Geochemical Characteristics and Information Extraction in GASH Ore Concentration Area, Eritrea
-
摘要:
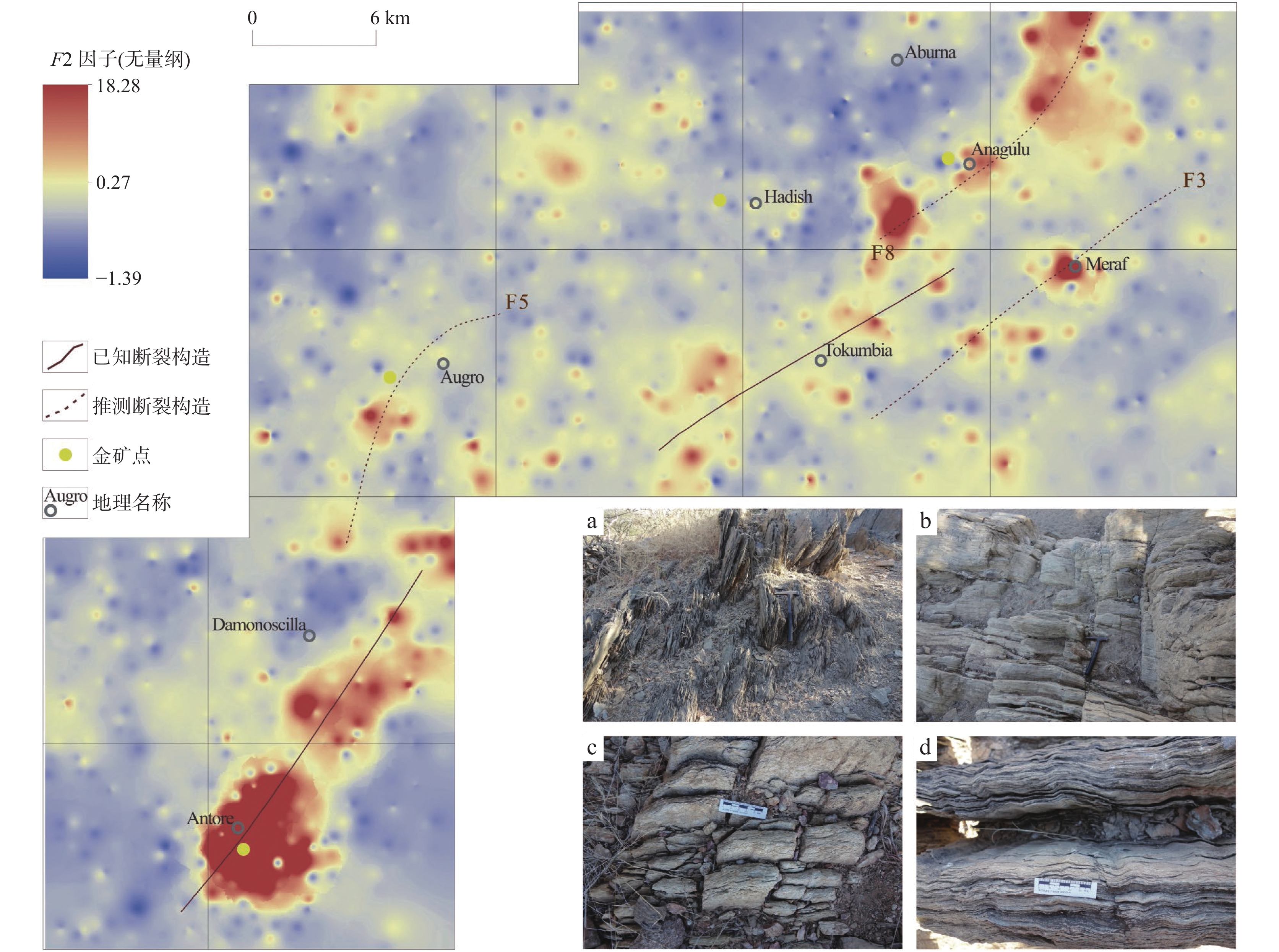
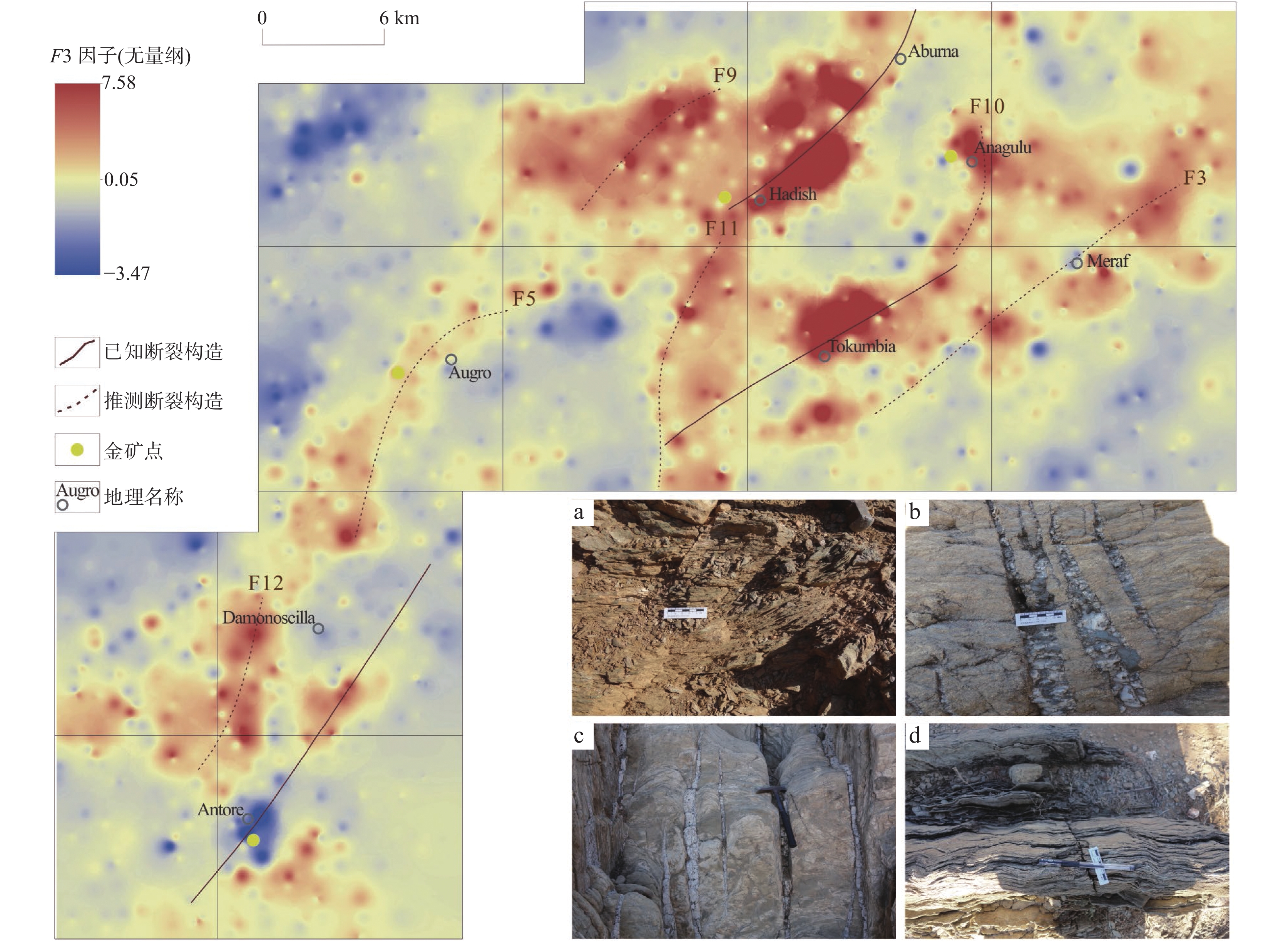
GASH金矿集区位于厄立特里亚西部的碧沙Au多金属成矿带,具有良好的区域成矿背景。区内1∶10万水系沉积物测量数据的地球化学特征表明,Au、Hg、As、W、Bi等元素呈强分异的分布特征,Au、As、Sb、W具有强富集的分布特征,显示优异的Au找矿前景。通过元素相关性分析,筛选出能够有效指导Au矿勘查的F5因子(Au-Hg元素组合)、指示区域断裂构造分布的F2因子(Ag-Bi-Mo-W元素组合)及F3因子(As-Sb-Pb元素组合),指示基性–超基性地质体分布的F1、F4特征因子。对F5因子得分开展异常信息提取,并结合矿产地质特征,圈定出可开展进一步原生岩金矿勘查工作的异常区8处,基于指示成矿热液活动的F2、F3、F5特征因子推断出NE、N–NE向的规模较大的断裂12条,为研究区的找矿预测及勘查工作部署提供了有利的地球化学依据。
Abstract:GASH Au ore concentration area belongs to Bisha gold metallogenic belt in West Eritrea, with a good regional metallogenic setting. The geochemistry of stream sediment mapping at scale of 1∶100,000 indicate: Au, Hg, As, W, Bi are characteristic of strong-differentiated distribution, Au, As, Sb, W are characteristic of strong-rich distribution, showing a good prospecting for Au exploration. Through the correlation analysis, F5 factor (Au-Hg association) is confined to guide the Au exploration, F2 factor (Ag-Bi-Mo-W association) and F3 factor (As-Sb-Pb association) which are confined to guide the distribution of fault structures, F1 and F4 factor are confined to guide the distribution of basic and ultrabasic geological unit. with the anomaly information extract from F5 factor combined with the geological characteristic, 8 anomaly area with good Au metallogenic prospecting were determined, base on the characteristic of F2, F3, F5 factors, which are useful in indicating the metallogenic hydrothermal activity, 12 regional fault with NE, N-NE attitude were deduced. All the information extracted are useful geochemical evidence to the following gold exploration and the work deployment.
-
Key words:
- Africa /
- Eritrea /
- gold /
- geochemical /
- anomaly extract /
- fault structure
-

-
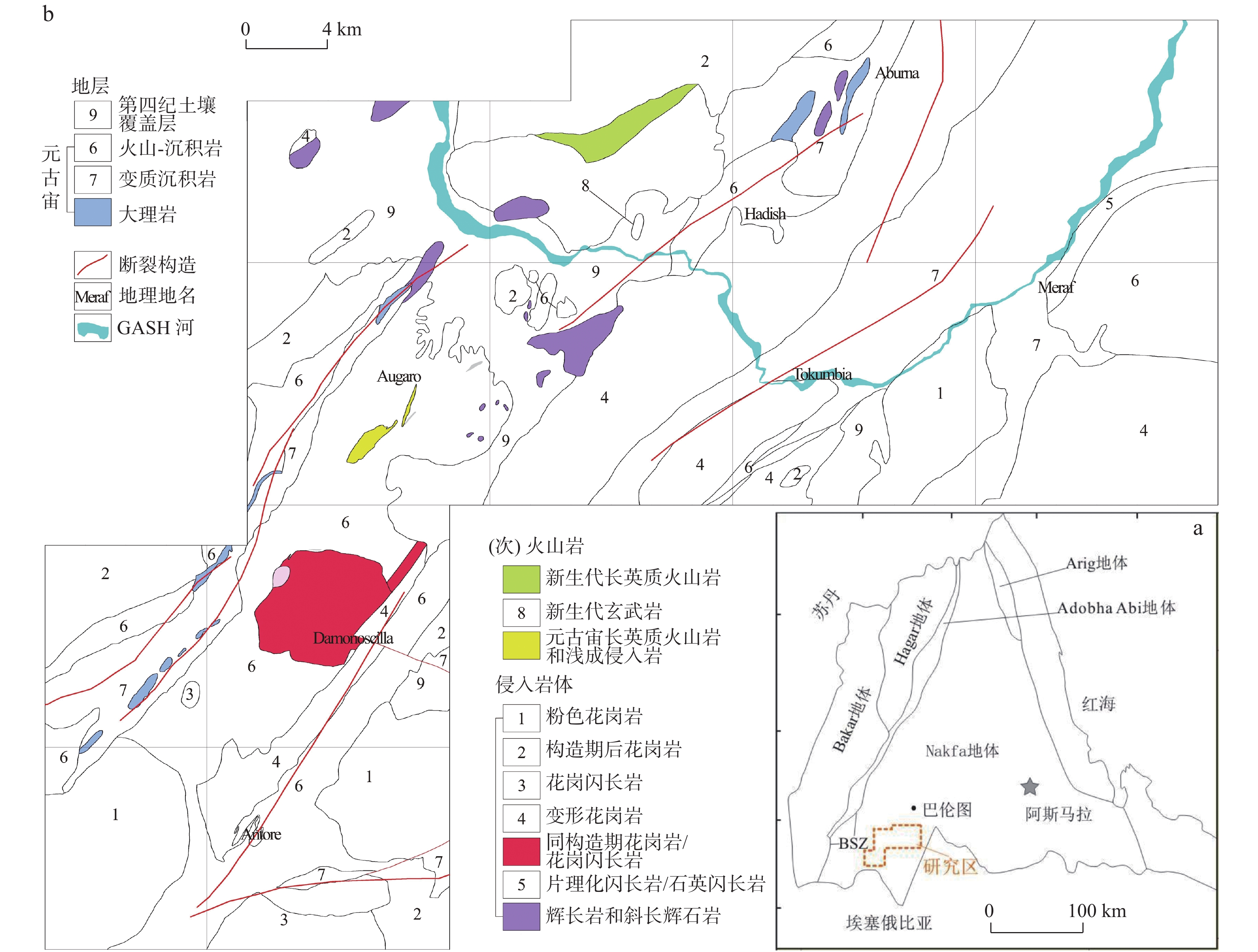
图 1 研究区地质构造简图(图a据赵凯,2018;图b据Greig,2004)
Figure 1.
表 1 各元素地球化学特征参数
Table 1. Statistical characteristics of elements geochemical values
元素 平均值 中值 最大值 均方差 克拉克值 变异系数 富集系数 Au 3.88 1.40 71.00 8.63 0.90 2.22 4.32 Ag 0.04 0.04 0.42 0.03 0.06 0.63 0.70 As 3.21 2.19 43.50 3.73 2.40 1.16 1.34 Sb 0.24 0.21 0.94 0.12 0.18 0.50 1.34 Hg 0.0049 0.004 0.05 0.01 0.01 2.24 0.49 W 0.85 0.62 17.30 1.18 0.60 1.40 1.41 Mo 0.64 0.54 9.10 0.57 0.50 0.88 1.29 Bi 0.09 0.06 4.37 0.21 0.14 2.22 0.67 Sn 1.26 1.21 3.73 0.40 1.40 0.32 0.90 Cu 37.04 30.60 169.00 23.66 26.00 0.64 1.42 Pb 8.05 7.60 34.30 3.02 15.00 0.37 0.54 Zn 51.67 46.80 187.00 25.36 76.00 0.49 0.68 Co 19.41 15.60 207.00 17.12 19.00 0.88 1.02 Cr 65.24 48.60 879.00 74.63 76.00 1.14 0.86 Ni 27.29 20.50 256.00 24.27 31.00 0.89 0.88 Ti 4422.00 4114.00 26651.00 2550.00 4000.00 0.58 1.11 V 129.22 117.00 804.00 72.53 112.00 0.56 1.15 Fe2O3 5.78 5.35 29.18 2.88 2.45 0.50 2.36 MgO 1.56 1.39 10.50 1.02 3.16 0.65 0.49 注:粗体标注元素变异系数大于1.3,富集系数大于1.2,在特征参数分析工作中需重点关注。Au含量为10–9;Fe2O3、MgO含量为%;其余元素含量为10–6。 表 2 研究区主要岩石单元Au含量特征
Table 2. The Au content of main rock unit in study area
岩石单元 Au含量均值(10–9) 岩性特征 元古宙火山岩 0.95 岩性以蚀变安山岩为主,在研究区广泛分布,整体呈NE向展布 元古宙变沉积岩 0.82 岩石的片理化特征明显,多与火元古宙山岩相邻分布,呈NE向展布 花岗岩区 1.74 颜色较闪长岩浅,常见构造变形特征,整体呈NE向展布,分布面积较大 闪长岩区 1.73 岩石具有明显的片理化特征,颜色较花岗岩深,区内分布面积相对较小 辉长-辉石岩区 0.61 岩石颜色较深,矿物颗粒较大,在区内呈零星分布 表 3 因子分析特征参数统计
Table 3. Characteristic parameters of factor analysis
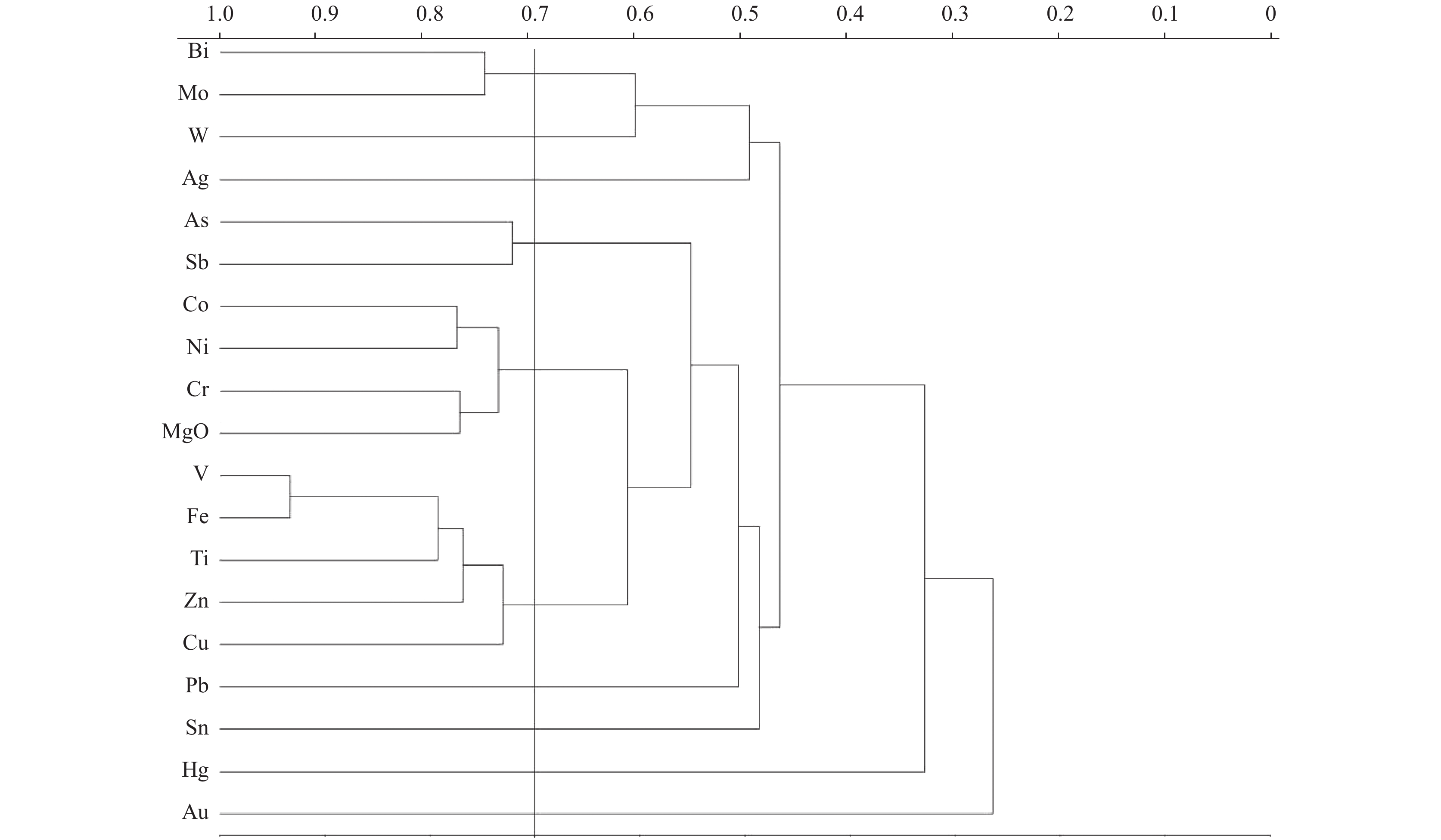
因子 因子特征值及方差贡献率 元素 正交旋转载荷矩阵 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累积贡献率(%) F1 F2 F3 F4 F5 F1 6.66 35.03 35.03 Ag 0.09 0.68 0.32 0.18 0.12 F2 2.86 15.08 50.11 As 0.10 0.02 0.84 0.14 0.04 F3 1.61 8.47 58.58 Bi −0.06 0.90 −0.07 −0.05 0.11 F4 1.54 8.13 66.70 Co 0.14 0.08 0.52 0.61 0.06 F5 1.02 5.36 72.06 Cr 0.31 −0.02 −0.08 0.82 0.01 F6 0.91 4.81 76.87 Cu 0.65 0.32 0.43 0.14 0.13 F7 0.72 3.81 80.69 Hg 0.09 0.12 0.15 0.02 0.75 F8 0.54 2.86 83.55 Mo 0.06 0.81 0.18 0.03 0.10 F9 0.53 2.78 86.33 Ni 0.15 −0.01 0.20 0.89 0.01 F10 0.48 2.55 88.88 Pb 0.12 0.21 0.61 −0.04 0.08 F11 0.42 2.20 91.08 Sb 0.11 0.15 0.88 0.11 0.08 F12 0.35 1.83 92.91 Sn 0.52 0.30 0.28 −0.13 0.11 F13 0.30 1.59 94.51 Ti 0.88 0.05 0.17 0.01 0.07 F14 0.27 1.41 95.91 V 0.79 0.13 0.22 0.28 0.08 F15 0.22 1.14 97.06 W −0.04 0.80 0.03 −0.03 0.10 F16 0.21 1.11 98.16 Zn 0.82 0.13 0.24 0.22 0.09 F17 0.20 1.06 99.22 Fe2O3 0.85 0.16 0.26 0.31 0.10 F18 0.08 0.44 99.67 MgO 0.52 0.05 −0.005 0.71 0.05 F19 0.06 0.33 100.00 Au −0.001 0.17 0.03 0.04 0.79 注:表中左侧粗体为特征值大于1的因子项,反映数据主要信息的主因子;右侧粗体反映5个主因子分别代表的元素载荷。 -
[1] 陈建平. 深地矿产资源定量预测理论与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2019
CHEN Jianping. Theory and method of quantitative prediction of deep mineral resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,2019.
[2] 成曦晖, 徐九华, 王建雄等. 厄立特里亚阿斯马拉VMS矿床S、Pb同位素对成矿物质来源的约束[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2017, 27(04): 795~810
CHENG Xihui, XU Jiuhua, WANG Jianxiong, et al. Sulfur and lead isotope constrains on source of ore-forming materials in Asmara VMS-type deposits, Eritrea[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals. 2017, 27(04): 795~810.
[3] 董凯. 甘肃白银厂铜矿成岩-成矿环境及其找矿意义[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2018
DONG Kai. Diagenesis-metallogenic environment of Baiyinchang copper deposit and its prospecting significance in Gansu[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2018.
[4] 窦小雨, 郭小刚, 周宏, 等. 甘肃白银厂铜多金属矿田地球化学场特征及信息提取[J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(6): 1139-1153 doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2022.06.001
DOU Xiaoyu, GUO Xiaogang, ZHOU Hong, et al. Geochemical field characteristics and information extraction of the Baiyinchang copper polymetallic ore field in Gansu Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(6): 1139-1153. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2022.06.001
[5] 蒋文程, 张有军, 谭宁, 等. 厄立特里亚阿斯马拉(Asmara)铜金多金属成矿带研究进展[J]. 矿产勘查, 2017, 8(04): 700~707 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2017.04.023
JIANG Wencheng, ZHANG Youjun, TAN Ning, et al. Progress of geological study in Asmara copper-gold polymetallic metallogenic belt, Eritrea[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2017, 8(04): 700~707. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2017.04.023
[6] 孔祥超, 万鹏, 卢文姬, 等. 新疆东昆仑大沙沟地区水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿方向研究[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(4): 116−127.
KONG Xiangchao, WAN Peng, LU Wenji, et al. Geochemical Characteristics and Ore−prospecting of Dashagou Area in East Kunlun, Xinjiang: Based on Stream Sediment Survey[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(4): 116−127.
[7] 刘亚剑, 范继璋, 李钟山, 等. 吉林省小石人金矿区微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2008, 38(2): 202~210 doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2008.02.018
LIU Yajian, FAN Jizhang, LI JongSan, et al. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements in the Xiaoshiren gold deposit in Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2008, 38(2): 202~210. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2008.02.018
[8] 刘永胜, 罗先熔, 曹佰迪, 等. 甘肃省礼县三峪地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(6): 340−351.
LIU Yongsheng, LUO Xianrong, CAO Baidi, et al. Soil Geochemical Characteristics and Prospecting Prediction in Sanyu Area, Li County, Gansu Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(6): 340-351.
[9] 刘旭洋. 湖南溆浦地区水系沉积物地球化学低弱异常识别[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021
LIU Xuyang. Identification of weak geochemical anomalies ofstream sediments in Xupu, Hunan Province[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021.
[10] 李福林, 向文帅, 王成刚, 等. 东北非重要铜金矿产资源分布及赋存形式[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(1): 119-128 doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.01.009
LI Filin, XIANG Wenshuai, WANG Chenggang, et al. Distribution and occurring state of copper-gold mineral resources in Northeast Africa[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(1): 119-128. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.01.009
[11] 李春华, 路来君, 王抵修. 地球化学元素空间定量组合求异模型及其应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(2): 461~468 doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2010.02.008
LI Chunhua, LU Laijun, WANG Dixiu. The combination of geochemistry elements in space quantitative of different model and its application[J]. Jourmal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(2): 461~468. doi: 10.13278/j.cnki.jjuese.2010.02.008
[12] 吕古贤, 孙岩, 刘德良, 等. 构造地球化学的回顾与展望[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 35(4): 479-494 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.04.002
LV Guxian, SUN Yan, LIU Deliang, et al. Tectono-geochemistry: A review[J]. Geotectonic et Metallogenia, 2011, 35(4): 479-494. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.04.002
[13] 彭礼贵, 任有祥, 李智佩, 等. 甘肃白银厂铜多金属矿床成矿模式[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1995
PENG Ligui, REN Youxiang, LI Zhipei, et al. Metallogenie model of Baiyinchang copper polymlallic deposit in Gansu[M]. Bejing: Geological Publishing House, 1995.
[14] 苏为华. 多指标综合评价理论与方法问题研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2000
SU Weihua. Research on the theory and method of multi-index comprehensive evaluation[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2000.
[15] 向文帅, 赵凯, 曾国平, 等. 东北非VMS矿床地质特征与研究进展[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(1): 129-140 doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.01.010
XIANG Wenshuai, ZHAO Kai, ZENG Guoping, et al. Geology of VMS deposits in Northeast Africa and their research progress[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(1): 129-140. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.01.010
[16] 向鹏, 王建雄. 厄立特里亚Koka金矿地质特征及矿床类型[J]. 矿物学报, 2013, (s2): 1067-1068 doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2013.s2.088
XIANG Peng, WANG Jianxiong. Ore geology character and type of Koka gold deposit, Eritrea[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2013, (s2): 1067-1068. doi: 10.16461/j.cnki.1000-4734.2013.s2.088
[17] 向文帅, 赵凯, 张紫程. 厄立特里亚Augaro金矿床碳氢氧硫同位素特征及其成因意义[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(4): 1284-1291 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.04.023
XIANG Wenshuai, ZHAO Kai, ZHANG Zicheng. Studies on C-H-O-S isotopes of Eritrea Augaro gold deposit and its implications for gold genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(4): 1284~1291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.04.023
[18] 向运川, 龚庆杰, 刘荣梅, 等. 区域地球化学推断地质体模型与应用-以花岗岩类侵人体为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(9): 2609-2618.
XIANG Yunchuan, GONG Qingie, LIU Rongmei, et al. Model and application of deducing geological body on regional geochemical survey data: A case study on granitic intrusions in China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(9): 2609 - 2618
[19] 徐云峰, 郝雪峰, 秦宇龙, 等. 四川岔河地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3): 624-638
XU Yunfeng, HAO Xuefeng, QIN Yulong, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province[J]. Ceophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 624~638.
[20] 姚华舟, 李建星, 吕鹏瑞, 等. 海上丝绸之路沿线陆域地质演化与成矿[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2019, 35(01): 1~19
YAO Huazhou, LI Jianxing, LI Pengrui, et al. Geological Evolution and Metallogenesis of the Land Area Along the Maritime Silk Route. Geology and Mineral R esourcesof South China, 2019, 35(1): 1-19.
[21] 姚旺, 卞姗姗, 余先川. 基于IFA的组合分析算法及其在矿产预测中的应用[J]. 地质学刊, 2018, 42(4): 623-631 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2018.04.012
YAO Wang, BIAN Shanshan, YU Xianchuan. IFA-based combination analysis algorithm and its application in mineral prediction[J]. Journal of Geology, 2018, 42(4): 623-631. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3636.2018.04.012
[22] 袁和, 罗先熔, 李武毅, 等. 西藏邦卓玛地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(3): 472-481 doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2017.03.007
YUAN He, LUO Xianrong, LI Wuyi, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil and prospecting prediction of the Bangzhuoma Region, Xizang[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(3): 472-481. doi: 10.12134/j.dzykt.2017.03.007
[23] 于俊博, 宋云涛, 郭志娟, 等. R型聚类分析在区域化探元素分组中的作用探讨[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(6): 771-776 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2014.06.20
YU Junbo, SONG Yuntao, GUO Zhijuan, et al. Discussion on the affection of the R-cluster analysis applied in grouping elements in regional geochemical exploration[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 36(6): 771-776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1749.2014.06.20
[24] 杨龙坤, 罗先熔, 文美兰, 等. 地电提取测量法在黑龙江金厂外围区寻找隐伏金矿的应用[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015, 35(4): 809-816 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2015.04.020
YANG Longkun, LUO Xianrong, WEN Meilan, et al. Application of geoelectric extraction method on prospecting for hidden gold deposit in peripheral area of Jinchang, Heilongjiang[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2015, 35(4): 809-816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2015.04.020
[25] 杨笑笑, 罗先熔, 郑超杰, 等. 衡阳盆地北缘国庆矿区土壤地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(4): 762-771 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.04.009
YANG Xiaoxiao, LUO Xianrong, ZHENG Chaojie, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil and prospecting direction in the Guoqing area, northern margin of the Hengyang Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(4): 762~771. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0495-5331.2018.04.009
[26] 袁玉涛. 化探数据处理方法对比研究-以乌日尼图钨钼矿床为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015
YUAN Yutao. Comparative Study on the Gochemical Exploration Data Processing Method: a Case of Wurinitu W-Mo Deposit [D]. Bei jing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
[27] 赵凯, 姚华舟, 王建雄, 等. 厄立特里亚Koka花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1): 156-167
ZHAO Kai, YAO Huazhou, WANG Jianxiong, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of Koka granites and their geological significances, Eritrea[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(1): 156-167.
[28] 赵凯, 姚华舟, 王建雄等. 厄立特里亚Koka金矿床成矿流体特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2018, 37(6): 1337-1348 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2018.06.012
ZHAO Kai, YAO Huazhou, WANG Jianxiong, et al. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of Koka gold deposit in Eritrea and their geological significances[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2018, 37(6): 1337-1348. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2018.06.012
[29] 赵少卿, 魏俊浩, 高翔, 等. 因子分析在地球化学分区中的应用: 以内蒙古石板井地区1: 5万岩屑地球化学测量数据为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(2): 27-34
ZHAO Shaoqing, WEI Junhao, GAO Xiang, et al. Factor analysis in the geochemical subdivisions: taking 1: 50000 debris geochemical survey in the Shibanjing area of Inner Mongolia as an example [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(2): 27-34.
[30] 张宝一, 陈伊如, 黄岸烁, 等. 地球化学场及其在隐伏矿体三维预测中的作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(2): 352-362
ZHANG Baoyi, CHEN Yiru, HUANG Anshuo, et al. Geochemical field and its roles on the 3D prediction of concealed ore bodies[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(2): 352-362.
[31] 张宝一, 代鹏遥, 蒙菲等. 基于距离场的三维矿体模型与地表化探数据的关联关系分析-以红透山铜矿田为例[J]. 地质论评, 2017, 63(2): 511-524
ZHANG Baoyi, DAI Pengyao, MENG Fei, et al. Weighted shortest-distance field-based relation analysis between 3D ore-body model and geochemical survey data on the ground surface-A case study in the Hongtoushan copper ore field, Fushun, China[J]. Geological Review, 2017, 63(2): 511-524.
[32] 张小静. 西昆仑地区地球化学异常识别及最小预测区划分[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009
ZHANG Xiaojing. The identification of geochemical anomalies and delineation of prospective mineralization areas in the region of West Kunlun[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.
[33] CHENG Qiuming. Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32(1-2): 314~324. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.10.002
[34] Greig C J. Peliminary Regional Geology of Augaro Area[R]. Nevsun Exploration Company, 2004.
[35] Ghebreab W, Greiling R O, Solomon S. Structural setting of Neoproterozoic mineralization, Asmara district, Eritrea[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2009, 55: 219~235. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2009.05.001
[36] Guiraud R, Bosworth W, Thierry J, et al. Phanerozoic geological evolution of Northern and Central Africa: An overview[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43(1/3): 83-143.
[37] Johnson P R, Andresen A, Collins A S, et al. Late Cryogenian-Ediacaran history of the Arabian-Nubian Shield: A review of depositional, plutonic, structural, and tectonic events, in the closing stages of the northern East African Orogen[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2011, 61(3): 167-232. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2011.07.003
[38] Johnson P R, Zoheir B A, Ghebreab W, et al. Gold-bearing volcanogenic massive sulfides and orogenic-gold deposits in the Nubian Shield. South African Journal of Geology[J]. 2017, 120: 63-76. doi: 10.25131/gssajg.120.1.63
[39] Perelló J, Sillitoe R H, Brockway H, et al. Metallogenic inception of the Arabian-Nubian Shield: Daero Paulos porphyry copper prospect, Eritrea. Gondwana Research[J]. 2020, 88: 106-125. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2020.06.021
[40] FU C, Chen K, Yang Q, et al. Mapping gold mineral prospectivity based on weights of evidence method in southeast Asmara, Eritrea. Journal of African Earth Sciences[J]. 2021, 176: 104-143.
[41] Stern R J. Neoproterozoic (900~550Ma) arc assembly and continental collision in the east Africa orogen: implications for the consolidation of Gondwanaland[J]. Annual Review of Earth &. Planetary Sciences, 1994, 22: 319-351.
[42] Teklay M. A Back-arc Palaeotectonic Setting for the Augaro Neoproterozoic Magmatic Rocks of Western Eritrea[J]. Gondwana Research, 2003, 6: 629-640. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)71012-1
-



 下载:
下载: