Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Geological Disasters in Yulin City Based on the Records from 1984 to 2022
-
摘要:
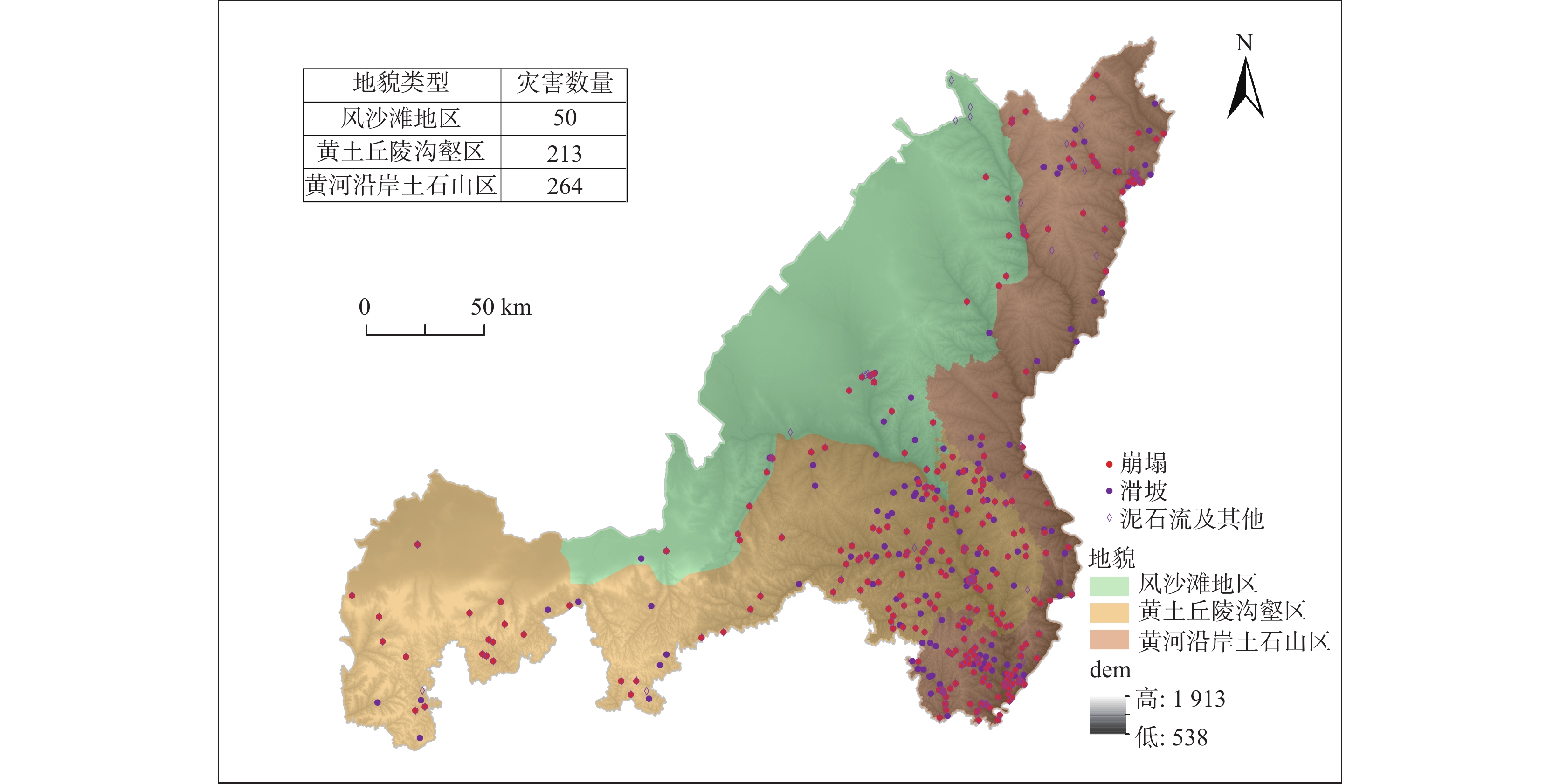
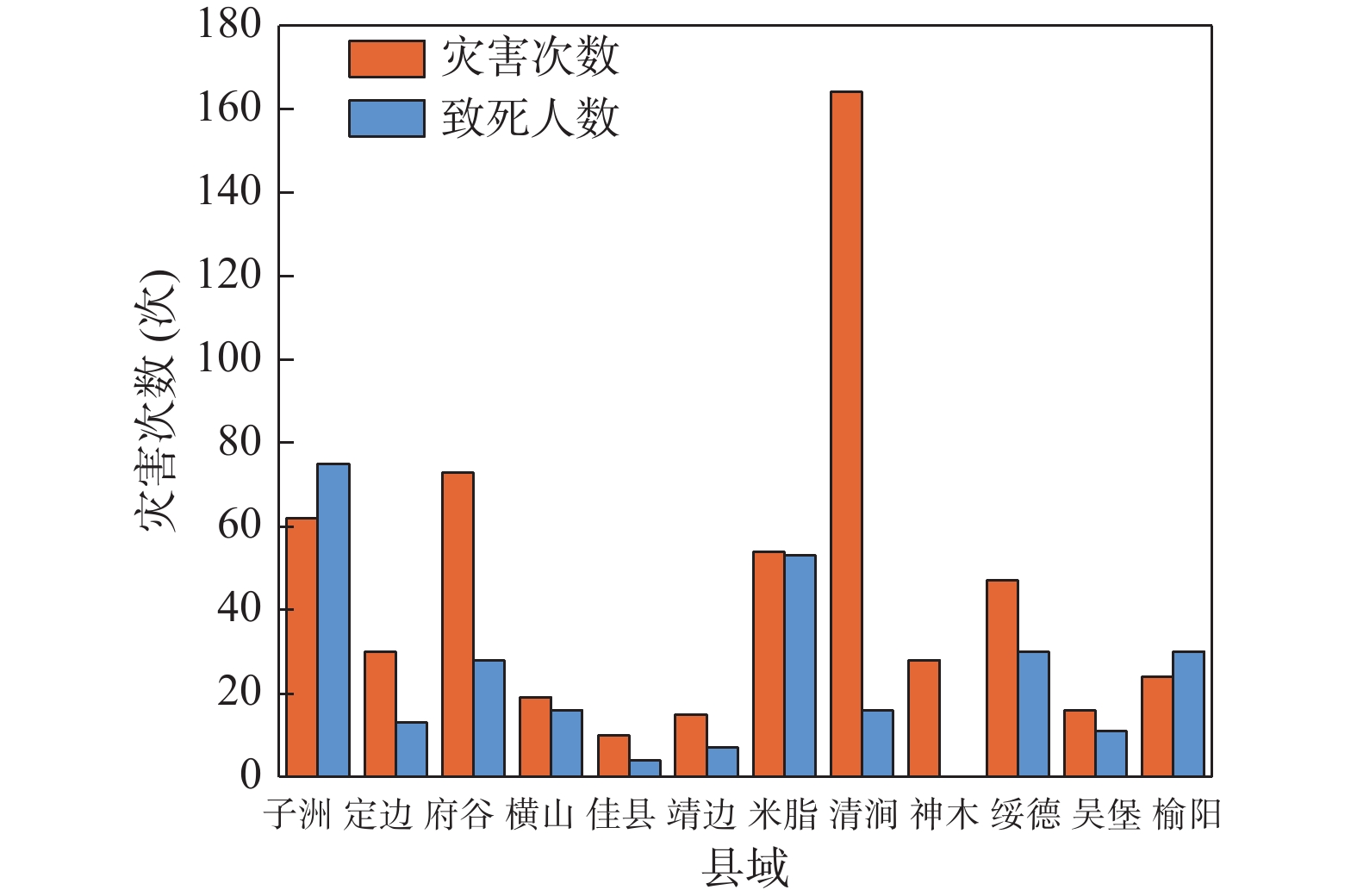
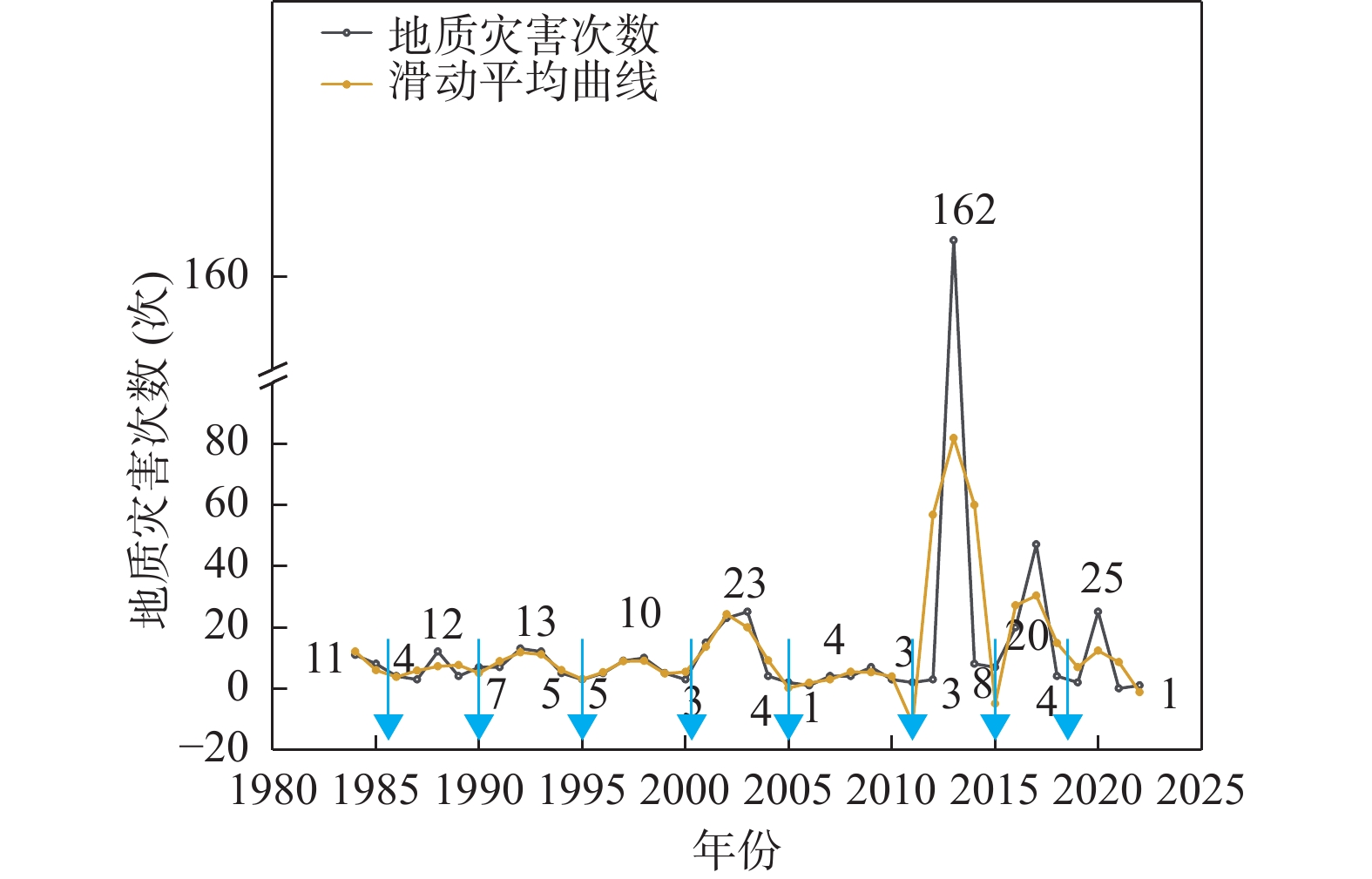
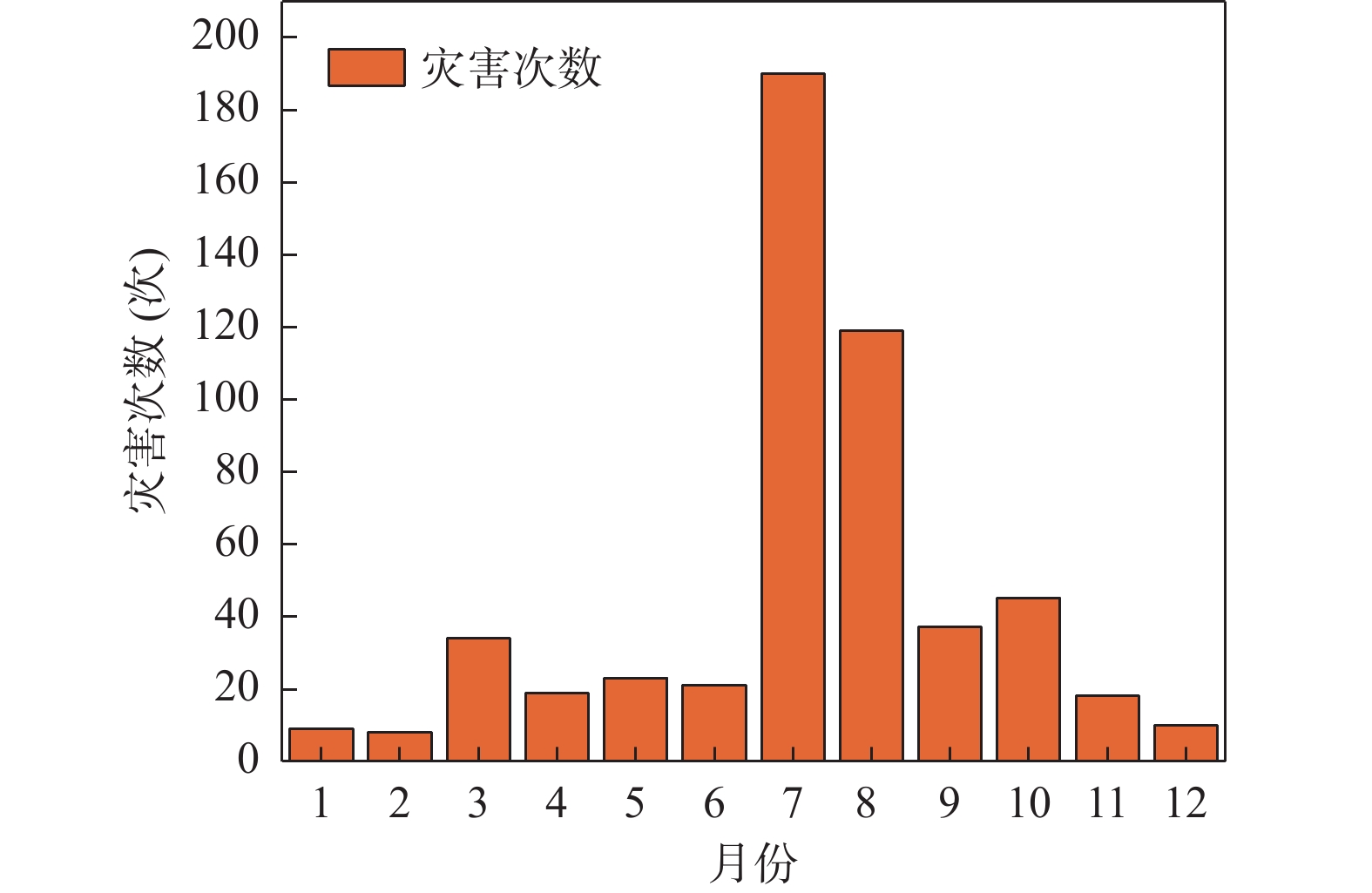
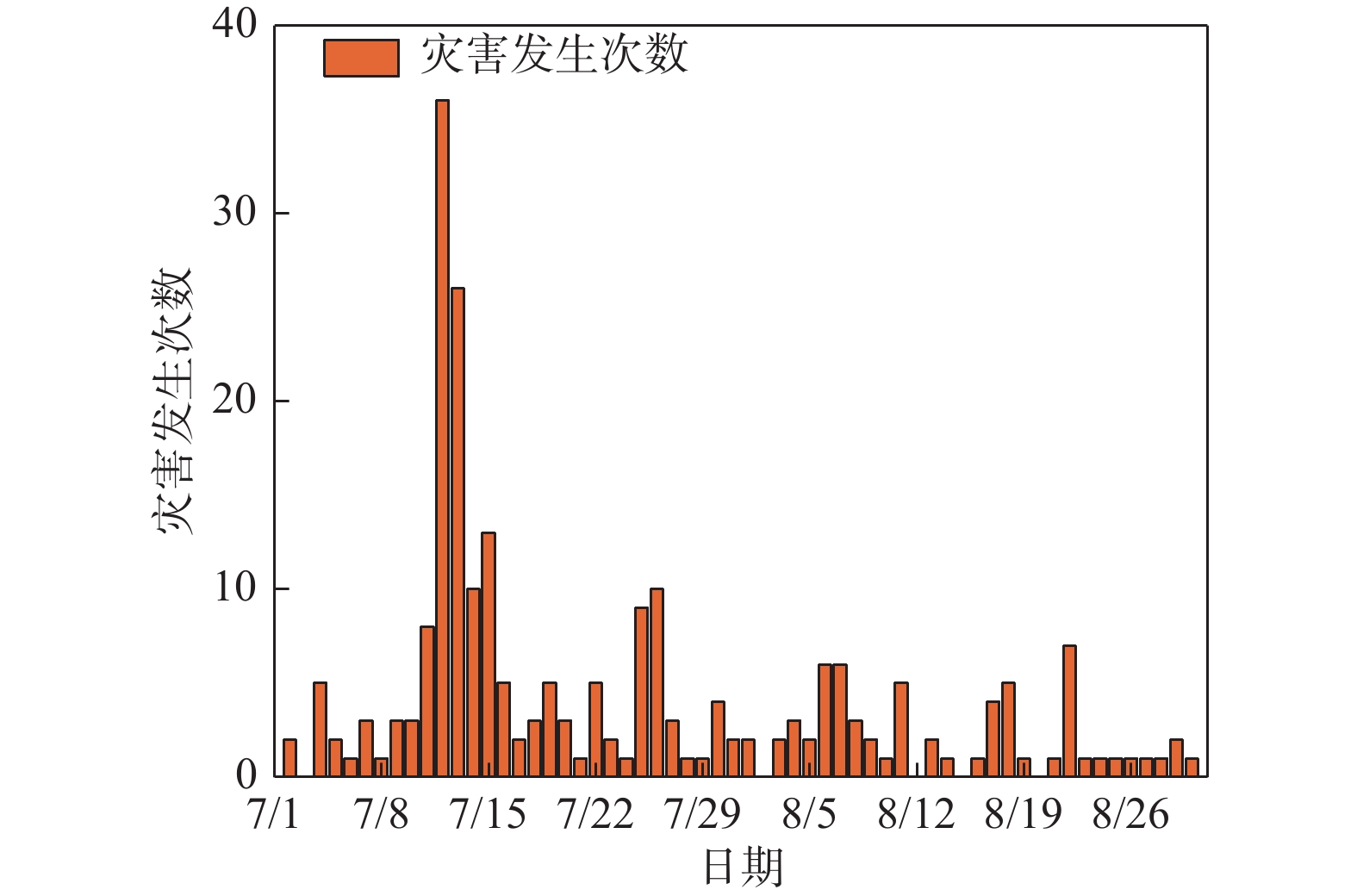
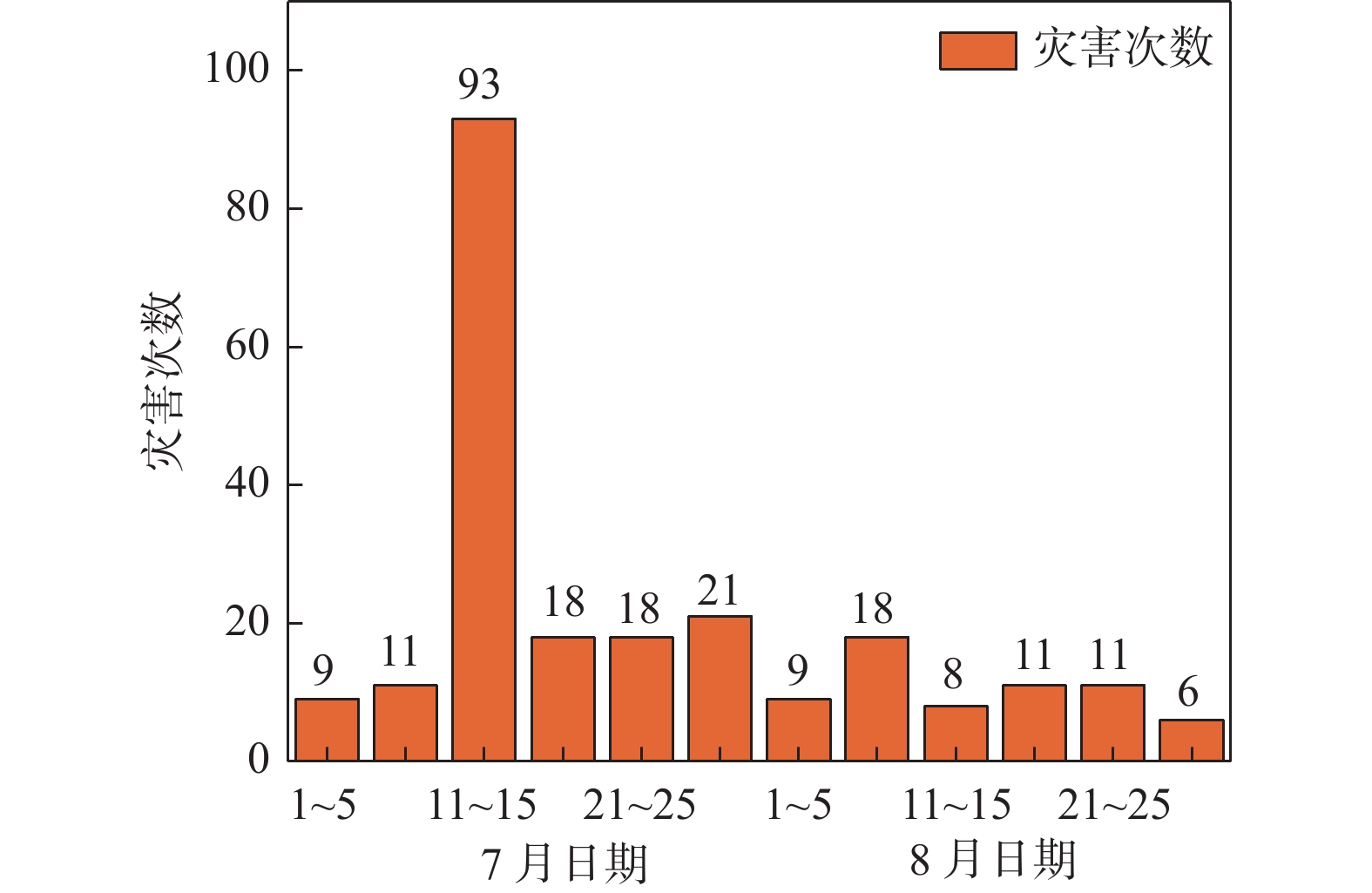
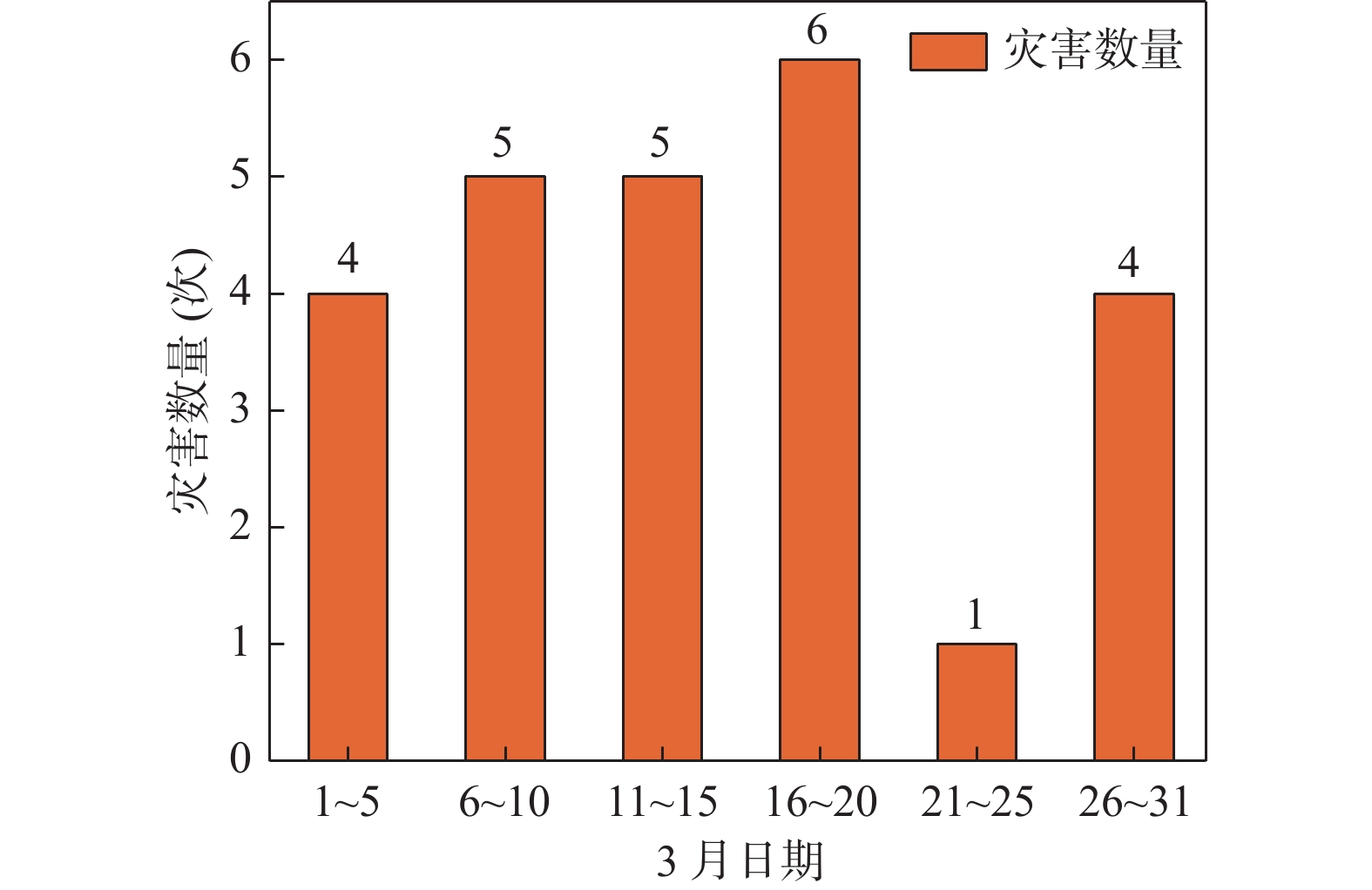
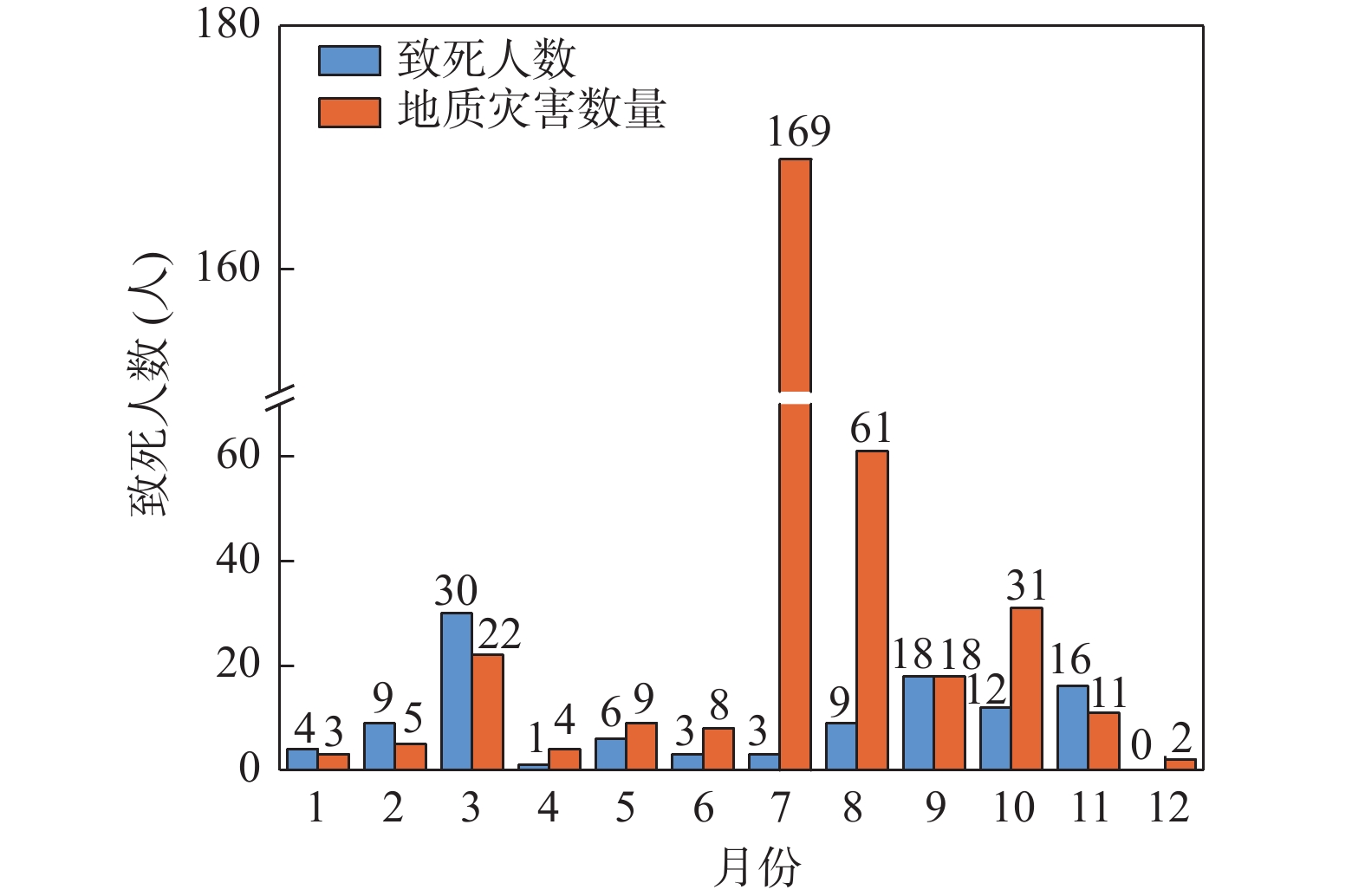
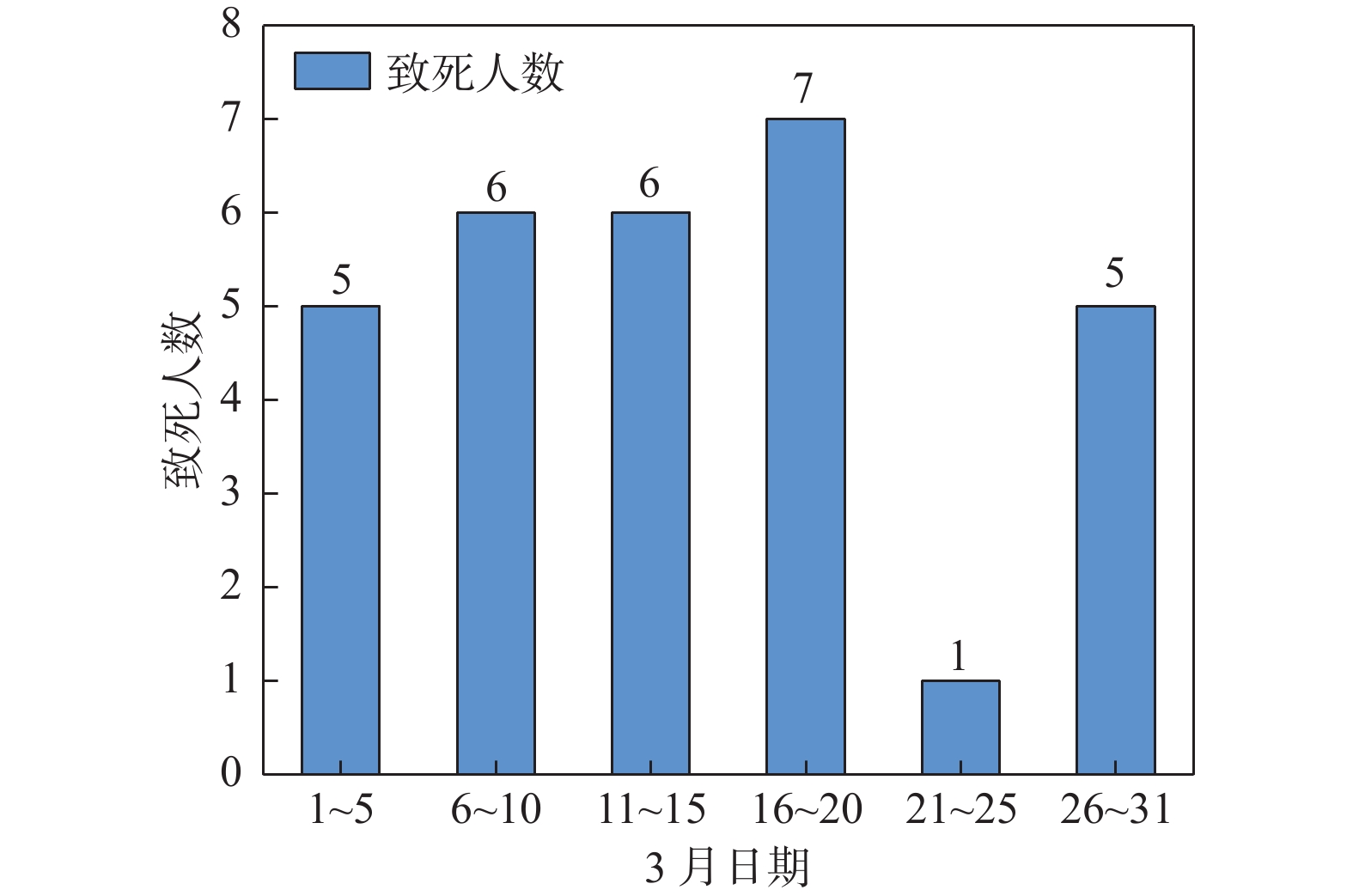
地质灾害时空分布规律研究是制定地质灾害防治计划和落实防灾减灾措施的重要基础。笔者系统分析1984~2022年榆林市有记录的527组地质灾害数据,总结榆林市地质灾害的时空分布规律。空间上,榆林市地质灾害主要发生于清涧、子洲、米脂等县域,在地貌上以黄土丘陵沟壑区为主,黄河沿岸土石山区次之,风沙滩地区不发育。在时间上,年内地质灾害发生主要集中在7~10月汛期,月内集中于7月11~15日,冻融期均有分布且致死人数最多。灾害数量、致死人数越多,其重现期越长。子洲县年地质灾害致死概率最高(16.5%),其次为米脂县(9.8%)和府谷县(5.6%)。由此提出下一步工作建议:①加强汛期降雨量与地质灾害发生概率定量关系研究,完善地质灾害气象预警阈值。②加强冻融机理研究,建立冻融型地质灾害防御方案。③加强“风险点+危险区”的双控机制研究。
Abstract:The study of the spatial and temporal distribution of geological disasters is an important basis for formulating geological disaster prevention plans and implementing disaster prevention and mitigation measures. This paper systematically analyzes 527 sets of geological disaster data recorded in Yulin City from 1984 to 2022. The spatial and temporal distribution rules of geological disasters in Yulin City has been summarized. Spatially, the geological disasters in Yulin City mainly occur in Qingjian, Zizhou, Mizhi Counties, and are mainly distributed in the earth−rock mountainous areas along the Yellow River and the loess hilly and gully areas. In terms of time, the number of geological disasters takes 5 years as a cycle, the flood season is frequent, concentrated on July 11~15, the freeze−thaw period is evenly distributed and the number of deaths is the largest. The more the number of disasters and deaths, the longer the return period. Zizhou County had the highest annual probability of death from geological disasters, 16.5%, followed by Mizhi County, 9.8%, and Fugu County, 5.6%. Therefore, the following suggestions are put forward: ① Strengthen the quantitative relationship between rainfall in flood season and the probability of geological disasters, and improve the meteorological warning threshold of geological disasters. ② Strengthen the study of freeze−thaw mechanism and establish a freeze−thaw geological disaster prevention plan. ③ Strengthen the research on the dual control mechanism of "risk point + risk area".
-

-
表 1 榆林市各区县滑坡崩塌数量表
Table 1. Number of landslide collapses in Yulin city
县区 类 型 榆阳 神木 府谷 定边 靖边 横山 绥德 米脂 佳县 吴堡 清涧 子州 崩塌 发生数(次) 6 11 43 26 6 8 38 29 8 7 110 34 致死灾害数(次) 1 0 3 4 2 4 5 10 2 1 2 11 死亡人数(人) 2 0 28 11 6 6 13 20 4 2 3 63 滑坡 发生数(次) 11 11 15 4 8 9 7 26 3 9 53 24 致死灾害数(次) 4 0 0 1 1 4 5 12 0 4 2 4 死亡人数(人) 26 0 0 2 1 10 16 31 0 10 13 7 表 2 年地质灾害发生频率 、年致死地质灾害发生频率、 年致死人数发生频率及其重现期表
Table 2. The frequency and return period of annual geological disasters, annual fatal geological disasters and annual fatalities
灾害发生
数(次)经验频率
(%)重现期
(a)致死灾害
数(次)致死灾害
所占比例(%)经验频率
(%)重现期
(a)致死人数
(人)经验频率
(%)重现期
(a)0 97.5 1 0 4.08 88.75 1 0 88.75 1 1 93.75 1 1 49.39 66.25 2 1 76.25 1 2 87.5 1 2 10.82 46.25 2 2 68.75 1 3 77.5 1 3 9.39 28.75 3 3 58.75 2 4 63.75 2 4 11.02 16.25 6 5 52.5 2 5 52.5 2 5 7.76 10 10 6 48.75 2 7 43.75 2 6 7.55 3.75 27 7 36.25 3 8 36.25 3 8 25 4 9 32.5 3 9 22.5 4 10 30 3 10 20 5 11 27.5 4 12 16.25 6 12 23.75 4 13 12.5 8 13 20 5 15 10 10 15 17.5 6 22 7.5 13 20 15 7 28 5 20 23 12.5 8 35 2.5 40 25 8.75 11 47 5 20 162 2.5 40 表 3 各区县人员年地质灾害致死概率表
Table 3. The annual death probability of geological disasters in each county
参数 县 区 林阳 神木 府谷 定边 靖边 横山 绥德 米脂 佳县 吴堡 清涧 子洲 V 0.100 0.000 0.100 0.047 0.025 0.057 0.104 0.183 0.014 0.043 0.057 0.269 PL 0.385 0.231 0.564 0.282 0.231 0.308 0.385 0.538 0.154 0.359 0.231 0.615 PLOL(%) 3.860 0.000 5.661 1.314 0.579 1.765 3.998 9.843 0.221 1.544 1.323 16.543 -
[1] 白永健, 铁永波, 倪化勇, 等. 鲜水河流域地质灾害时空分布规律及孕灾环境研究[J]. 灾害学, 2014, 29(04): 69-75 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2014.04.014
BAI Yongjian, TIE Yongbo, NI Huayong, et al. Temporal-Spatial Distribution and Environment Pregnant of Geohazards in Xianshui River of Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2014, 29 (4): 69-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2014.04.014
[2] 崔鹏, 胡凯衡, 陈华勇, 等. 丝绸之路经济带自然灾害与重大工程风险[J]. 科学通报, 2018, 63(11): 989-997 doi: 10.1360/N972017-00867
CUI Peng, HU Kaiheng, CHEN Huayong, et al. Risks along the Silk Road Economic Belt owing to natural hazards and construction of major projects[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2018, 63(11): 989-997. doi: 10.1360/N972017-00867
[3] 樊芷吟, 苟晓峰, 秦明月, 等. 基于信息量模型与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 工程地质学报, 2018, 26(02): 340-347 doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-052
FAN Zhiyin, GOU Xiaofeng, QIN Mingyue, et al. Information and Logistic Regression Models Based Coupling Analysis for Susceptibility of Geological Hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(02): 340-347. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017-052
[4] 何佳阳, 巨能攀, 解明礼, 等. 高山峡谷地区地质灾害隐患InSAR识别技术对比[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2023: 1–20. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220829.1632.004.html
HE Jiayang, JU Nengpan, JIE Mingli, et al. Comparison of InSAR Technology for Identification of Hidden Dangers of Geological Hazards in Alpine and Canyon Areas[J]. Earth Science, 2023: 1-20. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1874.P.20220829.1632.004.html
[5] 冷艳秋. 黄土水敏特性及其灾变机制研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2018
LENG Yanqiu. Research on water sensitivity characteristics and disaster mechanism of loess[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2018.
[6] 李守定, 乔华, 马世伟, 等. 基于温度-降雨双参数的新疆地质灾害预警模型[J]. 水利水电技术(中英文), 2021, 52(11): 207-218
LI Shouding, QIAO Hua, MA Shiwei, et al. Temperature-rainfall dual parameter-based early warming model for geological disasters in Xinjiang[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2021, 52(11): 207-218.
[7] 林两位, 王莉萍. 用Pearson-Ⅲ概率分布推算重现期年最大日雨量[J]. 气象科技, 2005(04): 314-317 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2005.04.006
LIN Liangwei, WANG Liping. Estimation of Annual Maximum Diurnal Precipitation for Reappearance Periods with Pearson-Ⅲ Distribution[J]. Meteorological Science and Technology, 2005(04): 314-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-6345.2005.04.006
[8] 刘文红. 黄土高原滑坡发育背景与成灾模式研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016.
LIU Wenhong. Study on the development background and disaster model of landslide in the Loess PlateauD]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2016.
[9] 马田田, 韦昌富, 陈盼, 等. 非饱和土毛细滞回与变形耦合弹塑性本构模型[J]. 岩土力学, 2012, 33(11): 3263-3270
MA Tiantian, WEI Changfu, CHEN Pan, et al. An elastoplastic constitutive model of unsaturated soils with capillary hysteresis and deformation coupling[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(11): 3263-3270.
[10] 彭建兵, 吴迪, 段钊, 等. 典型人类工程活动诱发黄土滑坡灾害特征与致灾机理[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(05): 971-980 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.021
PENG Jianbing, WU Di, DUAN Zhao, et al. Disaster Characteristics and Destructive Mechanism of Typical Loess Landslide Cases Triggered by Human Engineering Activities[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(05): 971-980. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.05.021
[11] 彭建兵, 王启耀, 庄建琦, 等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害形成动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(05): 714-730
PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, ZHUANG Jianqi, et al. Dynamic formation mechanism of landslide disaster on the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(05): 714-730.
[12] 申艳军, 杨更社, 荣腾龙, 等. 冻融循环作用下单裂隙类砂岩局部化损伤效应及端部断裂特性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2017, 36(03): 562-570
SHEN Yanjun, YANG Gengshe, RONG Tenglong, et al. Localized damage effects of quasi-sandstone with single fracture and fracture behaviors of joint end under cyclic freezing and thawing [J], Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2017, 36(03): 562-570.
[13] 孙萍萍, 张茂省, 冯立, 等. 黄土水敏性及其时空分布规律[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(02): 117-124
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, FENG Li, et al. Water Sensitivity of Loess and lts Spatial-Temporal Distribution on the Loess Plateau[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(02): 117-124.
[14] 孙萍萍, 张茂省, 贾俊等. 中国西部黄土区地质灾害调查研究进展[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(03): 96-107 doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2022.03.007
SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, JIA Jun, et al. Geo-hazards Research and Investigation in the Loess Regions of Western China [J], Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(03): 96-107. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2022.03.007
[15] 王潇. 冻融循环条件下陕北府谷地区砂岩物理力学性质研究[D]. 西安: 西安科技大学, 2014.
WANG Xiao. Study on the physical and mechanical properties of sandstone in Fugu region of Northern Shaanxi under the conditions of freeze-thaw cycles [D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2014.
[16] 王雁林, 任超, 李永红, 等. 关于构建陕西省地质灾害防治新机制的思考[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 50(03): 403-410
WANG Yanlin, REN Chao, LI Yonghong, et al. The construction of a new geological hazard prevention mechanism in Shaanxi Province [J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 50(03): 403-410.
[17] 伍艳, 蔡怀森, 刘慧, 等. 砒砂岩抗剪强度与其结构特征关系[J]. 水利水电科技进展, 2019, 39(05): 21-26
WU Yan, CAI Huaisen, LIU Hui, et al. Relationship between shear strength and structural characteristics of Pisha sandstone [J]. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resources, 2019, 39(05): 21-26.
[18] 熊德清, 崔笑烽. 喜马拉雅山脉地震带主要地质灾害与地形地貌关系——以西藏日喀则地区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(11): 1967-1980 doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.11.014
XIONG Deqing, CUI Xiaofeng. The relationship between main geological hazard and topography in the Himalayan seismic belt: A case study in the Xigaze area, Xizang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(11): 1967-1980. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2021.11.014
[19] 张卜平, 朱兴华, 成玉祥, 等. 黄土潜蚀机理及其致灾效应研究综述[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2021, 32(06): 41-52
ZHANG Buping, ZHU Xinghua, CHENG Yuxiang, et al. A review on loess subsurface-erosion mechanism and it's hazard effects [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(06): 41-52.
[20] 张林梵, 王佳运, 张茂省, 等. 基于BP神经网络的区域滑坡易发性评价[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(02): 260-270
ZHANG Linfan, WANG Jiayun, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Evaluation of Regional Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Based on BP Neural Network[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(02): 260-270.
[21] 张茂省, 孙传尧, 校培喜, 等. 延安市宝塔区地质灾害详细调查示范[J]. 西北地质, 2007, 40(02): 29-55 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2007.02.002
ZHANG Maosheng, SUN Chuanyao, XIAO Peixi, et al. A Demonstration Project for Detailed Geo-hazard Survey in the Baota District, Yan'an[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2007, 40(02): 29-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2007.02.002
[22] 张茂省, 党学亚. 干旱半干旱地区水资源及其环境问题: 陕北榆林能源化工基地例析[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014, 25–30.
ZHANG Maosheng, DANG Xueya. Water resources and Environmental Problems in arid and semi-arid Area-Case study of Yulin Energy and Chemical Industry Base in Northern Shaanxi [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014, 25–30.
[23] 张茂省, 黎志恒, 王根龙, 等. 白龙江流域地质灾害特征及勘查思路[J]. 西北地质, 2011, 44(03): 1-9
ZHANG Maosheng, LI Zhiheng, WANG Genlong, et al. The Geological Hazard Characteristics and Exploration ldeas of the Bailong River Basin[J], Northwestern Geology, 2011, 44(03): 1-9.
[24] 张茂省, 李同录. 黄土滑坡诱发因素及其形成机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2011, 19(04): 530-540 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.014
ZHANG Maosheng, LI Tonglu. Triggering Factors and Formation Mechanism of loess landslides[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(04): 530-540. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.014
[25] 张茂省, 唐亚明. 地质灾害风险调查的方法与实践[J]. 地质通报, 2008, No. 159(08): 1205-1216.
ZHANG Maosheng, TANG Yaming. Risk investigation method and practice of geohazards[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(8): 1205- 1216.
[26] Feng L, Zhang S, Jin Z, et al. The critical mechanics of the initiation of loess flow failure and implications for landslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 288: 106165.
[27] Zezere J L, Ferreira A B, Rodrigues M L. Landslides in the North of Lisbon Region (Portugal): Conditioning and triggering factors[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth Part A Solid Earth and Geodesy, 1999, 24(10): 925-934. doi: 10.1016/S1464-1895(99)00137-4
-




 下载:
下载: