Comparisons of the fluid inclusions in the main types of gold deposits in Jiaodong area and the indication on their metallogenic conditional differences: a case study of Shaling, Jiudian and Liaoshang gold deposits
-
摘要:
胶东是中国最重要的金矿集区, 破碎带蚀变岩型、石英脉型和黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿是区内的主要矿化类型, 前人对不同矿化类型成矿条件的差异性尚缺乏深入研究。对胶东3种矿化类型的代表性金矿床流体包裹体研究发现: 不同矿化类型金矿床主成矿期的流体包裹体具有相似的岩相学特征, 均发育H2O-CO2(Ⅱ-g型)、富CO2(ⅢCO2型)和水溶液包裹体(Ⅰ-l型和Ⅱ-l型)4种流体包裹体, 均属于CO2-H2O-NaCl±CH4体系。不同矿化类型的流体特征也有差异, 黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿的流体包裹体以盐度和均一温度较高明显区别于其他矿化类型, 石英脉型金矿流体包裹体以直径较大、三相包裹体占比略高, 区别于破碎带蚀变岩型金矿。破碎带蚀变岩型和石英脉型金矿成矿流体整体属于中—低温、中—低盐度、低密度流体, 黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿成矿流体属于中—高温、中—低盐度、低密度流体。对纱岭金矿床-1000~-2000 m海拔高程范围矿体中的流体包裹体研究表明, 在垂深2000 m深度范围内, 成矿流体除盐度有不明显的降低趋势外, 其他特征高度一致, 说明不同深度成矿流体具有一致的性质和物理化学条件。不同矿化类型和不同深度金矿成矿流体特征的总体一致性和部分差异性指示, 胶东金矿是在统一的成矿构造-流体背景下, 不同的局部环境中短时间集中爆发成矿的。
Abstract:Jiaodong area is the most important gold ore-concentrating area in China.The altered-rock-type in fractured zone, quartz-vein-type and pyrite-carbonate-vein-type gold deposits are the main mineralization types.Previous studies on the differences of mineralization conditions of different mineralization types are still lacking.Fluid inclusions of three typical gold deposits in Jiaodong are studied in this paper.The fluid inclusions of gold deposits of different mineralization types have similar petrographic characteristics in main mineralization stages.There are four types of fluid inclusions, including H2O-CO2(Ⅱ-g type), CO2-rich(ⅢCO2 type)and aqueous solution inclusions(Ⅰ-l type and Ⅱ-l type), which belong to CO2-H2O-NaCl±CH4 system.The fluid inclusions of pyrite-carbonate-vein-type gold deposit are obviously different from other types of mineralization due to higher salinity and homogenization temperature.The fluid inclusions of quartz-vein-type gold deposit are different from altered-rock-type gold deposit in fractured zone due to larger diameter and higher proportion of three-phase inclusions.The ore-forming fluid of altered-rock-type and quartz-vein-type gold deposits are belong to medium-low temperature, salinity and low density fluid as a whole, while the pyrite-carbonate-vein-type gold deposit belongs to medium-high temperature, medium-low salinity and low density fluid.The study of fluid inclusions in the ore-body at -1000 ~ -2000 m depth in the Shaling gold deposit show that the ore-forming fluids have the same characteristics except the salinity decrease in the vertical depth of 2000 m, indicating that ore-forming fluids at different depths have the same properties and physicochemical conditions.The general consistency and partial difference of the fluid characteristics of different gold deposits indicate that the Jiaodong gold deposit was formed in a short time under a unified metallogenic structure-fluid background in different local environments.
-

-
图 3 旧店金矿区地质简图[40]
Figure 3.
表 1 纱岭、旧店和辽上金矿床流体包裹体研究样品特征
Table 1. Samples schedule of fluid inclusions from Shaling, Jiudian and Liaoshang gold deposits
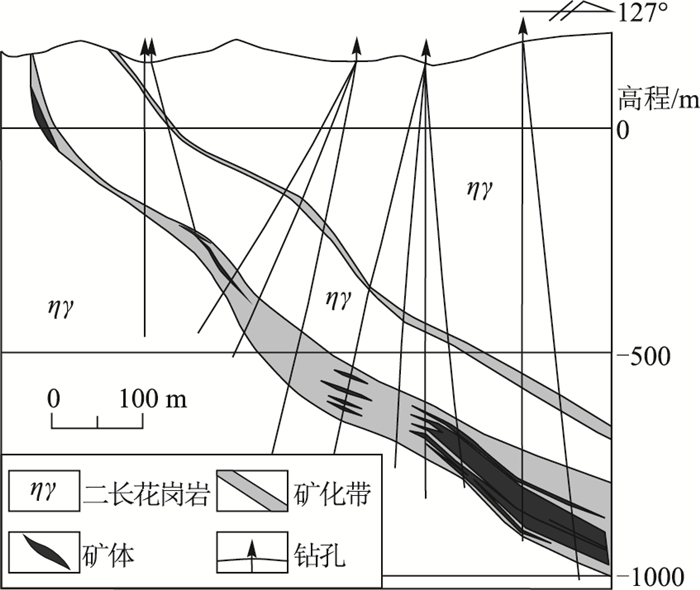
矿床名称 矿石类型 主成矿阶段 样品编号 围岩蚀变 样品描述 取样位置 纱岭 破碎蚀变岩型 金-石英-黄铁矿阶段 17S75 绢英岩化、黄铁矿化 黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩 320ZK722钻孔 旧店 石英脉型 金-石英-多金属硫化物阶段 17S32 硅化、黄铁矿化 黄铁矿化石英脉 4中段 辽上 黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型 金-黄铁矿-白云石阶段 17S24 碳酸盐化、黄铁矿化 黄铁矿化碳酸盐脉 +31 m中段 表 2 纱岭矿区不同深部流体包裹体特征
Table 2. Samples schedule of fluid inclusions at different depth from Shaling deposit
样品编号 钻孔编号 岩性描述 取样位置(垂深/m) 品位/10-6 勘探线编号 SL-1 ZK722 黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩 -1205 3.29 320 SL-18 ZK744 黄铁绢英岩化花岗质碎裂岩 -1588 5.89 320 SL-19 ZK740 黄铁绢英岩化花岗岩 -1883 14.31 320 SL-2 ZK704 黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩 -1114 1.10 256 SL-3 ZK766 黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩 -1488 3.00 256 SL-5 ZK752 黄铁绢英岩化碎裂岩 -1693 4.00 256 表 3 不同矿化类型流体包裹体岩相学特征
Table 3. Petrographic characteristics of fluid inclusions in different mineralization-type deposits
类型 亚类 成分 所占比例 单相包裹体
(Ⅰ型)纯液相包裹体(Ⅰ-l型) 盐水溶液 纱岭20%
旧店15%
辽上15%纯气相包裹体(Ⅰ-g型) 气相CO2±CH4 少量 两相包裹体
(Ⅱ型)两相包裹体(Ⅱ-l型) 盐水溶液、气态H2O 纱岭25%
旧店15%
辽上25%两相包裹体(Ⅱ-g型) 盐水溶液、气态CO2± H2O±CH4 纱岭30%
旧店40%
辽上45%三相包裹体
(Ⅲ型)富CO2三相包裹体(ⅢCO2型) 盐水溶液、液相CO2、气相CO2±CH4 纱岭25%
旧店30%
辽上15%表 4 纱岭、旧店和辽上金矿床流体包裹体测温结果
Table 4. Temperature measurement results of fluid inclusions in the main metallogenic epoch of Shaling, Jiudian and Liaoshang gold deposits
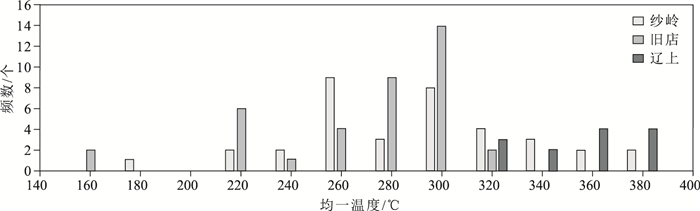
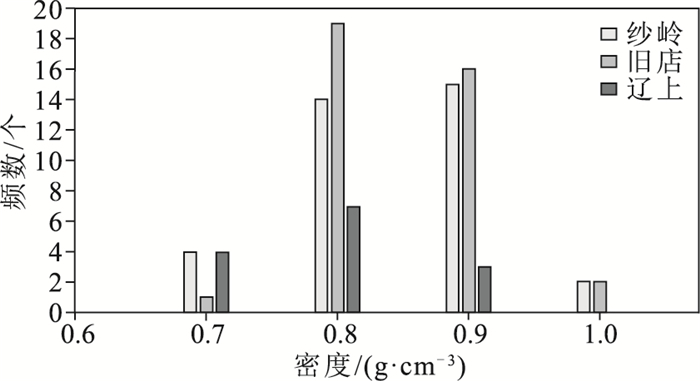
矿床名称 样品编号 包裹体类型 气相比例/% 大小/μm Tm CO2/℃ Tm,ice/℃ Tm cla/℃ Th CO2/℃ Th/℃ 盐度/%NaCl 密度/(g·cm-3) 纱岭 17S75 Ⅱ-l 15~35 5~10 -11.5~-0.7 205~367 1.22~15.47 0.59~0.93 Ⅱ-g、ⅢCO2 10~35 4~10 -57.6~-56.8 5.9~8.7 20.7~25.7 179~367 2.07~7.64 0.66~0.92 旧店 17S32 Ⅱ-g、ⅢCO2 10~45 5~17 -57.3~-56.8 4.5~9.5 28.5~31 160~320 1.63~9.69 0.75~0.93 辽上 17S24 Ⅱ-l 25 6 -3.2 317 5.26 0.73 Ⅱ-g、ⅢCO2 10~35 4~8 -62.2~-56.8 1.2~7.8 27.1~30.1 302~385 4.32~14.22 0.66~0.84 注:Tm CO2—CO2固相熔化温度;Tm, ice—冰点温度;Tm cla—水合物分解温度;Th CO2—CO2部分均一温度;Th—完全均一温度 表 5 纱岭金矿主成矿阶段流体包裹体均一温度、流体盐度及密度
Table 5. The homogenization temperature, sality and density of fluid inclusions in the main metallogenic epoch of Shaling gold deposit
样品编号 主要包裹体类型 均一温度/℃ 盐度/% NaCl 密度/(g·cm-3) 分布范围 主要集中 分布范围 主要集中 分布范围 主要集中 SL-1 Ⅱ-l型、Ⅱ-g型、ⅢCO2型 179~367 260~320 1.22~15.47 4.0~7.0 0.59~0.93 0.7~0.9 SL-18 Ⅱ-l型、Ⅱ-g型、ⅢCO2型 190~334 220~280 3.39~10.72 7.0~8.5 0.72~0.94 0.8~0.9 SL-19 Ⅱ-l型、Ⅱ-g型、ⅢCO2型 185~330 220~260 1.03~13.63 7.0~8.5 0.75~0.97 0.8~0.9 SL-2 Ⅱ-l型、Ⅱ-g型、ⅢCO2型 196~318 240~300 6.12~11.70 8.5~10 0.77~0.95 0.8~0.9 SL-3 Ⅱ-l型、Ⅱ-g型、ⅢCO2型 180~313 220~300 3.55~12.85 5.5~10 0.76~0.98 0.8~0.9 SL-5 Ⅱ-l型、Ⅱ-g型、ⅢCO2型 183~330 220~280 0.41~12.85 7.0~8.5 0.73~0.95 0.8~0.9 -
[1] 宋英昕, 宋明春, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿集区深部找矿重要进展及成矿特征[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3) : 4-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703003.htm
[2] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 等. 胶东金矿床: 基本特征和主要争议[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2018, 26(4) : 406-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201804006.htm
[3] 李国华, 丁正江, 宋明春, 等. 胶东新类型金矿——辽上黄铁矿碳酸盐脉型金矿[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(3) : 423-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201703012.htm
[4] 王志新, 焦秀美, 丁正江, 等. 胶莱盆地东北缘辽上式金矿构造控矿特征及找矿方向[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3) : 4-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703010.htm
[5] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2) : 215-236. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ202002002.htm
[6] 于学峰, 李大鹏, 田京祥, 等. 山东金矿深部勘查进展与成矿理论创新[J]. 山东国土资源, 2018, 34(5) : 1-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2018.05.001
[7] 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等. 流体包裹体[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2004: 1-486.
[8] 卢焕章. 流体不混溶性和流体包裹体[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5) : 1253-1261. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105002.htm
[9] 陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, 等. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(9) : 2085-2108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.009
[10] 张德会. 成矿作用地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015: 1-481.
[11] 周凤英, 李兆麟. 胶东台上金矿床矿物中包裹体研究[J]. 矿物学报, 1991, 11(4) : 403-412. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWXB199104014.htm
[12] 杨敏之. 金矿床围岩蚀变带地球化学——以胶东金矿床为例[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1998: 1-120.
[13] Fan H R, Zhai M G, Xie Y H, et al. Ore-forming fluids associated with granite-hosted gold mineralization at the Sanshandao deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2003, 38(6) : 739-750. doi: 10.1007/s00126-003-0368-x
[14] Fan H R, Hu F F, Yang K F, et al. Gold ore-forming fluids and metallogeny in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. 10th Biennial SGA Meeting of the Society for Geology Applied to Mineral Deposits, 2010: 219-221.
[15] Hu F F, Fan H R, Jiang X H, et al. Fluid inclusions at different depths in the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Geofluids, 2013, 13: 528-541 doi: 10.1111/gfl.12065
[16] Yang L Q, Deng J, Zhang J, et al. Decrepitation thermometry and compositions of fluid inclusions of the Damoqujia gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Implications for metallogeny and exploration[J]. Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2008, 19(4) : 378-390. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0705(08)60071-0
[17] Yang L Q, Deng J, Guo C Y, et al. Ore-Forming Fluid Characteristics of the Dayingezhuang Gold Deposit, Jiaodong Gold Province, China[J]. Resource Geology, 2009, 59(2) : 181-193. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-3928.2009.00089.x
[18] Yang L Q, Deng J, Guo L N, et al. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 585-602. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.021
[19] 卢焕章, Guha J, 方根保. 山东玲珑金矿的成矿流体特征[J]. 地球化学, 1999, 28(5) : 421-437. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1999.05.002
[20] 沈昆, 胡受奚, 孙景贵, 等. 山东招远大尹格庄金矿成矿流体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2000, 16(4) : 542-550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200004012.htm
[21] 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨进辉, 等. 胶东中生代构造体制转折过程中流体演化和金的大规模成矿[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(5) : 1317-1328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200505000.htm
[22] 毛景文, 李厚民, 王义天, 等. 地幔流体参与胶东金矿成矿作用的氢氧碳硫同位素证据[J]. 地质学报, 2005, 79(6) : 839-857. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.06.013
[23] 刘育, 杨立强, 郭林楠, 等. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床成矿流体组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2507-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409005.htm
[24] 陆丽娜, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳. 胶西北新城金矿成矿流体与矿床成因[J]. 矿床地质, 2011, 30(3) : 522-532. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.03.014
[25] 卫清, 范宏瑞, 蓝廷广, 等. 胶东寺庄金矿床成因: 流体包裹体与石英溶解度证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(4) : 1049-1062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201504013.htm
[26] 郭林楠. 胶东型金矿床成矿机理[D]. 中国地质大学(北京) 博士学位论文, 2016.
[27] 赵宏光, 孙景贵, 凌洪飞, 等. 胶东金矿成矿流体性质及其地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2005, 41(5) : 27-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2005.05.006
[28] Wen B J, Fan H R, Hu F F, et al. Fluid evolution and ore genesis of the giant Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-He-Ar isotopic compositions[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 171: 96-112. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2016.01.007
[29] 姜晓辉, 范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 等. 胶东三山岛金矿中深部成矿流体对比及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(5) : 1327-1340. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201105009.htm
[30] Li J J, Zhang P P, Li G H, et al. Formation of the Liaoshang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China: Evidence from geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Geological Journal, 2020, 55: 5903-5913. doi: 10.1002/gj.3718
[31] 宋明春, 崔书学, 伊丕厚, 等. 山东省胶西北金矿集中区深部大型-超大型金矿找矿与成矿模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010: 1-339.
[32] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9) : 2447-2467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201409001.htm
[33] Yang L Q, Guo L N, Wang Z L, et al. Timing and mechanism of gold mineralization at the Wang'ershan gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 88: 491-510. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.06.027
[34] Li S Z, Zhao G C, Santosh M, et al. Structural evolution of the southern segment of the Jiao-Liao-Ji belt, North China Craton[J]. Precam-brian Research, 2012, 200/203: 59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2012.01.007
[35] 宋明春, 李三忠, 伊丕厚, 等. 中国胶东焦家式金矿类型及其成矿理论[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(1) : 87-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201401008.htm
[36] 纪攀, 丁正江, 李国华, 等. 胶东辽上特大型金矿床地质特征[J]. 山东国土资源, 2016: 32(6) : 9-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2016.06.002
[37] 宋国政, 闫春明, 曹佳等. 胶东焦家成矿带超千米深部金矿勘查突破及意义[J]. 黄金科学技术, 2017, 25(3) : : 1-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKJ201703004.htm
[38] 宋明春, 徐军祥, 等. 大型-超大型矿床勘查方法与实践[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018: 1-397.
[39] 王燕, 卢作祥. 山东招掖金矿带焦家式金矿的矿床分带[J]. 地球科学, 1988, 13(2) : 137-146. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX198802005.htm
[40] 李波, 文志民, 段定群, 等. 旧店金矿床12号脉地质特征及深部矿体定位预测[J]. 黄金地质, 2012, 11(33) : 18-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJZZ201211006.htm
[41] 丁正江, 孙丰月, 赵财胜, 等. 山东胶莱盆地东北缘地区金矿成矿系列[J]. 矿床地质, 2010, 29(增刊) : 919-920. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ2010S1460.htm
[42] Roedder E. Fluid Inclusion, Review in Mineralogy[M]. Am. Mineralogical Society, 1984: 1-644.
[43] Touret J L R. Fluids in metamorphic rocks[J]. Lithos, 2001, 55: 1-25. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00036-0
[44] Van denKerkhof A M, Hein U F. Fluid inclusionpetrography[J]. Lithos, 2001, 55: 27-47. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00037-2
[45] 刘斌, 沈昆. 流体包裹体热力学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999: 1-290.
[46] Hall D L. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solution[J]. Econ Geology, 1988, 83: 197-202. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197
[47] Hass J L. Physical properties of the coexisting phases and thermochemical properties of the H2O component in boiling NaCl solution[J]. U S Geol. Surv. Bull., 1976, 1421A: 1-73.
[48] Bodnar R J. A method of calculating fluid inclusion volumes based on vapor bubble diameters and P-V-T-X properties of inclusion fluids[J]. Econ. Geol., 1983, 78(3) : 535-542. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.78.3.535
[49] Touret J. Equation of state of CO2: application to carbonic inclusions[J]. Bulletin Mineralogic, 1979, 102: 577-583. doi: 10.3406/bulmi.1979.7306
[50] 张海泉. 山东胶东地区焦家式金矿床中含金石英大脉流体包裹体的特征[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(5) : 456-461. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2005.05.011
[51] 宋明春, 宋英昕, 沈昆, 等. 胶东焦家深部金矿矿床地球化学特征及有关问题讨论[J]. 地球化学, 2013, 42(3) : 274-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2013.03.009
[52] Ling W L, Duan R C, Xie X J, et al. Contrasting geochemistry of the Cretaceous volcanic suites in Shandong Province and its implications for the Mesozoic lower crust delamination in the eastern North China craton[J]. Lithos, 2019, 113: 640-658.
[53] 匡永生, 庞崇进, 罗震宇, 等. 胶东青山群基性火山岩的Ar-Ar年代学和地球化学特征: 对华北克拉通破坏过程的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(4) : 1073-1091. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201204006.htm
[54] 李俊建, 罗镇宽, 刘晓阳, 等. 胶东中生代花岗岩及大型-超大型金矿床形成的地球动力学环境[J]. 矿床地质, 2005, 24(4) : 361-372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.04.002
[55] Guo L N, Deng J, Yang L Q, et al. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemical comparison of ore fluids[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103-434.
[56] 薛建玲, 庞振山, 李胜荣, 等. 胶东邓格庄金矿床成因: 地质年代学和同位素体系制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(5) : 1532-1550. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201905015.htm
[57] Saunders and Schoenly. Boiling, colloid nucleation and aggregation, and the genesis of bonanza Au-Ag ores of the Sleeper deposit, Nevada[J]. Mineral Deposita, 1995, 30: 199-210. doi: 10.1007/BF00196356
[58] Simon A C, Pettke T, Candela P A, et al. Gold partitioning in melt- vapor-brine systems[J]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta, 2005, 69: 3321-3335. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.028
[59] 李士先, 刘长春, 安郁宏, 等. 胶东金矿地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007: 129-160.
[60] 苗来成, 罗镇宽, 黄佳展, 等. 山东招掖金矿带内花岗岩类侵入体锆石SHRIMP研究及其意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1997, 27(3) : 207-213. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1997.03.002
[61] 张德会. 热液成矿作用地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020: 1-667.
-




 下载:
下载: