Near surface stratigraphic structure analysis in Nansha of Guangzhou thick overburden area: based on multi method results of 2D geophysics exploration
-
摘要:
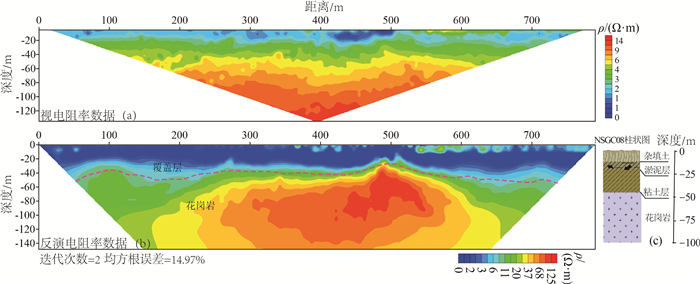
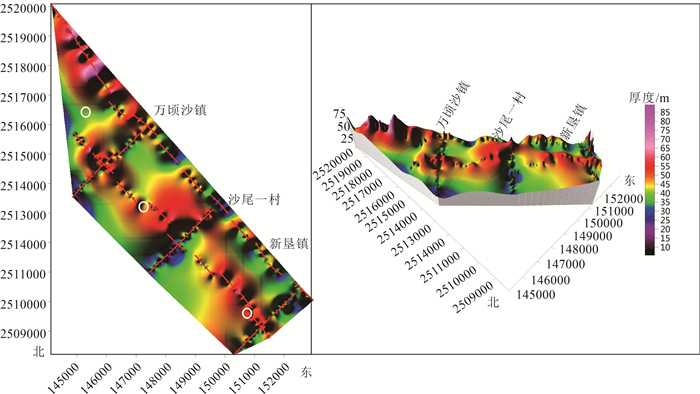
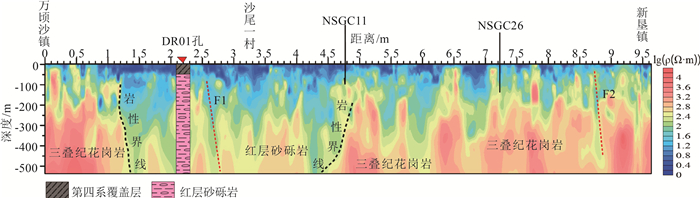
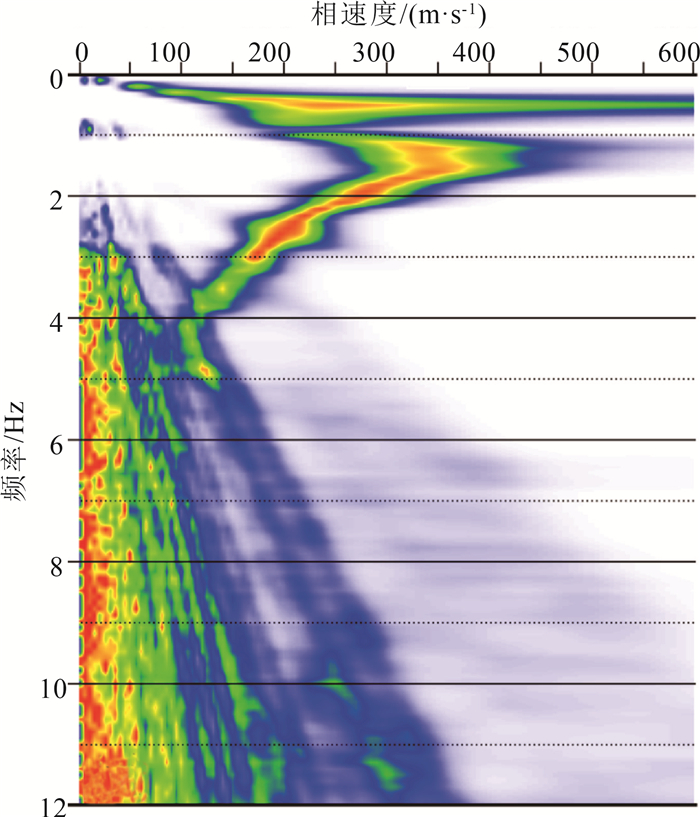
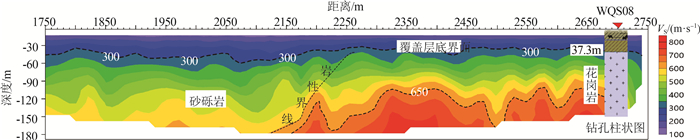
广州南沙地区的第四系覆盖层埋深、隐伏构造分布、下伏岩性特征直接影响该区重大基础工程建设。因地层结构成像地球物理方法适用性各不相同,基于该区域已有的工作基础,优选了高密度电法、微动、音频大地电磁测深(AMT)3种方法,辨识地层分布特征。基于各方法的采集参数试验、数据处理原理及处理步骤,以及探测南沙新区重点开发地区下的地下空间试验,总结了适合于探测该区域地下空间的3种物探手段。①高密度电法可较准确地分辨覆盖层与基岩分界面,反演的覆盖层深度与多处钻孔资料较吻合,可用多条剖面控制研究区的覆盖层厚度空间分布特征; ②AMT探测深度大,在试验中有效探测深度达500m,横向分辨率高,反演的电阻率断面可确定深部断裂和隐伏岩体分布; ③微动探测抗干扰能力强,对特殊场地背景可进行无损探测,解译的视S波速度分层结构,剖面反映的分层效果好。结合剖面内的钻孔资料,采用高密度电法、微动、AMT探测,可从电阻率、横波速度多参数准确地辨识地下空间地层结构特征,为城市地下空间开发提供基础资料。
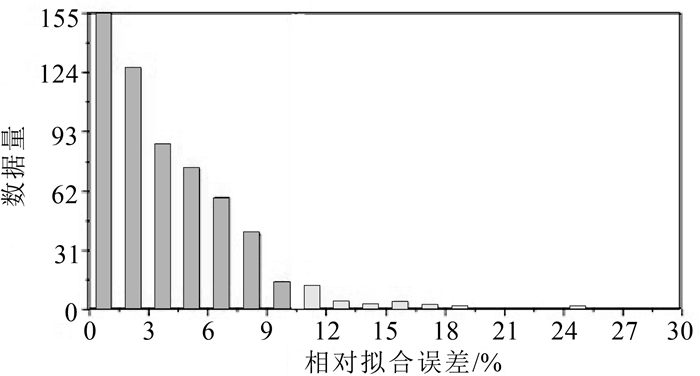
Abstract:The buried depth of Quaternary overburden,the distribution of concealed structures and the underlying rock characteristics directly affect the major infrastructure construction in Nansha,Guangzhou. Compared with the previous work methods mainly relying on drilling to find out the near surface stratum structure,this paper uses nondestructive geophysical methods to detect the near surface stratum distribution characteristics,which is more environmentally friendly,green and convenient. The applicability of geophysical methods for stratigraphic structure imaging is different,based on the existing work foundation in this area,in this paper,three methods of high density resistivity method,microtremor and audio magnetotelluric sounding(AMT) are optimized to identify the characteristics of stratigraphic distribution. Based on the acquisition parameter test,data processing principle and processing steps of each method,as well as the underground space test in the key development area of Nansha new area,the experience of three geophysical exploration methods suitable for detecting the underground space in this area is summarized. ①High density resistivity method can accurately distinguish the interface between overburden and bedrock,and the inversion overburden depth is consistent with the data of many boreholes. Multiple profiles can be used to control the spatial distribution characteristics of the thickness of overburden in the whole survey area. ②AMT has a large detection depth,in this paper,the effective detection depth is up to 500 meters and the lateral resolution is high. Inversion of resistivity section can determine the distribution of deep faults and concealed rock mass. ③Microtremor detection has strong anti-interference ability,it can be used for nondestructive detection of special site background. The interpreted apparent S-wave velocity layered structure has good layered effect of profile response. Combined with the borehole data in the profile,using high density electrical method,microtremor and AMT detection,the stratigraphic structure characteristics of underground space can be accurately identified from multiple parameters of resistivity and shear wave velocity,so as to provide basic data for the development of urban underground space.
-

-
表 1 研究区地层物性参数
Table 1. Physical property parameters of strata in the survey area
界 系 组 岩土名称 横波波速/(m·s-1) 纵波波速/(m·s-1) 密度/(g·cm-3) 新生界 第四系 杂填土 120~150 500~1200 1.5~1.7 万顷沙组 淤泥 100 1400 1.6 石牌组 细砂、中粗砂 150~240 1600~2000 1.7~1.8 古近系 莘庄村组 砂砾岩 300~500 1800 1.8 中生界 三叠系 花岗岩 300~1000 1800~3500 1.9~2.4 -
[1] Okada H. Theory of efficient array observations of microtremors with special reference to the SPAC method[J]. Exploration Geophysics, 2006, 37(1): 73-85. doi: 10.1071/EG06073
[2] Sant D A, Parvez I A, Rangarajan G, et al. Subsurface imaging of brown coal bearing tertiary sedimentaries-deccan trap interface using microtremor method[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2018, 159: 362-373. doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2018.09.008
[3] 陈松, 余绍文, 刘怀庆, 等. 高密度电法在水文地质调查中的应用研究——以江平圩幅为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(2): 849-855. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201702054.htm
[4] 陈小月. 广州市南沙区软土地面沉降特征及城市防灾减灾的建议[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护, 2018, 29(2): 17-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2018.02.004
[5] 董浩斌, 王传雷, 曾佐勋, 等. 高密度电法在信阳市燃气混气站场地隐伏断裂探测中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2003, 22(1): 101-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.01.020
[6] 董好刚, 路韬, 何万双, 等. 珠江三角洲沙湾断裂带第四纪活动性研究[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5): 1803-1813.
[7] 董好刚, 黄长生, 陈雯, 等. 珠江三角洲环境地质控制性因素及问题分析[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(2): 539-549. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.025
[8] 段波. 校正大地电磁测深中静态效应的首枝重合法[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1994, 24(4): 444-449. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ404.015.htm
[9] 方易小锁, 孟永东, 田斌, 等. 高密度电阻率法对不同电极排列的分辨率响应研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(6): 2421-2428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201906036.htm
[10] 高磊, 陈运坤, 屈尚侠, 等. 广州南沙区软土地面沉降特征及监测预警分析[J]. 人民长江, 2020, 51(增刊): 094-097. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE2020S2023.htm
[11] 顾勤平, 康清清, 许汉刚, 等. 薄覆盖层地区隐伏断层及其上断点探测的地震方法技术——以废黄河断层为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013, 56(5): 1609-1618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201305019.htm
[12] 何帅, 杨炳南, 李核良, 等. 音频大地电磁法对渝东南IV级地堑构造的识别及意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 270-276. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901031.htm
[13] 何正勤, 潘华, 胡刚, 等. 核电厂址隐伏断裂探测中的地震勘探方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(2): 326-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201002011.htm
[14] 黄兆辉, 底青云, 侯胜利. CSAMT的静态效应校正及应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2006, 21(4): 1290-1295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200604037.htm
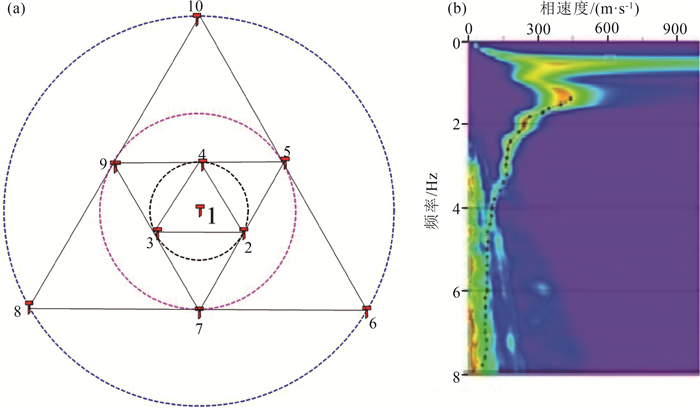
[15] 李井冈, 谢朋, 王秋良, 等. 不同台阵形式对微动探测结果的影响[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2020, 40(1): 98-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKXB202001019.htm
[16] 刘嘉麒, 刘强. 中国第四纪地层[J]. 第四纪研究, 2000, 20(2): 129-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200002002.htm
[17] 林良俊, 李亚民, 葛伟亚, 等. 中国城市地质调查总体构想与关键理论技术[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(6): 1086-1101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201706006.htm
[18] 李巧灵, 雷晓东, 李晨, 等. 微动测深法探测厚覆盖层结构-以北京城市副中心为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(4): 1635-1643. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201904045.htm
[19] 潘剑伟, 占嘉诚, 洪涛, 等. 地面核磁共振方法和高密度电阻率法联合找水[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3): 253-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803034.htm
[20] 彭建兵, 黄伟亮, 王飞永, 等. 中国城市地下空间地质结构分类与地质调查方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(3): 9-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201903005.htm
[21] 乔纪纲, 黄镇国, 黄光庆. 珠江三角洲第四系软土层DTM初步研究[J]. 佛山科学技术学院学报(自然科学版), 2002, 20(4): 47-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSDX200204011.htm
[22] 强建科, 阮百尧. 不同电阻率测深方法对旁侧不均匀体的反映[J]. 物探与化探, 2003, 27(5): 379-382. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH200305013.htm
[23] 仇根根, 方慧, 吕琴音, 等. 武夷山北段及相邻区深部电性构造与成矿分析: 基于三维大地电磁探测结果[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(4): 775-785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201904009.htm
[24] 孙勇军, 徐佩芬, 凌甦群, 等. 微动勘查方法及其研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2009, 24(1): 326-334. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ200901042.htm
[25] 徐佩芬, 李传金, 凌甦群, 等. 利用微动勘察方法探测煤矿陷落柱[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(7): 1923-1930. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200907029.htm
[26] 徐佩芬, 李世豪, 杜建国, 等. 微动探测: 地层分层和隐伏断裂构造探测的新方法[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5): 1841-1845. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201305028.htm
[27] 杨炳南, 周琦, 杜远生, 等. 音频大地电磁法对深部隐伏构造的识别与应用: 以贵州省松桃县李家湾锰矿为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(6): 26-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201506004.htm
[28] 杨利柯. 广州市南沙区软土分布特征及软基处理对策研究[D]. 华南理工大学硕士学位论文, 2016.
[29] 张若晗, 徐佩芬, 凌甦群, 等. 基于微动H/V谱比法的土石分界面探测研究——以济南中心城区为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(1): 339-350. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX202001038.htm
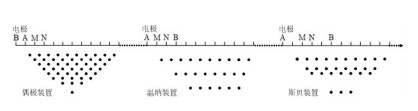
[30] 郑冰, 李柳德. 高密度电法不同装置的探测效果对比[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2015, 12(1): 33-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDQ201501007.htm
[31] 朱庆俊, 李凤哲, 王璇. AMT静态效应和对导电薄层分辨能力的正演模拟[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(2): 207-211.
-




 下载:
下载: