Research on the development protection planning of the national space in the Chengdu-Deyang-Meishan-Ziyang urban group constructions
-
摘要:
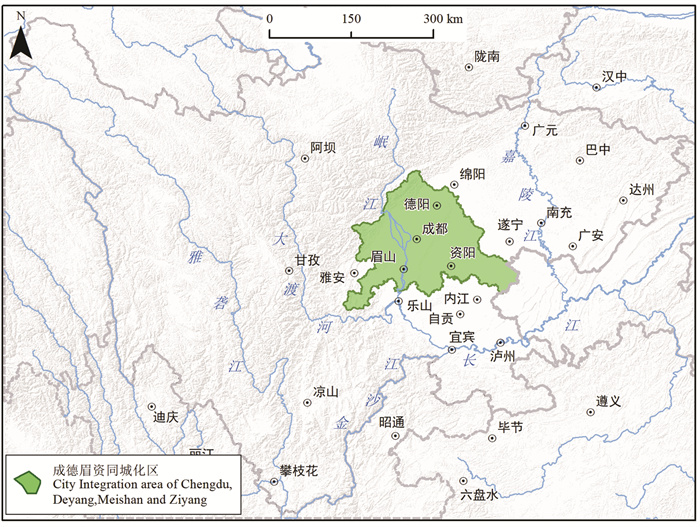
研究目的 本文旨在开展成-德-眉-资同城化建设区(四川省成都市、德阳市、眉山市、资阳市)生态安全、环境保护、农业生产、城镇建设的资源环境禀赋条件研究,初步提出国土空间开发保护策略。
研究方法 通过系统整理研究区以往地质调查等研究成果。
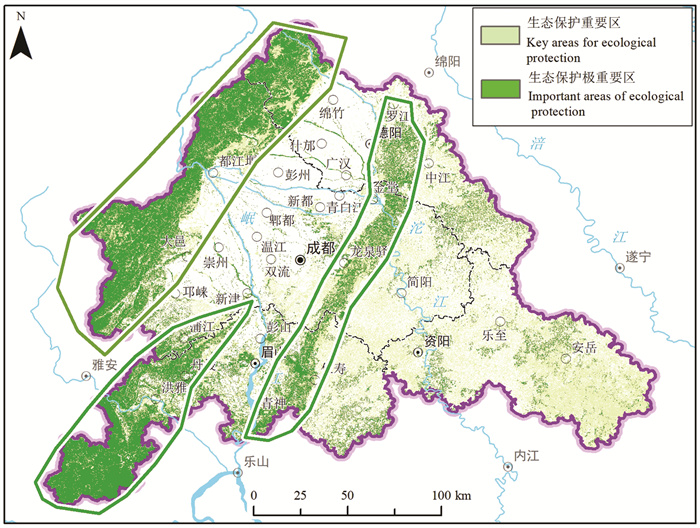
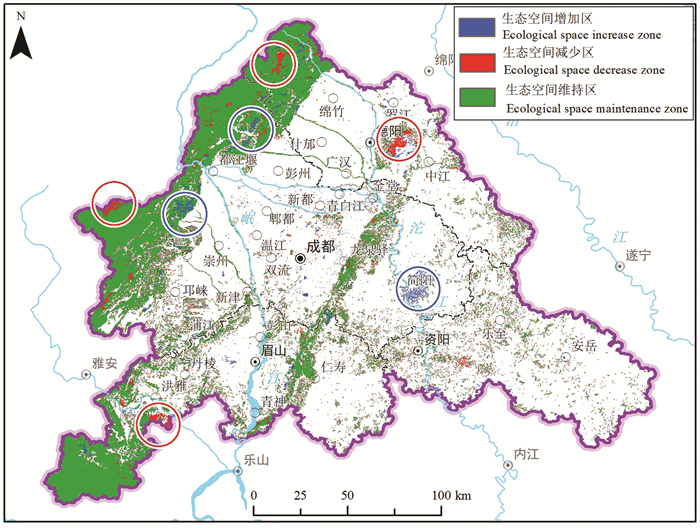
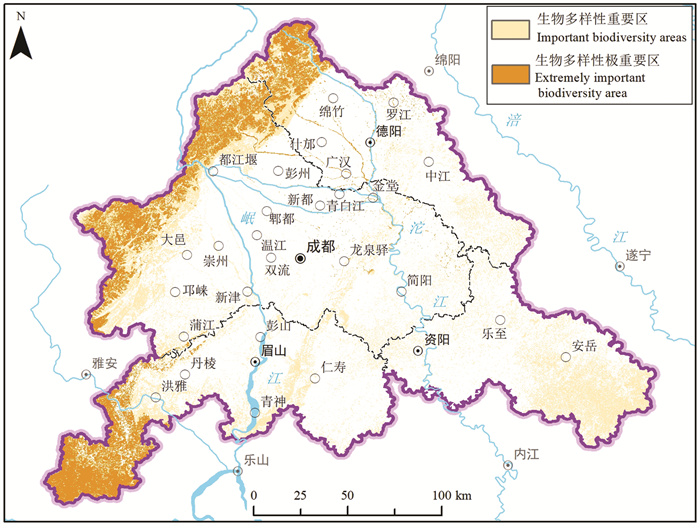
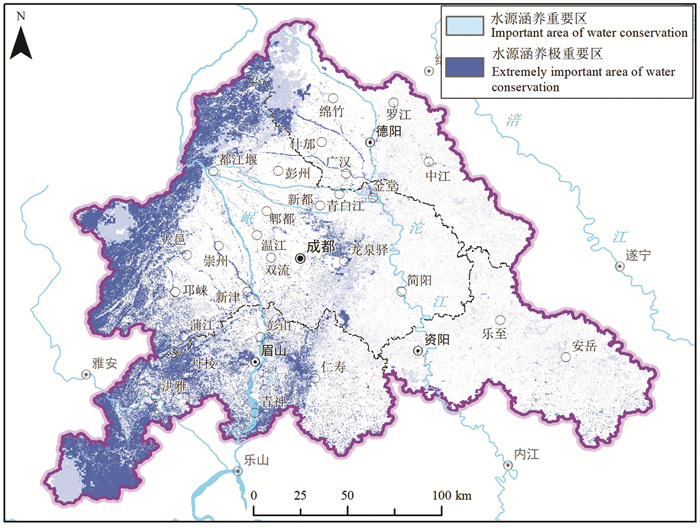
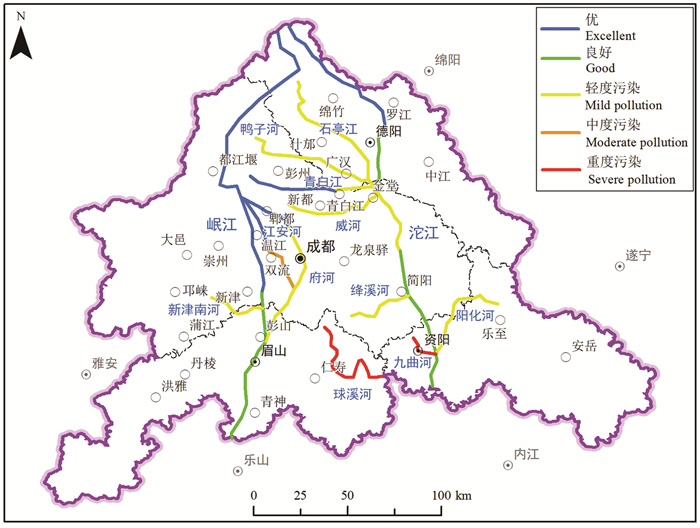
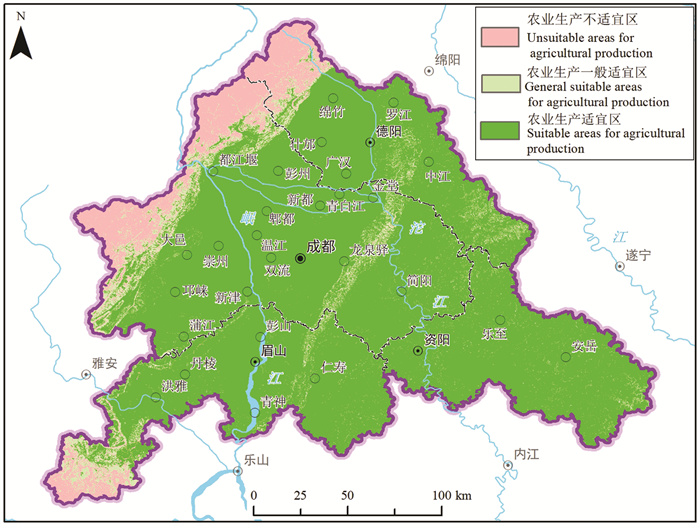
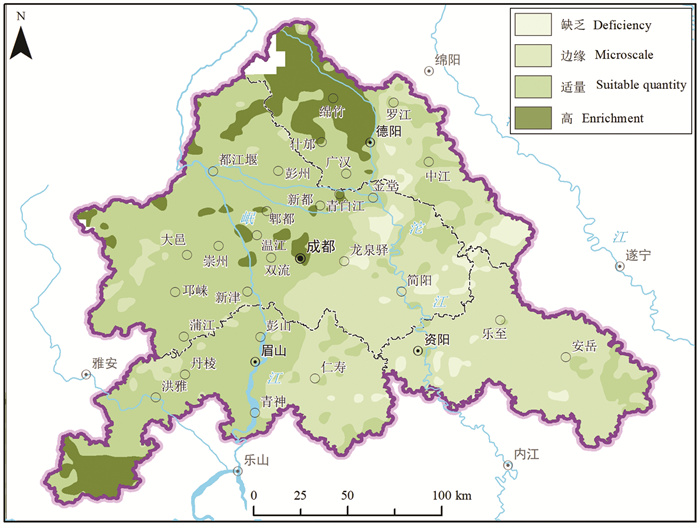
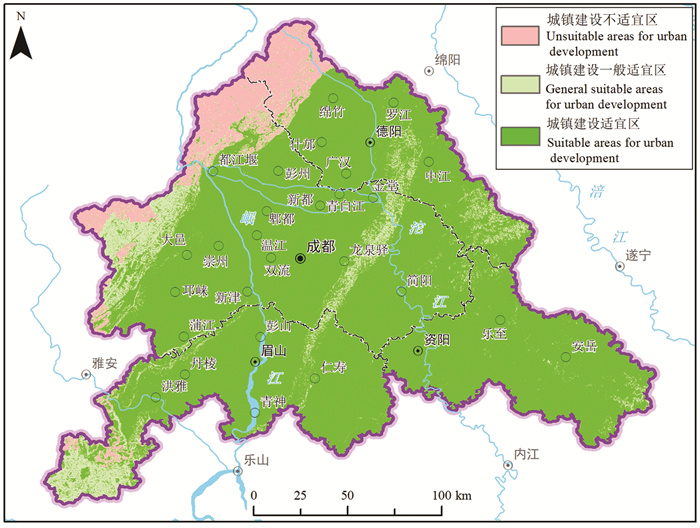
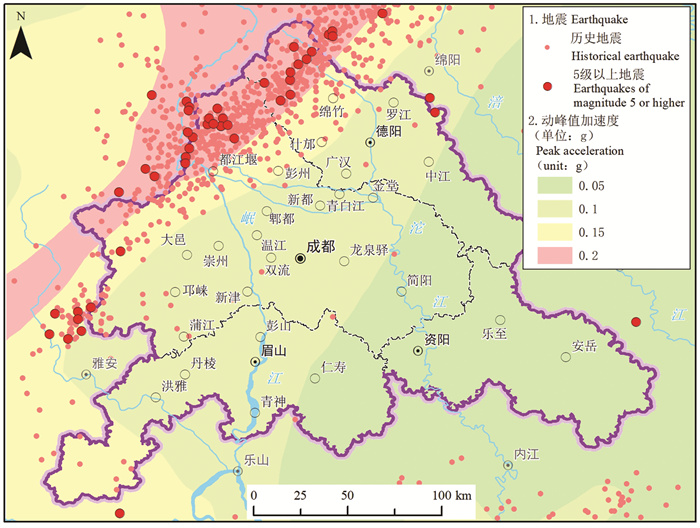
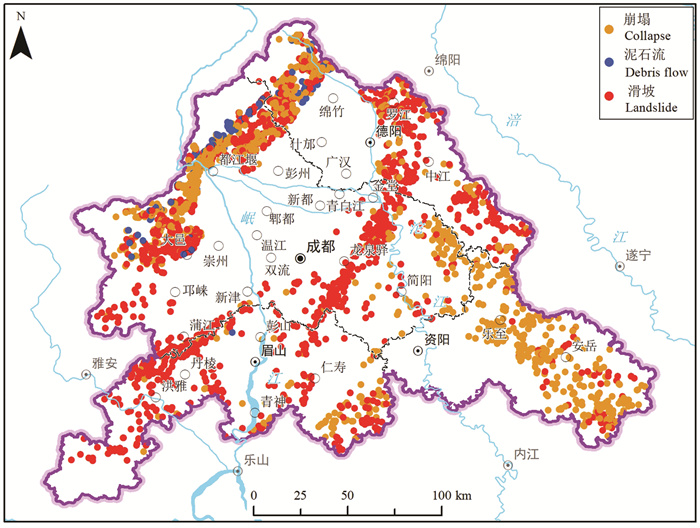
研究结果 成-德-眉-资同城化区资源环境条件总体较好,生态保护极重要区呈“东北向、三廊道”的空间特征,近30年来近80%地区生态空间维持良好,且生态空间增加区略大于减少区,生态功能逐年增强。大气环境较好,河流与地下水水质处于一般,河流水质总体“上游优、下游劣”,地下水劣V类水呈“城区大集中、城周小分散”的分布特征。农业生产适宜区分布广、集中连片,水土资源组合条件好,土壤养分、环境质量总体为优良,大部分地区含硒元素,局部为富硒地区。城镇建设适宜区分布广,水土资源禀赋较好,同时面临地震与地质灾害、洪涝的灾害风险。
结论 基于自然地理格局的相似性,建议成-德-眉-资同城化区形成一体化国土空间开发保护格局,打造区域性生态先行示范区,建立集中连片高标准农田示范区,规避自然灾害,优化空间格局,打造多中心、网络化、组团式的城镇化体系。
Abstract:This paper is the result of urban geological survey engineering.
Objective This paper aims to develop the study of natural resources endowment in ecological security, environmental protection, agricultural production and urban construction in Chengdu-Deyang-Meishan-Ziyang urbanization construction area, and propose the protection strategy of territory development preliminarily.
Methods This paper is carried by systematically organizing the research results of previous geological surveys in the study area.
Results The research shows that the resources and environmental conditions of the Chengdu-Deyang-Meishan-Ziyang urban groups are generally good, and the most important ecological protection area presents the spatial characteristics of "northeast orientation and three corridors". In the past 30 years, nearly 80% of the area has maintained good ecological space. In addition, the ecological space increase area is slightly larger than the decrease area, and the ecological function is strengthened year by year. The atmospheric environment is relatively good, the water quality of rivers and groundwater is on average, the water quality of rivers presents the spatial characteristics of "good upstream and poor downstream", and the groundwater which is Grade 5th of NSWS presents the spatial characteristics of "concentrated in urban area and scattered around urban area". Suitable areas for agricultural production are widely distributed, concentrated and contiguous, with good combination of water and soil resources overall good soil nutrients and environmental quality. Most areas contain selenium, and some are selenium-rich areas. Suitable areas for urban construction are also widely distributed, with good endowment of water and soil resources, but those areas are at the risk of earthquakes and geological disasters.
Conclusions Based on the similarity of natural geographic patterns, it is suggested that the Chengdu-Deyang-Meishan-Ziyang urban groups should form an integrated land space development, and protection pattern create a regional ecological pilot demonstration area. It also needs to establish a concentrated and contiguous high-standard farmland demonstration area to avoid natural disasters. It is suggested to optimize the spatial pattern and create a multi-center, networked and group-style urbanization system.
-

-
Cheng Jinhua, You Zhe. 2019. Scientific connotation and practical paths about the principle of "Taking mountains, rivers, forests, farmlands, lakes and grasslands as a life community"[J]. China Population, Resources and Environment, 29(2): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract).
China Geological Survey. 2018. Geological Environment Atlas of Important Economic Zones and Urban Agglomerations in China: Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1-24 (in Chinese).
Dong Shunli, Li Yong, Qiao Baocheng, Ma Bolin, Zhang Yi, Chen Hao, Yan Liang. 2008. Analysis of the new activity of the buried faults in the Chengdu Basin after the 8.0 magnitude Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 28(3): 1-7 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2008.03.001
Feng Xiangrong, Deng Ouping, Deng Liangji, Wu Ming, Yao Kun, Yang Zepeng. 2017. Flux characteristics of CO2, CH4 and N2O and their influencing factors in different types of ditches in the Chengdu plain[J]. Environmental Science, 38(12): 5344-5351 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Guo Ziqi, Li Shengwei, Wang Donghui, Li Hongyan, Wang Dewei, Song Zhi, Gu Hongyu. 2019. Environmental geology of the Longquanshan urban forest park, Chengdu, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(4): 90-99 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.04.010
Huang Changsheng, Zhou Yun, Zhang Shengnan, Wang Jietao, Liu Fengmei, Gong Chong, Yi Chengyun, Li Long, Zhou Hong, Wei Liangshuai, Pan Xiaodong, Shao Changsheng, Li Yiyong, Han Wenjing, Yin Zhibin, Li Xiaozhe. 2021. Groundwater resources in the Yangtze River Basin and its current development and utilization[J]. Geology in China, 48(4): 979-1000 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Jiang Yuehua, Lin Liangjun, Cheng Lide, Ni Huayong, Ge Weiya, Cheng Hangxin, Zhai Gangyi, Wang Guilin, Ban Yizhong, Li Yuan, Lei Mingtang, Tan Chengxuan, Su Jingwen, Zhou Quanping, Zhang Taili, Li Yun, Liu Hongyin, Peng Ke, Wang Hanmei. 2017. Research on conditions of resources and environment and major geological problems in the Yangtze River Economic Zone[J]. Geology in China, 44(6): 1045-1061 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Lin Yan, Bai Xiujia, Ye Zeyu, Zhang Heng. 2021. Assessment of agricultural production suitability in Nantong City based on ArcGIS technology[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 40(6): 968-977 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Yuan. 1986. Characteristics and division of river water pollution in Chengdu plain[J]. Sichuan Environment, 5(2): 40-52 (in Chinese).
Lu Ningsheng, Zhang Xiaoling, Kang Ping, Hua Ming, Du Yunsong, Chen Junhui, Xiang Weiguo, Lei Yu, Ou Yihan. 2021. Objective weather classification and typical process analysis of ozone pollution during spring in Chengdu Plain urban agglomeration[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 41(5): 1610-1627 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Ruan Chen, Wang Xiaoqi, Hu Lin, Huang Qing. 2008. Analysis of urban spatial development of major cities in urban agglom eration of the Chengdu plain using the Box model of atmospheric environment[J]. Sichuan Environment, 27(1): 46-51 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3644.2008.01.012
Song Zhi, Ni Huayong, Wang Donghui, et al. 2020. Map of Natural Resources and Geological Environment Supporting the Green Development of Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 8-29 (in Chinese).
Song Zhi, Le Qilang, Chen Xuyu, Yang Nan, Huang Tianju. 2021. A preliminary study on evaluating method of water resources carrying capacities of China and its application[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(1): 106-111 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Sun Shuming, Lu Lixia. 2021. Research on the formation mechanism of urban integration of Chengdu, Deyang, Meishan and Ziyang from the perspective of urban agglomeration[J]. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology, 38(4): 74-78 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4860.2021.04.011
Sun Zhangtao, Yu Zhengwei, Shu Siqi, Xu Chuangsheng, Shu Yang. 2023. Evaluation of ecosystem services of Chinese provincial land and suggestions for ecological geological survey[J]. Geology in China, 50(2): 479-494 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Xiqin, Xing Siqi, Zhang Yuan, Zhang Bing. 2009. Evaluation of coordinated development of economy-society-environment system in urban agglomeration of Chengdu Plain[J]. Ecological Economy, (2): 45-49 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Yuke, Chen Hao, Feng Xinglei, Chen Ming, Wang Donghui. 2019. Sedimentary characteristics and engineering geological significance of the middle Pleistocene Hejiang Formation in the eastern suburb platform on the Chengdu Plain, Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(3): 33-39 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei Haichuan, Yang Yongan, Xu Xiaoyun. 2018. Analysis on air quality of Chengdu Plain urban agglomeration in 2017[J]. Shandong Chemical Industry, 47(14): 191-194 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei Wei, Xia Junnan, Hong Mengyao, Bo Liming. 2021. The evolution of "Three-Zone Space" in the Yangtze River Economic Belt under major functional zoning strategy from 1980 to 2018[J]. Urban Geology, (3): 28-35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Yuntai, Ge Qianqian. 2018. Territorial spatial planning in the context of "Multiple Planning Integration": Taking Yulin Pilot as a case[J]. Land and Resources Information, (8): 22-29 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Yijia. 2005. Preliminary analysis on distribution of groundwater resources in Chengdu Plain[J]. Sichuan Water Resource, (4): 28-31 (in Chinese).
Zhou Daojing, Xu Yong, Wang Yafei, Zhou Kan, Liu Baoyin, Li Jiuyi, Fan Jie. 2020. Methodology and role of "Double Evaluation" in optimization of spatial development pattern[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 35(7): 814-824 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Kan, Li Jiuyi, Wang Qiang. 2021. Evaluation on agricultural production space and layout optimization based on resources and environmental carrying capacity: A case study of Fujian Province[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 41(2): 280-289 (in Chinese with English abstract).
成金华, 尤喆. 2019. "山水林田湖草是生命共同体"原则的科学内涵与实践路径[J]. 中国人口·资源与环境, 29(2): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGRZ201902001.htm
董顺利, 李勇, 乔宝成, 马博琳, 张毅, 陈浩, 闫亮. 2008. 汶川特大地震后成都盆地内隐伏断层活动性分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 28(3): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD200803001.htm
冯香荣, 邓欧平, 邓良基, 吴铭, 姚昆, 杨泽鹏. 2017. 成都平原不同类型沟渠CO2、CH4和N2O排放通量特征及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 38(12): 5344-5351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201712055.htm
郭子奇, 李胜伟, 王东辉, 李鸿雁, 王德伟, 宋志, 顾鸿宇. 2019. 浅析四川成都龙泉山城市森林公园主要环境地质问题[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 39(4): 90-99. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201904010.htm
黄长生, 周耘, 张胜男, 王节涛, 刘凤梅, 龚冲, 易秤云, 李龙, 周宏, 魏良帅, 潘晓东, 邵长生, 黎义勇, 韩文静, 尹志彬, 李晓哲. 2021. 长江流域地下水资源特征与开发利用现状[J]. 中国地质, 48(4): 979-1000. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20210401?st=search
姜月华, 林良俊, 陈立德, 倪化勇, 葛伟亚, 成杭新, 翟刚毅, 王贵玲, 班宜忠, 李媛, 雷明堂, 谭成轩, 苏晶文, 周权平, 张泰丽, 李云, 刘红樱, 彭柯, 王寒梅. 2017. 长江经济带资源环境条件与重大地质问题[J]. 中国地质, 44(6): 1045-1061. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20170601?st=search
林燕, 白秀佳, 叶泽宇, 张衡. 2021. 基于ArcGIS的南通市农业生产适宜性评价[J]. 地质通报, 40(6): 968-977. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD202106012.htm
刘源. 1986. 成都平原的河水污染特点及区划[J]. 四川环境, 5(2): 40-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ198602006.htm
卢宁生, 张小玲, 康平, 华明, 杜云松, 陈军辉, 向卫国, 雷雨, 欧奕含. 2021. 成都平原城市群春季臭氧污染天气客观分型与典型过程分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 41(5): 1610-1627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXX202105003.htm
阮晨, 汪小琦, 胡林, 黄庆. 2008. 基于大气环境箱式模型对成都平原城市群主要城市空间发展的评价分析[J]. 四川环境, 27(1): 46-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCHJ200801011.htm
宋志, 倪化勇, 王东辉, 等. 2020. 支撑服务成渝城市群绿色发展自然资源与地质环境图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 8-29.
宋志, 乐琪浪, 陈绪钰, 杨楠, 黄天驹. 2021. 水资源承载力评价方法初探以及在"以水四定"中的运用[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(1): 106-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD202101012.htm
孙书毓, 卢黎霞. 2021. 城市群视域下成德眉资同城化的形成机理研究[J]. 西南科技大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 38(4): 74-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MYJJ202104011.htm
孙张涛, 余正伟, 舒思齐, 许闯胜, 舒阳. 2023. 中国省域生态系统服务价值评价与生态地质调查工作建议[J]. 中国地质, 50(2): 479-494. http://geochina.cgs.gov.cn/geochina/article/abstract/20230211?st=search
王西琴, 邢思齐, 张远, 张兵. 2009. 成都平原城市群经济社会与资源环境协调发展评价[J]. 生态经济, (2): 45-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STJJ200902009.htm
王羽珂, 陈浩, 冯兴雷, 陈明, 王东辉. 2019. 成都平原东郊台地中更新统合江组沉积特征及工程地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 39(3): 33-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TTSD201903004.htm
魏海川, 杨永安, 许肖云. 2018. 2017年成都平原城市群空气质量状况分析[J]. 山东化工, 47(14): 191-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDHG201814081.htm
魏伟, 夏俊楠, 洪梦谣, 薄立明. 2021. 1980-2018年长江经济带主体功能空间演化研究[J]. 城市规划学刊, (3): 28-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXGH202103005.htm
赵雲泰, 葛倩倩. 2018. "多规合一"视角下的国土空间规划——以榆林试点为例[J]. 国土资源情报, (8): 22-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTZQ201808005.htm
郑义加. 2005. 成都平原地下水资源分布的初步分析[J]. 四川水利, (4): 28-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCSN200504015.htm
中国地质调查局. 2018. 中国重要经济区和城市群地质环境图集: 成渝城市群[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1-24.
周道静, 徐勇, 王亚飞, 周侃, 刘宝印, 李九一, 樊杰. 2020. 国土空间格局优化中的"双评价"方法与作用[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 35(7): 814-824. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYYX202007006.htm
周侃, 李九一, 王强. 2021. 基于资源环境承载力的农业生产空间评价与布局优化——以福建省为例[J]. 地理科学, 41(2): 280-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX202102011.htm
-



 下载:
下载: