Distribution and sources of heavy metals in bottom sediments of the Xiamen Bay, Fujian Province and its effects on ecological environment
-
摘要:
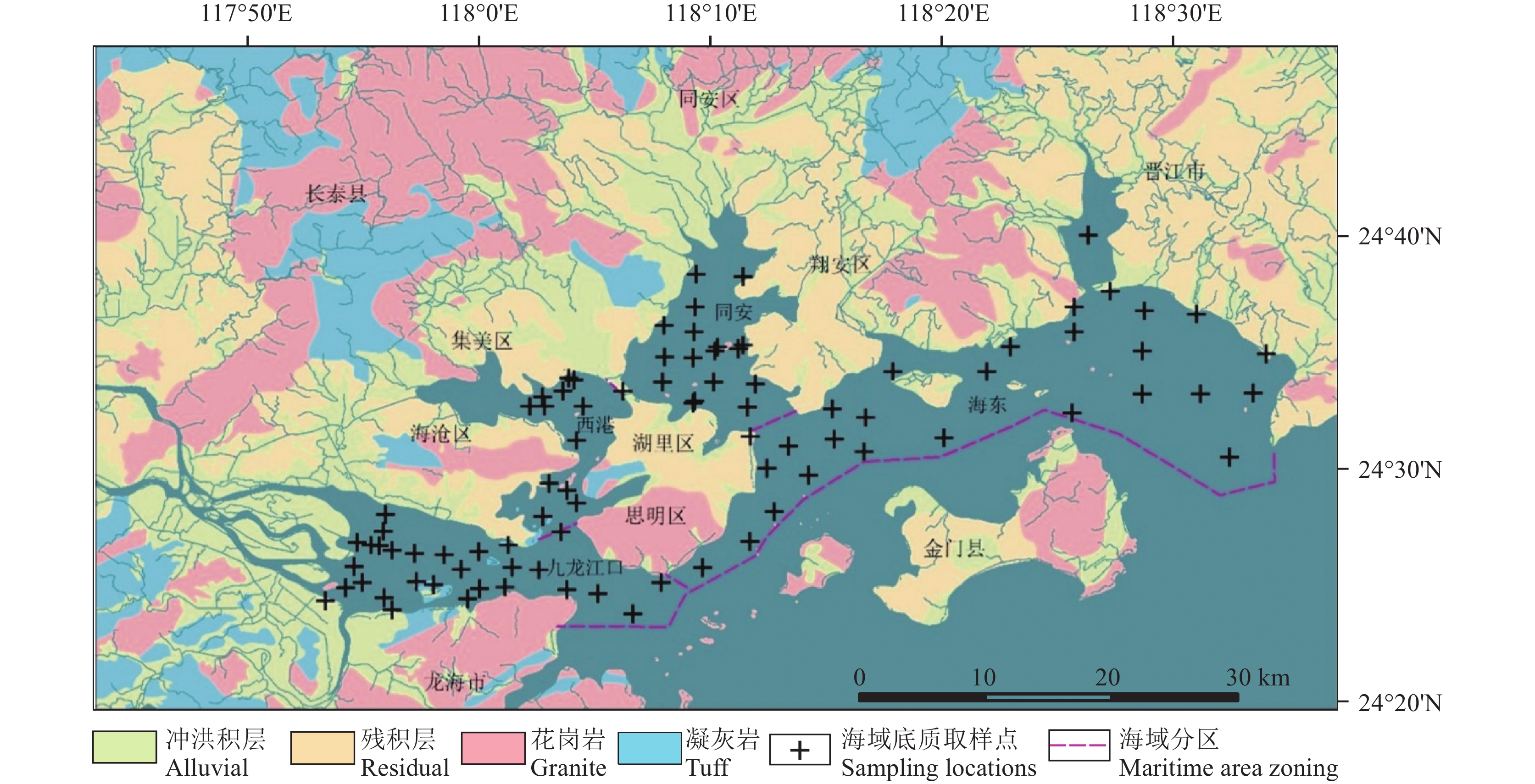
研究目的 厦门湾生态环境治理和厦门港口建设,造成厦门湾重金属含量变化较大,查明湾区重金属分布特征、演变及来源分析,对厦门湾重金属污染防治与生态风险管控具有重要意义。
研究方法 本文测定了厦门湾87个海域底质表层沉积物中的7种重金属的含量,分析了重金属分布特征、富集程度,并利用因子分解及主成分分析法,定量分析了重金属的主要来源。
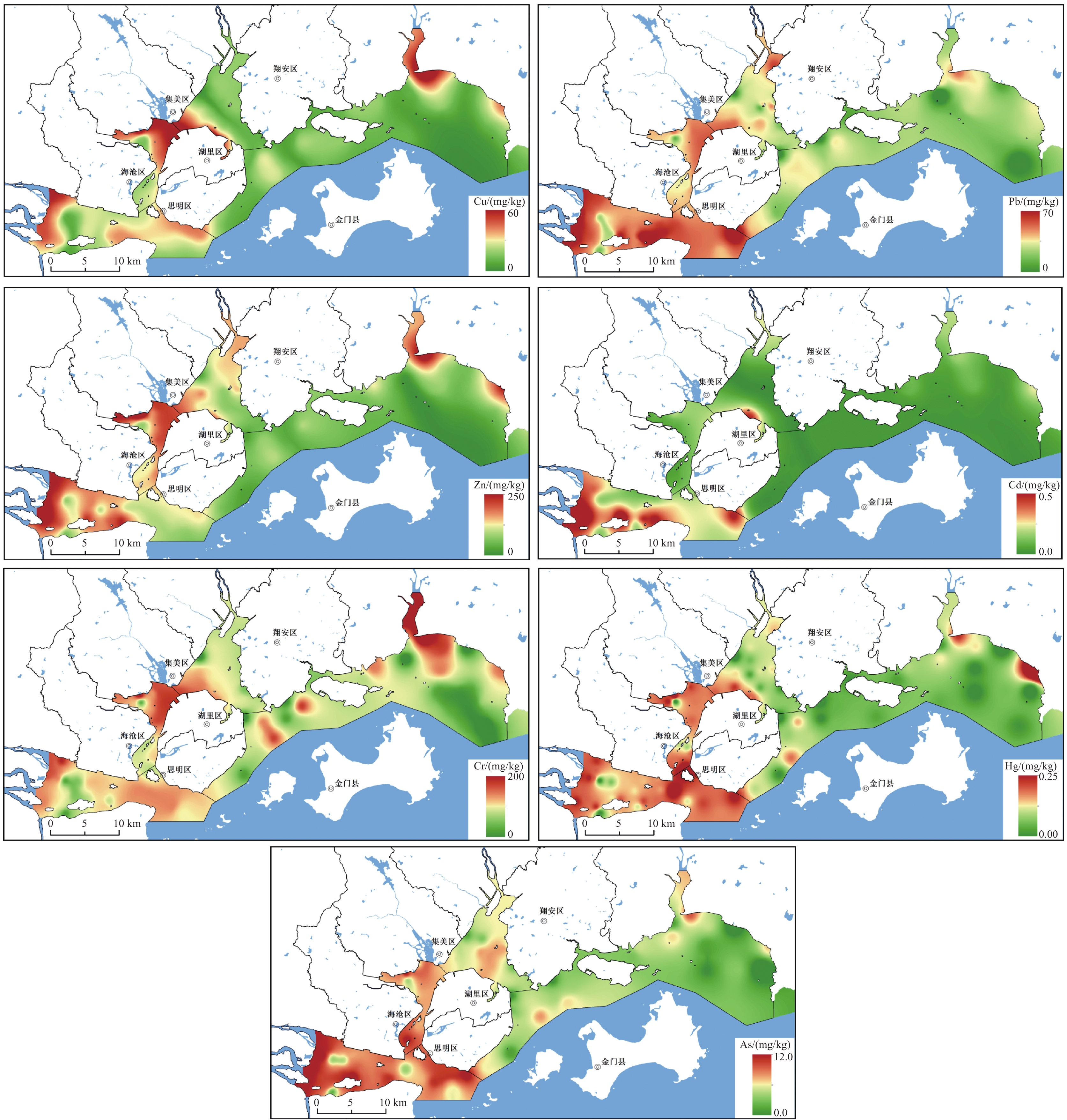
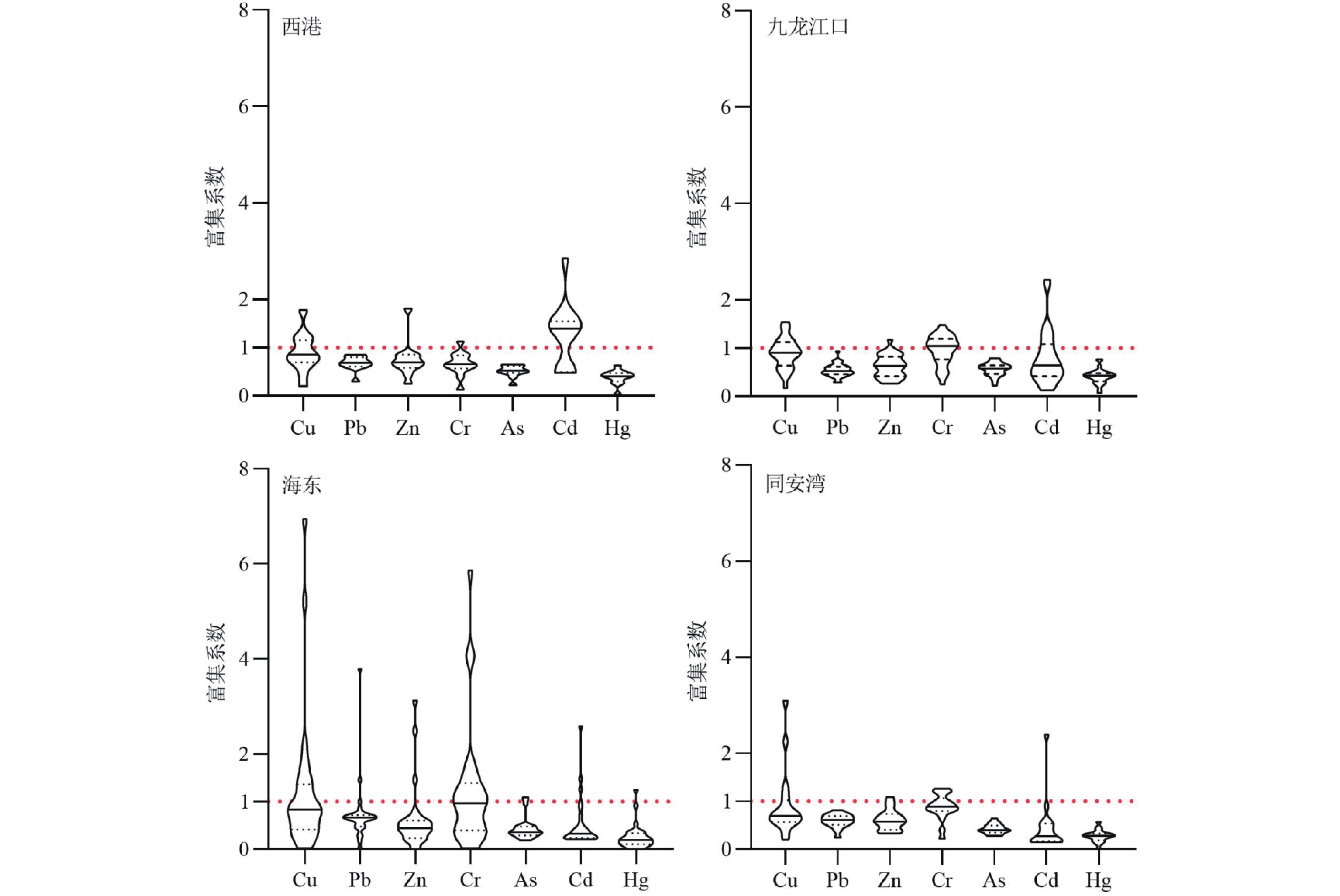
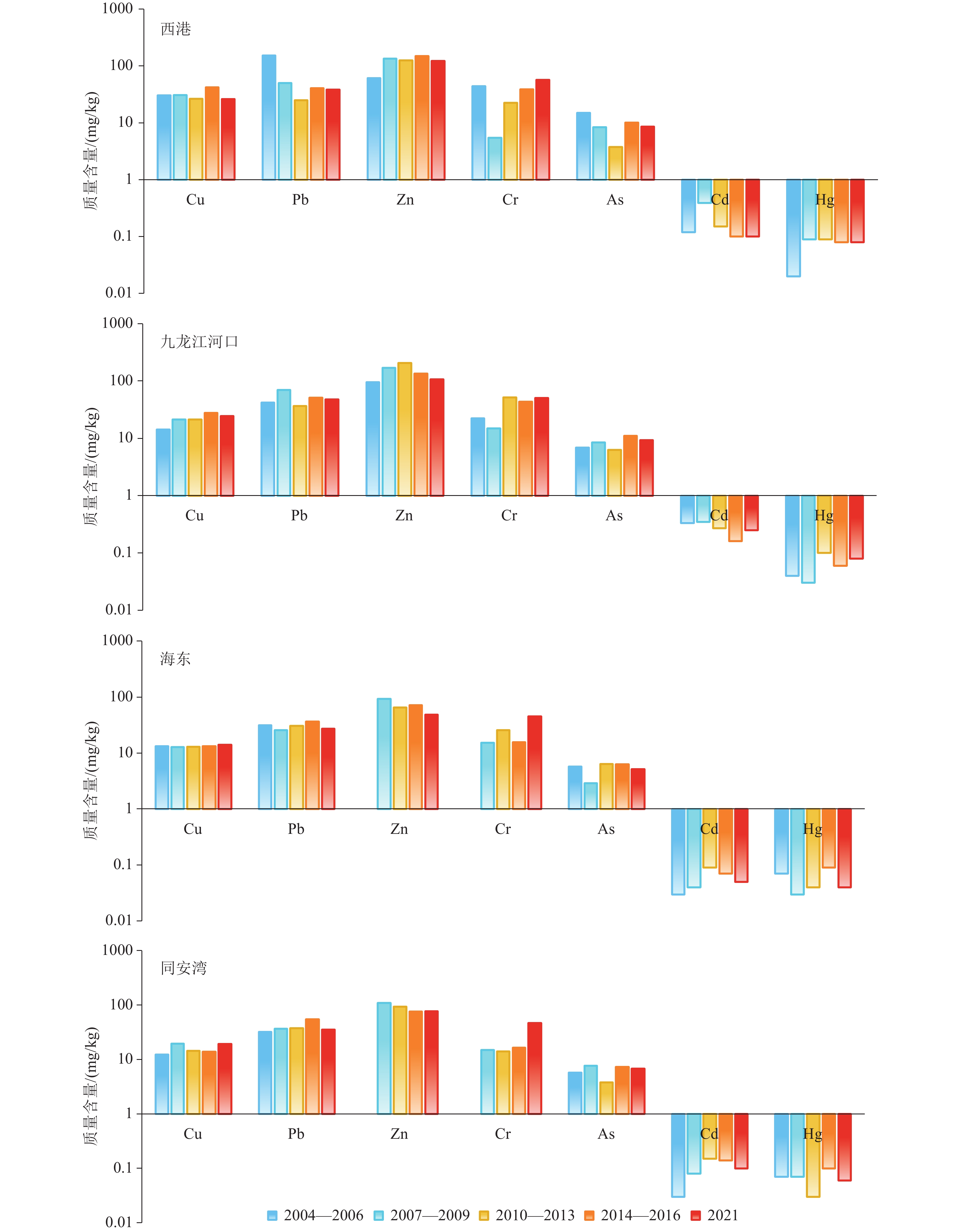
研究结果 厦门湾西港区重金属Cu(26.37 mg/kg)、Zn(122.58 mg/kg)、Cr(57.25 mg/kg)含量最高,九龙江口区Pb(48.03 mg/kg)、Cd(0.25 mg/kg)、Hg(0.085 mg/kg)、As(9.35 mg/kg)含量最高;西港Cu超一类标准率最高,达到25%;九龙江Zn超一类标准率次之,为20.69%。厦门湾重金属富集系数为Cu(1.01)> Cr(0.99)>Cd(0.70)>Zn(0.64)>Pb(0.63)>As(0.48)>Hg(0.33)。Cu表现为轻度富集,Cr与本底值接近。
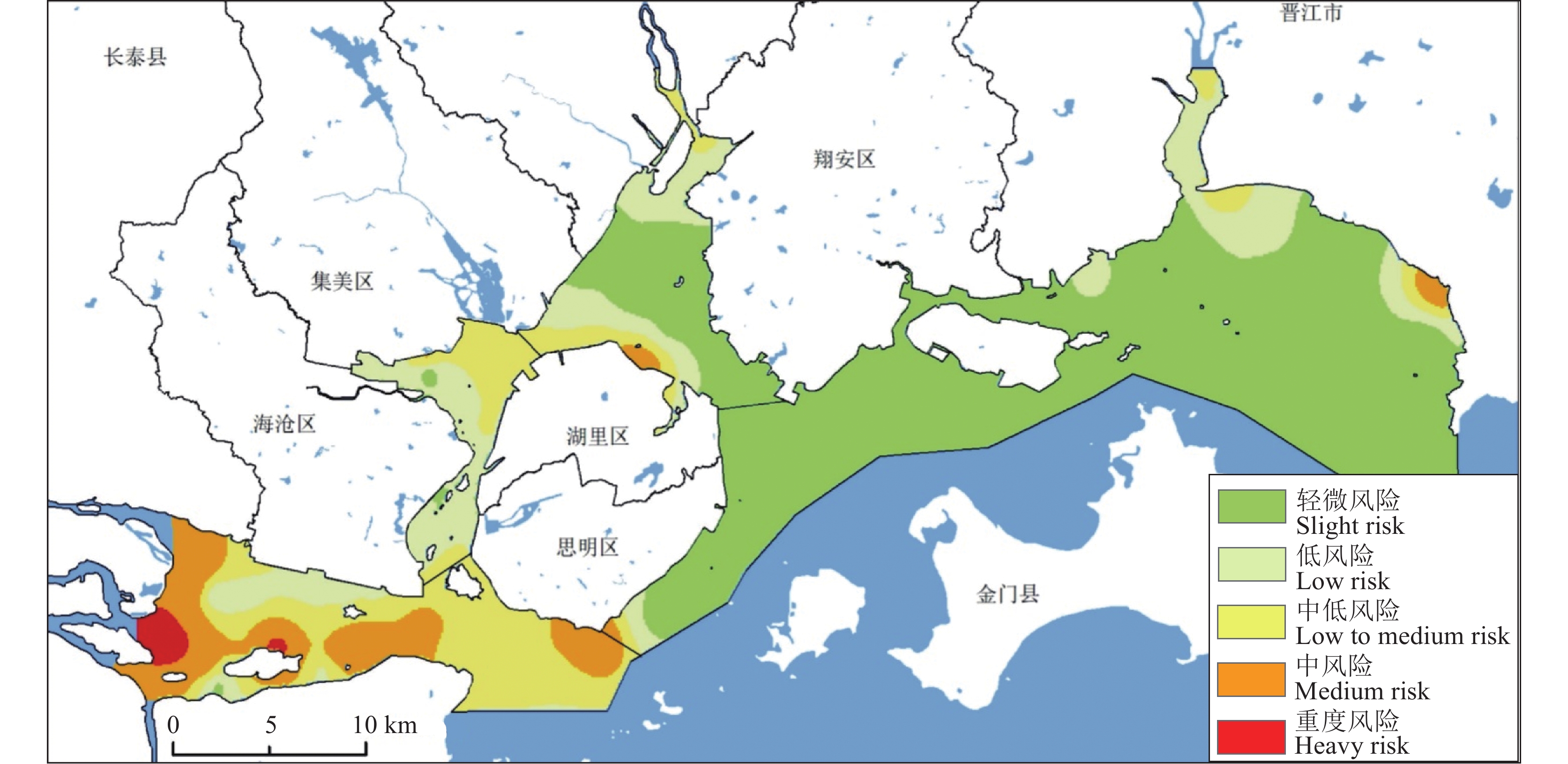
结论 厦门湾重金属的潜在来源中矿山冶炼贡献率为36.16%、天然母岩风化22.03%、农业与生活污水排放21.98%以及化石燃料燃烧19.83%;Cu、Zn、Cd、Cr主要来源矿山冶炼,As来源分别为燃料燃烧贡献率为85.76%和农业面源污染14.16%。Pb和Hg主要受母岩风化所控制。沉积物重金属潜在生态风险中、重度风险区主要集中在九龙江河口及厦门港附近。
Abstract:This paper is the result of marine geological survey engineering.
Objective The heavy metal contents in the Xiamen Bay have been greatly changed due to the ecological management in the bay and the port construction in Xiamen City. Identifying the distributions, evolution, and sources of heavy metals in the bay is significant for the prevention and control of heavy metal pollution, as well as ecological risk management.
Methods This study determined the contents of seven heavy metals in 87 surface samples from bottom sediments in the Xiamen Bay and the Jiulong River estuary, investigated the distributions and the degrees of enrichment of these heavy metals, and quantitatively analyzed the primary sources of these heavy metals using factor analysis and principal component analysis.
Results The western Xiamen Bay displays the highest average mass contents of heavy metals Cu (26.37 mg/kg), Zn (122.58 mg/kg), and Cr (57.25 mg/kg). In contrast, the Jiulong River estuary exhibits the highest contents of Pb (48.03 mg/kg), Cd (0.25 mg/kg), Hg (0.085 mg/kg), and As (9.35 mg/kg). Cu in the western Xiamen Bay exhibits the highest over−limit ratio of up to 25%, followed by Zn (20.69%) in the Jiulong River. In the Xiamen Bay, the enrichment coefficients of heavy metals decrease in the order of Cu (1.01), Cr (0.99), Cd (0.70), Zn (0.64), Pb (0.63), As (0.48), Hg (0.33), indicating that Cu is moderately enriched, Cr approximate to their background values, and Hg is severely enriched.
Conclusions The potential sources of the seven heavy metals in the Xiamen Bay include mine smelting, the weathering of natural parent rocks, the discharge of agricultural and domestic sewage, and fossil fuel combustion, which account for 36.16%, 22.03%, 21.98%, and 19.83%, respectively. Among these heavy metals, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Cr originate primarily from mine smelting, As from fuel combustion (85.76%) and agricultural non−point source pollution (14.16%), and Pb and Hg principally from the weathering of parent rocks. Zones with moderate and high ecological risks induced by heavy metals in sediments are concentrated in the Jiulong River estuary and the Xiamen Harbor.
-

-
表 1 厦门海域沉积物重金属含量背景值
Table 1. Background value of heavy metals in sediments of the Xiamen Sea Area
海域 Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr Hg As 西港 21.48 118.81 41.8 0.066 63.5 0.15 12.3 九龙江 20.0 125.9 65.6 0.237 38.7 0.15 12.3 海东 12.6 87.1 42.9 0.172 38.7 0.15 12.3 同安 15.1 91.6 45.0 0.197 38.7 0.15 12.3 注:单位为mg/kg。 表 2 厦门湾表层沉积物重金属含量
Table 2. Contents of heavy metals in the surface sediments in the Xiamen Bay
区域 项目 Cu Pb Zn Cd Cr Hg As 一类标准值/(mg/kg) 35.0 60.0 150.0 0.50 80.0 0.20 20.0 西港 含量范围/(mg/kg) 6.0~52.8 18~49 42~298 BDL~0.26 12~99 0.007~0.131 3.94~11.2 平均值/(mg/kg) 26.37 38.58 122.58 0.10 57.25 0.08 8.61 变异系数/% 47.50 22.10 51.60 83.60 39.20 39.90 23.30 超一类标准率/% 25.00 0.00 16.67 0.00 8.33 0.00 0.00 九龙江 含量范围/(mg/kg) 4.6~40.4 22~74 39~180 BDL~0.73 12~81 0.013~0.164 3.33~12.9 平均值/(mg/kg) 24.45 48.03 107.41 0.25 50.76 0.085 9.35 变异系数/% 36.80 26.20 39.50 71.50 33.20 37.80 27.70 超一类标准率/% 10.34 10.34 20.69 10.34 3.45 0.00 0.00 海东 含量范围/(mg/kg) BDL~65.4 BDL ~47 BDL~203 BDL~0.21 BDL~202 BDL~0.235 0.48~9.58 平均值/(mg/kg) 14.15 27.36 48.32 0.05 45.18 0.043 5.15 变异系数/% 96.40 42.70 91.30 149.50 92.90 107.300 41.80 超一类标准率/% 3.57 0.00 7.14 0.00 7.14 3.57 0.00 同安湾 含量范围/(mg/kg) 1.4~67.5 13~52 14~144 BDL~0.68 4~70 BDL~0.123 3.63~9.03 平均值/(mg/kg) 19.44 35.61 77.28 0.10 46.89 0.058 6.76 变异系数/% 81.10 30.60 43.30 174.40 35.30 50.200 21.50 超一类标准率/% 11.11 0.00 0.00 5.56 0.00 0.00 0.00 厦门湾合计 含量范围/(mg/kg) BDL~67.5 BDL~74 BDL~298 BDL~0.73 BDL~202 BDL~0.235 0.48~12.90 平均值/(mg/kg) 20.36 37.51 84.25 0.13 49.06 0.065 7.36 变异系数/% 65.40 37.60 62.20 122.20 57.00 62.000 37.90 超一类标准率/% 10.34 3.45 12.64 4.6 4.6 1.15 0 表 3 厦门湾近岸海域元素含量及粒度参数相关性分析
Table 3. Correlation analysis of element content and particle size parameters in the offshore marine areas of the Xiamen Bay
平均粒径 Cu Pb Zn Cd Cr Hg As Al2O3 Fe2O3 平均粒径 1.00 Cu 0.18 1.00 Pb 0.26* 0.70** 1.00 Zn 0.13 0.86** 0.71** 1.00 Cd 0.02 0.68** 0.68** 0.66** 1.00 Cr 0.25* 0.72** 0.50** 0.60** 0.34** 1.00 Hg 0.23* 0.71** 0.63** 0.70** 0.56** 0.48** 1.00 As 0.24* 0.62** 0.67** 0.71** 0.61** 0.42** 0.68** 1.00 Al2O3 0.57** 0.41** 0.53** 0.48** 0.34** 0.36** 0.54** 0.61** 1.00 Fe2O3 0.60** 0.45** 0.51** 0.46** 0.32** 0.38** 0.57** 0.63** 0.89** 1.00 注:*表明相关性在P<0.05水平下显著,**表明相关性在P<0.01水平下显著。Al2O3和Fe2O3的单位为%,其余元素含量的单位为mg/kg,平均粒径的单位为Φ。 表 4 不同来源贡献率PMF模型解析结果
Table 4. Contribution of different potential sources calculated by PMF model
元素 因子贡献/% 矿山冶炼 母岩风化 农业与污水 化石燃料 Cr 65.08 18.89 1.43 14.61 Ni 32.30 27.30 28.90 11.50 Zn 46.76 0.00 53.24 0.00 As 0.00 0.09 14.16 85.76 Pb 21.84 50.18 14.59 13.39 Cu 49.14 7.28 24.80 18.78 Cd 74.22 11.17 0.00 14.61 Hg 0.00 61.31 38.69 0.00 综合贡献率/% 36.17 22.03 21.98 19.83 表 5 各重金属背景值和毒性系数
Table 5. Background contents and toxicity index of heavy metals
指标值 Zn Pb Ni Hg Cu Cr Cd As Al 福建海岸带土壤
背景值/( mg/kg )83.6 39 17.4 0.063 22.4 40.7 0.06 6.38 9.79 重金属毒性系数 1 5 5 40 5 2 30 10 / 背景值(地壳)/( mg/kg ) 63 18 21 0.009 17 44 0.075 2.8 7.49 -
[1] Cao Shengwei, Liu Chunlei, Li Yasong, Li Jing, Hao Qichen, Gao Jie, Dong Yan, Lu Chenming. 2022. Sources and ecological risk of heavy metals in the sediments of offshore area in Quanzhou Bay, Fujian Province[J]. Geology in China, 49(5): 1481−1496 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[2] Chen H Z, Wang J G, Chen J M, Lin H, Lin C. 2016. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the surface sediments: A reexamination into the offshore environment in China[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 113(1/2): 132−140. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.08.079
[3] Chen Jian. 2016. General Report on Comprehensive Survey and Evaluation of Offshore Marine in Fujian Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press (in Chinese).
[4] Chen Song, Liao Wenzhuo, Xu Aiyu, Luo Bingkun. 1992. Chemical characteristics of surface sediment in West Xiamen Harbour[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 11(2): 131−137 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[5] Chen Song, Xu Aiyu, Luo Bingkun. 1987. Distribution and sources of heavy metals in sediments from the Xiamen harbour[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 6(2): 139−145 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[6] Dong Weifeng, Zhang Yu, Dai Guixiang, Su Rong, Yuan Chunwei, Liu Zhiyong. 2018. Spatial and temporal distribution and integrated ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in the surface sediments from Xiamen Sea Area over past 40 years[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 36(3): 89−95 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[7] Fu S F, Wu H Y, Chen H Z, Cai X Q, Pan Xi, Wu Y B. 2022. Spatiotemporal variation of surface sediment quality in the Xiamen Sea Area, China[J]. Journal of Environmental and Public Health, (12): 1−8.
[8] Hai Reti, Xie Tao, Qi Fengxia. 2006. Characteristics of distribution of heavy metals and mineral matter in sediments of Bohai Bay in Tianjin’s sea area[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 29(6): 6−8,42,115 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[9] Han Lu, Yu Ruilian, Hu Gongren, Yang Qiuli, He Haixing. 2017. Speciation and pollution assessment of heavy metals in the core sediment of Western Xiamen Bay[J]. Earth and Environment, 45(3): 342−347 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[10] He Haixing, Yu Ruilian, Hu Gongren, Yu Weihe, Zhou Chufan. 2014. Pollution history and source of heavy metals in coastal sediments from Xiamen Western Bay[J]. China Environmental Science, 34(4): 1045−1051 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[11] He Haixing. 2014. Pollution of Heavy Metals and Pb−Sr Isotopic Implication in the Offshore Sediments from Xiamen Western Bay[D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University (in Chinese with English abstract).
[12] Hong Liyu, Chen Weiqi, Hong Huasheng, Xu Li, Wang Xinhong. 2000. Concentrations and distributions of Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd in surface sediments from Xiamen Jinmen sea area[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 19(4): 441−445 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[13] Jin Yang, Jiang Yuehua, Zhou Quanping, Wang Xiaolong, Zhang Hong, Mei Shijia, Chen Zi, Yang Hai, Lü Jinsong, Hou Lili, Qi Qiuju, Jia Zhengyang, Yang Hui. 2024. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of sedimentary heavy metals from the Lower Mainstream of Yangtze River[J]. Geology in China, 51(1): 276−289 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[14] Li Guihai, Cao Zhimin, Lan Dongzhao, Xu Jiang, Guan Wei. 2008. Variation of depositional environment and accumulation of heavy metals in West Harbour, Xiamen[J]. Earth Science, 33(1): 124−130 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[15] Li Guihai. 2007. Environmental Geochemistry of Heavy Metals and Depositional Environment in Xiamen Seas[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China (in Chinese with English abstract).
[16] Li Guihai, Lan Dongzhao, Cao Zhimin, Xu Jiang, Wang Shanshan, Lan Binbin. 2007. Specificity and potential ecological risks of heavy metals in the sediments of the Xiamen Sea Area[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 26(1): 67−72 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] Li Qingsheng, Wang Cui, Jiang Jinlong, Huang Jinliang, Wu Yaojian. 2020. Pollution characteristics and source apportionment of heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Jiulong River Estuary[J]. Marine Sciences, 44(12): 32−43 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[18] Liao Wenzhuo, Pan Jiezai, Chen Song. 1983. The distribution and behaviour of Cd, Cu, Pb, in the surface sediments of the Jiulong river mouth and Xiamen harbour[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2(1): 47−53 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[19] Lin Cai, Lin Hui, Chen Jinmin, Chen Weifen, Lin Libin, Ji Weidong. 2011. Pollution assessment of heavy metals in the sediment of Jiulong River Estuary[J]. Marine Sciences, 35(8): 11−17 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[20] Lin Chengqi, Hu Gongren, Yu Ruilian. 2015. Lead pollution and isotopic tracing in intertidal sediments of Jiulong River downstream[J]. China Environmental Science, 35(8): 2503−2510 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[21] Liu Qiongyu, Hong Huasheng, Hong Liyu. 1995. Distribution features and sources of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd in Xiamen western sea sediments[J]. Marine Science Bulleten, 14(6): 46−52 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[22] Liu Shengran, Wang Tieyu, Yang Jie, Meng Jing, He Bo, Zhao Hui, Xiao Rongbo. 2019. Source apportionment methods of soil heavy metals in typical urban units: An empirical study[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 39(4): 1278−1289 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[23] Liu W X, Li X D, Shen Z G, Wang D C, Wai O W H, Li Y S. 2003. Multivariate statistical study of heavy metal enrichment in sediments of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Environmental Pollution, 121(3): 377−388. doi: 10.1016/S0269-7491(02)00234-8
[24] Liu Xiangqi, Song Lei, Wu Qilong, Li Guomin, Mao Xin. 2020. Application of the affinity propagation clustering algorithm based on grain−size distribution curve to discrimination of sedimentary environment—A case study in Baiyangdian area[J]. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 40(1): 198−209 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] Liu Yongqing. 1995. Study and application of the soil environmental background values in Fujian coastal zone[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 14(2): 68−73.
[26] Lü Ronghui. 1987. Study on heavy metal pollution status in Xiamen Port waters−(Ⅱ) Research on water quality, sediment and distribution characteristics of organisms in Xiamen Port waters[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 6(3): 1−8 (in Chinese).
[27] Ma R, Zhang B, Zhou X N. 2020. The effects of climate change and groundwater exploitation on the spatial and temporal variations of heavy metal content in maize in the Luan River catchment of China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 42(2): 1035−1052.
[28] Mao Xin, Liu Linjing, Song Lei, Jiang Gaolei, Li Junfeng, Li Changan. 2021. A 70 year sedimentary record of eco−environment changes in Baiyangdian Lake and its influencing factors[J]. Earth Science, 46(7): 2609−2620 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[29] Miao X Y, Hao Y P, Zhang F W, Zou S Z, Ye S Y, Xie Z Q. 2020. Correction to: Spatial distribution of heavy metals and their potential sources in the soil of Yellow River Delta: A traditional oil field in China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 42(2): 7−26.
[30] Nishijima W, Umehara A, Okuda T, Nakai S. 2015. Variations in macrobenthic community structures in relationto environmental variables in the Seto Inland Sea, Japan[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 92(1−2): 90−98. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2014.12.051
[31] Niu Hongyi, Wu Qunhe, Chen Xingeng. 2006. Distribution characteristics and correlations of heavy metals in the surface sediments in Guangzhou section of the Pearl River[J]. Ecology and Environment, 15(5): 954−959 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[32] Paatero P. 1997. Least squares formulation of robust non−negative factor analysis[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 37(1): 23−35. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(96)00044-5
[33] Peng Bo, Wang Jilong, Tong Meng, Wu Bin, Liu Xiaoqiang, Niu Shujie, Lin Mudong, Zhang Huua, Li Maotian, Yu Junjie. 2021. Heavy metal deposition and its impact on ecological environment in Sanduao Bay of Fujian Province during the past century under the influence of human activities[J]. Geology in China, 48(6): 1759−1769 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[34] Shen Chenyu, Yan Yu, Yu Reilian, Hu Gongren, Cui Jianyong, Yan Yan, Huang Huanbin. 2022. APCS−MLR combined with PMF Model to analyze the source of metals in sediment of Xinglin Bay suburban watershed, Xiamen[J]. Environmental Science, 43(5): 2476−2488 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[35] Sheng Dan. 2012. Chronology and Geochemistry of Intermediate Dikes, Host Granitoids and Enclaves in the Xiamen−−Zhangzhou Area[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English abstract).
[36] Soto−Jiménez M, Páez−Osuna F. 2001. Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn in lagoonal sediments from Mazatlán Harbor (SE Gulf of California): Bioavailability and geochemical fractioning[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 66(3): 350−356.
[37] Tu Chunlin, Yang Kun, He Chengzhong, Zhang Liankai, Li Bo, Wei Zong, Jiang Xin, Yang Minghua. 2023. Sources and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of small watersheds in typical coal mining areas of Eastern Yunnan[J]. Geology in China, 50(1): 206−221 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[38] Tang H J, Ke Z X, Yan M T, Wang W J, Nie H Y, Li B X, Zhang J P, Xu X R, Wang J. 2018. Concentrations, distribution, and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Daya Bay, China[J]. Water, 10(6): 780. doi: 10.3390/w10060780
[39] Wan Rui'an, Han Lu, Yu Ruilian, Hu Gongren, Cui Jianyong, Yan Yan, Huang Huanbin. 2019. Determination of background values of heavy metals in coastal sediment of the Western Bay, Xiamen[J]. Earth and Environment, 47(3): 352−360 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[40] Wang Weili, Geng Anchao, Liu Huatai, Gao Aiguo. 2013. Distribution and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the surface sediments from the Jiulongjiang River Estuary[J]. Advances in Marine Science, 27(4): 502−508 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[41] Wang Xin, Qiao Shuqing, Gao Jingjing, Zhu Aimei, Bu Wenrui, Guo Jingtian. 2013. Distribution patterns of heavy metals in surface sediments and environmental quality assessment on the adjacent sea area of Xiaomai Island[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 32(3): 287−295 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[42] Xia P, Meng X W Yin P, Cao Z M, Wang X Q. 2010. Eighty−year sedimentary record of heavy metal inputs in the intertidal sediments from the Nanliu River estuary, Beibu Gulf of South China Sea[J]. Environmental Pollution, 159(1): 92−99.
[43] Xu Q H, Ma W T, Chen W F. 1985. Application of factor analysis method in the study of sediment pollution in Xiamen Port[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 7(3): 306−312.
[44] Yu Ruilian, Yu Hewei, Hu Gongren, He Haixing, Lin Chengqi. 2013. Speciation and potential ecological risk of heavy metals in the surface sediments from upstream of Jiulong river estuary[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 32(12): 2321−2328 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[45] Zhang Haijun, Shi Benning, Jiao Xueyao, Wu Hailun, Zhou Lin, Shen Xiaoxue, Li Ruili. 2021. Spatial distribution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in Shenzhen coastal areas[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 57(4): 679−690 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[46] Zhang Shisan, Huang Yankuan, Zeng Xianshi. 1984. Content distribution of heavy metal elements in Jiulongjiang estuary sediments at different grain levels[J]. Environmental Science, 5(3): 31−35 (in Chinese with English abstract).
[47] 曹胜伟, 刘春雷, 李亚松, 李静, 郝奇琛, 高洁, 董岩, 陆晨明. 2022. 福建泉州湾近岸海域沉积物重金属来源分析与生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 49(5): 1481−1496. doi: 10.12029/gc20220508
[48] 陈坚. 2016. 福建省近海海洋综合调查与评价总报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
[49] 陈松, 廖文卓, 许爱玉, 骆炳坤. 1992. 厦门西港表层沉积物的化学特征[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 11(2): 131−137.
[50] 陈松, 许爱玉, 骆炳坤. 1987. 厦门港湾表层沉积物中重金属的富集和来源探讨[J]. 应用海洋学报, 6(2): 139−145.
[51] 董炜峰, 张瑜, 戴桂香, 苏荣, 袁春伟, 刘志勇. 2018. 近40a厦门海域表层沉积物重金属时空分布及综合生态风险评价[J]. 海洋学研究, 36(3): 89−95. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-909X.2018.03.010
[52] 海热提, 谢涛, 齐凤霞. 2006. 天津海域底质重金属分布与矿物质特征研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 29(6): 6−8, 42,115. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2006.06.003
[53] 韩璐, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 杨秋丽, 何海星. 2017. 厦门西港潮间带柱状沉积物重金属赋存形态与污染评价[J]. 地球与环境, 45(3): 342−347.
[54] 何海星. 2014. 厦门西港近岸海域沉积物重金属污染及铅锶同位素示踪研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学.
[55] 何海星, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 余伟河, 周楚凡. 2014. 厦门西港近岸沉积物重金属污染历史及源解析[J]. 中国环境科学, 34(4): 1045−1051.
[56] 洪丽玉, 陈伟琪, 洪华生, 徐立, 王新红. 2000. 厦门−金门海域表层沉积物中重金属铜铅锌镉的含量分布[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 19(4): 441−445. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2000.04.007
[57] 金阳, 姜月华, 周权平, 王晓龙, 张鸿, 梅世嘉, 陈孜, 杨海, 吕劲松, 侯莉莉, 齐秋菊, 贾正阳, 杨辉. 2024. 长江下游干流沉积物重金属特征及生态风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 51(1): 276−289.
[58] 李桂海. 2007. 厦门海域现代沉积环境及重金属元素的环境地球化学研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学.
[59] 李桂海, 曹志敏, 蓝东兆, 许江, 关伟. 2008. 厦门西港沉积环境变化及重金属的污染累积[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 33(1): 124−130.
[60] 李桂海, 蓝东兆, 曹志敏, 许江, 王珊珊, 蓝彬斌. 2007. 厦门海域沉积物中的重金属及其潜在生态风险[J]. 海洋通报, 26(1): 67−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.01.011
[61] 李青生, 王翠, 蒋金龙, 黄金良, 吴耀建. 2020. 九龙江口表层沉积物重金属的污染特征与来源分析[J]. 海洋科学, 44(12): 32−43.
[62] 廖文卓, 潘皆再, 陈松. 1983. 九龙江口厦门港沉积物中镉、铜、铅的分布和行为[J]. 应用海洋学学报, 2(1): 47−53.
[63] 林彩, 林辉, 陈金民, 陈维芬, 林力斌, 暨卫东. 2011. 九龙江河口沉积物重金属污染评价[J]. 海洋科学, 35(8): 11−17.
[64] 林承奇, 胡恭任, 于瑞莲. 2015. 福建九龙江下游潮间带沉积物铅污染及同位素示踪[J]. 中国环境科学, 35(8): 2503−2510. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.08.031
[65] 刘琼玉, 洪华生, 洪丽玉. 1995. 厦门西海域表层沉积物重金属的分布特征及来源探讨[J]. 海洋通报, 14(6): 46−52.
[66] 刘胜然, 王铁宇, 汤洁, 孟晶, 何博, 赵慧, 肖荣波. 2019. 典型城市单元的土壤重金属溯源方法与实证研究[J]. 生态学报, 39(4): 1278−1289.
[67] 刘祥奇, 宋磊, 吴奇龙, 李国民, 毛欣. 2020. 基于粒度分布曲线的邻近传播聚类算法在沉积环境识别中的应用—以白洋淀地区为例[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 40(1): 198−209.
[68] 刘用清. 1995. 福建省海岸带土壤环境背景值研究及其应用[J]. 海洋环境科学, 14(2): 68−73.
[69] 吕荣辉. 1987. 厦门港海域重金属污染状况研究—(Ⅱ)在厦门港海域水质、底质及生物体中分布特征的研究[J]. 海洋环境科学, 6(3): 1−8.
[70] 毛欣, 刘林敬, 宋磊, 姜高磊, 李峻峰, 李长安. 2021. 白洋淀近70年生态环境演化过程及影响因素[J]. 地球科学, 46(7): 2609−2620.
[71] 牛红义, 吴群河, 陈新庚. 2006. 珠江(广州河段)表层沉积物中重金属的分布特征及相关性研究[J]. 生态环境, 15(5): 954−959.
[72] 彭博, 王继龙, 同萌, 武彬, 刘晓强, 牛淑杰, 林沐东, 张华, 李茂田,于俊杰. 2021. 人类活动影响下福建三都澳近百年来重金属沉积记录及其对生态环境的影响[J]. 中国地质, 48(6): 1759−1769. doi: 10.12029/gc20210608
[73] 沈宸宇, 闫钰, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 崔建勇, 颜妍, 黄华斌. 2022. APCS−MLR结合PMF模型解析厦门杏林湾近郊流域沉积物金属来源[J]. 环境科学, 43(5): 2476−2488.
[74] 盛丹. 2012. 厦门—漳州地区白垩纪中性岩脉群、花岗岩类及其包体的年代学和地球化学[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京).
[75] 涂春霖, 杨坤, 和成忠, 张连凯, 李博, 魏总, 姜昕, 杨明花. 2023. 滇东典型煤矿区小流域沉积物重金属来源及风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 50(1): 206−221.
[76] 万瑞安, 韩璐, 于瑞莲, 胡恭任, 崔建勇, 颜研, 黄华斌. 2019. 厦门西港近岸沉积物中重金属元素背景值的确定[J]. 地球与环境, 47(3): 352−360.
[77] 王伟力, 耿安朝, 刘花台, 高爱国. 2013. 九龙江口表层沉积物重金属分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 海洋科学进展, 27(4): 502−508.
[78] 王昕, 乔淑卿, 高晶晶, 朱爱美, 卜文瑞, 郭敬天. 2013. 小麦岛附近海域表层沉积物重金属分布特征及环境评价[J]. 海洋通报, 32(3): 287−295.
[79] 于瑞莲, 余伟河, 胡恭任, 何海星, 林承奇. 2013. 九龙江河口上游表层沉积物中重金属赋存形态及生态风险[J]. 环境化学, 32(12): 2321−2328. doi: 10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.12.015
[80] 张海军, 史本宁, 焦学尧, 吴海轮, 周琳, 沈小雪, 李瑞利. 2021. 深圳近海环境重金属空间分布特征与风险评价[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 57(4): 679−690.
[81] 张士三, 黄衍宽, 曾石羡石. 1984. 九龙江口沉积物中重金属元素在不同粒级中的含量分配[J]. 环境科学, 5(3): 31−35.
-



 下载:
下载: