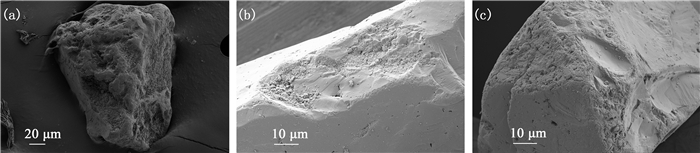
Age, sedimentary environment and tectonic setting of two lacustrine sediments of the Late Pleistocene in Qingshuihe Basin, Ningxia
-
摘要:
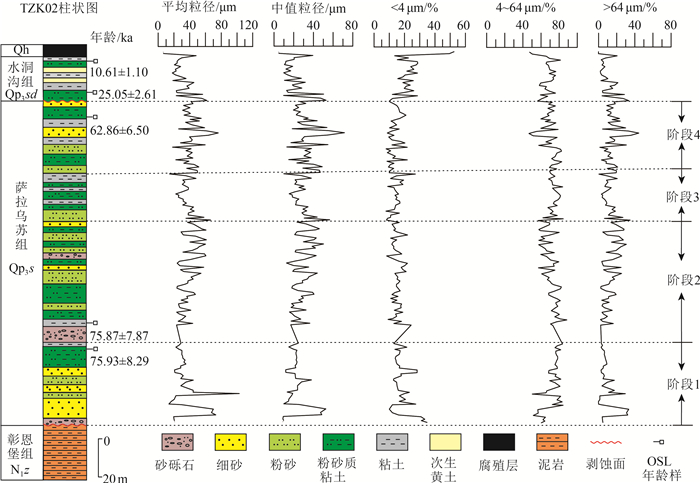
为了解宁夏清水河盆地晚更新世以来的沉积、构造演化规律,采用钻探、粒度分析、光释光测年等技术,对盆地中部发现的2期晚更新世湖相地层进行了沉积学、年代学研究。结果表明,下部湖相地层萨拉乌苏组的形成时代为76~63 ka,上部湖相地层水洞沟组形成时代为25~11 ka,二者之间存在明显的侵蚀面。根据沉积证据和粒度分析结果,将萨拉乌苏组自下而上划分为4个沉积阶段,构成了一个完整的湖进-湖退序列,代表了一期温暖湿润的气候环境;而水洞沟组为干冷环境下形成的浅湖。构造、环境对比分析表明,清水河盆地2期古大湖的形成、消亡指示该地区晚更新世经历了拉张-挤压-拉张的构造转换。两次拉张作用是萨拉乌苏湖和水洞沟湖形成的主要因素,古大湖发育的间断期存在的强烈构造隆升事件是导致萨拉乌苏湖消亡的根本原因,末次冰期MIS4和MIS2晚期的异常寒冷气候也是古湖衰退的原因之一。清水河盆地2期古湖的演化规律,为研究青藏高原周缘晚更新世古大湖形成与演化、古气候变迁及青藏高原的隆升提供了重要的证据。
Abstract:The sedimentology and chronology of the two Late Pleistocene lacustrine strata discovered in the middle of the basin were studied by means of drilling, grain size analysis and optically released luminescence dating in order to understand the sedimentary and tectonic evolution since the Late Pleistocene in Qingshuihe Basin, Ningxia. The results show that the lower part is the Salawusu Formation and the upper part is Shuidonggou Formation, which were formed at 76~63 ka and 25~11 ka, respectively. In addition, there is an obvious erosion surface between them. According to sedimentary evidence and grain size analysis results, the Salawusu Formation can be divided into four sedimentary stages from bottom to top, which constitute a complete set of lacustrine prograding and lacustrine recession sequence, representing a warm and humid climate environment. The Shuidonggou formation is a shallow lake formed in cold and dry environment. The comparative analysis of structure and environment shows that the formation and disappearance of the two ancient lakes in the late Pleistocene in Qingshuihe Basin indicate the transition of extensional-compression-extensional tectonic activity. The two extensional events were the main factors for the formation of Salawusu Lake and Shuidonggou Lake. The strong tectonic uplift event in the discontinuous period of the development of the ancient lake is the fundamental cause of the demise of the Salawusu Lake, and the abnormal cold in the late MIS 4 and MIS 2 of the last glacial period is also one of the reasons for the decline of the ancient lake. The evolution of the two ancient lakes in Qingshuihe Basin provides important evidence for the study of the formation and evolution of the ancient lakes, paleoclimate changes and uplift of the Xizang Plateau during the late Pleistocene.
-

-
表 1 光释光测年结果
Table 1. OSL dating results of samples from drill cores
实验编号 U /10-6 Th /10-6 K /% 环境剂量率/(Gy·ka-1) 测试粒径/μm 等效剂量/Gy 年龄/ka 2017-OSL-182 2.61 11.10 2.12 4.32 4~11 45.87±1.32 10.61±1.10 2017-OSL-188 2.84 11.00 1.87 4.08 4~11 102.19±2.94 25.05±2.61 2017-OSL-189 3.29 12.70 2.08 4.63 4~11 291.12±7.65 62.86±6.50 2017-OSL-192 2.99 11.80 2.25 4.60 4~11 349.35±9.70 75.87±7.87 2017-OSL-193 3.29 11.80 2.05 4.51 4~11 342.28±15.00 75.93±8.29 -
[1] 徐涛, 杨家喜, 刘源, 等. 宁夏南部晚更新世沉积物沉积特征及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4): 36-45. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201304005.htm
[2] 宁夏回族自治区地质调查院. 中国区域地质志-宁夏志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
[3] Shi W, Dong S W, Liu Y, et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the South Ningxia region, northeastern Xizang Plateau inferred from new structural investigations and fault kinematic analyses[J]. Tectonophysics, 2015, 649: 139-164. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2015.02.024
[4] 王斌, 秦向辉, 陈群策, 等. 鄂尔多斯地块西南缘宁夏固原地区原位地应力测量结果及其成因[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(7): 983-994. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20200705&flag=1
[5] Wang W T, Kirby E, Zhang P Z, et al. Tertiary basin evolution along the northeastern margin of the Xizang Plateau: Evidence for basin formation during Oligocene transtension[J]. Geological society of America Bulletin, 2013, 125(3/4): 377-400.
[6] 崔加伟, 李振宏, 刘锋, 等. 宁夏红寺堡盆地萨拉乌苏组地层时代重新厘定及意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2018, 24(2): 283-292. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX201802015.htm
[7] 陈敬安, 万国江, 唐德贵, 等. 洱海近代气候变化的沉积物粒度与同位素记录[J]. 自然科学进展, 2000, 10(3): 253-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ200003010.htm
[8] 陈敬安, 万国江, 张峰, 等. 不同时间尺度下的湖泊沉积物环境记录: 以沉积物粒度为例[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2003, 33(6): 563-568. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200306009.htm
[9] 殷志强, 秦小光, 吴金水, 等. 湖泊沉积物粒度多组分特征及其成因机制研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(2): 345-353. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2008.02.018
[10] 莱尔曼. 湖泊的化学地质学和物理学. 王苏民, 等译[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1989: 180-183.
[11] 李吉均. 中国西北地区晚更新世以来环境变迁模式[J]. 第四纪研究, 1990, 3: 197-204. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.03.001
[12] 李炳元. 青藏高原大湖期[J]. 地理学报, 2000, 55(2): 174-182. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2000.02.005
[13] 隆浩, 沈吉. 青藏高原及其邻区晚更新世高湖面事件的年代学问题——以柴达木盆地和腾格里沙漠为例[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 2015, 45: 52-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201501006.htm
[14] 张虎才, 马玉贞, 李吉均, 等. 距今42~18 ka腾格里沙漠古湖泊及古环境[J]. 科学通报, 2002, 47(24): 1847-1857. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.24.002
[15] 陈发虎, 范育新, 春喜, 等. 晚第四纪"吉兰泰-河套"古大湖的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 2008, (10): 1207-1219. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.10.013
[16] 白旸, 王乃昂, 何瑞霞, 等. 巴丹吉林沙漠湖相沉积的探地雷达图像及光释光年代学证据[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(4): 842-847. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS201104007.htm
[17] 杨劲松, 王永, 闵隆瑞, 等. 萨拉乌苏河流域第四纪地层及古环境研究综述[J]. 地质论评, 2012, 58(6): 1121-1132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2012.06.012
[18] 秦翔, 施炜, 李恒强, 等. 基于DEM地形特征因子的青藏高原东北缘宁南弧形断裂带活动性分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(2): 213-223.
[19] 靳鹤龄, 李明启, 苏志珠, 等. 萨拉乌苏河流域地层沉积时代及其反映的气候变化[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(3): 307-315. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2007.03.003
[20] 李保生, 靳鹤龄, 祝一志, 等. 萨拉乌苏河流域第四系岩石地层及其时间界限[J]. 沉积学报, 2004, 22(4): 676-682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.04.019
[21] 邵亚军. 萨拉乌苏河地区晚更新世以来的孢粉组合及其反映的古植被和古气候[J]. 中国沙漠, 1987, 7(2): 26-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS198702002.htm
[22] 孙东怀, 周杰, 蒋复初, 等. 末次间冰期黄土高原夏季风气候的初步研究[J]. 科学通报, 1995, 40(20): 1873-1873. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.20.014
[23] 孙东怀, 安芷生, 吴锡浩. 黄土高原夏季风气候格局的演化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(5): 417-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199605005.htm
[24] 孙继敏, 丁仲礼, 袁宝印, 等. 再论萨拉乌苏组的地层划分及其沉积环境[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1996, 16(1): 23-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ601.003.htm
[25] 张维岐, 焦德成, 柴炽章, 等. 宁夏香山-天景山弧形断裂带新活动特征及1709年中卫南7 1/2级地震形变带[J]. 地震地质, 1988, 10(3): 12-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ198803002.htm
[26] 张维歧, 焦德成, 柴炽章, 等. 天景山活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 2015: 93-99.
[27] 刘德成, 王旭龙, 高星, 等. 水洞沟遗址地层划分与年代测定新进展[J]. 科学通报, 2009, 54: 2879-2885. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200919008.htm
[28] 高星, 袁宝印, 裴树文, 等. 水洞沟遗址沉积-地貌演化与古人类生存环境[J]. 科学通报, 2008, 53(10): 1200-1206. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.10.012
[29] 陈晓龙, 范天来, 张复, 等. 鄂尔多斯高原周缘黄河阶地的形成与青藏高原隆升[J]. 地理科学进展, 2013, 32(4): 595-605. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKJ201304014.htm
[30] Jia L Y, Hu D G, Wu H H, et al. Yellow River terrace sequences of the Gonghe-Guide section in the northeastern Qinghai-Xizang: implications for plateau uplift[J]. Geomorphology, 2017, 295: 323-336. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2017.06.007
[31] Chlachula J. The Siberian loess record and its significance for reconstruction of Pleistocene climate change in north-central Asia[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22: 1879-1906. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00182-3
[32] Antje H L V. Global distribution of centennial-scale records for Marine Isotope Stage(MIS) 3: A database[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2002, 21: 1185-1212. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00139-1
[33] 崔之久, 陈艺鑫, 张威, 等. 中国第四纪冰期历史、特征及成因探讨[J]. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31(5): 749-764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2011.05.01
[34] 张珂, 刘开瑜, 杨景春. 宁夏清水河下游晚更新世冰卷泥的发现及意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 5(36): 714-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJDZ200005020.htm
[35] 高星, 李进增, Madsen D B, 等. 水洞沟的新年代测定及相关问题讨论[J]. 人类学学报, 2002, 21(3): 211-218. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3193.2002.03.005
[36] 雷祥义, 岳乐平. 陕西关中晚更新世黄土-古土壤序列特征及其记录的古环境变迁[J]. 地质论评, 1997, 43(5): 555-560. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1997.05.015
[37] Harris N. The elevation history of the Xizang Plateau and its implications for the Asian monsoon[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2006, 241: 4-15. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.07.009
[38] Coleman M, Hodges K. Evidence for Xizang plateau uplift before 14 Myr ago from a new minimum age for east west extension[J]. Nature, 1995, 374: 49-52. doi: 10.1038/374049a0
[39] 施雅风, 李吉均, 李炳元. 青藏高原晚新生代隆升与环境变化[M]. 广州: 广东科技出版社, 1998: 415-442.
[40] 张培震, 郑德文, 尹功明, 等. 有关青藏高原东北缘晚新生代扩展与隆升的讨论[J]. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(1): 5-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200601001.htm
[41] 张克信, 王国灿, 洪汉烈, 等. 青藏高原新生代隆升研究现状[J]. 地质通报, 2013, 32(1): 1-18. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20130101&flag=1
[42] 葛肖虹, 刘俊来, 任收麦, 等. 青藏高原隆升对中国构造-地貌形成、气候环境变迁与古人类迁徙的影响[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(3): 698-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.03.002
-




 下载:
下载: