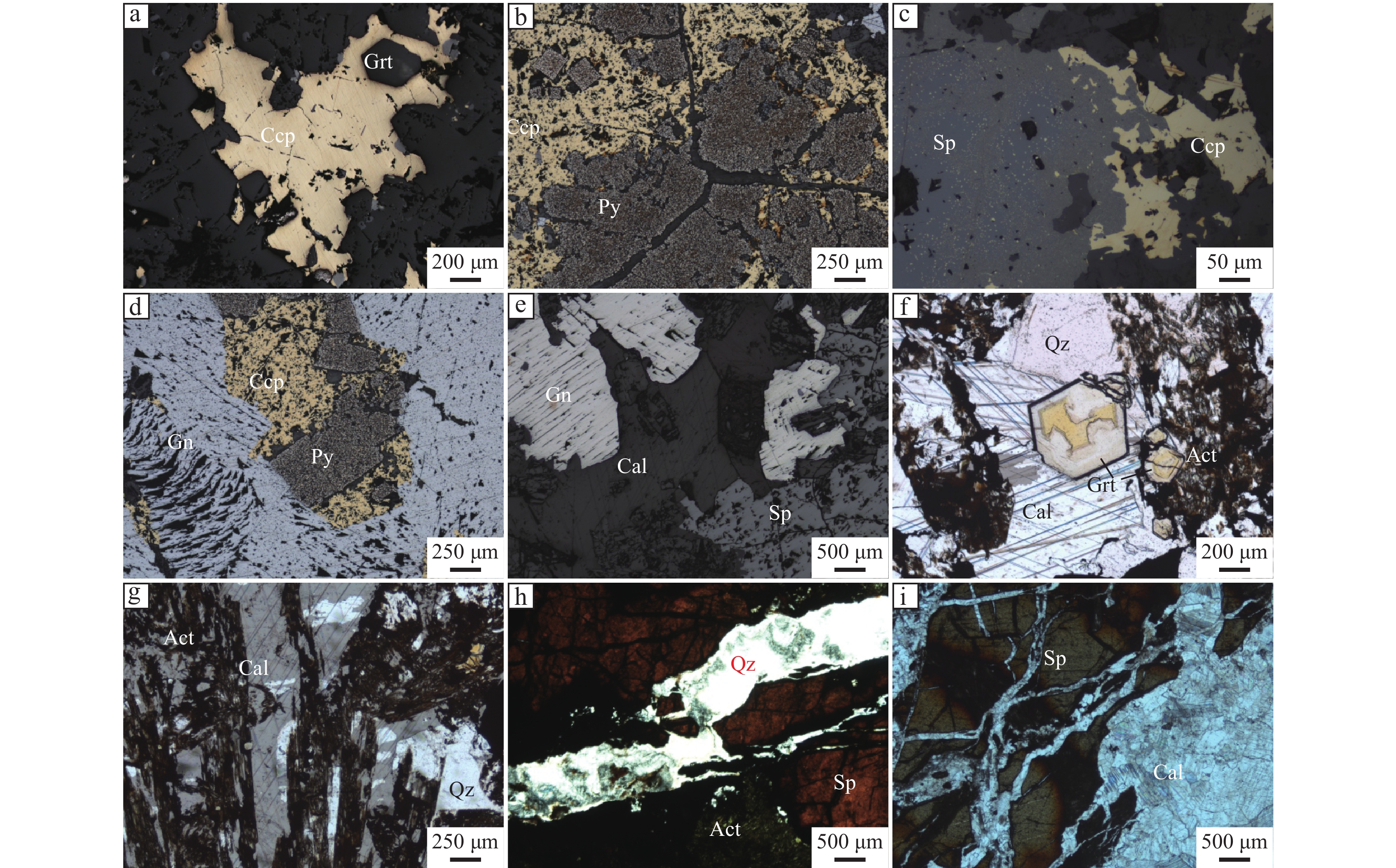
Genesis of the Arqiale Pb-Zn-Cu Deposit in the Western Tianshan, Xinjiang: Evidence from Fluid Inclusions and Isotopes
-
摘要:
阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床位于新疆西天山乌孙山脉西南缘,矿体产于下石炭统阿克沙克组灰岩中,其产状整体与地层基本一致。由于矿体具有层控特征,矿区地表和深部未见侵入岩体,导致该矿床与岩浆作用的关系尚不清楚。成矿过程大致可分为4个阶段:石榴子石–辉石阶段(I)、阳起石–黑柱石阶段(II)、石英–方解石–多金属硫化物阶段(III)和碳酸盐阶段(IV)。阶段Ⅱ阳起石与阶段Ⅲ石英、方解石和闪锌矿主要发育气液两相水包裹体(L–V型)以及少量单相液相水包裹体(L型)。阶段Ⅱ中阳起石L–V型包裹体均一温度和盐度分别为278~425 ℃和2.1~13.0 wt.% NaCl eqv,阶段Ⅲ热液矿物中L–V型包裹体均一温度和盐度分别为162~342 ℃和0.5~9.0 wt.% NaCl eqv。流体包裹体和C–H–O同位素组成特征显示,初始成矿流体主要为岩浆水,后期大气降水逐渐混入,导致成矿温度和盐度的降低以及矿物质的沉淀。矿石中硫化物的δ34S值变化范围较大(−7.57‰~1.30‰),Pb同位素具有壳幔混合特征。综合矿床地质、流体包裹体和同位素特征,推断阿尔恰勒属于远端矽卡岩型Pb–Zn–Cu矿床,其成矿物质具有深部岩浆和地层的混源特征。矿区内矿体由南侧浅部的Pb–Zn矿化逐步过渡到北侧深部的Cu±Zn矿化,暗示矿区北部深部可能存在隐伏的含矿岩体及接触带铜矿体。
Abstract:The Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit is located in the southwestern margin of the Wusun Mountain in the Western Tianshan, Xinjiang Province. The orebodies occur in the limestone of Lower Carboniferous Akeshake Formation and are generally consistent with the strata in occurrence. Considering that the orebodies are stratabound and no magmatic rocks are identified in the orefield, whether the deposit is related to magmatism remains controversial. Ore–forming process can be divided into four stages, including garnet-pyroxene stage (I), actinolite–ilvaite stage (II), quartz–calcite–polymetallic sulfide stage (III) and carbonate stage (IV). Two types of inclusions have been identified in the actinolite from stage Ⅱ and quartz, calcite and sphalerite from stage Ⅲ, including the two–phase aqueous inclusions (L–V type) and mono-phase liquid aqueous inclusions (L type). The L–V type inclusions in actinolite have homogenization temperatures and salinities ranging from 278℃ to 425 ℃ and 2.1 wt.% NaCl eqv to 13.0 wt.% NaCl eqv, respectively. By contrast, the L–V type inclusions in stage III hydrothermal minerals have homogenization temperatures and salinities ranging from 162℃ to 342 ℃ and 0.5 wt.% NaCl eqv to 9.0 wt.% NaCl eqv, respectively. Fluid inclusions and C–H–O isotopic compositions indicate that the initial ore-forming fluids were mainly source from magmatic water, with increasing input of meteoric water with time, leading to the decrease of temperatures and salinities, as well as the precipitation of ore-forming materials. The δ34S rations of sulfides in the ores have a wide range (−7.57‰~1.30‰), and the Pb isotopic compositions have the characteristics of crust–mantle mixing. Combined evidence from geology, fluid inclusions and S–Pb–C–H–O isotopes indicate that the Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit belongs to the distal skarn type deposit, with the ore–forming materials sourcing partially from the magmatic rocks at depth and partially from the strata. The orebodies in the ore field gradually transit from Pb–Zn orebodies at shallow in the south to Cu ± Zn orebodies at depth in the north, implying that the concealed causative intrusions and skarn Cu orebodies in the contact zone may occur in the deep part in the north of the mining area.
-
Key words:
- fluid inclusions /
- S–Pb isotope /
- Distal skarn deposit /
- Arqiale /
- Western Tianshan
-

-
图 1 中亚造山带构造简图(a、伊犁地块位置简图(b)和伊什基里克成矿带构造简图(c)(据魏虎等,2013;胡耀华,2016;Gao et al.,2009;Dai et al.,2019修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿区地质图(据Dai et al.,2019)
Figure 2.
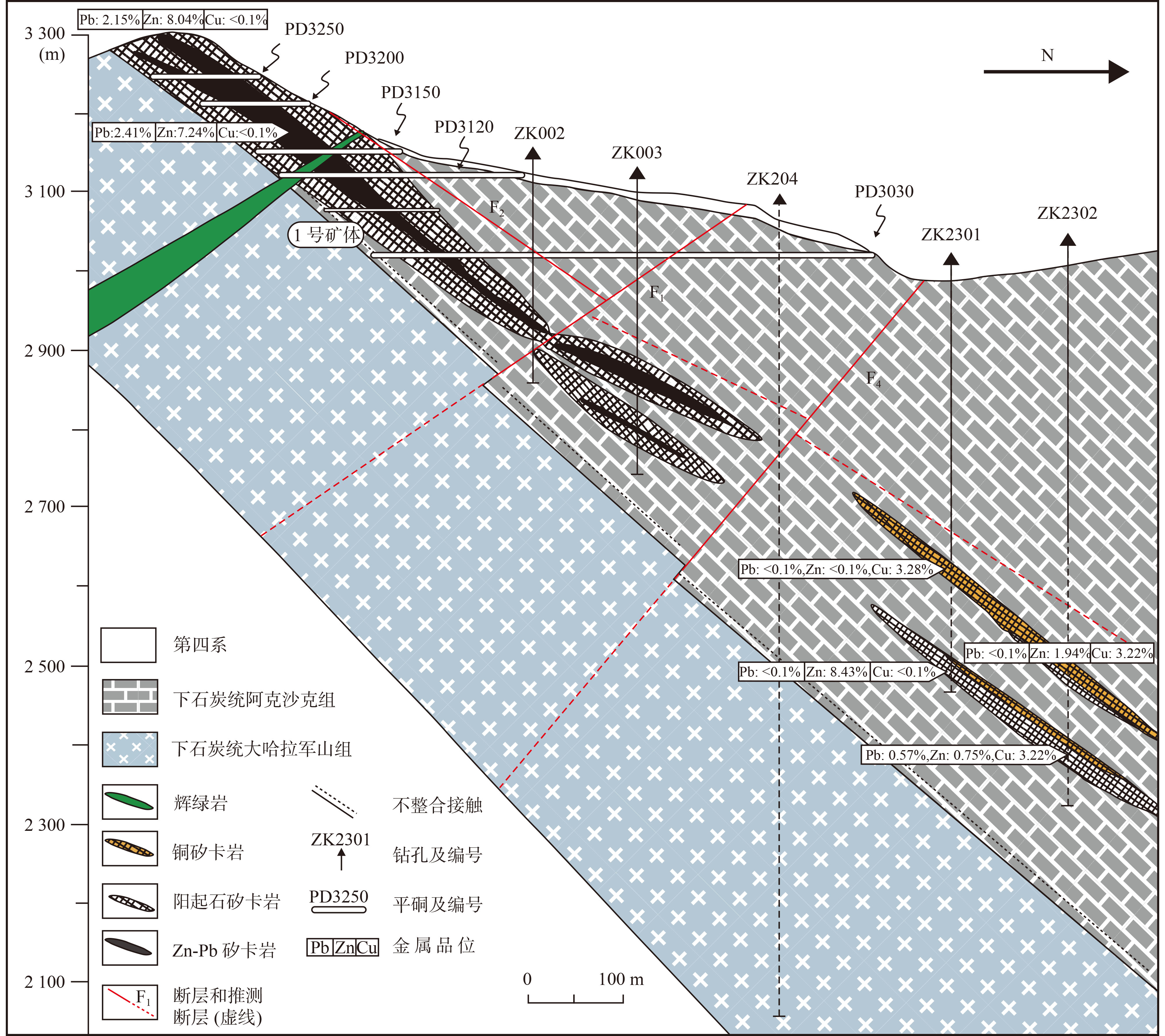
图 3 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床3号勘探线剖面图(据Dai et al.,2019修改)
Figure 3.
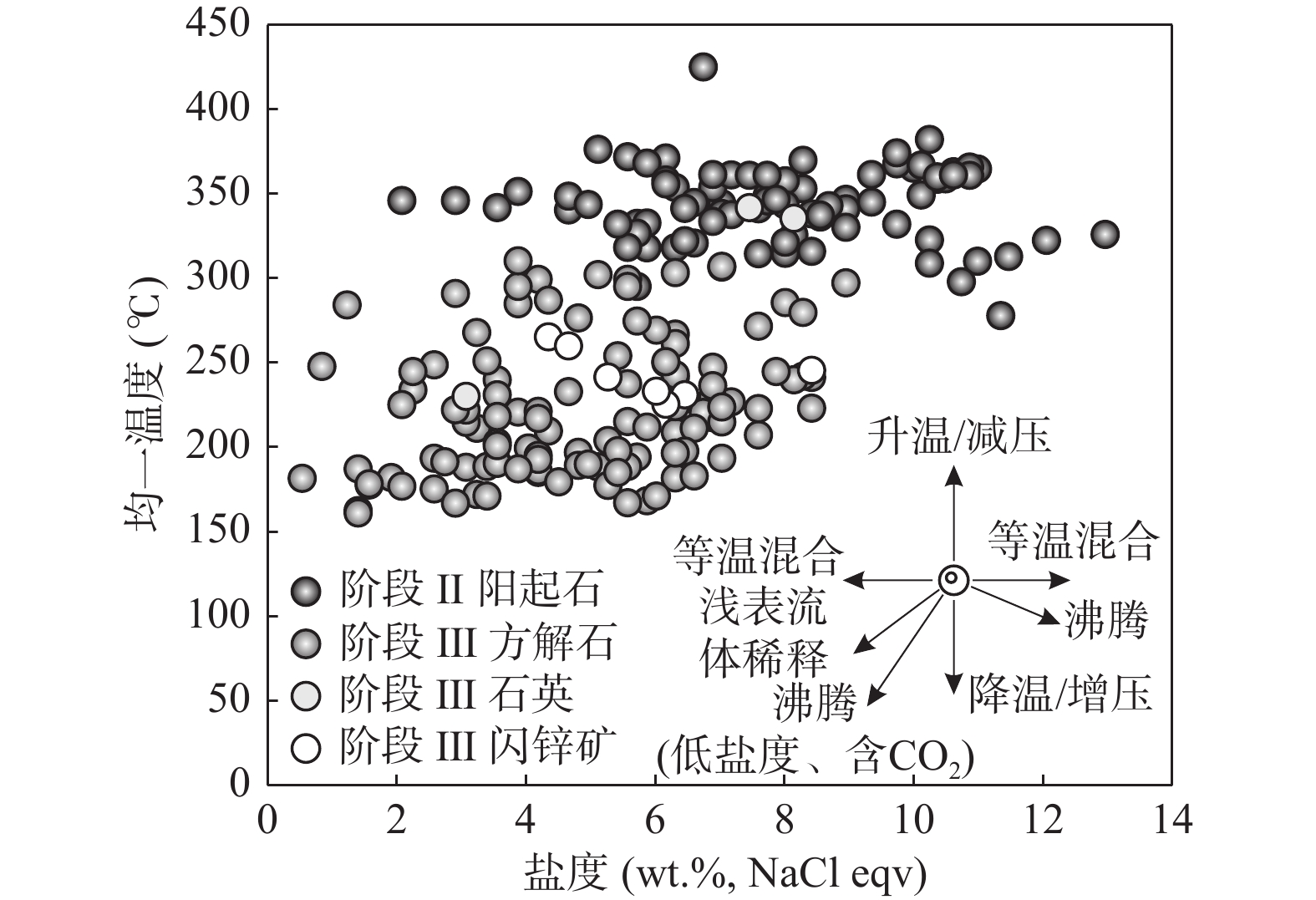
图 8 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床流体包裹体均一温度–盐度散点图(据Wilkinson,2001)
Figure 8.
图 9 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床成矿流体H–O同位素图解(底图a据Taylor,1974)和方解石–灰岩–大理岩的C–O同位素图解(底图b据Hedenquist et al.,1994)
Figure 9.
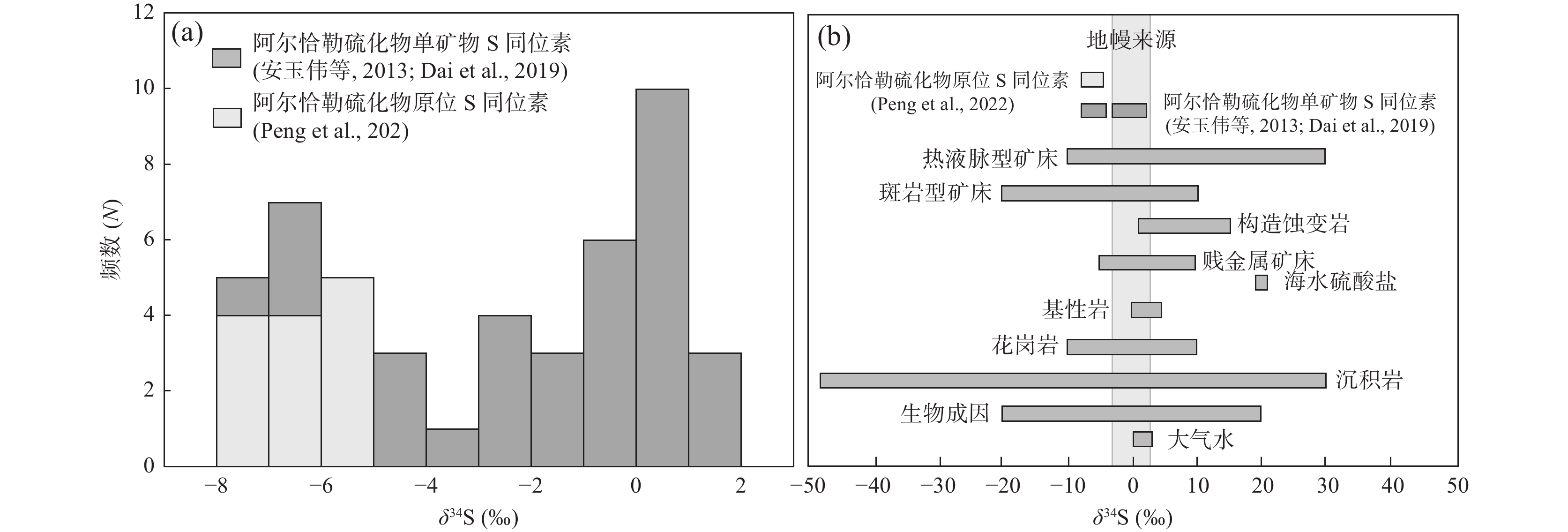
图 10 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿S同位素直方图(a)和其他S同位素储库对比(b)(其他储库据Hoefs,2009)
Figure 10.
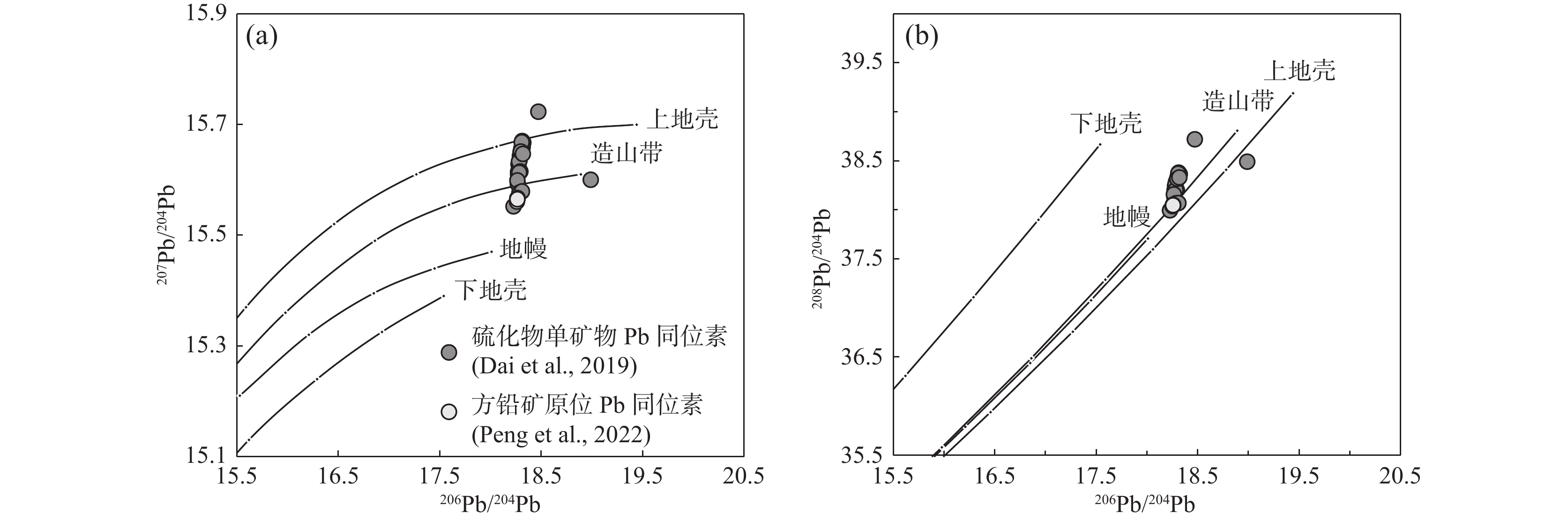
图 11 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床矿石中硫化物Pb同位素模式图(底图据Zartman et al.,1981修改)
Figure 11.
表 1 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床气液两相水流体包裹体显微测温结果
Table 1. Temperature measurement results of two–phase aqueous inclusions from the Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit
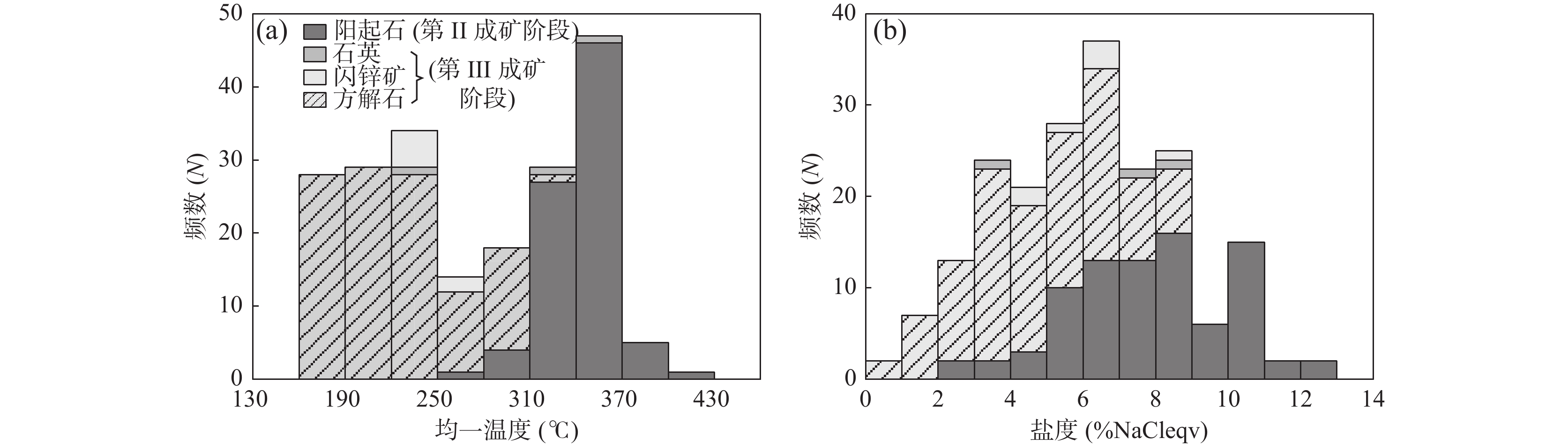
成矿阶段 宿主矿物 包裹体类型(数量) 冰点温度(℃) 均一温度(℃) 盐度(wt.% NaCl eqv) 密度(g/m³) 阶段Ⅱ 阳起石 L–V(84) −9.1~−1.2 278~425 2.1~13.0 0.6~0.9 阶段Ⅲ 闪锌矿 L–V(7) −5.4~−2.6 226~265 4.3~8.4 0.8~0.9 方解石 L–V(111) −5.8~−0.3 162~311 0.5~9.0 0.7~1.0 石英 L–V(3) −5.4~1.8 230~342 3.1~8.1 0.7~0.9 表 2 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床热液方解石、灰岩和大理岩C–O同位素组成
Table 2. C–O isotopic compositions of hydrothermal calcite, limestone and marble from the Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit
样号 样品名称 δ13CV-PDB(‰) δ18OV-PDB(‰) δ18OV-SMOW(‰) 资料来源 AE-46 方解石 0.4 −20.6 9.6 本文 AE-75-2 方解石 −0.6 −16.8 13.6 AE-95 方解石 −2.8 −26.6 3.5 AE-107 含化石灰岩 2.1 −13.3 17.1 AE-108 含化石灰岩 2.5 −19.8 10.5 AE-109 含化石灰岩 2.1 −14.6 15.9 AE-42 不含化石灰岩 0.5 −23.5 6.7 AE-50 不含化石灰岩 0.6 −20.7 9.5 AE-54 不含化石灰岩 0.3 −14.3 16.2 AE-58 大理岩 0.8 −22.1 8.1 AE-61 大理岩 −0.3 −20.8 9.5 AE-63 大理岩 2.0 −22.3 7.9 A6 方解石 0.4 −26.0 4.1 Dai et al.,2019 A10 方解石 0.9 −18.3 12.0 A19 方解石 0.1 −25.8 4.3 A20 方解石 −0.2 −26.4 3.7 A22 方解石 0.3 −22.3 7.9 A32 方解石 0.1 −25.4 4.7 A39 方解石 0.2 −24.8 5.4 A46 方解石 0.6 −19.5 10.8 A47 方解石 0.5 −19.7 10.6 A48 方解石 0.8 −19.2 11.1 A49 方解石 0.7 −18.6 11.7 A50 方解石 0.9 −19.0 11.3 A51 方解石 0.6 −19.0 11.3 A55 方解石 0.1 −25.5 4.6 A61 方解石 −0.9 −26.7 3.4 A73 方解石 1.1 −23.8 6.4 AE-75-1 方解石 −0.9 −25.4 4.8 Peng et al.,2022 AE-84 方解石 −1.9 −22.5 7.7 AE-112 方解石 −2.4 −26.1 4.0 AE-115 方解石 −1.0 −24.0 6.2 AE-120 方解石 −2.6 −26.9 3.2 表 3 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床矿石中硫化物S同位素组成
Table 3. Sulfur isotopic compositions of sulfides in the ores from the Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit
样品号 矿物 δ34SV-CDT(‰) 资料来源 样品号 矿物 δ34SV-CDT(‰) 资料来源 AECcp-1 黄铜矿 −5.63 Peng et al.,2022 A31-2 闪锌矿 0.70 Dai et al.,2019 AECcp-2 黄铜矿 −5.81 A45 闪锌矿 −7.00 AECcp-3 黄铜矿 −5.56 A52 闪锌矿 −4.10 AECcp-4 黄铜矿 −6.18 A53 闪锌矿 −6.80 AESpy-1 闪锌矿 −6.43 A54 闪锌矿 0.70 AESpy-2 闪锌矿 −6.03 A60-2 闪锌矿 −6.70 AESpy-3 闪锌矿 −5.92 A63 闪锌矿 0.70 AESpy-4 闪锌矿 −7.12 A82 闪锌矿 1.10 AEPy-1 黄铁矿 −7.13 A56 黄铜矿 −0.10 AEPy-2 黄铁矿 −7.57 A69 黄铜矿 1.20 安玉伟,2013 AEPy-3 黄铁矿 −7.47 A105 黄铜矿 0.90 AEPy-4 黄铁矿 −6.66 A91 黄铜矿 −2.60 A1-1 方铅矿 −0.50 Dai et al.,2019 A113 黄铁矿 −0.40 A2 方铅矿 −1.10 A112 黄铁矿 0.60 A7-1 方铅矿 −1.10 A115 黄铁矿 0.20 A9-1 方铅矿 −0.90 AQL01 方铅矿 1.30 A23 方铅矿 −0.80 AQL02 方铅矿 −4.70 A31-1 方铅矿 −1.50 AQL07 方铅矿 −3.70 A60-1 方铅矿 −7.10 AQL16 方铅矿 −2.60 A1-2 闪锌矿 0.90 AQL01 闪锌矿 −4.20 A4 闪锌矿 0.80 AQL02 闪锌矿 −0.10 A7-2 闪锌矿 0.50 AQL07 闪锌矿 −2.50 A9-2 闪锌矿 0.80 AQL16 闪锌矿 −2.20 表 4 阿尔恰勒Pb–Zn–Cu矿床矿石中硫化物Pb同位素组成
Table 4. Pb isotope compositions of sulfides of ores from the Arqiale Pb–Zn–Cu deposit
样号 矿物 206Pb/204Pb 207Pb/204Pb 208Pb/204Pb μ ω Th/U 来源 AE-81-13 方铅矿 18.267 15.567 38.065 9.41 35.46 3.65 Peng et al., 2022 AE-81-14 方铅矿 18.266 15.566 38.059 9.41 35.42 3.64 AE-81-15 方铅矿 18.262 15.561 38.049 9.40 35.36 3.64 AE-81-16 方铅矿 18.269 15.567 38.062 9.41 35.43 3.64 AE-81-17 方铅矿 18.266 15.565 38.058 9.41 35.41 3.64 A2 方铅矿 18.290 15.643 38.294 9.56 36.98 3.74 Dai et al.,2019 A7-1 方铅矿 18.277 15.628 38.242 9.53 36.70 3.73 A9-1 方铅矿 18.298 15.650 38.314 9.57 37.09 3.75 A23 方铅矿 18.305 15.656 38.338 9.59 37.21 3.76 A31-1 方铅矿 18.227 15.552 37.996 9.39 35.25 3.63 A60-1 方铅矿 18.318 15.659 38.348 9.59 37.21 3.76 A1-1 闪锌矿 18.286 15.635 38.282 9.55 36.88 3.74 A1-2 闪锌矿 18.272 15.614 38.201 9.51 36.43 3.71 A4 闪锌矿 18.282 15.633 38.262 9.54 36.80 3.73 A7-2 闪锌矿 18.300 15.651 38.319 9.58 37.11 3.75 A31-2 闪锌矿 18.273 15.610 38.190 9.50 36.34 3.70 A45 闪锌矿 18.295 15.615 38.204 9.51 36.32 3.70 A52 闪锌矿 18.270 15.592 38.134 9.46 35.96 3.68 A53 闪锌矿 18.285 15.613 38.204 9.50 36.36 3.70 A54 闪锌矿 18.266 15.599 38.159 9.48 36.14 3.69 A60-2 闪锌矿 18.324 15.667 38.365 9.61 37.32 3.76 A63 闪锌矿 18.990 15.600 38.491 9.41 33.79 3.48 A82 闪锌矿 18.473 15.723 38.720 9.70 38.49 3.84 A56 黄铜矿 18.314 15.670 38.381 9.61 37.47 3.77 A69 黄铜矿 18.287 15.577 38.068 9.43 35.45 3.64 A105 黄铜矿 18.308 15.668 38.372 9.61 37.45 3.77 A91 黄铜矿 18.300 15.651 38.317 9.58 37.10 3.75 A113 黄铁矿 21.518 15.946 38.182 10.79 28.83 2.59 A112 黄铁矿 18.319 15.647 38.331 9.57 37.02 3.74 A115 黄铁矿 18.310 15.579 38.070 9.43 35.36 3.63 -
安玉伟, 莫江平, 王夏杰. 新疆阿尔恰勒铅锌矿成因和找矿前景[J]. 矿床地质, 2012, S1: 247-248 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2012.s1.126
AN Yuwei, MO Jiangping, WANG Xiajie. Genesis and prospecting prospect of the Arqiale Pb-Zn deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2012, S1: 247-248. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2012.s1.126
安玉伟, 王夏杰. 新疆阿尔恰勒铅锌矿成矿模式[J]. 矿产与地质, 2013, 27(2): 102-105.
AN Yuwei and WANG Xiajie. Metallogenic model of Aerqiale Pb-Zn deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2013, 27(2): 102-105.
代俊峰. 新疆天山晚古生代岛弧环境矽卡岩型铅锌成矿作用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019, 1-170.
DAI Junfeng. Skarn type lead-zinc mineralization in Late Paleozoic island arc environment, Xinjiang, Tianshan[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosiences (Beijing), 2019, 1-170.
邓明国, 陈伟, 王学武, 等. 滇西芦子园远程矽卡岩Pb-Zn-Fe(Cu)多金属矿床流体包裹体初探及矿床成因探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(05): 1239-1257
DENG Mingguo, CHEN Wei, WANG Xuewu, et al. Fluid inclusion and ore genesis of the Luziyuan distal skarn Pb-Zn-Fe ( -Cu) poly-metallic deposit, West Yunnan, SW China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(05): 1239-1257.
高俊. 西南天山板块构造及造山运动动力学[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 1993, 1-90.
GAO Jun. Plate tectonics and geodynamics of orogenesis of the Southwest Tianshan Mountains[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1993, 1-90.
高俊, 钱青, 龙灵利, 等. 西天山的增生造山过程[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28: 1804-1816
GAO Jun, QIAN Qing, LONG Lingli et al. Accretionary orogenic process of Western Tianshan, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China. 2009, 28(12): 1804-1816
胡耀华. 西天山伊什基里克西段矿床成因类型及找矿方向探讨[J]. 新疆有色金属, 2016, S1: 1-4 doi: 10.16206/j.cnki.65-1136/tg.2016.s.001
HU Yaohua. Discussion on genetic types and prospecting direction of the Western Section of Yishjilik deposit in western Tianshan mountains[J]. Xinjiang Non-ferrous Metals, 2016, S1: 1-4. doi: 10.16206/j.cnki.65-1136/tg.2016.s.001
李俊明. 新疆昭苏县阿尔恰勒铅锌矿床成矿流体研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2019
LI Junming. Study on Ore-Forming Fluids of the Arqiale Lead-Zinc Deposit in Zhaosu, Xinjiang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019.
李永军, 庞振甲, 栾新东, 等. 西天山特克斯达坂花岗岩基的解体及钼找矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(4): 435-440.
LI Yongjun, PANG Zhenjia, LUAN Xindong, et al. Distribution of Tekesidaban granitic batholith and its significance for Mo prospecting, Western Tianshan Mountains[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2007, 31(4): 435-440.
李永军, 辜平阳, 庞振甲, 等. 西天山特克斯达坂库勒萨依序列埃达克岩的确立及钼找矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(12): 2713-2719.
LI Yongjun, Gu Pingyang, PANG Zhenjia, et al. Identification of the adakite rocks of Kulesayi series and its significance of Mo prospecting in the Tekesidaban of western Tianshan[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(12): 2713-2719.
李永胜, 张帮禄, 公凡影, 等. 湖南康家湾大型隐伏铅锌矿床成因探讨: 流体包裹体、氢氧同位素及硫同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(06): 1847-1866 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.06.13
LI Yongsheng, ZHANG Banglu, GONG Fanying, et al. Genesis of the giant Kangjiawan lead-zinc ore deposit in Hunan Province: Evidences from fluid inclusion, H-O and S isotope[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(6): 1847–1866. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.06.13
刘斌, 沈昆. 流体包裹体热力学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999, 1-289
LIU Bin and SHEN Kun. Fluid inclusion thermophysics[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999, 1-289.
牛佳, 郑义, 周永章, 等. 桂中盘龙铅锌矿流体包裹体特征及其对钦杭成矿带热水喷流-改造成矿作用的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(03): 753-766
NIU Jia, ZHENG Yi, ZHOU Yongzhang, et al. A fluid inclusions study of the Panlong lead-zinc deposit and its implication for genesis[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(3): 753-766
牛旭宁. 西藏蒙亚啊铅锌矿床成因与找矿方向研究[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
NIU Xuning. The genesis and prospecting direction of the Mengyaa Pb-Zn Deposit in Xizang[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing). 2019.
秦来勇, 莫江平, 徐庆鸿, 等. 新疆阿尔恰勒铅锌矿床地质特征及找矿潜力分析. 矿产勘查, 2012, 3: 319-324
QIN Laiyong, MO Jiangping, XU Qinghong, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting potential analysis of Arqiale Pb-Zn deposit in Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2012, 3: 319-324.
魏虎, 张英宁. 2013. 新疆伊什基里克西段铜多金属成矿地质条件及找矿方向[J]. 新疆地质, 31: 172-178.
WEI Hu, ZHANG Yingning. Ore-Forming Conditions and Exploration Direction of Copper-Polymetallic Deposits in the West Yishijilike Region, Xinjian[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2013, 31: 172-178.
温春齐, 多吉. 矿床研究方法[M]. 成都: 四川科学技术出版社, 2009, 1–230.
WEN Chunqi and DUO Ji. Methods of deposit research[M]. Chengdu: Sichuan Science and Technology Press, 2009, 1–230.
张海坤, 胡鹏 , 曹亮, 等. 印度尼西亚戴里Sedex型铅锌矿集区成矿流体特征及成矿物质来源: 流体包裹体及同位素地球化学证据[J]. 地质科技通报. 2020, 39(03): 170–177.
ZHANG Haikun, HU Peng, CAO Liang, et al. Characteristics of mineralization fluids and mineralization material sources of the Sedex type Dairi Pb-Zn ore concentration area in Indonesia: Evidence from fluid inclusions and isotopic geochemistry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 170–177.
朱烨. 新疆昭苏县阿尔恰勒铅锌矿地质特征及找矿预测[D]. 桂林:桂林理工大学, 2018.
ZHU Ye. Geological Features and Ore-Prospecting Prediction of Aerqiale Lead-Zinc Deposit in Zhaosu County, Xinjiang[D]. Guilin: Guilin University of Technology, 2018.
朱志敏, 赵振华, 熊小林. 西天山特克斯北中酸性火成岩地球化学特征及成因意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(7): 2145-2157.
ZHU Zhimin, ZHAO Zhenhua, XIONG Xiaolin. Geochemistry and geodynamics of intermediate-acid igneous rocks in northern Tekesi[J]. Western Tianshan Mountains. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28 (7): 2145–2157.
Andrew A, Godwin CI, Sinclair AJ. Mixing line isochrons: A new interpretation of galena lead isotope data from southeastern British Columbia[J]. Economic Geology, 1984, 79: (5): 919-932.
Boveiri Konari M, Rastad E, Peter J M. A sub-seafloor hydrothermal syn-sedimentary to early diagenetic origin for the Gushfil Zn-Pb-(Ag-Ba) deposit, south Esfahan[J]. Neues Jahrbuch Fur Mineralogie-Abhandlungen, 2017, 194(1), 61–90. doi: 10.1127/njma/2016/0041
Bao Z H, Cai K D, Sun M, et al. Continental crust melting induced by subduction initiation of the South Tianshan Ocean: Insight from the Latest Devonian granitic magmatism in the southern Yili Block, NW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2018, 153: 100–117.
Chaussidon M and Lorand J P. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): An ion microprobe study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(10): 2835-2846 doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90018-G
Chen F C, Deng J, Shu Q H, et al. Geology, fluid inclusion and stable isotopes (O, S) of the Hetaoping distal skarn Zn-Pb deposit, northern Baoshan block, SW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 90: 913~927. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.013
Claypool G E, Holser W T, Kaplan L R, et al. The age curves of sulfur and oxygen isotopes in marine sulfate and their mutual interpretation[J]. Chemical Geology, 1980, 28: 199-260. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(80)90047-9
Dai J F, Xue C J, Chi G X, et al. Geological, geochronological and geochemical characteristics and genesis of the Arqiale skarn Zn-Pb deposit, Western Tianshan, Northwest China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 106: 79~96. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.01.020
Deer W A, Howie R A, Zussman J. An Introduction to the Rock Forming Minerals[J]. 3rd Edition. Longman, London: London the Mineralogical Society, 2013, 150~151.
Doe B R, Zartman R E. Plumbotectonics: The phanerozoic. In: Barnes H L (ed. ). Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1979, 22–70.
Ehya F. The Paleozoic Ozbak-Kuh carbonate-hosted Pb-Zn deposit of East Central Iran: isotope (C, O, S, Pb) geochemistry and ore genesis[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2014, 108, 123–136. doi: 10.1007/s00710-013-0279-1
Gao J, Long L, Klemd R, et al. Tectonic evolution of the South Tianshan Orogen and adjacent regions, NW China: Geochemical and age constraints of granitoid rocks[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2009, 98: 1221-1238. doi: 10.1007/s00531-008-0370-8
Glorie S, De Grave J, Buslov M M, et al. Formation and Palaeozoic evolution of the Gorny-Altai-Mongolia Suture Zone (South Siberia): Zircon U/Pb Constraints on the igneous record[J]. Gondwana Research, 2011, 20: 465-484. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.03.003
Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Economic Geology, 1988, 83(1): 197-202 doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.83.1.197
Hedenquist J W, Lowenstern J B. The role of magmas in the formation of hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Nature, 1994, 370: 519. doi: 10.1038/370519a0
Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry. sixth edition ed[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2009, 285.
Hoefs J. Stable isotope geochemistry[M]. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. 1997.
Leach D L, Bradley D C, Huston D, et al. Sediment-Hosted Lead-Zinc Deposits in Earth History[J]. Economic Geology, 2010, 105 (3), 593–625. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.105.3.593
Leach D L, Marsh E, Emsbo P, et al. Nature of hydrothermal fluids at the shale-hosted Red Dog Zn-Pb-Ag deposits, Brooks Range, Alaska [J]. Economic Geology, 2004, 99: 1449-1480 doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.99.7.1449
Leach D L, Sangster D F, Kelley K D, et al. Sediment-hosted lead-zinc deposits: A global perspective[J]. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 2005, 561-607.
Long L, Gao J, Klemd R, et al. Geochemical and geochronological studies of granitoid rocks from the Western Tianshan Orogen: implications for continental growth in the Southwestern Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos, 2011, 126 (3-4): 321–340.
Lin L, Qian Q, Wang Y, et al. Gabbroic pluton in the Dahalajunshan Formation volcanic rocks from northern Zhaosu, Western Tianshan: Age, geochemistry and geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31, 1749-1760.
Massawe R J, Lentz D R. Petrogenesis and U–Pb (titanite) age of Cu–Ag skarn mineralization in the McKenzie Gulch area, northern New Brunswick, Canada[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 232, 106902 doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2021.106902
Meinert L D. , Dipple G M, Nicolesu W. World skarn deposits. In: Hedenquist JW, Thompson JFH, Goldfarb RJ, and Richards JP (eds.)[J]. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 2005, 299–336.
Ohmoto H, Rye R O. Isotopes of sulfur and carbon. In: Barnes H L[J]. Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Deposits, 1979, 2nd Edition. New York: John Wiley and Sons: 509–611.
Ohmoto H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67: 551-578. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.67.5.551
Peng Y W, Zou H, Leon B, et al. A newly identified Permian distal skarn deposit in the Western Tianshan, China: New evidence from geology, garnet U-Pb geochronology and S-Pb-C-H-O isotopes of the Arqiale Pb Zn Cu deposit[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 143: 104754. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2022.104754
Rollinson H R. Using Geochemical Data: Evaluation, Presentation, Interpretation. Harlow[M]. Longman Scientific and Technical Press, 1993, 306–308.
Rajabi A, Rastad E, Canet C, et al. The Early Cambrian Chahmir shalehosted Zn–Pb deposit, Central Iran: an example of vent-proximal SEDEX mineralization[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2015, 50, 571–590. doi: 10.1007/s00126-014-0556-x
Samson I M, Russell M J. Genesis of the Silvermines zinc lead-barite deposit, Ireland: Fluid inclusion and stable isotope evidence[J]. Economic Geology, 1987, 82: 371-394. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.82.2.371
Serguei G S, Sergey G K, Svetlana S D, et al. Geology, mineralization, fluid inclusion, and stable isotope characteristics of the Sinyukhinskoe Cu-Au skarn deposit, Russian Altai, SW Siberia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 112: 103039. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103039
Sheppard S M F. Characterization and isotopic variations in natural waters[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy, 1986, 16: 165-183.
Shu Q H, Chang Z S, Mavrogenes J. Fluid compositions reveal fluid nature, metal deposition mechanisms, and mineralization potential: an example at the Haobugao Zn–Pb skarn[J]. China Geology, 2021, 49.
Sun G T, Zhou J X, Luo K, et al. New insights into the hydrothermal evolution of skarn deposits: A case study of the Dongzhongla Pb-Zn deposit in Xizang, SW China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 191, 104215. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104215
Su W B, Cai K D, Sun M, et al. Carboniferous volcanic rocks associated with back-arc extension in the western Chinese Tianshan, NW China: Insight from temporal-spatial character, petrogenesis and tectonic significance[J]. Lithos, 2018, 310-311: 241–254.
Taylor H P. The Application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition[J]. Economic Geology, 1974, 69: 843–883.
Vezzoni S, Dini A, Sergio Rocchi S. Reverse telescoping in a distal skarn system(Campiglia Marittima, Italy)[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 77, 176–193. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.03.001
Wang C M, Deng J, Carranza EJM et al. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 56: 327-351. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.004
Wilkinson JJ. Fluid inclusions in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Lithos, 2001, 55(1-4): 229~272. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(00)00047-5
Xiao W, Windley B F, Allen M B, et al. Paleozoic Multiple Accretionary and Collisional Tectonics of the Chinese Tianshan Orogenic Collage[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013, 23: 1316-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.01.012
Xu R, Lia W C, Deng M G, et al. Genesis of the superlarge Luziyuan Zn-Pb-Fe(-Cu) distal skarn deposit in western Yunnan (SW China): Insights from ore geology and C-H-O-S isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 109: 944-955.
Xu X Y, Wang H L, Li P, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of Paleozoic intrusions in the Nalati(Narati) area In western Tianshan, Xinjiang, China: implications for Paleozoic tectonic evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 72: 33-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.023
Yu J, Li N, Qi N, et al. Carboniferous-Permian Tectonic Transition Envisaged in Two Magmatic Episodes at the Kuruer Cu-Au Deposit, Western Tianshan (NW China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 153: 395-411. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.07.048
Zartman RE and Doe BR. Plumbotectonics: The model[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 175(1-2): 135-162.
Zaw K, Peters S G, Cromie P, et al. Nature, diversity of deposit types and metallogenic relations of South China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 31, 3-47. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.10.006
Zhao C T, Sun J G, Chu X L, et al. Metallogeny of the Ergu Fe-Zn polymetallic deposit, central Lesser Xing’an Range, NE China: Evidence from skarn mineralogy, fluid inclusions and H-O-S-Pb isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 135 104227.
Zhu X Y, Zhen S M, Cheng X Y, et al. The sulfur-lead isotope geochemistry of MVT Pb-Zn deposits in Devonian system in South China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2017, 91, 213–231.
-




 下载:
下载: