The fluid inclusions, H-O-C-S-Pb isotopic characteristics and genesis of the Liaoshang gold deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula
-
摘要:
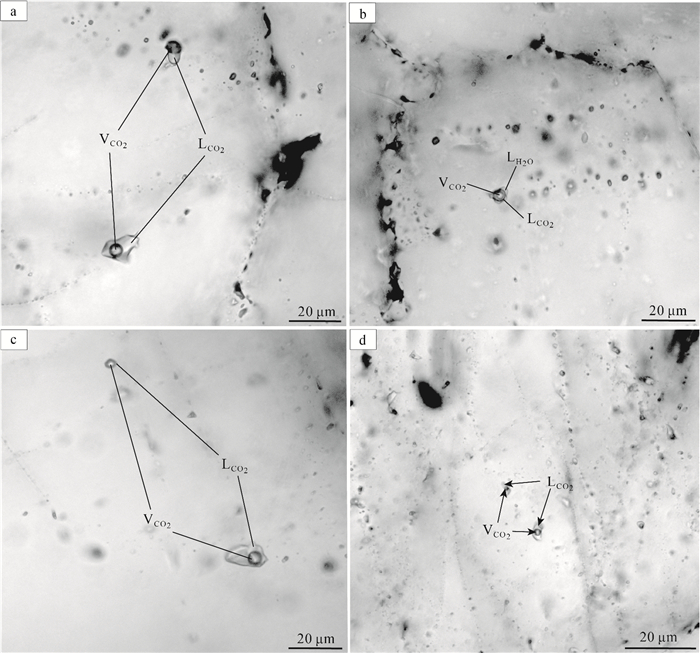
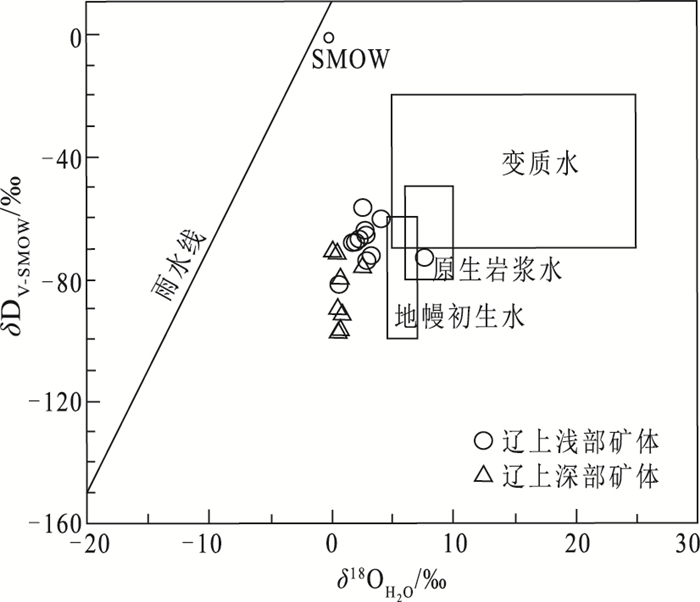
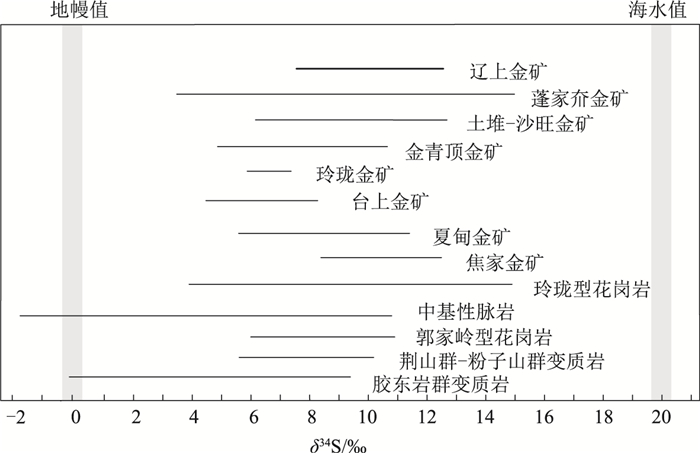
辽上金矿床位于胶莱盆地东北缘, 是胶东东部唯一的超大型金矿床。通过流体包裹体和氢-氧-碳-硫-铅同位素地球化学特征研究, 探讨辽上金矿的成因。主成矿阶段流体包裹体完全均一温度变化范围为125~345℃, 主成矿温度集中于260~320℃, 盐度为2.22%~13.87%NaCleqv, 流体密度为0.68~1.02 g/cm3, 成矿流体属于中—低温度、中—低盐度、低密度, 为富含CO2的还原性质热液体系。氢、氧同位素(δD=-82.6‰~-68.9‰, δ18OW-SMOW=-0.24‰~+3.33‰)和流体包裹体成分指示, 成矿流体为地幔初生水热液及岩浆热液+大气降水的混合流体。碳、氧同位素组成(δ13CPDB=-2.9‰~-4.7‰, δ18OSMOW=6.9‰~9.6‰, )指示成矿流体中碳来源于花岗岩源区。矿石δ34S介于7.6‰~12.6‰之间, 206Pb/204Pb值为17.202~17.955, 207Pb/204Pb值为15.457~15.577, 208Pb/204Pb值为37.729~38.341, 指示铅源主要来自下地壳的早前寒武纪变质岩系, 可能有少量幔源铅的贡献。研究认为, 辽上金矿床是与早白垩世伟德山型花岗岩有关的岩浆热液金矿, 与壳幔混合花岗岩浆活动有关的岩浆热液、地幔流体在热隆-伸展构造作用下与大气降水混合产生流体不混溶而成矿。
Abstract:The Liaoshang gold deposit is located in the northeastern margin of the Jiaolai Basin.It is the only super-large gold deposit in the eastern part of the Jiaodong Peninsula.This paper discusses the genesis of the Liaoshang gold deposit through fluid inclusions and H-O-C-S-Pb isotopic geochemistry.The fluid inclusions in the main ore-forming stage have a completely uniform temperature range of 125~345℃, the main metallogenic temperature range of 260~320℃, salinity of 2.22%~13.87%NaCleqv, and fluid density of 0.68~1.02 g/cm3, indicating that the ore-forming fluid is a reductive hydrothermal system with medium-low temperature, medium-low salinity, low density, and rich in CO2. H and O isotopes(δD=-82.6‰~-68.9‰, δ18OW-SMOW=0.24‰~+3.33‰) and fluid inclusion composition indicate that the ore-forming fluid is a mixed fluid of mantle hydrothermal fluid and magmatic hydrothermal fluid + atmospheric precipitation.The carbon and oxygen isotope composition(δ13CPDB=-2.9‰~-4.7‰, and δ18OSMOW=6.9‰~9.6‰, ) indicate that C in the ore-forming fluid originated from the granite source area.The δ34S of the ore ranges from 7.6‰ to 12.6‰.206Pb/204Pb ratios ranging from 17.202 to 17.955, 207Pb/204Pb ratios ranging from 15.457 to 15.577, and 208Pb/204Pb ratios ranging from 37.729 to 38.341, indicate that the lead source is the Early Cambrian metamorphic rock series mainly from the lower crust, mixed with mantle-derived lead.Studies indicate that the Liaoshang gold deposit is a magmatic hydrothermal gold deposit related to the Early Cretaceous Weideshan-type granite.The mixture of magmatic hydrothermal fluids related to the activity of crust-mantle mixed granite magma, mantle fluids and atmospheric precipitation produced fluid immiscible mineralization under the effect of heat uplift-extension structure.
-
Key words:
- fluid inclusions /
- ore-forming fluid /
- H-O-C-S-Pb isotopes /
- genesis of deposit /
- Liaoshang gold deposit /
- Jiaodong
-

-
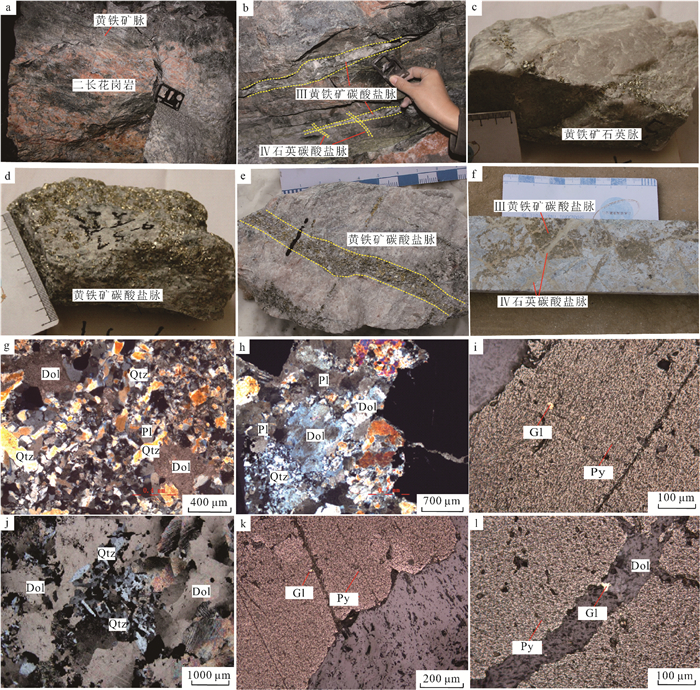
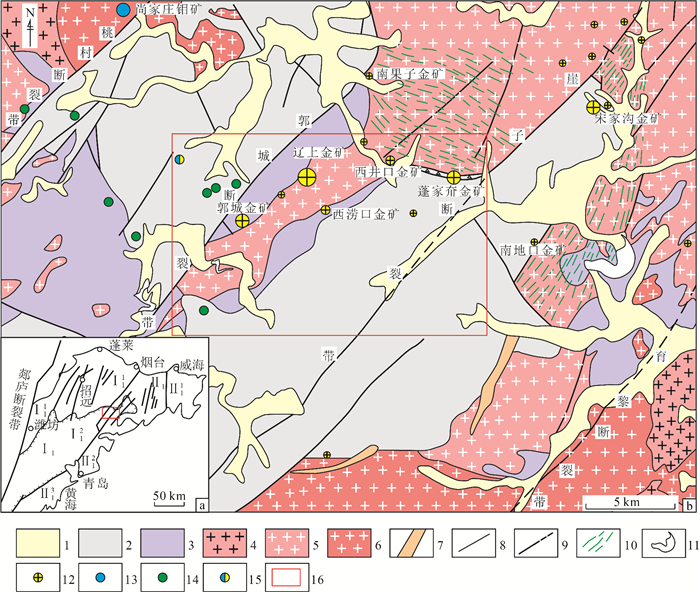
图 1 胶东辽上金矿床区域地质图(a)和金属矿产分布图(b) [2]
Figure 1.
图 2 辽上金矿区地质简图[12]
Figure 2.
图 5 辽上金矿床成矿流体δ18O-δD图解(底图据参考文献[33])
Figure 5.
图 6 辽上金矿床碳-氧同位素组成图解(底图据参考文献[36])
Figure 6.
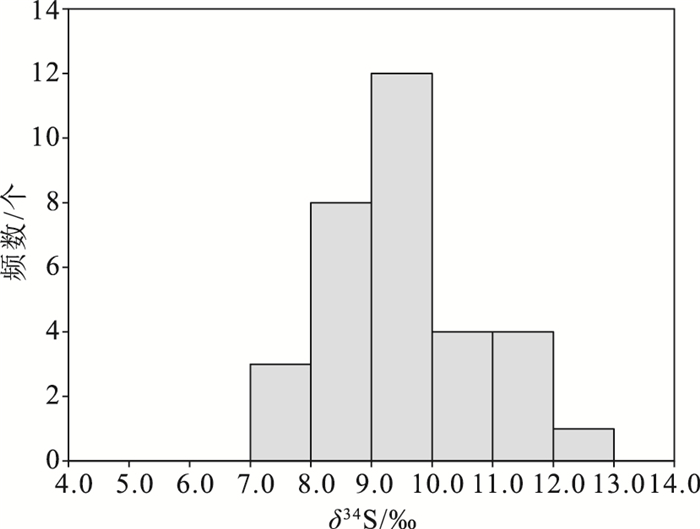
图 8 辽上金矿床黄铁矿δ34S值分布图(据参考文献[12]修改)
Figure 8.
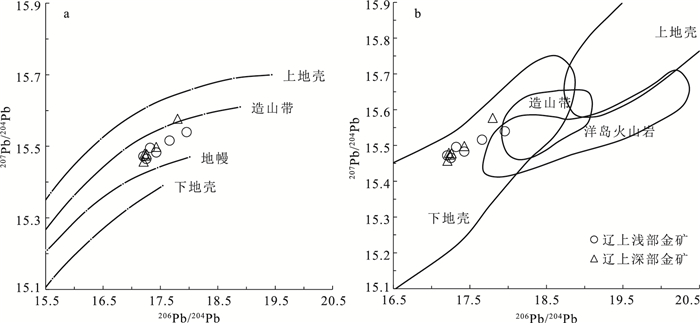
图 9 辽上金矿床矿石铅同位素模式图(a)及构造环境判别图(b) (底图据参考文献[42])
Figure 9.
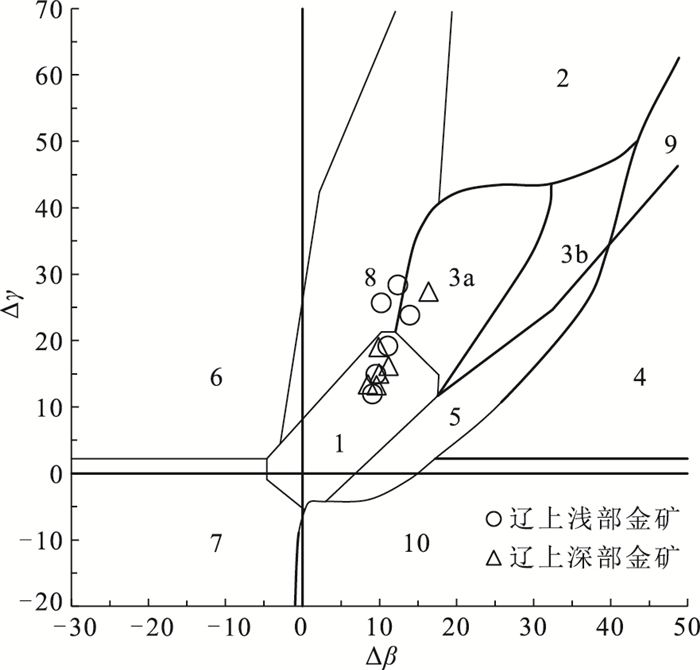
图 10 辽上金矿床矿石铅同位素Δβ-Δγ成因判别图解(底图据参考文献[44])
Figure 10.
表 1 辽上金矿床流体包裹体显微测温结果及参数
Table 1. Microthermometric data and relative parameters of fluid inclusions in the Liaoshang gold deposit
样品号 测定矿物 测点数/个 类型 大小/μm 气液比/% 冰点温度
Ti/℃均一温度
Th/℃盐度/%NaCleqv 密度/(g·cm-3) 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 范围 均值 LS1 石英 5 H2O包裹体 8~12 10~20 -5.3~-8.2 -6.7 125~160 147 8.28~11.93 10.06 0.968~1.022 0.991 LS-5-① 石英 6 H2O包裹体 8~18 10~20 -4.3~-6.2 -5.1 140~150 145 6.88~9.47 7.94 0.974~0.987 0.979 LS-5-② 石英 3 H2O-CO2
三相包裹体12~20 30~40 6.8~7.9 7.4 275~290 283 4.14~6.12 5.04 0.775~0.811 0.787 石英 4 H2O包裹体 8~20 30~35 -3.7~-4.8 -4.23 190~245 229 6.01~7.59 6.77 0.864~0.929 0.88 LS12 石英 7 H2O-CO2
三相包裹体3~25 20~40 7.2~8.7 7.63 215~345 316 2.62~5.41 4.62 0.679~0.869 0.723 石英 16 H2O包裹体 2~10 15~20 -4.7~-5.4 -5.1 205~285 251 7.45~8.41 8.05 0.819~0.915 0.862 石英 6 CO2两相包裹体 2~4 20~30 30~31.2 30.6 XLK-6 石英 6 H2O-CO2
三相包裹体6~15 15~25 1.5~8.9 5.5 260~270 265 2.22~13.87 7.93 0.788~0.907 0.844 表 2 辽上金矿床石英的氢氧同位素组成
Table 2. H and O isotopic compositons of quartz in the Liaoshang gold deposit
样品号 位置 矿物 成矿阶段 δ18OQz-SMOW/‰ 均一温度/℃ δ18OW-SMOW/‰ δDSMOW/‰ LS-1 辽上浅部 石英 主成矿阶段 10.4 295 3.33 -73.4 LS-4 石英 主成矿阶段 10.5 283.3 2.98 -75 LS-5 石英 主成矿阶段 11.4 241.7 2.05 -68.9 LS-6 石英 主成矿阶段 9 265 0.73 -82.6 XL74ZK1-2 辽上深部 石英 主成矿阶段 8.3 270 0.24 -71.3 XL74ZK1-4 石英 主成矿阶段 9.2 264.5 0.91 -80.3 XLK-2 石英 主成矿阶段 10.9 265 2.63 -76.4 XLK-6 石英 主成矿阶段 9.1 260 0.61 -72 表 3 辽上金矿白云石碳氧同位素组成
Table 3. The C-O isotopic compositons of dolomite in the Liaoshang gold deposit
‰ 矿床 样号 矿物 δ13CV-PDB δ18OPDB δ18OSMOW 辽上浅部矿体 LS-5 白云石 -4.1 -20.8 9.4 LS-6 白云石 -4.4 -20.9 9.4 LS-9 白云石 -4.7 -20.7 9.6 辽上深部矿体 XL74ZK1-4 白云石 -2.9 -23.3 6.9 XL74ZK1-7 白云石 -4.4 -21.1 9.1 XLK-1 白云石 -3.7 -21.9 8.3 XLK-6 白云石 -4.3 -21 9.3 表 4 辽上金矿床黄铁矿样品δ34S组成
Table 4. The S isotopic compositon of pyrites in the Liaoshang gold deposit
样号 矿床 矿物 34S/‰ 来源 LS-1 辽上 黄铁矿 8.8 [21] LS-4 9.4 09LS-2 黄铁矿 8.2 [22] 09LS-4 8.3 09LS-5 8.3 LK10 黄铁矿 9.7 [23] LK12 9.5 LK14 9.3 LK15 9.7 B21 西涝口 黄铁矿 7.8 [22] B04 7.6 B42 8.8 B48 8.7 B49 8.6 B36 9 B30 8.9 B31 9.4 B39 9.5 B40 9.5 B47 7.6 LS-1 辽上浅部矿体 黄铁矿 10.7 本文 LS-3 10.7 LS-4 10.2 LS-5 9.8 LS-6 10.3 LS-9 9.8 XL74ZK1-4 辽上深部矿体 黄铁矿 11.2 XL74ZK1-7 11.2 XLK-1 11 XLK-2 11.4 XLK-5 9.8 XLK-6 12.6 表 5 辽上金矿床矿石矿物铅同位素组成及源区特征值
Table 5. Lead isotope composition and parameters of sulfide in the Liaoshang gold deposit
矿床 样号 矿物 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb 206Pb/207Pb TCDT/Ma μ ω Th/U △β △γ 辽上浅部矿体 LS-1 黄铁矿 17.319 15.496 37.999 1.1176 826 9.41 40.2 4.13 11.05 19.2 LS-3 黄铁矿 17.426 15.483 38.24 1.1255 736 9.36 40.46 4.18 10.21 25.67 LS-4 黄铁矿 17.253 15.465 37.729 1.1156 839 9.36 39.05 4.04 9.03 11.96 LS-5 黄铁矿 17.658 15.516 38.341 1.1381 608 9.39 39.73 4.09 12.36 28.38 LS-6 黄铁矿 17.202 15.472 37.84 1.1118 882 9.38 40 4.13 9.49 14.94 LS-9 黄铁矿 17.955 15.54 38.171 1.1554 424 9.4 37.4 3.85 13.92 23.82 辽上深部矿体 XL74ZK1-4 黄铁矿 17.261 15.478 37.993 1.1152 847 9.38 40.38 4.17 9.88 19.04 XL74ZK1-7 黄铁矿 17.224 15.479 37.844 1.1127 874 9.39 39.94 4.12 9.94 15.05 XLK-1 黄铁矿 17.206 15.457 37.783 1.1132 863 9.35 39.54 4.09 8.51 13.41 XLK-2 黄铁矿 17.427 15.498 37.886 1.1245 752 9.39 38.97 4.02 11.18 16.17 XLK-5 黄铁矿 17.24 15.474 37.777 1.1141 857 9.38 39.46 4.07 9.62 13.25 XLK-6 黄铁矿 17.798 15.577 38.304 1.1426 578 9.5 39.29 4 16.34 27.38 -
[1] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 赵财胜, 等. 山东胶莱盆地东北缘地区金矿成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊) : 919-920. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1460.htm
[2] 李国华, 丁正江, 纪攀, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘地区金矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(6) : 1029-1036. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201606003.htm
[3] 宋英昕, 宋明春, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿集区深部找矿重要进展及成矿特征[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3) : 4-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703003.htm
[4] 李国华, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东新类型金矿——辽上黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(3) : 423-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201703012.htm
[5] 李勇, 丁正江, 薄军委, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘地区成矿元素地球化学特征及成矿潜力分析[J]. 黄金, 2018, 39(8) : 15-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201808004.htm
[6] 纪攀, 丁正江, 李国华, 等. 胶东辽上特大型金矿床地质特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2016, 32(6) : 9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2016.06.002
[7] 罗忠明. 山东牟平辽上金矿床地质特征[J]. 山东地质, 2000, 16(3) : 22-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI200003004.htm
[8] 范存琨, 李希良, 宋学法. 山东牟平辽上金矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 中国科技信息, 2010, 10: 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XXJK201010010.htm
[9] 孙玉龙, 殷国鹏, 邱介玲, 等. 胶东辽上金矿床成因与找矿方向研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(2) : 209-215. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201102011.htm
[10] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 刘福来, 等. 胶东中生代动力学演化及主要金属矿床成矿系列[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(10) : 3045-3080. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201510011.htm
[11] 李红梅, 魏俊浩, 王启, 等. 山东土堆-沙旺金矿床同位素组成特征及矿床成因讨论[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(6) : 791-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201006004.htm
[12] 薄军委, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东辽上金矿床C、O、S、Pb同位素组成及矿床成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2) : 321-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2021.02.010
[13] 王志新, 焦秀美, 丁正江, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘辽上式金矿构造控矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3) : 61-69. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703010.htm
[14] 张连昌, 沈远超, 曾庆栋, 等. 山东中生代胶莱盆地北缘金矿床硫铅同位素地球化学[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(4) : 380-384. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.04.049
[15] 张连昌, 沈远超, 刘铁兵, 等. 山东蓬家夼金矿硫铅碳氧同位素地球化学[J]. 矿物学报, 2002, 22(3) : 255-260. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2002.03.012
[16] Bozzo A T, Chen J R, Barduhn A J. The properties ofhydrates of chlorine and carbon dioxide[C]//Fourth International Symposium on Fresh Water the Sea, 1973, 3: 437-451.
[17] Potter R W Ⅱ, Clynne M A, Brown D L. Freezing point depression of aqueous sodium chloride solutions[J]. Economic Geology, 1978, 73: 284-285. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.73.2.284
[18] 刘斌, 沈昆. 流体包裹体热力学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 1-290.
[19] Shepherd T J, Rankin A H, Alderton D H M. A practical guide to fluid inclusion studies[M]. Blackie: Chapman & Hall, 1985: 1-239.
[20] 张理刚. 稳定同位素在地质科学中的应用: 金属活化热液成矿作用及找矿[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1985.
[21] 税棚. 胶莱盆地东北缘郭城-辽上金矿地质特征及成因机制[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2019.
[22] 孙兴丽. 山东胶莱盆地西涝口金矿床的特征和成因[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2014.
[23] Tan J, Wei J H, Li Y J, et al. Origin and geodynamic significance of fault-hosted massive sulfide gold deposits from the Guocheng-Liaoshang metallogenic belt, eastern Jiaodong Peninsula: Rb-Sr dating, and H-O-S-Pb isotopic constraints[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 65: 687-700.
[24] Hoefs J. Stable Isotope Geochemistry[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1997: 1-201.
[25] Pirajno F. Hydrothermal Processes and Mineral Systems[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2008: 1-597.
[26] Fu Y G, Hu G Y, Tang J X, et al. Low-sulfidation epithermal Ag-Pb-Zn deposit in Sinongduo, Tibet: tracer application of Si-H-O stable isotope geochemistry[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(4) : 836-848.
[27] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm
[28] Fan H R, Zhai M G, Xie Y H, et al. Ore-Forming Fluids Associated with Granite-Hosted Gold Mineralization at the Sanshandao Deposit, Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003, 38(6) : 739-750. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0368-x
[29] 毛景文, 李厚民, 王义天, 等. 地幔流体参与胶东金矿成矿作用的氢氧碳硫同位素证据[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(6) : 839-857. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.06.013
[30] 王庆飞, 邓军, 赵鹤森, 等. 造山型金矿研究进展: 兼论中国造山型金成矿作用[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(6) : 2155-2186. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201906029.htm
[31] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 沈昆, 等. 胶东焦家深部金矿矿床地球化学特征及有关问题讨论[J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(3) : 274-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.03.009
[32] 朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 等. 克拉通破坏型金矿床[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2015, 45(8) : 1153-1168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201508006.htm
[33] Taylor H P. The Application of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Studies to Problems of Hydrothermal AlTeration and Ore Deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69(6) : 843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843
[34] 盛鹏. 山东省辽上金矿成因矿物学与成矿物质来源研究[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 硕士学位论文, 2019.
[35] 刘家军, 何明勤, 李志明, 等. 云南白秧坪银铜多金属矿集区碳氧同位素组成及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2004, 23(1) : 1-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2004.01.001
[36] 刘建明, 刘家军, 顾雪祥. 沉积盆地中的流体活动及其成矿作用[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1997, 16(4) : 341-352. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW704.006.htm
[37] 王义文, 朱奉三, 宫润谭. 构造同位素地球化学—胶东金矿集中区硫同位素再研究[J]. 黄金, 2002, 23(4) : 1-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ200204000.htm
[38] 杨忠芳, 徐景奎, 赵伦山. 胶东区域地壳演化与金成矿作用地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 1-125.
[39] Rye R O, Ohmoto H. Sulfur and carbon isotopes and ore genesis: A review[J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69: 826-842. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.826
[40] 张连昌, 沈远超, 刘铁兵, 等. 浅议胶东金矿集中区矿床类型与成矿系统[J]. 矿床地质, 2002, 21(增刊) : 779-782. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2002S1208.htm
[41] 王斌, 宋明春, 霍光, 等. 胶东晚中生代花岗岩的源区性质与构造环境演化及其对金成矿的启示[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2021, 40(2) : 288-320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2021.02.009
[42] Zartman R E, Doe B R. Plumbotectonics-the model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 75(1/2) : 135-162.
[43] Stacey J S, Kramers J D. Approximation of Terrestrial Lead Isotope Evolution by a Two-Stage Model[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1975, 26: 207-221. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6
[44] 朱炳泉, 李献华, 戴谟. 地球科学中同位素体系理论与应用——兼论中国大陆壳幔演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998: 216-230.
[45] 李增达, 于晓飞, 王全明, 等. 胶东三佛山花岗岩的成因: 成岩物理化学条件、锆石U-Pb年代学及Sr-Nd同位素约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(2) : 447-468. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201802018.htm
[46] Song M C, Zhou J B, Song Y X, et al. Mesozoic Weideshan granitoid suite and its relationship to large-scale gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5703-5724. doi: 10.1002/gj.3607
[47] 宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 等. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(1) : 87-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201401008.htm
[48] 宋明春, 张军进, 张丕建, 等. 胶东三山岛北部海域超大型金矿床的发现及其构造-岩浆背景[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(2) : 365-383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201502012.htm
[49] Mingchun Song, Sanzhong Li, M. Santosh, et al. Types, characteristics and metallogenesis of gold deposits in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Eastern North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 612-625. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.019
[50] 宋明春, 李杰, 周建波, 等. 胶东早白垩世高镁闪长岩类的发现及其构造背景[J], 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1) : 279-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202001022.htm
[51] 陈衍景, Pirajno F, 赖勇, 等. 胶东矿集区大规模成矿时间和构造环境[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(4) : 907-922. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200404013.htm
[52] 宋明春, 李杰, 李世勇, 等. 鲁东晚中生代热隆伸展构造及其动力学背景[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(4) : 941-964. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201804001.htm
[53] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J], 矿床地质, 2020b, 39(2) : 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm
[54] 宋明春, 伊丕厚, 徐军祥, 等. 胶西北金矿阶梯式成矿模式[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2012, 42(7) : 992-1000. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201207006.htm
① 山东省第三地质矿产勘查院. 山东省牟平区辽上金矿深部及外围详查报告. 2014.
-



 下载:
下载: