Age revision of the Xiala Formation in Konglong area, Nangren County, Xizang, and its constraints on the sedimentary evolution of the Gangdese belt in the Middle and Late Permian
-
摘要:
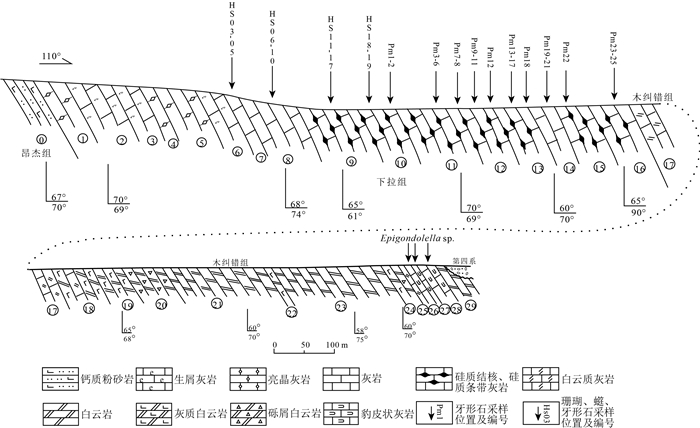
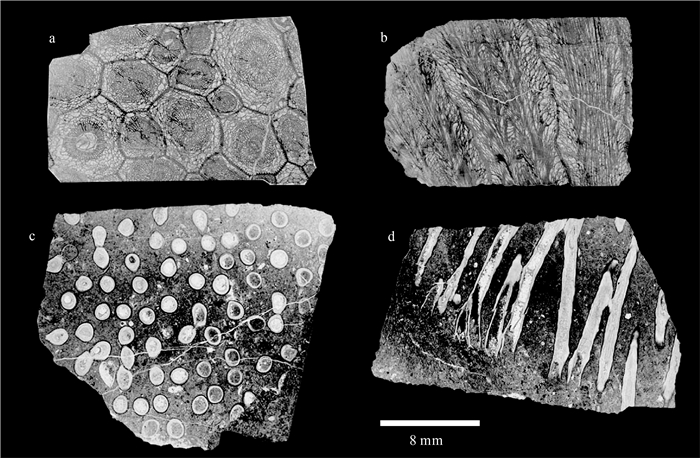
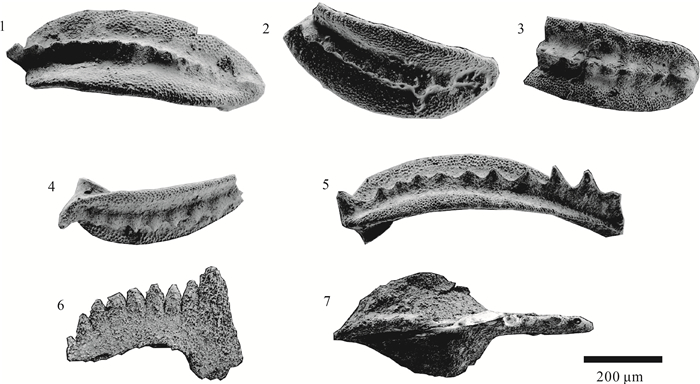
冈底斯在晚二叠世是否隆升长期存在争议。通过详细的地层和古生物工作,报道了西藏昂仁县孔隆地区发现的连续海相沉积剖面,将下拉组分为2个岩性段,下部岩性以生屑灰岩和微晶灰岩为主,产珊瑚化石Wentzelella typica和Neokueichowpora gemina,类化石Rugososchwagerina,Neoschwagerina sp.和Nankinella sp.,时代为中二叠世沃德期—卡匹敦期。上部岩性以硅质结核灰岩和结晶灰岩为主,在其中发现牙形石Neogondolella cf.leveni, Hindeodus typicalis, Clarkina orientalis,Clarkina longicuspidata等,时代为吴家坪晚期。将下拉组时代修订为中二叠世沃德期—晚二叠世吴家坪期,并推测其顶部的时代可能进入晚二叠世长兴期。认为冈底斯西部在中二叠世—晚二叠世为连续的海相沉积环境,中、晚二叠世之交不存在构造隆升事件。冈底斯西部在晚二叠世及三叠纪为古陆的观点,需要被重新考虑。
Abstract:The existence of the uplift event in the Gondese belt during Late Permian is still long debated.On the basis of the detailed stratigraphic and paleontological works, this paper reports a continuous marine sedimentary section found in Konglong area, Nangren County, Xizang.The Xiala Formation is divided into two lithologic parts.The lower part mainly consists of bioclastic limestone and microcrystalline limestone, and the coral samples Wentzelella typical, Neokueichowpora gemina and fusulinid samples Rugososchwagerina, Neoschwagerina sp., Nankinella sp. were found in this part.The age of the lower part of the Xiala Formation is the Middle Permian Wordian to Capitanian.The lower part mainly consists of nodular limestone and crystalline limestone.The conodont specimens found in this part are grouped into Neogondolella cf. leveni, Clarkina orientalis, Clarkina longicuspidata and Hindeodus typicalis, they are from the Wuchiapingian to Changhsingian.The age of the Xiala Formation was redefined to the Middle Permian Ward to Late Permian Wujiaping, and the age of the topmost part of the Xiala Formation may extend to Changhsingian stage.We conclude that the study area was a continuous marine depositional environment during the Middle Permian-Late Permian period, and there was no tectonic uplift event at the turn of the Middle Permian and the Late Permian.The view that western Gangdise was a land during the Late Permian and Triassic should be reconsidered.
-
Key words:
- the Gangdese /
- Permian /
- Xiala Formation /
- age revision /
- Xizang /
- geological survey engineering
-

-
[1] Cheng H, Liu Y M, Vervoort J D. Combined U-Pb, Lu-Hf, Sm-Nd and Ar-Ar multichronometric dating on the Bailang eclogite constrains the closure timing of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean in the Lhasa terrane, Xizang[J]. Gondwana Research, 2015, 28: 1482-1499. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.017
[2] Jin Y G, Wang Y, Henderson C, et al. The Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point(GSSP) for the base of Changhsingian Stage(Upper Permian) [J]. Episodes, 2006, 29(3) : 175-182. doi: 10.18814/epiiugs/2006/v29i3/003
[3] Ji Z S, Wu G C, Yao J X. The Gangdise during Triassic: sea rather than land[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, sup(87) : 34-35.
[4] Pan G T, Wang L Q, Li R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Xizang plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53: 3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018
[5] Qiao F, Xu H P, Zhang Y C. Changhsingian(Late Permian) foraminifers from the topmost part of the Xiala Formation in the Tsochenarea, Central Lhasa Block, Xizang and their Geological Implications[J]. Palaeoworld, 2019, 28(3) : 303-319. doi: 10.1016/j.palwor.2018.10.007
[6] Yuan D X, Zhang Y C, Shen S Z, et al. First records of wuchiapingian(Late Permian) conodonts in the Xainza Area, Lhasa block, Xizang, and their palaeobiogeographic implications[J]. Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology, 2014, 38: 546-556. doi: 10.1080/03115518.2014.920149
[7] Yin A, Harrinson M. Geologic evolustion of the Himalayan-Xizang orogeny[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2000, 28: 211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
[8] Zhu D C, Zhao Z D, Niu Y L, et al. The Lhasa terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 301: 241-255.
[9] Zhang Y C, Shen S Z, Zhang Y J. Middle permian foraminifers from the Zhabuye and Xiadong areas in the central Lhasa block and their paleobiogeographic implications[J], Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 175: 109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.01.008
[10] 陈清华, 王建平, 王绍兰, 等. 西藏措勤盆地上二叠统的发现及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 1998, 43(19) : 2111-2114. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1998.19.023
[11] 程立人, 王天武, 李才, 等. 藏北申扎地区上二叠统木纠错组的建立及皱纹珊瑚组合[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(3) : 140-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.03.006
[12] 黄韶春, 龚臣, 赵希良, 等. 西藏措勤县打加错地区硅质岩中首次发现晚三叠世放射虫化石及其意义[J]. 资源调查与环境, 2013, 34(4) : 216-220. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2013.04.002
[13] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春, 等. 西藏措勤县敌布错地区"下拉组"中发现晚三叠世诺利期高舟牙形石[J]. 地质通报, 2006, 25(1/2) : 138-141. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20060121&flag=1
[14] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春, 等. 西藏冈底斯西段措勤地区海相三叠系的划分[J]. 地质通报, 2007a, 26(8) : 947-952. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=200708154&flag=1
[15] 纪占胜, 姚建新, 武桂春. 西藏西部狮泉河地区二叠纪和三叠纪牙形石的发现及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2007b, 26(4) : 383-397. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20070464&flag=1
[16] 李俊, 刘函, 黄金元, 等. 西藏昂仁县孔隆地区木纠错组诺利期牙形石的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(8) : 2957-2963. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202008016.htm
[17] 李志宏. 湖北五峰上二叠统吴家坪组下部牙形石动物群[J]. 中国地质科学院宜昌地质矿产研究所文集, 1991, 17: 100-108. https://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGDJ199112003006.htm
[18] 梅仕龙, 金玉玕, 瓦特罗B R. 川东北二叠纪吴家坪期牙形石(刺) 序列及其世界对比[J]. 微体古生物学报, 1994, 11(2) : 121-139. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSGT402.000.htm
[19] 潘桂棠, 王立全, 朱弟成. 青藏高原区域地质调查中几个重大科学问题的思考[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(1) : 12-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.01.007
[20] 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等. 冈底斯造山带的时空构造及演化[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(3) : 521-533.
[21] 彭勃, 赵拓飞, 李宝龙, 等. 西藏拉萨地块阿翁错北二长花岗岩成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石地球化学及Hf同位素制约[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2022, 52(5) : 1594-1609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ202205011.htm
[22] 任纪舜, 肖黎薇. 1: 25万地质填图进一步揭开了青藏高原大地构造的神秘面纱[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(1) : 1-11. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040107&flag=1
[23] 沈树忠, 梅仕龙, 王向东. 巴基斯坦盐岭地区二叠纪生物地层研究的新进展[J]. 古生物学报, 2003, 42(2) : 168-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX200302001.htm
[24] 王志浩. 陕西汉中梁山地区二叠纪—早三叠世牙形刺[J]. 古生物学报, 1978, 17(2) : 213-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX197802008.htm
[25] 吴旌, 徐亚东, 安显银, 等. 冈底斯新元古代—中生代沉积盆地演化[J]. 地球科学, 2014, 39(8) : 1052-1063. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201408009.htm
[26] 武桂春, 纪占胜, 姚建新, 等. 纳木错西岸白云岩的时代修订及油浸现象发现的意义[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 12: 2867-2880. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201712020.htm
[27] 武桂春, 纪占胜, 孙倩, 等. 西藏仲巴县仁多地区早三叠世牙形石及冈底斯西部早三叠世古地理格局[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(4) : 409-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201804004.htm
[28] 夏代祥, 刘世坤. 西藏自治区岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1997.
[29] 西藏地质局综合普查大队. 西藏申扎地区古生代地层的新发现[J]. 地质论评, 1980, 26(2) : 162. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP198002011.htm
[30] 杨式溥, 范影年. 西藏石炭纪腕足动物及其古动物地理区系特征[C]//青藏高原地质文集(11). 北京: 地质出版社, 1983: 265-289.
[31] 郑有业, 许荣科, 王成源, 等. 冈底斯西缘早三叠世牙形石的发现及淌那勒组的建立[J]. 地球科学, 2007, 37(7) : 916-921. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200707006.htm
[32] 张予杰, 朱同兴, 袁东勋, 等. 西藏申扎地区二叠系下拉组中吴家坪期化石的发现及其意义[J]. 地层学杂志, 2014, 38(1) : 25-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DCXZ201401003.htm
[33] 周幼云, 江元生, 王明光. 西藏措勤—申扎二叠系敌布错组的建立及其特征[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(2) : 79-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.02.006
[34] 张克信, 赖旭龙, 童金南, 等. 全球界线层型华南浙江长兴煤山剖面牙形石序列研究进展[J]. 古生物学报, 2009, 48(3) : 474-486. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSWX200903017.htm
-



 下载:
下载: