REVIEW ON THE DEVELOPMENT OF VOLCANIC HAZARD ZONATION IN CHINA
-
摘要:
火山灾害区划是防御和减轻火山灾害的一种有效的方法.以中国境内规模最大、喷发危险性最高、潜在火山灾害最强的长白山天池火山为例,回顾我国火山灾害区划研究历史,讨论典型火山喷发活动引起的主要火山灾害类型、成灾机制和灾害效应,总结不同历史阶段各种不同类型火山灾害区划图的优缺点,并结合目前国际上火山灾害区划的研究现状和编图技术,对我国未来编制具有概率含义的火山灾害区划图的思路提出展望.
Abstract:Volcanic hazard evaluation and zonation, as the effective countermeasures, plays an important role in volcanic emergency response and hazard mitigation. Taking Changbaishang volcano as an example, this paper reviews on the study history of volcanic hazard zonation in China. The major types of volcanic hazards in China, which are potentially related with the active volcanoes, involve tephra fallout, pyroclastic flow, lava flow and lahar. The volcanic zoning maps of Changbaishan volcano compiled in 2000 and 2012 respectively show the progresses in volcanic hazard assessment and hazard zonation of China. It is proposed that the probabilistic method such as "event tree" should be applied in compiling the volcanic hazard map of China in future, which represents the most-up-to-date technical trend in volcanic hazard zonation in the world.
-
Key words:
- volcanic hazard zonation /
- Changbaishan volcano /
- tephra /
- pyroclastic flow /
- lava flow, lahar /
-

-
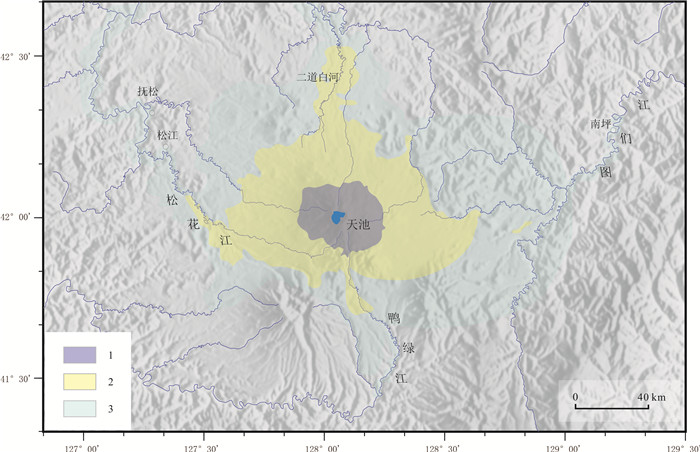
图 1 长白山天池火山灾害区划图(据文献[22]修改)
Figure 1.
-
[1] 魏海泉. 火山灾害的类型、预测与防治[J]. 地质灾害与防治, 1991, 2(2): 96-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH199102016.htm
Wei H Q. The types, prediction and control of volcanic hazards[J]. Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1991, 2(2): 96-98. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH199102016.htm
[2] 许建东. 我国火山灾害的主要类型及火山灾害区划图编制现状探讨[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2006, 1(3): 266-272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.03.012
Xu J D. The major types of potential volcanic hazard of China and hazard mapping technique[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2006, 1(3): 266-272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5722.2006.03.012
[3] Favalli M, Tarquini S, Fornaciai A, et al. A new approach to risk assessment of lava flow at Mount Etna[J]. Geology, 2009, 37(12): 1111-1114. doi: 10.1130/G30187A.1
[4] Doocy S, Daniels A, Dooling S, et al. The human impact of volcanoes: A historical review of events 1900-2009 and systematic literature review[J]. PLOS Currents Disasters, 2013, doi: 10.1371/currents.dis.841859091a706efebf8a30f4ed7a1901.
[5] Stothers R B. The great Tambora eruption in 1815 and its aftermath [J]. Science, 1984, 224(4654): 1191-1198. doi: 10.1126/science.224.4654.1191
[6] 许建东, 王佳龙. 汤加海底火山喷发特征与灾情启示[J]. 城市与减灾, 2022(1): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSJZ202201002.htm
Xu J D, Wang J L. Characteristics and revelation of the 2022 eruption of Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai volcano[J]. City and Disaster Reduction, 2022(1): 1-6. (in Chinese) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CSJZ202201002.htm
[7] Scarpa R, Tilling R I. Monitoring and mitigation of volcano hazards [M]. Berlin: Springer, 1996.
[8] Machida H. The stratigraphy, chronology and distribution of distal marker-tephras in and around Japan[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 1999, 21(1/3): 71-94.
[9] Pan B, de Silva S L, Xu J D, et al. The VEI-7 millennium eruption, Changbaishan-Tianchi volcano, China/DPRK: new field, petrological, and chemical constraints on stratigraphy, volcanology, and magma dynamics[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2017, 343: 45-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2017.05.029
[10] Sun C Q, Plunkett G, Liu J Q, et al. Ash from Changbaishan millennium eruption recorded in Greenland ice: Implications for determining the eruption's timing and impact[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2014, 41(2): 694-701. doi: 10.1002/2013GL058642
[11] Xu J D, Liu G M, Wu J P, et al. Recent unrest of Changbaishan volcano, Northeast China: A precursor of a future eruption?[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2012, 39(16): L16305. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2012GL052600
[12] 金伯禄, 张希友. 长白山火山地质研究[M]. 延吉: 东北朝鲜民族教育出版社, 1994.
Jin B L, Zhang X Y. Research on volcanic geology in Changbai Mountains[M]. Yanji: Education Press of Northeast China Korean Minority, 1994. (in Chinese)
[13] 杨清福, 原晓军, 武成智, 等. 中朝边境天池破火山口湖底地形多波束测深探测[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(1): 185-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201801016.htm
Yang Q F, Yuan X J, Wu C Z, et al. The multibeam sounding exploration of the Tianchi caldera lakebed topography at the China- North Korea border[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(1): 185- 193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201801016.htm
[14] 刘若新, 魏海泉, 李继泰. 长白山天池火山近代喷发[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1998.
Liu R X, Wei H Q, Li J T. The recent eruptions of Changbaishan Tianchi volcano[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1998. (in Chinese)
[15] 洪汉净, 吴建平, 王庆良, 等. 中国火山危险性等级与活动性分类[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(3): 447-458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.03.001
Hong H J, Wu J P, Wang Q L, et al. Volcanic threat levels and classification of volcanic activity in China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2007, 29(3): 447-458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.03.001
[16] 许建东. 火山灾害与火山喷发预测预警[J]. 城市与减灾, 2017 (1): 11-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2017.01.004
Xu J D. Volcanic hazard and eruption early warning[J]. City and Disaster Reduction, 2017(1): 11-15. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2017.01.004
[17] Sun C Q, Liu J Q, You H T, et al. Tephrostratigraphy of Changbaishan volcano, Northeast China, since the mid-Holocene[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 177: 104-119. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.10.021
[18] Pan B, de Silva S L, Xu J D, et al. Late Pleistocene to present day eruptive history of the Changbaishan-Tianchi volcano, China/DPRK: New field, geochronological and chemical constraints[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2020, 399: 106870. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2020.106870
[19] Xu J D, Pan B, Liu T Z, et al. Climatic impact of the Millennium eruption of Changbaishan volcano in China: New insights from high- precision radiocarbon wiggle-match dating[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2013, 40(1): 54-59. doi: 10.1029/2012GL054246
[20] Oppenheimer C, Wacker L, Xu J D, et al. Multi-proxy dating the 'Millennium Eruption' of Changbaishan to late 946 CE[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2017, 158: 164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.12.024
[21] Sun C Q, Wang L, Plunkett G, et al. Ash from the Changbaishan Qixiangzhan eruption: A new early Holocene marker horizon across East Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2018, 123(8): 6442-6450. https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1029/2018JB015983
[22] 杨清福, 姜朝松, 刘若新. 三个火山区火山灾害区划图的编制与减灾对策研究[M]. 吉林省地震局, 2000.
Yang Q F, Jiang C S, Liu R X. Compiling volcanic hazard maps of the three volcanoes and their hazard mitigation[M]. Earthquake Agency of Jilin Province, 2000. (in Chinese)
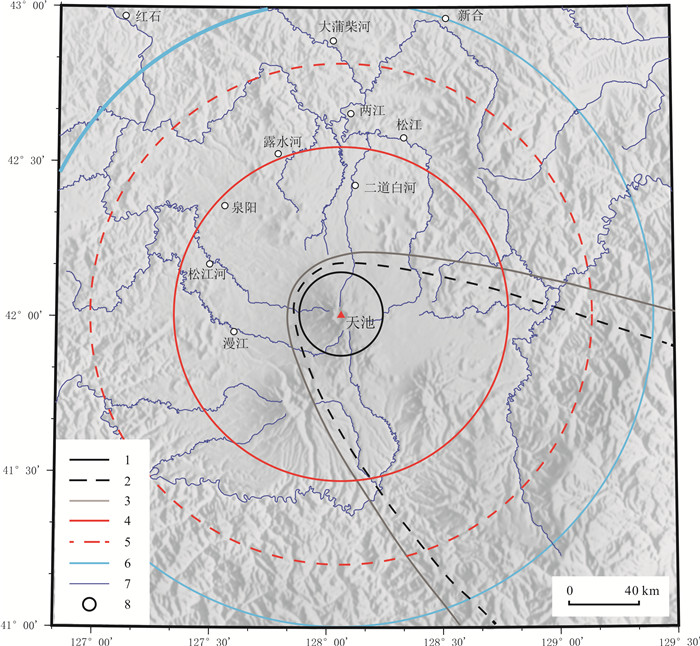
[23] Wan Y, Xu J D, Pan B, et al. Volcanic hazard mapping for Changbaishan-Tianchi region, China[J/OL]. Journal of Earth Science. (2021-11-01). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CAPJ&dbname=CAPJLAST&filename=ZDDY20211028000&uniplatform=NZKPT&v=iZnSxizK2gnZ7AaF2u02bVjByag61irqpF2co1b6PWHaLrnZ_Kk59CytBjz-IN4w.
[24] 于红梅, 许建东, 赵谊. 长白山天池火山千年大喷发空降碎屑物的数值模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(3): 522-534. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.03.008
Yu H M, Xu J D, Zhao Y. A numerical simulation of tephra transport and deposition for millennium eruption of Changbaishan Tianchi volcano[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2007, 29(3): 522-534. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2007.03.008
[25] 王新茹, 赵波, 万园, 等. 长白山天池火山碎屑流灾害区划[J]. 震灾防御技术, 2015, 10(2): 262-270. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-2011012477.htm
Wang X R, Zhao B, Wan Y, et al. Pyroclastic flow hazard zonation of Changbaishan Tianchi volcano[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 2015, 10(2): 262-270. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-85402-2011012477.htm
[26] 潘波, 许建东, 林旭东, 等. 基于热流变运动学模型的长白山熔岩流数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(9): 2317-2324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.09.015
Pan B, Xu J D, Lin X D, et al. Modeling the lava flow of Changbaishan volcano, China based on kinematic thermo-rheological model[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(9): 2317-2324. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.09.015
[27] 万园, 许建东, 林旭东, 等. 基于数值模拟的长白山天池火山泥石流灾害展布范围分析及预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2011, 41(5): 1638-1645. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105044.htm
Wan Y, Xu J D, Lin X D, et al. Analysis to the lahars extent in Changbai Mountains by numerical simulation[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2011, 41(5): 1638-1645. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201105044.htm
[28] Neri A, Aspinall W P, Cioni R, et al. Developing an event tree for probabilistic hazard and risk assessment at Vesuvius[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 2008, 178(3): 397-415. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.05.014
-



 下载:
下载: