Nd–Hf Isotopic Characteristics, Evolution Trend and Tectonic Setting of Triassic Magmatic Rocks in the Eastern Segment of East Kunlun Orogeny
-
摘要:
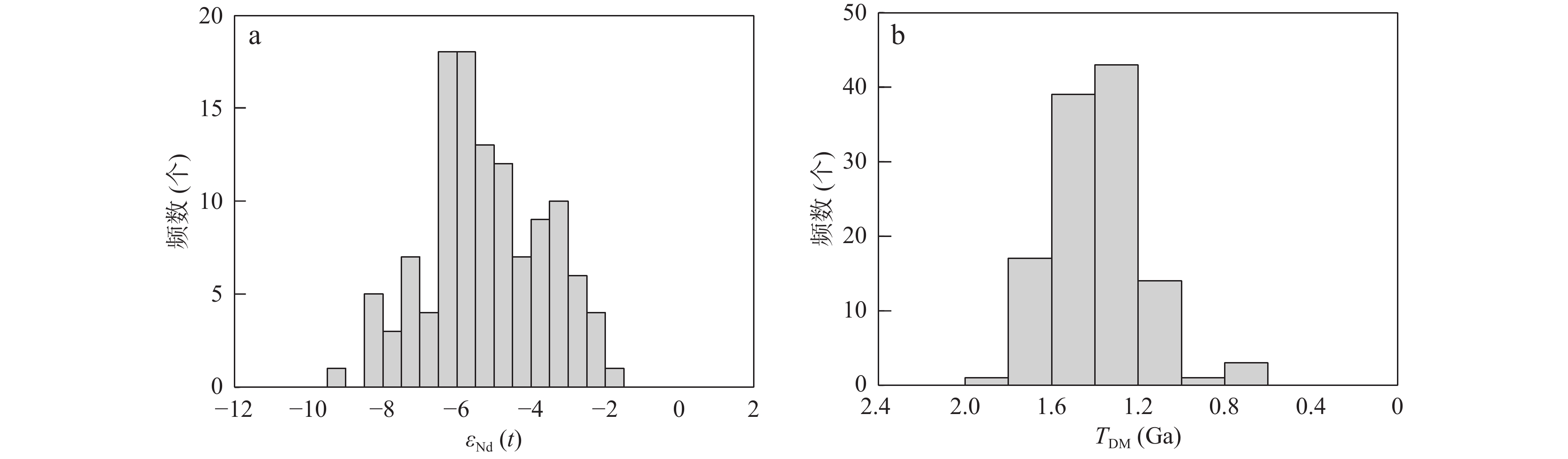
作为中央造山系西段的重要组成部分,东昆仑造山带以大面积区域性展布的三叠纪岩浆岩为鲜明特色。依据收集的东昆仑东段三叠纪岩浆岩96件锆石U–Pb年代学数据,限定三叠纪岩浆作用时间为252~212 Ma。结合岩石组合,将其进一步划分为早(252~238 Ma)、中(238~226 Ma)、晚(226~212 Ma)3期,其中岩浆活动峰值为早期(252~238 Ma)。Nd同位素数据(106件)统计结果表明:东昆仑东段三叠纪岩浆岩εNd(t)值为–9.4~–1.7,大多为–6.5~–3.0;Nd模式年龄TDM(Nd)为0.72~1.88 Ga,大多为1.00~1.80 Ga。Hf同位素数据(全岩、锆石;41件)统计结果表明:东昆仑东段三叠纪岩浆岩εHf(t)值变化较大(–8.4~+12.4),主要为–4.5~+2.0;地壳模式年龄TDMC(Hf)值为0.49~ 1.80 Ga,大多为1.15~1.55 Ga。整体而言,三叠纪岩浆岩物源以中元古代壳源物质的再造为主,新生地壳(<1.0 Ga)和古元古代地壳有所参与,但比例小。从岩浆活动早期(252~238 Ma)到中期(238~226 Ma)再到晚期(226~212 Ma),εNd(t)值在岩浆活动早期(特别是在早三叠世)较高,正的εHf(t)值占据很大比例,物源中存在较多的新生物质;中期以较低的εNd(t)值和负的εHf(t)值为主,Hf模式年龄显示出现古元古代物质;晚期Nd–Hf模式年龄揭示较古老的壳源组分增多。这种岩浆岩物源演变趋势,与东昆仑东段三叠纪具俯冲到同碰撞再到碰撞后的构造演化背景一致。
Abstract:As a major component of the western segment of the Central Orogenic System, the East Kunlun Orogeny is characterized by the largely exposed of Triassic magmatic rocks. Based on the collected zircon U–Pb geochronological data of 96 Triassic magmatic rocks in the eastern segment of the East Kunlun orogeny, the Triassic magmatic activity is limited to 212~252 Ma, and can be further divided into three stages: early– (238~252 Ma), middle– (226~238 Ma) and late–stage (212~226 Ma). Among them, the peak magmatic period is the early stage (238~252 Ma). The statistical results of 106 Nd isotopes of Triassic magmatite in the eastern segment of the East Kunlun Orogeny show that εNd(t) values range from –9.4 to –1.7, mainly concentrated between –6.5 and –3.0, and the Nd model ages (TDM(Nd)) range from 0.72 to 1.88 Ga, mainly concentrated between 1.00 and 1.80 Ga. The statistical results of 41 Hf isotopes (whole rock, zircon) of Triassic magmatite show that εHf(t) values vary greatly (–8.4 to +12.4), mainly concentrated between –4.5 and +2.0, and the crustal model ages (TDMC(Hf)) range from 0.49 to 1.80 Ga, mainly concentrated between 1.15 and 1.55 Ga. Overall, the Triassic magmatic rocks are mainly derived from the reworking of Mesoproterozoic crustal materials, with minor involvement of juvenile crust (< 1.0 Ga) and Paleoproterozoic crustal materials. From the early stage (237~250 Ma) to middle stage (226~238 Ma) and then to late stage (212~226 Ma), the Nd–Hf isotopic parameters seems exhibit a certain evolutionary trend. In the early stage especially in the early Triassic, the εNd(t) values are higher, and positive εHf(t) values occupy a large proportion, indicating the presence of more juvenile material in the source. In the middle stage, lower εNd(t) values and negative εHf(t) values dominate the major proportion, and Hf model ages (TDMC(Hf)) reveals the presence of Paleoproterozoic crustal material. In the late stage, the Nd–Hf model ages reveal an increase in older crustal source components. This magmatic source evolutionary trend is consistent with the tectonic evolution setting of subduction to collision and then to post–collision in the eastern segment of the East Kunlun orogeny in Triassic period.
-
Key words:
- magmatic rock /
- zircon geochronology /
- Nd–Hf isotopes /
- juvenile crust /
- the eastern part of East Kunlun
-

-
表 1 东昆仑东段三叠纪岩浆岩锆石U–Pb年代学数据、全岩Nd同位素数据和全岩与锆石Hf同位素数据表
Table 1. zircon U–Pb ages, whole rock Nd isotopes and Hf isotopes (whole and zircon) of the Triassic Magmatite from the eastern part of East Kunlun orogeny
年龄
编号样品号 岩性 结晶
年龄误差 测年方法 εNd (t)值
(均值)Nd模式年龄TDM (Ma)值 (均值) εHf (t)值
(均值)Hf模式年龄TDMC (Ma)
值 (均值)数据来源 (Ma) (Ma) 1 08BL08-1 花岗闪长岩 252 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.30 1.58 Zhang et al.,2012 2 14-SST-37 花岗斑岩 252 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb1.56~12.41 (6.14) 0.49~1.183 (0.89) Ren et al.,2016 3 DL09-21 花岗闪长岩 251 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.57 1.23 2.72 1.11 Huang et al.,2014 4 DL09-27 花岗闪长岩 251 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.63 1.19 2.11 1.15 Huang et al.,2014 5 10NM63-10 苏长辉长岩 251 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–7.36~–3.61
(–5.18)1.32~1.62
( 1.46)–2.39~1.06
(–0.88)1.21~1.43 (1.34) 熊富浩等,2011 6 XH040916-6 花岗闪长岩 251 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.00 1.15 Chen et al.,2012 7 DL09-18 花岗闪长岩 251 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.82 1.13 3.35 1.07 Huang et al.,2014 8 DL09-15 花岗闪长岩 250 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.12~–3.14 (–3.63) 1.32~1.36
( 1.34)3.30 1.07 Huang et al.,2014 9 XH040915-4 花岗闪长岩 250 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.41 1.26 Chen et al.,2012 10 DL09-31 镁铁质暗色微粒包体 250 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.15~–2.07 (–2.11) 0.74~0.74 (0.74) –3.08 1.47 Huang et al.,2014 1.54 1.18 11 DL09-13 花岗闪长岩 249 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.47~–2.15 (–3.31) 1.11~1.39
( 1.25)2.37 1.13 Huang et al.,2014 12 11BL03-1 granodiorite 249 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXiong et al.,2014 13 DL09-30 花岗闪长岩 249 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–1.67 0.72 2.09 1.15 Huang et al.,2014 14 br01-1 角闪辉长岩 249 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb熊富浩等,2011 15 DL09-17 镁铁质暗 249 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.92 1.61 4.35 1.00 Huang et al.,2014 16 DL09-22 镁铁质暗 249 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.95 1.27 4.44 1.00 Huang et al.,2014 17 DL09-07 镁铁质暗 249 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.19 1.31 3.89 1.03 Huang et al.,2014 18 DL09-08 花岗闪长岩 248 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.69 1.32 3.18 1.08 Huang et al.,2014 –1.38 1.37 19 XH040916-8B 花岗岩 248 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbChen et al.,2012 20 DL09-24 镁铁质暗 248 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.03 1.57 3.93 1.03 Huang et al.,2014 1.74 1.17 21 09NM66-1 quartz diorite 248 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXiong et al.,2014 22 ZW-14 二长花岗岩 246 2 ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb强娟,2008 23 XH040916-8A 英云闪长岩 245 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.73 1.45 Chen et al.,2012 24 BLGTC104-B1 granite 245 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.32~–3.31 (–3.31) 1.08~1.16 (1.12) –1.38~1.71 (0.23) 1.17~1.36 (1.26) Ding et al.,2014 25 HSG5-1 流纹岩 245 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.75~–4.17 (–4.49) 1.29~1.32 (1.31) –4.18~0.19 (–1.48) 1.26~1.54 (1.37) Li et al.,2015a 26 AK18 花岗斑岩 244 2 SIMS
锆石 U–Pb刘建楠等,2012 27 14-SST-51 花岗闪长岩 244 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.72~1.01 (–1.77) 1.21~1.51 (1.39) Ren et al.,2016 28 BLG-XJ-B8 granite 244 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.59 1.07 –3.68~1.33 (–0.16) 1.19~1.51 (1.28) Ding et al.,2014 29 BLG-XJ-B9 granite 244 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.24~–3.14 (–3.19) 0.99~1.16 (1.08) –1.52~1.67 (0.29) 1.17~1.37 (1.26) Ding et al.,2014 30 HSG1-2 流纹岩 244 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.93~–4.56 (–5.22) 1.31~1.45 (1.37) –2.94~1.37 (–0.79) 1.19~1.46 (1.32) Li et al.,2015a 31 ASH- 2# 闪长岩 244 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb李碧乐等,2012 32 08BL10-1 花岗闪长岩 244 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.30~–4.74 (–5.02) 1.42~1.63 (1.53) Zhang et al.,2012 33 DG25-4 流纹质凝灰岩 244 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb吴芳,2010 34 13NGT-04-1 Host granodioriteite 243 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–7.13~–5.76 (–6.31) 1.44~1.8 (1.61) –0.97~2.44 (0.4) 1.12~1.33 (1.25) Xia et al.,2015a 35 (13NGT-04-2) Dioritic enclave 243 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–8.30~–5.76 (–6.86) 1.40~1.88 (1.58) –3.51~1.67 (–1.02) 1.17~1.50 (1.34) Xia et al.,2015a 36 09dl36 -1 quartz diorite 243 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.24 1.52 –3.69~–2.38 (–2.99) 1.42~1.51 (1.46) Xiong et al.,2014 37 08BL01-2 花岗闪长岩 243 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–7.46~–5.22 (–6.10) (1.23~1.77)/ 1.49 Zhang et al.,2012 38 QW1032 花岗闪长岩 242 6 SHRIMPⅡ
锆石U–PbLiu et al.,2004 39 XH040916-1 碱性花岗岩 242 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.62 1.69 Chen et al.,2012 40 XH040915-5 花岗闪长岩 241 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.84 1.32 Chen et al.,2012 41 11BL01-2 granodiorite 241 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXiong et al.,2014 42 08BL01-03 石英闪长岩 241 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.44 1.54 Zhang et al.,2012 43 09NM52-1 granodiorite 241 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.49 1.43 Xiong et al.,2014 44 Q1013 暗色微粒包体 241 5 SHRIMPⅡ
锆石U–PbLiu et al.,2004 45 XH040916-3 花岗闪长岩 241 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.84 1.32 Chen et al.,2012 46 QW1160 角闪辉长岩 239 6 SHRIMPⅡ
锆石U–PbLiu et al.,2004 47 XH040914-5 钾长花岗岩 239 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–9.40 1.67 Chen et al.,2012 48 09NM73-1 syenogranite 239 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.78 1.41 –6.85~–3.85 (–4.87) 1.51~1.7 (1.58) Xiong et al.,2014 49 11ASY-008 石英闪长岩 238 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb李金超等,2014 50 WSA-6 黑云母花岗岩 238 2 ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb强娟等,2008 51 14-SST-74 花岗闪长岩 237 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–8.39~0.51 (–2.80) 1.24~1.80 (1.45) Ren et al.,2016 52 09DL31-1 syenogranite 236 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.67 1.33 Xiong et al.,2014 53 09DL40-2 granitic porphyry 236 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–7.79~–6.89 (–7.34) 1.36~1.53 (1.45) Xiong et al.,2014 54 HMH-2 花岗闪长岩 235 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–4.40~–3.85 (–4.12) 1.23~1.29 (1.25) 张宏飞等,2006 55 11HR 07 花岗闪长斑岩 235 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb宋忠宝等,2013 56 XH040917-1A 闪长岩 235 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.38 1.48 Chen et al.,2012 57 14-SST-59 钾长花岗岩 234 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.79~3.82 (–0.14) 1.02~1.51 (1.27) Ren et al.,2016 58 14-SST-44 钾长花岗岩 233 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.12~4.38 (–0.39) 0.99~1.40 (1.29) Ren et al.,2016 59 B-006 花岗闪长斑岩 233 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXia et al.,2014 60 B-004 二长花岗斑岩 232 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXia et al.,2014 61 14-SST-42 钾长花岗岩 232 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.46~4.96 (0.99) 0.95~1.42 (1.20) Ren et al.,2016 62 11BL06-1 syenogranite 232 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.39~–5.88 (–6.13) 1.09~1.19 (1.14) Xiong et al.,2014 63 08BL09 正长花岗岩 231 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.09 1.3 Zhang et al.,2012 64 XH040916-4 花岗闪长岩 229 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.53 1.11 Chen et al.,2012 65 1059 花岗岩 228 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbDai et al.,2013 66 RSX12-48 rhyolite porphyry 228 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.10 1.42 –0.93 1.32 Hu et al.,2016 –1.45 1.35 67 SQ-04-1 斜长花岗岩 227 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–8.21~0.15 (–5.1) 1.25~1.78 (1.58) Xia et al.,2015b 68 JDG-PD1-N22 granodiorite porphyry 227 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–8.29~–7.88 (–8.12) 1.59~1.66 (1.63) Li et al.,2015a 69 2228—8 花岗闪长岩 227 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石U–Pb李小江等,2015 70 SQ-04-2 斜长花岗岩 227 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.92~0.42 (–4.48) 1.23~1.7 (1.54) Xia et al.,2015b 71 Jan-98 闪长岩 226 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb李佐臣等,2013 72 12NM29-5 MMEs 225 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXiong et al.,2014 73 11124/2 花岗闪长岩 225 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb陈国超等,2013a 74 11124/1 闪长质包体 225 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb陈国超等,2013a 75 DQ2-5 花岗闪长岩 224 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石U–Pb杨拴海等,2015 76 09DL40-1 porphyritic granodiorite 224 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.89 1.22 –3.41~–1.05 (–2.53) 1.33~1.48 (1.42) Xiong et al.,2014 77 Sd-2 石英闪长玢岩 223 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb刘建平等,2012 78 XA30-1 二长花岗岩 223 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.72~–3.82 (–4.91) 1.18~1.35 (1.26) 罗明非等,2014 79 ST05 石英闪长岩 223 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.05~4.06 (1.13) 1.00~1.39 (1.19) Wang et al.,2016 80 ZK2523B-02 石英闪长岩 223 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbWang et al.,2016 81 NMHX-1-2 Granodiorites 222 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXia et al.,2014 82 NMHX-03 Gabbroic enclaves 222 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXia et al.,2014 83 14-SST-08 Granodiorites 221 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石U–PbRen et al.,2016 84 XA-63-1 花岗闪长岩 221 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.44~–5.23 (–5.83) 1.43~1.48 (1.46) 罗明非等,2014 85 NMHX-02 Diorite enclaves 220 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–PbXia et al.,2014 86 3154—5 granodiorite 220 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石U–PbYang et al.,2015 87 Sg-1 花岗斑岩 220 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb刘建平等,2012 88 3154-TW-5 花岗闪长岩 219 5 LA–ICP–MS
锆石U–Pb徐多勋等,2015 89 14-SST-20 花岗斑岩 219 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石U–PbRen et al.,2016 90 11136/3 石英闪长岩 218 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb陈国超等,2013a 91 WQ-4 花岗闪长岩 218 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–6.12~–4.77 (–5.56) 1.32~1.7 (1.53) 张宏飞等,2006 92 XI01-B1 diorite 215 3 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.06 1.32 –4.21~–0.61 (–2.27) 1.29~1.52 (1.4) Ding et al.,2014 93 XI01-B2 diorite 215 4 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–5.70~–5.16 (–5.43) 1.4~1.45 (1.43) –4.37~–2.19 (–3.05) 1.39~1.53 (1.44) Ding et al.,2014 94 ZW-06 二长花岗岩 215 1 ICP–MS
锆石U–Pb强娟,2008 95 DL09-01 流纹岩 214 1 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–2.96~–2.96 (–2.96) 1.37~1.42 (1.4) 1.05 1.18 丁烁等,2011 96 DL09-05 流纹岩 212 2 LA–ICP–MS
锆石 U–Pb–3.06~–3.04 (–3.05) 1.41~1.51 (1.46) 0.50 1.22 丁烁等,2011 -
[1] 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑造山带晚三叠世岩浆混合作用: 以和勒冈希里克特花岗闪长岩体为例[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(4): 1044-1065.
CHEN Guochao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Late Triassic magma mixing in the East Kunlun orogenic belt: A case study of Helegang Xilikete granodiorites[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(4):1044-1065.
[2] 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑洪水川地区科科鄂阿龙岩体锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013a, 87(02): 178-196
Chen G C, Pei X Z, Li R B, et al. Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Geochemical Characteristics and Geological Significance of Cocoe A'Long Quartz Diorites Body from the Hongshuichuan Area in East Kunlun[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013a, 87(02): 178-196.
[3] 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑东段香加南山花岗岩基的岩浆混合成因: 来自镁铁质微粒包体的证据[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(04): 226-40
Chen G C, Pei X Z, Li R B, et al. Genesis of magma mixing and mingling of xiangjiananshan granite batholith in the eastern section of east kunlun orogen: evidence from mafic microgranular enclaves(mmes). Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(04): 226-40.
[4] 陈宣华, 尹安, George G, 等. 柴达木盆地东部基底花岗岩类岩浆活动的化学地球动力学[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(2): 157-171.
CHEN Xuanhua, YIN An, George G, et al. Chemical Geodynamics of Granitic Magmatism in the Basement of the Eastern Qaidam Basin, Northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 2011, 85(2): 157-171.
[5] 谌宏伟, 罗照华, 莫宣学, 等. 东昆仑造山带三叠纪岩浆混合成因花岗岩的岩浆底侵作用机制[J]. 中国地质, 2005, 32(03): 386-395.
Chen H W , Luo Z H , Mo X X , et al. Underplating mechanism of Triassic granite of magma mixing origin in the East Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Geology in China, 2005, 32(3): 393-395.
[6] 丁烁, 黄慧, 牛耀龄, 等. 东昆仑高Nb-Ta流纹岩的年代学、地球化学及成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(12): 3603-3614
Ding S, Huang H, Niu Y L, et al. Geochemistry, geochronology and petrogenesis of East Kunlun high Nb-Ta rhyolites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(12): 3603-3614.
[7] 郭正府, 邓晋福. 青藏东昆仑晚古生代末—中生代中酸性火成岩与陆内造山过程[J]. 现代地质, 1998, 12(03): 344-352
Guo ZF, Deng JF. Late palaeozoic mesozoic intracontinental orogenic process and intermedate acidic igneous rocks from the eastern kunlun mountains of northwestern china [J]. Geoscience, 1998, 12(03): 344-352.
[8] 侯增谦、郑远川、卢占武、许博、王长明、张洪瑞. 青藏高原巨厚地壳: 生长, 加厚与演化[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(10): 2797–2815 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.001
HOU ZQ, ZHENG YC, LU ZW, et al. Growth, thickening and evolution of the thickened crust of the Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(10): 2797–2815. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.001
[9] 姜春发. 中央造山带几个重要地质问题及其研究进展[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(8): 453-455.
JIANG Chunfa. Several important geological problems about the Central Orogenic Belt and progress in its research [J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(8): 453-455.
[10] 李碧乐, 孙丰月, 于晓飞, 等. 东昆中隆起带东段闪长岩U-Pb年代学和岩石地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, (04): 1163-1172
LI BL, SUN FY, YU XF, et al. U-Pb dating and geochemistry of diorite in the eastern section from eastern Kunlun middle uplifted basement and granitic belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(4): 1163-1172
[11] 李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等. 东昆仑东段晚古生代—中生代若干不整合面特征及其对重大构造事件的响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(5): 244-254.
LI Ruibao, PEI Xianzhi, LI Zuochen, et al. Geological characteristics of Late Palaeozoic-Mesozoic unconformities and their response to some significant tectonic events in eastern part of Eastern Kunlun [J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(5): 244-254.
[12] 李金超, 贾群子, 杜玮, 等. 东昆仑东段阿斯哈矿床石英闪长岩 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及岩石地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2014, 44(4): 1188-1199.
LI Jinchao, JIA Qunzi, DU Wei, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon dating and geochemical characteristics of quartz diorite in Asiha gold deposit in east segment of the eastern Kunlun[J]. Journal of Jilin University, 2014, 44(4):1188-1199
[13] 李小江, 李佐臣, 杨拴海, 等.西秦岭西段然果儿岗花岗闪长岩体锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J].新疆地质, 2015, 33(3): 1-66.
LI Xiaojiang, LI Zuochen, YANG Shuanhai, et al. Zircon U-Pb Dating of Ranguoergang Granodiorite in Western Section of West Qinling, and its Geological Significance[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2015, 33(3): 1-66.
[14] 李佐臣, 裴先治, 刘战庆, 等.东昆仑南缘布青山构造混杂岩带哥日卓托闪长岩体年代学, 地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2013, 87(8): 1089-1103.
LI Zuochen, PEI Xianzhi, LIU Zhanqing, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Gerizhuotuo diorites from the Buqingshan tectonic Melange belt in the Southern margin of East Kunlun and their geologic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2013, 87(8): 1089-1103.
[15] 刘成东, 莫宣学, 罗照华, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩类Pb-Sr-Nd-O 同位素特征[J].地球学报, 2003, 58(6): 584-588.
LIU Chengdong, Mo Xuanxue, LUO Zhaohua, et al. Pb-Sr-Nd-O isotope characteristics of granitoids in East Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2003, 58(6), 584-588.
[16] 刘成东, 张文秦, 莫宣学, 等. 东昆仑约格鲁岩体暗色微粒包体特征及成因[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(11): 739-744.
LIU Chengdong, ZHANG Wenqin, MO Xuanxue, et al. Features and origin of mafic microgranular enclaves in the Yuegelu granite in the Eastern Kunlun[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(11), 739-744.
[17] 刘建楠, 丰成友, 亓锋, 等. 青海都兰县下得波利铜钼矿区锆石U-Pb测年及流体包裹体研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(02): 679-690
LIU JN, FENG CY, YUAN F, et al. SIMS zircon U-Pb dating and fluid inclusion studies of Xiadeboli Cu-Mo ore district in Dulan County, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(02): 679-690.
[18] 刘建平, 赖健清, 谷湘平, 等. 青海赛什塘铜矿区侵入岩体地球化学及锆石LA-ICPMS U-Pb年代学[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2012, 22(03): 622-632
LIU JP, LAI JQ, GU XP, et al. Geochemistry and zircon LA-ICPMS U-Pb geochronology of intrusive body in Saishitang copper deposit, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(03): 622-632.
[19] 罗明非, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 东昆仑香日德地区晚三叠世花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、岩石成因和构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3229-3241
LUO MF, MO XX, YU XH et al. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb age dating, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of the Late Triassic granites from the Xiangride area, East Kunlun[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(11): 3229-3241.
[20] 罗照华, 曹永清. 东昆仑印支晚期幔源岩浆活动[J]. 地质通报, 2002, 21(06): 292-297
Luo Z H, CAO YQ. Late Indosinian mantle-derived magmatism in the East Kunlun[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2002, 21(6): 292-297
[21] 罗照华, 邓晋福, 曹永清, 等. 青海省东昆仑地区晚古生代—早中生代火山活动与区域构造演化[J]. 现代地质, 1999, 13(01): 51-56
LUO ZH, DENG JF, CAO YQ, ET AL. On late Paleozoic early Mesozoic volcanism and regional tectonic evolution of eastern kunlun, qinghai province[J]. Geoscience, 1999, 13(01): 51-56.
[22] 马昌前, 熊富浩, 尹烁, 等. 造山带岩浆作用的强度和旋回性: 以东昆仑古特提斯花岗岩类岩基为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(12): 3555-68.
MA CQ, XIONG FH, YIN S, et al. Intensity and cyclicity of orogenic magmatism: An example from a Paleo-Tethyan granitoid batholith, Eastern Kunlun, northern Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(12): 3555-3568.
[23] 莫宣学. 岩浆作用与青藏高原演化[J]. 高校地质学报, 2011, 12(03): 351-67 doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2011.03.004
Mo X X. Magmatism and evolution of the Xizang Plateau[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2011, 12(03): 351-67. doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2011.03.004
[24] 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等.东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J].高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 403-414
MO Xuanxue, LUO Zhaohua, DENG Jinfu, et al. Granitoids and Crustal Growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3): 1089-1103.
[25] 潘裕生, 方爱民. 中国青藏高原特提斯的形成与演化[J]. 地质科学, 2010, 45(1): 92-101.
PAN Yusheng, FANG Aimin. Formation and evolution of the Tethys in the Xizang Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2010, 45(1): 92-101.
[26] 强娟. 青藏高原东北缘宗务隆构造带花岗岩及其构造意义[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2008: 1−64
QIANG Juan. The granitiods in zongwulong tectonic zone on the northeastern margin of the qinghai-Xizang plateau and its tectonic significance[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2008: 1−64.
[27] 任海东, 王涛. 东昆仑—西秦岭造山带对接处三叠纪花岗质岩石时空演化、物源特征对比及其大地构造意义[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(s): 59-63
Ren H D, Wang T. Temporal-spatial Variations, Sources and Tectonic Significances of the Triassic Granitic Rocks in the Junction Part of the East Kunlun and West Qinling Orogen, Central China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(s): 59-63.
[28] 任纪舜. 昆仑—秦岭造山系的几个问题[J]. 西北地质, 2004, 1-5
REN JS. Some problems on the Kunlun-Qinling orogenic system[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2004, 1-5.
[29] 宋忠宝, 张雨莲, 陈向阳, 等. 东昆仑哈日扎含矿花岗闪长斑岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2013, 32(1): 157-168.
SONG Zhongbao, ZHANG Yulian, CHEN Xiangyang, et al. Geochemical characteristics of Harizha granite diorite -porphyry in East Kunlun and their geological implications[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(01): 157-168.
[30] 田龙, 康磊, 刘良, 等. 东昆仑巴什尔希晚奥陶世二长花岗岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 28-−45.
TIAN Long, KANG Lei, LIU Liang, et al. Petrogenesis and Geological Implications of Bashenerxi Monzogranite from East Kunlun Orogen Belt[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 28-45.
[31] 王涛, 黄河, 宋鹏, 等. 地壳生长及深部物质架构研究与问题: 以中亚造山带(北疆地区)为例[J].地球科学, 2020, 45(7): 2326-2344.
WANG Tao, HUANG He, SONG Peng, et al. Studies of Crustal Growth and Deep Lithospheric Architecture and New Issues: Exemplified by the Central Asian Orogenic Belt (Northern Xinjiang)[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(7): 2326-2344.
[32] 王涛, 侯增谦. 同位素填图与深部物质探测(Ⅰ): 揭示岩石圈组成演变与地壳生长[J]. 地学前缘, 2018, 25: 1-19
WANG T, HOU ZQ. Isotopic mapping and deep material probing (Ⅰ): revealing the compositional evolution of the lithosphere and crustal growth processes[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2018, 25: 1-19.
[33] 王新宇, 陈能松, 陈海, 等. 柴达木周缘印支期花岗岩同位素地球化学特征及其对基底属性的制约[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(1): 13-19.
WANG Xinyu, CHEN Nengsong, CHEN Hai, et al. Isotopic Geochemistry Characters of Indosinian Granites around Qaidam Basin and its Constraints on Basement Affinity[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(1): 13-19.
[34] 王永标, 黄继春. 海西—印支早期东昆仑造山带南侧古海洋盆地的演化[J].地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1997, 22(4): 33-36.
WANG Yongbiao, HUANG Jichun. Paleo-ocean evolution of the southern Eastern Kunlun orogenic belt during Heacy-early Indosinian[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1997, 22(4):33-36.
[35] 吴芳, 张绪教, 张永清, 等. 东昆仑闹仓坚沟组流纹质凝灰岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质力学学报, 2010, 16(01): 44-50
Wu F, Zhang X J, Zhang Y Q, et al. Zircon u-pb ages for rhyolitic tuffs of the naocangjiangou formation in the east kulun orogenic belt and their implication[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2010, 16(01): 44-50.
[36] 吴树宽, 陈国超, 李积清, 等. 东昆仑东段沟里地区战红山过铝质流纹斑岩年代学、岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 92−108.
WU Shukuan, CHEN Guochao, LI Jiqing, et al. Geochronology, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of Zhanhongshan Peraluminous Rhyolite Porphyry in Gouli Area, Eastern Section of East Kunlun[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 92−108.
[37] 熊富浩, 马昌前, 张金阳, 等. 东昆仑造山带早中生代镁铁质岩墙群LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年、元素和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(11): 3350-3364
Xiong F H, Ma C Q, Zhang J Y, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating, elements and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry of the Early Mesozoic mafic dyke swarms in East Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(11): 3350-3364
[38] 徐多勋, 杨拴海, 李瑞保, 等.西秦岭西段塔洞花岗闪长岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J].地球科学与环境学报, 2015, 37(3): 22-33.
XU Duoxun, YANG Shuanhai, LI Ruibao, et al. Geochronological, geochemical characteristics and geological significance of tadong granodiorite pluton in the western section of West Qinling[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences & Environment, 2015, 37(3):22-33.
[39] 杨拴海, 李瑞保, 王伟峰, 等. 西秦岭西段曲如沟花岗闪长岩年代学、地球化学特征及构造意义研究[J]. 西北地质, 2015, 48 (2): 57-72.
YANG Shuanhai, LI Ruibao, WANG Weifeng, et al. Geochronology,Geochemical Characteristics and Tectonic Significance of Qurugou Granodiorite in Western Section of West Qinling Orogen[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2015, 48 (2): 57-72.
[40] 殷鸿福, 张克信. 东昆仑造山带的一些特点[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 1997, 22(4): 3-6.
YIN Hongfu, ZHANG Kexin. Characteristics of the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic belt[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 1997, 22(4): 3-6.
[41] 袁万明, 莫宣学, 喻学惠, 等. 东昆仑印支期区域构造背景的花岗岩记录[J]. 地质论评, 2000, 46(02): 203-211 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.02.012
Yuan WM, Mo XX, Yu XH. The record of Indosinian tectonic setting from the granotoid of eastern Kunlun Mountains [J]. Geological Review, 2000, 46(02): 203-211. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.02.012
[42] 翟明国. 花岗岩: 大陆地质研究的突破口以及若干关键科学问题——“岩石学报”花岗岩专辑代序[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(01): 1-12
Zhai MG. Granites: Leading study issue for continental evolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 201733(01): 1-12.
[43] 张国伟, 柳小明. 关于“中央造山带”几个问题的思考[J]. 地球科学, 1998: 9-14
ZHANG GW, LIU XM. Some remarks on china central orogenic system. Geological science, 1998: 9-14.
[44] 张宏飞, 陈岳龙, 徐旺春, 刘荣, 袁洪林, 柳小明. 青海共和盆地周缘印支期花岗岩类的成因及其构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2006, 22(12): 2910-22
ZHANG HF, CHEN YL, XU WC, ET AL. Granitoids around Gonghe basin in Qinghai province: petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(12): 2910-22.
[45] 钟大赉, 丁林, 张进江, 等. 中国造山带研究的回顾和展望[J]. 地质论评, 2002, 147-52
ZHONG DL, DING L, ZHANG JJ. Study of Orogenic Belts in China: Retrospects and Prospects[J]. Geological Review, 2002, 147-52.
[46] 张智勇, 殷鸿福, 王秉璋, 等. 昆秦接合部海西期苦海-赛什塘分支洋的存在及其证据[J].地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(6): 691-696.
ZHANG Zhiyong, YIN Hongfu, WANG Bingzhang, et al. Presence and Evidence of Kuhai-Saishitang Branching Ocean in Copulae between Kunlun-Qinling Mountains[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2004, 29(6):691-696
[47] 翟明国, 张旗, 陈国能, 等. 大陆演化与花岗岩研究的变革[J]. 科学通报, 2016, 61(13): 1414-1420.
ZHAI M G, ZHANG Q, CHEN G N, et al. Adventure on the research of continental evolution and related granite geochemistry (in Chinese). Chin Sci Bull, 2016, 61(13): 1414–1420
[48] 郑永飞, 陈伊翔, 戴立群, 等. 发展板块构造理论:从洋壳俯冲带到碰撞造山带[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2015, 45(6): 711-735.
ZHENG Yongfei, CHEN Yixiang, DAI Liqun, et al. 2015. Developing plate tectonics theory from oceanic subduction zones to collisional orogens[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 58: 1045–1069
[49] CHEN XH, GEORGE G, YIN An, et al. Paleozoic and Mesozoic Basement Magmatisms of Eastern Qaidam Basin, Northern Qinghai‐Xizang Plateau: LA‐ICP‐MS Zircon U‐Pb Geochronology and its Geological Significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica‐English Edition, 2012, 86(2): 350-369. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2012.00665.x
[50] Chen X H, Gehrels G, Yin A, et al. Geochemical and Nd–Sr–Pb–O isotopic constrains on Permo–Triassic magmatism in eastern Qaidam Basin, northern Qinghai-Xizang plateau: Implications for the evolution of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 114: 674-692
[51] DAI JG, WANG C, HOURIGAN J, et al. Multi-stage tectono- Mag Matic events of the Eastern Kunlun Range, northern Xizang: Insights from U–Pb geochronology and (U–Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 599(0): 97-106.
[52] DING QF, JIANG SY, SUN FY. Zircon U–Pb geochronology, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic compositions of the Triassic granite and diorite dikes from the Wulonggou mining area in the Eastern Kunlun Orogen, NW China: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2014, 205(0): 266-283.
[53] DONG YP, HE DF, SUN SS, ET AL. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186, 231–261. . doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.006
[54] Hawkesworth C J, Dhuime B, Pietranik A B, et al. The generation and evolution of the continental crust [J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2010, 167(2):229-248.
[55] Hawkesworth C, Cawood P, Dhuime B. 2013. Continental growth and the crustal record[J]. Tectonophysics, 2013, 609(1): 651−660.
[56] Hu Y, Niu YL, Li J, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the late Triassic Mafic dikes and felsic volcanic rocks in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245: 205−222.
[57] Hawkesworth C J, Kemp A I. The differentiation and rates of generation of the continental crust [J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 226: 134-143.
[58] HUANG H, NIU YL, NOWELL G, et al. Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic belt, northern Xizang Plateau: Implications for continental crust growth through syn-collisional felsic Mag Matism[J]. Chemical Geology, 2014, 370(0): 1-18.
[59] LI BL, ZHI Y, ZHANG L, et al. U–Pb dating, geochemistry, and Sr–Nd isotopic composition of a granodiorite porphyry from the Jiadanggen Cu–(Mo) deposit in the Eastern Kunlun metallogenic belt, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 67: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.11.008
[60] LI XW, HUANG X, LUO MF, et al. Petrogenesis and geodynamic implications of the Mid-Triassic lavas from East Kunlun, northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105(0): 32-47.
[61] Liu C, Mo X, Luo Z, et al. Mixing events between the crust- and Mantle-derived Mag Mas in eastern kunlun: Evidence from zircon SHRIMP II chronology[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(8): 828−834.
[62] Liu H. Petrology, geochemistry and geochronology of late Triassic volcanics, Kunlun orogenic belt, western China: Implications for tectonic setting and petrogenesis[J]. Geochemical Journal, 2005, 39(1):1−20.
[63] Niu Y L, Zhao Z D, Zhu D C, et al. Continental Collision Zones are Primary Sites for Net Continental Crust Growth: A Testable Hypothesis[J]. Earth‐Science Reviews, 2013, 127: 96-110
[64] Ren H D, Wang T, Zhang L, et al. Ages, Sources and Tectonic Settings of the Triassic Igneous Rocks in the Easternmost Segment of the East Kunlun Orogen, central China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2016, 90(2): 641-668.
[65] Rudnick, R. L. Making continental crust[J]. Nature, 1995, 378, 571–578. doi: 10.1038/378571a0
[66] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M, Mcculloch M T. Geochemistry of loess, continental crustal composition and crustal model ages[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1983, 47(11):1897-1905.
[67] Vervoort J D, Plank T, Prytulak J. The Hf–Nd isotopic composition of marine sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2011, 75 (20), 5903−5926
[68] Wang H, Feng C, Li D, et al. Geology, geochronology and geochemistry of the Saishitang Cu deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, NW China: Constraints on ore genesis and tectonic setting[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 43−59.
[69] Wang T, Jahn B M, Kovach V P, et al. Nd–Sr isotopic mapping of the Chinese Altai and implications for continental growth in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt[J]. Lithos, 2009, 110(1-4):359-372
[70] XIA R, WANG C M, DENG J, et al. Crustal thickening prior to 220 Ma in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Insights from the Late Triassic granitoids in the Xiao-Nuomuhong pluton[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 93: 193-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.07.013
[71] Xia R, Wang C, Qing M, et al. Zircon U–Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr–Nd–Pb–Hf–O isotopes for the Nan'getan granodiorites and Mafic microgranular enclaves in the East Kunlun Orogen: Record of closure of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Lithos, 2015a, 234–235(3): 47–60.
[72] XIA R, WANG C, QING M, et al. Molybdenite Re–Os, zircon U–Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis of the Shuangqing Fe–Pb–Zn–Cu skarn deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015b, 66(0): 114-131.
[73] XIONG FH, Ma CQ, ZHANG J, et al. Reworking of old continental lithosphere: an important crustal evolution mechanism in orogenic belts, as evidenced by Triassic I-type granitoids in the East Kunlun orogen, Northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 2014, 171(6): 847-863. doi: 10.1144/jgs2013-038
[74] Yang G, Yang S, Wei L, et al. Petrogenesis and geodynamic significance of the Late Triassic Tadong adakitic pluton in West Qinling, central China[J]. International Geology Review, 2015, 57(13):1755−1771
[75] ZHANG JY, MA CQ, XIONG FH, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Late Permian–Middle Triassic calc-alkaline granites in the Balong region, eastern Kunlun Orogen, China[J]. Geological Magazine, 2012, 149(05): 892-908. doi: 10.1017/S0016756811001142
[76] ZHU DC, WANG Q, WEINBERG RF, et al. Interplay between oceanic subduction and continental collision in building continental crust [J]. Nature communications, 2022, 13: 7141. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34826-0
[77] ZHU DC, WANG Q, WEINBERG RF, et al. Continental Crustal Growth Processes Recorded in the Gangdese Batholith, Southern Xizang[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2023, 51: 155–88. doi: 10.1146/annurev-earth-032320-110452
-




 下载:
下载: