Trace Element Geochemical Characteristics of Gold−Bearing Pyrite from the Shijia Gold Deposit in Penglai, Shandong Province and Its Constraints on Ore−Forming Fluids
-
摘要:
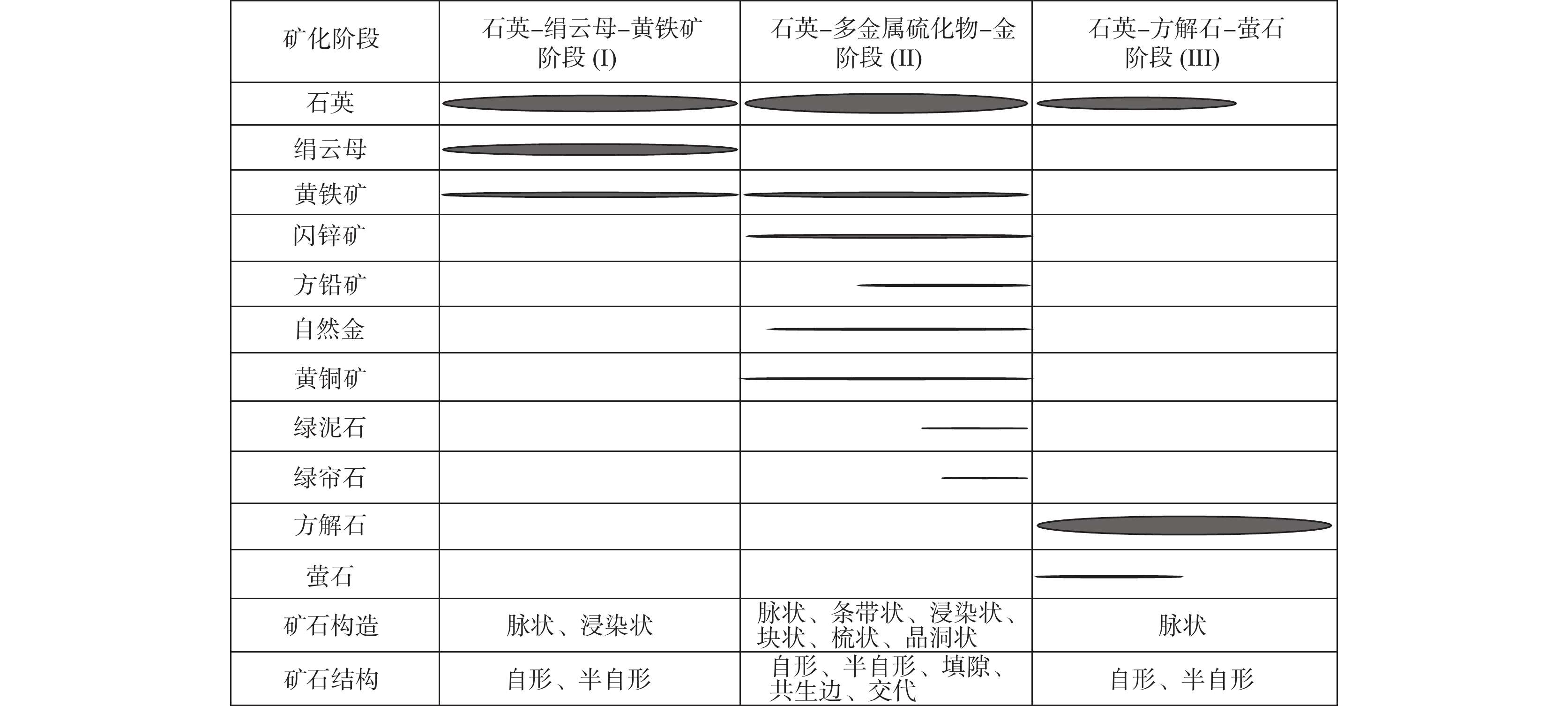
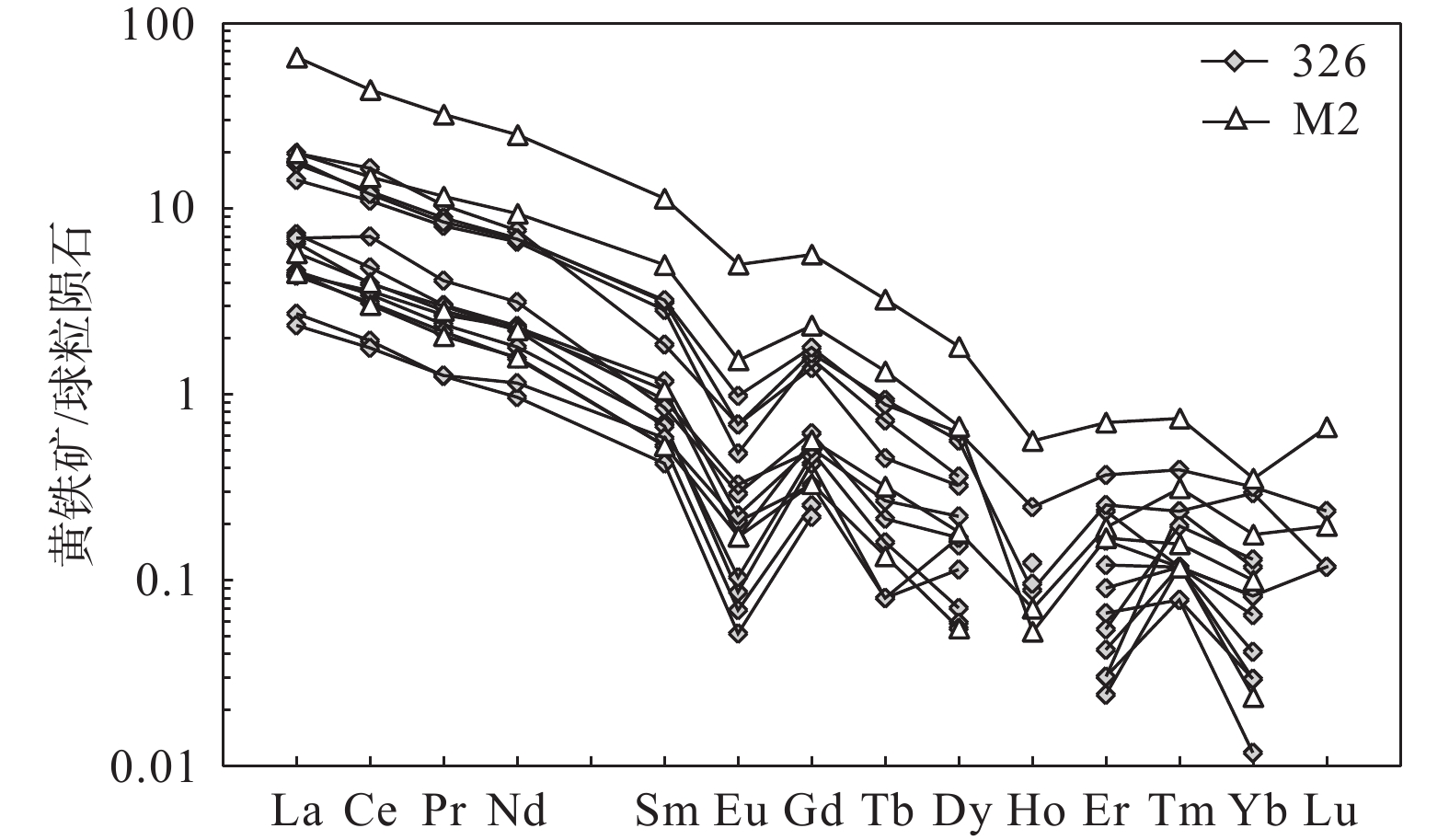
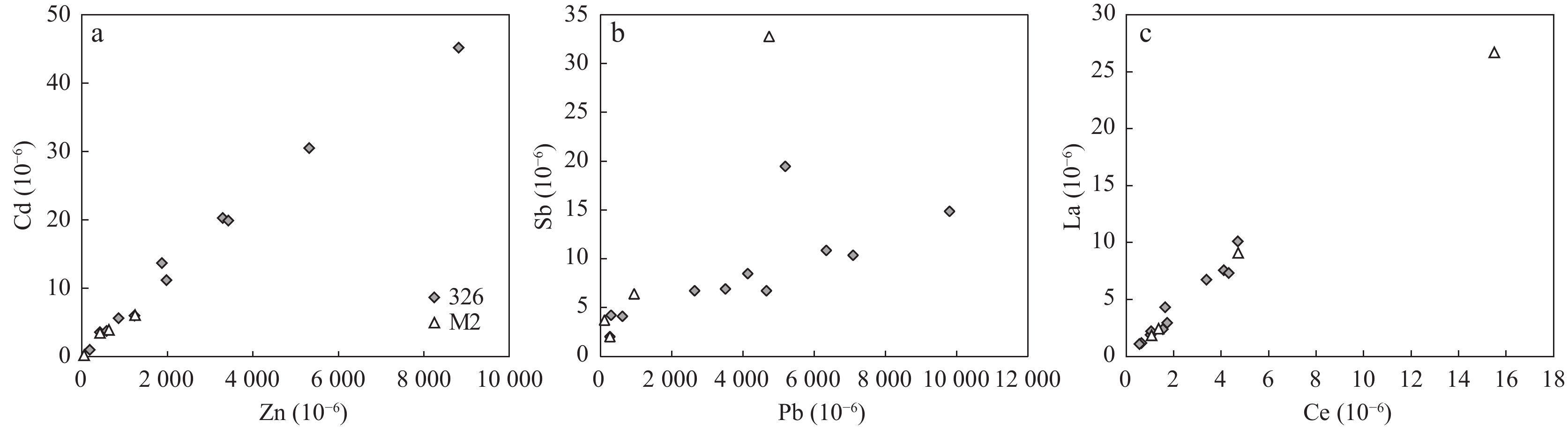
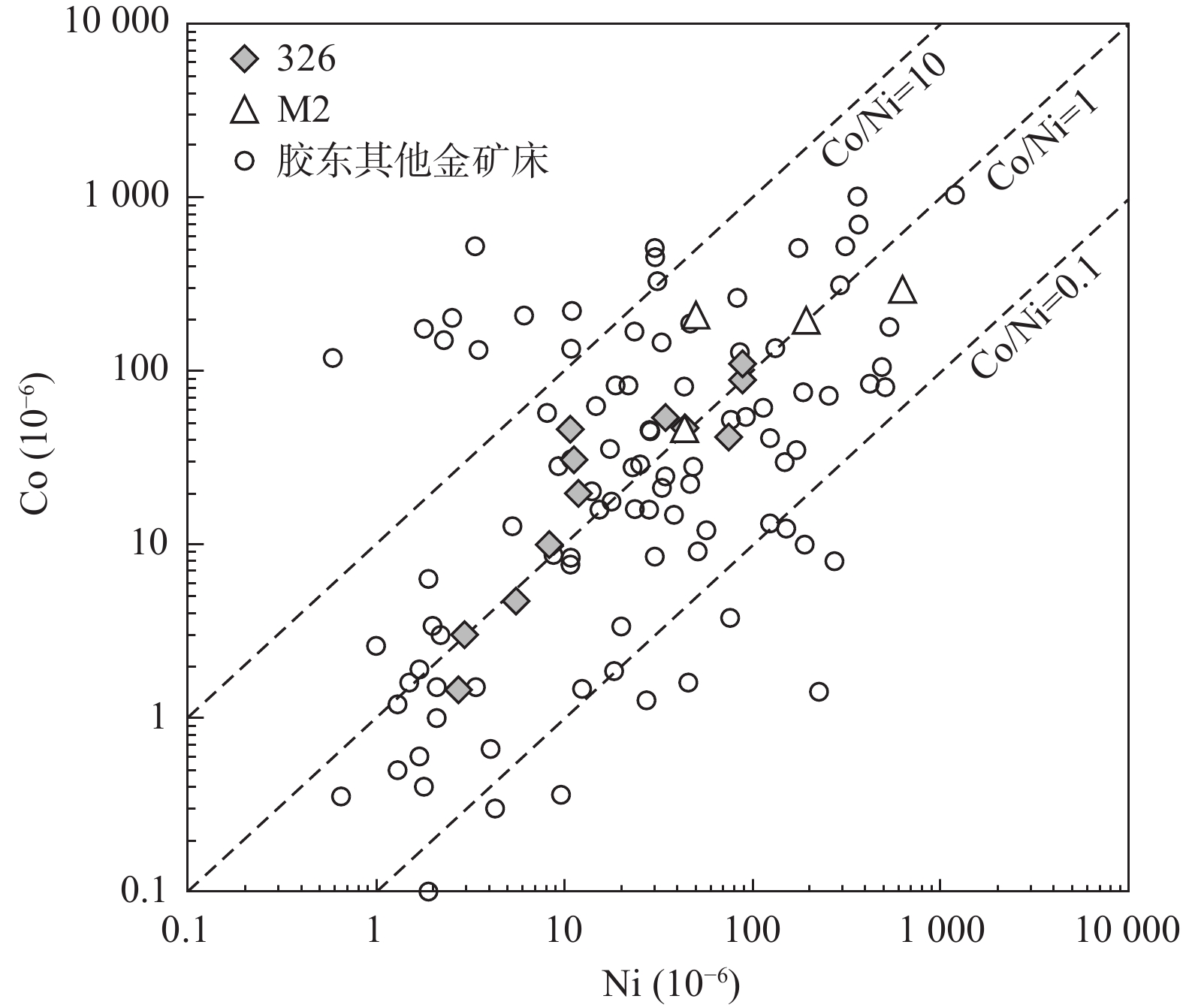
石家金矿床是位于胶东蓬莱−栖霞成矿带北段的一个石英脉型金矿床,其成矿过程大致可以分为石英−黄铁矿−绢云母阶段(Ⅰ)、石英−多金属硫化物−金阶段(Ⅱ)和石英−方解石−萤石阶段(Ⅲ)。为探讨石家金矿床成矿流体的性质,采用电感耦合等离子质谱仪(ICP−MS)技术,对石英−多金属硫化物−金阶段与自然金共生的黄铁矿开展微量元素分析。结果表明,黄铁矿富集Cu、Pb、Zn等亲硫元素,并且主要以矿物包裹体的形式赋存于黄铁矿中。稀土元素总量较低(ΣREE值为2.55×10−6~20.94×10−6),呈现出轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素亏损的配分模式,LREE/HREE与(La/Yb)N值分别为16.15~52.12和18.26~481.62。黄铁矿表现出显著的Eu负异常(δEu值为0.16~0.62)而无明显Ce异常(δCe值为0.89~1.33),Hf/Sm、Th/La、Nb/La值均小于1。结合前人流体包裹体的研究,认为黄铁矿是在流体不混溶的作用下,从富Cl的还原性流体中沉淀的。Y/Ho、Zr/Hf、Nb/Ta值变化范围大,暗示成矿过程中热液体系受到了干扰,可能有大气降水的加入。Co、Ni含量和Co/Ni值显示黄铁矿为热液成因,成矿流体具有变质热液的特点,可能与富集岩石圈地幔的去挥发分作用有关。
Abstract:The Shijia gold deposit is a quartz−vein type gold deposit located in the north of the Penglai−Qixia gold belt in Jiaodong. The mineralization process of Shijia can be roughly divided into quartz−pyrite−sericite (I), quartz−polymetallic sulfide−gold (II) and quartz−calcite−fluorite (III) stages. The rare earth element (REE) and trace elements of pyrite coexisting with natural gold in the quartz−polymetallic sulfide−gold stage was analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP−MS) to discuss the properties of ore−forming fluids in the Shijia gold deposit. Results show that pyrite is relatively enriched in sulphophile elements such as Cu, Pb, Zn, and mainly occurs in pyrite in the form of mineral inclusions. The contents of REE in pyrite are relatively low, enriched in LREE, and depleted in HREE, with ΣREE, LREE/HREE values and (La/Yb)N values of 2.55×10−6~20.94×10−6, 16.15~52.12 and of 18.26~481.62, respectively. Pyrite shows significant negative Eu anomalies (δEu=0.16~0.62) but no obvious Ce anomalies (δCe=0.89~1.33), and Hf/Sm, Th/La, Na/La ratios are all less than 1. Combined with previous studies of fluid inclusions, it is indicating that pyrite is precipitated from a reducing fluid dominated by Cl−enriched under the mechanism of fluid immiscibility. The wide variation range of Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and Nb/Ta ratios suggests that the hydrothermal system was disturbed during the mineralization process, which may be related to the addition of meteoric water. The contents of Co and Ni and the Co/Ni values indicate that the pyrite is of hydrothermal origin, and the ore−forming fluids are presumed to be similar to the metamorphic fluid which may be associated with the devolatilization of the enriched lithospheric mantle.
-
Key words:
- pyrite /
- rare−earth elements /
- trace elements /
- ore−forming fluids /
- Shijia gold deposit /
- Jiaodong
-

-
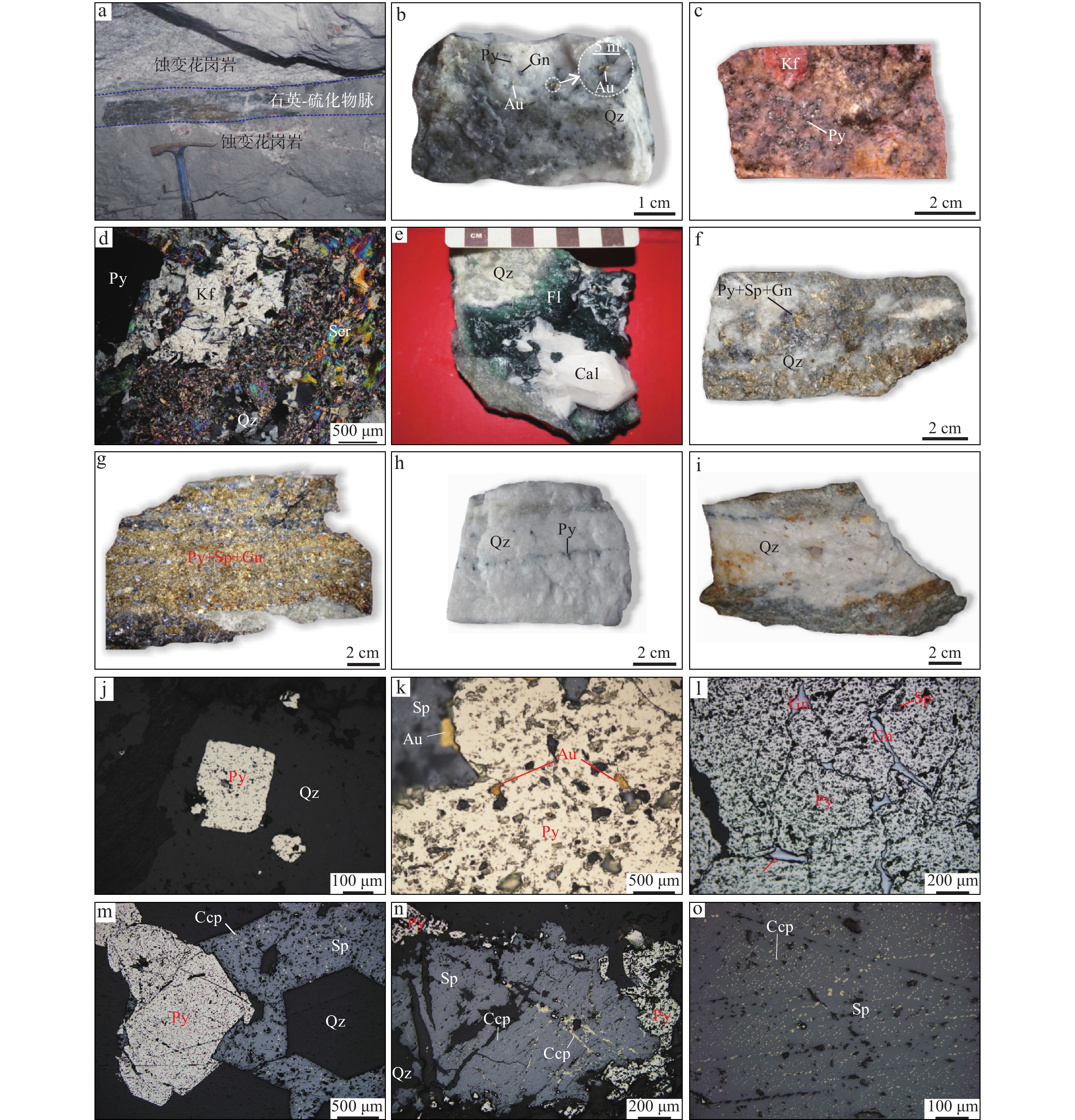
图 1 胶东半岛大地构造位置图(a)(据Zhao et al.,2005修改)、胶东金矿集区金矿床分布图(b)(据Deng et al.,2020修改)、 大柳行地区地质简图(c)(据Feng et al.,2020修改)
Figure 1.
图 6 石家金矿床主成矿阶段黄铁矿稀土元素配分曲线(球粒陨石REE数据据Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 6.
表 1 石家金矿床主成矿阶段黄铁矿微量元素分析品采样位置统计表
Table 1. Location of trace element analysis sample of ore–main stage pyrite from the Shijia gold deposit
序号 样品编号 矿体编号 勘探线编号 采样深度(m) 样品类型 1 SJ-1Py 326 28线 −595 含黄铁矿石英脉 2 SJ-2Py 326 28线 −555 含黄铁矿石英脉 3 SJ-3Py 326 28线 −515 含黄铁矿石英脉 4 SJ-4Py 326 28线 −475 含黄铁矿石英脉 5 SJ-5Py 326 28线 −435 含黄铁矿石英脉 6 SJ-6Py 326 28线 −395 多金属硫化物石英脉 7 SJ-7Py 326 28线 −355 乳白色石英–多金属硫化物脉 8 SJ-8Py 326 32线 −315 乳白色石英–多金属硫化物脉 9 SJ-9Py 326 40线 −280 乳白色石英–多金属硫化物脉 10 SJ-10Py 326 40线 −240 乳白色石英硫化物脉 11 SJ-11Py 326 52~56线 −205 乳白色石英硫化物脉 12 SJ-12Py 326 56线 −165 乳白色石英硫化物脉 13 SJ-13Py M2 12线 −745 石英硫化物脉 14 SJ-14Py M2 4线 −635 石英硫化物脉 15 SJ-15Py M2 4线 −595 含黄铁矿石英脉 16 SJ-16Py M2 4线 −555 石英硫化物脉 表 2 石家金矿床主成矿阶段黄铁矿稀土元素含量(10−6)及其特征值统计表
Table 2. REE content (10−6) and characteristic values of the ore–main stage pyrite from the Shijia gold deposit
样品
编号La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu ΣREE LREE/HREE (La/Yb)N δEu δCe SJ-1Py 1.09 2.11 0.23 0.84 0.11 0.005 0.087 0.003 0.029 – 0.004 0.003 0.005 – 4.51 33.42 156.37 0.16 1.04 SJ-2Py 1.73 2.95 0.29 1.09 0.14 0.019 0.102 0.006 0.018 – 0.011 0.002 0.005 – 6.36 43.19 248.19 0.48 1.02 SJ-3Py 4.7 10.1 0.99 3.56 0.28 0.04 0.285 0.017 0.082 – 0.039 0.003 0.007 – 20.11 45.44 481.62 0.43 1.15 SJ-4Py 1.03 1.91 0.21 0.73 0.08 0.004 0.052 – 0.015 – 0.005 0.002 0.002 – 4.04 52.12 369.41 0.19 1.01 SJ-5Py 1.55 2.41 0.28 1.04 0.1 0.006 0.096 – 0.039 – 0.005 0.006 0.02 – 5.56 32.49 55.59 0.18 0.89 SJ-6Py 1.64 4.33 0.39 1.47 0.13 0.017 0.127 0.008 0.043 – 0.015 0.003 0.014 – 8.19 37.98 84.03 0.4 1.33 SJ-7Py 3.38 6.75 0.77 3.09 0.44 0.028 0.32 0.027 0.092 – 0.027 0.003 0.014 – 14.93 29.92 173.18 0.23 1.03 SJ-8Py 4.11 7.57 0.85 3.24 0.48 0.04 0.342 0.035 0.143 0.005 0.042 0.006 0.05 0.003 16.92 26.02 58.96 0.3 0.99 SJ-9Py 0.64 1.19 0.12 0.45 0.07 0.003 0.045 – 0.014 – 0.007 0.003 0.011 – 2.55 30.9 41.73 0.17 1.05 SJ-10Py 0.56 1.09 0.12 0.54 0.09 0.012 0.067 0.003 0.043 – 0.009 0.005 0.022 – 2.56 16.15 18.26 0.48 1.03 SJ-11Py 4.32 7.34 0.81 3.2 0.49 0.057 0.367 0.033 0.159 0.014 0.061 0.01 0.054 0.006 16.92 23.03 57.38 0.41 0.96 SJ-12Py 1.05 2.21 0.26 1.07 0.18 0.013 0.106 0.01 0.056 – 0.02 0.003 0.014 0.003 4.99 22.54 53.8 0.29 1.05 SJ-13Py 15.5 26.7 3.06 11.7 1.74 0.291 1.17 0.122 0.46 0.032 0.117 0.019 0.06 0.017 60.99 29.54 185.30 0.62 0.95 SJ-14Py 1.37 2.45 0.268 1.04 0.162 0.01 0.117 0.012 0.046 0.004 0.032 0.008 0.03 0.005 5.55 20.87 32.76 0.22 0.99 SJ-15Py 4.72 9.1 1.11 4.4 0.766 0.089 0.485 0.05 0.171 0.003 0.028 0.004 0.017 – 20.94 26.63 199.16 0.45 0.97 SJ-16Py 1.07 1.86 0.196 0.74 0.081 0.01 0.068 – 0.014 – – 0.003 0.004 – 4.05 44.46 191.88 0.41 1.00 注:–表示低于检测限。 表 3 石家金矿床主成矿阶段黄铁矿微量元素含量(10−6)及其特征值统计表
Table 3. Trace elements content (10−6) and characteristic values of the ore−main stage pyrite from the Shijia gold deposit
样品
编号SJ-
1PySJ-
2PySJ-
3PySJ-
4PySJ-
5PySJ-
6PySJ-
7PySJ-
8PySJ-
9PySJ-
10PySJ-
11PySJ-
12PySJ-
13PySJ-
14PySJ-
15PySJ-
16PyLi 0.32 0.278 0.319 0.319 0.537 0.801 0.386 0.291 0.325 0.396 0.854 0.242 0.55 0.185 0.33 0.268 Be 0.004 0.011 0.009 − 0.002 0.014 − 0.033 0.008 0.006 0.024 0.004 0.022 0.003 0.003 0.005 Sc 0.275 0.23 0.252 0.371 0.036 0.293 0.374 0.495 0.435 0.268 0.39 0.28 0.429 0.275 0.229 0.29 V 0.263 0.197 0.303 0.256 0.453 0.37 0.26 0.745 0.479 0.329 1.29 0.28 0.429 0.442 0.217 0.239 Cr 0.726 − 1.92 1.89 0.745 0.008 2.25 3.47 1.06 0.215 2.16 0.08 1.55 1.07 − − Co 88.2 46.8 19.6 4.72 3.01 1.45 9.97 110 30.8 45.9 41.7 53.9 209 196 295 46.4 Ni 88.7 43.9 11.9 5.55 2.96 2.75 8.33 88.8 11.3 10.8 74.8 34.5 50.1 193 629 43.7 Cu 157 133 186 231 293 198 179 27.9 125 147 263 67.8 21.5 85.6 184 131 Zn 858 419 5316 3292 >10000 3426 8811 185 576 1871 1979 1230 51.4 632 1245 425 Ga 0.447 0.398 0.913 0.914 1.2 1.1 0.917 0.562 0.405 0.657 0.673 0.403 0.425 1.36 0.38 0.408 Rb 0.416 0.299 0.421 0.351 0.585 0.447 0.521 2.42 0.787 0.737 1.43 0.394 0.804 0.472 0.272 0.31 Sr 3.24 1.01 4.05 2.14 4.34 4.55 3.05 3.35 2.95 5.06 4.31 1.27 0.871 1.01 1.15 1.04 Y 0.069 0.074 0.135 0.584 0.116 0.203 0.191 0.403 0.085 0.217 0.425 0.153 0.719 0.194 0.252 0.055 Mo 0.013 0.294 0.158 0.006 0.028 − − 0.048 0.229 0.59 0.43 0.502 0.083 0.055 0.832 0.276 Cd 5.63 3.59 30.5 20.3 63.7 19.9 45.2 1.01 3.79 13.7 11.2 6 0.22 3.93 6.1 3.49 In 0.844 6.2 2.23 1.92 2.04 0.467 0.155 0.039 0.173 0.176 0.057 0.021 0.008 0.247 0.216 6.11 Sb 4.14 2.04 6.75 10.9 14.9 19.5 8.52 4.26 6.93 10.4 76.8 6.75 3.74 32.8 6.44 2.06 Cs 0.009 0.007 0.005 0.007 0.008 0.017 0.007 0.046 0.011 0.015 0.026 0.007 0.025 0.009 0.006 0.002 Ba 1.33 1.05 2.19 1.39 1.99 1.35 1.74 6.75 2.48 2.93 6.25 2.16 1.87 1.72 1.84 1.32 La 1.09 1.73 4.7 1.03 1.55 1.64 3.38 4.11 0.644 0.558 4.32 1.05 15.5 1.37 4.72 1.07 Sm 0.107 0.143 0.284 0.081 0.103 0.13 0.436 0.481 0.065 0.089 0.492 0.18 1.74 0.162 0.766 0.081 Ho − − − − − − − 0.005 − − 0.014 − 0.032 0.004 0.003 − W 0.007 0.026 0.018 0.005 − − − 0.044 0.009 0.017 0.128 − 0.026 0.072 0.008 0.024 Pb 616 268 4661 6342 9802 5189 4136 298 3511 7095 >10000 2647 117 4737 947 265 Bi 1.67 16.7 1.43 0.892 0.174 − − 4.68 0.199 0.489 0.309 0.253 2.95 1.19 2.64 16 Th 0.039 0.131 0.122 0.009 0.057 0.057 0.132 1.54 0.243 0.046 1.17 0.667 0.517 1.06 0.083 0.068 U 0.014 0.105 0.033 0.015 0.01 0.04 0.056 0.306 0.056 0.076 0.125 0.539 0.07 0.394 0.044 0.025 Nb 0.009 0.024 0.029 0.02 0.023 0.022 0.018 0.447 0.024 0.009 0.086 0.013 0.015 0.062 0.003 0.011 Ta 0.003 0.004 0.004 − 0.005 0.006 0.003 0.02 0.005 0.006 0.007 0.005 0.005 0.013 0.002 0.004 Zr 0.368 0.4 0.406 0.374 0.407 0.335 0.488 1.89 0.581 0.443 1.33 1.4 0.513 1.69 0.356 0.359 Hf 0.008 0.01 0.022 0.008 0.012 0.018 0.021 0.117 0.017 0.016 0.056 0.086 0.022 0.054 0.018 0.012 Sn 3.76 11.6 11.8 20.8 7.49 8.06 10.5 0.541 2.73 3.22 1.32 0.613 0.17 2.81 0.53 11.4 Co/Ni 0.99 1.07 1.65 0.85 1.02 0.53 1.20 1.24 2.73 4.25 0.56 1.56 4.17 1.02 0.47 1.06 Hf/Sm 0.07 0.07 0.08 0.10 0.12 0.14 0.05 0.24 0.26 0.18 0.11 0.48 0.01 0.33 0.02 0.15 Nb/La 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.11 0.04 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.00 0.05 0.00 0.01 Th/La 0.04 0.08 0.03 0.01 0.04 0.03 0.04 0.37 0.38 0.08 0.27 0.64 0.03 0.77 0.02 0.06 Y/Ho − − − − − − − 80.60 − − 30.36 − 22.47 48.50 84.00 − Zr/Hf 46.00 40.00 18.45 46.75 33.92 18.61 23.24 16.15 34.18 27.69 23.75 16.28 23.32 31.30 19.78 29.92 Nb/Ta 3.00 6.00 7.25 − 4.60 3.67 6.00 22.35 4.80 1.50 12.29 2.60 3.00 4.77 1.50 2.75 注:−表示低于检测限。 -
[1] 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 等. 黄铁矿微量元素地球化学特征及其对成矿流体性质的指示[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2004, 23(1): 1-4
Bi X W, Hu R Z, Peng J T, et al. REE and HFSE geochemical characteristics of pyrites in Yao’an gold deposit: Tracing ore forming fluid signatures[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2004, 23(1): 1-4.
[2] 陈炳翰, 王中亮, 李海林, 等. 胶东台上金矿床成矿流体演化: 载金黄铁矿稀土元素和微量元素组成约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2518-2532
Chen B H, Wang Z L, Li H L, et al. Evolution of ore fluid of the Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong: Constraints on REE and trace element component of auriferous pyrite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 30(9): 2518-2532.
[3] 丁振举, 刘丛强, 姚书振, 等. 东沟坝多金属矿床喷流沉积成矿特征的稀土元素地球化学示踪[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(4): 792-798 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2003.04.022
Ding Z J, Liu C Q, Yao S Z, et al. The Characteristics of exhalation-sedimentary deposit of Donggouba polymetal deposit: evidence from ore’s REE composition[J]. Acta Petrological Sinica, 2003, 19(4): 792-798. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2003.04.022
[4] 范宏瑞, 冯凯, 李兴辉, 等. 胶东-朝鲜半岛中生代金成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(10): 3225-3238.
Fan H R, Feng K, Li X H, et al. Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong and Korean peninsula[J]. Acta Petrological Sinica, 2016, 32(1): 3225-3258.
[5] 范宏瑞, 李兴辉, 左亚彬, 等. LA-(MC)-ICPMS和(Nano)SIMS硫化物微量元素和硫同位素原位分析与矿床形成的精细过程[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(12): 3479-3496
Fan H R, Li X H, Zuo Y B, et al. In-situ LA-(MC)-ICPMS and (Nano)SIMS trace elements and sulfur isotope analyses on sulfides and application to confine metallogenic process of ore deposit. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(12): 3479-3496.
[6] 冯李强. 山东蓬莱石家金矿床成因与找矿方向[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2022
FENG Liqiang. Genesis and prospecting direction of the Shijia gold deposit, Penglai, Shandong Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2022.
[7] 高山, 骆庭川, 张本仁, 等. 中国东部地壳的结构和组成[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 1999, 29(3): 204-213
Gao S, Luo T C, Zhang B R, et al. The structure and composition of the crust in eastern China[J]. Science in China (Series D), 1999, 29(3): 204-213.
[8] 顾雪祥, 刘建明, Oskar S, 等. 湖南沃溪金-锑-钨矿床成因的稀土元素地球化学证据[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(5): 428-437 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.05.002
Gu X X, Liu J M, Oskar S, et al. REE geochemical evidence for the genesis of the Woxi Au-Sb-W deposit, Hunnan Province[J]. Geochimica, 2005, 34(5): 428-437. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.05.002
[9] 顾雪祥, 李葆华, 章永梅, 等. 矿床学研究方法及应用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2019
GU Xuexiang, LI Baohua, ZHANG Yongmei, et al. Methods and Applications of Ore Deposit Study[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2019.
[10] 郭林楠, 黄春梅, 张良, 等. 胶东罗山金矿床成矿流体来源: 蚀变岩型和石英脉型矿石载金黄铁矿稀土和微量元素特征约束[J]. 现代地质, 2019, 33(1): 121-136
Guo L N, Huang C M, Zhang L, et al. Source of ore-forming fluids in the Luoshan gold deposit, Jiaodong: Constrains from REE and trace element features of auriferous pyrite in the altered-rock type and auriferous quartz vein type ores[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 3(1): 121-136.
[11] 孔庆波. 苏鲁地体古元古代花岗质片麻岩锆石的U-Pb定年、REE和Lu-Hf同位素特征[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(1): 51-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.007
Kong Q B. Zircon U-Pb dating, REE and Lu-Hf isotopic characteristics of Paleoproterozoic orthogneiss in Sulu UHP terrane, eastern China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(1): 51-62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.01.007
[12] 李厚民, 沈远超, 毛景文, 等. 石英、黄铁矿及其包裹体的稀土元素特征——以胶东焦家式金矿为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2003, 19(2): 267-274 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2003.02.008
Li H M, Shen Y C, Mao J W, et al. REE features of quartz and pyrite and their fluids inclusions: an example of Jiaojia-type gold deposits, northwestern Jiaodong peninsula[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2003, 19(2): 267-274. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.2003.02.008
[13] 李杰, 宋明春, 梁金龙, 等. 焦家深部金矿床成矿流体来源: 来自黄铁矿微量元素及S-He-Ar同位素的约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(1): 297-313 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.23
Li J, Song M C, Liang J L, et al. Source of ore-forming fluids of the Jiaojia deeply-seated gold deposit: Evidences from trace elements and sulfur-helium-argon isotopes of pyrite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(1): 297-313. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.01.23
[14] 李秀章, 王勇军, 李衣鑫, 等. 胶东蓬莱黑岚沟金矿床黄铁矿微区地球化学特征及对成矿流体的启示[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(6): 1023-1038
Li X Z, Wang Y J, Li Y X, et al. Micro-geochemical characteristic of pyrites in the Heilangou gold deposit of penglai area and its implications for ore-forming fluid, Jiaodong gold province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(6): 1023-1038.
[15] 刘福来, 薛怀明, 刘平华. 苏鲁超高压岩石部分熔融时间的准确限定: 来自含黑云母花岗岩中锆石U-Pb定年、REE和Lu-Hf同位素的证据. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(5): 1039-1055
Liu F L, Xue H M, Liu P H. Partial melting time of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks in the Sulu UHPterrane: Contrained by zircon U-Pb ages, trace elements and Lu-Hf isotope compositions of biotite-bearing granite[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(5): 1039-1055.
[16] 马玉波, 杜晓慧, 张增杰, 等. 青城子层状/脉状铅锌矿床稀土元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(6): 1236-1248
Ma Y B, Du X H, Zhang Z J, et al. REE geochemical characteristics of Qingchengzi stratiform/veined Pb-Zn ore district[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(6): 1236-1248.
[17] 任凤楼, 柳忠泉, 邱连贵, 等. 胶莱盆地莱阳期原型盆地恢复[J]. 沉积学报, 2008, 26(2): 221-233 doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2008.02.006
Ren F L, Liu Z Q, Qiu L G, et al. The prototype character of Jiaolai basinin Cretaceous Laiyang Period[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2008, 26(2): 221-233. doi: 10.14027/j.cnki.cjxb.2008.02.006
[18] 邱志伟, 李占轲, 袁中正. 胶东三山岛金矿床黄铁矿显微结构和微量元素特征: 对金富集机制的指示[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(1): 290-308 doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.1.dqkx202201023
Qiu Z W, Li Z K, Yuan Z Z. Microstructure and trace elements of pyrite from Sanshandao gold deposit in Jiaodong district: Implications for mechanism of gold enrichment[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(1): 290-308. doi: 10.3321/j.issn.1000-2383.2022.1.dqkx202201023
[19] 赛盛勋, 邱昆峰. 胶东乳山金矿床成矿过程: 周期性压力波动诱发的流体不混溶[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(5): 1547-1566 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.14
Sai S X, Qiu K F. Ore-forming processes of the Rushan gold deposit, Jiaodong: Fluid immiscibility induced by episodic fluid pressure fluctuations[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(5): 1547-1566. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.14
[20] 申俊峰, 李胜荣, 马广钢, 等. 玲珑金矿黄铁矿标型特征及其大纵深变化规律与找矿意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(3): 55-75
Shen J F, Li S R, Ma G G, et al. Typomorphic characteristics of pyrite from the Linglong gold deposi: Its vertical variation and prospecting significance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(3): 55-75.
[21] 宋明春, 林少一, 杨立强, 等. 胶东金矿成矿模式[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 215-236 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2020.02.002
Song M C, Lin S Y, Yang L Q, et al. Metallogenic model of Jiaodong Peninsula gold deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2): 215-236. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2020.02.002
[22] 王立强, 程文斌, 罗茂澄, 等. 西藏蒙亚啊铅锌矿床金属硫化物、石英稀土元素组成特征及其成因研究[J]. 中国地质, 2012, 39(3): 740-749 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.03.015
Wang L Q, Cheng W B, Luo M C, et al. A study of metallic sulfides, quartz REE composition characteristics and genesis of the Mengya’a lead-zinc deposit[J]. Geology in China, 2012, 39(3): 740-749. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.03.015
[23] 续海金, 宋衍茹, 叶凯. 苏鲁超高压地体部分熔融时间的厘定: 荣成花岗质片麻岩中浅色条带的锆石U-Pb定年、微量元素和Lu-Hf同位素证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(5): 1594-1606
Xu H J, Song Y R, Ye K, et al. Partial melting time of the Sulu UHP terrane: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, trace element and Lu-Hf isotope composition of leucosome in Rongcheng granitic gneiss[J]. Acta Petrologica Sincia, 2013, 29(5): 1594-1606.
[24] 严育通, 李胜荣, 贾宝剑, 等. 中国不同成因类型金矿床的黄铁矿成分标型特征及统计分析[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(4): 214-226
Yan Y T, Li S R, Jia B J, et al. Composition typomorphic characteristics and statistic analysis of pyrite in gold deposits of different genetic types[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(4): 214-226.
[25] 杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 等. 胶东中生代金成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2447-2467
Yang L Q, Deng J, Wang Z L, et al. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(9): 2447-2467.
[26] 张红雨, 赵青青, 赵刚, 等. LA-ICP-MS原位微区分析黄铁矿微量元素技术方法及其在金矿床研究中的应用[J]. 矿床地质, 2022, 41(6): 1-18
Zhang H Y, Zhao Q Q, Zhao G, et al. In situ LA-ICP-MS trace element analysis of pyrite and its application in study of Au deposit[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2022, 41(6): 1-18.
[27] 张英帅, 顾雪祥, 章永梅, 等. 山东蓬莱石家金矿原生晕地球化学特征及深部找矿预测[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(1): 258−269.
ZHANG Yingshuai, GU Xuexiang, ZHANG Yongmei, et al. Geochemical characteristics of primary halos and deep prospecting prediction of the Shijia gold deposit in Penglai, Shandong Province[J]. Geosciences, 2021, 35(1): 258−269.
[28] 甄世民, 庞振山, 朱晓强, 等. 山西梨园金矿黄铁矿微量元素及S-Pb-He-Ar同位素地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(2): 373-390 doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.3.27
Zhen S M, Pang Z S, Zhu XQ, et al. The characteristics of trace elements and S, Pb, He and Ar isotopes in the Liyuan gold deposit in Shanxi Province, and their siginificance[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2020, 27(2): 373-390. doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.3.27
[29] Ames L, Zhou G Z, Xiong B C. Geochronology and isotopic character of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism with implications for collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtze cratons, central China[J]. Tectonics, 1996, 15: 472-89.
[30] Bau M. REE mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid-rock interaction and the significance of the oxidation state of europium[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 93: 219-230. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(91)90115-8
[31] Bau M, Dulskip. Comparative study of yttrium and rare-earth element behaviours in fluorine-rich hydrothermal fluids[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1995, 119(2): 213-223.
[32] Bralia A, Sabatini G, Troja F. A revaluation of the Co/Ni ratio in pyrite as geochemical tool in ore genesis problems[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1979, 14(3): 353-374.
[33] Deng J, Yang L Q, Groves D I, et al. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 208: 103274. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103274
[34] Deng J, Wang Q F, Liu X F, et al. The formation of the Jiaodong gold province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2022, 96(6): 1801-1820. doi: 10.1111/1755-6724.15026
[35] Douville E, Bienvenu P, Charlou J L. Yttrium and rare-earth elements in fluids from various deep-sea hydrothermal systems[J]. Geochimicaet Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(5): 627-643. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00024-1
[36] Feng L Q, Gu X X, Zhang Y M, et al. Geology and geochronology of the Shijia gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 120: 103432. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103432
[37] Goldfarb R J, Santosh M. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?[J] Geoscience Frontiers, 2014, 5(2): 139-153. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2013.11.001
[38] Henderson P. Rare earth element geochemistry[M]. Amsterdam: Elseriver Science Publishers, 1984: 123-125.
[39] Hu H L, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Ore-forming processes in the Wang’ershan gold deposit (Jiaodong, China): Insight from microtexture, mineral chemistry and sulfur isotope compositions[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2022, 123: 103600.
[40] Jahn B M, Liu D Y, Wan Y S, et al. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry[J]. American Journal of Science, 2008, 308: 232-269. doi: 10.2475/03.2008.03
[41] Large R R, Danyushevsky L V, Hollit C, et al. Gold and trace element zonation in pyrite using a laser imaging technique: Implications for the timing of gold in orogenic and Carlin-style sediment hosted deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2009, 104(5): 635-668. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.5.635
[42] Li L, Santosh M, Li S R. The ‘Jiaodong type’ gold deposits: Characteristics, origin and prospecting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 589-611. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.06.021
[43] Mao G Z, Hua R M, Gao J F, et al. Existing forms of REE in gold-bearing pyrite of the Jinshan gold deposit, Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2009, 27(6): 1079-1087. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(08)60392-0
[44] Mao J W, Wang Y T, Li H M, et al. The relationship of mantle-derived fluids to gold metallogenesis in the Jiaodong Peninsula: evidence from D-O-C-S isotope systematics. Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 33: 361-381.
[45] Mills R A, Elderfield H. Rare earth element geochemistry of hydrothermal deposits from the active TAG Mound, 26°N Mid-Atlantic Ridge.[J] Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(17): 3511-3524.
[46] Oreskes N, Einaodi MT. Origin of rare earth element-enriched hematite breccias at the Olympic Dam Cu-U-Au-Ag deposit, Roxby Downs, South Australia[J]. Economic Geology, 1990, 85: 1-28. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.85.1.1
[47] Tang J, Zheng Y F, Wu Y B, et al. Geocheronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane: Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogeny[J]. Precambrian Research, 2007, 152(1-2): 48-82. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2006.09.001
[48] Schade J, Cornell D H, Theart H F J. Rare-earth element and isotopic evidence for the genesis of the Prieska massive sulfide deposit, South Africa[J]. Economic Geology, 1989, 84(1): 49-63. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.84.1.49
[49] Shanon R D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic in halides and chalcogenides[J]. Acta Crystallographica, 1976, A32: 751-767.
[50] Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematic of oceanic basalts: Implications for composition and process[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 1989, 42(1): 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[51] Sverjensky D A. Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 67: 70-78. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90039-6
[52] Voute F, Hagemann S G, Evans N J, et al. Sulfur isotopes, trace element, and textural analyses of pyrite, arsenopyrite and base metal sulfides associated with gold mineralization in the Pataz-Parcoy district, Peru: implication for paragenesis, fluid source, and gold deposition mechanisms[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2019, 54: 1077-1100. doi: 10.1007/s00126-018-0857-6
[53] Wang H, Lan T G, Fan H R, et al. Fluid origin and critical ore-forming processes for the giant gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from in situ elemental and oxygen isotopic compositions of quartz and LA-ICP-MS analysis of fluid inclusions[J]. Chemical Geology, 2022, 608: 121027. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2022.121027
[54] Yang K F, Fan H R, Santosh M, et al. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton[J]. Lithos, 2012: 146-147: 112-127. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035
[55] Yang Q Y, Santosh M, Shen J F, et al. Juvenile vs. recycled crust in NE China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and an integrated model for Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Gondwana Research, 2014, 25(4): 1445-1468. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.003
[56] Yaxley G M, Green D H, Kamenetsky V. Carbonatite metasomatism in the southeastern Australian lithosphere[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1998, 39: 1917-1930. doi: 10.1093/petroj/39.11-12.1917
[57] Zhao G C, Sun M, Wilde S A, et al. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited[J]. Precambrian Research, 2005, 136(2): 177-202. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
[58] Zhao K D, Jiang S Y. Rare-earth element and yttrium analyses of sulfides from the Dachang Sn-polymetallie ore field, Guangxi Province, China: Implication for ore genesis[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2007, 41(2): 121-134. doi: 10.2343/geochemj.41.121
-




 下载:
下载: