Mineralogical Characteristics and Metallogenic Indication of Gold−Bearing Sulfides in the Jinpenliang Gold Deposit, Zhashui−Shanyang Ore Cluster Area, South Qinling
-
摘要:
金盆梁金矿床位于南秦岭柞水−山阳金多金属矿集区北部,矿体呈近东西向赋存于上泥盆统桐峪寺组的沉积建造中,受左行韧性断层控制。关于矿石矿物学与金成矿过程尚缺乏系统的认识。基于岩矿相学鉴定、背散射电子图像(BSE)、能谱(EDS)及电子探针分析(EPMA)等方法,查明矿石组构与载金硫化物毒砂、黄铁矿、辉锑矿及白铁矿的矿物学特征,探讨金的赋存状态与成矿物理化学条件,初步厘定矿床成因类型。结果显示,热液成矿期的金矿化以微细浸染型为主,可划分为黄铁矿−毒砂−硅化(Ⅰ)、石英−辉锑矿−白铁矿±锑氧化物(Ⅱ)及方解石−石英(Ⅲ)3个阶段。不同载金硫化物的“不可见金”赋存状态差异显著,由毒砂的晶格金Au+,到早世代黄铁矿(Py-1)的晶格金Au+−纳米金Au0,至晚世代黄铁矿(Py-2)和白铁矿的纳米金Au0。金属矿物组合由毒砂−黄铁矿至辉锑矿−白铁矿,成矿流体由较高温的相对自然金不饱和状态,逐渐演化为相对低温的自然金饱和状态。金盆梁金矿床形成于较高硫逸度的中高温、中浅成环境,属于卡林型金矿床。
Abstract:The Jinpenliang gold deposit is located in the northern part of the Zhashui−Shanyang ore cluster area, South Qinling. The E−W trending main orebodies, occurring in sedimentary rocks of the Upper Devonian Tongyusi Formation, are strictly controlled by the left−lateral ductile faults. To date, there is still insufficient understanding of the ore mineralogy and gold mineralization processes. In this paper, we obtain data from a variety of experimental methods, such as petrographic identification, Back−Scattered Electron imaging (BSE), Energy Dispersive Spectrometry (EDS), and Electron Probe Micro−Analysis (EPMA), to determine the mineralogical characteristics of gold−bearing sulfides (arsenopyrite, pyrite, stibnite, and marcasite), and discuss the chemical states of Au and physicochemical conditions for gold mineralization. The results show that the micro−disseminated gold mineralization in hydrothermal period can be divided into three stages: pyrite−arsenopyrite−silicification stage (Ⅰ), quartz−stibnite−marcasite±antimony oxides stage (Ⅱ), and calcite−quartz stage (Ⅲ). The occurrence states of “invisible gold” vary greatly among different gold−bearing sulfides, from Au+ in arsenopyrite to Au+ and Au0 in early generation pyrite (Py-1), then to Au0 in late generation pyrite (Py-2) and marcasite. The metal mineral assemblage changes from arsenopyrite−pyrite to stibnite−marcasite, while the ore−forming fluid gradually evolves from relatively high−temperature solutions unsaturated with respect to native gold to low−temperature solutions saturated with respect to native gold. The Jinpenliang gold deposit is a Carlin−type gold deposit, which was formed in a medium−high temperature and shallow−moderate depth with logf(S2) ranging from −8.5 to −4.5.
-
Key words:
- occurrence state of gold /
- arsenopyrite geothermometer /
- EPMA /
- gold−bearing sulfides /
- Jinpenliang /
- south Qinling
-

-
图 1 秦岭造山带构造单元(a)及柞水–山阳矿集区地质图(b)(据Ding et al.,2022修改)
Figure 1.
图 2 金盆梁金矿床地质图(据苏选民等,2012)
Figure 2.
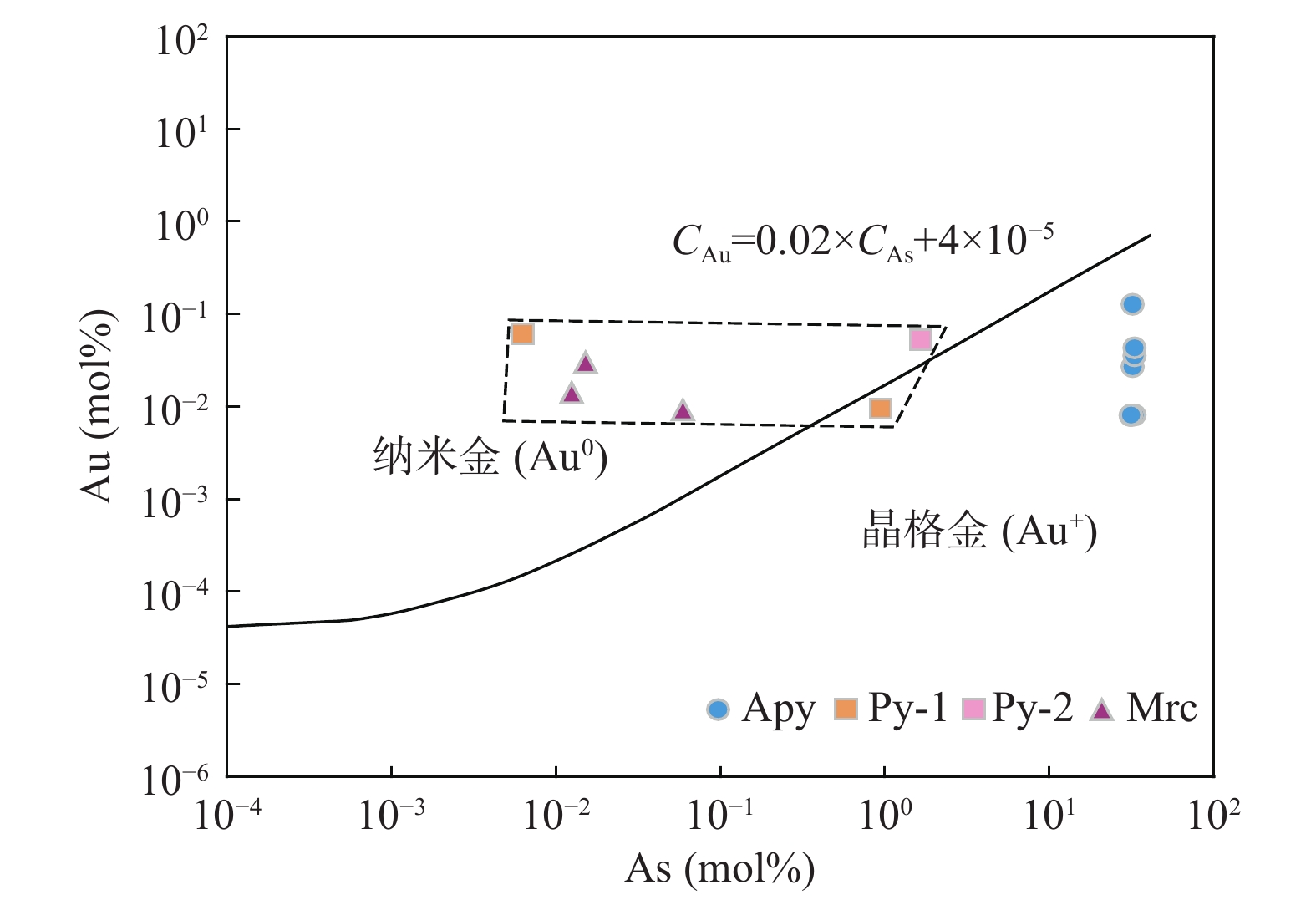
图 8 金盆梁金矿床毒砂、黄铁矿及白铁矿Au–As关系图(拟合曲线据Reich et al.,2005)
Figure 8.
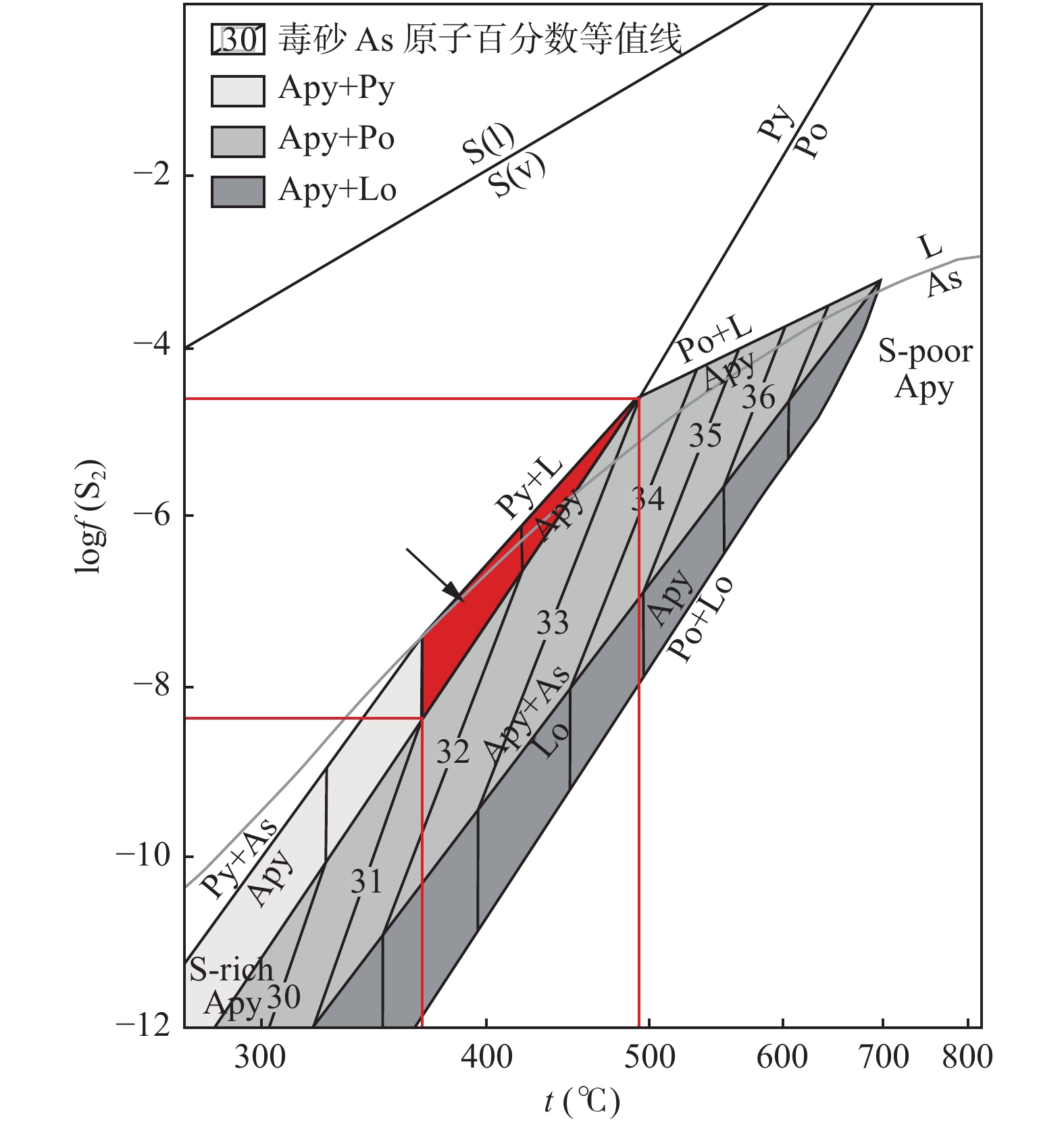
图 9 毒砂地质温度计的logf(S2)–t图解(据Sharp et al.,1985;Zhang et al.,2018)
Figure 9.
表 1 金盆梁金矿床矿石类型与硫化物特征表
Table 1. Ore types and sulfide characteristics of the Jinpenliang gold deposit
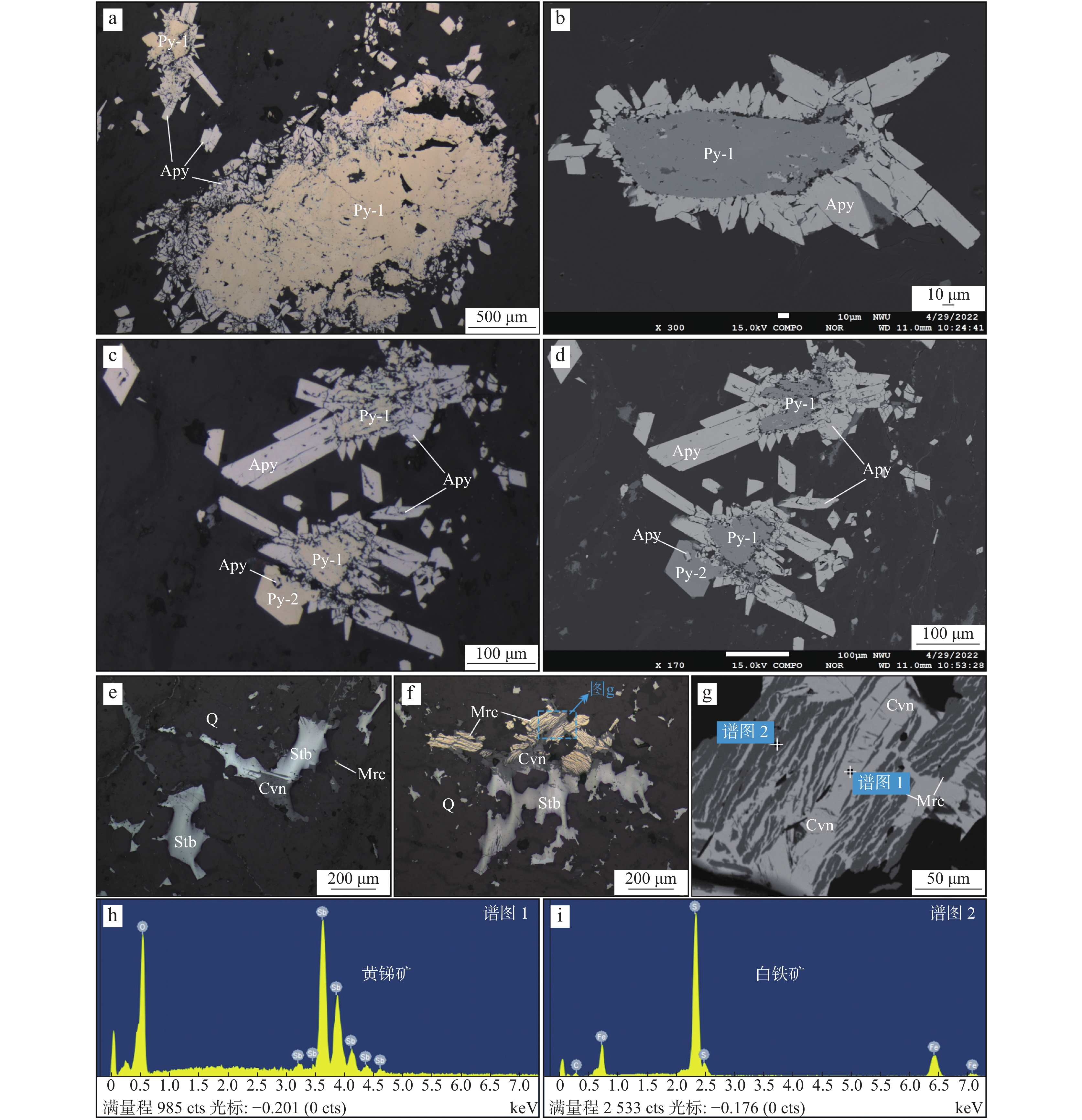
矿石类型 金属硫化物 特征描述 素描图 毒砂–黄铁绢英岩型 Apy 毒砂(Apy)呈亮白色针柱状、菱形、茅状自形晶,常见晶面裂纹与孔隙;呈独立放射状或沿早世代黄铁矿边部交代形成毒砂–黄铁矿集合体 
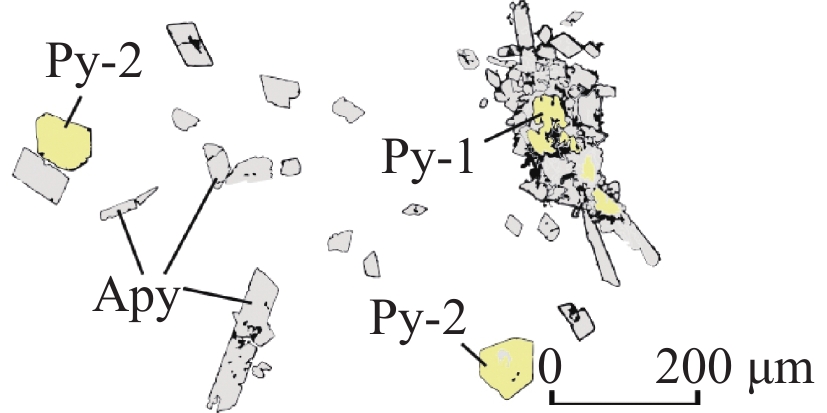
Py-1 早世代黄铁矿(Py-1)呈浅黄色–黄白色中粗粒他形晶,孔隙与裂纹发育;内部结构均一,增生环带不明显,边部多被自形–半自形毒砂交代浸蚀 Py-2 晚世代黄铁矿(Py-2)呈黄白色细粒自形–半自形晶,孔隙与裂纹较少,内部为均质结构;多独立产出,偶见内部包含自形毒砂颗粒 石英–辉锑矿脉型 Stb 辉锑矿(Stb)反射色为白色–灰白色,多色性极为显著,多呈半自形针柱状、粒状晶,易磨光,常见擦痕。可见白铁矿、黄锑矿(Cvn)等交代辉锑矿 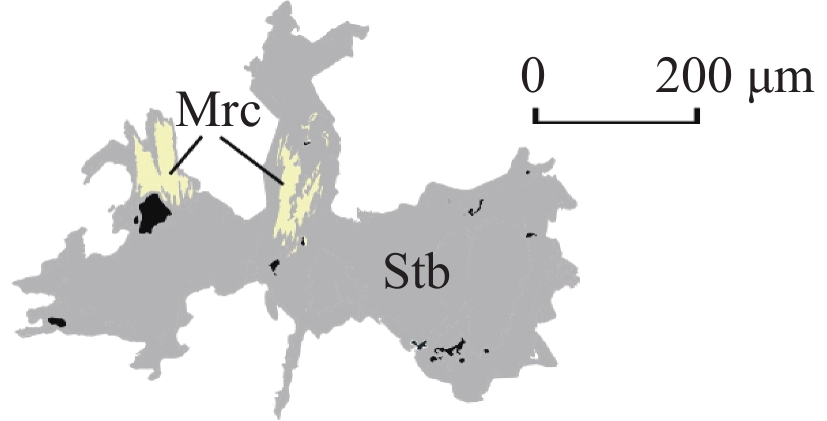
Mrc 白铁矿(Mrc)呈浅黄白色自形板柱状晶,以似节理状的密集条纹切面为鉴别特征,大多沿辉锑矿边部或内部交代产出,极少数独立赋存于石英中 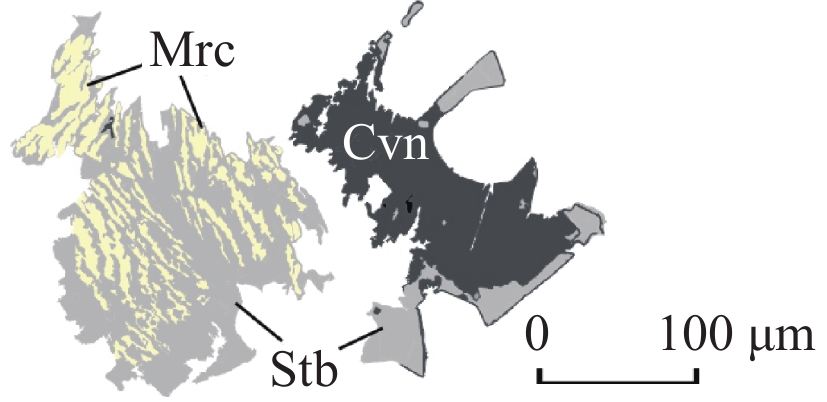
表 2 金盆梁金矿床载金硫化物电子探针分析结果表(%)
Table 2. EMPA data (%) of Au–bearing sulfides in the Jinpenliang gold deposit
测点号 矿物 Au S Pb Bi Ag Cd Sb Te Se As Zn Cu Ni Co Fe Mn Ti Total 计算化学式 JPL-gb6-1 毒砂
(Apy)− 19.49 − 0.03 − − 0.10 − − 46.05 0.09 0.02 0.05 0.03 35.12 0.04 0.04 101.06 Fe1.03As1.01S JPL-gb6-2 − 20.86 − − − 0.03 0.79 − − 43.05 − 0.00 − − 35.48 0.03 0.00 100.24 Fe0.98As0.88S JPL-gb6-3 0.10 19.99 − − − 0.03 0.33 − − 44.33 − − − 0.03 35.55 0.01 − 100.36 Fe1.02As0.95S JPL-gb6-6 0.03 19.44 − − 0.02 0.06 0.09 − − 45.44 0.07 − − 0.08 35.41 − 0.03 100.68 Fe1.05As1.00S JPL-gb6-8 0.13 19.21 − − − 0.06 0.53 − − 45.55 0.02 − − 0.10 35.62 − − 101.21 Fe1.06As1.01S JPL-gb6-10 0.47 19.92 − − 0.06 − − − − 44.31 0.01 0.07 0.03 0.09 35.50 − − 100.45 Fe1.02As0.95S JPL-gb6-11 0.16 19.44 − 0.15 0.01 − 0.01 − − 45.66 0.02 − 0.10 0.09 35.73 − − 101.36 Fe1.06As1.01S JPL-gb6-13 0.03 20.53 0.06 − 0.06 0.07 0.99 − − 43.59 0.03 − 0.05 0.05 35.52 0.01 0.03 101.03 Fe0.99As0.91S JPL-gb6-16 − 19.81 − − 0.02 0.05 0.55 − − 44.27 0.00 0.11 0.00 0.07 35.44 − − 100.33 Fe1.03As0.96S JPL-gb6-18 − 19.55 0.05 − 0.05 0.01 0.61 − − 44.69 0.01 − − 0.04 35.63 − − 100.65 Fe1.05As0.98S JPL-gb6-19 0.03 20.43 − − − 0.01 0.78 − − 43.57 − 0.01 − 0.05 35.16 − 0.03 100.07 Fe0.99As0.91S JPL-gb6-4 早世代
黄铁矿
(Py-1)− 52.37 0.04 − 0.02 − − − 0.02 0.01 − − 0.07 0.14 47.18 0.02 − 99.86 Fe0.52S JPL-gb6-7 0.05 51.61 − − 0.01 − − − − 1.75 − − − 0.09 46.59 − − 100.09 Fe0.52S JPL-gb6-9 − 51.39 0.14 − 0.05 − − − 0.03 0.06 0.11 0.11 0.03 0.09 47.04 0.00 − 99.05 Fe0.53S JPL-gb6-14 0.30 52.14 − − 0.04 − 0.00 − − 0.01 0.06 0.05 0.26 0.05 46.25 − 0.02 99.18 Fe0.51S JPL-gb6-15 − 52.55 0.01 0.02 − − − − − 0.04 − − 0.20 0.15 46.77 − 0.02 99.75 Fe0.51S JPL-gb6-5 晚世代
黄铁矿
(Py-2)− 52.31 − − − 0.01 − − − 1.18 0.06 − − 0.05 46.12 − − 99.74 Fe0.51S JPL-gb6-12 − 51.95 − − 0.01 − 0.06 − − 0.70 0.04 − − 0.12 46.59 − 0.03 99.50 Fe0.51S JPL-gb6-17 − 52.18 0.12 − − 0.03 0.01 − − 0.45 0.06 − 0.01 0.04 47.01 − 0.01 99.91 Fe0.52S JPL-gb6-20 0.25 50.67 − − − − − − − 3.04 − 0.13 0.05 0.04 46.02 − − 100.21 Fe0.52S JPL-gb5-1 辉锑矿
(Stb)− 27.27 − 0.01 − − 71.58 − − 0.09 0.05 0.04 − − 0.00 0.05 − 99.10 Sb0.69S JPL-gb5-4 − 28.66 − 0.15 − 0.03 71.03 0.04 − 0.07 − − 0.05 − 0.04 − − 100.06 Sb0.65S JPL-gb5-5 0.26 27.64 0.09 − − − 71.08 − − 0.11 − 0.01 − − 0.02 0.00 0.00 99.22 Sb0.68S JPL-gb5-7 − 28.68 0.17 − 0.12 0.03 71.05 − 0.01 0.12 − − 0.03 − − − − 100.20 Sb0.65S JPL-gb4-1 − 28.32 − 0.13 0.03 0.02 70.92 0.04 0.01 0.09 − 0.06 0.02 0.00 0.03 0.01 − 99.69 Sb0.66S JPL-gb4-4 − 28.98 − − − − 71.52 0.02 − 0.16 − 0.03 − − 0.02 − − 100.74 Sb0.65S JPL-gb4-5 − 27.36 0.40 − − 0.07 71.89 0.06 − 0.09 0.03 0.07 0.13 0.06 0.00 − − 100.16 Sb0.69S JPL-gb4-6 0.29 27.97 − − − 0.02 71.24 0.01 − 0.16 0.09 0.01 − − − 0.01 − 99.79 Sb0.67S JPL-gb4-9 0.04 28.90 0.12 − − 0.06 70.78 0.02 − 0.21 0.05 − 0.06 0.01 − − − 100.24 Sb0.64S JPL-gb4-10 − 29.03 − 0.06 − − 71.02 0.07 0.01 0.11 − 0.07 0.04 − 0.01 0.01 − 100.43 Sb0.64S JPL-gb4-11 − 28.73 − − 0.01 0.04 70.49 0.12 − 0.11 − 0.04 − − − − − 99.54 Sb0.65S JPL-gb4-12 0.15 28.31 − − 0.03 0.07 71.26 0.00 0.00 0.11 − 0.03 0.00 0.01 0.04 − 0.02 100.04 Sb0.66S JPL-gb4-2 白铁矿
(Mrc)0.16 52.84 − − − − 0.20 − − − 0.17 − 0.12 0.16 46.49 0.03 − 100.18 Fe0.51S JPL-gb4-3 0.05 52.61 − 0.09 0.06 0.01 1.27 − 0.00 0.11 0.02 − 0.15 0.12 46.49 0.02 0.00 100.98 Fe0.51S JPL-gb4-7 0.14 48.73 − − 0.01 0.00 4.54 − 0.01 0.03 − − 0.05 0.22 41.19 − − 94.90 Fe0.49S JPL-gb4-8 − 48.14 − − − 0.02 3.88 − 0.01 − 0.02 − 0.09 0.22 41.43 − 0.04 93.86 Fe0.49S JPL-gb5-3 0.07 52.97 − − − 0.01 0.25 − − 0.02 0.04 − 0.13 0.24 45.87 − − 99.61 Fe0.50S JPL-gb5-6 − 52.27 − − − − 0.13 − − − − 0.09 − 0.14 45.56 − − 98.19 Fe0.50S JPL-gb5-8 0.07 52.57 − − − 0.08 0.09 − 0.03 − 0.04 − 0.08 0.17 45.89 0.05 − 99.06 Fe0.50S JPL-gb5-9 − 53.65 − − 0.03 − − − 0.00 0.01 0.07 − 0.16 0.09 46.80 0.01 − 100.83 Fe0.50S 注:“−”表示低于检出限。 -
[1] 陈衍景, 张静, 张复新, 等. 西秦岭地区卡林—类卡林型金矿床及其成矿时间、构造背景和模式[J]. 地质论评, 2004, 50(2): 134-152 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.02.004
Chen Yanjing, Zhang Jing, Zhang Fuxin, et al. Carlin and Carlin-like gold deposit in western Qinling Mountains and their metallogenic time, tectonic setting and model[J]. Geological Review, 2004, 50(2): 134-152. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2004.02.004
[2] 丁坤. 南秦岭柞-山矿集区典型金矿床成矿作用与成矿动力学背景[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020
DING Kun. Metallogenesis and metallogenic dynamics background of typical gold deposits in Zha-shan ore concentration area, South Qinling[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2020
[3] 丁坤, 王瑞廷, 刘凯, 等. 南秦岭柞水-山阳矿集区夏家店金矿床黄铁矿微量元素和氢、氧、硫同位素对矿床成因的制约[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(6): 1622-1632
DING Kun, WANG Ruiting, LIU Kai, et al. Pyrite trace element, hydrogen, oxygen, and sulfur isotope geochemistry of the Xiajiadian gold deposit in Zhashui-Shanyang orefield, south Qinling orogen, and its metallogenic constraints[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(6): 1622-1632.
[4] 丁坤, 王瑞廷, 王智慧, 等. 南秦岭柞水-山阳矿集区王家坪金矿床地质特征及矿床成因探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(1): 167-178
DING Kun, WANG Ruiting, WANG Zhihui, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Wangjiaping gold deposit in Zhashui-Shanyang ore concentration area of south Qinling[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(1): 167-178.
[5] 方维萱, 芦继英. 陕西银硐子-大西沟菱铁银多金属矿床热水沉积岩相特征及成因[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(3): 431-438
FANG Weixuan, LU Jiying. Genesis and characteristics of hydrothermal sedimentary facies Forsiderite-silver-polymetallic deposits in Yindongzi and Daxigou, Shanxi, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2000, 18(3): 431-438.
[6] 高菊生, 王瑞廷, 张复新, 等. 南秦岭寒武系黑色岩系中夏家店金矿床地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6): 1371-1378
GAO Jusheng, WANG Ruiting, ZHANG Fuxin, et al. Geology and geochemistry of the Xiajiadian gold deposit in the Cambrian black rock series in the South Qinling[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6): 1371-1378.
[7] 葛战林, 郝迪, 张晓星, 等. 东秦岭大蛇沟钨矿区赋矿围岩成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学和地球化学证据[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(6): 1633-1650
GE Zhanlin, HAO Di, ZHANG Xiaoxing, et al. Petrogenesis of host rocks in the Dashegou tungsten orefield, East Qinling Orogen: Evidences from zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(6): 1633-1650.
[8] 胡楚雁. 黄铁矿的微量元素及热电性和晶体形态分析[J]. 现代地质, 2001, 15(2): 238-241
HU Chuyan. Characteristics of trace elements, thermoelectricity and crystal form of pyrite[J]. Geoscience, 2001, 15(2): 238-241.
[9] 胡文宣, 张文兰, 胡受奚, 等. 含金毒砂中晶格金的确定及其形成机理研究[J]. 地质学报, 2001(3): 410-418
HU Wenxuan, ZHANG Wenlan, HU Shouxi, et al. Determination of structural gold in Au-bearing arsenopyrite and its formation mechanism[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2001(3): 410-418.
[10] 华曙光, 王力娟, 贾晓芳, 等. 陕西镇安丘岭卡林型金矿金的赋存状态和富集机理[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2012, 37(5): 989-1002
HUA Shuguang, WANG Lijuan, JIA Xiaofang, et al. Occurrence and enrichment mechanism of gold in the Qiuling Carlin-type gold deposit, Zhen’an county, Shaanxi province, China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2012, 37(5): 989-1002.
[11] 姜寒冰, 杨合群, 赵国斌, 等. 西秦岭成矿带区域成矿规律概论[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 187−202.
JIANG Hanbing, YANG Hequn, ZHAO Guobin, et al. Discussion on the Metallogenic Regularity in West Qinling Metallogenic Belt, China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 187−202.
[12] 李九玲, 亓锋, 徐庆生. 矿物中呈负价态之金—毒砂和含砷黄铁矿中“结合金”化学状态的进一步研究[J]. 自然科学进展, 2002, 12(9): 952-958
LI Jiuling, QI Feng, XU Qingsheng. The negative valence gold in mineral: A further study on the chemical state of “bound gold” in arsenian pyrites and arsenopyrites[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2002, 12(9): 952-958.
[13] 李平, 陈隽璐, 张越, 等. 商丹俯冲增生带南缘土地沟–池沟地区侵入岩形成时代及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 10−27.
LI Ping, CHEN Junlu, ZHANG Yue, et al. The Formation Age of Intrusions from Tudigou–Chigou Region in Southern Margin of Shangdan Subduction–Accretion Belt and Its Geological Significance. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 10−27.
[14] 李雪松, 姚志亮, 王小平, 等. 陕西省柞水县金盆梁金多金属矿勘探(1500 m标高以下)工作总结[R]. 西安: 西安西北有色物探总队有限公司, 2021.
[15] 刘家军, 刘冲昊, 王建平, 等. 西秦岭地区金矿类型及其成矿作用[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5): 1-16
LIU Jiajun, LIU Chonghao, WANG Jianping, et al. Classification and mineralization of the gold deposit in the western Qinling region, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(5): 1-16.
[16] 刘凯, 王瑞廷, 樊忠平, 等. 秦岭造山带柞水-山阳矿集区夏家店金矿床成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(6): 1278-1296
LIU Kai, WANG Ruiting, FAN Zhongping, et al. Metallogenic age of Xiajiadian gold deposit in the Zhashui-Shanyang ore concentration, Qinling orogenic belt and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(6): 1278-1296.
[17] 刘仕玉, 刘玉平, 叶霖, 等. 滇东南都龙超大型锡锌多金属矿床黄铁矿LA-ICPMS微量元素组成研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(4): 1196-1212 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.04.14
LIU Shiyu, LIU Yuping, YE Lin, et al. LA-ICPMS trace elements of pyrite from the super-large Dulong Sn-Zn polymetallic deposit, southeastern Yunnan, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(4): 1196-1212. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.04.14
[18] 刘英俊, 马东升. 金的地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1991
LIU Yingjun, MA Dongsheng. The Geochemistry of gold[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1991.
[19] 毛景文. 西秦岭地区造山型与卡林型金矿床[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(1): 11-13
MAO Jingwen. Geology, distribution and Classification of gold deposits in the western Qinling belt, central China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemisty, 2001, 20(1): 11-13.
[20] 陕西省地质调查院. 中国区域地质志·陕西志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017
Shaanxi Institute of Geological Survey. The regional geology of China, Shaanxi Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017.
[21] 沈关文, 张良, 孙思辰, 等. 江南造山带万古金矿床含金硫化物组构与金沉淀机制[J]. 岩石学报, 2022, 38(1): 91-108 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.01.07
SHEN Guanwen, ZHANG Liang, SUN Sichen, et al. Textures of gold-bearing sulfides and gold precipitation mechanism, Wangu gold deposit, Jiangnan Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2022, 38(1): 91-108. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2022.01.07
[22] 苏选民, 马秋峰, 韩玉信. 陕西省柞水县金盆梁金多金属矿普查2012年总结[R]. 西安: 陕西省地质矿产勘查开发局第二综合物探大队, 2012.
[23] 孙宁岳, 李国武, 申俊峰, 等. 黄铁矿精细结构与晶胞参数的关系及其标型意义[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(4): 333−342.
SUN Ningyue, LI Guowu, SHEN Junfeng, et al. Relationship between Fine Structure and Cell Parameters of Pyrite and Their Typomorphic Significance[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(4): 333−342.
[24] 汪超, 王瑞廷, 刘云华, 等. 陕西商南三官庙金矿床地质特征、金的赋存状态及矿床成因探讨[J]. 矿床地质, 2021, 40(3): 491-508
WANG Chao, WANG Ruiting, LIU Yunhua, et al. Geological characteristics, modes of occurrence of gold and genesis of San’guanmiao gold deposit, Shangnan, Shaanxi Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2021, 40(3): 491-508.
[25] 王瑞廷, 冀月飞, 成欢, 等. 南秦岭柞水-山阳矿集区金铜矿床成矿规律与找矿方向[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(6): 1487-1503
WANG Ruiting, JI Yuefei, CHENG Huan, et al. Metallogenic regularities and future prospecting direction of gold-copper deposits in the Zhashui-Shanyang orefield, Southern Qinling Orogen[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(6): 1487-1503.
[26] 王宗起, 闫全人, 闫臻, 等. 秦岭造山带主要大地构造单元的新划分[J]. 地质学报, 2009, 83(11): 1527-1546
WANG Zongqi, YAN Quanren, YAN Zhen, et al. New division of the main tectonic units of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2009, 83(11): 1527-1546.
[27] 吴发富, 王宗起, 闫臻, 等. 秦岭山阳-柞水地区燕山期中酸性侵入岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素组成[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2): 451-471
WU Fafu, WANG Zongqi, YAN Zhen, et al. Geochemical characteristics, zircon U-Pb ages and Lu-Hf isotopic composition of the Yanshanian intermediate-acidic plutons in the Shanyang-Zhashui areas, Qinling Orogenic Belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(2): 451-471.
[28] 谢桂青, 任涛, 李剑斌, 等. 陕西柞山盆地池沟铜钼矿区含矿岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄和岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1): 15-26
XIE Guiqing, REN Tao, LI Jianbin, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and petrogenesis of ore-bearing granitoid for the Chigou Cu-Mo deposit form the Zhashan basin, Shaanxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(1): 15-26.
[29] 熊潇, 朱赖民, 张国伟, 等. 南秦岭柞水-山阳矿集区小河口矽卡岩型铜矿床矿物化学及其成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(8): 2597-2614 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.08.16
XIONG Xiao, ZHU Laimin, ZHANG Guowei, et al. Mineral chemistry of the Xiaohekou skarn copper deposit in the Zhashui-Shanyang ore cluster area, South Qinling and its metallogenic significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(8): 2597-2614. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.08.16
[30] 闫臻, 王宗起, 陈雷, 等. 南秦岭山阳-柞水矿集区构造-岩浆-成矿作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(2): 401-414
YAN Zhen, WANG Zongqi, CHEN Lei, et al. Tectono-magmatism and metallogeneses of Shanyang-Zhashui ore concentration area in Qinling Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(2): 401-414
[31] 员媛娇, 范成龙, 吕喜平, 等. 电子探针和LA-ICP-MS技术研究内蒙古浩尧尔忽洞金矿床毒砂矿物学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(2): 211-225
YUAN Yuanjiao, FAN Chenglong, LYU Xiping, et al. Application of EPMA and LA-ICP-MS to study mineralogy of arsenopyrite from the Haoyaoerhudong gold deposit, Inner Mongolia, China[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(2): 211-225.
[32] 张博, 李诺, 陈衍景. 热液矿床金的赋存状态及研究方法[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25(5): 251-265
ZHANG Bo, LI Nuo, CHEN Yanjing. Occurrence state of gold in hydrothermal deposits and related research methods[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25(5): 251-265.
[33] 张国伟, 郭安林, 董云鹏, 等. 关于秦岭造山带[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5): 746-768
ZHANG Guowei, GUO Anlin, DONG Yunpeng, et al. Rethinking of the Qinling Orogen[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(5): 746-768.
[34] 张嘉升, 潘爱芳, 樊会民, 等. 陕西柞水地区金盆梁金矿区水系沉积物地球化学特征与找矿方向[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2014, 36(4): 55-63 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2014.04.005
ZHANG Jiasheng, PAN Aifang, FAN Huimin, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediment in Jinpenliang gold mining area of Zhashui area, Shaanxi and its prospecting direction[J]. Journal of Earth Science and Environment, 2014, 36(4): 55-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2014.04.005
[35] 张然, 肖志斌, 付超, 等. 胶东地区新立金矿中金矿物和载金黄铁矿成因矿物学特征及地质意义[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(6): 997-1006 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.6.ykcs202206011
ZHANG Ran, XIAO Zhibin, FU Chao, et al. Genetic mineralogy and geological significance of gold minerals and gold-bearing pyrites from the Xinli gold deposit in the Jiaodong area[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(6): 997-1006. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2022.6.ykcs202206011
[36] 张亚峰, 陈国超, 杨玲, 等. 西秦岭凤县北部罗汉寺岩组沉积时代和源区特征: 来自LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄证据[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(3): 805-823
ZHANG Yafeng, CHEN Guochao, YANG Ling, et al. A study of the provenance and sedimentary age of the Luohansi Formation in the Fengxian County, eastern part of West Qinling Orogenic belt: Evidence from LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(3): 805-823.
[37] 赵静, 梁金龙, 韩波. 水银洞金矿与阳山金矿载金矿物成分分析及金的赋存状态[J]. 科技通报, 2017, 33(1): 24-31 doi: 10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2017.01.006
ZHAO Jing, LIANG Jinlong, HAN Bo. The component analyses of Au-Bearing minerals and the occurrence of gold in Shuiyindong and Yangshan Carlin-type gold deposits, China[J]. Bulletin of Science and Technology, 2017, 33(1): 24-31. doi: 10.13774/j.cnki.kjtb.2017.01.006
[38] 赵珊茸, 边秋娟, 凌其聪. 结晶学及矿物学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2004
ZHAO Shanrong, BIAN Qiujuan, LING Qicong. Crystallography and mineralogy[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2004.
[39] 周学武, 李胜荣, 鲁力, 等. 辽宁丹东五龙矿区石英脉型金矿床的黄铁矿标型特征研究[J]. 现代地质, 2005, 19(2): 231-238 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.011
Zhou Xuewu, Li Shengrong, Lu Li, et al. Study of pyrite typomorphic characteristics of Wulong quartz-vein-type gold deposit in Dandong, Liaoning Province, China[J]. Geoscience, 2005, 19(2): 231-238. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.011
[40] 朱赖民, 郑俊, 熊潇, 等. 南秦岭柞水-山阳矿集区园子街岩体岩石地球化学与成矿潜力探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(5): 189-205
ZHU Laimin, ZHENG Jun, XIONG Xiao, et al. Petrogeochemistry and mineralization potential of the Yuanzijie intrusion in the Zhashui-Shanyang ore deposit cluster in southern Qinling[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(5): 189-205.
[41] Arehart G B, Chryssoulis S L, Kesler S E. Gold and arsenic in iron sulfides from sediment-hosted disseminated gold deposits; implications for depositional processes[J]. Economic Geology, 1993, 88(1): 171-185. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.88.1.171
[42] Bateman R, Hagemann S. Gold mineralisation throughout about 45 Ma of Archaean orogenesis: Protracted flux of gold in the Golden Mile, Yilgarn craton, Western Australia[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2004, 39(5-6): 536-559. doi: 10.1007/s00126-004-0431-2
[43] Bralia A, Sabatini G, Troja F. A revaluation of the Co/Ni ratio in pyrite as geochemical tool in ore genesis problems: Evidences from southern Tuscany pyritic deposits[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1979, 14(3): 353-374.
[44] Cabri L J, Newville M, Gordon R A, et al. Chemical speciation of gold in arsenopyrite[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2000, 38(5): 1265-1281. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.38.5.1265
[45] Choi S G, Youm S J. Compositional variation of arsenopyrite and fluid evolution at the Ulsan deposit, southeastern Korea: A low-sulfidation porphyry system[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2000, 38(3): 567-583. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.38.3.567
[46] Cline J S, Hofstra A H, Muntean J L, et al. Carlin-type gold deposit in Nevada: Critical geologic characteristics and viable model[J]. Economic Geology, 2005, 100th Anniversary Volume: 451−484.
[47] Cook N J, Chryssoulis S L. Concentrations of “Invisible Gold” in the common sulfides[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1990, 28(1): 1-16.
[48] Deditius A P, Utsunomiya S, Renock D, et al. A proposed new type of arsenian pyrite: Composition, nanostructure and geological significance[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2008, 72(12): 2919-2933. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.03.014
[49] Ding K, Yang X Q, Wang H, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the granite porphyry from the Qinglingou gold deposit, South Qinling, China: Implication for petrogenesis and mineralization[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(6): 707. doi: 10.3390/min12060707
[50] Fleet M E, Chryssoulis S L, Maclean P J, et al. Arsenian pyrite from gold deposits: Au and As distribution investigated by SIMS and EMP, and color staining and surface oxidation by XPS and LIMS[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1993, 31(1): 1-17.
[51] Fleet M E, Mumin A H. Gold-bearing arsenian pyrite and marcasite and arsenopyrite from Carlin Trend gold deposits and laboratory synthesis[J]. American Mineralogist, 1997, 82(1-2): 182-193. doi: 10.2138/am-1997-1-220
[52] Fougerouse D, Reddy S M, Aylmore M, et al. A new kind of invisible gold in pyrite hosted in deformation-related dislocations[J]. Geology, 2021, 49(10): 1225-1229. doi: 10.1130/G49028.1
[53] Goldfarb R J, Berger B R, George M W, et al. Tellurium[A]. In: Critical mineral resources of the United States—Economic and environmental geology and prospects for future supply[R]. Reston: U. S. Geological Survey, 2017, R1−R14.
[54] Gopon P, Douglas J O, Auger M A, et al. A nanoscale investigation of Carlin-type gold deposits: An atom-scale elemental and isotopic perspective[J]. Economic Geology, 2019, 114(6): 1123-1133. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4676
[55] Groves D I, Goldfarb R J, Gebre-Mariam M, et al. Orogenic gold deposits: A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1998, 13(1): 7-27.
[56] Gu X X, Zhang Y M, Ge Z L, et al. Mineralization and genesis of the orogenic gold system in the Kalamaili area, East Junggar, Xinjiang, northwestern China[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2023.
[57] Hofstra A H, Cline J S. Characteristics and models for Carlin-type gold deposits[J]. Reviews in Economic Geology, 2000, 13: 163-220.
[58] Kretschmar U, Scott S D. Phase relations involving arsenopyrite in the system Fe-As-S and their application[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1976, 14(3): 364-386.
[59] Lentz D R. Sphalerite and arsenopyrite at the Brunswick No. 12 massive-sulfide deposit, Bathurst Camp, New Brunswick: Constraints on P-T evolution[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2002, 40(1): 19-31. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.40.1.19
[60] Liang Q L, Xie Z J, Song X Y, et al. Evolution of invisible au in arsenian pyrite in carlin-type Au deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2021, 116(2): 515-526. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4781
[61] Liu J J, Dai H Z, Zhai D G, et al. Geological and geochemical characteristics and formation mechanisms of the Zhaishang Carlin-like type gold deposit, western Qinling Mountains, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 64: 273-298. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.07.016
[62] Loftus-Hills G, Solomon M. Cobalt, nickel and selenium in sulphides as indicators of ore genesis[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1967, 2(3): 228-242.
[63] Ma Y B, Zhu L M, Lu R K, et al. Geology and in-situ sulfur and lead isotope analyses of the Jinlongshan Carlin-type gold deposit in the Southern Qinling Orogen, China: Implications for metal sources and ore genesis[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2020, 126: 103777. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103777
[64] Mao J W, Qiu Y M, Goldfarb R J, et al. Geology, distribution, and classification of gold deposits in the western Qinling belt, central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37: 352-377. doi: 10.1007/s00126-001-0249-0
[65] Palenik C S, Utsunomiya S, Reich M, et al. “Invisible” gold revealed: Direct imaging of gold nanoparticles in a Carlin-type deposit[J]. American Mineralogist, 2004, 89(10): 1359-1366. doi: 10.2138/am-2004-1002
[66] Reich M, Kesler S E, Utsunomiya S, et al. Solubility of gold in arsenian pyrite[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2005, 69(11): 2781-2796. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.011
[67] Sharp Z D, Essene E J, Kelly W C. A re-examination of the arsenopyrite geothermometer: Pressure considerations and applications to natural assemblages[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1985, 23(4): 517-534.
[68] Shenberger D M, Barnes H L. Solubility of gold in aqueous sulfide solutions from 150 to 350 °C[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1989, 53(2): 269-278. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90379-7
[69] Simon G, Kesler S E, Chryssoulis S. Geochemistry and textures of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite, Twin Creeks, Nevada: Implications for deposition of gold in Carlin-type deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1999a, 94(3): 405-421. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.94.3.405
[70] Simon G, Huang H, Penner-Hahn J E, et al. Oxidation state of gold and arsenic in gold-bearing arsenian pyrite[J]. American Mineralogist, 1999b, 84(7-8): 1071-1079. doi: 10.2138/am-1999-7-809
[71] Su W C, Zhang H T, Hu R Z, et al. Mineralogy and geochemistry of gold-bearing arsenian pyrite from the Shuiyindong Carlin-type gold deposit, Guizhou, China: Implications for gold depositional processes[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6): 653-662. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0328-9
[72] Wu X, Delbove F. Hydrothermal synthesis of gold-bearing arsenopyrite[J]. Economic Geology, 1989, 84(7): 2029-2032. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.84.7.2029
[73] Zhang B, Li N, Shu S P, et al. Textural and compositional evolution of Au-hosting Fe-S-As minerals at the Axi epithermal gold deposit, Western Tianshan, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 100: 31-50. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.08.002
[74] Zhang Z Y, Wang Y H, Zhang F F, et al. Origin of high Ba-Sr granitoids at Chigou in central China and implications for Cu mineralization: Insights from whole-rock geochemistry, zircon U-Pb dating, Lu-Hf isotopes and molybdenite Re-Os systematics[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 138: 104416. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104416
-




 下载:
下载: