Regional Variation and Influencing Factors of Shear Strength Parameters of Malan Loess in Lüliang Area
-
摘要:
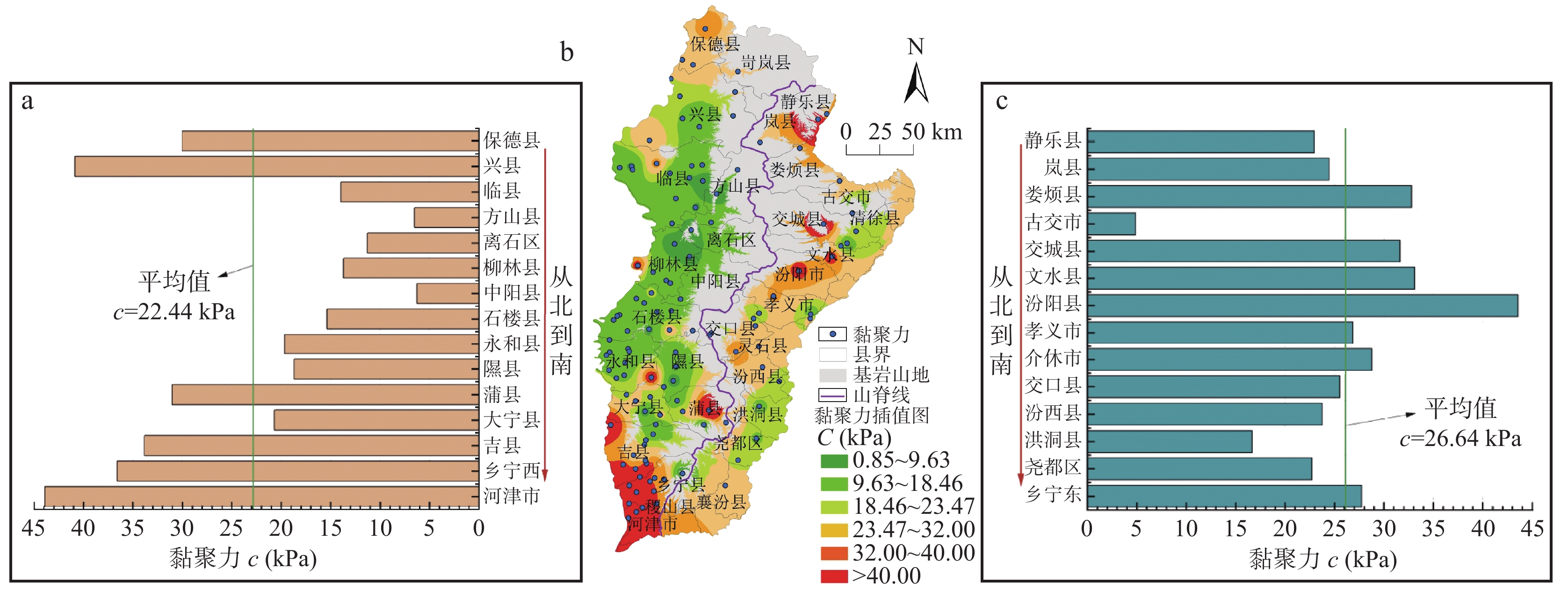
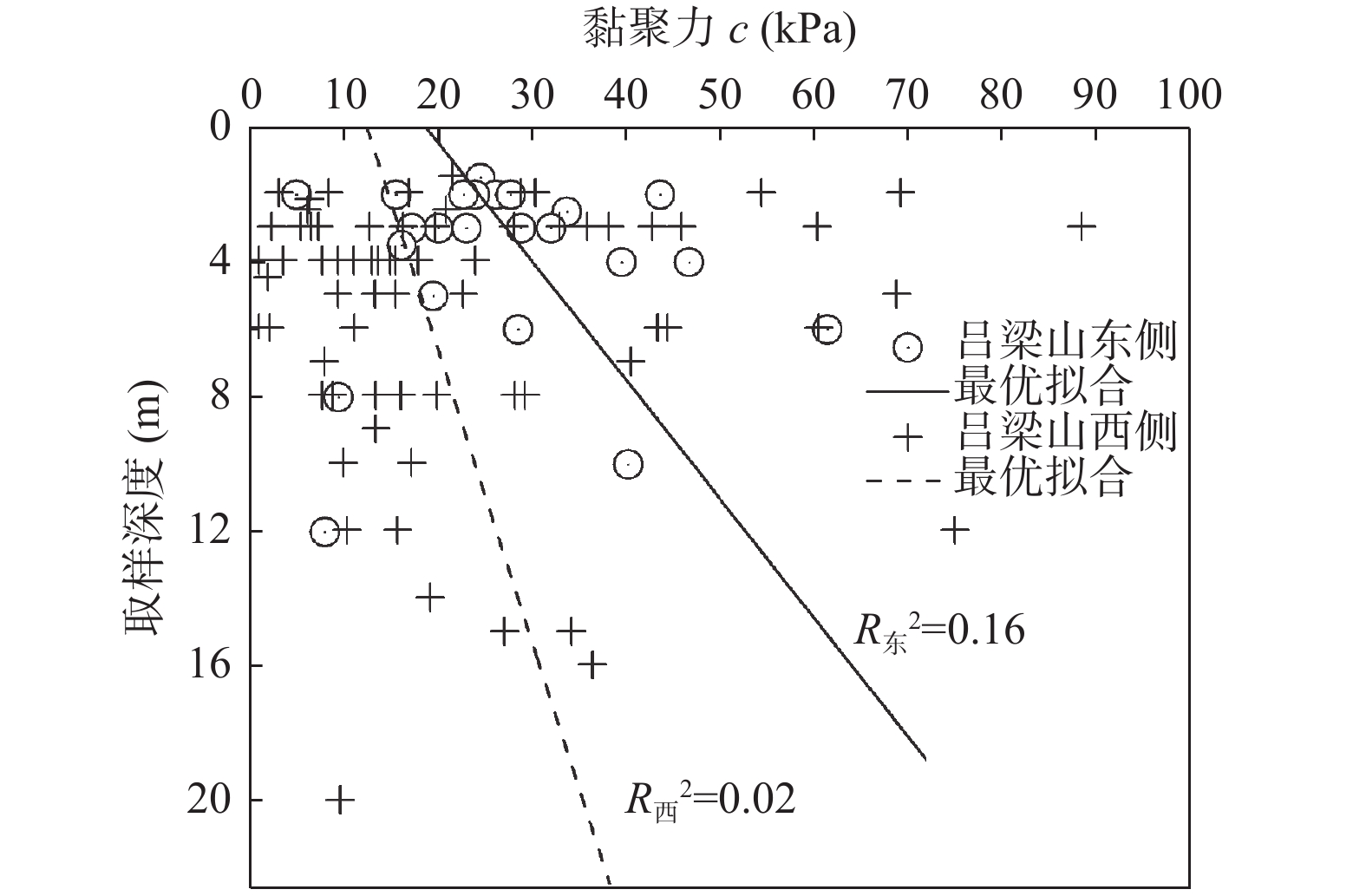
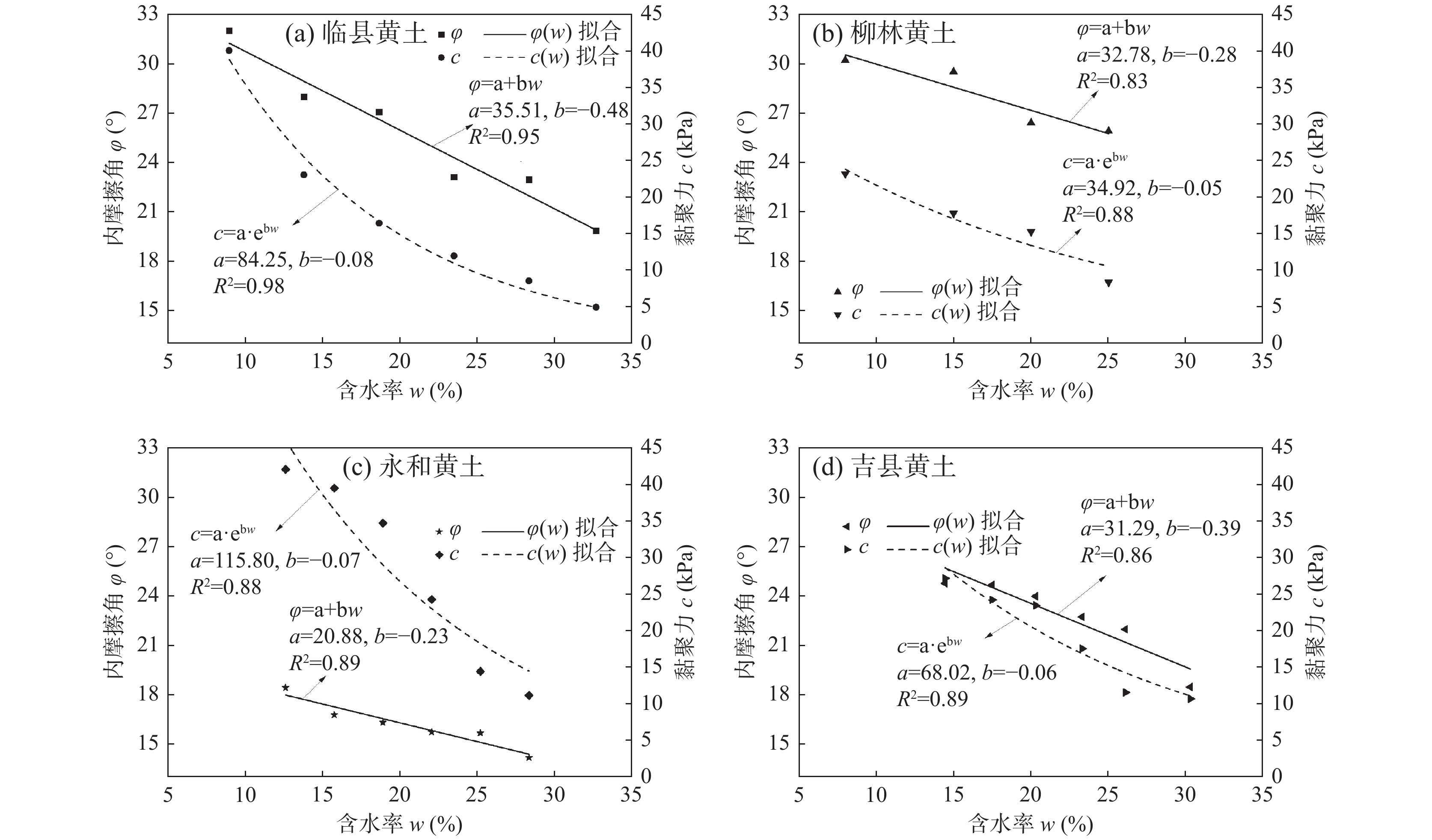
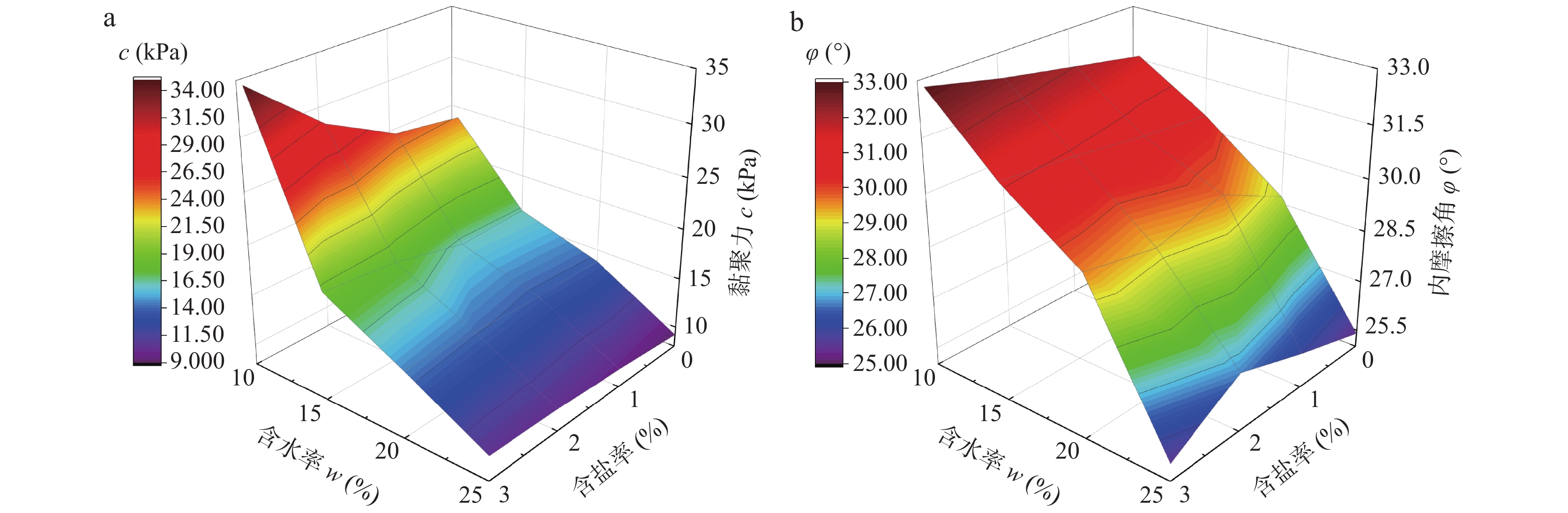
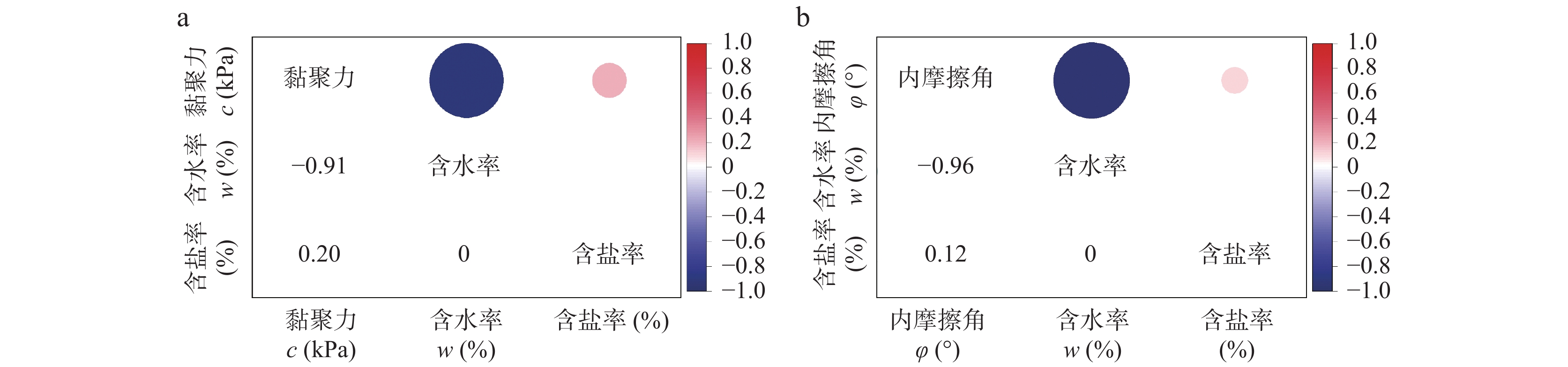
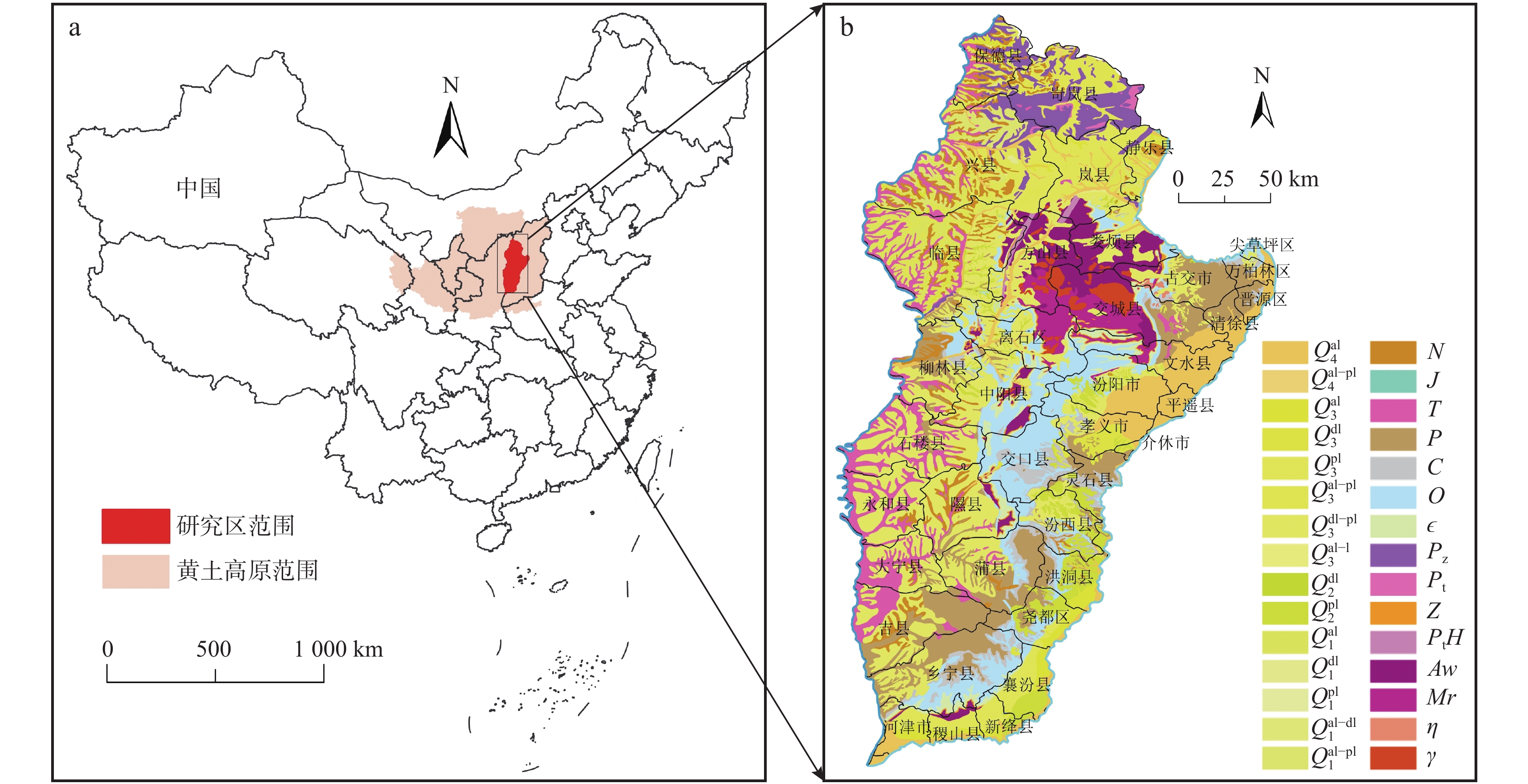
为探索吕梁山区原状马兰黄土抗剪强度参数区域上的变化规律,以该地区29个区县94个取样点的马兰黄土为研究对象,通过直剪试验及其影响因素试验,分析区内马兰黄土抗剪强度参数的空间变化规律,及其抗剪强度参数c、φ与天然含水率、天然干密度、增湿含水率、含盐率等影响因素的变化规律。结果表明:在水平地域上,抗剪强度参数c、φ表现为东高西低、南高北低;在垂直空间上,表现为从表层向下黏聚力逐渐增大、内摩擦角逐渐降低的趋势;吕梁山东、西两侧原状马兰黄土抗剪强度参数c、φ受天然含水率、天然干密度的影响较小,离散程度较大;在天然状态条件下,随着含水率的增加,黏聚力c与增湿含水率具有良好的负指数函数关系,内摩擦角φ与增湿含水率呈负线性关系;在同一含水率条件下,含盐率与抗剪强度参数c、φ具有正相关关系;与含盐率相比,增湿含水率对c、φ的影响作用更为显著。该研究可为该地区马兰黄土地层的工程建设及防灾减灾工作提供基础和必备条件。
Abstract:Taking the undisturbed Malan loess from 94 sampling points in 29 counties in Lüliang Area as the research object, the undisturbed Malan loess was subjected to direct shear tests and undisturbed loess wetting water content and salt content shear tests to reveal the loess in the area. The regional distribution of loess shear strength parameters in the area is revealed, and the influencing factors of undisturbed Malan Loess shear strength parameters are analyzed. The results show that in the horizontal area, the shear strength parameters c and φ of the undisturbed Malan loess in the Lüliang area are higher on the east side than on the west side; in the vertical space, the correlation between c and φ and the sampling depth is low. The experiment of influencing factors also reveals that c, φ have discrete distribution with natural water content and natural dry density. Under the condition of wetting water content, undisturbed Malan loess c has a good exponential function relationship with wetting water content, φ has a linear negative correlation with wetting water content, and salinity has a positive correlation with c and φ. The effect of salt content on increasing internal friction angle is more obvious than that of cohesion. Compared with salt content, moisture content has a more significant effect on c and φ. This research provides the foundation and necessary conditions for solving the geological disasters in the Loess Plateau of western Shanxi Province.
-
Key words:
- Malan loess /
- cohesion /
- internal friction angle /
- wetting water content /
- salt content /
- Lüliang area
-

-
表 1 研究区马兰黄土物理力学指标统计结果表
Table 1. Statistical results of physical and mechanical indexes of Malan loess in the study area
区域 指标 含水率w (%) 干密度ρd(g/cm3) 相对
密度Gs孔隙比e 饱和度Sr(%) 液限wL(%) 塑限wP(%) 塑性指数Ip(%) 内摩擦角φ (°) 内聚力c (kPa) 东侧 最小值 2.75 1.26 2.62 0.71 7.52 11.40 25.72 8.32 21.71 4.88 最大值 18.14 1.84 2.77 1.50 61.42 20.20 46.39 27.84 39.40 61.52 平均值 9.63 1.43 2.67 1.05 24.61 17.27 31.87 14.61 30.75 26.64 标准差 3.96 0.12 0.04 0.19 10.85 1.91 3.89 4.09 4.15 13.36 变异系数 0.4114 0.0820 0.0141 0.1839 0.4407 0.1103 0.1219 0.2799 0.1349 0.5016 西侧 最小值 2.95 1.30 2.35 0.49 2.66 3.66 25.61 6.87 2.55 0.85 最大值 19.15 1.88 2.85 1.23 51.75 28.10 40.75 34.10 44.97 88.62 平均值 9.11 1.48 2.67 1.01 25.00 17.83 31.43 13.60 27.13 22.44 标准差 2.88 0.11 0.10 0.25 8.83 4.15 2.46 5.01 9.28 19.42 变异系数 0.3161 0.0739 0.0374 0.2469 0.3531 0.2330 0.0781 0.3684 0.3419 0.8657 注:表中数据由长安大学地质工程与测绘学院实验中心测试完成(2016~2020年)。 -
曹晓毅, 李萍. 含水量对晋西黄土抗剪强度影响的试验[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2014, 42(05): 77-80+99 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2014.05.015
CAO Xiao-yi, LI Ping. Experiment study on relationship between water content and shear strength of loess in west Shanxi Province[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2014, 42(05): 77-80+99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1986.2014.05.015
董鸾花, 李萍, 夏增选, 等. 基于参数相关的Bayes估计及在黄土边坡可靠度分析中的应用[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(4): 186-193
DONG Luanhua, LI Ping, XIA Zengxuan, et al. Parameters-based Bayes Estimation and Its Application in the Reliability Analysis of Loess Slope[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(4): 186-193
范兴科, 蒋定生, 赵合理. 黄土高原浅层原状土抗剪强度浅析[J]. 土壤侵蚀与水土保持学报, 1997, (4): 70-76
FAN Xing-ke, JIANG Ding-sheng, ZHAO He-li. Analysis on shear strength of shallow undisturbed soil in Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 1997, (4): 70-76.
郭倩怡, 王友林, 谢婉丽, 等. 黄土湿陷性与土体物性指标的相关性研究[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(1): 212-221
GUO Qianyi, WANG Youlin, XIE Wanli, et al. Study on Correlation between Loess Collapsibility and Soil Physical Property Index[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(1): 212-221.
郭晓娟. 冻融循环作用下吕梁地区马兰黄土强度参数及边坡稳定性研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2020
GUO Xiaojuan. Study on Slope Stability and Strengrh Parameters of Malan Loess under Freezing and Thawing Cycle in Lvliang Area[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2020.
郭义龙. 吕梁地区黄土湿陷性与物理指标及结构性的研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020
GUO Yilong. Study On Collapsibility, Physical Index And Structure Of Loess In Luliang Area[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020.
洪勃, 杜少少, 李喜安, 等. 泾河南塬黄土的渗透特征及孕灾机制[J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(03): 75-79
HONG Bo, DU Shao-shao, LI Xi-an, et al. Infiltration Characteristics and Disaster-forming Mechanism of Loess in South Jinghe Tableland[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(03): 75-79.
巨玉文, 齐琼, 董震, 等. 山西西部地区黄土地质灾害与降雨的关联性分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2016, 25(01): 81-87
JU Yu-wen, QI Qiong, DONG Zhen, et al. Analysis of relevance between loess geological disasters and rainfalls in the western area of Shanxi Province[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2016, 25(01): 81-87.
李萍, 白健忠, GRIFFITHS D V, 等. 黄土边坡可靠度的随机有限元分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2019, 41(1): 116-126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2019.01.010
LI Ping, BAI Jian-zhong, GRIFFITHS D V, et al. Random Finite Element Analysis for the Reliability of Loess Slopes[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2019, 41(1): 116-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2019.01.010
刘畅, 张平松, 杨为民, 等. 税湾地震黄土滑坡的岩土动力特性及其稳定性评价[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(4): 176-185
LIU Chang, ZHANG Pingsong, YANG Weimin, et al. Geotechnical Dynamic Characteristics and Stability Evaluation of Loess Landslides in Shuiwan Earthquake, Tianshui, Gansu[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(4): 176-185.
刘晓京, 陈新建, 冯满, 等. 可溶盐对原状黄土强度影响的试验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(S): 652-656
LIU Xiao-Jing, CHEN Xin-jian, FENG Man, et al. Study of Influence of Soluble Salts on Original Loess Strength[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(S): 652-656.
吕萌. 山西省黄土崩塌地质灾害的现状及水敏感性分析[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2016
LV Meng. The Present Situation of the Loess Collapse of Geological Disasters in Shanxi Province and the Water Sensitivity Analysis[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2016.
落合博贵, 陈丽华. 晋西黄土力学强度特性及滑坡发生机理的研究[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 1994, 16(S4): 93-100 doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.1994.s4.001
OCHIAI Hiroki, CHEN Li-hua. Study on mechanical strength characteristics of loess and mechanism of landslide in western Shanxi[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 1994, 16(S4): 93-100. doi: 10.13332/j.1000-1522.1994.s4.001
孙萍萍, 张茂省, 冯立, 等. 黄土水敏性及其时空分布规律[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): 117-124
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, FENG Li, et al. Water Sensitivity of Loess and Its Spatial-Temporal Distribution on the Loess Plateau[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(2): 117-124
王林浩, 白晓红, 冯俊琴. 压实黄土状填土抗剪强度指标的影响因素探讨[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2010, 32(S2): 132-135
WANG Lin-hao, BAI Xiao-hong, FENG Jun-qin. Discussion on shearing strength influencing factors of compacted loess-like backfill[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2010, 32(S2): 132-135.
王硕, 刘占辉. 非饱和重塑黄土抗剪强度影响因素的试验研究[J]. 石家庄铁道大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 23(03): 86-89+93 doi: 10.13319/j.cnki.sjztddxxbzrb.2010.03.020
WANG Shuo, LIU Zhan-hui. Test Study on Influence Factor of Shear Strength of Unsaturated Remolded Loess[J]. Journal of Shijiazhuang Railway Institute(Natural Science), 2010, 23(03): 86-89+93. doi: 10.13319/j.cnki.sjztddxxbzrb.2010.03.020
谢庆勇. 吕梁机场工程黄土边坡的敏感性分析[J]. 路基工程, 2012, (01): 135-137 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2012.01.039
XIE Qing-yong. Sensitivity Analysis for Loess Slope of Lvliang Airport[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2012, (01): 135-137. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8825.2012.01.039
徐少雄, 赵景波, 杜卓群. 吕梁山地形对气候的影响分析[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020, (05): 176-9+84.
XU Shao-xiong, ZHAO Jing-bo, DU Zhuo-qun. Analysis on Influence of Lvliang Mountain Terrain on Climate[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020, (05): 176-179+84.
于慧丽, 龙建辉, 刘海松, 等. 吕梁山区黄土边坡工程地质分区及强度参数选取[J]. 工程地质学报, 2014, 22(01): 152-159 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.01.021
YU Hui-li, LONG Jian-hui, LIU Hai-song, et al. Engineering Geology Division of Loess Slope and Its Strength Parameter Selection in Lvliang Mountainous Area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(01): 152-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2014.01.021
张玲玲, 龙建辉, 邢鲜丽, 等. 冻融循环作用下吕梁地区马兰黄土性质研究[J]. 太原理工大学学报, 2021, 52(04): 557-563 doi: 10.16355/j.cnki.issn1007-9432tyut.2021.04.007
ZHANG Ling-ling, LONG Jian-hui, XING Xian-li, et al. Study on the Properties of Malan Loessin Lvliang Area Under Freeze-thaw Cycles[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University of Technology, 2021, 52(04): 557-563. doi: 10.16355/j.cnki.issn1007-9432tyut.2021.04.007
赵杰, 巨玉文. 冻融循环对永和原状黄土影响的试验研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2016, 16(28): 269-272 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.28.049
ZHAO Jie, JU Yu-wen. Test Research on Influence of Freezing and Thawing Cycle on Undisturbed Loess in Yonghe[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2016, 16(28): 269-272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2016.28.049
Cui Y, Xu C, Xu S, et al. Small-scale catastrophic landslides in loess areas of China: an example of the March 15, 2019, Zaoling landslide in Shanxi Province[J]. Landslides, 2019, 17(3): 669-676.
Juang C H, Dijkstra T, Wasowski J, et al. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 251: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.01.019
Li X A, Hong B, Wang L, et al. Microanisotropy and preferred orientation of grains and aggregates (POGA) of the Malan loess in Yan’an, China: a profile study[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 79(4): 1893-1907.
Liu J-W, Fan H-H, Song X-Y, et al. Characteristics of Shear Strength and Deformation of Compacted Q3 Loess[J]. Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, 2020,57(1):65-72.
Tang D Q, Peng J B, Wang Q Y, et al. Lvliang Typical Loess Landslide Mechanism and Characteristics[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2011, 90-93: 1313-1317. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.90-93.1313
Tang Y, Bi Y, Guo Z, et al. A Novel Method for Obtaining the Loess Structural Index from Computed Tomography Images: A Case Study from the Lvliang Mountains of the Loess Plateau (China)[J]. Land, 2021, 10(3): 291. doi: 10.3390/land10030291
Tang Y, Feng F, Guo Z, et al. Integrating Principal Component Analysis with Statistically-Based Models for Analysis of Causal Factors and Landslide Susceptibility Mapping: A Comparative Study from the Loess Plateau Area in Shanxi (China)[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 277.
Wang J, Xu Y, Ma Y, et al. Study on the Deformation and Failure Modes of Filling Slope in Loess Filling Engineering: A Case Study at a Loess Mountain Airport[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(12): 2423-2435. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1046-5
Wang J, Zhang D, Wang N, et al. Mechanisms of wetting-induced loess slope failures[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(5): 937-953. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01144-4
-



 下载:
下载: