Research on the genetic model and exploration progress of hot dry rock resources on the southeast coast of China
-
摘要:
干热岩是一种重要的地热资源,绝大部分以开采地壳中生代以来中酸性侵入岩体中所蕴含的热量为主。东南沿海地区是中国最主要的高放射性花岗岩分布区,发育大面积的中生代酸性花岗岩体,是寻找干热岩的良好靶区。通过研究东南沿海大地构造背景、区域大地热流分布、地壳厚度、居里面埋深及新构造等条件,分析了东南沿海干热岩资源的赋存背景,对福建地区是否存在干热岩进行了探讨,并通过控热构造分析提出了东南沿海干热岩资源的成因模式,初步建立了东南沿海干热岩成藏的三元聚热模型,总结了漳州、惠州等地区的干热岩资源靶区勘查进展,相关研究为今后中国东南沿海地区干热岩勘查评价提供了基础。
Abstract:Hot dry rock (HDR) is an important geothermal resource, whose exploitation mostly centers on the heat contained in the intermediate-acid intrusive rock mass of the crust since the Mesozoic. The southeast coast is the main distribution area of highly radioactive granites in China, with a large area of developed Mesozoic acid granite intrusions, which makes it a target area for HDR prospecting. By studying the tectonic background of the southeast coast, regional terrestrial heat flow distribution, crustal thickness, buried depth of the curie surface and new structures, the occurrence background of HDR resources on the southeast coast and the existence of HDR resources in Fujian were analyzed and discussed. Based on the analysis of the heat-controlling structure, a genetic model of HDR resources on the southeast coast was proposed and a ternary heat accumulation model for HDR accumulation on the southeast coast was preliminary established. The exploration targeting at HDR resources in Zhangzhou, Huizhou, etc. was summarized. The progress and related research provide the basis for future exploration and evaluation of HDR resources on the southeast coast of China.
-
Key words:
- HDR resources /
- southeast coast /
- genetic model /
- exploration progress
-

-
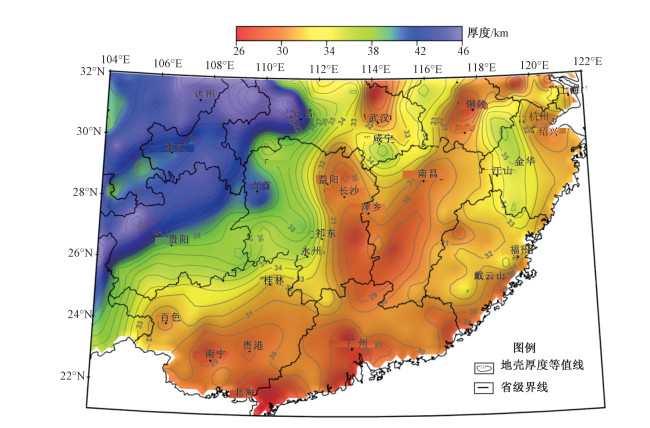
图 1 东南沿海部分地区地壳厚度图(Guo et al., 2019)
Figure 1.
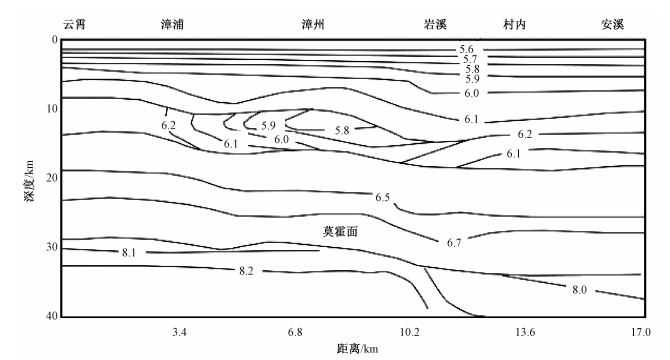
图 2 YCA测线P波波速等值线剖面图(熊绍柏等,1991)
Figure 2.
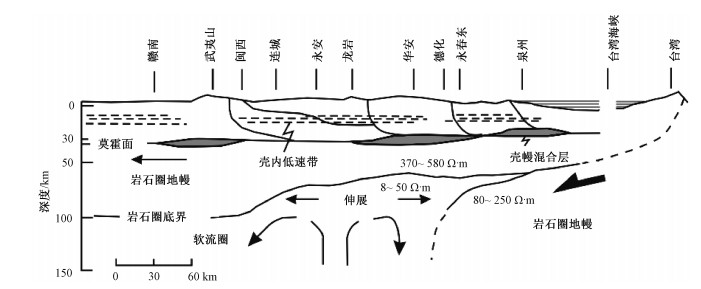
图 3 江西南部—福建—台湾综合地球物理剖面图(Zhou and Li, 2000)
Figure 3.
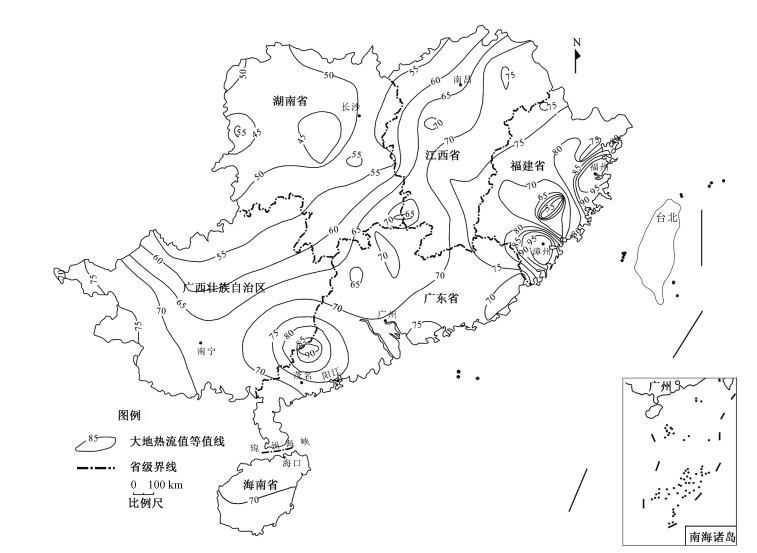
图 4 中国东南沿海地区大地热流值等值线图(蔺文静等,2016)
Figure 4.
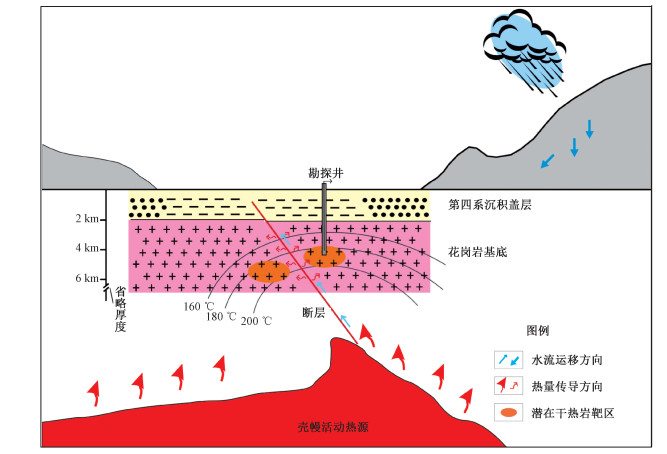
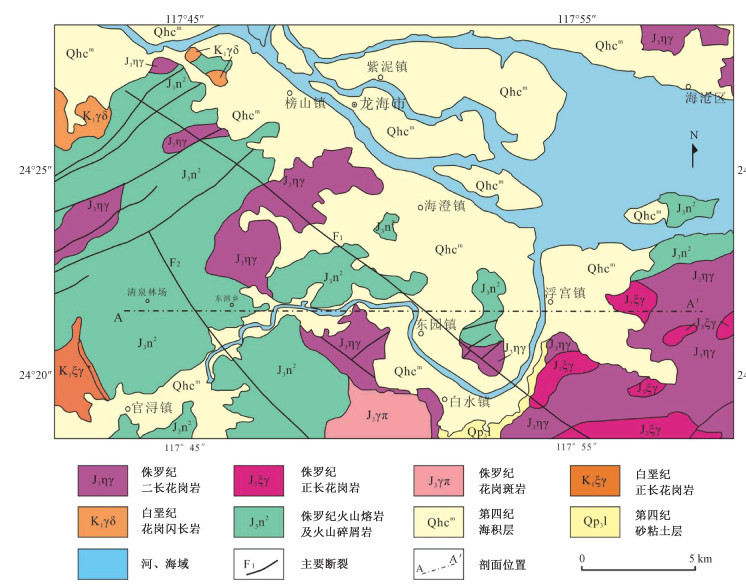
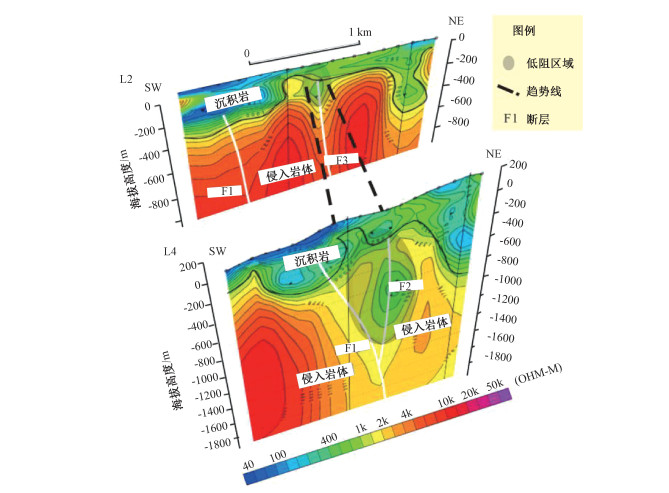
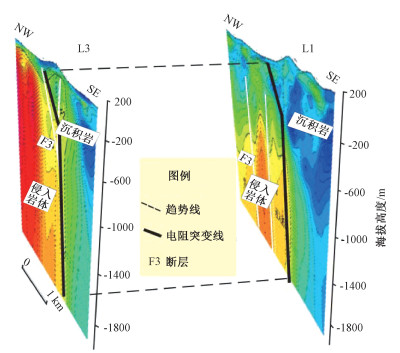
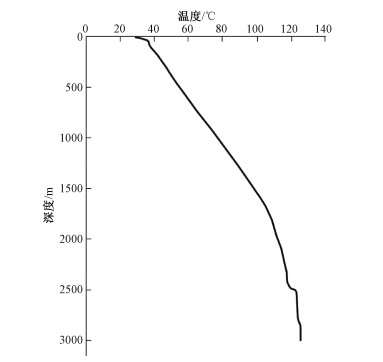
图 6 漳州地区地质简图(A-A′为物探综合剖面)(蔺文静等,2015)
Figure 6.
表 1 东南沿海地区不同岩石类型的单位体积生热率(赵平等,1995;林乐夫等,2017)
Table 1. Heat production per unit volume of different rock types on the southeast coast of China(Zhao et al., 1995; Lin et al., 2017)
岩石类型 平均单位体积生热率/
(μW/m3)不同时代花岗岩 晋宁期花岗岩 3.1 加里东期花岗岩 3.3 印支期花岗岩 3.9 燕山早期花岗岩 5.2 燕山晚期花岗岩 6.4 凝灰岩 2.7 碳酸盐岩 0.59 表 2 模型主要参数表
Table 2. Main parameters of the model
模型部分 孔隙度 渗透率/
m2热导率/
W/(m·K)热储 0.01 1×10-17 3.4 浅部断裂 0.05 1×10-12 5.5 深部断裂 0.02 1×10-17 5.5 -
CHEN P R, HUA R M, ZHANG B T, et al., 2002. Early Yanshanian post-orogenic granitoids in the Nanling region:petrological constraints and geodynamic settings[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 45(8):755-768. http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/BF02878432
GAN H N, WANG G L, LIN W J, et al., 2015. Research on the occurrence types and genetic models of hot dry rock resources in China[J]. Science & Technology Review, 33(19):22-27. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjdb201519006
GAO J, ZHANG H J, ZHANG S Q, et al., 2018. Three-dimensional Magnetotelluric imaging of the geothermal system beneath the Gonghe Basin, northeast Tibetan plateau[J]. Geothermics, 76:15-25. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2018.06.009
GUO L H, GAO R, SHI L, et al., 2019. Crustal thickness and Poisson's ratios of South China revealed from joint inversion of receiver function and gravity data[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 510:142-152. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2018.12.039
HE Z L, ZHANG Y, FENG J Y, et al., 2020. Classification of geothermal resources based on engineering considerations and HDR EGS site screening in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(1):81-93. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy202001010
LIAO Z J, 2012. Deep-circulation hydrothermal systems without magmatic heat source in Fujian Province[J]. Geoscience, 26(1):85-98. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201201009
LIAO Z J, WAN T F, ZHANG Z G, 2015. The Enhanced Geothermal System(EGS):huge capacity and difficult exploitation[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 22(1):335-344. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201501029
LIN L F, SUN Z X, WANG A D, et al., 2017. Radioactive geochemical characteristics of Mesozoic granites from Nanling region and southeast coastal region and their constraints on lithospheric thermal structure[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 36(4):488-500 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201704004
LIN W J, LIU Z M, MA F, et al., 2012. An estimation of HDR resources in China's mainland[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 33(5):807-811 (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201205018.htm
LIN W J, LIU Z M, WANG W L, et al., 2013. The assessment of geothermal resources potential of China[J]. Geology in China, 40(1):312-321 (in Chinese) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DIZI201301023.htm
LIN W J, WANG F Y, GAN H N, et al., 2015. Site selection and development prospect of a hot dry rock resource project in Zhangzhou geothermal field, Fujian province[J]. Science & Technology Review, 33(19):28-34 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjdb201519007
LIN W J, GAN H N, WANG G L, et al., 2016. Occurrence prospect of HDR and target site selection study in Southeastern of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(8):2043-2058. (in Chinese) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201608031
LIN W J, GAN H N, WANG G L, et al., 2019. Geothermal resources survey of Xiamen-Qiongbei region of southeast China continent[R]. Beijing: China Geological Survey. (in Chinese)
LU C, LIN W J, GAN H N, et al., 2017. Occurrence types and genesis models of hot dry rock resources in China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(19):646 doi: 10.1007/s12665-017-6947-4
LU C, Wang G L, 2015. Current status and prospect of hot dry rock research[J]. Science & Technology Review, 33(19):13-21. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjdb201519005
Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2006. The future of geothermal energy: impact of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) on the United States in the 21st Century[R]. Cambridge: MIT Press.
NIAN W Z, 2008. Formation model of geothermal field and its relation with control structure in Zhangzhou[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 15(4):30-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzktaq200804009
PANG Z H, 1987. Zhangzhou basin geothermal system——Genesis model, energy potential and the occurrence of thermal water[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology and Geophysics, CAS. (in Chinese with English abstract)
TAO J H, LI W X, LI X H, et al., 2013. Petrogenesis of early Yanshanian highly evolved granites in the Longyuanba area, southern Jiangxi Province:Evidence from zircon U-Pb dating, Hf-O isotope and whole-rock geochemistry[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 56(6):922-939. doi: 10.1007/s11430-013-4593-6
TENG J W, SI X, ZHUANG Q X, et al., 2017. Abnormal structure of crust and mantle and analysis of deep thermal potential in Fujian continental margin[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 17(17):6-38. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxjsygc201717002
WAN T F, CHU M J, CHEN M Y, 1988. Thermal regimes of the Lithophere and geothermal resources potential in Fujian Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 62(2):178-189 (in Chinese with English abstract)
WANG G L, LIN W J, ZHANG W, et al., 2016. Research on Formation Mechanisms of Hot Dry Rock Resources in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 90(4):1418-1433. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.12776
WANG G L, MA F, LIN W J, et al., 2015. Reservoir stimulation in hot dry rock resource development[J]. Science & Technology Review, 33(11):103-107. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KJDB201511038.htm
WANG T, GUO L, LI S, et al., 2019. Some important issues in the study of granite tectonics[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5):899-919.(in Chinese with English abstract) http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlxxb201905019
WANG Y J, FAN W M, SUN M, et al., 2007. Geochronological, geochemical and geothermal constraints on petrogenesis of the Indosinian peraluminous granites in the South China Block:a case study in the Hunan Province[J]. Lithos, 96(3-4):475-502. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.11.010
WU F Y, LI X H, YANG J H, et al., 2007. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6):1217-1238. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200706001
XIONG L P, HU S B, 1994. Analysis on the thermal conductivity of rocks from SE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 10(3):323-329 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB199403009.htm
XIONG S B, JIN D M, SUN K Z, et al., 1991. Some characteristics of deep structure of the Zhangzhou geothermal field and it's neighbourhood in the Fujian Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 34(1):55-63. (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199101006.htm
ZHANG S S, ZHANG L, TIAN C C, et al., 2019. Occurrence geological characteristitics and development potential of hot dry rocks in Qinghai Gonghe basin[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(4):501-508. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHAO P, WANG J Y, WANG J A, et al., 1995. Characteristics of heat production distribution in SE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 11(3):292-305 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB199503004.htm
ZHENG H W, GAO R, LI T D, et al., 2013. Collisional tectonics between the Eurasian and Philippine sea plates from tomography evidences in southeast China[J]. Tectonophysics, 606:14-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.03.018
ZHOU X M, LI W X, 2000. Origin of Late Mesozoic igneous rocks in southeastern china:implications for lithosphere Subduction and Underplating of mafic magmas[J]. Tectonophysics, 326(3-4):269-287. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040195100001207/pdf?md5=498f70655f1dbfbb3a2e4e7738d90458&pid=1-s2.0-S0040195100001207-main.pdf&_valck=1
ZHOU X R, CHEN A G, SONG X H, et al., 1988. Research on the genesis and Rb-Sr isotope age of granitic intrusion of Zhangzhou, Fujian, China[J]. Bulletin of Nanjing Institute of Geological Mineral ang Resources (2):58-70. (in Chinese with English abstract)
ZHUANG Q X, 2016. Research on hot dry rock exploration of Fujian Province[J]. Energy and Environment(1):2-5, 19. (in Chinese)
陈培荣, 华仁民, 章邦桐, 等, 2002.南岭燕山早期后造山花岗岩类:岩石学制约和地球动力学背景[J].中国科学(D辑), 32(4):279-289. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgkx-cd200204003
甘浩男, 王贵玲, 蔺文静, 等, 2015.中国干热岩资源主要赋存类型与成因模式[J].科技导报, 33(19):22-27. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.19.002
何治亮, 张英, 冯建赟, 等, 2020.基于工程开发原则的干热岩目标区分类与优选[J].地学前缘, 27(1):81-93. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy202001010
廖志杰, 2012.福建无岩浆热源的深循环水热系统[J].现代地质, 26(1):85-98. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.01.009
廖志杰, 万天丰, 张振国, 2015.增强型地热系统:潜力大、开发难[J].地学前缘, 22(1):335-344. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjdb201232009
林乐夫, 孙占学, 王安东, 等, 2017.南岭地区与东南沿海地区中生代花岗岩放射性地球化学特征及岩石圈热结构对比研究[J].岩石矿物学杂志, 36(4):488-500. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2017.04.004
蔺文静, 刘志明, 马峰, 等, 2012.我国陆区干热岩资源潜力估算[J].地球学报, 33(5):807-811. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201205018
蔺文静, 刘志明, 王婉丽, 等, 2013.中国地热资源及其潜力评估[J].中国地质, 40(1):312-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.01.021
蔺文静, 王凤元, 甘浩男, 等, 2015.福建漳州干热岩资源选址与开发前景分析[J].科技导报, 33(19):28-34. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.19.003
蔺文静, 甘浩男, 王贵玲, 等, 2016.我国东南沿海干热岩赋存前景及与靶区选址研究[J].地质学报, 90(8):2043-2058. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.08.031
蔺文静, 甘浩男, 王贵玲, 等, 2019.东南沿海厦门-琼北地区地热资源调查[R].北京: 中国地质调查局.
陆川, 王贵玲, 2015.干热岩研究现状与展望[J].科技导报, 33(19):13-21. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.19.001
粘为振, 2008.漳州地热田成因模式及其与控制构造的关系研究[J].安全与环境工程, 15(4):30-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1556.2008.04.009
庞忠和, 1987.漳州盆地地热系统-成因模式、热能潜力与热水分布规律的研究[D].北京: 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所.
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis_Y056398.aspx 陶继华, 李武显, 李献华, 等, 2013.赣南龙源坝地区燕山期高分异花岗岩年代学、地球化学及锆石Hf-O同位素研究[J].中国科学:地球科学, 43(5):760-778. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201305006
滕吉文, 司芗, 庄庆祥, 等, 2017.福建陆缘壳幔异常结构与深部热储潜能分析[J].科学技术与工程, 17(17):6-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.17.002
万天丰, 褚明记, 陈明佑, 1988.福建省岩石圈的热状态与地热资源的远景评价[J].地质学报, 62(2):178-189. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE198802007.htm
王贵玲, 马峰, 蔺文静, 等, 2015.干热岩资源开发工程储层激发研究进展[J].科技导报, 33(11):103-107. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2015.11.018
王涛, 郭磊, 李舢, 等, 2019.花岗岩大地构造研究的若干重要问题[J].地质力学学报, 25(5):899-919. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190518&journal_id=dzlxxb
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等, 2007.花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J].岩石学报, 23(6):1217-1238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.06.001
熊亮萍, 胡圣标, 1994.中国东南地区岩石热导率值的分析[J].岩石学报, 10(3):323-329. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1994.03.010
熊绍柏, 金东敏, 孙克忠, 等, 1991.福建漳州地热田及其邻近地区的地壳深部构造特征[J].地球物理学报, 34(1):55-63. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.1991.01.006
张盛生, 张磊, 田成成, 等, 2019.青海共和盆地干热岩赋存地质特征及开发潜力[J].地质力学学报, 25(4):501-508. http://journal.geomech.ac.cn/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?flag=1&file_no=20190407&journal_id=dzlxxb
赵平, 汪集旸, 汪缉安, 等, 1995.中国东南地区岩石生热率分布特征[J].岩石学报, 11(3):292-305. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1995.03.011
周珣若, 陈安国, 宋新华, 等, 1988.福建漳州花岗岩侵入体的Rb-Sr同位素年龄及其成因的初步探讨[J].中国地质科学院南京地质矿产研究所所刊(2):55-67. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000002240686
庄庆祥, 2016.福建省干热岩地热资源勘查研究[J].能源与环境(1):2-5, 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9064.2016.01.001
-



 下载:
下载: