Characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes and hydrochemistry in the groundwater of Ejina plain, Inner Mongolia and its hydrochemical evolution
-
摘要:
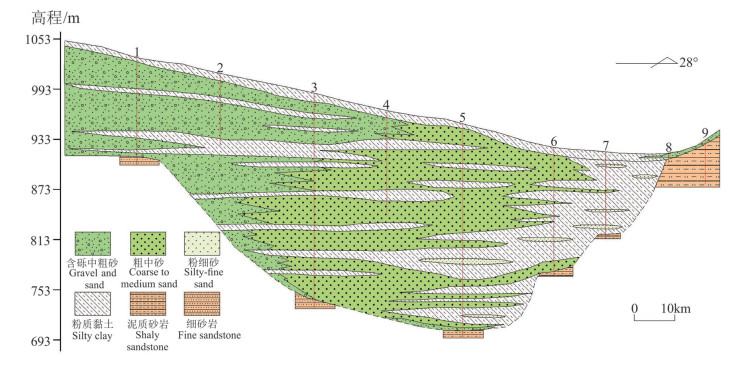
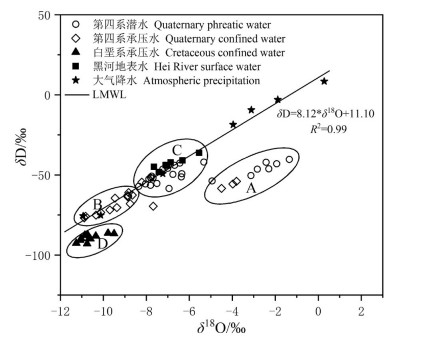
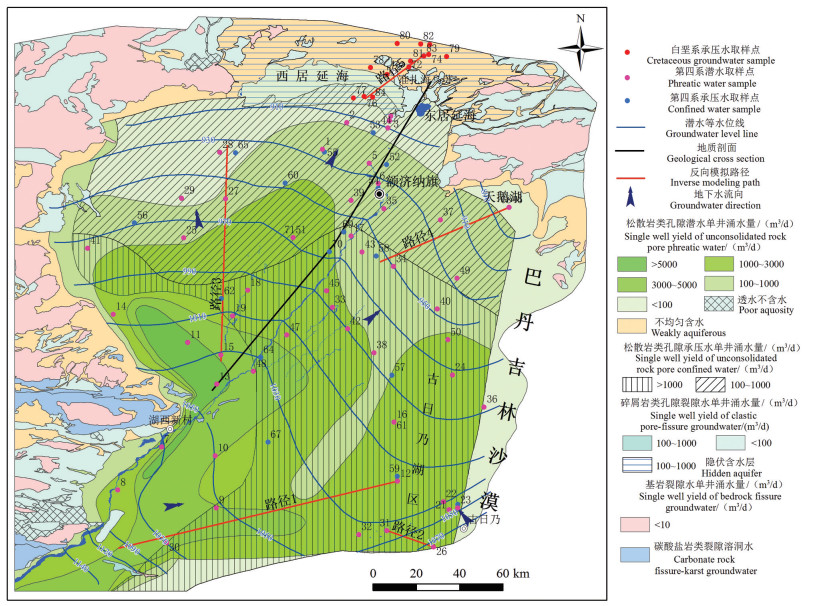
研究目的 为研究内蒙古额济纳平原地下水水化学特征及其演化规律,于2020年8月采集水样87组,氢氧同位素样品69组。
研究方法 综合运用数理统计、离子比例分析、水文地球化学模拟等方法,分析额济纳平原第四系地下水及北部白垩系地下水水文地球化学特征,探讨水文地球化学演化规律。
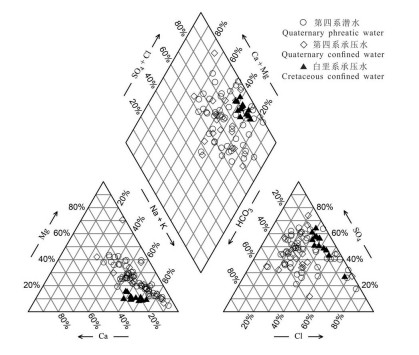
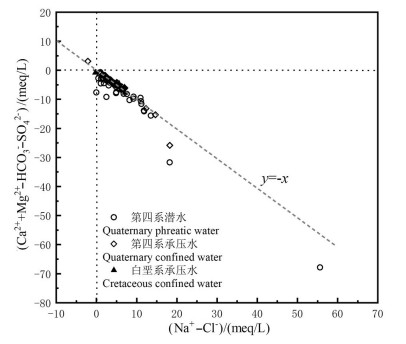
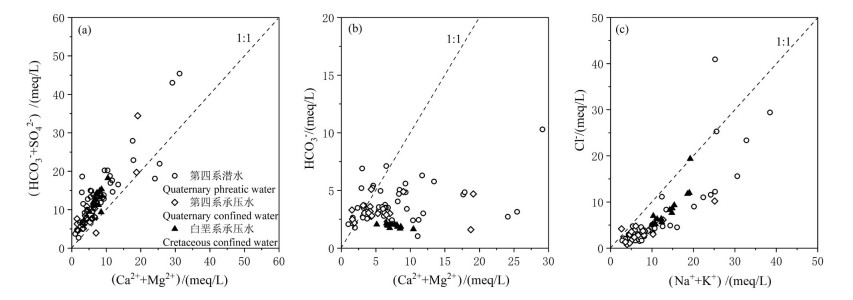
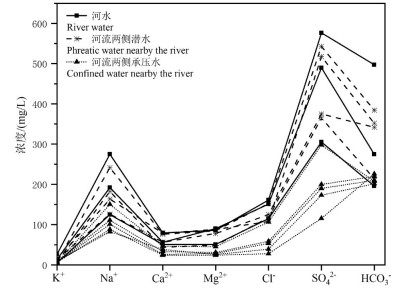
研究结果 结果表明:(1)该区地下水水化学类型以SO4-Na型为主。地下水中阴离子以SO42-为主,其次为Cl-;阳离子以Na+为主,Ca2+与Mg2+浓度差异不大。(2)研究区地下水SO42-、Cl-、TDS、总硬度、Na+和Mg2+浓度具有第四系承压水>第四系潜水>白垩系承压水的特点。(3)第四系潜水离子组分主要受溶滤作用、混合作用控制,局部地区受蒸发作用影响显著;第四系承压水离子组分主要受溶滤作用和阳离子交换作用控制;平原北部白垩系承压水离子组分受溶滤作用及阳离子交换作用控制。研究区地下水中主要离子来自岩盐、碳酸岩盐和石膏的溶解。
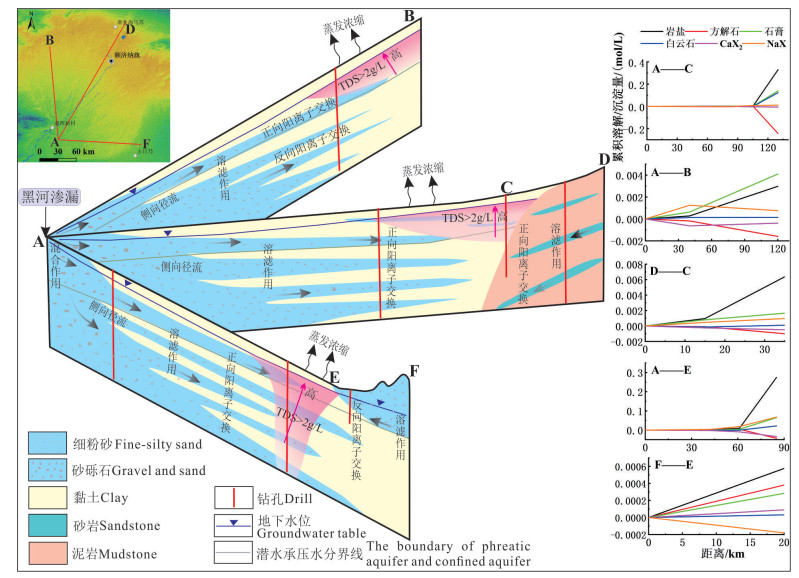
结论 沿地下水流向,第四系潜水离子浓度组分呈增加趋势,在额济纳平原内部第四系潜水和承压水中主要发生岩盐、白云石和石膏溶解、方解石沉淀以及正向阳离子交换作用;研究区东南部沙漠与平原交错带主要发生岩盐、白云石和石膏溶解、方解石沉淀以及反向阳离子交换;平原区北部白垩系承压水中主要发生岩盐、白云石和石膏溶解、方解石沉淀以及正向阳离子交换。
Abstract:This paper is the result of mineral exploration engineering.
Objective In order to study the hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Ejina plain, Inner Mongolia, 87 water quality samples and 69 hydrogen and oxygen isotope samples were collected in August 2020.
Methods Based on the methods of mathematical statistics, ion ratio, and hydrogeochemical simulation, the hydrogeochemical characteristics and the hydrochemical evolution rule of groundwater stored in Quaternary aquifer and Cretaceous aquifer were analyzed.
Results The results showed that: (1) The groundwater was mainly SO4-Na type. SO42- was the main anion, followed by Cl-. Na+ was the main cation, followed by Ca2+ and Mg2+, there was little difference between Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations. (2) The concentrations of SO42-, Cl-, TDS, total hardness, Na+ and Mg2+ decreased in the order of Quaternary confined water> Quaternary phreatic water> Cretaceous confined water. (3) Quaternary phreatic ions were mainly controlled by leaching and mixing process, and some areas were significantly affected by evaporation. The ions of Quaternary confined water were mainly controlled by leaching and cation exchange. The ions of the Cretaceous confined water in the northern part of the plain were controlled by leaching and cation exchange. The main ions of groundwater in the study area came from the dissolution of halite, carbonates and gypsum.
Conclusions Along the direction of groundwater flow, the concentration of ion components in Quaternary phreatic showed an increasing trend. In the Quaternary phreatic and confined water in the Ejina plain, the main water- rock interaction processes were dissolution of halite, dolomite and gypsum, precipitation of calcite, and positive cation exchange. In the interlaced zone between the desert and the plain in the southeast of the study area, the dissolution of halite, dolomite and gypsum, the precipitation of calcite, and reverse cation exchange mainly occurred. Halite, dolomite and gypsum dissolution, calcite precipitation, and positive cation exchange mainly occurred in the Cretaceous confined water in the northern plain.
-

-
表 1 地下水水化学指标统计结果(mg/L,pH除外)
Table 1. Statistical results of hydrochemical parameters of groundwater (mg/L, except pH)
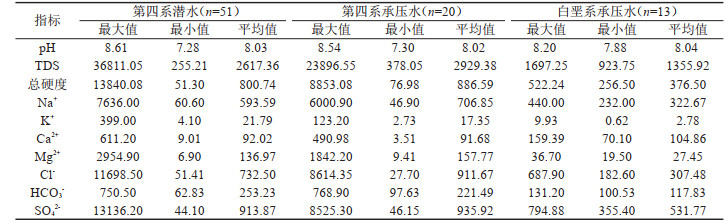
表 2 各路径起点和终点水样的饱和指数
Table 2. Saturation index of the water sample at the starting and ending of each path
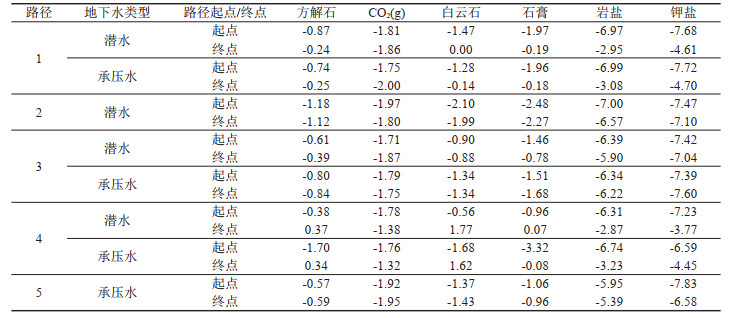
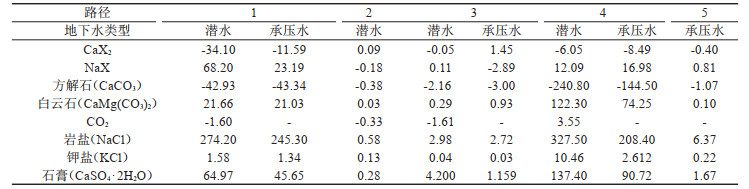
表 3 矿物在各路径上的溶解/沉淀量(mmol/L)
Table 3. Calculated amount of mineral dissolution or precipitation of each path (mmol/L)
-
Acheampong S Y, Hess J W. 1998. Hydrogeologic and hydrochemical framework of the shallow groundwater system in the southern Voltaian sedimentary basin[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, (6): 527-537.
Barzegar R, Moghaddam A A, Nazemi A H, Adamowski J. 2018. Evidence for the occurrence of hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater of Khoy plain, northwestern Iran, using ionic ratios and geochemical modeling[J]. Environment Earth Sciences, 77(16): 597. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7782-y
Barzegar R, Moghaddam A A, Tziritis E, Fakhri M S, Soltani S. 2017. Identification of hydrogeochemical processes and pollution sources of groundwater resources in the Marand plain, northwest of Iran[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(7): 1-16.
Chen Jiansheng, Wang Jiyang, Zhao Xia, Sheng Xuefen, Gu Weizu, Chen Liang, Su Zhiguo. 2004. Study of groundwater supply of the confined aquifers in the Ejin Basin based on isotopic methods[J]. Geological Review, 50(6): 649-658(in Chinese with English abstract).
Gates J B, Edmunds W M, Darling W G, Ma J Z, Pang Z H, Young A A. 2008. Conceptual model of recharge to southeastern Badain Jaran Desert groundwater and lakes from environmental tracers[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 23: 3519-3534. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.07.019
Khairy H S, Janardhana M R. 2014. Hydrogeochemistry and quality of groundwater of coastal unconfined aquifer in Amol-Ghaemshahr Plain, Mazanda-ran Province, northern Iran[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 71(11): 4767-4782. doi: 10.1007/s12665-013-2868-z
Li Xiaohan, Zhang Yilong, Wang Rui, Li Zhenghong. 2018. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation mechanism of groundwater in Hohhot basin[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 16(4): 136-145 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu Jun, Chen Zongyu, Wang Lijuan, Zhang Yilong, Li Zhenghong, Xu Jiaming, Peng Yurong. 2016. Chemicaland isotopic constrains on the origin of brine and saline groundwater in Hetao plain, Inner Mongolia[J]. Environmental Science Pollution Research, 23: 15003-15014. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6617-1
Qian Yunping, Wang ling. 2008. Application of Isotope Hydrological Technology in the Study of Water Cycle in the Heihe River Basin[M]. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 117-138(in Chinese).
Ruan Yunfeng, Zhao Liangju, Yao Zhijun, Xiao Honglang, Cheng Guodong. 2016. Spatial differentiation characteristics and impact factors of groundwater conductance in the Heihe River basin[J]. Journal of Beijing Normal University (Natural Science), 52(3): 289-296(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shang Weilin, Ma Wenxue. 2012. Hydrogeochemical characteristics analysis of Ceke port[J]. China Mine Engineering, 41(4): 56-61(in Chinese with English abstract).
Shen Zhaoli, Zhu Wanhua, Zhong Zoushen. 1990. Fundamentals of Hydrogeochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 53(in Chinese).
Soumya B S, Sekhar M, Riotte J, Audry S, Lagane C, Braun J. 2011. Inverse models to analyze the spatiotemporal variations of chemical weathering fluxes in a granito-gneissic watershed: Mule Hole, South India[J]. Geoderma, 165(1): 12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.06.015
Su Yonghong, Zhu Gaofeng, Feng Qi, Chang Zongqiang, Si Jianhua, Xi Haiyang, Cao Shengkui. 2009. Chemical evolution of shallow groundwater and the residence time in the Ejina Basin[J]. Arid Land Geography, 32(4): 544-551(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wang Ping, Yu Jingjie, Pozdniakov S P, Grinevsky S O, Liu Changming. 2014. Shallow groundwater dynamics and its driving forces in extremely arid areas: A case study of the lower Heihe River in northwestern China[J]. Hydrological Processes, 28(3): 1539-1553. doi: 10.1002/hyp.9682
Wang Ping. 2018. Progress and prospect of research on water exchange between intermittent rivers and aquifers in arid regions of northwestern China[J]. Progress in Geography, 37(2): 183-197(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18306/dlkxjz.2018.02.002
Wang Zhen, Guo Huaming, Liu Haiyan, Zhao Weiguang, Liu Shuai, Wang Jiao, Shen Mengmeng. 2021. Hydrochemical and hydrogen and oxygen isotope characteristics of subsurface water in the Maqu Plateau[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 48(1): 18-26(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wei Xing, Zhou Jinlong, Nai Weihua, Zeng Yanyan, Fan Wei, Li Bin. 2019. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Kashgar delta area in Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Science, 40(9): 4042-4051(in Chinese with English abstract).
Wen Xiaohu, Wu Yanqing, Su Jianping, Zhang Yinghua, Liu Famin. 2006. Groundwater salinization characteristics and mechanism in Ejin Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 26(5): 836-841 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Wu Xuanmin, Shi Shengsheng, Li Zhiheng. 2004. Research on Groundwater Utilization and Ecological Environment Protection in Ejina Basin of Heihe River in Northwest China[M]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia People's Publishing House, 49-54(in Chinese).
Wu Yanqing, Zhang Yinghua, Wen Xiaohu, Su Jianping. 2010. Hydrological Cycle and Water Resources Simulation in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 56-63(in Chinese).
Xi Haiyang, Feng Qi, Si Jianhua, Chang Zongqiang, Su Yonghong. 2012. A review of river course leakage in the Ejina Delta in the lower reaches of Heihe River[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 41(7): 33-37(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Guanghui. 2017. The Groundwater Source Discussion of Gurinai Lake Area of Alxa in Inner Mongolia[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 1-64 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Tao, Cai Wutian, Li Yingzhi, Zhang Zhiyin, Geng Tingting, Bian Chao, Zhao Miao, Cai Yuemei. 2017. Major ionic features and their possible controls in the water of the Niyang River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 38(11): 4537-4545(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Yinghua, Wu Yanqing, Su Jianping, Wen Xiaohu. 2006. Mechanism of groundwater replenishment in Ejin Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 26(1): 96-102(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhang Zhenyu, Zhao Pei, Chang Xiangsheng, Wang Yunze, Dong Guotao. 2019. Analysis of groundwater depth change in Ejina Oasis from 1992 to 2015[J]. Yellow River, 41(7): 33-37(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhao Liangju, Ruan Yunfeng, Xiao Honglang, Zhou Maoxian, Cheng Guodong. 2014. Application of radioactive trituium isotope in studying water cycle of the Heihe River Basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 34(5): 959-972 (in Chinese with English abstract).
Zheng Zhaoxian, Zhang Hongda, Chen Zongyu, Li Xufeng, Zhu Pucheng, Cui Xiaoshun. 2017. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic indicators of hydraulic fracturing flow back fluids in shallow groundwater and stream water, derived from Dameigou shale gas extraction in the northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 51: 5889-5898.
Zhou Jinmei, Jiang Zhongcheng, Xu Guangli, Qin Xiaoqun, Huang Qibo, Zhang Liankai. 2019. Major ionic characteristics and controlling factors of karst groundwater at Xiangshui, Chongzuo[J]. Environmental Science, 40(5): 2143-2151(in Chinese with English abstract).
Zhou Yangxiao, Li Wenpeng. 2011. Groundwater Monitoring Information System Model and Sustainable Development[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 45-48(in Chinese).
陈建生, 汪集旸, 赵霞, 盛雪芬, 顾慰祖, 陈亮, 苏治国. 2004. 用同位素方法研究额济纳盆地承压含水层地下水的补给[J]. 地质论评, 50(6): 649-658. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP200406014.htm
李潇瀚, 张翼龙, 王瑞, 李政红. 2018. 呼和浩特盆地地下水化学特征及成因[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 16(4): 136-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NSBD201804018.htm
钱云平, 王玲. 2008. 同位素水文技术在黑河流域水循环研究中的应用[M]. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 117-138.
阮云峰, 赵良菊, 姚治君, 肖洪浪, 程国栋. 2016. 黑河流域地下水电导率空间分异特征及影响因素研究[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版), 52(3): 289-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSDZ201603008.htm
商玮麟, 马文学. 2012. 策克口岸水文地球化学特征分析[J]. 中国矿山工程. 41(4): 56-61. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKS201204019.htm
沈照理, 朱宛华, 钟左燊. 1990. 水文地球化学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 53.
苏永红, 朱高峰, 冯起, 常宗强, 司建华, 席海洋, 曹生奎. 2009. 额济纳盆地浅层地下水演化特征与滞留时间研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 32(4): 544-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL200904010.htm
王平. 2018. 西北干旱区间歇性河流与含水层水量交换研究进展与展望[J]. 地理科学进展, 37(2): 183-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201802003.htm
王振, 郭华明, 刘海燕, 赵威光, 刘帅, 王娇, 沈萌萌. 2021. 玛曲高原区潜水水化学和氢氧同位素特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 48(1): 18-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202101003.htm
魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 曾妍妍, 范薇, 李斌. 2019. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水化学特征及演化规律[J]. 环境科学, 40(9): 4042-4051. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201909022.htm
温小虎, 仵彦卿, 苏建平, 张应华, 刘发民. 2006. 额济纳盆地地下水盐化特征及机理分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 26(5): 836-841. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS200605032.htm
武选民, 史生胜, 黎志恒. 2004. 西北黑河额济纳盆地地下水利用与生态环境保护研究[M]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古人民出版社, 49-54.
仵彦卿, 张应华, 温小虎, 苏建平. 2010. 中国西北黑河流域水文循环与水资源模拟[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 56-63.
席海洋, 冯起, 司建华, 常宗强, 苏永红. 2012. 黑河下游额济纳三角洲河道渗漏对地下水补给研究综述[J]. 冰川冻土, 34(5): 1241-1247. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201205028.htm
张光辉. 2017. 内蒙古阿拉善古日乃湖地区地下水来源探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-64.
张涛, 蔡五田, 李颖智, 张智印, 耿婷婷, 边超, 赵淼, 蔡月梅. 2017. 尼洋河流域水化学特征及其控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 38(11): 4537-4545. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201711012.htm
张应华, 仵彦卿, 苏建平, 温小虎. 2006. 额济纳盆地地下水补给机理研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 26(1): 96-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS200601016.htm
张震域, 赵沛, 畅祥生, 王云泽, 董国涛. 2019. 额济纳绿洲1992-2015年地下水埋深变化分析[J]. 人民黄河, 41(7): 33-37.
赵良菊, 阮云峰, 肖洪浪, 周茅先, 程国栋. 2014. 氚同位素在黑河流域水循环研究中的应用[J]. 第四纪研究, 34(5): 959-972. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201405006.htm
周巾枚, 蒋忠诚, 徐光黎, 覃小群, 黄奇波, 张连凯. 2019. 崇左响水地区岩溶地下水主要离子特征及控制因素[J]. 环境科学, 40(5): 2143-2151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201905017.htm
周仰效, 李文鹏. 2011. 地下水监测信息系统模型及可持续开发[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 45-48.
-



 下载:
下载: