Genesis of Jinqingding gold deposit in eastern Jiaodong Peninsula: constrain from trace elements of sulfide ore and wall-rock
-
摘要:
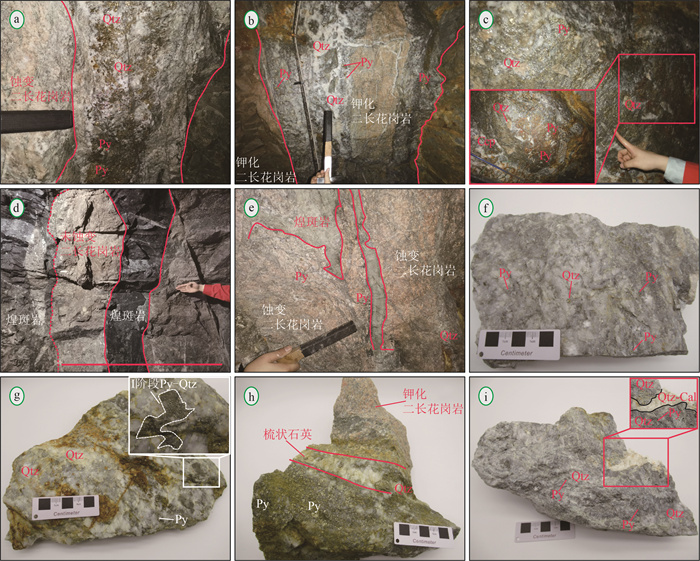
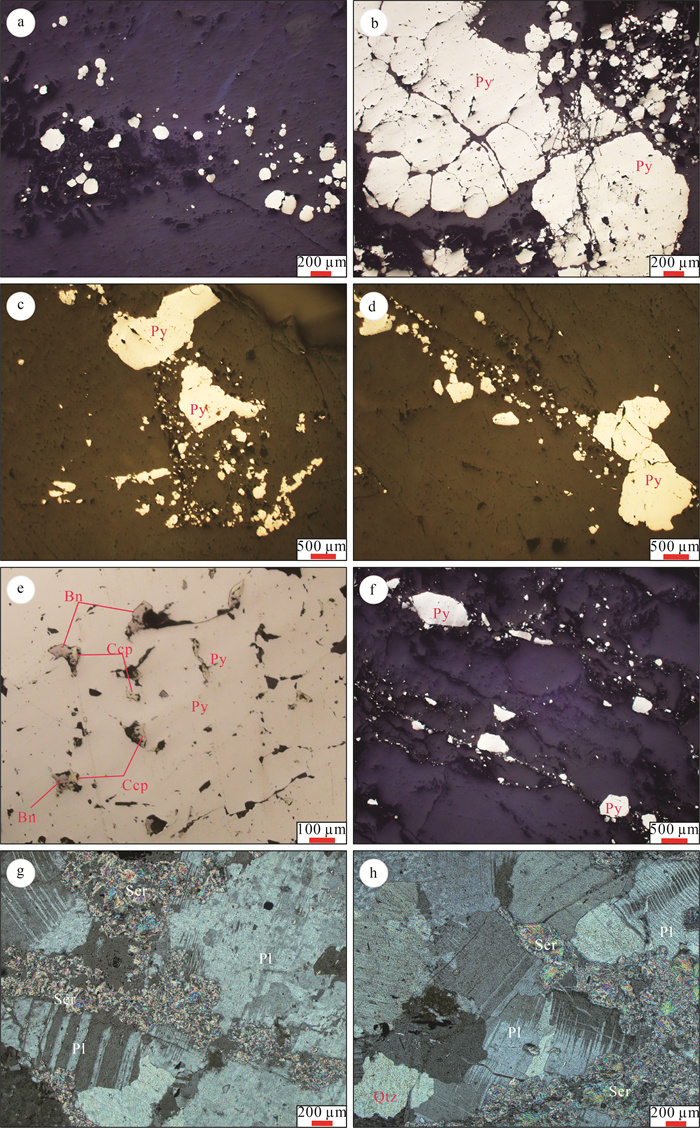
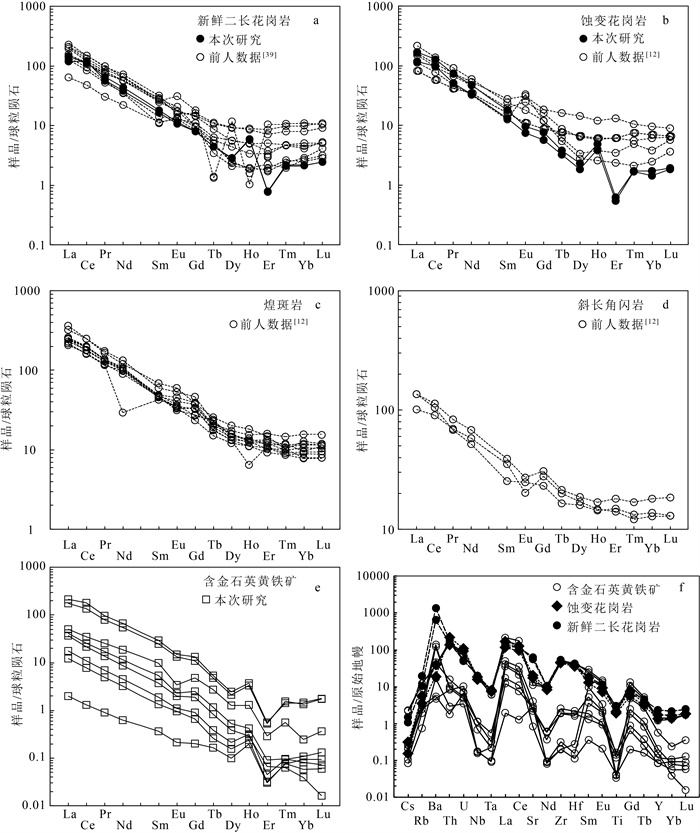
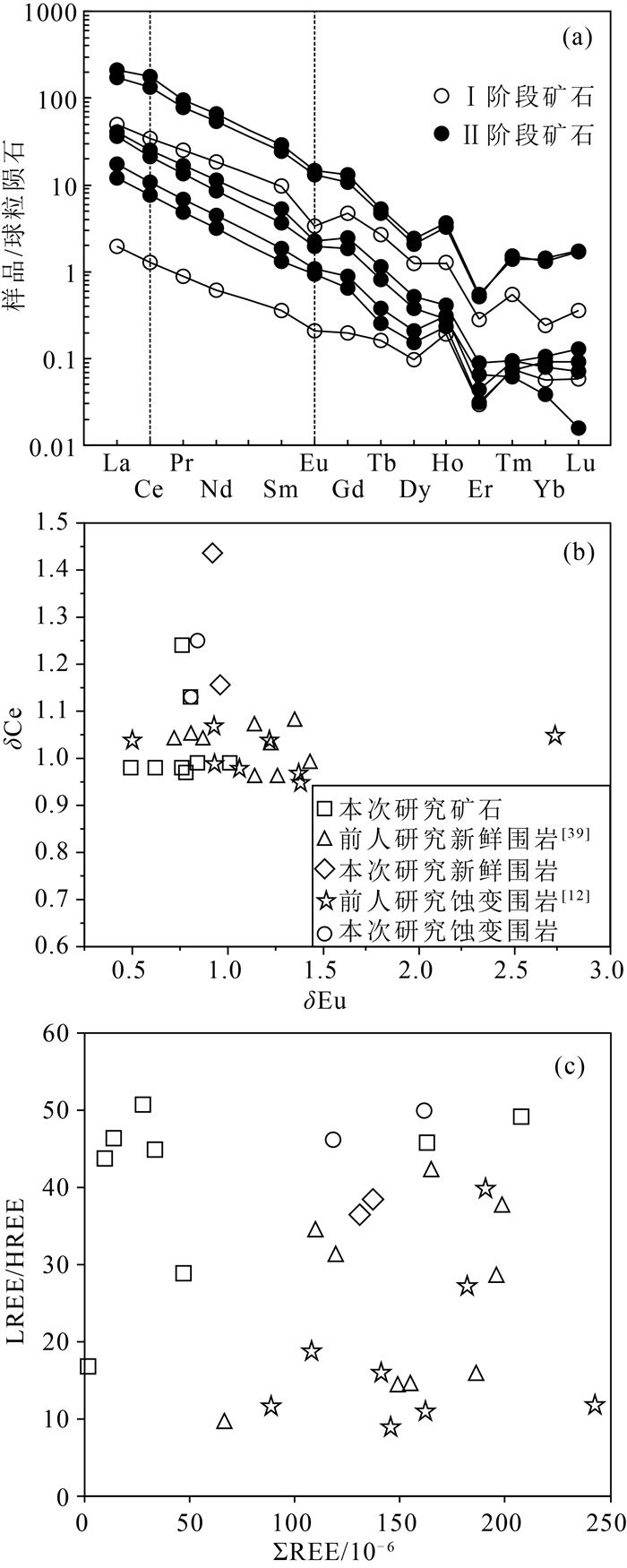
金青顶矿床是胶东东部牟平-乳山成矿带最大的金矿床(>35 t, 平均品位10 g/t), 矿化类型主要为硫化物石英脉型。在野外地质调查的基础上, 利用微量元素组成对金青顶矿床的成矿流体地球化学性质和成矿物质来源进行了研究, 并将金青顶矿床成因确定为受断裂控制的热液脉型金矿床。矿石稀土元素总量变化范围较大, 呈现出明显的轻稀土元素富集和重稀土元素亏损的特征(LREE/HREE=16.75~50.60), 负Eu异常显著, Ce异常不明显。Hf/Sm、Th/La、Nb/La等特征元素比值均小于1, 暗示成矿流体为富Cl体系。结合前人稳定同位素的研究, Ⅰ~Ⅱ阶段矿石δEu值逐渐减小, 可能有大气降水的加入, 说明金青顶矿床成矿流体为岩浆水和大气降水混合来源热液。硫化物矿石、蚀变和新鲜围岩Y/Ho值显示, 蚀变的围岩可为金成矿作用提供必要的成矿物质。
Abstract:The Jinqingding deposit is the largest gold deposit(> 35 t, average grade 10 g/t) within the Muping-Rushan metallogenic belt of eastern Jiaodong, and the main mineralization category is sulfide quartz-vein category.Based on the study of geological survey as well as trace element composition systematically, the geochemical characteristics of ore-forming fluid and source of ore-forming materials are constrained, and conducts the genesis of Jinqingding deposit as a hydrothermal vein-type gold deposit controlled by faults.In this study, the total rare earth elements(ΣREEs) in the ore varies widely, showing obvious light rare earth elements enrichment and heavy rare earth elements depletion(LREE/HREE=16.75~50.60), with strong negative Eu anomaly and insignificant Ce anomaly.The ratios of Hf/Sm, Th/La, and Nb/La are all less than 1, suggesting that the ore-forming fluid belongs to Cl-rich system.Combined with previous studies on stable isotopes, the δEu value of the ore from stage Ⅰ to Ⅱ gradually decreases in this study, and there may be the addition of meteoric water, indicating that the ore-forming fluid is a mixture of magmatic water and meteoric water.The Y/Ho ratio of sulfide ore, altered and fresh wall-rock implies that altered wall-rock can provide the necessary ore-forming material for gold mineralization.
-

-
表 1 金青顶金矿床硫化物矿石与围岩稀土元素组成
Table 1. Rare earth elements composition of sulfide ore and wall-rock in Jinqingding gold deposit
10-6 样品编号 20JQD- 1-1 20JQD- 1-2 20JQD- 2-1 20JQD- 2-2 20JQD- 3-1 20JQD- 3-2 20JQD- 5-1 20JQD- 5-2 20JQD- 8-1 20JQD- 8-2 20JQD- 9 20JQD- 10 Ⅱ阶段矿石 Ⅰ阶段矿石 Ⅱ阶段矿石 蚀变围岩 新鲜围岩 La 2.88 4.08 11.79 0.46 8.51 9.58 50.54 41.02 40.02 27.46 28.19 34.22 Ce 4.63 6.60 21.19 0.78 13.07 15.56 108.08 80.91 76.99 58.74 72.53 69.26 Pr 0.46 0.66 2.38 0.08 1.26 1.58 9.04 7.46 6.93 4.81 5.44 6.29 Nd 1.47 2.10 8.56 0.29 4.03 5.33 30.49 25.24 21.97 15.32 17.92 20.58 Sm 0.20 0.28 1.49 0.06 0.56 0.80 4.41 3.79 2.70 1.99 2.55 2.77 Eu 0.05 0.06 0.20 0.01 0.11 0.13 0.86 0.76 0.54 0.42 0.62 0.67 Gd 0.13 0.18 0.98 0.04 0.38 0.51 2.71 2.20 1.54 1.15 1.64 1.66 Tb 0.01 0.01 0.10 0.01 0.03 0.04 0.20 0.17 0.14 0.12 0.16 0.17 Dy 0.04 0.05 0.32 0.03 0.10 0.13 0.62 0.53 0.57 0.46 0.73 0.72 Ho 0.01 0.02 0.07 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.21 0.19 0.27 0.22 0.34 0.33 Er 0.01 0.01 0.05 / 0.01 0.01 0.09 0.09 0.10 0.09 0.13 0.13 Tm / / 0.01 / / / 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.05 Yb 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.24 0.22 0.28 0.24 0.37 0.36 Lu / / 0.01 / / / 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 Y 0.13 0.19 0.89 0.13 0.24 0.32 2.22 1.91 2.68 2.15 3.67 3.64 ΣREE 9.92 14.07 47.18 1.79 28.10 33.72 207.57 162.67 152.13 111.09 130.74 137.29 LREE/HREE 43.71 46.34 28.81 16.75 50.60 44.78 49.05 45.71 49.91 46.13 36.47 38.42 LaN/YbN 131.54 160.74 208.20 34.53 928.30 511.85 149.52 131.18 101.89 83.54 54.87 67.78 δEu 1.01 0.84 0.49 0.78 0.76 0.62 0.76 0.80 0.82 0.85 0.92 0.96 δCe 0.99 0.99 0.98 0.97 0.98 0.98 1.24 1.13 1.13 1.25 1.44 1.16 表 2 金青顶金矿床硫化物矿石与围岩微量元素组成
Table 2. Trace elements composition of sulfide ore and wall-rock in Jinqingding gold deposit
10-6 样品编号 20JQD- 1-1 20JQD- 1-2 20JQD- 2-1 20JQD- 2-2 20JQD- 3-1 20JQD- 3-2 20JQD- 5-1 20JQD- 5-2 20JQD- 8-1 20JQD- 8-2 20JQD- 9 20JQD- 10 Ⅱ阶段矿石 Ⅰ阶段矿石 Ⅱ阶段矿石 蚀变围岩 新鲜围岩 Cs 0.04 0.05 0.04 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.41 0.44 0.03 0.06 0.20 0.28 Rb 7.34 11.29 5.74 7.04 1.73 4.46 28.16 28.19 8.15 12.94 24.16 45.09 Ba 337.13 109.64 11.41 13.16 41.02 291.35 92.92 90.29 45.57 95.74 1562.78 3310.39 Th 0.26 0.46 0.24 0.05 0.08 0.30 4.76 4.23 6.40 3.98 4.56 5.34 U 0.04 0.06 0.08 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.63 0.59 0.87 0.75 0.40 0.42 Nb 0.17 0.28 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.27 4.54 4.88 4.52 3.89 4.90 4.93 Ta / 0.01 / / / / 0.09 0.08 0.11 0.10 0.11 0.12 La 2.88 4.08 11.79 0.46 8.51 9.58 50.54 41.02 40.02 27.46 28.19 34.22 Ce 4.63 6.60 21.19 0.78 13.07 15.56 108.08 80.91 76.99 58.74 72.53 69.26 Sr 18.63 18.47 29.36 20.83 6.06 16.17 80.67 95.49 147.21 125.37 401.84 459.54 Nd 0.17 0.28 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.27 4.54 4.88 4.52 3.89 4.90 4.93 Zr 7.55 9.90 0.78 0.79 1.23 7.28 171.59 195.07 170.80 178.54 188.42 205.48 Hf 0.20 0.23 0.03 0.01 0.02 0.17 4.45 4.59 3.82 4.10 4.17 4.51 Sm 0.20 0.28 1.49 0.06 0.56 0.80 4.41 3.79 2.70 1.99 2.55 2.77 Eu 0.05 0.06 0.20 0.01 0.11 0.13 0.86 0.76 0.54 0.42 0.62 0.67 Ti 53.26 73.40 17.46 18.40 14.97 63.45 869.63 886.42 954.11 854.40 1337.97 1218.07 Gd 0.13 0.18 0.98 0.04 0.38 0.51 2.71 2.20 1.54 1.15 1.64 1.66 Tb 0.01 0.01 0.10 0.01 0.03 0.04 0.20 0.17 0.14 0.12 0.16 0.17 Y 0.13 0.19 0.89 0.13 0.24 0.32 2.22 1.91 2.68 2.15 3.67 3.64 Yb 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.24 0.22 0.28 0.24 0.37 0.36 Lu / / 0.01 / / / 0.04 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.06 Y/Ho 25.3 25.3 19.1 27.1 22.5 22.0 24.7 22.3 26.6 24.6 28.2 28.6 Co 14.90 11.17 27.33 2.23 62.74 35.06 64.26 71.39 0.29 0.42 0.54 0.49 Ni / 1.96 2.45 0.96 3.97 2.79 3.88 6.79 0.19 0.34 0.20 0.17 Hf/Sm 0.98 0.83 0.02 0.22 0.03 0.21 1.01 1.21 / / / / Th/La 0.09 0.11 0.02 0.11 0.01 0.03 0.09 0.10 / / / / Nb/La 0.06 0.07 / 0.10 / 0.03 0.09 0.12 / / / / Y/Ho 25.32 25.30 19.13 27.06 22.49 21.97 24.66 22.32 / / / / Co/Ni / 5.71 11.18 2.31 15.81 12.58 16.56 10.51 / / / / Nb/Ta 56.04 36.78 12.27 34.30 30.76 59.81 52.06 57.98 / / / / Zr/Hf 38.53 42.12 25.94 65.61 73.71 42.07 38.59 42.48 / / / / -
[1] Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization: a case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 165-178. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.006
[2] Deng J, Yang L Q, Groves D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2020, 208: 103274. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103274
[3] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30: 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm
[4] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm
[5] Goldfarb R J, Santosh M. The dilemma of theJiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?[J]Geoscience Frontiers, 2014, 5: 139-153. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.11.001
[6] Groves D I, Santosh M. The giant Jiaodong gold province: The key to a unified model for orogenic gold deposits?[J]Geoscience Frontiers, 2016, 7: 409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2015.08.002
[7] 胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 沈昆, 等. 胶东乳山脉状金矿床成矿流体性质与演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(5): 1329-1338. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200505001.htm
[8] 应汉龙. 胶东金青顶和邓格庄金矿床的同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 贵金属地质, 1994, 3: 201-207. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GJSD403.005.htm
[9] 胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 胶东乳山金矿蚀变岩中绢云母40Ar/39Ar年龄及其对金成矿事件的制约[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 2: 109-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200602000.htm
[10] Li J W, Vasconcelos P M, Zhou M F, et al. Geochronology of the Pengjiakuang and Rushan gold deposits, eastern Jiaodong gold province, northeastern China: implications for regional mineralization and geodynamic setting[J]. Economic Geology, 2006, 101: 1023-1038. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.101.5.1023
[11] Sai S X, Deng J, Qiu K F, et al. Textures of auriferous quartz-sulfide veins and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Rushan gold deposit: Implications for processes of ore-fluid infiltration in the eastern Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 117: 103254. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103254
[12] 李旭芬. 胶东牟平-乳山金矿带金青顶金矿矿床成因与找矿方向研究[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文, 2011.
[13] 丁振举, 姚书振, 刘丛强, 等. 东沟坝多金属矿床喷流沉积成矿特征的稀土元素地球化学示踪[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 4: 792-798. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200304021.htm
[14] 马玉波, 杜晓慧, 张增杰, 等. 青城子层状/脉状铅锌矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(6): 1236-1248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.06.010
[15] 郭林楠, 黄春梅, 张良, 等. 胶东罗山金矿床成矿流体来源: 蚀变岩型和石英脉型矿石载金黄铁矿稀土与微量元素特征约束[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1): 121-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201901012.htm
[16] Li J, Cai W Y, Li B, et al. Paleoproterozoic SEDEX-type stratiform mineralization overprinted by Mesozoic vein-type mineralization in the Qingchengzi Pb-Zn deposit, Northeastern China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 184: 104009. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104009
[17] Li J, Wang K Y, Cai W Y, et al. Triassic gold-silver metallogenesis in Qingchengzi orefield, North China Craton: Perspective from fluid inclusions, REE and H-O-S-Pb isotope systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 121: 103567. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103567
[18] 翟明国. 华北前寒武纪成矿系统与重大地质事件的联系[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29: 1759-1773. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305023.htm
[19] Goldfarb R J, Qiu K F, Deng J, et al. Orogenic Gold Deposits of China[J]. Society of Economic Geologists Special Publications, 2019, 22: 263-324.
[20] Yang J H, Wu F Y, Wilde S A. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale Late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: an association with lithospheric thinning[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2003, 23: 125-152. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(03)00033-7
[21] Yang J H, Wu F Y. Triassic magmatism and its relation to decratonization in the eastern North China Craton[J]. Science in China, 2009, 52: 1319-1330. doi: 10.1007/s11430-009-0137-5
[22] Li J, Cai W Y, Wang K Y, et al. Initial decratonization of the eastern North China Craton: New constraints from geochronology, geochemistry, and Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic igneous rocks in the Qingchengzi district[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 3796-3820. doi: 10.1002/gj.3635
[23] Yang K F, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012, 146: 112-127.
[24] 王世进, 万渝生, 宋志勇, 等. 鲁东文登地区文登型(超单元)花岗岩体的SHRIMP锆石年代学[J]. 山东国土资源, 2012, 28(2): 1-5, 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2012.02.002
[25] Ma L, Jiang S Y, Dai B Z, et al. Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China: zircon U-Pb geochronological geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence[J]. Lithos, 2013, 162: 175-194.
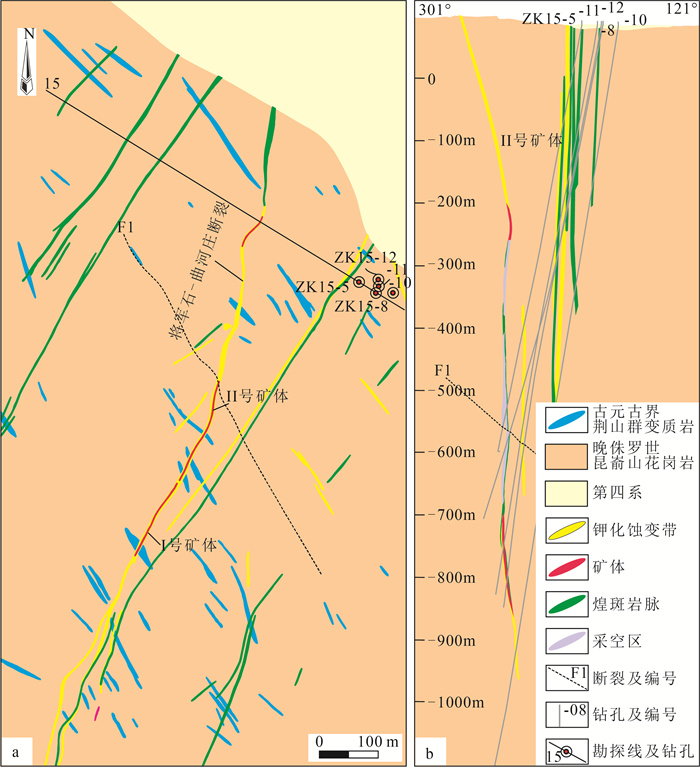
[26] 张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 等. 胶莱盆地及其邻区白垩纪—古新世沉积构造演化历史及其区域动力学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2008, 9: 1229-1257. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200809007.htm
[27] 朱日祥, 孙卫东. 大地幔楔与克拉通破坏型金矿[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2021, 51, doi: 10.1360/SSTe-2020-0305.
[28] Hou M L, Jiang Y H, Jiang S Y, et al. Contrasting origins of late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: implications for crustal thickening to delamination[J]. Geological Magazine, 2007, 144: 619-631. doi: 10.1017/S0016756807003494
[29] Li X H, Fan H R, Zhang Y W, et al. Rapid exhumation of the northern Jiaobei Terrane, North China Craton in the Early Cretaceous: Insights from Al-in-hornblende barometry and U-Pb geochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 160: 365-379. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.10.001
[30] Song M C, Zhou J B, Song Y X, et al. Mesozoic Weideshan granitoid suite and its relationship to large-scale gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5703-5724. doi: 10.1002/gj.3607
[31] 王斌, 宋明春, 霍光, 等. 胶东晚中生代花岗岩的源区性质与构造环境演化及其对金成矿的启示[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2): 288-320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2021.02.009
[32] 陈炳翰. 牟乳金矿带成矿作用地球化学[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)硕士学位论文, 2017.
[33] Zhang Y W, Hu F F, Fan H R, et al. Fluid evolution and gold precipitation in the Muping gold deposit(Jiaodong, China): insights from in-situ trace elements and sulfur isotope of sulfides[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 218: 106617. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2020.106617
[34] 胡芳芳, 范宏瑞, 杨进辉, 等. 胶东乳山含金石英脉型金矿的成矿年龄: 热液锆石SHRIMP法U-Pb测定[J]. 科学通报, 2004, (12): 1191-1198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.12.014
[35] 郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, 等. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞-碰撞后构造过程: 锆石U-Pb年代学[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(4): 1281-1301. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200504025.htm
[36] 赛盛勋, 邱昆峰. 胶东乳山金矿床成矿过程: 周期性压力波动诱发的流体不混溶[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5): 1547-1566. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202005014.htm
[37] 尹升, 张海芳, 王芳, 等. 山东金青顶金矿床Ⅱ号矿体成矿特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2015, 31(11): 9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.11.003
[38] Liu Y S, Zong K Q, Kelemen P B, et al. Geochemistry and magmatic history of eclogites and ultramafic rocks from the Chinese continental scientific drill hole: Subduction and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism of lower crustal cumulates[J]. Chemical Geology, 2008, 247(1/2): 133-153.
[39] 凌洪飞, 胡受奚, 孙景贵, 等. 胶东金青顶和大尹格庄金矿床花岗质围岩的蚀变地球化学研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, (2): 187-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2002.02.011
[40] 陈海燕, 李胜荣, 张秀宝, 等. 胶东金青顶金矿床围岩蚀变特征与金矿化[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2012, 31(1): 5-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2012.01.002
[41] Boynton W V. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteoritestudies[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1984: 63-114.
[42] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[43] Shannon R D. Revised Effective Ionic Radii and Systematic Studies of Interatomic Distances in Halides and Chalcogenides[J]. Acta Cryst, 1976, 32: 751-767. doi: 10.1107/S0567739476001551
[44] Jiang S Y, Yu J M, Lu J J. Trace and rare-earth element geochemistry in tourmaline and cassiterite from the Yunlong tin deposit, Yunnan, China: implication for migmatitic-hydrothermal fluid evolution and ore genesis[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 209: 193-213. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.04.021
[45] 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等. 黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体性质的指示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2004, (1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2004.01.001
[46] Mills R, Elderfield H. Rare earth elemen t geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from the active TAG M ount, 26°N mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Geochimica et cosmochimica acta, 1995, 59(17): 3511-3524. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00224-N
[47] Anenburg M, Mavrogenes J A, Frigo C, et al. Rare earth element mobility in and around carbonatites controlled by sodium, potassium, and silica[J]. Science Advances, 2020, 6: eabb6570. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abb6570
[48] Ayers J C, Watson E B. Apatite/fluid partitioning of rare-earth elements and strontium: Experimental results at 1.0 GPa and 1000℃ and application to models of fluid-rock interaction[J]. Chemical Geology, 1993, 110: 299-314. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(93)90259-L
[49] Keppler H. Constraints from partitioning experiments on the composition of subduction zone fluids[J]. Nature, 1996, 380: 237-240. doi: 10.1038/380237a0
[50] 刘善宝. 山东乳山金青顶金矿田成矿规律及其成矿远景研究[D]. 长安大学博士学位论文, 2005.
[51] 翟建平, 胡凯, 陆建军. 乳山金矿床的成因机制—成矿流体和H, O, Sr同位素证据[J]. 科学通报, 1996, (12): 1119-1121. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1996.12.017
[52] 高太忠, 赵伦山, 杨敏之. 山东牟乳金矿带成矿演化机理探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2001, (2): 155-160. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2001.02.007
[53] 张运强, 李胜荣, 陈海燕, 等. 胶东金青顶金矿床成矿流体来源的黄铁矿微量元素及He-Ar同位素证据[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(1): 195-204. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.01.019
[54] Bau M, Dulski P. Comparing yttrium and rare earths in hydrothermal fluids from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: Implications for Y and REE behavior during near-vent mixing and for the Y/Ho ratio of Proterozoic seawater[J]. Chemical Geology, 1999, 155: 77-99. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(98)00142-9
[55] 王文元, 高建国, 侬阳霞, 等. 云南禄劝噜鲁铅锌矿床稀土元素和微量元素地球化学[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2017, 35(3): 418-430. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTXB201703014.htm
[56] 郭林楠. 胶东型金矿床成矿机理[D]. 中国地质大学(北京)博士学位论文, 2016.
[57] Guo L N, Goldfarb R J, Wang Z L, et al. A comparison of Jiaojia- and Linglong-type gold deposit ore-forming fluids: Do they differ?[J]Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88: 511-533. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.003
[58] Guo L N, Deng J, Yang L Q, et al. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemical comparison of ore fluids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103434. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103434
[59] Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al. Orogenic gold deposits: a proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13: 7-27. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
[60] Goldfarb R J, Groves D I, Gardoll S. Orogenic gold and geologic time: a synthesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2001, 18: 1-75. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00016-6
[61] 曾国平, 向文帅, 吴发富, 等. 东北非与中国胶东造山型金矿对比及对非洲找矿勘查的启示[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(1): 48-59. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20220104&flag=1
-



 下载:
下载: