Gravity and Magnetic Anomalies and Prospecting Prediction of Iron Polymetallic Deposits in the Downstream of Nalingguole River
-
摘要:
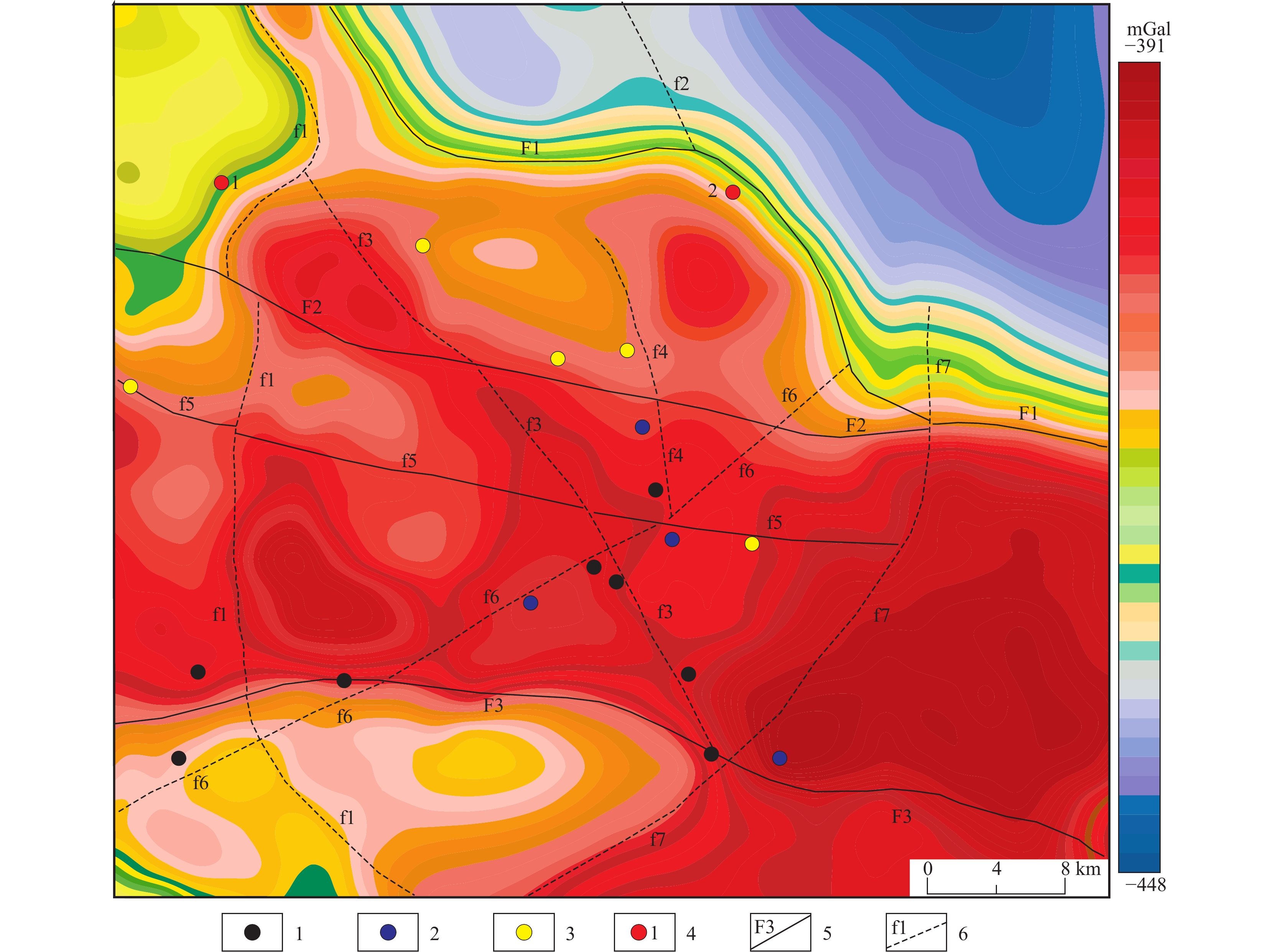
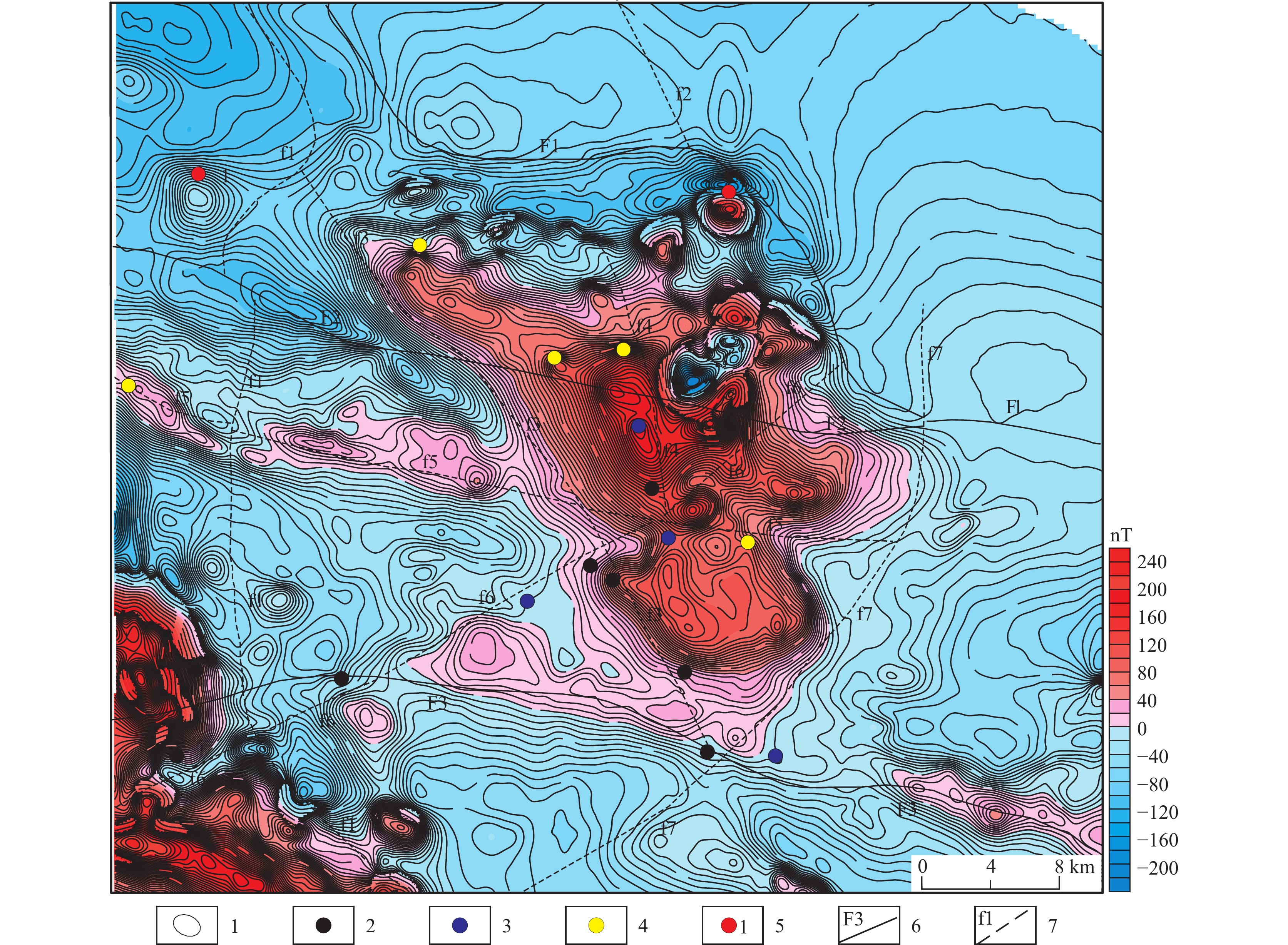
那陵郭勒河下游地区以第四系覆盖为主,已发现多个铁多金属矿床,同时受覆盖的影响,找矿工作难度增大。笔者以1∶5万航磁及1∶20万区域重力资料研究分析了那陵郭勒河下游重磁异常的展布特征,推断了研究区的断裂构造;根据南部基岩出露区地层、岩体与重磁场的关系,推断划分了覆盖区下地层及侵入岩的分布情况。结合地质特征与矿产的分布关系,认为中、小型铁多金属矿床分布主要与中部圈定的岩体密切相关,且位于推断岩体的边部,矿(化)点主要分布于推断断裂的附近,受断裂控制明显。圈定找矿靶区2处,为后期柴达木盆地周缘覆盖区(半覆盖区)的找矿及靶区优选提供有利的证据。
Abstract:The downstream area of the Nalingguole river is predominantly covered by Quaternary sediments. Several polymetallic ore deposits, primarily composed of iron, have been discovered in this region. However, the presence of sediment cover has increased the difficulty of prospecting activities. In this study, the author analysied of the distribution characteristics gravity and magnetic anomalies, and inferred the fault structure of the study area in the downstream structures of the Nalingguole river, focusing on 1∶50,000 aeromagnetic anomaly data and 1∶200,000 regional gravity data. Based on the relationship between strata, rock mass, gravity and magnetic field in the southern bedrock outcropping area, deduced and divided the distribution of strata and intrusive rocks under the overlying area. Moreover, the mineral occurrences are predominantly found near inferred fault lines, indicating a clear influence of fault control. Two prospective mining targets were identified, providing favorable evidence for future ore exploration and target selection in the (partially) covered areas surrounding the Qaidam basin.
-

-
表 1 那陵郭勒河下游岩石物性统计表
Table 1. Statistical table of rock physical properties in the downstream in Nalingguole river
大类 代号 岩石名称 数量(块) 磁化率(10−6×4π·SI) 密度(g/cm3) 变化范围 平均值 变化范围 平均值 地层 Q 黏土、砂、砾石 30 1.43~2.24 1.83 C1d 灰岩 19 1.3~5.0 1.9 2.63~2.84 2.76 C1s 复成分岩屑砂岩 5 7.5~8.8 8.8 2.59~2.66 2.61 OQ3 灰岩 94 1.3~719.5 80.1 2.57~2.82 2.73 大理岩 74 18.2~1462.2 379.9 2.56~2.83 2.73 OQ2 大理岩 60 14.2~584.3 90.1 2.43~3.12 2.89 构造角砾岩 17 29.3~255.5 92.4 2.38~2.82 2.58 蚀变安山质玄武岩 50 16.8~888.9 88.2 2.84~3.14 3.02 OQ1 长石石英砂岩 60 37.9~1507.2 151.9 2.52~2.82 2.70 粉砂质板岩 120 2.5~3353.5 28.9 1.72~2.84 2.72 石英质板岩 5 2.5~23.9 15.1 2.69~2.82 2.71 Pt1J 片麻岩 82 3.8~45.2 22.6 2.59~3.07 2.73 侵入岩 正长花岗岩 12 2.5~2800.9 12.3 2.52~2.66 2.61 二长花岗岩 238 5.0~4797.9 348.8 2.54~2.87 2.62 花岗闪长岩 36 110.0~3007.8 783.8 弱磁铁矿化花岗岩 35 526.0~4489.1 2355.7 2.64~2.67 2.65 磁铁矿化花岗岩 40 290.4~6013.8 2556.8 2.65~2.68 2.66 矿石 磁铁矿 54 10209.2~467590.4 76112.0 3.24~4.72 4.17 表 2 那陵郭勒河下游地层及侵入岩物性及重磁场特征统计表
Table 2. Statistical table of stratigraphic and intrusive petrophysical and gravity magnetic characteristics in the downstream in Nalingguole river
大类 代号 物性特征 可形成的重磁异常场 出露区重磁异常特征 地层 Q 低密度 重力低异常、负磁异常或无磁异常 东北角重力低异常、宽缓的负磁磁异常 C1d 高密度,低磁化率 重力高异常、负磁异常或无磁异常 重力高异常、正磁异常背景,局部有磁力高和磁力低伴生的磁异常 C1s 低密度,低磁化率 重力低异常、负磁异常或无磁异常 重力低、负磁异常带 OQ 高密度、中低磁化率 重力高异常、整体呈负磁异常或无磁异常,局部有弱磁异常 重力高异常、负磁异常为主,均布由正负伴生的磁异常 Pt1J 高密度、低磁化率 重力高异常、负磁异常或无磁异常 露头处形成重力高及低缓磁异常 侵入岩 低密度、中高磁化率 重力低异常、正磁异常 重力低异常、正磁异常区(西南角) 矿体 高密度、高磁化率 重力高异常、正磁异常 重力场梯级带,偏正异常,磁法正异常 -
[1] 白生龙,刘国燕,李建亮,等. 东昆仑沙丘低缓磁异常区深部铁多金属矿床找矿标志[J]. 矿产勘查,2019,10(1):118–124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.01.015
BAI Shenglong, LIU Guoyan, LI Jianliang, et al. Study on the prospecting signs of deep iron polymetallic deposits in the low-rate magnetic anomaly area of the east Kunlun Dune[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(1): 118-124. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.01.015
[2] 曹德智,袁桂林,郑振华,等. 它温查汉西铁多金属矿地球物理特征及磁法物探找矿方法优选研究[J]. 青海大学学报(自然科学版),2014,32(4):71–79. doi: 10.13901/j.cnki.qhwxxbzk.2014.04.014
CAO Dezhi, YUAN Guilin, ZHENG Zhenhua, et al. Study on optimization of magnetic--geophysical prospecting methods in thickly covered area in Tawenchahan in East Kunlun in Qinghai[J]. Journal of Qinghai University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 32(4): 71-79. doi: 10.13901/j.cnki.qhwxxbzk.2014.04.014
[3] 丰成友,李东生,吴正寿,等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格成矿带矿床类型、时空分布及多金属成矿作用[J]. 西北地质,2010,43(4):10–17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2010.04.002
FENG Chengyou, LI Dongsheng, WU Zhengshou, et al. Major types, time-Space distribution and metallogeneses of polymetallic deposits in the qimantage metallogenic belt, Eastern Kunlun Area [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(4): 10-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2010.04.002
[4] 高鹏,耿涛,冀显坤,等. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区激电测量中常见问题及解决方法[J]. 西北地质,2017,50(4):232–237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.04.025
GAO Peng, GENG Tao, JI Xiankun, et al. Common Problems and Countermeasures about the Induced Polarization Method Used in Qimantage area, East Kunlun [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2017, 50(4): 232-237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2017.04.025
[5] 郭广慧, 钟世华, 李三忠, 等. 运用机器学习和锆石微量元素构建花岗岩成矿潜力判别图解: 以东昆仑祁漫塔格为例[J/OL]. 西北地质, 2023: 1−14. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023158
GUO Guanghui, ZHONG Shihua, LI Sanzhong, et al. Constructing Discrimination Diagrams for Granite Mineralization Potential by Using Machine Learning and Zircon Trace Elements: Example from the Qimantagh, East Kunlun[J/OL]. Northwestern Geology, 2023: 1−14. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023158
[6] 李东生,张文权,田承盛,等. 青海祁漫塔格地区主要矿床类型找矿方法探讨[J]. 西北地质,2013,46(4):131–141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.04.012
LI Dongsheng, ZHANG Wenquan, TIAN Chengsheng, et al. Discussion on the metallogenic characteristics and ore-prospecting methods of qimantage Region, Qinghai Province [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2013, 46(4): 131-141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.04.012
[7] 李文渊. 祁漫塔格找矿远景区地质组成及勘查潜力[J]. 西北地质,2010,43(4):1–9.
LI Wenyuan. The Geological Composition and Metallogenetic Prospect in the Qimantage Prospective Region, East Kunlun [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(4): 1-9.
[8] 李玉春,张爱奎,张培青,等. 青海祁漫塔格沙丘地区侵入岩地质、地球化学特征及找矿意义[J]. 西北地质,2013,46(3):70–82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.03.005
LI Yuchun, ZHANG Aikui, ZHANG Peiqing, et al. The Geological and Geochemical Characteristics of the Intrusive Rock and Prospecting Significance in Shayiu Areas, Qimantage Metallogenic Belt, Qinghai Province [J], Northwestern Geology, 2013, 46(3): 70-82. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.03.005
[9] 刘彦,严加永,吴明安. 基于重力异常分离方法寻找深部隐伏铁矿-以安徽泥河铁矿为例[J]. 地球物理学报,2012,55(12):4181–4193.
LIU Yan, YAN Jiayong, WU Mingan. Exploring deep concealed ore bodies based on gravity separation methods: A case study of the Nihe iron deposit [J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(12): 4181- 4193.
[10] 刘嘉情, 钟世华, 李三忠, 等. 基于机器学习和全岩成分识别东昆仑祁漫塔格斑岩-矽卡岩矿床成矿岩体和贫矿岩体[J/OL]. 西北地质, 2023: 1−16. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023155
LIU Jiaqing, ZHONG Shihua, LI Sanzhong, et al. Identification of Mineralized and Barren Magmatic Rocks from the Qimantagh, East Kunlun Based on Machine Learning and Whole−Rock Compositions[J/OL]. Northwestern Geology, 2023: 1−16. doi: 10.12401/j.nwg.2023155
[11] 马忠元,刘光莲,汪周鑫,等. 东昆仑西段它温查汉西铁金多金属矿成矿模式探讨[J]. 新疆地质,2022,40(3):362–367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2022.03.007
MA Zhongyuan, LIU Guanglian, WANG Zhouxin, et al. Discussion on the Metallogenic Model of Tawenchahanxi Iron Polymetallic Deposit in the Western Part of East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2022, 40(3): 362-367. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2022.03.007
[12] 潘力, 何青林, 陈康, 等. 利用重磁资料解译川西地区深层断裂构造及预测火山岩顶界面深度[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50(2): 240−248.
PAN Li, HE Qinglin, CHEN Kang, et al. Application of gravity and magnetic data to the interpretation of deep fault structures and prediction of volcanic rock top interface depth in the western Sichuan Basin, China [J], Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2023, 50(2): 240−248.
[13] 乔耿彪,伍跃中. 东昆仑祁漫塔格地区花岗岩成因类型对成矿作用的控制[J]. 西北地质,2010,43(4):134–142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2010.04.016
QIAO Gengbiao, WU Yuezhong. Genetic Types of Granite Controlled the Mineralization in Qimantage Area, Eastern Kunlun [J], Northwestern Geology, 2010, 43(4): 134-142. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2010.04.016
[14] 田承盛,丰成友,李军红,等. 青海它温查汉铁多金属矿床40Ar-39Ar年代学研究及意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志,2013,32(1):169–176.
TIAN Chengsheng, FENG Chengyou, LI Junhong, et al. 40Ar-39Ar geochronology of Tawenchahan Fe-polymetallic deposit in qimantag Mountain of qinghai Province and its geological implications[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2013, 32(1): 169-176.
[15] 王谦身,滕吉文,张永谦,等. 鄂尔多斯-中秦岭-四川东部的重力异常场与深部地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报,2015,58(2):532–541. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150216
WANG Qianshen, TENG Jiwen, ZHANG Yongqian, et al. Gravity anomalies and deep crustal structure of the Ordos basin-middle Qinling orogen-eastern Sichuan basin[J]. Chinese J. Geophys. (in Chinese), 2015, 58(2): 532-541. doi: 10.6038/cjg20150216
[16] 张文权,张爱奎,孟军海,等. 高精度磁测反演技术在沙丘地区找矿中的应用[J]. 西北地质,2012,45(1):277–282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2012.01.035
ZHANG Wenquan, ZHANG Aikui, MENG Junhai, et al. Application Inversion technology into Dune with High-Precision Magnetic Survey [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2012, 45(1): 277-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2012.01.035
[17] 赵政璋, 李永铁, 叶和飞, 等. 青藏高原大地构造特征及盆地演化[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001
ZHAO Zhengzhang, LI Yongtie, YE Hefei, et al. Tectonic characteristics and basin evolution of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[M]. Beijing: Science Publishing House, 2001.
-




 下载:
下载: