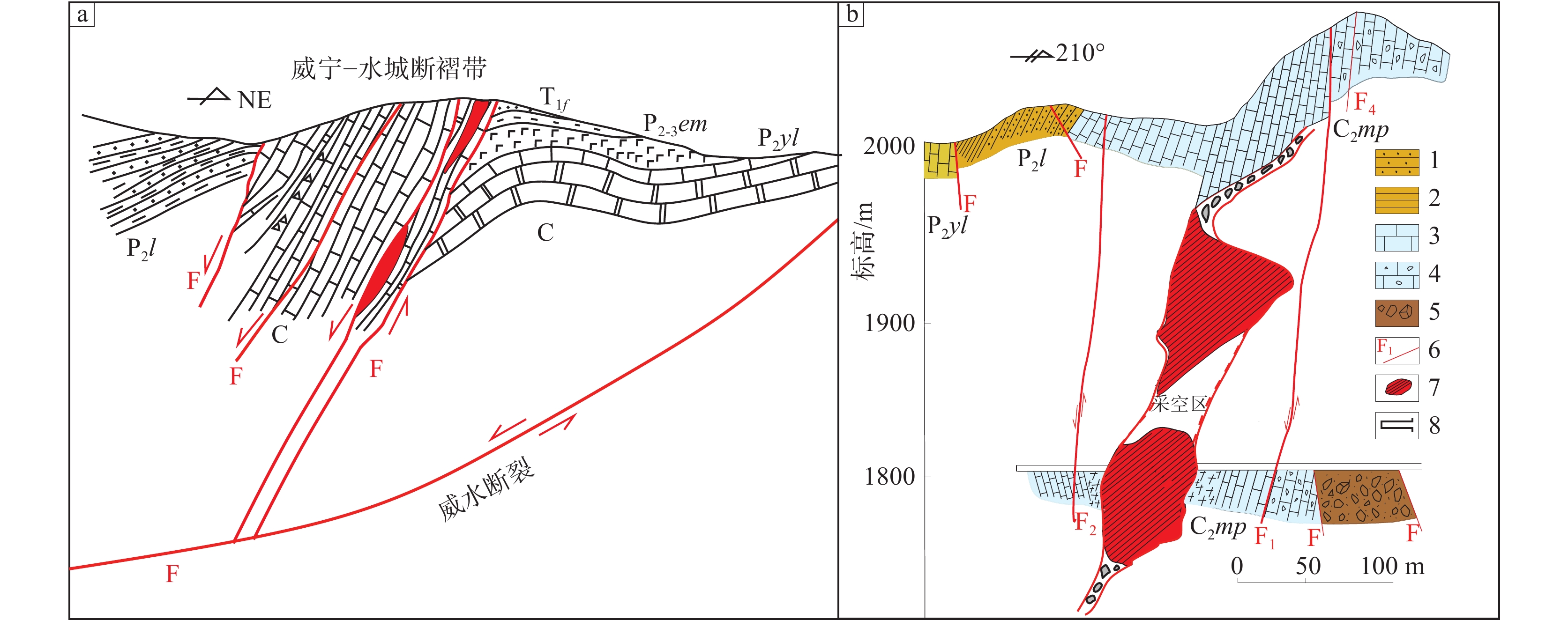
图 6 青山铅锌矿床F2断裂剖面图素描图(据韩润生等, 2020修改)
Figure 6.
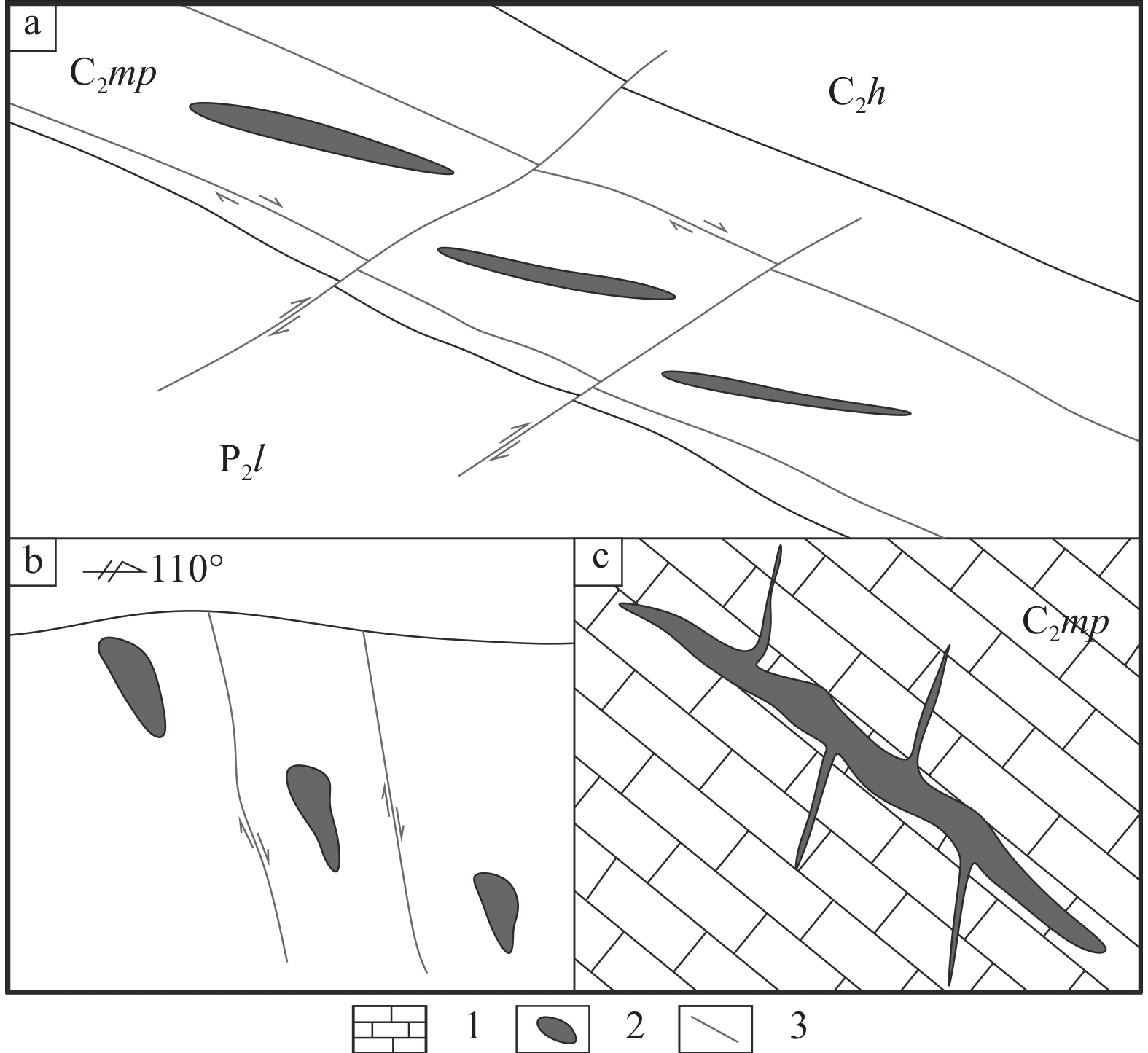
图 15 青山铅锌矿床矿化样式图(a,据韩润生等, 2020修改;b,据钱建平, 2001修改)
Figure 15.
表 1 青山铅锌矿床成矿阶段划分
Table 1. Classification of metallogenic stages of the Qingshan Pb−Zn deposit
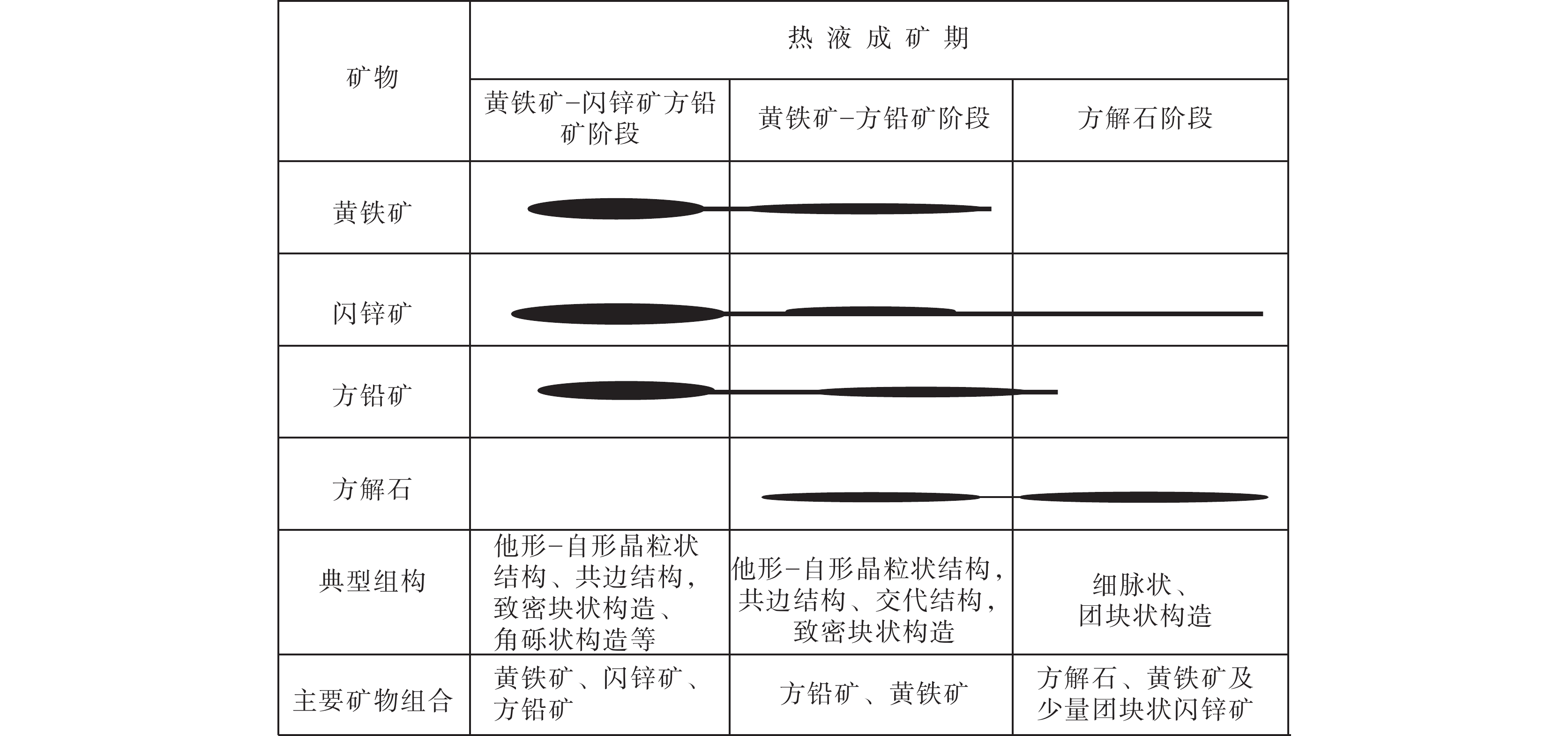
表 2 青山铅锌矿床构造等级划分及其控矿特征
Table 2. Structural classification and ore−controlling characteristics in the Qingshan lead−zinc deposit
成矿构造等级 矿集区构造(一级) 矿床构造(二级) 矿体构造(三级) 矿脉构造(四级) 构造类型 威水断裂;
威水背斜北西向右行
斜落断裂断裂;层间破碎带 节理;裂隙 矿化样式 条带状 雁列式 似层状、块状型 平行脉型 主要特征 多条同向斜落走滑的扭张性断裂控制了威宁—水城成矿亚带呈NW向延伸 NW向扭张性断裂与其上升盘的背斜
组成的断褶构造中发育铅锌矿体;断
裂带中矿体呈雁列式分布,并向同方
向倾斜矿体呈块状产于层
间断裂中产于块状矿体旁侧平行排列的节理内 成矿结构面 张扭性断裂带 扭张性和次级压扭性断裂 层间断裂 扭性−压扭性裂隙 表 3 青山铅锌矿床断裂构造岩微量元素含量(10−6)
Table 3. Trace element content of faulted tectonic rocks in the Qingshan lead−zinc deposit (10−6)
序号 样号 中段编号 Ag As Cd Cu Pb Sb Zn 1 QS−253 (1) 0.24 4.50 2.86 2.40 98.00 1.18 383.00 2 QS−255 (1) 0.09 7.70 4.64 3.40 92.60 2.25 537.00 3 QS−260 (1) 0.07 5.90 1.62 2.70 138.50 1.51 449.00 4 QS−268 (1) 0.04 1.70 0.47 4.70 21.60 1.82 48.00 5 QS−52 (2) 5.32 177.00 20.90 11.80 1020.00 75.10 5750.00 6 QS−53 (2) 5.15 81.50 2.41 6.30 344.00 20.40 458.00 7 QS−56 (2) 22.00 64.60 33.10 4.00 3450.00 95.60 8610.00 8 QS−60 (2) 0.22 11.70 1.66 1.70 230.00 1.78 656.00 9 QS−66-1 (2) 0.04 1.10 0.62 2.10 51.40 0.21 187.00 10 QS−71 (2) 0.25 5.60 2.28 1.50 199.00 11.20 441.00 11 QS−72 (2) 0.18 6.40 1.73 1.50 151.00 4.99 391.00 12 QS−80-2 (2) 0.08 23.0 6.41 1.80 211.00 19.40 264.00 13 QS−83 (2) 0.10 339.00 10.55 2.70 714.00 173.50 2940.00 14 QS−86 (2) 2.82 82.50 35.10 3.10 3460.00 24.30 3200.00 15 QS−87 (2) 0.07 1.30 3.26 1.50 66.60 0.68 159.00 注:(1)为1826 m中段样品;(2)为1743 m中段样品。测试单位:广州澳实分析测试中心,测试数据误差在5%以内。 -
[1] Chen Da. 1999. Geological feature and controls on Qingshan Pb−Zn deposit in Shuicheng Country, Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 16(1): 35−39 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Chen Da, Zeng Dehong. 2000. Characteristics of Ore−controlling Faults and Prospecting Evaluation in Qingshan−Hengtang lead−zinc deposits in Shuicheng, Guizhou Province[J]. Guizhou Geology, 17(1): 46−51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[3] Chen Shijie. 1986. Research on the genesis of lead−zine ore−deposits in Western Guizhou and Northeastern Yunnan[J]. Guizhou Geology, (3): 3−14 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[4] Cheng Chen, Han Runsheng, Wang Lei, Xiao Xianguo, He Zhiwei, Li Bo, Zhou Xuanling. 2019. The generation, development and ore−controlling of structures of the Fulaichang lead−zinc deposit, northeastern Guizhou[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(1): 90−104 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Dong Jialong. 2008. Study on Metallogenic Regularity and Ore−prospecting of Pb−Zn Deposit in northwest Guizhou Province[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 23−26(in Chinese).
[6] Gu Shangyi. 2007. Study on the sulfur isotopic compositions of lead−zinc deposits in northwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Guizhou University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 36(1): 8−11. (in Chinese with English abstract
[7] Han R S, Chen J, Wang F, Wang X K, Li Y. 2015. Analysis of metal–element association halos within fault zones for the exploration of concealed ore−bodies—A case study of the Qilinchang Zn–Pb–(Ag–Ge) deposit in the Huize mine district, northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 159(11): 62−78.
[8] Han R S, Wang L, Ma D Y, Gu X C, Fan Z G. 2010. “Giant pressure shadow” structure and ore−finding method of tectonic stress field in the Tongchang Cu−Au polymetallic orefield, Shaanxi, China: II. Dynamics of tectonic ore−forming processes and prognosis of concealed ores[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 29(4): 455−463. doi: 10.1007/s11631-010-0479-x
[9] Han Runsheng, Chen Ji, Hang Zhilong, Ma Deyun, Xue Chuandong, Li Yuan, Zou Haijun, Li Bo, Hu Yuzhao, Ma Gengsheng, Huang Deyong, Wang Xuekun. 2006. Tectonic−Metallogenic Dynamics and Location Prediction of Concealed Ore Deposits—A Case Study of the Huize Superlarge Lead−Zinc (Ag, Ge) Deposit in Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1–170(in Chinese).
[10] Han Runsheng, Chen Jin, Li Yuan, Ma Deyun, Zhao Deshun, Ma Gengsheng. 2001. Ore−controlling tectonics and prognosis of concealed ores in Huize Pb−Zn deposit, Yunnan[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 21(2): 265−269 (in Chinese with English abstract
[11] Han Runsheng, Hun Yuzhao, Wang Xuekun, Hang Zhilong, Chen Jin, Wang Feng, Wu Peng, Li Bo, Wang Hongjiang, Dong Yin, Lei Li. 2012. Mineralization model of rich Ge−Ag−bearing Zn−Pb polymetallic deposit concentrated district in northeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(2): 280−294 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Han Runsheng, Ma Deyun, Liu Congqiang. 2003. Tectonic Mineralization Dynamics of Shaanxi Copper Plant Ore Field [M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 3−10 (in Chinese).
[13] Han Runsheng, Wang Feng, Zhao Gaoshan, Wang Jin, Zhou Xueming, Wang Xuekun. 2010. New progress in deep prospecting of the Zhaotong Maoping lead−zinc deposit in the ore−gathering area of northeast Yunnan[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 275 (in Chinese).
[14] Han Runsheng, Wang Mingzhi, Jin Zhongguo. 2020. Ore−controlling mechanism of NE−trending ore−forming structural system at Zn−Pb polymetallic ore concentration area in northwestern Guizhou[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(3): 850−868 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Han Runsheng, Zhang Yan, Wang Feng, Li Wenyao. 2019. Metallogenic Mechanism of Germanium−rich Pb−Zn Deposit and Optimization of Ore−prospecting Target Area in the Ore−gathering Area of Northeast Yunnan Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 125−126 (in Chinese).
[16] Han Runsheng, Wang Feng, Hu Yuzhao, Wang Xuekun, Ren Tao, Qiu Wenlong, Zhong Kanghui. 2014. Metallogenic tectonic dynamics and chronology constrains on the Huize−type (HZT) germanium−rich silver−zinc−lead deposits[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(4): 758−771 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Han Runsheng. 2003. Preliminary discussion on research contents and methods of tectono−metallogenic dynamics and concealed ore orientation prognosis[J]. Geology and Prospecting, (1): 7−11 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Hu Ruizhong, Chen Wei, Bi Xianwu, Fu Shangling, Yin Runsheng, Xiao Jiafei. 2020. Control of the Precambrian basement on the formation of the Mesozoic largescale low−temperature mineralization in the Yangtze Craton[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(2): 137−150 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Hu Xiaoyan, Cai Guosheng, Su Wenchao, Zeng Daoguo, Wang Die. 2013. Characteristics of ore forming fluid in sphalerite of Saojiwan lead−zinc deposit in the northwest of Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 33(3): 302−307 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Huang Zhilong, Hu Ruizhong, Su Wenchao, Wen Hanjie, Liu Yan, Fu Yazhou. 2011. A study on the large−scale low−temperature metallogenic domain in Southwestern China−−Significance, history and new progress[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 31(3): 309−314(in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Jin Zhongguo. 2008. The Metallogenic Regularity and Prospecting Forecast of Lead−Zinc Ore in Northwestern Guizhou[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 56−60 (in Chinese).
[22] Jin Zhongguo, Huang Zhilong. 2009. Lead−zinc mineralization characteristics and exploration potential of the Yadu−Mangdong fault belt in Northwestern Guizhou[J]. Geology and Exploration, 45(2): 20−26 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Liao Wen. 1984. Discussion on the isotopic composition and metallogenic model of Sulfur and lead in lead−zinc areas in eastern Yunnan and Western Guizhou Provinces[J]. Geology and Exploration, (1): 2−8 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[24] Liu Cheng. 2015. Tectonic Evolution and its Controlling on the Mineralization for MVT Pb−Zn Deposits in Western Marginal Area of Yangtze Plate[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 35−45(in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Liu Hechang. 1996. The metallogenic model of Yunnan, Sichuan and Guizhou lead−zinc metallogenic areas[J]. Yunnan Geology, 15(1): 41−51 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] Liu Youping. 2002. Preliminary study on the metallogenic regulation and the prospecting model for the Pb−Zn deposits in the areas of Southwest Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, (3): 30−35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[27] Luo Wei, Kong Ling, Jin Zhongguo, Dai Tagen. 2010. Study of ore−controlling structure and mineralization process of the lead−zinc deposits in the Northwest Guizhou[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 24(1): 35−43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] Mao Jianquan, Zhang Qihou, Gu Shangyi. 1997. The geological characteristics and tectonic evolution of Shuicheng fault subsidence[J]. Fournal of Guzhou University of Technology, (2): 4−9 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Mou Baolei. 1999. Element Geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Peking University Press (in Chinese).
[30] Ou Jinxiu. 1996. Geological characteristics and ore−control geological conditions of Qingshan Lead−Zinc deposit, Guizhou[J]. Journal of Guilin Institute of Technology, (3): 277−282 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[31] Qian Jianping. 2001. Tectono−dynamic mineralization in Weining−Shuicheng Pb−Zn ore belt, Northwestern Guizhou[J]. Geology−Geochemistry, 29(3): 134−139 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Qin Shourong, Liu Aimin. 1998. A discussion on the Limalayan tectonic movement in Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 15(2): 105−114 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[33] Sun Jiacong, Han Runsheng. 2016. Theory and Method of Field Geomechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 86−100(in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Wang Jiangzhen, Li Changyang, Li Zeqing, Li Baohua, Li Zhouwen. 2002. The comparison of Mississippi Valley−Type lead−zinc deposits in southwest of China and in mid−continent of United States[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 21(2): 127−132(in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Wang Mingzhi, Han Runsheng, Zhou Wei, Song Danhui, Luo Da, Zhou Jianfei, Wu Ruilin. 2019. Ore−forming structure analysis of the liangyan lead−zinc mining area in northwestern Guizhou deposit concentration district, China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(2): 187−197 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Wang Xinwei, Guo Tonglou, Wo Yujin, Zhou Yan, Wu Lizhi, Zhang Rongqiang, Li Shuangjian. 2013. Characteristics of deep structural segmentation and transformation of the Yaziluo fault zone[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 34(2): 220−228 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[37] Wang Xinwei, Wo Yujin, Zhou Yan, Zhang Rongqiang, Li Shuangjian. 2010. The kinematics of the fold−thrust zones in the western Yangtze Area[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(3): 200−212 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Wu Genyao, Wang Weifeng, Chi Hongxing. 2012. Basin evolution and later reformation of marine sediments in southern Guizhou Depression and neighboring areas[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 14(4): 507−521 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[39] Xiao Xianguo, Huang Zhilong, Zhou Jiaxi, Jin Zhongguo, Li Xiaobiao, Zhang Weilun. 2011. Several problems involved in genetic studies on the Pb−Zn deposits, Northwest Guizhou Province, China[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 31(3): 419−424 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Xie Jiarong. 1963. General theory of Mineral deposits in China[M]. Beijing: Academic Publishing House, 112−121(in Chinese).
[41] Zhang Changqing, Mao Jingwen, Wu Suoping, Li Houmin, Liu Feng, Guo Baojian, Gao Derong. 2005. Distribution, characteristics and genesis of Mississippi Valley−Type lead−zinc deposits in Sichuan−Yunnan−Guizhou area[J]. Mineral Deposits, 24(3): 336−348 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Zhang Changqing, Yu Jinjie, Mao Jingwen, Rui Zongyao. 2009. Advances in the study of Mississippi Valley−type deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 28(2): 195−210 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[43] Zhang Deming, He Lianglun, Zeng Guangqian, Yang Kunguang, Dai Chuangu, Zhang Hui. 2014. Superimposed deformation and its controlling effect on Pb−Zn deposits of Guanziyao region in West Guizhou[J]. Guizhou Geology, 31(4): 241−251 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[44] Zhang Rongqiang, Zhou Yan, Wang Xinwei, Li Shuangjian, Li Song. 2009. Structural features and tectonic evolution of the Wei−Zi−Luo fault zone in southweste Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 15(2): 178−189 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhang Weiji. 1984. On the sedimentary genesis and metallogenic regularity of the Pb−Zn deposit in northeast Yunnan[J]. Geology and Exploration, (7): 11−16 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Lü Z C, Zhu X K, Gao J G, Mirnejad H. 2014. Geology, isotope geochemistry and ore genesis of the shanshulin carbonate−hosted Pb–Zn deposit, southwest China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 63: 209−225. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.05.012
[47] Zhou J, Huang Z, Yan Z. 2013. The origin of the Maozu carbonate−hosted Pb–Zn deposit, southwest China: Constrained by C–O–S–Pb isotopic compositions and Sm–Nd isotopic age[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 73: 39−47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.04.031
[48] Zhou J, Huang Z, Zhou M, Li X, Jin Z. 2013. Constraints of C–O–S–Pb isotope compositions and Rb–Sr isotopic age on the origin of the Tianqiao carbonate−hosted Pb–Zn deposit, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 53: 77−92. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.01.001
[49] Zhu Luyan, Su Wenchao, Shen Nengping, Cai Jiali, Zhang Zhengwei, Zhaohai, Xie Peng. 2016. Fluid inclusion and sulfur isotopic studies of lead−zinc deposits, northwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(11): 3431−3440 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[50] 陈大. 1999. 水城青山铅锌矿床地质特征及控矿因素初探[J]. 贵州地质, 16(1): 35−39.
[51] 陈大, 曾德红. 2000. 青山—横塘矿区铅锌矿床控矿断裂特征及找矿评价[J]. 贵州地质, 17(1): 46−51.
[52] 陈士杰. 1986. 黔西滇东北铅锌矿成因探讨[J]. 贵州地质, (3): 3−14.
[53] 成晨, 韩润生, 王雷, 肖宪国, 何志威, 李波, 周暄翎. 2019. 黔西北福来厂铅锌矿床构造成生发展及其控矿作用[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(1): 90−104.
[54] 董家龙. 2008. 黔西北地区铅锌矿矿床成矿规律与找矿研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 23−26.
[55] 顾尚义. 2007. 黔西北地区铅锌矿硫同位素特征研究[J]. 贵州工业大学学报(自然科学版), 36(1): 11−14.
[56] 贵州省地质矿产局. 1987. 中华人民共和国地质矿产部地质专报: (一) 区域地质 (第7号), 贵州省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 731−742.
[57] 韩润生. 2003. 初论构造成矿动力学及其隐伏矿定位预测研究内容和方法[J]. 地质与勘探, (1): 7−11.
[58] 韩润生, 陈进, 黄智龙, 马德云, 薛传东, 李元, 邹海俊, 李勃, 胡煜昭, 马更生, 黄德镛, 王学焜. 2006. 构造成矿动力学及隐伏矿定位预测——以云南会泽超大型铅锌(银、锗)矿床为例[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1–170.
[59] 韩润生, 陈进, 李元, 马德云, 赵德顺, 马更生. 2001. 云南会泽铅锌矿床构造控矿规律及其隐伏矿预测[J]. 矿物学报, 21(2): 265−269.
[60] 韩润生, 胡煜昭, 王学琨, 黄智龙, 陈进, 王峰, 吴鹏, 李波, 王洪江, 董英, 雷丽. 2012. 滇东北富锗银铅锌多金属矿集区矿床模型[J]. 地质学报, 86(2): 280−294. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.02.007
[61] 韩润生, 马德云, 刘丛强. 2003. 陕西铜厂矿田构造成矿动力学[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 3−10.
[62] 韩润生, 王峰, 胡煜昭, 王学焜, 任涛, 邱文龙, 钟康惠. 2014. 会泽型(HZT)富锗银铅锌矿床成矿构造动力学研究及年代学约束[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 38(4): 758−771.
[63] 韩润生, 王峰, 赵高山, 王进, 周高明, 王学琨. 2010. 滇北东矿集区昭通毛坪铅锌矿床深部找矿新进展[J]. 地学前缘, 17(3): 275−275.
[64] 韩润生, 王明志, 金中国. 2020. 黔西北铅锌多金属矿集区成矿构造体系及其控矿机制[J]. 地质学报, 94(3): 850−868.
[65] 韩润生, 张艳, 王峰, 吴鹏, 邱文龙, 李文尧. 2019. 滇东北矿集区富锗铅锌矿床成矿机制与找矿靶区优选[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 125−126.
[66] 胡瑞忠, 陈伟, 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 陈伟, 毕献武, 付山岭, 尹润生, 肖加飞. 2020. 扬子克拉通前寒武纪基底对中生代大面积低温成矿的制约[J]. 地学前缘, 27(2): 137−150.
[67] 胡晓燕, 蔡国盛, 苏文超, 曾道国, 王蝶. 2013. 黔西北筲箕湾铅锌矿床闪锌矿中的成矿流体特征[J]. 矿物学报, 33(3): 302−307.
[68] 黄智龙, 胡瑞忠, 苏文超, 温汉捷, 刘燊, 符亚洲. 2011. 西南大面积低温成矿域: 研究意义、历史及新进展[J]. 矿物学报, 31(3): 309−314.
[69] 金中国. 2008. 黔西北地区铅锌矿控矿因素、成矿规律与找矿预测[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社: 56−60.
[70] 金中国, 黄智龙. 2009. 黔西北垭都−蟒硐断裂带铅锌成矿地质特征及找矿潜力分析[J]. 地质与勘探, 45(2): 20−26.
[71] 廖文. 1984. 滇东、黔西铅锌金属区硫、铅同位素组成特征与成矿模式探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, (1): 2−8.
[72] 刘成. 2015. 扬子板块西缘大地构造演化对MVT铅锌矿形成的制约[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 35−45.
[73] 刘幼平. 2002. 黔西北地区铅锌矿成矿规律及找矿模式初探[J]. 贵州地质, (3): 30−35.
[74] 柳贺昌. 1996. 滇, 川, 黔铅锌成矿区的成矿模式[J]. 云南地质, 15(1): 41−51.
[75] 罗卫, 孔令, 金中国, 戴塔根. 2010. 黔西北地区铅锌矿床控矿构造与成矿[J]. 矿产与地质, 24(1): 35−43.
[76] 毛健全, 张启厚, 顾尚义. 1997. 水城断陷的地质特征及构造演化[J]. 贵州工业大学学报, (2): 4−9.
[77] 牟保磊. 1999. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 北京大学出版社: 38−41.
[78] 欧锦秀. 1996. 贵州水城青山铅锌矿床的成矿地质特征[J]. 桂林工学院学报, (3): 277−282.
[79] 钱建平. 2001. 黔西北威宁−水城铅锌矿带动力成矿作用研究[J]. 地球与环境, 29(3): 134−139.
[80] 秦守荣, 刘爱民. 1998. 论贵州喜山期的构造运动[J]. 贵州地质, 15(2): 105−114.
[81] 孙家骢, 韩润生. 2016. 矿田地质力学理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 86−100.
[82] 汪新伟, 郭彤楼, 沃玉进, 周雁, 吴莉芝, 张荣强, 李双建. 2013. 垭紫罗断裂带深部构造分段特征及构造变换作用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 34(2): 220−228.
[83] 汪新伟, 沃玉进, 周雁, 张荣强, 李双建. 2010. 上扬子地区褶皱−冲断带的运动学特征[J]. 地学前缘, 17(3): 200−212.
[84] 王奖臻, 李朝阳, 李泽琴, 李葆华, 刘文周. 2002. 川、滇、黔交界地区密西西比河谷型铅锌矿床与美国同类矿床的对比[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 21(2): 127−132.
[85] 王明志, 韩润生, 周威, 宋丹辉, 罗达, 周剑飞, 吴睿林. 2019. 黔西北矿集区亮岩铅锌矿区成矿构造解析[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(2): 187−197.
[86] 吴根耀, 王伟锋, 迟洪星. 2012. 黔南坳陷及邻区盆地演化和海相沉积的后期改造[J]. 古地理学报, 14(4): 507−521.
[87] 肖宪国, 黄智龙, 周家喜, 金中国, 李晓彪, 张伦尉. 2011. 黔西北铅锌矿床成因研究中的几个问题[J]. 矿物学报, 31(3): 419−424.
[88] 谢家荣. 1963. 中国矿床学总论[M]. 北京: 学术书刊出版社, 112−121.
[89] 张德明, 何良伦, 曾广乾, 杨坤光, 戴传固, 张慧. 2014. 黔西罐子窑地区叠加变形及其对铅锌矿床的控制作用[J]. 贵州地质, 31(4): 241−251.
[90] 张荣强, 周雁, 汪新伟, 李双建, 李松. 2009. 贵州西南部威−紫−罗断裂带构造特征及演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 15(2): 178−189.
[91] 张位及. 1984. 试论滇东北铅锌矿床的沉积成因和成矿规律[J]. 地质与勘探, (7): 11−16.
[92] 张长青, 毛景文, 吴锁平, 李厚民, 刘峰, 郭保健, 高德荣. 2005. 川滇黔地区MVT铅锌矿床分布、特征及成因[J]. 矿床地质, 24(3): 336−348.
[93] 张长青, 余金杰, 毛景文, 芮宗瑶. 2009. 密西西比型(MVT)铅锌矿床研究进展[J]. 矿床地质, 28(2): 195−210.
[94] 朱路艳, 苏文超, 沈能平, 董文斗, 蔡佳丽, 张正伟, 赵海, 谢鹏. 2016. 黔西北地区铅锌矿床流体包裹体与硫同位素地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 32(11): 3431−3440.
-



 下载:
下载: