Ocean−Continent Transition Process and Magmatism in Orogenic Belts: A Case Study of Paleozoic Granites in the Dulan Area of East Kunlun
-
摘要:
洋陆转换过程中俯冲−碰撞(增生)−后碰撞各阶段具有不同岩浆作用,其中板片俯冲和岩石圈拆沉−减薄机制尤其受到关注。东昆仑造山带位于青藏高原北部,是秦祁昆中央造山带的重要组成部分,在早古生代经历了原特提斯洋陆转化过程。笔者通过对东昆仑东段都兰地区古生代花岗岩进行年代学、全岩地球化学和Sr−Nd−Hf同位素研究,认为浪木日中志留世(429±4 Ma)花岗岩形成于洋壳俯冲阶段,具有埃达克质岛弧岩浆属性,与热俯冲机制下的洋壳部分熔融有关;希望沟与哈日扎早泥盆世(416~403 Ma)花岗岩形成于后碰撞阶段,分别显示I型和A型花岗岩特征,与新生下地壳的部分熔融和岩石圈减薄作用有关。综合区域古生代花岗岩地球化学资料表明,东昆仑东西段岩浆岩差异可能是洋脊俯冲所致。
Abstract:The subduction−collision (accretion)−post−collision stages in the ocean−continent transition process have different magmatisms, among which the slab subduction and lithosphere delamination−thinning mechanisms have received special attention. The East Kunlun orogenic belt is located in the northern part of the Qinghai−Xizang Plateau, and is an important part of the Qin−Qi−Kun central orogenic belt, which has experienced the transformation process of the Proto−Tethys Ocean and Continent in the Early Paleozoic. Based on the geochronology, whole−rock geochemistry and Sr−Nd−Hf isotope studies of the Paleozoic granites in the Dulan area, eastern Kunlun, this paper suggests that the Langmuri Middle Silurian (429±4 Ma) granites were formed in the subduction stage of the oceanic crust. It has the property of adakitic island arc magma, which is related to the partial melting of oceanic crust under the mechanism of thermal subduction. The Xiwanggou and Harizha Early Devonian (416 ~ 403 Ma) granites were formed in the post−collision stage, showing the characteristics of I−type and A−type granites, respectively, which are related to the partial melting of the young lower crust and thinning of the lithosphere. The comprehensive regional Paleozoic granite geochemical data indicate that the difference of magmatic rocks in the east and west of East Kunlun may be caused by ocean ridge subduction.
-
Key words:
- geochemistry /
- ridge subduction /
- adakite /
- zircon U−Pb chronology /
- Sr−Nd−Hf isotope /
- East Kunlun
-

-
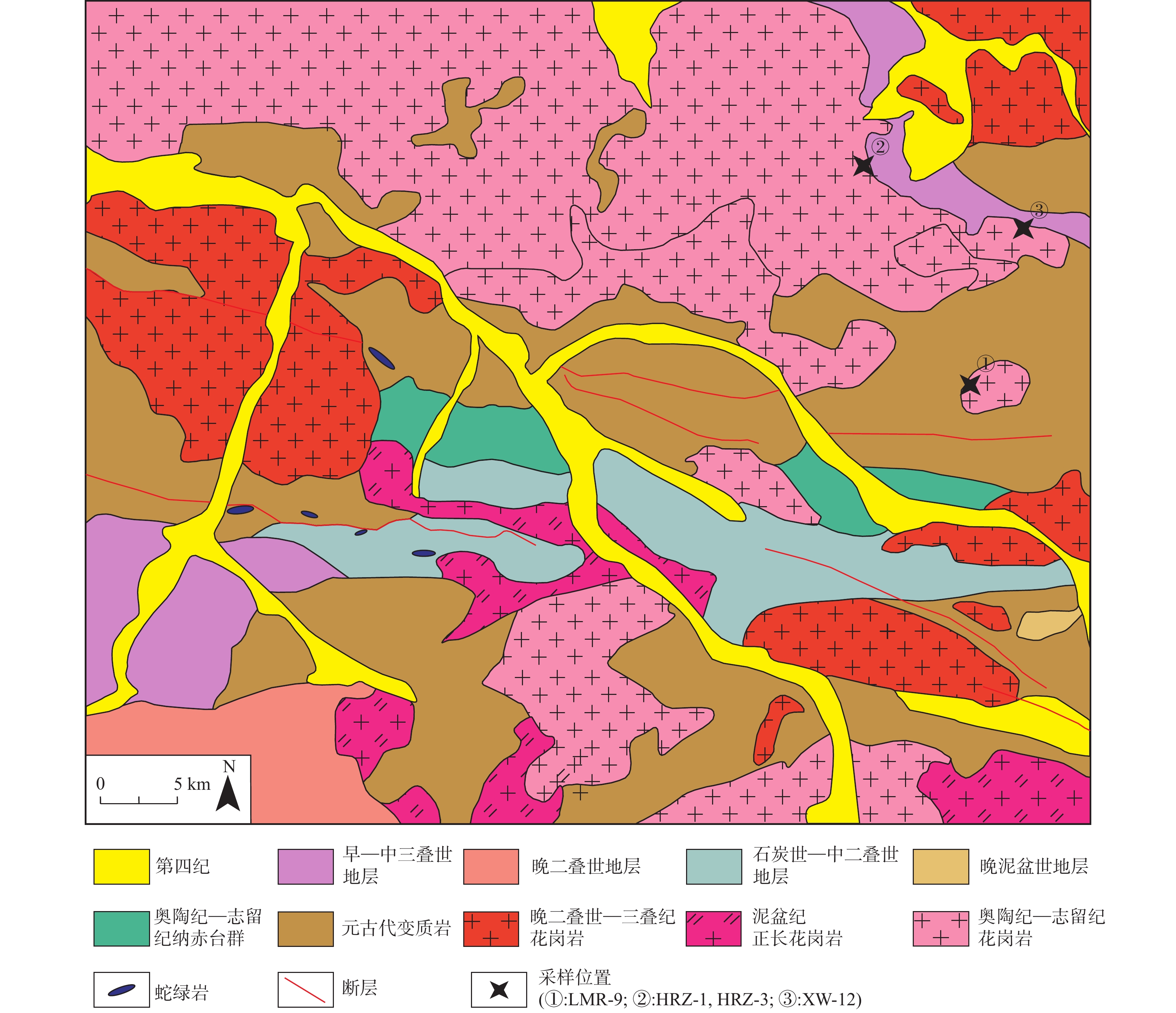
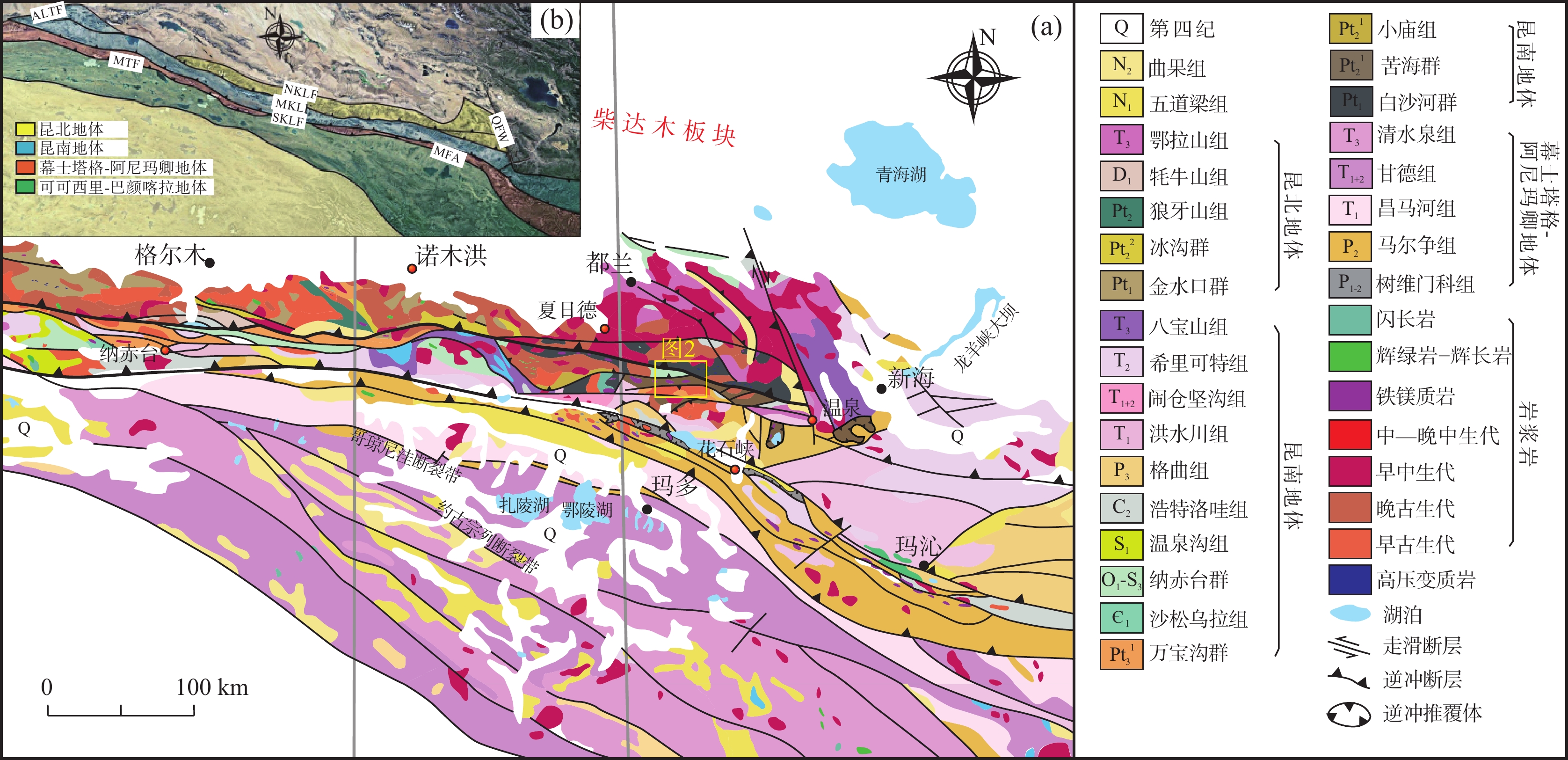
图 1 东昆仑造山带地质图(a)和构造地块划分图(b)(据Yu et al.,2020)
Figure 1.
图 2 研究区地质图及采样位置(据Chen et al.,2020a修改)
Figure 2.
图 7 球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分配图(a、c、e)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b、d、f) (标准化值据Sun et al.,1989)
Figure 7.
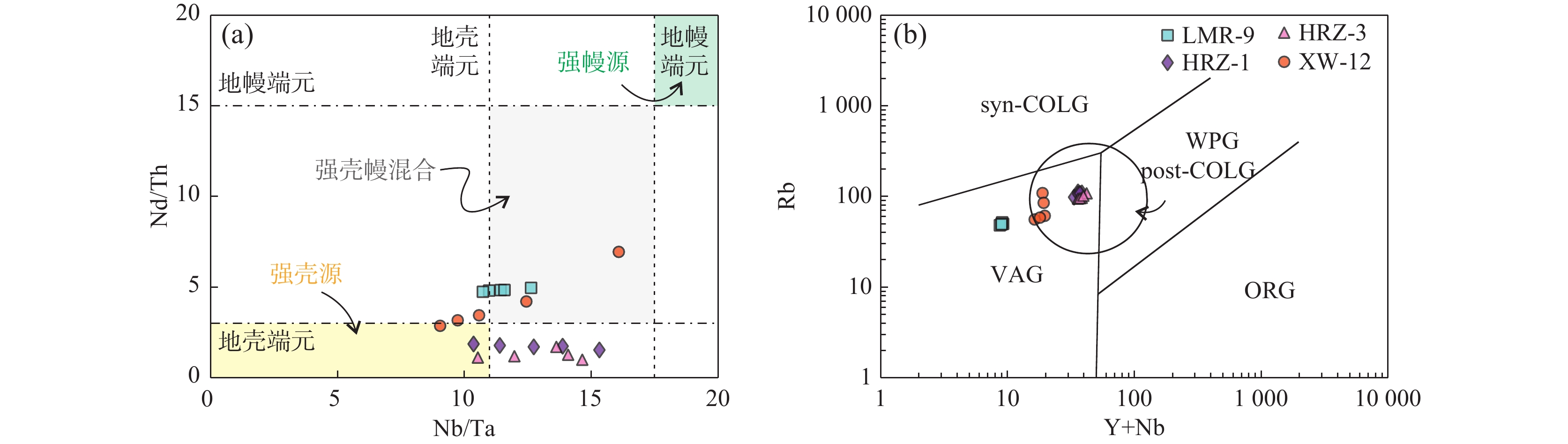
图 9 东昆仑东段花岗岩Nb/Ta–Nd/Th图解(a)(据Barth et al.,2000)和构造环境图解(b)(据Pearce,1996)
Figure 9.
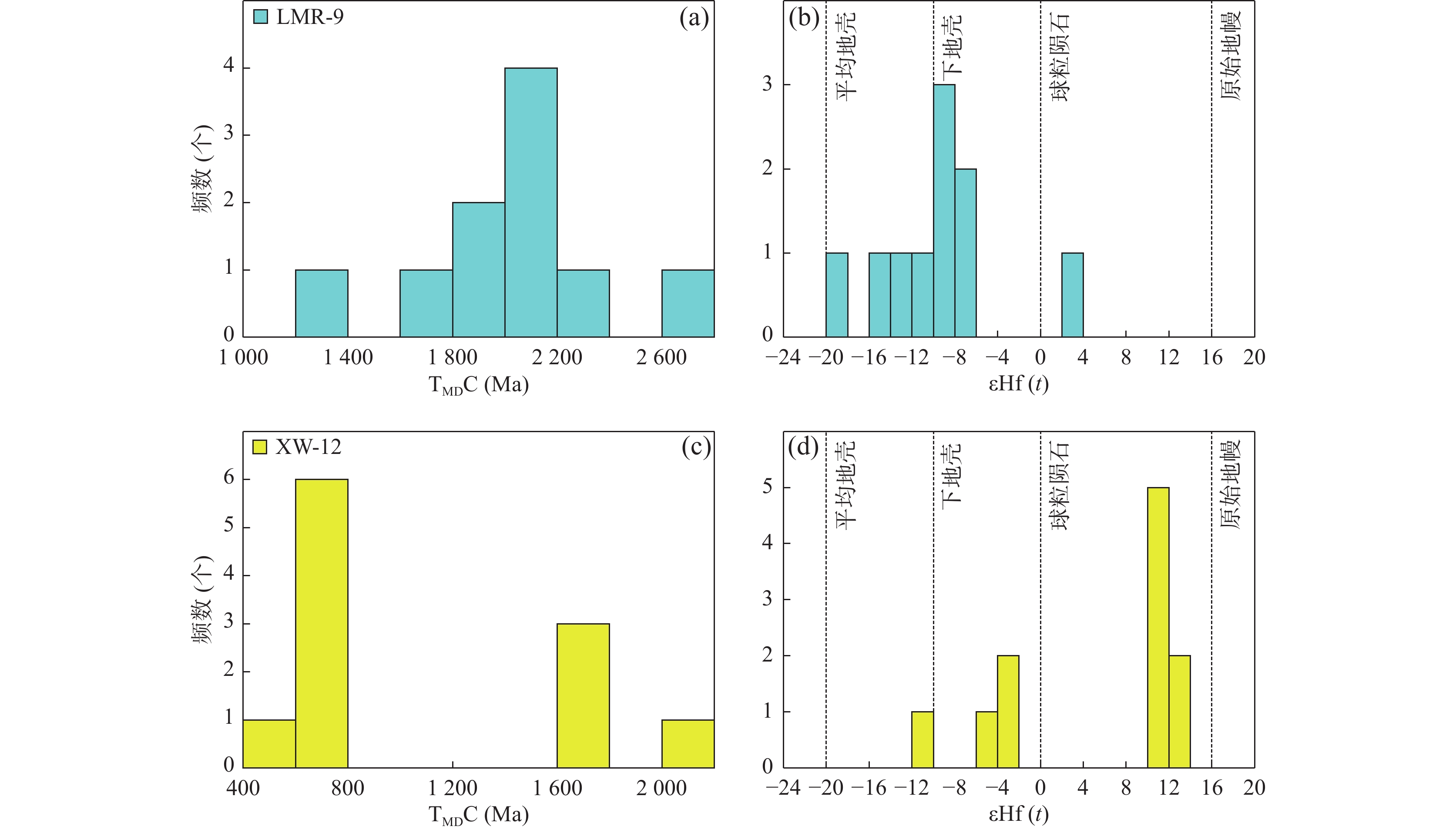
图 10 LMR-9和XW-12锆石TDMC(Ma)和εHf(t)频数直方图(据吴福元等,2007a)
Figure 10.
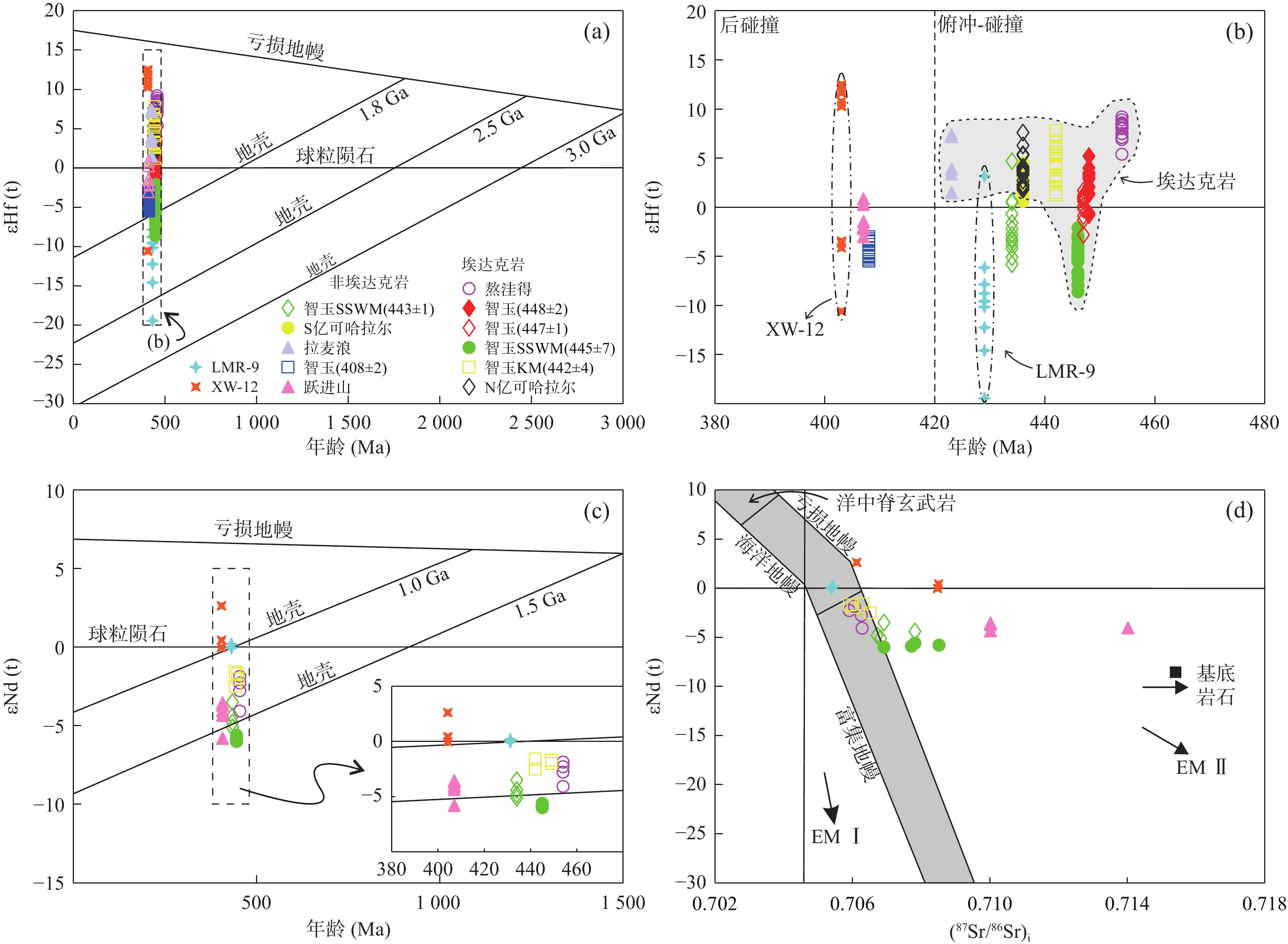
图 11 浪木日、希望沟花岗岩锆石Hf–Sr–Nd同位素特征图(底图d据Zhang et al.,2021)
Figure 11.
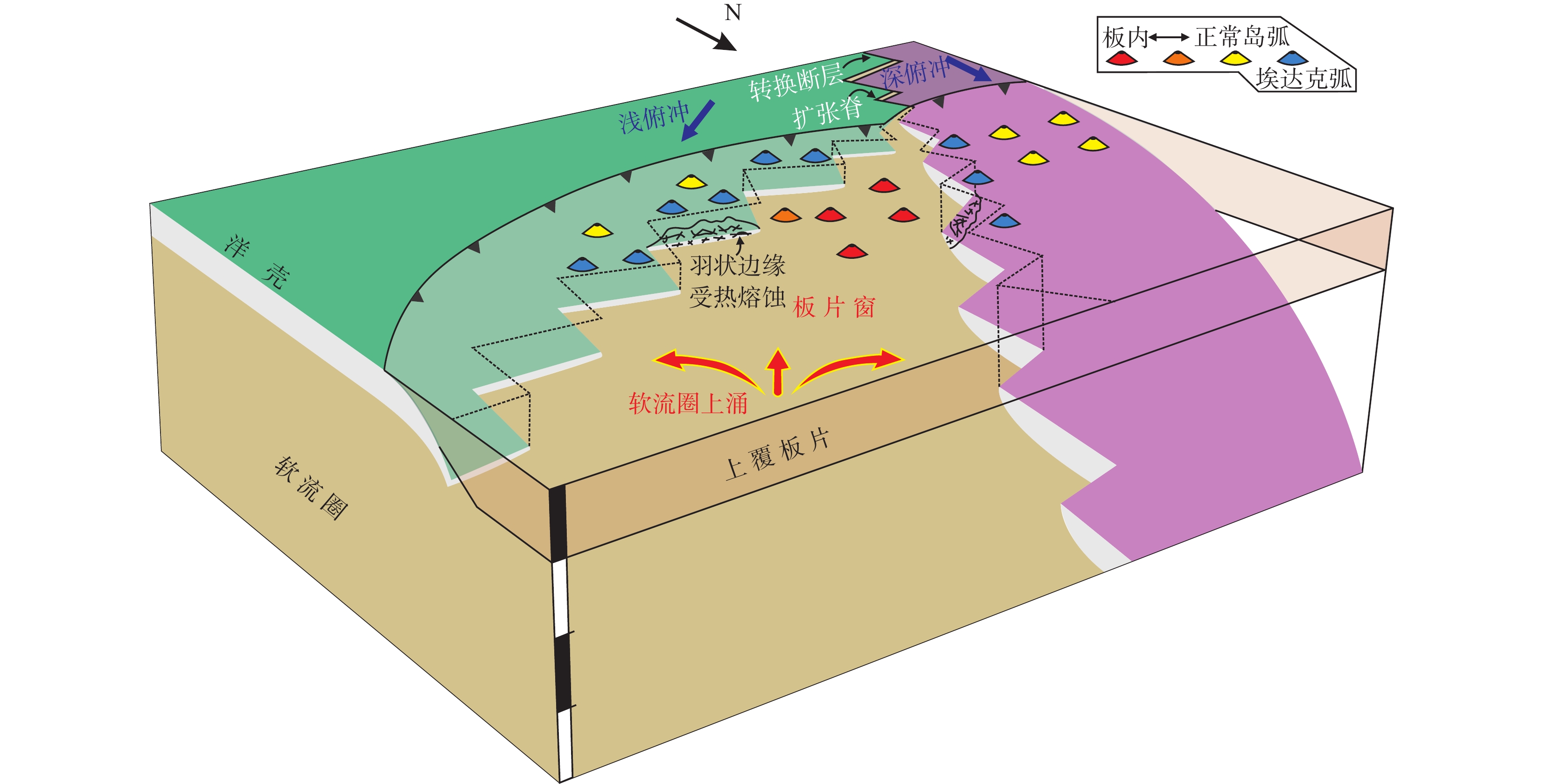
图 13 东昆仑造山带原特提斯洋脊俯冲模型图(据Windley et al.,2018修改)
Figure 13.
表 1 都兰地区样品岩相学特征描述
Table 1. Petrographic characteristics of samples from the Dulan area
样品地点 样品号 采样位置 岩性特征 矿物组成 样品特征 浪木日 LMR-9 N 35°46'21''
E 98°38'47''黑云母花岗闪长岩 长石(60%)
石英(20%)
黑云母(15%)
白云母(5%)斜长石晶体粒径为1 ~ 4.5 mm,可见明显绢云母化;石英晶体呈粒状,无色,正低突起,粒径为1 ~ 2.5 mm;黑云母呈褐色,多色性明显,同时可见少量片状白云母,发育一组极完全解理,粒径为0.25 ~ 1 mm (图3a、图3b) 哈日扎 HRZ-1 N 35°54′26″
E 98°36′28″似斑状二长花岗岩 斜长石(40%)
碱性长石(30%)
石英(20%)
黑云母(10%)斜长石粒径为1.5 ~ 4 mm,蚀变程度低;石英呈粒状,粒径为 1.5 ~ 4 mm,呈乳白色,包裹体较多,表面较浑浊;黑云母呈深褐色,片状,粒径为 0.5 ~ 1 mm,多色性明显;碱性长石为钾长石,晶体形态呈粒状,部分泥化,粒径为0.5 ~ 1 mm (图3c、图3d) HRZ-3 N 35°54′26″
E 98°36′28″花岗闪
长岩斜长石(60%)
碱性长石(15%)
石英(15%)
黑云母(10%)斜长石晶体粒径为1 ~ 4 mm;石英晶体呈粒状,无色,正低突起,粒径为 0.5 ~ 4 mm;碱性长石为钾长石,呈粒状,部分泥化,粒径为 1 ~ 2 mm;黑云母呈深褐色,多色性明显;镜下可见角闪石,褐色,蚀变不明显(图3e、图3f) 希望沟 XW-12 N 35°52'51''
E 98°42'24''花岗闪
长岩斜长石(70%)
石英(20%)
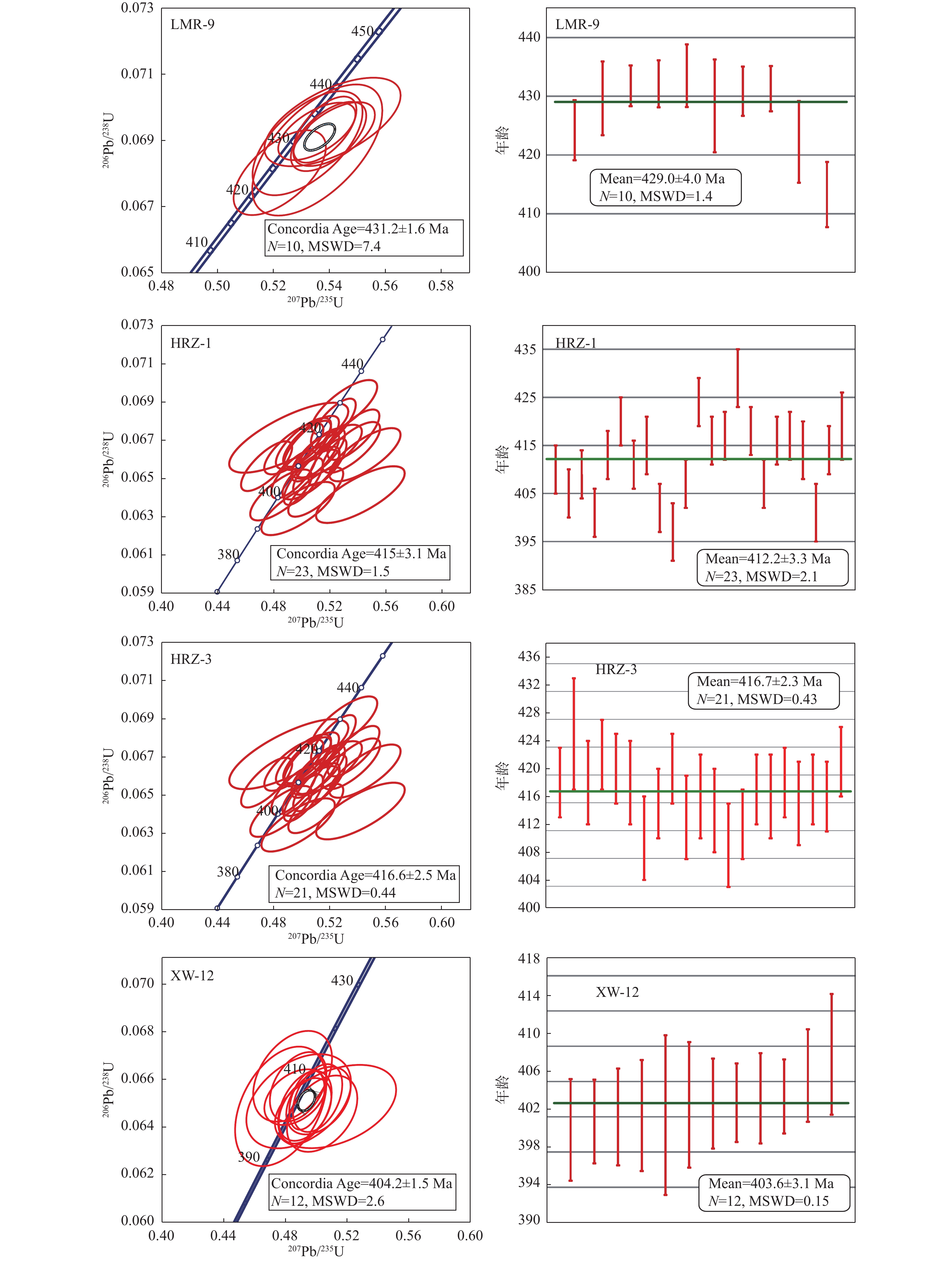
黑云母(10%)斜长石晶体粒径为1 ~ 3 mm,绢云母化明显;石英晶体呈粒状,颜色为无色,粒径为1 ~ 4 mm,由于包裹体较多,表面浑浊;黑云母呈黑–棕色,具一组极完全解理,多色性明显(图3g、图3h) 表 2 东昆仑都兰地区浪木日黑云母花岗闪长岩(LMR-9)锆石 LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 定年数据表
Table 2. Zircon LA–ICP–MS U–Pb dating data of biotite granodiorite (LMR-9) in Langmuri, Dulan area, East Kunlun
测点号 238U 232Th Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 10−6 10−6 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ LMR-9-02 316.325 6.351 0.020 077 0.056 335 0.001 638 0.541 065 0.016 034 0.069 559 0.000 885 0.098 356 0.021 291 LMR-9-04 698.218 29.668 0.042 491 0.056 643 0.000 818 0.539 660 0.008 877 0.069 121 0.000 693 0.021 201 0.000 840 LMR-9-07 1281.839 110.004 0.085 817 0.057 725 0.001 061 0.526 948 0.011 890 0.066 208 0.000 916 0.033 476 0.001 380 LMR-9-08 671.123 9.016 0.013 434 0.055 888 0.001 016 0.532 169 0.012 949 0.068 916 0.001 040 0.028 004 0.002 348 LMR-9-09 1120.577 300.149 0.267 852 0.056 240 0.000 904 0.535 645 0.015 310 0.068 710 0.001 311 0.023 340 0.000 794 LMR-9-10 421.336 58.694 0.139 306 0.056 000 0.000 827 0.535 485 0.009 094 0.069 275 0.000 574 0.025 243 0.000 969 LMR-9-11 2289.009 42.755 0.018 679 0.056 511 0.000 848 0.541 654 0.009 595 0.069 193 0.000 639 0.029 508 0.001 831 LMR-9-17 1394.080 76.079 0.054 573 0.056 275 0.000 703 0.538 376 0.007 418 0.069 328 0.000 661 0.020 995 0.000 658 LMR-9-19 753.590 51.631 0.068 513 0.058 110 0.001 524 0.539 648 0.016 456 0.067 694 0.001 153 0.004 164 0.001 038 LMR-9-23 318.174 13.328 0.041 888 0.055 494 0.001 028 0.522 255 0.010 862 0.068 024 0.000 848 0.021 305 0.001 701 测点号 238U/232Th 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ LMR-9-02 130.655 000 18.584 22 465.6 64.4 439.1 10.6 433.5 5.3 1896.2 391.8 LMR-9-04 23.236 260 0.463 315 477.7 31.9 438.2 5.9 430.9 4.2 424.0 16.6 LMR-9-07 12.144 750 0.578 212 519.3 40.3 429.8 7.9 413.3 5.5 665.5 27.0 LMR-9-08 80.145 330 4.656 936 447.9 40.4 433.2 8.6 429.6 6.3 558.2 46.2 LMR-9-09 3.582 419 0.084 373 461.9 35.6 435.5 10.1 428.4 7.9 466.3 15.7 LMR-9-10 9.336 152 0.477 850 452.4 32.8 435.4 6.0 431.8 3.5 503.9 19.1 LMR-9-11 52.205 370 1.212 468 472.5 33.2 439.5 6.3 431.3 3.9 587.8 35.9 LMR-9-17 18.235 300 0.440 723 463.2 27.7 437.4 4.9 432.1 4.0 420.0 13.0 LMR-9-19 15.621 370 0.719 202 533.9 57.4 438.2 10.9 422.2 7.0 84.0 20.9 LMR-9-23 24.343 330 0.497 610 432.2 41.3 426.7 7.2 424.2 5.1 426.1 33.7 表 3 东昆仑都兰地区哈日扎似斑状二长花岗岩(HRZ-1)锆石 LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 定年数据表
Table 3. Zircon LA–ICP–MS U–Pb dating data of porphyritic monzogranite (HRZ-1) in Harizha, Dulan area, East Kunlun
测点号 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ HRZV-1-01 0.052 45 0.001 31 0.474 83 0.012 02 0.065 66 0.000 86 0.021 22 0.000 35 305.0 34.0 395.0 8.0 410.0 5.0 424.0 7.0 HRZV-1-02 0.056 03 0.000 98 0.501 06 0.009 23 0.064 86 0.000 81 0.020 84 0.000 28 454.0 20.0 412.0 6.0 405.0 5.0 417.0 6.0 HRZV-1-03 0.056 58 0.001 18 0.510 35 0.010 92 0.065 42 0.000 83 0.021 81 0.000 35 475.0 26.0 419.0 7.0 409.0 5.0 436.0 7.0 HRZV-1-04 0.054 85 0.001 64 0.485 13 0.014 5 0.064 15 0.000 88 0.020 55 0.000 42 406.0 42.0 402.0 10.0 401.0 5.0 411.0 8.0 HRZV-1-05 0.055 86 0.001 21 0.509 52 0.011 27 0.066 15 0.000 85 0.021 8 0.000 34 447.0 27.0 418.0 8.0 413.0 5.0 436.0 7.0 HRZV-1-06 0.057 84 0.001 29 0.536 81 0.012 19 0.067 31 0.000 87 0.022 88 0.000 35 524.0 28.0 436.0 8.0 420.0 5.0 457.0 7.0 HRZV-1-07 0.057 06 0.000 92 0.518 35 0.008 91 0.065 88 0.000 81 0.020 82 0.000 26 494.0 18.0 424.0 6.0 411.0 5.0 416.0 5.0 HRZV-1-08 0.056 54 0.001 81 0.517 8 0.016 51 0.066 42 0.000 93 0.020 27 0.000 43 474.0 46.0 424.0 11.0 415.0 6.0 406.0 9.0 HRZV-1-09 0.057 51 0.001 44 0.509 9 0.012 94 0.064 3 0.000 85 0.021 9 0.000 4 511.0 33.0 418.0 9.0 402.0 5.0 438.0 8.0 HRZV-1-11 0.056 85 0.001 99 0.497 31 0.017 29 0.063 44 0.000 92 0.020 74 0.000 49 486.0 51.0 410.0 12.0 397.0 6.0 415.0 10.0 HRZV-1-12 0.054 94 0.001 14 0.494 19 0.010 58 0.065 23 0.000 83 0.020 01 0.000 27 410.0 26.0 408.0 7.0 407.0 5.0 400.0 5.0 HRZV-1-13 0.055 8 0.001 09 0.522 47 0.010 54 0.067 91 0.000 85 0.016 99 0.000 25 444.0 24.0 427.0 7.0 424.0 5.0 341.0 5.0 HRZV-1-14 0.058 25 0.001 46 0.535 3 0.013 54 0.066 64 0.000 88 0.022 16 0.000 37 539.0 33.0 435.0 9.0 416.0 5.0 443.0 7.0 HRZV-1-15 0.054 76 0.001 17 0.504 01 0.011 07 0.066 75 0.000 85 0.021 91 0.000 31 402.0 27.0 414.0 7.0 417.0 5.0 438.0 6.0 HRZV-1-16 0.055 95 0.001 62 0.530 39 0.015 41 0.068 75 0.000 94 0.021 64 0.000 44 450.0 40.0 432.0 10.0 429.0 6.0 433.0 9.0 HRZV-1-17 0.054 87 0.001 41 0.506 57 0.013 13 0.066 96 0.000 88 0.019 86 0.000 35 407.0 35.0 416.0 9.0 418.0 5.0 397.0 7.0 HRZV-1-18 0.056 31 0.001 47 0.506 36 0.013 33 0.065 22 0.000 86 0.018 06 0.000 34 465.0 35.0 416.0 9.0 407.0 5.0 362.0 7.0 HRZV-1-19 0.053 84 0.001 51 0.494 25 0.013 91 0.066 58 0.000 89 0.020 86 0.000 34 364.0 40.0 408.0 9.0 416.0 5.0 417.0 7.0 HRZV-1-20 0.054 36 0.001 39 0.501 14 0.012 98 0.066 85 0.000 88 0.020 05 0.000 35 386.0 35.0 412.0 9.0 417.0 5.0 401.0 7.0 HRZV-1-22 0.059 65 0.001 83 0.545 0.016 75 0.066 26 0.000 92 0.019 87 0.000 4 591.0 43.0 442.0 11.0 414.0 6.0 398.0 8.0 HRZV-1-23 0.061 22 0.002 38 0.541 74 0.020 87 0.064 17 0.000 98 0.009 02 0.000 2 647.0 56.0 440.0 14.0 401.0 6.0 181.0 4.0 HRZV-1-24 0.056 1 0.001 23 0.513 25 0.011 52 0.066 35 0.000 85 0.019 58 0.000 28 456.0 28.0 421.0 8.0 414.0 5.0 392.0 6.0 HRZV-1-25 0.052 99 0.003 08 0.490 66 0.028 04 0.067 15 0.001 21 0.020 55 0.000 57 328.0 97.0 405.0 19.0 419.0 7.0 411.0 11.0 表 4 东昆仑都兰地区哈日扎花岗闪长岩(HRZ-3)锆石 LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 定年数据表
Table 4. Zircon LA–ICP–MS U–Pb dating data of granodiorite (HRZ-3) in Harizha, Dulan, East Kunlun
测点号 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ HRZV-3-01 0.053 56 0.001 54 0.494 79 0.014 27 0.067 01 0.000 91 0.020 58 0.000 36 353.0 41.0 408.0 10.0 418.0 5.0 412.0 7.0 HRZV-3-02 0.053 23 0.003 18 0.500 27 0.029 34 0.068 18 0.001 26 0.021 21 0.000 81 339.0 99.0 412.0 20.0 425.0 8.0 424.0 16.0 HRZV-3-03 0.056 41 0.001 97 0.521 01 0.018 04 0.067 0.000 97 0.018 99 0.000 35 469.0 51.0 426.0 12.0 418.0 6.0 380.0 7.0 HRZV-3-04 0.056 14 0.001 37 0.523 22 0.012 9 0.067 62 0.000 88 0.021 78 0.000 31 458.0 32.0 427.0 9.0 422.0 5.0 435.0 6.0 HRZV-3-06 0.056 29 0.001 13 0.522 0.010 79 0.067 26 0.000 85 0.020 18 0.000 31 464.0 25.0 426.0 7.0 420.0 5.0 404.0 6.0 HRZV-3-07 0.058 65 0.002 23 0.541 27 0.020 36 0.066 95 0.001 01 0.021 36 0.000 54 554.0 56.0 439.0 13.0 418.0 6.0 427.0 11.0 HRZV-3-08 0.053 26 0.002 45 0.482 31 0.021 92 0.065 69 0.001 05 0.020 96 0.000 56 340.0 74.0 400.0 15.0 410.0 6.0 419.0 11.0 HRZV-3-09 0.055 9 0.001 56 0.512 41 0.014 35 0.066 49 0.000 9 0.019 15 0.000 37 448.0 38.0 420.0 10.0 415.0 5.0 383.0 7.0 HRZV-3-10 0.057 35 0.001 42 0.531 92 0.013 33 0.067 29 0.000 88 0.020 72 0.000 33 505.0 33.0 433.0 9.0 420.0 5.0 415.0 7.0 HRZV-3-11 0.052 32 0.001 7 0.477 74 0.015 52 0.066 24 0.000 93 0.020 87 0.000 48 299.0 48.0 397.0 11.0 413.0 6.0 417.0 10.0 HRZV-3-13 0.054 93 0.001 68 0.504 21 0.015 41 0.066 58 0.000 92 0.021 04 0.000 41 409.0 44.0 415.0 10.0 416.0 6.0 421.0 8.0 HRZV-3-15 0.058 02 0.001 67 0.530 33 0.015 34 0.066 3 0.000 91 0.021 9 0.000 4 531.0 39.0 432.0 10.0 414.0 6.0 438.0 8.0 HRZV-3-16 0.056 8 0.002 03 0.512 54 0.018 19 0.065 44 0.000 95 0.019 28 0.000 35 484.0 53.0 420.0 12.0 409.0 6.0 386.0 7.0 HRZV-3-17 0.053 71 0.001 29 0.488 4 0.011 9 0.065 95 0.000 86 0.020 98 0.000 36 359.0 32.0 404.0 8.0 412.0 5.0 420.0 7.0 HRZV-3-18 0.054 14 0.001 54 0.498 83 0.014 22 0.066 83 0.000 9 0.020 72 0.000 32 377.0 40.0 411.0 10.0 417.0 5.0 415.0 6.0 HRZV-3-19 0.053 95 0.001 89 0.495 93 0.017 26 0.066 66 0.000 96 0.021 5 0.000 43 369.0 52.0 409.0 12.0 416.0 6.0 430.0 9.0 HRZV-3-20 0.054 31 0.001 17 0.502 2 0.011 11 0.067 05 0.000 86 0.018 98 0.000 25 384.0 28.0 413.0 8.0 418.0 5.0 380.0 5.0 HRZV-3-21 0.055 99 0.002 27 0.513 65 0.020 61 0.066 52 0.001 02 0.020 83 0.000 47 452.0 62.0 421.0 14.0 415.0 6.0 417.0 9.0 HRZV-3-22 0.055 82 0.001 49 0.514 25 0.013 87 0.066 8 0.000 89 0.021 56 0.000 41 445.0 37.0 421.0 9.0 417.0 5.0 431.0 8.0 HRZV-3-23 0.054 97 0.001 13 0.504 89 0.010 68 0.066 61 0.000 85 0.020 14 0.000 31 411.0 26.0 415.0 7.0 416.0 5.0 403.0 6.0 HRZV-3-24 0.055 4 0.001 46 0.515 74 0.013 73 0.067 5 0.000 9 0.021 75 0.000 36 428.0 36.0 422.0 9.0 421.0 5.0 435.0 7.0 表 5 东昆仑都兰地区希望沟花岗闪长岩(XW-12)锆石 LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 定年数据表
Table 5. LA–ICP–MS U–Pb dating data of the granodiorite (XW-12) zircon in Xiwanggou, Dulan area, East Kunlun
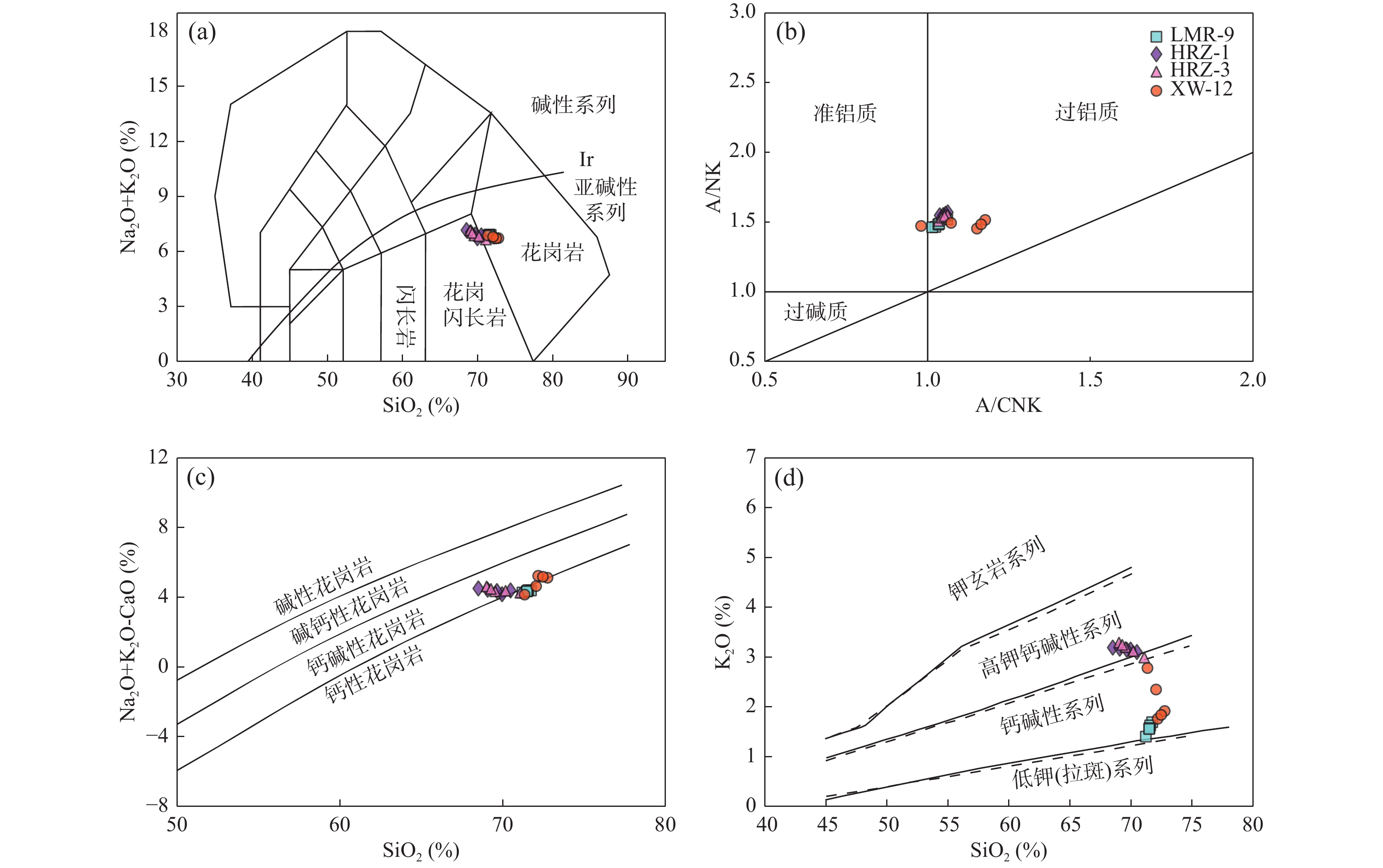
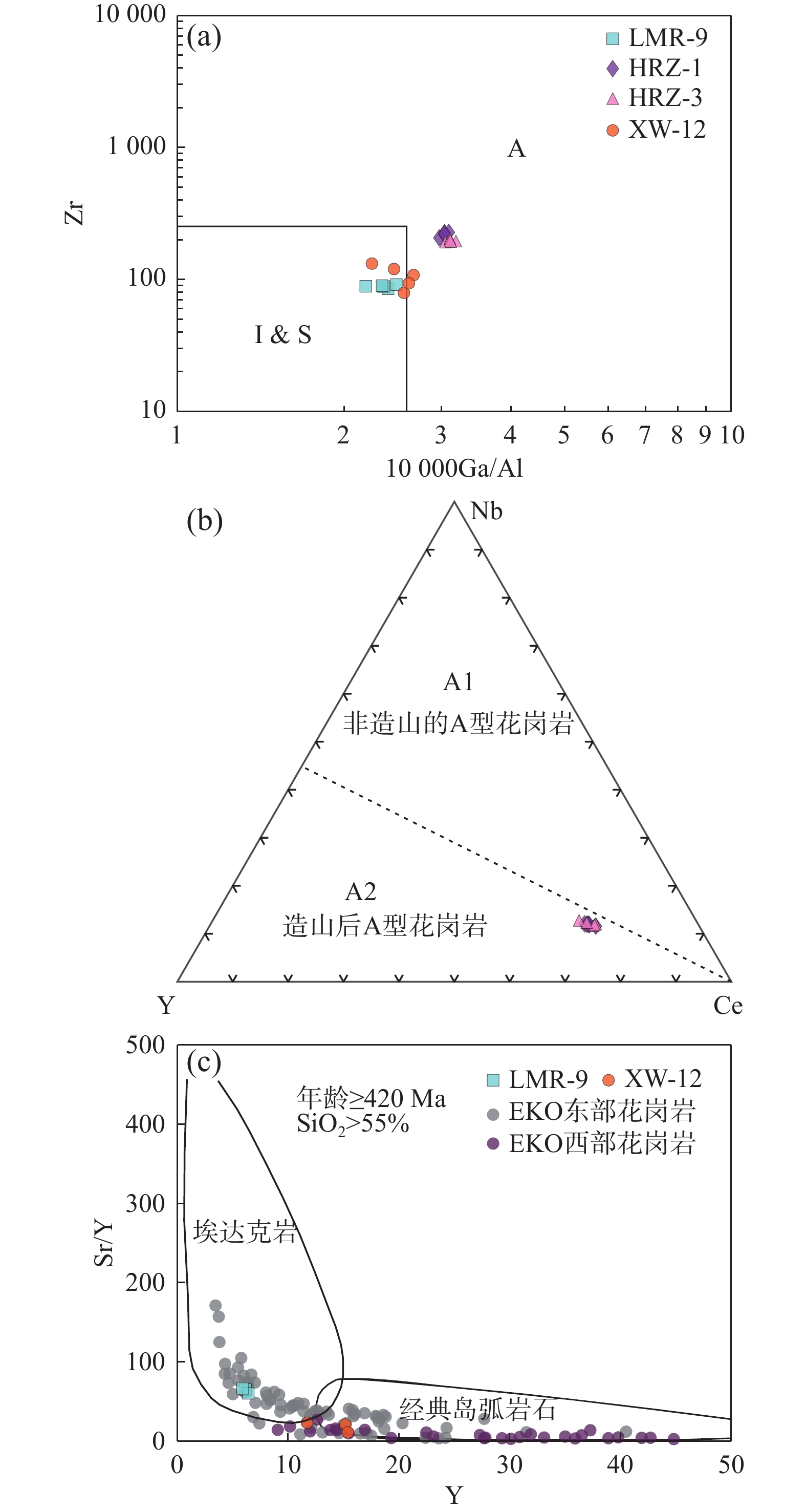
测点号 238U 232Th Th/U 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 10–6 10–6 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ 比值 1σ XW-12-03 222.038 77.943 0.351 037 0.053 771 0.002 176 0.476 970 0.019 547 0.064 376 0.001 493 0.020 698 0.000 928 XW-12-05 390.010 224.742 0.576 248 0.055 657 0.001 278 0.492 616 0.011 468 0.064 342 0.000 907 0.019 634 0.000 446 XW-12-06 308.777 3.886 0.012 587 0.054 606 0.001 612 0.486 234 0.013 135 0.064 725 0.000 695 0.024 073 0.003 252 XW-12-07 2705.775 36.420 0.013 460 0.057 055 0.002 729 0.512 476 0.025 946 0.064 37 0.001 040 0.066 743 0.003 946 XW-12-08 243.035 66.346 0.272 987 0.056 431 0.001 616 0.501 419 0.013 779 0.064 593 0.000 844 0.021 364 0.001 055 XW-12-09 200.146 87.528 0.437 321 0.054 623 0.002 524 0.488 593 0.022 397 0.064 57 0.001 177 0.021 824 0.000 926 XW-12-17 282.261 106.744 0.378 176 0.056 385 0.001 208 0.500 838 0.010 560 0.064 691 0.000 847 0.020 414 0.000 683 XW-12-19 245.495 104.976 0.427 609 0.053 623 0.002 023 0.484 635 0.016 876 0.065 515 0.001134 0.020 101 0.001 307 XW-12-20 435.646 51.163 0.117 441 0.057 011 0.001 658 0.503 790 0.015 055 0.064 099 0.000 953 0.036 289 0.002 546 XW-12-21 3968.980 47.722 0.012 024 0.055 292 0.000 751 0.493 886 0.007 562 0.064 609 0.000 736 0.020 955 0.000 869 XW-12-22 257.169 118.039 0.458 993 0.055 688 0.001 387 0.492 718 0.011 250 0.064 258 0.000 783 0.020 524 0.000 624 XW-12-23 202.007 91.347 0.452 196 0.054 323 0.001 255 0.488 256 0.012 107 0.065 118 0.000 866 0.020 815 0.000 599 测点号 238U/232Th 207Pb/206Pb 207Pb/235U 206Pb/238U 208Pb/232Th 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ 年龄(Ma) 1σ XW-12-03 2.835 826 0.081 675 361.5 91.3 396.0 13.4 402.2 9.0 414.1 18.4 XW-12-05 1.812 681 0.043 438 438.7 51.1 406.7 7.8 402.0 5.5 393.0 8.8 XW-12-06 106.235 400 9.505 966 396.1 66.2 402.3 9.0 404.3 4.2 480.8 64.2 XW-12-07 75.778 780 2.710 546 493.7 105.4 420.1 17.4 402.1 6.3 1 305.9 74.8 XW-12-08 3.770 071 0.073 742 469.4 63.4 412.7 9.3 403.5 5.1 427.3 20.9 XW-12-09 2.325 497 0.074 162 396.8 103.6 404.0 15.3 403.4 7.1 436.4 18.3 XW-12-17 2.512 113 0.106 452 467.6 47.4 412.3 7.1 404.1 5.1 408.5 13.5 XW-12-19 2.258 608 0.074 207 355.3 85.2 401.2 11.5 409.1 6.9 402.2 25.9 XW-12-20 8.548 346 0.440 448 492.0 64.1 414.3 10.2 400.5 5.8 720.5 49.7 XW-12-21 81.329 490 2.320 900 424.1 30.3 407.6 5.1 403.6 4.5 419.2 17.2 XW-12-22 2.146 288 0.071 575 439.9 55.4 406.8 7.7 401.5 4.7 410.6 12.4 XW-12-23 2.296 398 0.080 975 384.4 51.9 403.7 8.3 406.7 5.2 416.4 11.9 表 6 东昆仑都兰地区LMR-9、HRZ-1、HRZ-3和XW-12花岗岩主微量元素统计表
Table 6. Major and trace elements of LMR-9, HRZ-1, HRZ-3 and XW-12 granites in the Dulan area of East Kunlun
样品号 LMP-9-1 LMR-9-2 LMR-9-3 LMR-9-4 LMR-9-5 HRZ-1-1 HRZ-1-2 HRZ-1-3 HRZ-1-4 HRZ-1-5 HRZ-3-1 HRZ-3-2 HRZ-3-3 HRZ-3-4 HRZ-3-5 XW-12-1 XW-12-2 XW-12-3 XW-12-4 XW-12-5 SiO2 71.73 71.57 71.21 71.50 71.48 68.50 70.48 69.96 69.64 69.07 69.01 69.54 71.08 69.27 70.17 72.18 72.75 71.34 72.47 72.05 Al2O3 15.87 15.41 15.39 15.56 15.61 15.76 14.72 14.44 14.97 15.36 15.02 14.88 14.44 14.95 14.69 14.65 15.20 14.42 14.93 14.81 TFe2O3 1.94 1.94 1.90 1.93 1.92 3.19 3.16 3.14 3.16 3.18 3.14 3.30 3.06 3.22 3.14 1.76 1.83 2.51 1.80 2.17 MgO 0.85 0.85 0.89 0.86 0.86 1.07 1.07 1.06 1.07 1.07 1.08 1.11 1.01 1.10 1.05 0.94 0.81 0.89 0.88 0.85 CaO 2.51 2.52 2.58 2.53 2.54 2.66 2.49 2.54 2.56 2.61 2.53 2.53 2.39 2.53 2.46 1.47 1.60 2.72 1.54 2.16 Na2O 5.21 5.29 5.45 5.32 5.33 3.98 3.77 3.57 3.77 3.88 3.86 3.67 3.65 3.77 3.71 4.95 4.81 4.10 4.88 4.45 K2O 1.69 1.63 1.40 1.57 1.56 3.19 3.10 3.15 3.15 3.17 3.29 3.20 2.99 3.25 3.12 1.76 1.92 2.78 1.84 2.35 TiO2 0.21 0.21 0.21 0.21 0.21 0.42 0.40 0.40 0.41 0.41 0.39 0.43 0.42 0.41 0.41 0.16 0.16 0.15 0.16 0.16 P2O5 0.08 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.14 0.13 0.14 0.14 0.14 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.13 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 MnO 0.03 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.04 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.04 0.04 0.07 0.04 0.05 LOI 0.44 0.37 0.56 0.45 0.48 0.73 0.61 1.13 0.83 0.78 0.90 1.29 0.78 1.09 0.94 1.44 1.26 1.35 1.35 1.31 A/CNK 1.06 1.02 1.01 1.03 1.04 1.06 1.04 1.04 1.05 1.05 1.03 1.05 1.06 1.04 1.05 1.15 1.18 0.98 1.16 1.08 Na2O+K2O 6.90 6.92 6.85 6.89 6.88 7.16 6.88 6.72 6.92 7.04 7.15 6.87 6.65 7.01 6.83 6.71 6.73 6.88 6.72 6.80 Li 9.26 8.06 9.41 8.91 9.19 29.92 29.56 27.25 28.91 29.41 14.87 23.59 24.37 19.23 21.80 11.56 11.57 6.88 11.57 9.22 Be 1.94 1.69 1.62 1.75 1.77 3.61 3.44 3.02 3.36 3.48 3.56 3.26 3.38 3.41 3.40 2.35 2.28 2.36 2.32 2.32 Sc 3.81 3.54 3.69 3.68 3.72 8.09 7.64 6.92 7.55 7.82 8.68 7.79 6.90 8.24 7.57 3.86 4.24 3.07 4.05 3.66 Ti 1 108.422 1 229.558 1 273.744 1 203.908 1 195.358 3 066.467 2 986.563 2 943.558 2 998.863 3 032.665 3 018.183 3 148.628 3 096.428 3 083.405 3 089.916 936.65 1 147.271 979.35 1041.96 1063.31 V 14.95 15.73 17.13 15.94 16.01 49.32 48.53 46.95 48.27 48.80 49.85 48.88 47.29 49.36 48.32 11.34 12.90 15.70 12.12 14.30 Mn 299.72 279.84 275.23 284.93 286.63 587.28 600.79 564.37 584.15 585.71 561.75 584.52 561.32 573.13 567.23 304.24 384.02 635.96 344.13 509.99 Co 3.97 3.01 3.10 3.36 3.48 7.97 7.44 7.36 7.59 7.78 8.00 7.55 6.88 7.78 7.33 3.15 2.91 2.40 3.03 2.65 Ni 3.58 4.57 5.51 4.55 4.55 13.03 9.91 8.52 10.49 11.76 9.20 9.56 8.51 9.38 8.95 1.83 4.65 3.02 3.24 3.83 Cu 4.12 3.00 2.81 3.31 3.41 7.13 6.52 5.28 6.31 6.72 6.52 5.99 4.85 6.26 5.55 4.26 4.32 4.27 4.29 4.30 Zn 36.40 30.31 30.40 32.37 33.05 63.87 62.73 61.64 62.75 63.31 61.48 63.44 56.32 62.46 59.39 32.14 19.26 15.93 25.70 17.59 Ga 18.39 19.59 20.25 19.41 19.35 25.32 24.08 22.70 24.03 24.68 25.30 23.99 23.73 24.65 24.19 17.42 21.47 19.58 19.45 20.53 As 0.51 0.36 0.45 0.44 0.47 1.92 1.65 1.66 1.74 1.83 2.21 1.64 2.08 1.92 2.00 0.91 0.92 1.04 0.91 0.98 Rb 49.89 51.81 48.12 49.94 49.31 109.38 112.15 98.21 106.58 107.98 94.81 96.53 108.32 95.67 101.99 55.74 61.19 109.01 58.46 85.10 Sr 400.01 384.93 395.64 393.53 396.39 308.50 290.25 280.95 293.23 300.87 325.46 306.96 278.41 316.21 297.31 270.62 316.08 171.27 293.35 243.68 Y 6.16 6.37 5.94 6.16 6.09 24.23 22.36 20.63 22.41 23.32 22.31 23.26 26.13 22.78 24.46 11.71 15.16 15.39 13.44 15.28 Zr 88.92 85.44 91.68 88.68 89.76 225.93 227.59 206.98 220.17 223.05 195.79 192.46 204.06 194.13 199.09 132.14 108.16 79.44 120.15 93.80 Nb 3.05 2.69 2.75 2.83 2.88 14.29 13.55 12.80 13.55 13.92 13.61 15.18 15.84 14.40 15.12 4.65 4.47 3.48 4.56 3.97 Mo 1.36 0.09 0.32 0.59 0.76 0.49 0.54 0.47 0.50 0.49 0.61 1.22 0.58 0.91 0.75 0.55 0.23 0.11 0.39 0.17 Cd 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.27 0.24 0.23 0.25 0.26 0.18 0.27 0.21 0.22 0.22 0.03 0.04 0.08 0.04 0.06 In 0.03 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.05 0.06 0.06 0.03 0.01 0.04 0.02 0.02 Cs 2.15 2.63 2.11 2.30 2.19 5.88 5.94 3.32 5.05 5.46 4.62 5.88 8.12 5.25 6.68 2.76 3.42 3.54 3.09 3.48 Ba 172.80 208.31 160.70 180.60 171.36 446.67 394.25 439.75 426.89 436.78 540.73 548.37 387.79 544.55 466.17 260.98 310.79 246.74 285.89 278.77 La 7.89 9.02 8.18 8.36 8.14 40.74 39.40 38.12 39.42 40.08 41.33 43.18 40.95 42.25 41.60 10.97 13.61 8.97 12.29 11.29 Ce 18.06 19.93 17.55 18.51 18.04 79.90 76.81 76.98 77.89 78.89 80.79 87.51 81.96 84.15 83.06 25.87 32.43 19.17 29.15 25.80 Pr 2.56 2.91 2.72 2.73 2.67 9.14 8.72 8.66 8.84 8.99 9.27 9.85 9.51 9.56 9.53 3.60 4.72 2.78 4.16 3.75 Nd 10.72 11.44 10.64 10.93 10.76 30.90 29.48 29.45 29.94 30.42 30.57 32.91 32.10 31.74 31.92 13.84 18.35 10.31 16.10 14.33 Sm 2.45 2.26 2.07 2.26 2.26 6.26 5.71 5.61 5.86 6.06 6.06 6.49 7.07 6.27 6.67 3.03 3.67 1.91 3.35 2.79 Eu 0.53 0.51 0.54 0.53 0.53 0.71 0.66 0.66 0.68 0.69 0.72 0.73 0.70 0.72 0.71 0.63 0.75 0.70 0.69 0.72 Gd 1.86 1.74 1.64 1.75 1.75 6.23 5.88 5.72 5.94 6.08 6.06 6.45 6.92 6.26 6.59 2.79 2.97 1.53 2.88 2.25 Tb 0.27 0.27 0.27 0.27 0.27 0.80 0.75 0.71 0.75 0.78 0.77 0.83 1.01 0.80 0.91 0.42 0.53 0.25 0.47 0.39 Dy 1.37 1.30 1.21 1.29 1.29 3.84 3.47 3.14 3.48 3.66 3.45 3.96 4.75 3.70 4.23 2.39 2.86 1.16 2.62 2.01 Ho 0.22 0.26 0.24 0.24 0.23 0.75 0.71 0.65 0.71 0.73 0.71 0.75 0.88 0.73 0.81 0.43 0.60 0.21 0.52 0.41 Er 0.56 0.59 0.58 0.58 0.57 2.20 2.00 1.81 2.00 2.10 2.04 2.10 2.35 2.07 2.21 1.20 1.49 0.51 1.34 1.00 Tm 0.08 0.09 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.31 0.27 0.25 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.28 0.32 0.28 0.30 0.17 0.25 0.07 0.21 0.16 Yb 0.45 0.51 0.50 0.49 0.48 2.04 1.78 1.56 1.80 1.92 1.80 1.85 1.98 1.82 1.90 1.03 1.39 0.45 1.21 0.92 Lu 0.08 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.07 0.32 0.28 0.26 0.29 0.31 0.29 0.28 0.29 0.28 0.29 0.16 0.22 0.06 0.19 0.14 Hf 2.59 2.50 2.66 2.58 2.61 5.67 5.62 5.18 5.49 5.58 5.00 4.86 5.05 4.93 4.99 3.95 3.24 2.30 3.59 2.77 Ta 0.24 0.25 0.26 0.25 0.25 1.38 0.98 0.84 1.06 1.22 0.93 1.11 1.50 1.02 1.26 0.51 0.42 0.22 0.47 0.32 W 0.11 0.15 0.17 0.14 0.14 0.22 0.20 0.23 0.21 0.22 0.25 0.26 0.23 0.26 0.24 0.54 0.84 0.64 0.69 0.74 Tl 0.32 0.31 0.28 0.30 0.30 0.96 0.94 0.81 0.91 0.94 0.82 0.88 0.93 0.85 0.89 0.35 0.39 0.58 0.37 0.49 Pb 11.59 12.02 11.66 11.76 11.67 22.84 21.37 19.21 21.14 21.99 20.90 17.62 17.93 19.26 18.60 12.87 14.23 2.95 13.55 8.59 Bi 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.06 0.06 0.07 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.09 0.11 0.13 0.10 0.12 Th 2.16 2.38 2.24 2.26 2.22 16.58 16.93 19.22 17.57 17.08 30.65 19.31 28.75 24.98 26.86 4.83 5.33 1.49 5.08 3.41 U 0.84 0.85 0.85 0.85 0.85 3.66 3.37 6.74 4.59 4.13 2.83 4.33 3.56 3.58 3.57 1.67 1.64 0.91 1.66 1.27 Sr/Y 64.92 60.46 66.57 63.98 65.16 12.73 12.98 13.62 13.11 12.92 14.59 13.20 10.66 13.89 12.28 23.11 20.84 11.13 21.98 15.99 La/Yb 17.55 17.60 16.43 17.19 17.06 19.96 22.10 24.39 22.15 21.05 22.94 23.37 20.63 23.15 21.89 10.63 9.82 19.83 10.22 14.82 ΣREE 53.26 57.28 52.22 54.25 53.25 208.36 198.28 194.21 200.28 204.32 206.46 220.42 216.92 213.44 215.18 78.24 98.99 63.48 88.61 81.23 注:主量元素含量为%,微量元素含量为10−6。 表 7 都兰地区希望沟(XW-12)和浪木日(LMR-9)花岗岩Sr–Nd同位素分析结果统计表
Table 7. Sr–Nd isotope analysis results of Xiwanggou (XW-12) and Langmuri (LMR-9) granites in Dulan area
样品 t 87Rb/86Sr 87Sr/86Sr 2σ (87Sr/86Sr)i 147Sm/144Nd 143Nd/144Nd 2σ εNd(t) TDM TDMC XW-12-1 404.2 0.703 068 0.712 507 0.000 006 0.708 460 0.149 059 0.512 511 0.000 007 −0.02 1 509 1 151 XW-12-2 404.2 0.679 441 0.712 399 0.000 007 0.708 488 0.150 046 0.512 537 0.000 007 0.44 1 470 1 114 XW-12-3 404.2 2.241 488 0.719 008 0.000 006 0.706 106 0.138 614 0.512 619 0.000 009 2.63 1 081 935 LMR-9-1 431.2 0.411 167 0.707 943 0.000 008 0.705 418 0.145 764 0.512 503 0.000 009 0.17 1 454 1 157 LMR-9-2 431.2 0.414 724 0.707 912 0.000 010 0.705 365 0.143 810 0.512 486 0.000 010 −0.05 1 450 1 176 LMR-9-3 431.2 0.400 268 0.707 862 0.000 011 0.705 404 0.142 422 0.512 495 0.000 009 0.2 1 403 1 155 表 8 都兰地区浪木日花岗岩(LMR-9)锆石Hf同位素分析结果统计表
Table 8. Zircon Hf isotope analysis results of the Langmuri granite (LMR-9) in the Dulan area
测点号 176Lu/177Hf 176Yb/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 1σ 年龄(Ma) εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM TDMC fs LMR-9-02 0.001 02 0.040 28 0.281 96 0.000 02 433.500 −28.7 −19.445 1 816 2 641 −0.969 158 LMR-9-04 0.000 06 0.002 72 0.282 26 0.000 02 430.856 −18.2 −8.776 1 370 1 970 −0.998 141 LMR-9-07 0.000 40 0.015 83 0.282 61 0.000 02 413.270 −5.8 3.176 898 1 200 −0.988 073 LMR-9-08 0.000 07 0.002 90 0.282 28 0.000 02 429.622 −17.3 −7.856 1 334 1 911 −0.997 936 LMR-9-09 0.001 00 0.040 40 0.282 10 0.000 02 428.381 −23.7 −14.589 1 620 2 334 −0.969 885 LMR-9-10 0.000 54 0.023 66 0.282 24 0.000 02 431.785 −18.9 −9.598 1 415 2 023 −0.983 855 LMR-9-11 0.000 39 0.018 30 0.282 24 0.000 02 431.293 −18.9 −9.548 1 409 2 019 −0.988 149 LMR-9-17 0.000 03 0.001 52 0.282 22 0.000 02 432.107 −19.6 −10.153 1 424 2 058 −0.999 027 LMR-9-19 0.000 17 0.007 71 0.282 34 0.000 02 422.247 −15.4 −6.147 1 264 1 798 −0.994 911 LMR-9-23 0.000 04 0.001 70 0.282 16 0.000 01 424.241 −21.6 −12.253 1 498 2 184 −0.998 878 表 9 都兰地区希望沟花岗岩(XW-12)锆石Hf同位素分析结果统计表
Table 9. Zircon Hf isotope analysis results of Xixigou granite (XW-12) in Dulan area
测点号 176Lu/177Hf 176Yb/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf 1σ 年龄(Ma) εHf(0) εHf(t) TDM TDMC fs XW-12-03 0.000 70 0.029 57 0.282 88 0.000 02 402.183 3.8 12.490 523 597 −0.978 974 XW-12-05 0.001 00 0.043 04 0.282 86 0.000 02 401.979 3 11.628 559 652 −0.969 740 XW-12-06 0.000 13 0.005 96 0.282 22 0.000 02 404.299 −19.4 −10.597 1 420 2 065 −0.996 001 XW-12-07 0.002 47 0.095 41 0.282 44 0.000 02 402.146 −11.6 −3.438 1 189 1 611 −0.925 707 XW-12-08 0.000 98 0.039 53 0.282 82 0.000 02 403.495 1.7 10.338 611 736 −0.970 458 XW-12-09 0.001 77 0.079 19 0.282 84 0.000 02 403.356 2.3 10.751 599 709 −0.946 745 XW-12-17 0.000 79 0.033 14 0.282 86 0.000 02 404.089 3.2 11.863 550 639 −0.976 080 XW-12-19 0.000 49 0.020 10 0.282 42 0.000 02 409.077 −12.5 −3.655 1 163 1 630 −0.985 350 XW-12-21 0.002 24 0.086 49 0.282 42 0.000 02 403.594 −12.4 −4.140 1 214 1 656 −0.932 477 XW-12-22 0.000 93 0.037 91 0.282 82 0.000 02 401.470 1.7 10.265 612 739 −0.971 948 XW-12-23 0.000 65 0.026 48 0.282 87 0.000 02 406.677 3.5 12.284 535 614 −0.980 550 -
[1] 陈加杰, 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑沟里地区晚奥陶世花岗闪长岩地球化学特征及其对原特提斯洋演化的制约[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882
CHEN Jiajie, FU Lebing, WEI Junhao, et al. Geochemical characteristics of late ordovician granodiorite in Gouli Area, eastern Kunlun orogenic belt, Qinghai Province: Implications on the evolution of Proto-Tethys ocean[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882.
[2] 陈加杰, 冷成彪, 付乐兵, 等. 东昆仑德龙花岗岩成因及对古特提斯洋演化的制约[J/OL]. 地球科学, 2022: 1−17.
CHEN Jiajie, LENG Chengbiao, FU Lebing, et al. Genesis of Delong Granite in East Kunlun Orogen and Its Implication on the Evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J/OL]. Earth Science, 2022: 1−17.
[3] 陈能松, 孙敏, 张克信, 等. 东昆仑变闪长岩体的40Ar-39Ar和U-Pb年龄: 角闪石过剩Ar和东昆仑早古生代岩浆岩带证据[J]. 科学通报, 2000(21): 2337-2342
CHEN Nengsong, SUN Min, ZHANG Kexin, et al. 40Ar-39Ar and U-Pb ages of metadiorite from the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Evidence for Early-Paleozoic magmatic zone and excess argon in amphibole minerals[J]. Cinese Science Bulletin, 45(21): 2337-2342.
[4] 陈能松, 李晓彦, 张克信, 等. 东昆仑山香日德南部白沙河岩组的岩石组合特征和形成年代的锆石Pb-Pb定年启示[J]. 地质科技情报, 2006(06): 1-7
CHEN Nengsong, LI Xiaoyan, ZHANG Kexin, et al. Lithological characteristics of the Baishahe Formation to the south of Xiangride town, eastern Kunlun Mountains and its age constrained from zircon Pb-Pb dating[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(6): 1-7.
[5] 陈有炘, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等. 东昆仑东段纳赤台岩群变火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(06): 240-254
CHEN Youxin, PEI Xianzhi, LI Ruibao, et al. Zircon U-Pb age, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of metavolcanic rocks from Naij Tal Group, east section of East Kunlun[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(6): 240-254.
[6] 崔圆圆, 赵志丹, 蒋婷, 等. 赣南早古生代晚期花岗岩类年代学、地球化学及岩石成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(11): 4011-4024
CUI Yuanyuan, ZHAO Zhidan, JIANG Ting, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Early Paleozoic granitoids in southern Jiangxi Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(11): 4011-4024.
[7] 邓晋福, 刘翠, 冯艳芳, 等. 关于火成岩常用图解的正确使用: 讨论与建议[J]. 地质论评, 2015, 61(04): 717-734
DENG Jinfu, LIU Cui, FENG Yanfang, et al. On the correct application in the common igneous petrological diagrams: discussion and suggestion[J]. Geological Review, 2015, 61(4): 717-734.
[8] 丰成友, 王松, 李国臣, 等. 青海祁漫塔格中晚三叠世花岗岩: 年代学、地球化学及成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(02): 665-678
FENG Chengyou, WANG Song, LI Guocheng, et al. Middle to Late Triassic granitoids in the Qimantage area, Qinghai Province, China: Chronology, geochemistry and metallogenic significances[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(2): 665-678.
[9] 冯建赟, 裴先治, 于书伦, 等. 东昆仑都兰可可沙地区镁铁-超镁铁质杂岩的发现及其LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(01): 28-38
FENG Jianbin, PEI Xianzhi, YU Shulun, et al. The discovery of the mafic-ultramafic melange in Kekesha area of Dulan County, East Kunlun region, and its LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(1): 28-38.
[10] 国显正, 贾群子, 钱兵, 等. 东昆仑高压变质带榴辉岩和榴闪岩地球化学特征及形成动力学背景[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2017, 39(06): 735-750
GUO Xianzheng, JIA Qunzi, QIAN Bing, et al. Geochemical characteristics of eclogites and garnet-amphibolites in East Kunlun high pressure metamorphic belt and their geodynamic setting[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2017, 39(6): 735-750.
[11] 国显正, 贾群子, 李金超, 等. 东昆仑高压变质带榴辉岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(12): 4300-4318
GUO Xianzheng, JIA Qunzi, LI Jinchao, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry and their geological significances of eclogites from east Kunlun high-pressure metamorphic belt[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(12): 4300-4318.
[12] 孔会磊, 栗亚芝, 李金超, 等. 东昆仑希望沟橄榄辉长岩的岩石成因: 地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄与Hf同位素制约[J]. 中国地质, 2021, 48(01): 173-188.
KONG Huilei, LI Yazhi, LI Jinchao, et al. Petrogenesis of Xiwanggou olivine gabbro in East Kunlun Mountains: Constraints from geochemistry, zircon U − Pb dating and Hf isotopes[J]. Geology in China, 2021, 48(1): 173- 188.
[13] 寇林林, 张森, 钟康惠, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟金矿矿集区韧性剪切带构造变形特点研究[J]. 中国地质, 2015, 42(02): 495-503
KOU Linlin, ZHANG Sen, ZHONG Kanghui, et al. A study of the deformation characteristics of the ductile shear zone in the Wulonggou gold ore concentration area, East Kunlun, Qinghai[J]. Geology in China, 2015, 42(2): 495-503.
[14] 李怀坤, 陆松年, 相振群, 等. 东昆仑中部缝合带清水泉麻粒岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2006(06): 311-321.
LI Huaikun, LU Songnian, XIANG Zhenqun, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age of the granulite from the Qingshuiquan area, Central Eastern Kunlun Suture Zone[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(6): 311.
[15] 李文渊. 古亚洲洋与古特提斯洋关系初探[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(08): 2201-2210
LI Wenyuan. The primary discussion on the relationship between Paleo-Asian Ocean and Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(8): 2201-2210.
[16] 刘彬, 马昌前, 张金阳, 等. 东昆仑造山带东段早泥盆世侵入岩的成因及其对早古生代造山作用的指示[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(06): 1785-1807
LIU Bin, MA Changqian, ZHANG Jinyang, et al. Petrogenesis of Early Devonian intrusive rocks in the east part of Eastern Kunlun Orogen and implication for Early Palaeozoic orogenic processes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(6): 1785-1807.
[17] 刘彬, 马昌前, 郭盼, 等.东昆仑中泥盆世A型花岗岩的确定及其构造意义[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 2013, 38(5): 947−962.
LIU Bin, MA Changqian, GUO Pan, et al. Discovery of the Middle Devonian A-type granite from the Eastern Kunlun Orogen and its tectonic implications[J]. Earth Science, 2013, 38(5): 947−962.
[18] 刘成东, 莫宣学, 罗照华, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩类Pb-Sr-Nd-O同位素特征[J]. 地球学报, 2003(06): 584-588 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.06.020
LIU Chengdong, MO Xuanxue, LUO Zhaohua, et al. Pb-Sr-Nd-O isotope characteristics of granitoids in East Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2003: 584-588. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2003.06.020
[19] 陆露, 吴珍汉, 胡道功, 等. 东昆仑牦牛山组流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(04): 1150-1158
LU Lu, WU Zhenhan, HU Daogong, et al. Zircon U-Pb age for rhyolite of the Maoniushan Formation and its tectonic significance in the East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(4): 1150-1158.
[20] 陆露, 张延林, 吴珍汉, 等. 东昆仑早古生代花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2013, 34(04): 447-454
LU Lu, ZHANG Yanlin, WU Zhenhan, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating of Early Paleozoic granites from the East Kunlun Mountains and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2013, 34(4): 447-454.
[21] 罗明非. 东昆仑东段早古生代—早中生代花岗岩类时空格架及构造意义[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015
LUO Mingfei. Spatial-temporal patter and geological implications of Early Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt (eastern segment)[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015.
[22] 孟庆鹏. 青海东昆仑浪木日铜镍矿矿床地质特征及成因探讨[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019
MENG Qingpeng. Study on geological characteristics and genesis of Langmuri copper-nickel deposit in Eastern Kunlun, Qinghai [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.
[23] 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007(03): 403-414.
MO Xuanxue, LUO Zhaohua, DENG Jinfu, et al. Granitoids and crustal growth in the East-Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3), 403-414.
[24] 祁生胜, 宋述光, 史连昌, 等. 东昆仑西段夏日哈木-苏海图早古生代榴辉岩的发现及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11): 3345-3356
QI Shengsheng, SONG Shuguang, SHI Lianchang, et al. Discovery and its geological significance of Early Paleozoic eclogite in Xiarihamu-Suhaitu area, western part of the East Kunlun[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(11): 3345-3356.
[25] 任军虎, 柳益群, 周鼎武, 等. 东昆仑小庙基性岩脉地球化学及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2010, 40(04): 859-868
REN Junhu, LIU Yiqun, ZHOU Dingwu, et al. Geochemical Characteristics and LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Dating of Basic Dykes in the Xiaomiao Area, Eastern Kunlun[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 2010, 40(4): 859-868.
[26] 田龙, 康磊, 刘良, 等. 东昆仑巴什尔希晚奥陶世二长花岗岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 28-45.
TIAN Long, KANG Lei, LIU Liang, et al. Petrogenesis and Geological Implications of Bashenerxi Monzogranite from East Kunlun Orogen Belt[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 28−45.
[27] 王秉璋, 张金明, 李五福, 等. 昆仑河早古生代两期埃达克质侵入岩的发现及其对东昆仑碰撞造山过程的启示[J]. 岩石学报, 2023, 39(03): 763-784 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.03.09
WANG BingZhang, ZHANG JinMing, LI WuFu, et al. Discovery of two stages of the Early Paleozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Kunlun River area, East Kunlun: Implications for collisional orogenic processes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2023, 39(3): 763-784. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2023.03.09
[28] 王强, 赵振华, 简平, 等. 德兴花岗闪长斑岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年代学和Nd-Sr同位素地球化学[J]. 岩石学报, 2004(02): 315-324
WANG Qiang, ZHAO ZhenHua, JIAN Ping, et al. SHRIMP zircon geochronology and Nd-Sr isotopic geochemistry of the Dexing granodiorite porphyries[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(2): 315-324.
[29] 王德滋, 刘昌实, 沈渭洲, 等. 桐庐I型和相山S型两类碎斑熔岩对比[J]. 岩石学报, 1993, 9(01): 44-54
WANG Dezi, LIU Changshi, SHEN Weizhou, et al. The contrast between Tonglu I-type and Xiangshan S-type clastoporphyritic lava[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 1993, 9(1): 44-54.
[30] 王涛, 李彬, 陈静, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟地区早志留世花岗岩锆石年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2016, 36(02): 62-70
WANG Tao, LI Bin, CHEN Jing, et al. Characteristics of chronology and geochemistry of the early Silurian monzogranite in the Wulonggou area, East Kunlun and its geological significance[J]. Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 2016, 36(2): 62-70.
[31] 王艺龙, 李艳军, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟地区晚志留世A型花岗岩成因: U-Pb年代学、地球化学、Nd及Hf同位素制约[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(04): 1219-1236
WANG Yilong, LI Yanjun, WEI Junhao, et al. Origin of Late Silurian A-type granite in Wulonggou area, East Kunlun orogen: Zircon U-Pb age, geochemistry, Nd and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(4): 1219-1236.
[32] 魏小林, 张得鑫, 甘承萍, 等. 卡而却卡地区新元古代变质侵入岩体的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2016, 31(02): 236-244
WEI Xiaolin, ZHANG Dexin, GAN Chengping, et al. Discovery and body in the geological significance of Neoproterozoic intrusive Kaerqueka area of the East Kunlun Mountain[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2016, 31(2): 236-244.
[33] 吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 等. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(06): 1217-1238
WU Fuyuan, LI Xianhua, YANG Jinhui, et al. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(6): 1217-1238.
[34] 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(02): 185-220
WU Fuyuan, LI Xianhua, ZHEN Yongfei, et al. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(2): 185-220.
[35] 吴福元, 万博, 赵亮, 等. 特提斯地球动力学[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(06): 1627−1674
WU Fuyuan, WAN Bo, ZHAO Liang, et al. Tethyan geodynamics [J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(6): 1627−1674.
[36] 吴树宽, 陈国超, 李积清, 等. 东昆仑东段沟里地区战红山过铝质流纹斑岩年代学、岩石成因及构造意义[J]. 西北地质, 2023, 56(2): 92−108.
WU Shukuan, CHEN Guochao, LI Jiqing, et al. Geochronology, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of Zhanhongshan Peraluminous Rhyolite Porphyry in Gouli Area, Eastern Section of East Kunlun[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2023, 56(2): 92−108.
[37] 吴元保, 郑永飞. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约[J]. 科学通报, 2004(16): 1589-1604 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002
WU Yuanbao and ZHENG Yongfei. Zircon genetic mineralogy and its constraints on U-Pb age interpretation[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004, 49(16): 1589-1604. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002
[38] 徐恒, 豆松, 李晓峰, 等. 云南凤庆邦漂地区花岗伟晶岩地球化学及其成因[J]. 矿物岩石, 2022, 42(01): 42-53
XU Heng, DOU Feng, LI Xiaofeng, et al. Geochemistry and genesis of granitic pegmatite in Bangpiao area, Fengqing county, Yunnan provice[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2022, 42(1): 42-53.
[39] 许继峰, 邬建斌, 王强, 等. 埃达克岩与埃达克质岩在中国的研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2014, 33(01): 6-13
XU JiFeng, WU Jian Bin, WANG Qiang, et al. Research advances of adakites and adakitic rocks in China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2014, 33(1): 6-13.
[40] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 等. 青藏高原与大陆动力学——地体拼合、碰撞造山及高原隆升的深部驱动力[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(02): 221-238
XU Zhiqin, YANG Jingsui, LI Haibin, et al. Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and continental dynamics: Deep driving forces of terrane consolidation collisional orogenesis and plateau uplift[J]. Geology of China, 2006, 33(2): 221-238.
[41] 尹福光, 罗亮, 任飞. 再造西南“三江”造山带洋陆转换过程中的构造与古地理[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(11): 1899-1914 doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.11.001
YIN Fuguang, LUO Liang, REN Fei. Reconstructing the tectonics and paleogeography during the ocean-land transition of the “Sanjiang” orogenic belt in southwest China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(11): 1899-1914. doi: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2022.11.001
[42] 张斌, 孔会磊, 李智明, 等. 东昆仑哈日扎铅锌多金属矿区英云闪长岩锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(05): 9-17
ZHANG Bin, KONG Huilei, LI Zhiming, et al. Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemical and geological significance of the tonalites from the Harizha lead-zinc polymetallic mine in east Kunlun mountains[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(5): 9-17.
[43] 张亮, 李碧乐, 刘磊, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟地区早泥盆世双峰式侵入岩年代学、地球化学及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(07): 2007-2028 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.07.04
ZHANG Liang, LI Bile, LIU Lei, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological significance of the Early Devonian bimodal intrusive rocks in Wulonggou area, East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(7): 2007-2028. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.07.04
[44] 张亚峰, 裴先治, 丁仨平, 等. 东昆仑都兰县可可沙地区加里东期石英闪长岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄及其意义[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(01): 79-85
ZHANG Yafeng, PEI Xianzhi, DING SaPing, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of quartz diorite at the Kekesha area of Dulan County, eastern section of the East Kunlun orogenic belt, China and its significance[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(1): 79-85.
[45] 张耀玲, 胡道功, 石玉若, 等. 东昆仑造山带牦牛山组火山岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其构造意义[J]. 地质通报, 2010, 29(11): 1614-1618
ZHANG Yaolin, HU Daogong, SHI Yuruo, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb ages and tectonic significance of Maoniushan Formation volcanic rocks in East Kunlun orogenic belt, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2010, 29(11): 1614-1618.
[46] 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 等. 俯冲带部分熔融[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(09): 2589-2615 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.09.01
ZHANG Zeming, DING Huixia, DONG Xin, et al. Partial melting of subduction zones[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(9): 2589-2615. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.09.01
[47] 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 等. 俯冲带变质作用与构造机制[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(11): 3377-3398 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.08
ZHANG Zeming, DING Huixia, DONG Xin, et al. Metamorphism and tectonic mechanisms of subduction zones[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 3377-3398. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.08
[48] 朱云海, 林启祥, 贾春兴, 等. 东昆仑造山带早古生代火山岩锆石SHRIMP年龄及其地质意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑: 地球科学), 2005(12): 1112-1119
ZHU Yunhai, LIN Qixiang, JIA Chunxing, et al. SHRIMP zircon ages of the Early Paleozoic volcanic rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen and their geological significance[J]. Science in China: SerD, 2005, 35(12): 1112-1119.
[49] Barth M G, McDonough W F, Rudnick Roberta L. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 165: 197-213. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00173-4
[50] Bonin B. A-type granites and related rocks: evolution of a concept, problems and prospects[J]. Lithos, 2007, 97(1): 1–29.
[51] Breitsprecher K, Thorkelson D J, Groome W G, et al. Geochemical confirmation of the Kula-Farallon slab window beneath the Pacific Northwest in Eocene time[J]. Geol , 2003, 31, 351. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2003)031<0351:GCOTKF>2.0.CO;2
[52] Chen J J, Fu L B, Selby D, et al. Multiple episodes of gold mineralization in the East Kunlun Orogen, western Central Orogenic Belt, China: Constraints from Re-Os sulfide geochronology[J]. Ore Geology Reviews , 2020a, 123, 103587. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103587
[53] Chen J J, Fu L B, Wei J H, et al. Proto-Tethys magmatic evolution along northern Gondwana: Insights from Late Silurian–Middle Devonian A-type magmatism, East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Xizang Plateau, China[J]. Lithos, 2020b, 356-357(3): 105304.
[54] Defant M J and Drummond M S. Derivation of some morden arc magmas by of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0
[55] Dong G C, Luo M F, Mo X X, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of early Paleozoic granitoids in East Kunlun belt: Evidences from geochronology, geochemistry and isotopes[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2018, 9(5): 1383-1397. doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2018.03.003
[56] Dong J L, Song S G, Su L, et al. Early Devonian mafic igneous rocks in the East Kunlun Orogen, NW China: Implications for the transition from the Proto- to Paleo-Tethys oceans[J]. Lithos, 2020, 376-377(11): 105771.
[57] Dong Y P, He D F, Sun S S, et al. Subduction and accretionary tectonics of the East Kunlun orogen, western segment of the Central China Orogenic System[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2018, 186(11): 231-261.
[58] Drummond M S, Defant M J, Kepezhinskas P K. Petrogenesis of slab-derived trondhjemite- tonalite-dacite/adakite magmas[J]. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh, 1996, 87(1-2), 205-215. doi: 10.1017/S0263593300006611
[59] Eby G N. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Geology, 1992, 20 (7): 641–644. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
[60] Elburg M A, Van Bergen M, Hoogewerff J, et al. Geochemical trends across an arc-continent collision zone: magma sources and slab-wedge transfer processes below the Pantar Strait volcanoes, Indonesia[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2002, 66(15): 2771-2789. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00868-2
[61] Faure G. Principles of Isotope Geology[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 1986: 567.
[62] Frost B R, Barnes C G, Collins W J, et al. A Geochemical Classification for Granitic Rocks[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2001, 42(11): 2033-2048. doi: 10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033
[63] Gao S, Rudnick R L, Yuan H L, et al. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton[J]. Nature, 2005, 432 (7019): 892-897.
[64] Griffin W L, Pearson N J, Belousova E, et al. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2000, 64(1): 133-147. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
[65] He D F, Dong Y P, Liu X M, et al. Tectonothermal events in East Kunlun, Northern Xizang Plateau: evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronology[J]. Gondwana Res, 2016, 30: 179–190. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.08.002
[66] Hou Z Q, Gao Y F, Qu X M, et al. Origin of adakitic intrusives generated during mid-Miocene east–west extension in southern Xizang[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 220(1-2): 139-155. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00007-X
[67] Huang H, Niu Y L, Mo X X. Garnet effect on Nd-Hf isotope decoupling: evidence from the Jinfosi batholith, Northern Xizang Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2017, 274: 31-38.
[68] Kong X C, Li S Z, Suo Y H, et al. Hot and cold subduction systems in the Western Pacific Ocean: insights from heat flows: Heat flows in the Western Pacific Ocean[J]. Geol. J, 2016, 51: 593-608. doi: 10.1002/gj.2802
[69] Li R B, Pei X Z, Li Z C, et al. Geochemistry and zircon U–Pb geochronology of granitic rocks in the Buqingshan tectonic mélange belt, northern Xizang Plateau, China and its implications for Prototethyan evolution[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 105: 374–389. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.02.004
[70] Li S Z, Zhao S J, Liu X, et al. Closure of the Proto-Tethys Ocean and Early Paleozoic amalgamation of microcontinental blocks in East Asia[J]. Earth Sci. Rev, 2018, 186, 37–75. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.011
[71] Luais B, de Veslud C L C, Géraud Y, et al. Comparative behavior of Sr, Nd and Hf isotopic systems during fluid-related deformation at middle crust levels[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2009, 73(10): 2961-2977. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2008.12.026
[72] Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5): 635-643. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
[73] Martin H. Adakitic magmas: Modern analogues of Archaean granitoids[J]. Lithos, 1999, 46(3): 411-429. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00076-0
[74] McCrory P A, Willson D S, Stanley R G. Continuing evolution of the Pacific-Juan de Fuca-North America slab window system—A Trench-ridge-transform example from the Pacific rim[J]. Tectonophysics, 2009, 464(1-4): 30-42. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2008.01.018
[75] Mckenzie D P. Some remarks on the movement of small melt fractions in the mantle[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1989, 95: 53-72. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(89)90167-2
[76] Meng F C, Zhang J X, Cui M. H. Discovery of Early Paleozoic eclogite from the East Kunlun, Western China and its tectonic significance[J]. Gondwana Research, 2013 23(2): 825-836. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2012.06.007
[77] Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3–4): 215-224. doi: 10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
[78] Molnar P, England P. Temperatures in zones of steady-state underthrusting of young oceanic lithosphere. Earth and Planetary Science Letters [J], 1995, 131(1-2): 57-70.
[79] Norbu N, Liu Y G, Li J C, et al. The Silurian-Devonian granitoids in the East Kunlun orogenic belt, northern Qinghai-Xizang plateau, China: origin and tectonic implications[J]. Geosci J, 2021, 25: 763–786. doi: 10.1007/s12303-021-0017-3
[80] Pearce J A. Sources and settings of granitic rocks[J]. Episodes 19, 1996, 120–125.
[81] Peacock S M and Wang K. Seismic consequences of warm versus cool subduction metamorphism: Examples from southwest and northeast Japan[J]. Science, 1999, 286(5441): 937-939. doi: 10.1126/science.286.5441.937
[82] Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of Eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area, northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58: 63−81.
[83] Roberts M P and Clemens J D. Origin of high-potassium, talc-alkaline, I-type granitoids[J]. Geology, 1993, 21(9): 825-828. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0825:OOHPTA>2.3.CO;2
[84] Sun S S and McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 1989, 42, 313-345. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
[85] Tatsumi Y, Hanyu T. Geochemical modeling of dehydration and partial melting of subducting lithosphere: Toward a comprehensive understanding of high‐Mg andesite formation in the Setouchi volcanic belt, SW Japan[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2003, 4(9).
[86] Thompson A B. Some time-space relationships for crustal melting and granitic intrusion at various depths[J]. Geological Society, 1999, 168(1): 7-5. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.1999.168.01.02
[87] Thorkelson D J and Breitsprecher K. Partial melting of slab window margins: genesis of adakitic and non-adakitic magmas[J]. Lithos, 2005, 79, 25-41. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.049
[88] Wang Q, McDermott F, Xu J F, et al. Cenozoic K-rich adakitic volcanic rocks in the Hohxil area, northern Xizang: lower-crustal melting in an intracontinental setting[J]. Geology, 2005, 33(6): 465-468. doi: 10.1130/G21522.1
[89] Wang X X, Hu N G, Wang T, et al. Late Ordovician Wanbaogou granitoid pluton from the southern margin of the Qaidam basin: Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age, Hf isotope and geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(9): 2950-2962.
[90] Whalen J B, Currie K L, Chappell B W. A⁃Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1987, 95(4): 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202
[91] Wilson M. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach[M]. Chapman and Hall, London, 1989.
[92] Windley B F and Xiao W J. Ridge subduction and slab windows in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Tectonic implications for the evolution of an accretionary orogen[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 61, 73-87. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2018.05.003
[93] Xia R, Wang C, Qing M, et al. Molybdenite Re-Os, zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analysis of the Shuangqing Fe-Pb-Zn-Cu skarn deposit, East Kunlun Mountains, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 66, 114-131. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.024
[94] Xin W, Sun F Y, Li L, et al. The Wulonggou metaluminous A2-type granites in the Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China: Rejuvenation of subduction-related felsic crust and implications for post-collision extension[J]. Lithos, 2018, 312–313, 108–127.
[95] Xu J F, Shinjo R, Defant M J, et al. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of east China: partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(12): 1111-1114. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2
[96] Yang H, Zhang H F, Xiao W J, et al. Multiple Early Paleozoic granitoids from the southeastern Qilian orogen, NW China: Magma responses to slab roll–back and break–off[J]. Lithos, 2021, 380–381: 105910.
[97] Yang J H, Wu F Y, Wilde S A, et al. Tracing magma mixing in granite genesis: In situ U–Pb dating and Hf–isotope analysis of zircons[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 153(2): 177–190.
[98] Yang J S, Robinson P T, Jiang C F, et al. Ophiolites of the Kunlun Mountains, China and their tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 1996, 258(1−4): 215−231.
[99] Yu M, Dick J M, Feng C Y, et al. The tectonic evolution of the East Kunlun Orogen, northern Xizang Plateau: A critical review with an integrated geodynamic model[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 191(4): 104168.
[100] Zhang J, Yu M, Wang H, et al. Geodynamic Setting and Cu-Ni Potential of Late Permian Xiwanggou Mafic-Ultramafic Rocks, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, NW China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 9: 666967. doi: 10.3389/feart.2021.666967
[101] Zhang J W, Liang X, Wang F Y, et al. CorelKit: An Extensible CorelDraw VBA Program for Geoscience Drawing[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2022, 1-23.
[102] Zhou B, Dong Y, Zhang F, et al. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb geochronology of granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, northern Xizang Plateau: origin and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, Special Issue on Crustal evolution in Asia: Correlations and connections, 2016, 130: 265–281.
-



 下载:
下载: