Analysis of White Pollution of River Aluminum in Stone CoalMining Area in Haoping River Basin and Its Causes
-
摘要:
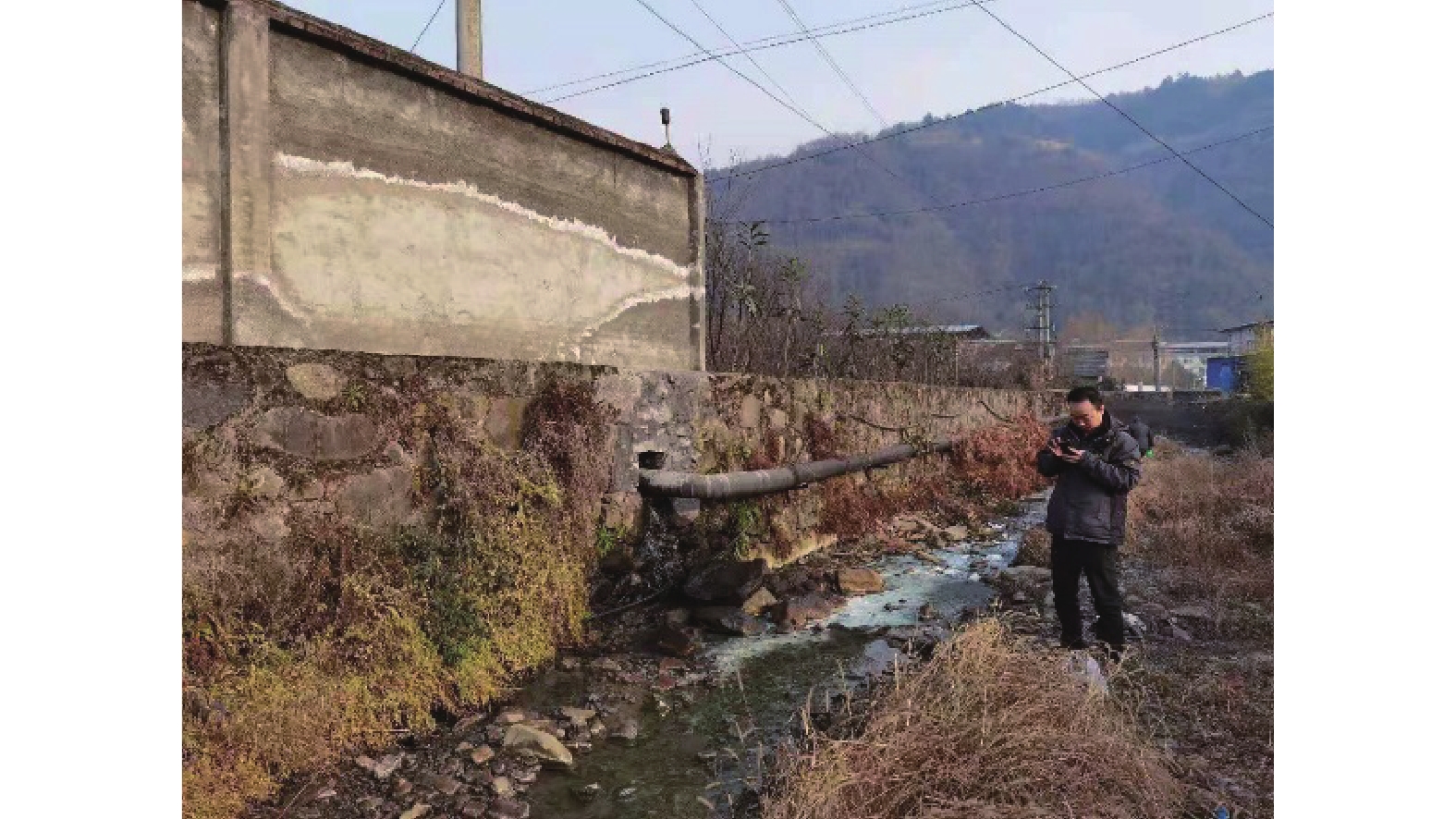
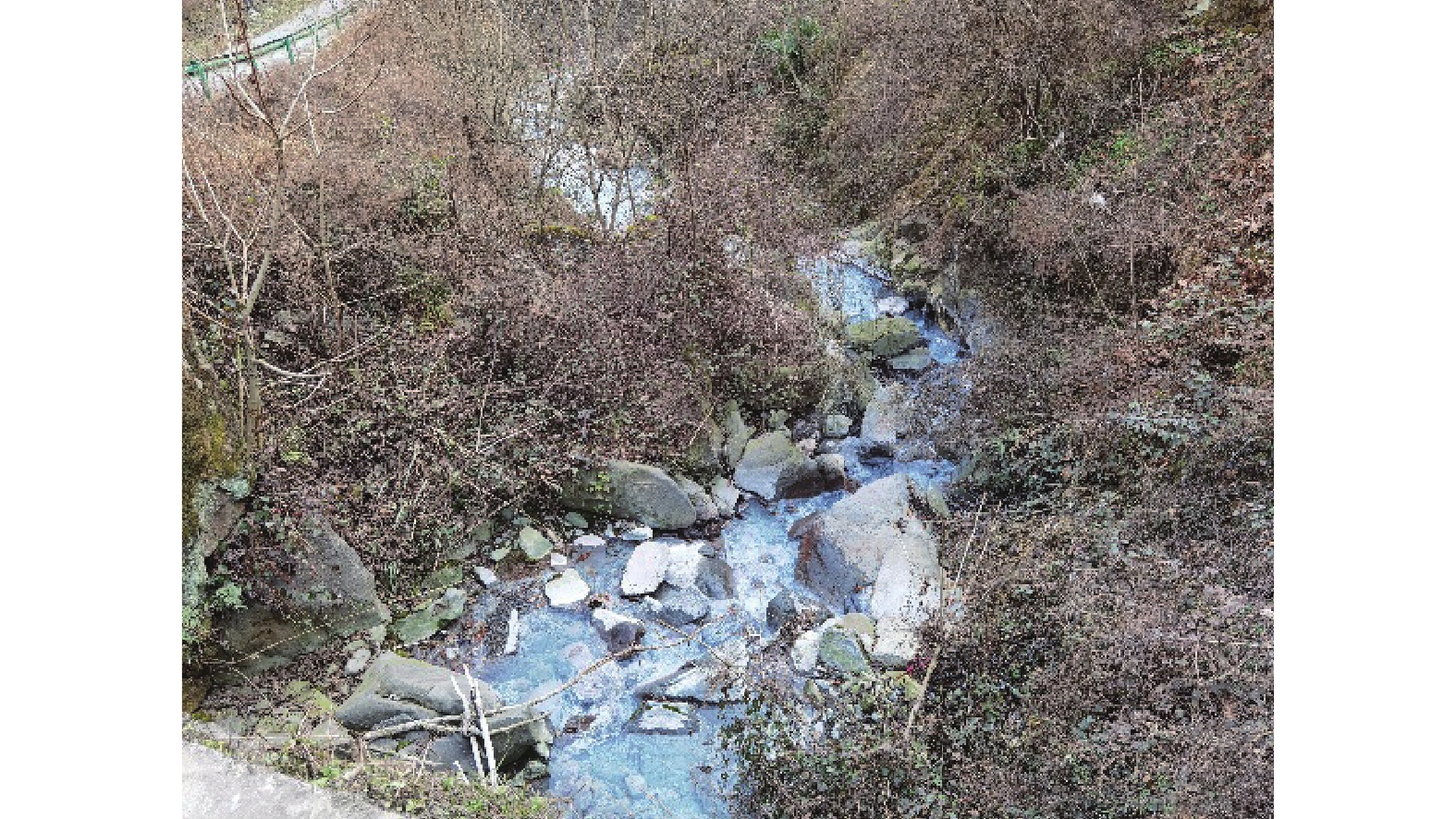
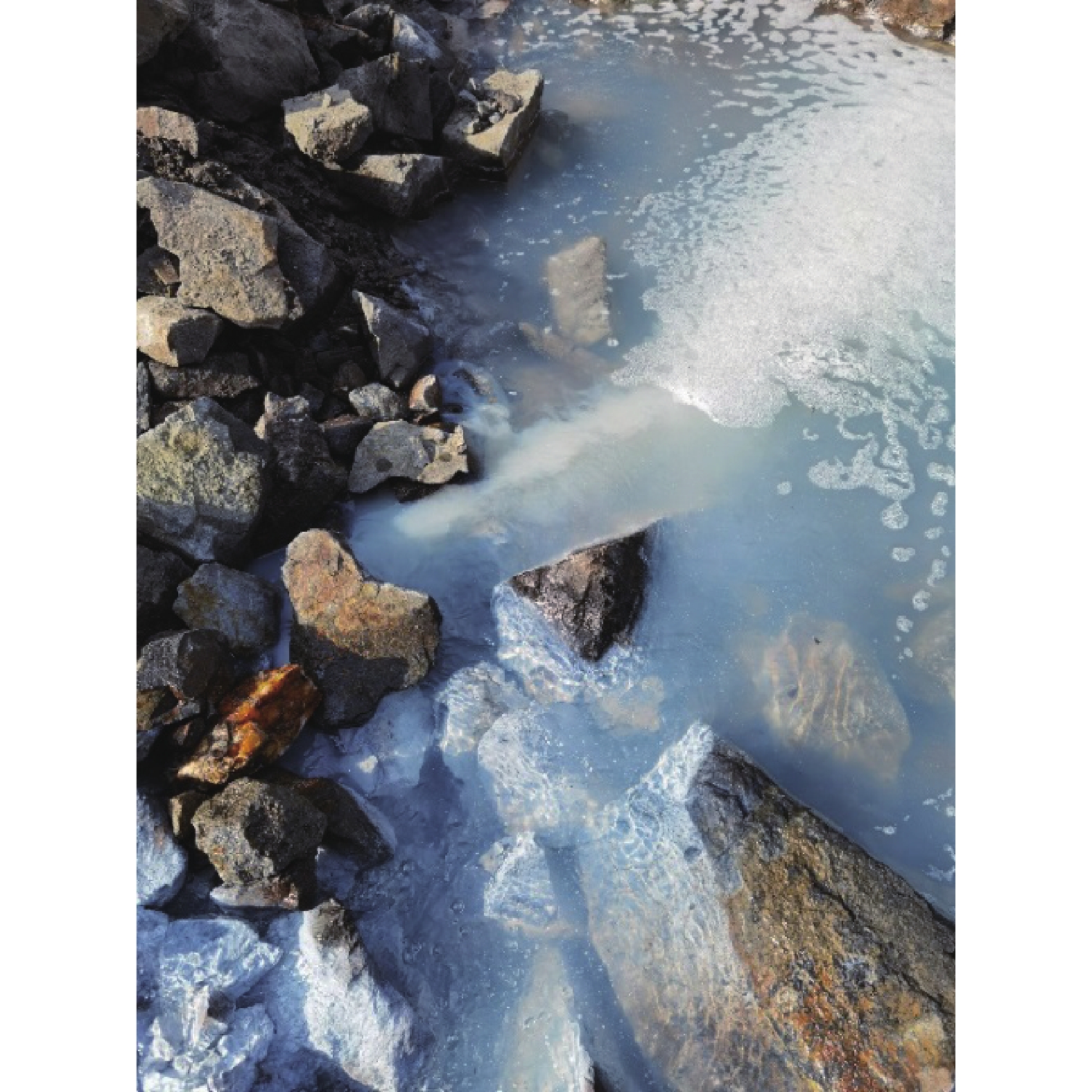
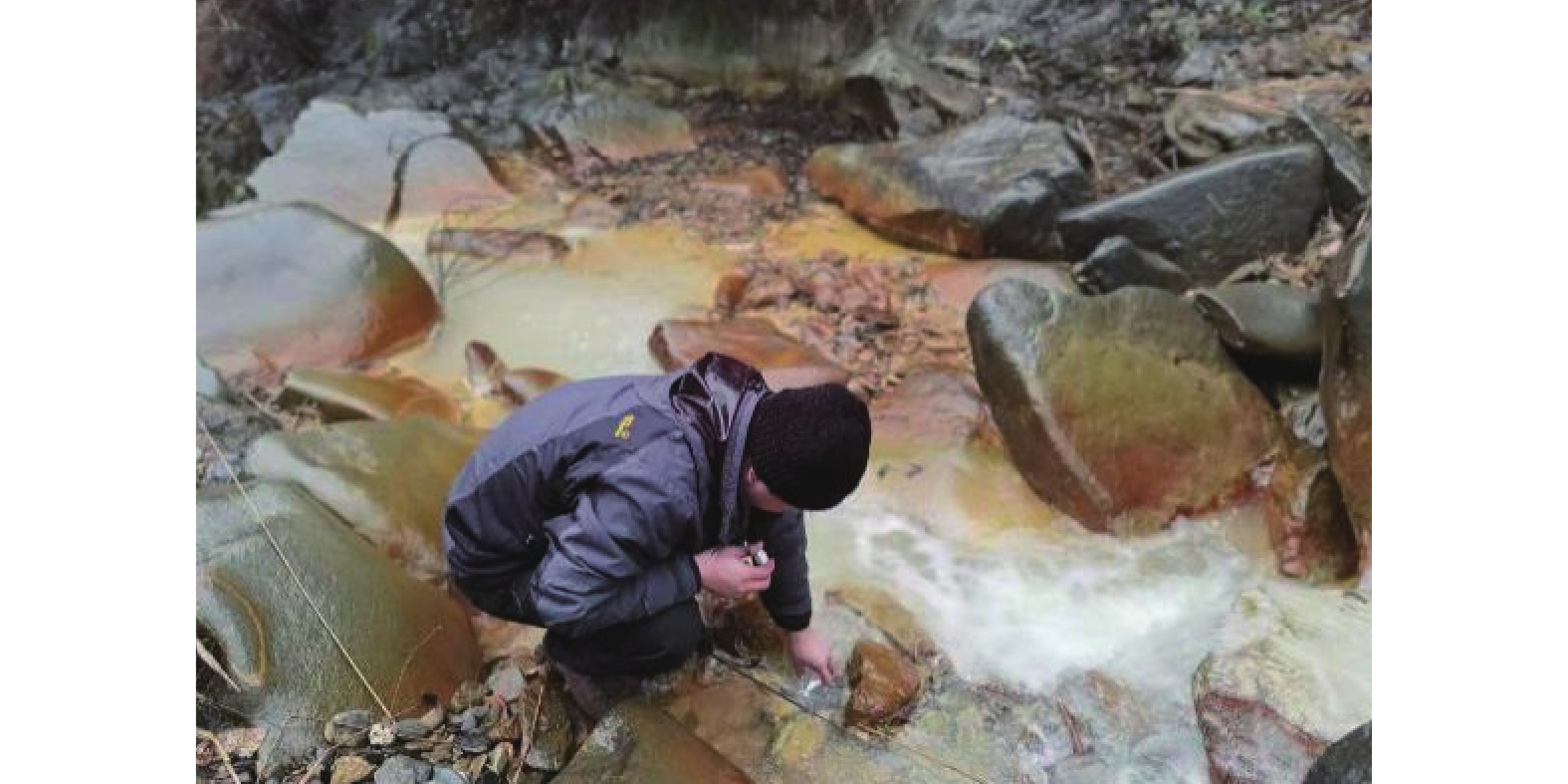
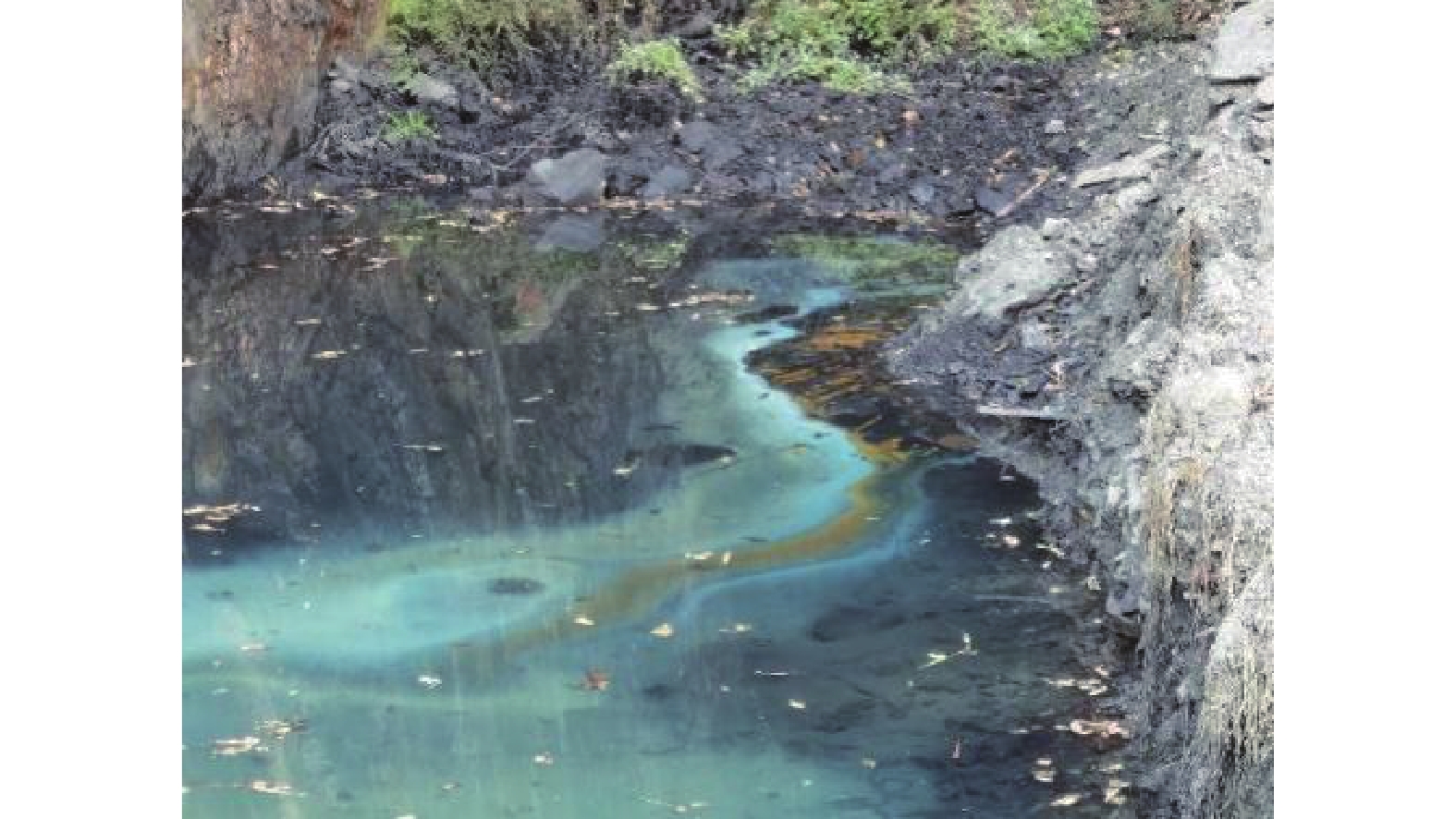
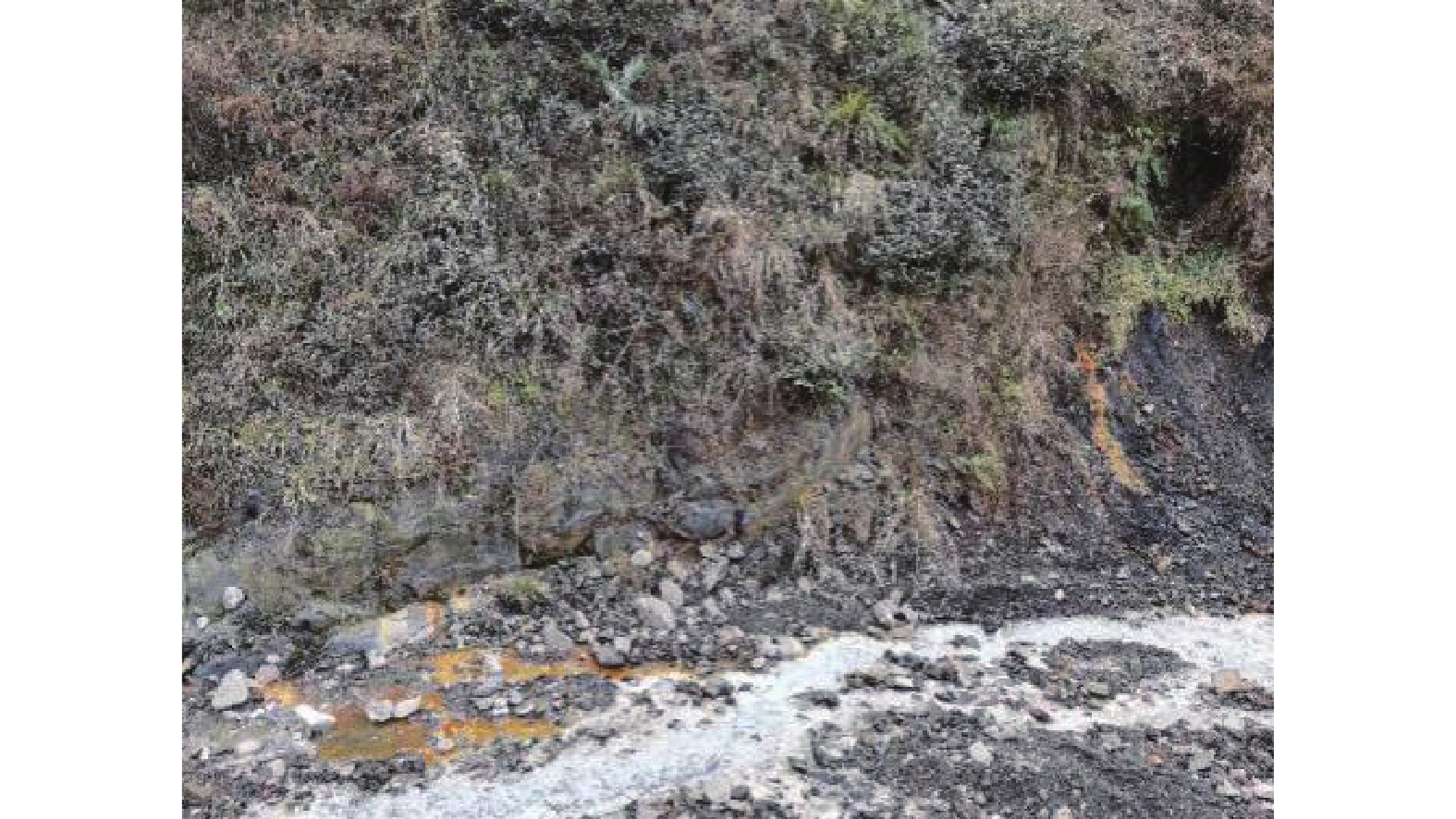
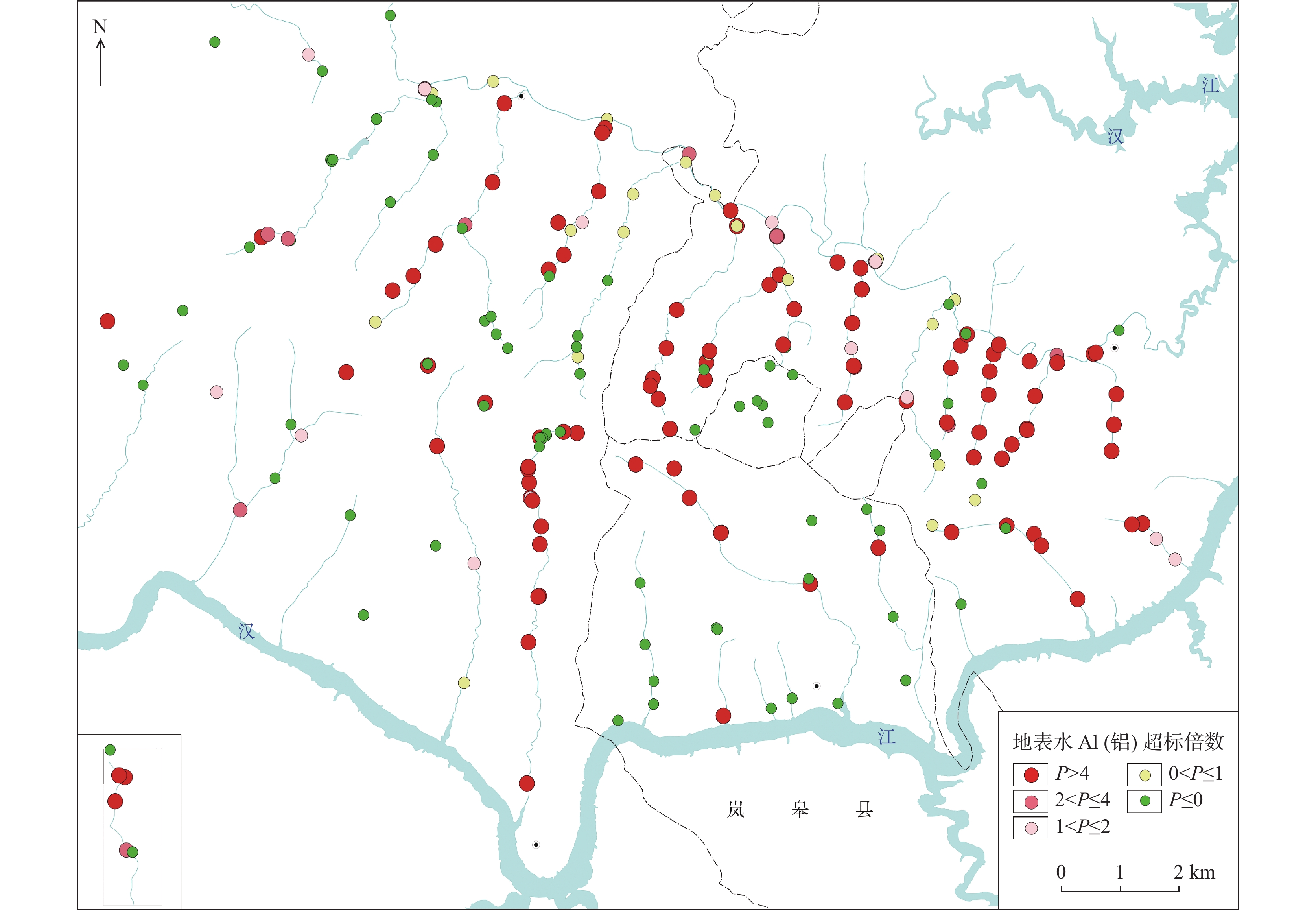
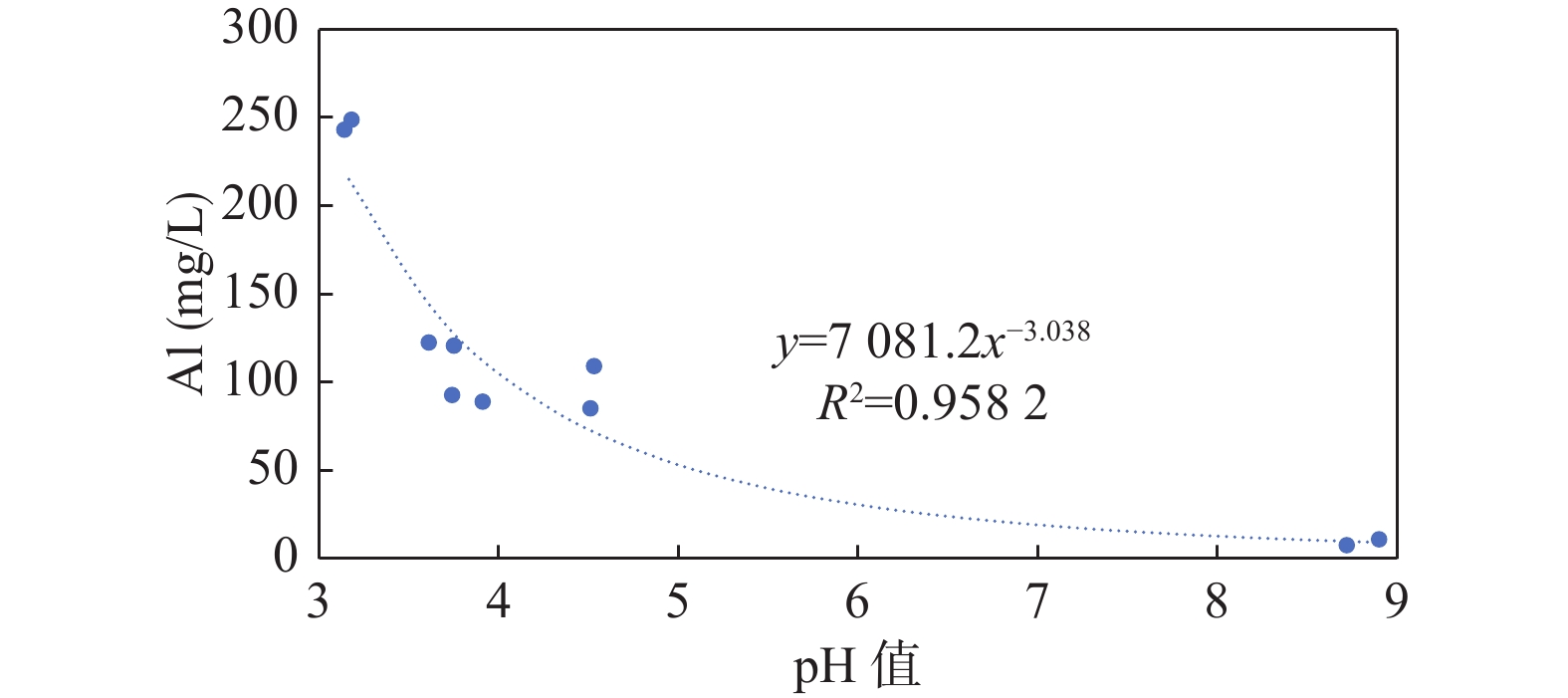
矿山酸性水及其伴生的重金属污染是含黄铁矿矿山最主要、综合治理难度最大的污染问题。为了查明蒿坪河流域废弃石煤矿开采河流铝的白色污染及成因问题,2021年以来进行了卫星遥感解译、无固定翼无人机航测、样品采集与分析、主要河流断面水质动态监测等工作。结果表明:① 研究区河流普遍存在铝的白色污染,其形成可见3种模式:两条沟道不同酸碱度的河水混合后形成白水带;河道河水自然跌水后在河床形成白色污染物;河水自然演化形成酸性水、酸性磺水与酸性白水。② 河水铝离子污染普遍且超标严重,216件河水中Al离子平均含量为8.6 mg/l,样品超标率65.8%,19条河流断面3次河水中Al离子的平均超标率90.48%。③ 河流中铝来自于石煤矿及其围岩中酸性溶解作用长石的结果,废渣堆底部流水是河流铝的主要污染源。④ 河水中铝离子与pH具有显著的负相关关系,河水酸度愈大,河水中铝离子含量愈高;河水中白色无定形胶凝状物形成后,河水中铝离子含量显著降低。河水pH的升高,是河流白色污染物形成的主要因素。河水中铝的白色污染物具有无定形特点,化学组分复杂,是硫酸根、氢氧根及铝构成的复杂化合物。铝的白色无定形胶凝状物具有吸附河水中重金属离子的能力。研究成果可为研究区铝的污染防治提供重要的理论依据。
Abstract:Acid mine drainage and its associated heavy metal pollution are the most important mine pollution problems in pyrite−bearing mining areas and the most difficult to comprehensively treat. In order to find out the white pollution and causes of aluminum mining rivers from abandoned stone coal mines in the Haoping river basin, satellite remote sensing interpretation, non−fixed−wing UAV aerial survey, sample collection and analysis, and dynamic monitoring of water quality in major river sections have been carried out since 2021. The results show that, ①white pollution of aluminum is common in rivers in the study area, and three patterns can be seen: the two channels are mixed with river water with different pH degrees to form white water belts; after the natural fall of the river water, white pollutants are formed on the rock surface of the riverbed; river water naturally evolves to form acidic water, acidic sulfur water, and acidic white water. ②Aluminum ion pollution in river water was widespread and seriously exceeded the standard, the average content of Al ions in 216 river waters was 8.6 mg/l, the sample exceeded the standard rate by 65.8%, and the average excess rate of Al ions in the three river waters of 19 river sections was 90.48%. ③ The aluminum in the river comes from the result of the acid water dissolution of feldspar in the stone coal mine and its surrounding rock, and the flowing water at the bottom of the waste residue pile is the main source of pollution of the river aluminum. ④ Aluminum ions in river water have a significant negative correlation with pH, and the greater the acidity of river water, the higher the content of aluminum ions in river water; after the formation of white amorphous gels in river water, the content of aluminum ions in river water decreased significantly. The increase in the pH of river water is the main factor in the formation of white pollutants in rivers. The white pollutants of aluminum in river water have amorphous characteristics, complex chemical composition, and are complex compounds composed of sulfate, hydroxide and aluminum. The white amorphous gel of aluminum has the ability to adsorb heavy metal ions in river water. The research results can have important theoretical and practical application value for the pollution prevention and control of aluminum in the research area.
-
Key words:
- stone coal mining area /
- white pollution of the river /
- aluminum ions /
- genesis analysis /
- Haoping river
-

-
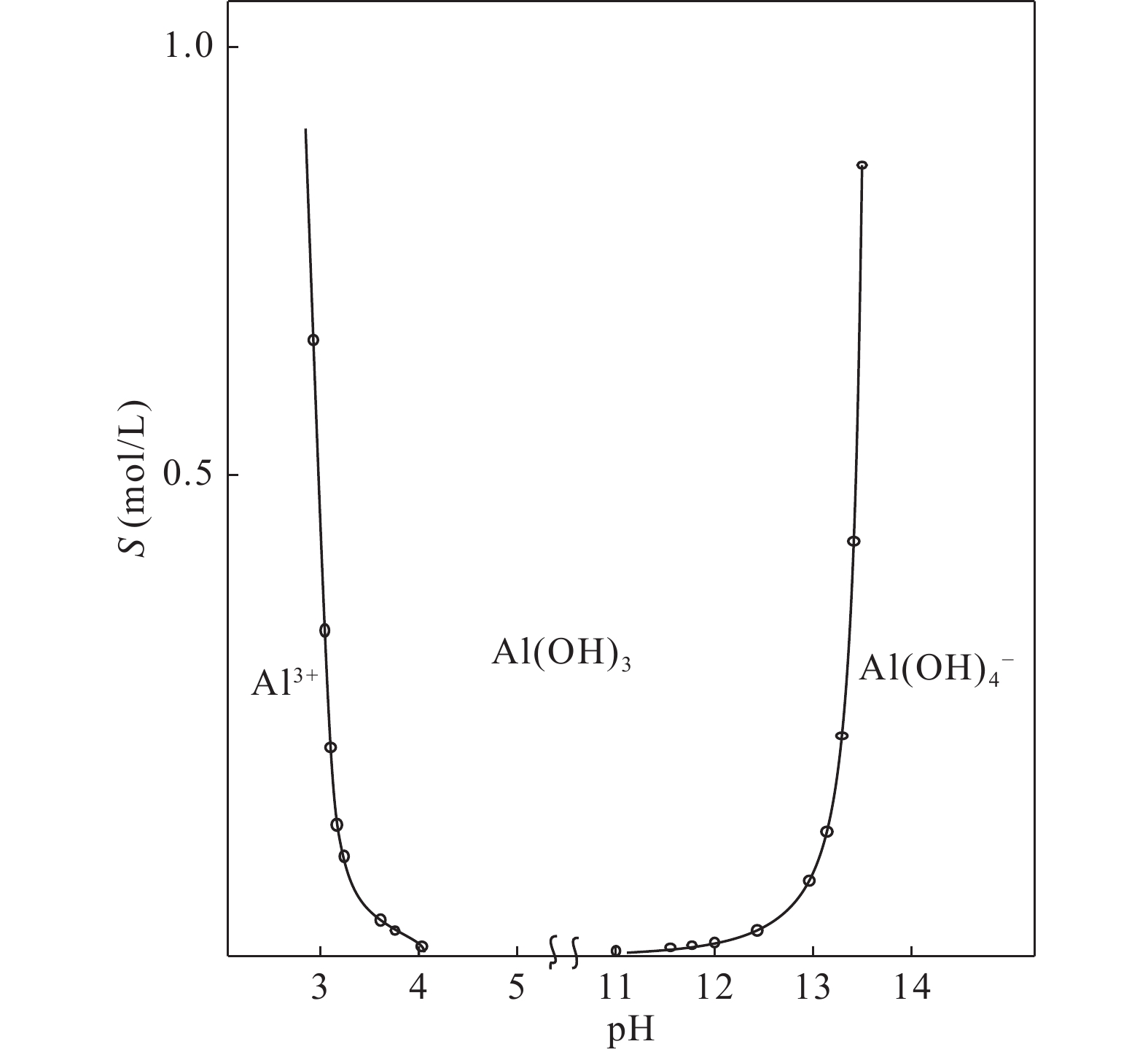
图 16 Al(OH)3的溶度积S与pH关系图(无机化学,2001)
Figure 16.
表 1 研究区河水中有关参数含量特征值统计表
Table 1. Characteristic values of relevant parameter content in river water in the study area
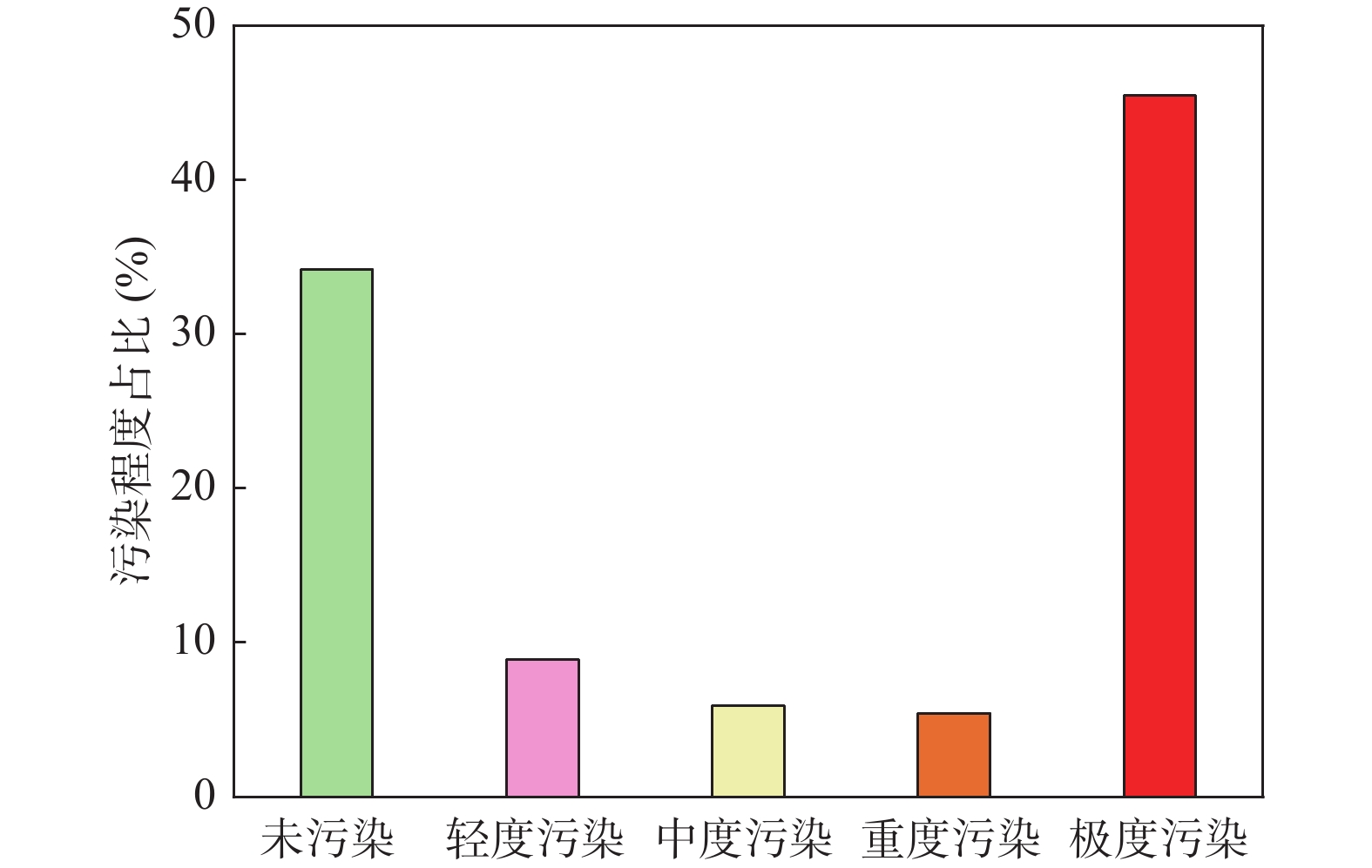
特征值 pH值 Al(mg/L) SO42–(mg/L) 最小值 2.76 0.012 6.21 最大值 9.34 186 6963 平均值 5.94 8.6 478.58 众数 6.68 –① 169.0 中位数 6.35 0.67 135.0 标准离差 1.43 82.58 997.1 标准限值③ 6~9 0.2② 250 注:①污染物未检出的含量按0处理;②铝执行生活饮用水卫生标准(GB5749–2006);③其余污染物执行《地表水环境质量标准(GB3838–2002)》二类水标准。 表 2 主要河流断面3期河水样品污染物参数的平均值统计表
Table 2. Average of pollutant parameters of river water samples from phase 3 of major river sections
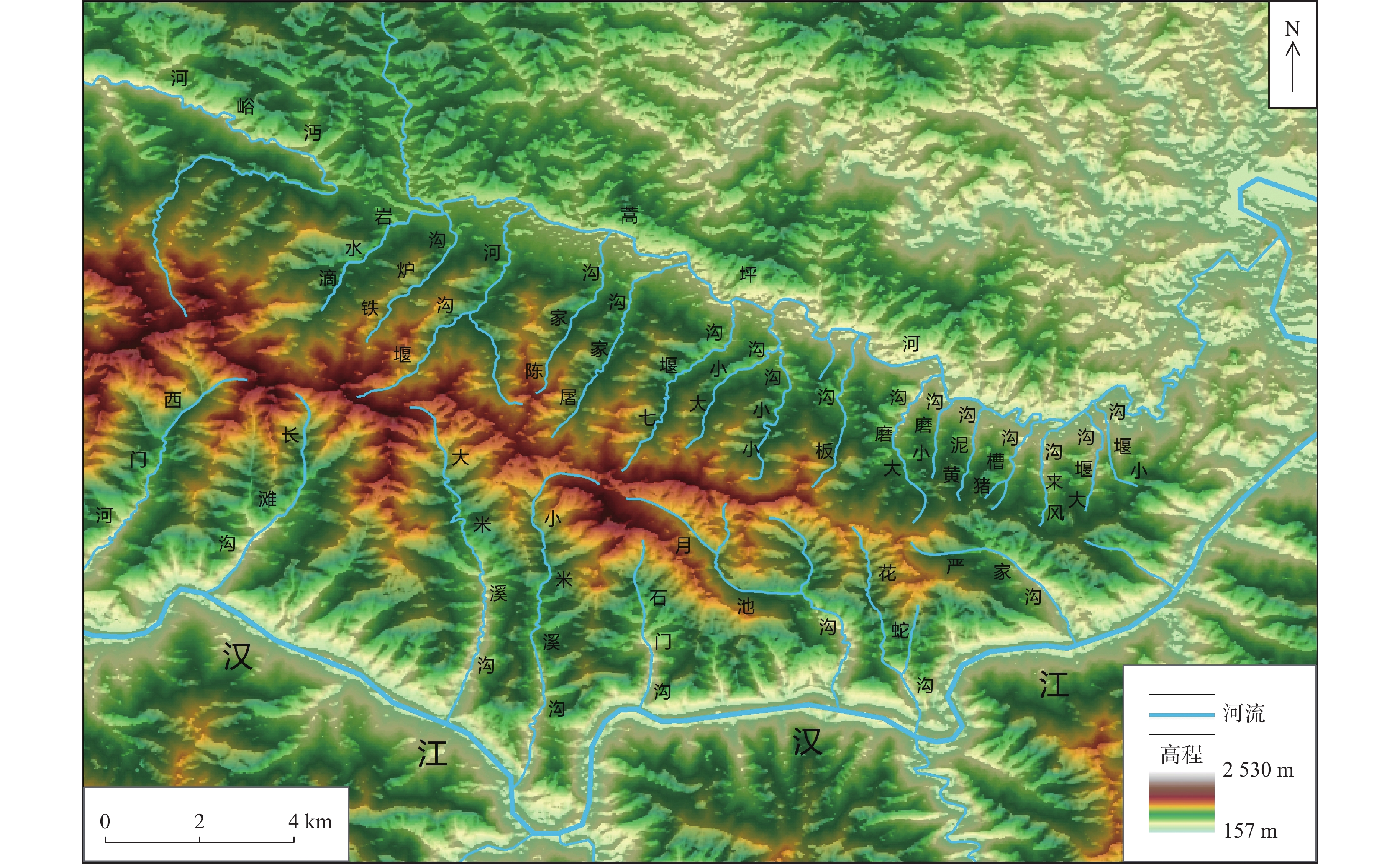
河流名称及断面 pH值 Al(mg/L) Fe(mg/L) SO42−(mg/L) 蒿坪河(滴水崖水库下游) 7.31 0.079 0.014 110.000 北沟口 6.97 0.696 0.014 73.033 铁炉沟口 7.25 0.066 0.014 95.433 堰沟河口 5.65 2.033 0.116 321.333 陈家沟口 4.6 11.881 0.076 471.000 涂家沟口 7.18 0.338 0.030 256.500 七堰沟口 6.32 1.818 0.014 135.833 大(小)沟口 7.42 3.349 0.244 150.333 板沟口 5.94 0.603 0.023 154.500 大磨沟口 7.08 0.201 0.033 170.500 小磨沟口 3.61 45.542 0.796 1133.333 黄泥沟口 4.03 43.061 0.368 856.667 猪槽沟口 4.27 59.106 0.406 926.667 大堰沟口 7.21 2.203 0.017 265.167 蒿坪河入汉江回水区断面 7.32 1.783 0.011 90.000 蒿坪河入汉滨区断面 7.34 0.322 0.050 163.750 勉汝河 6.88 0.498 0.014 86.933 小米溪沟废渣坝下 3.26 179.657 8.023 3336.667 小米溪沟污水处理厂出水口下游 3.39 119.734 13.133 2250.833 小米溪沟口 4.42 53.927 0.176 1171.167 大米溪沟口 7.55 0.249 0.014 98.167 标准限值 6~9 0.2 0.3 250 表 3 研究区石煤矿石及围岩中主要化学组分含量
Table 3. The content of chemical components in rock, coal ore and surrounding rock in the study area
SiO2(%) Al2O3(%) FeO(%) Fe2O3(%) MnO(%) 石煤矿石 47.60 6.52 2.4 1.75 0.076 石煤角砾岩 39.87 16.29 1.8 5.57 0.044 粗面岩和碱性玄武岩 40.24 12.12 8.17 6.33 0.162 板岩 52.84 13.09 2.49 3.93 0.12 表 4 露天煤矿2#废渣堆底部渗流水pH及污染物含量及超标倍数
Table 4. pH and pollutant content and excessive multiple of seepage water at the bottom of the 2# waste residue pile in open–pit coal mine
送样号 pH值 Al SO42− TFe 备注 含量(mg/L) 超标倍数 含量(mg/L) 超标倍数 含量(mg/L) 超标倍数 S21-1 3.0 116 579 3250 12 42.6 141 废渣堆底部渗流水 S21-2 3.02 152 759 4920 18.68 63.501 210.67 S21-4 3.06 134 669 2080 7.32 27.45 90.5 S21-5 3.26 57.6 287 2100 7.4 68.901 228.67 S21-6 3.15 4.98 23.9 2070 7.28 306.579 1020.93 S21-7(对照点) 6.62 1 - - - 上游支沟清水 相关标准值 6~9 0.2 250 0.3 表 5 七堰沟上游溪水中pH及污染物超标倍数统计表
Table 5. The pH and pollutants in the upstream stream of Qi Yangou exceeded the standard multiple
采样点 pH Al SO42– TFe 河流颜色 S21-11 4.44 40.25 – – 沟脑溪流清水 S21-16 4.37 76.50 0.104 – 沟脑溪流清水 S21-17 4.50 40.05 – – 河水白色浑浊 S21-12 7.08 – – – 清水 S21-13 8.05 – – – 局部可见磺水 S21-14 5.53 3.05 – – 可见白色污染 S21-15 6.36 0.75 – – 河水白色浑浊 S21-18 4.80 10.05 – – 河床可见白色沉淀物 注:“–”表示未超标地表水二类标准。 表 6 河水中pH值与污染物的相关关系统计表
Table 6. Correlation between pH and pollutants in river water
pH值 Al Fe SO42– pH 1 Al −0.799** 1 Fe −0.576** 0.824** 1 SO42- −0.814** 0.993** 0.822** 1 注:*表示p<0.05;**表示p<0.01。 表 7 小米溪沟河水沿程河水颜色、pH值及Al离子含量统计表
Table 7. The color, pH and aluminum ion content of the river along the Xiaomixigou river
样号 河水颜色 pH值 Al(mg/L) S423 石煤矿废渣库坝下10 m处清水 3.14 243.20 S424 河水进入酸碱中和处理站之前的清水 3.18 248.88 S425 酸碱中和处理站排水,清水 8.9 11.00 S427 处理站排水与河水混合后河水,淡黄色 8.72 7.67 S428 淡黄色 3.75 120.78 S429 黄色,浑浊 3.91 89.03 S430 黄色,浑浊 4.53 109.19 S432 中游黄中带白,浑浊 3.61 122.57 S433 下游黄白,浑浊 3.74 92.81 S434 汉江汇水前黄中带白,浑浊 4.51 85.25 -
[1] 陈谦, 杨晓松, 吴义千等. 有色金属矿山酸性废水成因及系统控制技术[J]. 矿冶, 2005, 14(04): 71-74 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2005.04.020
CHEN Qian, YANG Xiaosong, WU Yiqian, et al. Formation of waste water from nonferrous metal mine and its systematical control technique[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2005, 14(04): 71-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2005.04.020
[2] 陈华清, 张天亮, 龚慧山, 等.矿山酸性水中铝相次生矿物及环境学意义的研究进展. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 1-11.
CHEN Huaqing, ZHANG Tianliang, GONG Huishan, et al. Research Progress of Aluminum−Phase Secondary Minerals and Their Environmental Significance in Acid Mine Water. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 1-11.
[3] 陈西民, 马合川, 魏东等. 安康石煤资源特征及勘查开发建议[J]. 陕西地质, 2010, 28(01): 1-5+81 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2010.01.001
CHEN Ximin, MA Hechuan, WEI Dong, et al. An kang stone coal resource characteristics and exploration and development suggestions[J]. Geology of Shananxi, 2010, 28(01): 1-5+81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6996.2010.01.001
[4] 崔炜, 张佳伟, 苏文让, 等. 石煤采矿区水流域重金属污染治理实践[J]. 《环境工程》编委会, 工业建筑杂志社有限公司. 《环境工程》2019年全国学术年会论文集[C]. 《工业建筑》杂志社有限公司, 2019: 6
CUI Wei, ZHANG Jiawei, SU Wenrang, et al. Prractice of Heavy Metal Pollution Control in Water Basin of Stone Coal Mining Area[J]. Editorial Board of Environmental Engineering, Industrial Architecture Magazine. Proceedings of the 2019 National Annual Conference of Environmental Engineering[C]. Industrial Construction Magazine Limited, 2019: 6.
[5] 崔雅红, 崔炜, 孟庆俊等. 陕西蒿坪石煤矿区重金属污染及生态风险评价[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2021, 41(02): 157-162 doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2021.02.022
CUI Yahong, CUI Wei, MENG Qingjun, et al. Heavy Metal Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment in Haoping Stone Coal Mine Area of Shaanxi Province[J]. Conservation and Utilization of MineralResources, 2021, 41(02): 157-162. doi: 10.13779/j.cnki.issn1001-0076.2021.02.022
[6] 大连理工大学无机化学教研室编. 无机化学第四版[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2001
Department of Inorganic Chemistry, Dalian University of Technology. The fourth edition of inorganic chemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2001.
[7] 杜蕾, 朱晓丽, 安毅夫等. 石煤尾矿区土壤重金属污染风险评价[J]. 化学工程, 2018, 46(03): 6-9+15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2018.03.002
DU Lei, ZHU Xiaoli, AN Yifu, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metalsin a stone-like coal tailing using TCLP and Hakanson method[J]. Chemical Engineering(China), 2018, 46(03): 6-9+15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2018.03.002
[8] 贾晓丹, 王晖, 徐友宁. 某钼矿集中开采区尾矿库排水重金属环境风险等级及其贡献率分析. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 152−161.
JIA Xiaodan, WANG Hui, XU Youning. Analysis of Heavy Metal Environmental Risk Level and Contribution Rate of Tailings Storerooms of A Molybdenum Mine. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 152-161.
[9] 贾志刚, 吕婷婷. 安康市双龙一带斑鸠关组地质特征及其含石煤性分析[J]. 煤, 2014, 23(02): 52-53+76.
[10] 栾兆坤. 水中铝的形态及其形态研究方法[J]. 环境化学, 1987(01): 46-56
LUAN Zhaokun. The speciation and speciation study of aluminum in water[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1987(01): 46-56.
[11] 李美蓉, 宋来弟, 于海鹏等. 酸碱度对长石溶蚀及增孔效应的影响[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 45(05): 33-41
LI Meirong, SONG Laidi, YU Haipeng, et al. Influence of pH value on feldspar dissolution and pore-increasing effect[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science), 2021, 45(05): 33-41.
[12] 罗孝俊, 杨卫东, 李荣西等. pH值对长石溶解度及次生孔隙发育的影响[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2001, 20(02): 103-107 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.02.007
LUO Xiaojun, YANG Weidong, LI Rong xi, et al. Effects of pH on the Solubility of the Feldspar and the Development of Secondary Porosity[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 2001, 20(02): 103-107. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.02.007
[13] 倪师军, 李珊, 李泽琴等. 矿山酸性废水的环境影响及防治研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2008, 23(05): 501-508 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.05.010
NI Shijun, LI Shan, LI Zeqin, et al. Progress in the Research of Acid Mine Drainage Impact and Remediation[J]. Advances In Earth Science, 2008, 23(05): 501-508. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.05.010
[14] 庞洁. 铝对人体的毒性及相关食品安全问题研究进展[J]. 内科, 2011, 6(05): 470-473. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7768.2011.05.038
[15] 王晓勇, 徐友宁, 赵振宏等. 石煤矿区酸性废水稳定同位素特征及地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 1-7
WANG Xiaoyong, XU Youning, ZHAO Zhenhong, et al. Stable Isotope Characteristics and Geological Significance of Acid Wastewater in a Stone Coal Mining Area[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 1-7.
[16] 王银川, 李昭坤, 翟自峰等. 山西本溪组铝土矿成矿条件及成矿规律探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2011, 44(4): 82-88 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2011.04.011
WANG Yinchuan, LI Zhaokun, ZHAI Zifeng, et al. Benxi Formation Bauxite Mineralization Condition and Rule in Shanxi Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2011, 44(4): 82-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2011.04.011
[17] 徐友宁. 陕西某石煤矿集中开采区河流白色污染的形成机制与演化[R]. 全国土壤修复大会, 2021.
[18] 赵玲, 李官, 王荣锌. 金属矿山酸性废水治理技术现状与展望[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2009, 27(10): 13-15 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2009.10.008
ZHAO Ling, LI Guan, WANG Rongxin. Treatment Techniques and Developmental Trends of Metal Mines Acid Wastewater[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2009, 27(10): 13-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2009.10.008
[19] 章丽萍. 浅谈铝污染与人体健康[J]. 大同医学专科学校学报, 2005(02): 27-28.
[20] 周闻达, 向武, 金丽, 等. 石煤矿山酸性废水自净化机理及防治对策[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2020, 43(08): 20-27 doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.08.004
ZHOU Wenda, XIANG Wu, JIN Li, et al. The Self-purification Mechanism and Control Counter measures of Cadmium-rich Acid Mine Drainage of Stone Coal Mines[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2020, 43(08): 20-27. doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.08.004
[21] Alasfar H Reema, Isaifan J Rima. Aluminum environmental pollution: the silent killer[J]. Environmental science and pollution research international, 2021, 28(33): 44587-44597. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-14700-0
[22] Banfield J F, Eggleton R A. Analytical transmission electron microscope studies of plagioclase, muscovite, and K-feldspar weathering[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1990, 38(1): 77-89. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1990.0380111
[23] Bao Y P, Guo C L, Lu G N, Yi X Y, Wang H, Dang Z. Role of microbial activity in Fe(III) hydroxysulfate mineral transformations in an acid mine drainage-impacted site from the Dabaoshan Mine[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 616-617: 647-657. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.10.273
[24] Caraballo M A, Wanty R B, Verplanck P L, Navarro-Valdivia L, Ayora C, Hochella M F. Aluminum mobility in mildly acidic mine drainage: Interactions between hydrobasaluminite, silica and trace metals from the nano to the meso-scale[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 519: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.04.013
[25] Cong Lu, Bo Yang, Xing Cui, Sichang Wang, Chengtun Qu, Weiwei Zhang, Bo Zhou. Characteristics and Environmental Response of White Secondary Mineral Precipitate in the Acid Mine Drainage From Jinduicheng Mine, Shaanxi, China[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 2021 107: 1012–1021. doi: 10.1007/s00128-021-03355-9
[26] Furrer G, Phillips B L, Ulrich K-U, Pöthig R, Casey W. The origin of aluminum flocs in polluted streams[J]. Science, 2002, 297: 2245-2247. doi: 10.1126/science.1076505
[27] Gilles G , Cecile G. Study of aluminium concentration and speciation of surface water in four catchments in the Limousin region (France)[J]. Journal of Inorganic Biochemistry 97 (2003) 16–25.
[28] Igbokwe Onyebuchi Ikechukwu, Igwenagu Ephraim, Igbokwe Afifi Nanacha. Aluminium toxicosis: a review of toxic actions and effects[J]. Interdisciplinary toxicology, 2019, 12(2): 45-70. doi: 10.2478/intox-2019-0007
[29] Kumar B, Singh U K. Source apportionment of heavy metals and their ecological risk in a tropical river basin system[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2018, 25(25): 25443−25457.
[30] Li M R, Li C C, Xing J T, Sun X T, Yuan G H, Cao Y C. An experimental study on dynamic coupling process of alkaline feldspar dissolution and secondary mineral precipitation[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2019, 38(6): 872-882. doi: 10.1007/s11631-019-00326-0
[31] Liu Q Y, Chen B H, Haderlein S, Gopalakrishnan G, Zhou Y Z. Characteristics and environmental response of secondary minerals in AMD from Dabaoshan Mine, South China[J]. Ecotoxicology Environmental Safety, 2018, 155(1): 50-58.
[32] Manuel, M. A. , Grathwohl, P. , Johnson, K. W. , & Eberl, D. D. Natural and Anthropogenic Transport Mechanisms Drive the Formation and Fate of Aluminum Hydroxide Mineral Particles in Streams and Rivers[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 53(2), 493–504.
[33] Nordstrom D K, Ball J W. The geochemical behavior of aluminum in acidified surface waters[J]. Science, 1986, 232: 54-56. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4746.54
[34] Sanchez España J. , Yusta I. , Burgos W. The geochemistry of dissolved aluminum at low pH: Hydrobasaluminite formation and interaction with silica, trace metals and microbial cells under anoxic conditions [J]. Chemical Geology, 2016, 192: 70-96.
-



 下载:
下载: