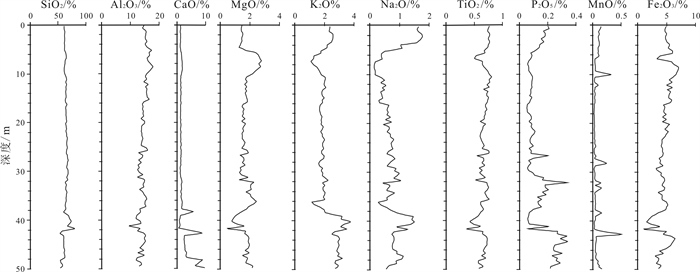
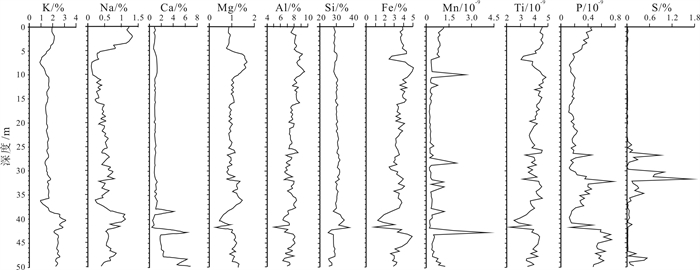
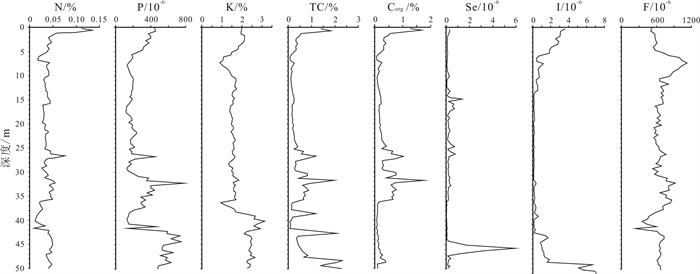
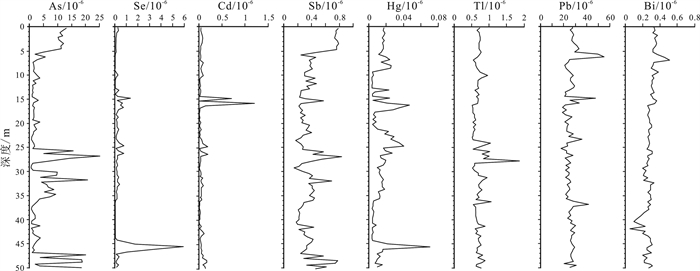
Vertical characteristics and content grade of chemical elements in the ground substrate (0-50 m deep) of Baiquan area, Songnen Plain
-
摘要:
对黑龙江省拜泉县BQZK05汽车钻取得的50 m以浅土质基质样品进行了分析, 获得全芯土质主量元素、矿质元素、有益元素和有毒元素垂向分布特征, 并对全芯土质部分化学元素进行了质量评价.结果显示, 主量元素CaO含量属于三等中等级, MgO含量属于二等较丰富级, Fe2O3含量属于二等较丰富级; 矿质元素Fe含量属于四等较缺乏级, Mn含量属于三等中等级, S含量属于一等丰富级; 有益元素Se含量属于适量级, I含量属于缺乏级, F含量属于高含量级, K含量为中上等(3级); 有毒元素含量远低于农用地土壤污染风险筛选值和管制值, 土壤环境质量为一等清洁级.
Abstract:By analyzing the soil substrate samples in the depth of 0-50 m from borehole BQZK05 in Baiquan County, Heilongjiang Province, the study ascertains the vertical distribution characteristics of major, mineral, beneficial and toxic elements, and evaluates the quality of some chemical elements in the soil. The results show that the CaO content belongs to Grade Ⅲ(medium), MgO content Grade Ⅱ(rich), and Fe2O3 content Grade Ⅱ(rich) in terms of major elements. Of the mineral elements, Fe content belongs to Grade Ⅳ (deficient), Mn content Grade Ⅲ(medium), and S content Grade Ⅰ(abundent). In terms of beneficial elements, the Se content belongs to moderate grade, I content the deficient grade, F content the high grade, and K content the middle-high grade. The content of toxic elements is much lower than the risk screening value and control value of agricultural land soil pollution, and the soil environment quality is first-class clean.
-
Key words:
- black soil /
- ground substrate /
- element content grade /
- Songnen Plain
-

-
表 5 土壤环境质量标准值
Table 5. Standard values of soil environment quality
级别 一级 二级 三级 土壤pH值 自然背景 6.5~7.5 >7.5 镉 ≤0.2 0.2~1 >1 汞 ≤0.15 0.15~1.5 >1.5 砷 水田 ≤15 15~30 >30 旱地 ≤15 15~40 >40 铜 农田等 ≤35 35~400 >400 果园 - 150~400 >400 铅 ≤35 35~500 >500 铬 水田 ≤90 90~400 >400 旱地 ≤90 90~300 >300 锌 ≤100 100~500 >500 镍 ≤40 40~200 >200 六六六 ≤0.05 0.05~1 >1 滴滴涕 0.05 0.05~1 1 含量单位: 10-6. 表 6 土壤环境地球化学等级划分
Table 6. Geochemical grading of soil environment
质量等级 一等(清洁) 二等(轻微污染) 三等(轻度污染) 四等(中度污染) 五等(重度污染) 环境指数 Pi≤1 1<Pi≤2 2<Pi≤3 3<Pi≤5 Pi; 5 -
[1] 自然资源部. 自然资源调查监测体系构建总体方案[Z]. 2020.
Ministry of Natural Resources. General scheme for construction of natural resources survey and monitoring system[Z]. 2020. (in Chinese)
[2] 魏丹, 杨谦, 迟凤琴. 东北黑土区土壤资源现状与存在问题[J]. 黑龙江农业科学, 2006(6): 69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2767.2006.06.024
Wei D, Yang Q, Chi F Q. The soil resource conditions and the problems in Northeast black soil regions[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2006(6): 69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2767.2006.06.024
[3] Hao C L, Xiao W H, Zhou Y Y, et al. Phosphorus balance in typical rainfield of black soil region in Northeast China[J]. Geosciences Journal, 2019, 23(4): 637-648. doi: 10.1007/s12303-018-0069-1
[4] 曹野. 东北地区耕地质量等级评价与现状分析[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2017.
Cao Y. Cultivated land quality evaluation and present situation analysis in Northeast China[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017.
[5] 韩晓增, 邹文秀. 我国东北黑土地保护与肥力提升的成效与建议[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2): 206-212.
Han X Z, Zou W X. Effects and suggestions of black soil protection and soil fertility increase in Northeast China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(2): 206-212.
[6] 张哲寰, 宋运红, 赵君, 等. 黑龙江省讷河市土壤某些微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2019, 28(4): 378-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.04.011
Zhang Z H, Song Y H, Zhao J, et al. Trace element geochemistry of the soil in Nehe City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2019, 28(4): 378-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2019.04.011
[7] 张哲寰, 戴慧敏, 宋运红, 等. 黑龙江省乌裕尔河流域土壤中某些微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5): 1097-1104.
Zhang Z H, Dai H M, Song Y H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of some soil trace elements in the Wuyuer River Basin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1097-1104.
[8] 李延生. 黑龙江省扎龙湿地土壤地球化学特征及生态环境意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(4): 512-516.
Li Y S. Soil geochemical characteristics and ecological environment significance of the Zhalong wetlands in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 34(4): 512-516.
[9] 陆继龙, 周云轩, 周永昶, 等. 黑土农业区常量和微量元素环境地球化学特征[J]. 农业环境与发展, 2002(1): 27-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2002.01.014
Lu J L, Zhou Y X, Zhou Y C, et al. Environmental geochemical characteristics of major and trace elements in black soil of agricultural areas[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2002(1): 27-29. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4944.2002.01.014
[10] 刘银飞, 孙彬彬, 贺灵, 等. 福建龙海土壤垂向剖面元素分布特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(4): 713-721.
Liu Y F, Sun B B, He L, et al. Vertical distribution of elements in soil profiles in Longhai, Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4): 713-721.
[11] 张哲寰, 赵君, 戴慧敏, 等. 黑龙江省讷河市土壤-作物系统Se元素地球化学特征[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(1): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.01.005
Zhang Z H, Zhao J, Dai H M, et al. Geochemistry of selenium in soil-crop system of Nehe City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(1): 38-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1947.2020.01.005
[12] 韩晓萌, 戴慧敏, 梁帅, 等. 黑龙江省拜泉地区典型黑土剖面元素地球化学特征及其环境指示意义[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 556-563.
Han X M, Dai H M, Liang S, et al. Element geochemistry of the typical black soil sections in Baiquan area, Heilongjiang Province: Environmental implication[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 556-563.
[13] 刘希瑶, 刘澎, 刘驰. 典型黑土中有机质和养分元素的变化分析[J]. 地质与资源, 2022, 31(4): 500-507. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.010
Liu X Y, Liu P, Liu C. Variation characteristics of organic matters and nutrient elements in typical black soil[J]. Geology and Resources, 2022, 31(4): 500-507. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.010
[14] 杨贺平. 典型黑土地土壤有机质含量空间变化特征研究--以绥化市北林区为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2022, 31(4): 508-515, 499. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.010
Yang H P. Spatial variation characteristics of soil organic matter content in typical black soil: A case study of Beilin District in Suihua City, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2022, 31(4): 508-515, 499. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.010
[15] 翟富荣, 梁帅, 戴慧敏. 东北黑土地地球化学调查研究进展与展望[J]. 地质与资源, 2020, 29(6): 503-509, 532. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.010
Zhai F R, Liang S, Dai H M. Geochemical survey of black land in Northeast China: Progress and prospect[J]. Geology and Resources, 2020, 29(6): 503-509, 532. doi: 10.13686/j.cnki.dzyzy.2025.01.010
[16] 宋运红, 刘凯, 戴慧敏, 等. 松辽平原典型黑土-古土壤剖面AMS 14C年龄首次报道[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1926-1927.
Song Y H, Liu K, Dai H M, et al. The first report of the AMS 14C age of mollisol-paleosol profile of Songliao Plain[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1926-1927.
[17] 中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0295-2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0295-2016 Determination of land quality geochemical evaluation[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[18] 龚子同, 黄荣金, 张甘霖. 中国土壤地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014: 207.
Gong Z T, Huang R J, Zhang G L. Soil geography of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014: 207. (in Chinese)
[19] 陈文轩, 李茜, 王珍, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属空间分布特征及污染评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833.
Chen W X, Li Q, Wang Z, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in arable land soil of China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6): 2822-2833.
[20] 生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618-2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
-



 下载:
下载: